What kinds of energy do you see?
|
|
|
- Kristin Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Energy Transfer ICP
2 FTF Day 2 April 16, 2012 HW: none Topic: Light (last day) Questions: 1. When light passes through a prism, which colors of light are bent the most? 2. Which two colors of paint could you combine to make purple? 3. Which two colors of light could you combine to make yellow?
3 Vocabulary Types of energy Kinetic energy- Energy that something has because its moving. Thermal energy energy that something has because its hot (or not hot = little thermal E)
4 What kinds of energy do you see?
5 Potential energy stored energy. Often written as PE Chemical energy energy stored in bonds between atoms Gravitational energy energy stored in an object because of its position relative to the ground. (high up= lots of potential energy) How else can energy be stored?
6 Ways to Transfer Heat Conduction heat transferred from atom to atom (think of objects that are touching) Convection heat transferred because gasses or liquids are circulating Radiation heat lost or gained because of electromagnetic radiation (infrared, light, gamma, etc.) Latent Heat heat lost or gained when the object changes phase (gas to liquid, solid to liquid, etc.)
7 Reactions Endothermic a process that takes in thermal energy from its surroundings (products have more energy than the ingredients you started with.) Example - Exothermic a process that releases thermal energy to its surroundings (products have less energy than the ingredients you started with) Example-
8 Measuring thermal energy Calories or calories units for measuring the amount of energy in a substance. 1 calorie is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 cm 3 of water up 1 degree Celsius. 1 Calorie = 1000 calories (capitol C is what you see on food packages) Calorimetry - the measuring of thermal energy in a system.
9 The Big Picture Law of conservation of energy Energy may neither be created nor destroyed. Therefore, the sum of all the energy in the system is a constant.
10 FTF Day 3 April 18, 2012 HW: Bring book to class tomorrow. Study for vocab quiz on Monday. Topic: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Questions 1. What is the law of conservation of energy? 2. As the pendulum reaches the bottom of its arch, what happens to its speed? (Kinetic Energy) 3. As it reaches the bottom, what happens to its height? (Potential Energy)
11 Activities Phet lab: Skate Park Basics bit.ly/y7iucb
12 FTF Day 4 April 19, 2012 HW: BRING BOOK Tomorrow. Study for vocab quiz, Monday Topic: Energy Transfer Question: 1. The units for measuring energy are or. 2. Imagine you and your snowboard have 20 Joules of potential energy (PE) at the top of a hill. If you coast to the bottom of the hill, how much kinetic energy (KE) will you have? 3. What if, you measure the amount of energy you have at the bottom and it comes out to be less than 20. Where did the rest of the energy go?
13 Activities Phet Lab: Skate Park Basics
14 ICP: FTF Day 5 April 20, 2012 HW: Study for vocab quiz Monday Questions from book due today. Topic: PE KE Questions: At the top of the arc, the pendulum has 0 Joules of KE and 10 Joules of PE. At the bottom of the arc, the pendulum will have Joules of KE and Joules of PE.
15 Activities Book Work Read 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, and 6.7 Answer Pg
16 FTF Day (we didn t do this one yet) April?, 2012 HW: Topic: Potential, Kinetic, and Thermal energy Questions: 1. Why didn t the bucket hit the volunteer in the face? 2. The ATC slowed down the climber s decent. The climber s Kinetic Energy was transferred to energy due to friction between the rope and the ATC. (wait for pictures..)
17 ATC ATC stands for Air Traffic Controller.
18 ATC ATC stands for Air Traffic Controller.
19 atch?v=yo4qsog7bc8
20
21
22 An egg being cooked in a pan
23 A cake being cooked in the oven
24 Icing a sprained ankle
25 Blowing on your hands to warm them or blowing on your soup to cool it.
26 A tanning booth works this way
27 Burgers on a gas grill.
28 A radiator circulates fluid through the engine to keep it cool.
29 A thermos insulates hot cocoa by preventing this kind of heat transfer.
30 The sun heats your car
31 A hair dryer works this way
32 FTF Day 6 April 26, 2012 HW: wear closed toad shoes Topic: Heat of vaporization, heat of fusion Question: Metabolism is the process of breaking down food so your body can utilize the energy stored in carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Is metabolism endothermic or exothermic?
33 See PPT titled heat of fusion and vaporization for slides from today.
34 Energy and States of Matter Changes of State Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 34
35 Melting and Freezing A substance is melting while it changes from a solid to a liquid. is freezing while it changes from a liquid to a solid. such as water has a freezing (melting) point of 0 C. Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 35
36 Calculations Using Heat of Fusion The heat of fusion is the amount of heat released when 1 gram of liquid freezes (at its freezing point). is the amount of heat needed to melt 1 gram of a solid (at its melting point). for water (at 0 C) is 80. cal 1 g water 36
37 Calculation Using Heat of Fusion The heat needed to freeze (or melt) a specific mass of water (or ice) is calculated using the heat of fusion. Heat = g water x 80. cal 1 g water Example: How much heat in cal is needed to melt 15.0 g of water? 15.0 g water x 80. cal = 1200 cal 1 g water 37
38 Learning Check A. How many calories are needed to melt 5.00 g of ice at 0 C? 1) 80. cal 2) 400 cal 3) 0 cal B. How many calories are released when 25.0 g of water at 0 C freezes? 1) 80. cal 2) 0 cal 3) 2000 cal 38
39 Solution A. How many calories are needed to melt 5.00 g of ice at 0 C? 2) 400 cal 5.00 g x 80. cal 1 g B. How many calories are released when 25.0 g of water at 0 C freezes? 3) 2000 cal 25 g x 80. cal 1 g 39
40 Sublimation Sublimation occurs when particles change directly from solid to a gas. is typical of dry ice, which sublimes at -78 C. takes place in frost-free refrigerators. is used to prepare freezedried foods for long-term storage. 40
41 Evaporation and Condensation Water evaporates when molecules on the surface gain sufficient energy to form a gas. condenses when gas molecules lose energy and form a liquid. Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 41
42 Boiling At boiling, all the water molecules acquire enough energy to form a gas. bubbles appear throughout the liquid. Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 42
43 Heat of Vaporization The heat of vaporization is the amount of heat absorbed to vaporize 1 g of a liquid to gas at the boiling point. released when 1 g of a gas condenses to liquid at the boiling point. Boiling Point of Water = 100 C Heat of Vaporization (water) = 540 cal 1 g water 43
44 Learning Check How many kilocalories (kcal) are released when 50.0 g of steam from a volcano condenses at 100 C? 1) 27 kcal 2) 540 kcal 3) 2700 kcal 44
45 Solution How many kilocalories (kcal) are released when 50.0 g of steam in a volcano condenses at 100 C? 1) 27 kcal 50.0 g steam x 540 cal x 1 kcal = 27 kcal 1 g steam 1000 cal 45
46 Summary of Changes of State 46
47 Heating Curve A heating curve illustrates the changes of state as a solid is heated. uses sloped lines to show an increase in temperature. uses plateaus (flat lines) to indicate a change of state. Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 47
48 Learning Check A. A flat line on a heating curve represents 1) a temperature change. 2) a constant temperature. 3) a change of state. B. A sloped line on a heating curve represents 1) a temperature change. 2) a constant temperature. 3) a change of state. 48
49 Solution A. A flat line on a heating curve represents 2) a constant temperature. 3) a change of state. B. A sloped line on a heating curve represents 1) a temperature change. 49
50 Cooling Curve A cooling curve illustrates the changes of state as a gas is cooled. uses sloped lines to indicate a decrease in temperature. uses plateaus (flat lines) to indicate a change of state. Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 50
51 Learning Check Use the cooling curve for water to answer each. A. Water condenses at a temperature of 1) 0 C. 2) 50 C. 3) 100 C. B. At a temperature of 0 C, liquid water 1) freezes. 2) melts. 3) changes to a gas. C. At 40 C, water is a 1) solid. 2) liquid. 3) gas. D. When water freezes, heat is 1) removed. 2) added. 51
52 Solution Use the cooling curve for water to answer each. A. Water condenses at a temperature of 3) 100 C. B. At a temperature of 0 C, liquid water 1) freezes. C. At 40 C, water is a 2) liquid. D. When water freezes, heat is 1) removed. 52
53 Heat Calculations To reduce swelling, you put 250 g of ice on your sprained ankle. If the ice (at 0 C) melts and warms to body temperature (37.0 C), how many calories are removed from the body? 53
54 Heat Calculations To reduce swelling, you put 250 g of ice on your sprained ankle. If the ice (at 0 C) melts and warms to body temperature (37.0 C), how many calories are removed from the body? Step 1: Diagram the changes 37 C temperature increase 0 C solid liquid (melting) 54
55 Heat Calculations Step 2: How is the ice changing? (2 formulas) Ice is melting and then increasing in temperature from 0 to 37.0 C. Heat of fusion = g of ice x 80.0 cal 1 g ice Heat to increase temperature = g of ice x T x 1 cal Then add them together. 1 g/1 C 55
56 Step 3: Plug value into equations Heat = 250 g of ice x 80.0 cal = 20,000 cal 1 g ice Heat = 250 g of ice x 37 C 1 cal = 9,250 cal 1g/1 C Add them together: 20, ,250 = 29,250 calories = Calories (Kcal) 56
57 FTF Day 7 April HW: Calorimetry lab due tomorrow, test on Wednesday Make a clues sheet Topic: calories /gram If it takes 1 calorie to raise the temperature of 1 gram of H20 by 1 degree celcius, How many calories are required to raise the temperature of 100 grams of water by 1 degree C? A tic-tac contains 2000 calories (2 Calories, or Kilocalories) of potential energy. If you used all those calories to raise the temp of 100 G of water, how much would the temperature increase?
Chapter 5 Energy and States of Matter. Changes of State. Melting and Freezing. Calculations Using Heat of Fusion
 Chapter 5 Energy and States of Matter Changes of State 5.6 Melting and Freezing 5.7 Boiling and Condensation 1 2 Melting and Freezing A substance is melting while it changes from a solid to a liquid. A
Chapter 5 Energy and States of Matter Changes of State 5.6 Melting and Freezing 5.7 Boiling and Condensation 1 2 Melting and Freezing A substance is melting while it changes from a solid to a liquid. A
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state.
 Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
What are the states of Matter?
 What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
4. Every CHANGE in matter includes a change in, which is conserved in a chemical reaction and. TRANSFORMED from one form to another.
 Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
Chapter 4. Properties of Matter
 Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
solid IMF>liquid IMF>gas IMF Draw a diagram to represent the 3 common states of matter of a given substance: solid liquid gas
 Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
THERMODYNAMICS. Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer.
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing this unit,
THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing this unit,
Temp vs. Heat. Absolute Temperature Scales. Common Temperature Scales. Thermal Energy. Heat and Temperature are not the same!!
 Thermal Energy Heat and Temperature are not the same!! Cold is the absence of heat, not an energy Same concept as light/dark Cold can t come in, heat flows out Heat flows from High Temp Low Temp Temp vs.
Thermal Energy Heat and Temperature are not the same!! Cold is the absence of heat, not an energy Same concept as light/dark Cold can t come in, heat flows out Heat flows from High Temp Low Temp Temp vs.
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY. Mrs. Brayfield
 CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
Physics Mechanics
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 35 Heat 2 Definition and Units of Heat Heat is a form of energy, and therefore is measured in joules. There are other units of heat, the most common one is the kilocalorie:
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 35 Heat 2 Definition and Units of Heat Heat is a form of energy, and therefore is measured in joules. There are other units of heat, the most common one is the kilocalorie:
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7
 Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7 Bill Nye - Energy I. PS.6a - Potential & Kinetic Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. B. Energy is either Potential or Kinetic. a. Potential Energy
Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7 Bill Nye - Energy I. PS.6a - Potential & Kinetic Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. B. Energy is either Potential or Kinetic. a. Potential Energy
2,000-gram mass of water compared to a 1,000-gram mass.
 11.2 Heat To change the temperature, you usually need to add or subtract energy. For example, when it s cold outside, you turn up the heat in your house or apartment and the temperature goes up. You know
11.2 Heat To change the temperature, you usually need to add or subtract energy. For example, when it s cold outside, you turn up the heat in your house or apartment and the temperature goes up. You know
We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much its temperature will change heat capacity.
 3/3 Measuring Heat If all we do is add heat to a system its temperature will rise. How much the temperature rises depends on the system. We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much
3/3 Measuring Heat If all we do is add heat to a system its temperature will rise. How much the temperature rises depends on the system. We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much
ENERGY. Unit 12: IPC
 ENERGY Unit 12: IPC WHAT IS ENERGY? Energy- is the ability to do work. Energy is the ability to cause a change. Energy can change an object s: motion shape temperature color THERMAL internal motion of
ENERGY Unit 12: IPC WHAT IS ENERGY? Energy- is the ability to do work. Energy is the ability to cause a change. Energy can change an object s: motion shape temperature color THERMAL internal motion of
Notes: Matter and Change
 Name Chemistry-PAP Notes: Matter and Change Period: I. What is Chemistry? is the study of composition, structure, and properties of matter and energy associated with the changes it undergoes. is defined
Name Chemistry-PAP Notes: Matter and Change Period: I. What is Chemistry? is the study of composition, structure, and properties of matter and energy associated with the changes it undergoes. is defined
Phase Change Diagram. Rank Solids, liquids and gases from weakest attractive forces to strongest:
 Unit 11 Kinetic molecular theory packet Page 1 of 13 Chemistry Unit 11 Kinetic Theory Unit Quiz: Test Objectives Be able to define pressure and memorize the basic pressure units. Be able to convert to/from:
Unit 11 Kinetic molecular theory packet Page 1 of 13 Chemistry Unit 11 Kinetic Theory Unit Quiz: Test Objectives Be able to define pressure and memorize the basic pressure units. Be able to convert to/from:
Chemistry Heat Review. Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy:
 Chemistry Heat Review Name Date Vocabulary Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy: Formulas Heat of phase change Heat for temperature increase Heat of reaction Endothermic/Exothermic
Chemistry Heat Review Name Date Vocabulary Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy: Formulas Heat of phase change Heat for temperature increase Heat of reaction Endothermic/Exothermic
Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy
 Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Chapter 14 Heat. Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Thermochemistry. Energy (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10. Energy. Energy
 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry. Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake. Chapter 2. Energy and Matter Pearson Education, Inc.
 General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2.1 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat.
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2.1 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat.
CALORIEMETRY. Similar to the other forms of the energy, The S.I unit of heat is joule. joule is represented as J.
 CALORIEMETRY CALORIMETRY Heat is the kinetic energy due to random motion of the molecules of a substance is called heat energy. Heat is a an invisible energy, that causes in us the sensation of hotness
CALORIEMETRY CALORIMETRY Heat is the kinetic energy due to random motion of the molecules of a substance is called heat energy. Heat is a an invisible energy, that causes in us the sensation of hotness
8.5 - Energy. Energy The property of an object or system that enables it to do work. Energy is measured in Joules (J).
 Work Work The process of moving an object by applying a force. Work = Force x displacement. Work is measured in Joules (J) or Newton-meters (Nm). W = Fd Example: To prove his strength, a weightlifter pushes
Work Work The process of moving an object by applying a force. Work = Force x displacement. Work is measured in Joules (J) or Newton-meters (Nm). W = Fd Example: To prove his strength, a weightlifter pushes
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry
 CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
Recap. There are 3 different temperature scales: Celsius, Kelvin, and Fahrenheit
 Recap Temperature, T, is related to the average kinetic energy of each atom/molecule the given material consists of: The ideal gas law relates pressure to density and temperature: There are 3 different
Recap Temperature, T, is related to the average kinetic energy of each atom/molecule the given material consists of: The ideal gas law relates pressure to density and temperature: There are 3 different
Thermodynamics - Heat Transfer June 04, 2013
 THERMODYNAMICS - Heat and Heat Transfer: Heat (Q) is a form of Energy that is transferred between an object and another object or its surrounding environment due to a difference in Temperature. Heat is
THERMODYNAMICS - Heat and Heat Transfer: Heat (Q) is a form of Energy that is transferred between an object and another object or its surrounding environment due to a difference in Temperature. Heat is
Chapter 23 Changes of Phase. Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1
 Chapter 23 Changes of Phase Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1 Kinetic Theory Matter exists in three common states or phases solid, liquid and gas. A fourth state plasma makes up over 90% of our universe.
Chapter 23 Changes of Phase Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1 Kinetic Theory Matter exists in three common states or phases solid, liquid and gas. A fourth state plasma makes up over 90% of our universe.
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Preview. Heat Section 1. Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium. Section 2 Defining Heat. Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase
 Heat Section 1 Preview Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Section 2 Defining Heat Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase Heat Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 6E describe how the
Heat Section 1 Preview Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Section 2 Defining Heat Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase Heat Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 6E describe how the
Energy Transformations
 Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. Part A: Freezing Water
 Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Matter and Energy Review Packet
 Name Date Matter and Energy Review Packet 1. A compound differs from a mixture in that a compound always has a (1) homogeneous composition (2) maximum of two components (3) minimum of three components
Name Date Matter and Energy Review Packet 1. A compound differs from a mixture in that a compound always has a (1) homogeneous composition (2) maximum of two components (3) minimum of three components
Thermal Energy. Practice Quiz Solutions
 Thermal Energy Practice Quiz Solutions What is thermal energy? What is thermal energy? Thermal energy is the energy that comes from heat. This heat is generated by the movement of tiny particles within
Thermal Energy Practice Quiz Solutions What is thermal energy? What is thermal energy? Thermal energy is the energy that comes from heat. This heat is generated by the movement of tiny particles within
The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce Heat, q or Q, is ; flows due to temperature differences (always to )
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II. Unit 5
 Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Unit 15 Energy and Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 15 Energy and Thermochemistry Notes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincochem.pbworks.com
Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 15 Energy and Thermochemistry Notes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincochem.pbworks.com
Section 16.3 Phase Changes
 Section 16.3 Phase Changes Solid Liquid Gas 3 Phases of Matter Density of Matter How packed matter is (The amount of matter in a given space) Solid: Liquid: Gas: High Density Medium Density Low Density
Section 16.3 Phase Changes Solid Liquid Gas 3 Phases of Matter Density of Matter How packed matter is (The amount of matter in a given space) Solid: Liquid: Gas: High Density Medium Density Low Density
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Energy, Temperature, & Heat. Energy, Temperature, & Heat. Temperature Scales 1/17/11
 Energy, Temperature, & Heat Energy is the ability to do work (push, pull, lift) on some form of matter. Chapter 2 Potential energy is the potential for work (mass x gravity x height) Kinetic energy is
Energy, Temperature, & Heat Energy is the ability to do work (push, pull, lift) on some form of matter. Chapter 2 Potential energy is the potential for work (mass x gravity x height) Kinetic energy is
SPH3U1 Lesson 03 Energy
 THERMAL ENERGY AND LATENT HEAT LEARNING GOALS Students will learn: Heat changes the amount of thermal energy in an object Temperature is a measure of the average thermal energy in an object Heat capacity
THERMAL ENERGY AND LATENT HEAT LEARNING GOALS Students will learn: Heat changes the amount of thermal energy in an object Temperature is a measure of the average thermal energy in an object Heat capacity
Chapter 2 Energy and Matter
 Chapter 2 Energy and Matter Energy makes objects move makes things stop is needed to do work Kinetic Energy Work is done when you climb you lift a bag of groceries you ride a bicycle you breathe your heart
Chapter 2 Energy and Matter Energy makes objects move makes things stop is needed to do work Kinetic Energy Work is done when you climb you lift a bag of groceries you ride a bicycle you breathe your heart
Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]?
![Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]?](/thumbs/78/77877522.jpg) Warm up 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? 4) What is the concentration of H 2 SO 4 if 30.1 ml
Warm up 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? 4) What is the concentration of H 2 SO 4 if 30.1 ml
Energy. Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Energy Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1 Energy is a substance like quantity that can cause change. Makes objects move. Makes things stop. Is needed to do work.
Energy Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1 Energy is a substance like quantity that can cause change. Makes objects move. Makes things stop. Is needed to do work.
Bernoulli s Principle. Application: Lift. Bernoulli s Principle. Main Points 3/13/15. Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper
 Bernoulli s Principle Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper Where the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. Due to continuous flow of a fluid: what goes in must come out! Fluid
Bernoulli s Principle Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper Where the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. Due to continuous flow of a fluid: what goes in must come out! Fluid
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206. GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206
 GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206 Be curious o How do they determine how many calories are in food? o Why do we put salt on the roads in winter? o What does Beano do? o Why do stalactites and stalagmites
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206 Be curious o How do they determine how many calories are in food? o Why do we put salt on the roads in winter? o What does Beano do? o Why do stalactites and stalagmites
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
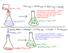 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry
 Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
THERMOCHEMISTRY. This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity and specific heat.
 I Name _ Date _ Class _ THERMOCHEMISTRY SECTION 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY-HEAT AND WORK (pages 505-510) This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity
I Name _ Date _ Class _ THERMOCHEMISTRY SECTION 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY-HEAT AND WORK (pages 505-510) This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity
Topic 3: Thermal physics 3.1 Thermal concepts
 Understandings: Molecular theory of solids, liquids and gases Temperature and absolute temperature Internal energy Specific heat capacity Phase change Specific latent heat Applications and skills: Describing
Understandings: Molecular theory of solids, liquids and gases Temperature and absolute temperature Internal energy Specific heat capacity Phase change Specific latent heat Applications and skills: Describing
October 5 A. Bell Work B. Have 4.2 Notes I Out for a stamp C. Today we will work on 4.2 Notes II D. Homework: 4.2 Notes II (due tomorrow end of
 October 5 A. Bell Work B. Have 4.2 Notes I Out for a stamp C. Today we will work on 4.2 Notes II D. Homework: 4.2 Notes II (due tomorrow end of class) Read 4.3 and take notes (due Monday) 4.2 Key Concept:
October 5 A. Bell Work B. Have 4.2 Notes I Out for a stamp C. Today we will work on 4.2 Notes II D. Homework: 4.2 Notes II (due tomorrow end of class) Read 4.3 and take notes (due Monday) 4.2 Key Concept:
Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo. Notes: Unit 7 Heat.
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Notes: Unit 7 Heat 1 Name: KEY IDEAS Heat is a transfer of energy (usually thermal energy) from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature. Thermal
Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Notes: Unit 7 Heat 1 Name: KEY IDEAS Heat is a transfer of energy (usually thermal energy) from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature. Thermal
2 Changes of State KEY IDEAS READING TOOLBOX ADDING AND REMOVING ENERGY. States of Matter. As you read this section, keep these questions in mind:
 CHAPTER 3 States of Matter 2 Changes of State SECTION KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens when a substance changes from one state of matter to another? What happens
CHAPTER 3 States of Matter 2 Changes of State SECTION KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens when a substance changes from one state of matter to another? What happens
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
q = m. C p. T q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C) UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
Name Date Class THERMOCHEMISTRY
 Name Date Class 17 THERMOCHEMISTRY SECTION 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK (pages 505 510) This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity
Name Date Class 17 THERMOCHEMISTRY SECTION 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK (pages 505 510) This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity
Name... Class... Date... Specific heat capacity and specific latent heat
 Specific heat capacity and specific latent heat Specification references: P3.2.2 Temperature changes in a system and specific heat capacity P3.2.3 Changes of heat and specific latent heat Aims This is
Specific heat capacity and specific latent heat Specification references: P3.2.2 Temperature changes in a system and specific heat capacity P3.2.3 Changes of heat and specific latent heat Aims This is
Chapter 3. Basic Principles. Contents
 Chapter 3. Basic Principles Contents 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Heat 3.3 Sensible Heat 3.4 Latent Heat 3.5 Evaporative Cooling 3.6 Convection 3.7 Transport 3.8 Energy Transfer Mediums 3.9 Radiation 3.10 Greenhouse
Chapter 3. Basic Principles Contents 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Heat 3.3 Sensible Heat 3.4 Latent Heat 3.5 Evaporative Cooling 3.6 Convection 3.7 Transport 3.8 Energy Transfer Mediums 3.9 Radiation 3.10 Greenhouse
2 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
 CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy 17. Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes 17.3 in Changes of State 17.4 Calculating s of Reaction Why does lava cool faster in water
CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy 17. Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes 17.3 in Changes of State 17.4 Calculating s of Reaction Why does lava cool faster in water
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Energy, Heat and Temperature. Introduction
 Energy, Heat and Temperature Introduction 3 basic types of energy: Potential (possibility of doing work because of composition or position) Kinetic (moving objects doing work) Radiant (energy transferred
Energy, Heat and Temperature Introduction 3 basic types of energy: Potential (possibility of doing work because of composition or position) Kinetic (moving objects doing work) Radiant (energy transferred
Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo. Student Version. Notes: Unit 6A Heat
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Student Version Notes: Unit 6A Heat Name: KEY IDEAS Heat is a transfer of energy (usually thermal energy) from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature.
Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Student Version Notes: Unit 6A Heat Name: KEY IDEAS Heat is a transfer of energy (usually thermal energy) from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature.
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Topic 19b. Thermal Properties of Matter
 Topic 19b The infra-red image of a head shows the distribution of heat. Different colours indicate different temperatures. Which do you think are the warmest regions? Thermal Properties of Matter contents
Topic 19b The infra-red image of a head shows the distribution of heat. Different colours indicate different temperatures. Which do you think are the warmest regions? Thermal Properties of Matter contents
Temperature, Heat, and Expansion
 Thermodynamics (Based on Chapters 21-24) Temperature, Heat, and Expansion (Ch 21) Warmth is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Temperature (21.1) The measure of how hot and cold things are is temperature.
Thermodynamics (Based on Chapters 21-24) Temperature, Heat, and Expansion (Ch 21) Warmth is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Temperature (21.1) The measure of how hot and cold things are is temperature.
Thermochemistry. Section The flow of energy
 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 - The flow of energy What is Energy? Energy is the capacity for doing work or supplying heat Energy does not have mass or volume, and it can only be detected because of its
Thermochemistry Section 17.1 - The flow of energy What is Energy? Energy is the capacity for doing work or supplying heat Energy does not have mass or volume, and it can only be detected because of its
Agenda. Chapter 10, Problem 26. All matter is made of atoms. Atomic Structure 4/8/14. What is the structure of matter? Atomic Terminology
 Agenda Today: HW Quiz, Thermal physics (i.e., heat) Thursday: Finish thermal physics, atomic structure (lots of review from chemistry!) Chapter 10, Problem 26 A boy reaches out of a window and tosses a
Agenda Today: HW Quiz, Thermal physics (i.e., heat) Thursday: Finish thermal physics, atomic structure (lots of review from chemistry!) Chapter 10, Problem 26 A boy reaches out of a window and tosses a
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. Problems: , , 5.100, 5.106, 5.108, , 5.121, 5.126
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Problems: 5.1-5.95, 5.97-98, 5.100, 5.106, 5.108, 5.118-5.119, 5.121, 5.126 Energy: Basic Concepts and Definitions energy: capacity to do work or to produce heat thermodynamics:
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Problems: 5.1-5.95, 5.97-98, 5.100, 5.106, 5.108, 5.118-5.119, 5.121, 5.126 Energy: Basic Concepts and Definitions energy: capacity to do work or to produce heat thermodynamics:
Unit 6: Energy. Aim: What is Energy? Energy: Energy is required to bring about changes in matter (atoms, ions, or molecules).
 Name: Date: Unit 6: Energy Aim: What is Energy? Energy: Energy is required to bring about changes in matter (atoms, ions, or molecules). Physical Changes Chemical Changes Example: Example: Energy is measured
Name: Date: Unit 6: Energy Aim: What is Energy? Energy: Energy is required to bring about changes in matter (atoms, ions, or molecules). Physical Changes Chemical Changes Example: Example: Energy is measured
Properties of Matter
 Properties of Matter Chapter 4 Hein and Arena Version 1.0 Eugene Passer Chemistry Department Bronx Community 1 College John Wiley and Sons, Inc Properties of Substances 2 Properties of a Substance A property
Properties of Matter Chapter 4 Hein and Arena Version 1.0 Eugene Passer Chemistry Department Bronx Community 1 College John Wiley and Sons, Inc Properties of Substances 2 Properties of a Substance A property
Station 1: Temperature
 Station 1: Temperature Temperature is the measure of kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. The movement of particles is actually what we measure as temperature. As we heat up substances, the
Station 1: Temperature Temperature is the measure of kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. The movement of particles is actually what we measure as temperature. As we heat up substances, the
Today. Work, Energy, Power loose ends Temperature Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Today Announcements: HW#5 is due by 8:00 am Wed. Feb. 5th. Extra Credit Exam due by Tomorrow 8am. Work, Energy, Power loose ends Temperature Second Law of Thermodynamics ISP09s9 Lecture 11-1- Energy and
Today Announcements: HW#5 is due by 8:00 am Wed. Feb. 5th. Extra Credit Exam due by Tomorrow 8am. Work, Energy, Power loose ends Temperature Second Law of Thermodynamics ISP09s9 Lecture 11-1- Energy and
Chemistry Review Unit 5 Physical Behavior of Matter
 Chemistry Review Phases of Matter, Changes of Phase, Substances, Mixtures, Solutions, Effect of Solute on Solution, Energy, Kinetics of Solids, Liquids and Gases Matter, Phases and Gas Laws 1. Matter is
Chemistry Review Phases of Matter, Changes of Phase, Substances, Mixtures, Solutions, Effect of Solute on Solution, Energy, Kinetics of Solids, Liquids and Gases Matter, Phases and Gas Laws 1. Matter is
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Thermodynamics and States of Matter
 Thermodynamics and States of Matter There are three states (also called phases) ) of matter. The picture to the side represents the same chemical substance, just in different states. There are three states
Thermodynamics and States of Matter There are three states (also called phases) ) of matter. The picture to the side represents the same chemical substance, just in different states. There are three states
Per 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture
 er 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic icture 5. How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? ) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) Watch
er 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic icture 5. How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? ) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) Watch
Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is energy? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: What is work? Q: Potential Energy
 Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 2 Matter and Energy. 2.1 Classification of Matter. Matter. Pure Substances
 Slide 1 Chapter 2 Matter and Energy 1 2.1 Classification of Matter Slide 2 2 Matter Matter is the material that makes up all things is anything that has mass and occupies space Slide 3 Pure Substances
Slide 1 Chapter 2 Matter and Energy 1 2.1 Classification of Matter Slide 2 2 Matter Matter is the material that makes up all things is anything that has mass and occupies space Slide 3 Pure Substances
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20
 Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy
 I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
Broughton High School. Thermal Energy. Physical Science Workbook Chapter 6 Thermal Energy 2016 Mr. Davis
 1 Thermal Energy Vocabulary for Chapter 6 Thermal Energy Broughton High School Physical Science Vocabulary No.# Term Page # Definition 2 1. Degrees 2. Higher Specific Heat 3. Heat of Vaporization 4. Radiation
1 Thermal Energy Vocabulary for Chapter 6 Thermal Energy Broughton High School Physical Science Vocabulary No.# Term Page # Definition 2 1. Degrees 2. Higher Specific Heat 3. Heat of Vaporization 4. Radiation
Calculate the mass of L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure.
 148 Calculate the mass of 22650 L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure. 1 - Convert the volume of oxygen gas to moles using IDEAL GAS EQUATION 2 - Convert moles oxygen gas to mass using formula
148 Calculate the mass of 22650 L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure. 1 - Convert the volume of oxygen gas to moles using IDEAL GAS EQUATION 2 - Convert moles oxygen gas to mass using formula
Page 1 SPH3U. Heat. What is Heat? Thermal Physics. Waterloo Collegiate Institute. Some Definitions. Still More Heat
 SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
Duncan. Q = m. C p. T. Q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat capacity (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C)
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES SECTION (A): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (B): phase(s) of matter = energy difference at same temp = temp is called the SECTION (C): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (D): phase(s) of matter
HEAT ENERGY NOTES SECTION (A): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (B): phase(s) of matter = energy difference at same temp = temp is called the SECTION (C): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (D): phase(s) of matter
The Can Demonstration
 The Can Demonstration With your table, make a prediction as to what will happen to the can. Discuss why you think that the can imploded. What are some reasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xg5niowf_zw&t=28s
The Can Demonstration With your table, make a prediction as to what will happen to the can. Discuss why you think that the can imploded. What are some reasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xg5niowf_zw&t=28s
Ch 100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
 Ch 100: Fundamentals for Chemistry Chapter 4: Properties of Matter Lecture Notes Physical & Chemical Properties Physical Properties are the characteristics of matter that can be changed without changing
Ch 100: Fundamentals for Chemistry Chapter 4: Properties of Matter Lecture Notes Physical & Chemical Properties Physical Properties are the characteristics of matter that can be changed without changing
Page #1 & Activity #54-Drive a Nail
 Name: Page #1 & Activity #54-Drive a Nail Quiz Act # s 54-63 Study Guide 1.) What is the definition of energy? (page 1) The ability to do work. (anything that can cause an object to change, work or move)
Name: Page #1 & Activity #54-Drive a Nail Quiz Act # s 54-63 Study Guide 1.) What is the definition of energy? (page 1) The ability to do work. (anything that can cause an object to change, work or move)
Start Part 2. Tro's "Introductory Chemistry", Chapter 3
 Start Part 2 1 Separation of Mixtures Separate mixtures based on different physical properties of the components. Physical change. Different Physical Property Boiling point State of matter (solid/liquid/gas)
Start Part 2 1 Separation of Mixtures Separate mixtures based on different physical properties of the components. Physical change. Different Physical Property Boiling point State of matter (solid/liquid/gas)
Core Concepts. PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e. Chapter 4 Heat and Temperature. New Symbols for this Chapter 2/14/2011
 PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e Chapter 4 Heat and Temperature Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. New Symbols for this Chapter
PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e Chapter 4 Heat and Temperature Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. New Symbols for this Chapter
Temperature and Its Measurement
 Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 26
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 26 Chapter 14: Heat 14.1 Internal Energy 14.2 Heat 14.3 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat 14.5 Phase Transitions 14.6 Thermal Conduction 14.7 Thermal Convection 14.8 Thermal Radiation
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 26 Chapter 14: Heat 14.1 Internal Energy 14.2 Heat 14.3 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat 14.5 Phase Transitions 14.6 Thermal Conduction 14.7 Thermal Convection 14.8 Thermal Radiation
Unit 3: States of Matter, Heat and Gas Laws
 Unit 3 - Stevens 1 Unit 3: States of Matter, Heat and Gas Laws Vocabulary: Solid Term Definition Example Liquid Gas No definite shape, but definite volume; Particles close together, but can move around
Unit 3 - Stevens 1 Unit 3: States of Matter, Heat and Gas Laws Vocabulary: Solid Term Definition Example Liquid Gas No definite shape, but definite volume; Particles close together, but can move around
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes
 Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
q = m x C x ΔT or, think of it as unit cancellation: = ( ) (
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Heat, Kinetic Energy, and Changes in State of Matter *Kinetic Energy=the energy associated with *Temperature=measure of the of a sample. *Heat=is measured as the that is
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Heat, Kinetic Energy, and Changes in State of Matter *Kinetic Energy=the energy associated with *Temperature=measure of the of a sample. *Heat=is measured as the that is
Thermal energy. Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules.
 Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3. Temperature & Heat
 Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics Specific Heat (Capacity) Specific Heat Latent Heat
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics Specific Heat (Capacity) Specific Heat Latent Heat
Notes: Matter & Change (text Ch. 1 &10)
 Name Per. Notes: Matter & Change (text Ch. 1 &10) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to get missing
Name Per. Notes: Matter & Change (text Ch. 1 &10) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to get missing
Study Guide Unit 3 Chapter 6 DRAFT
 Study Guide Unit 3 Chapter 6 DRAFT Unit 3 BIG IDEAS Energy can be transformed from one type into another. Energy transformation systems often involve thermal energy losses and are never 100 % efficient.
Study Guide Unit 3 Chapter 6 DRAFT Unit 3 BIG IDEAS Energy can be transformed from one type into another. Energy transformation systems often involve thermal energy losses and are never 100 % efficient.
