Readout of LYSO using a new silicon photodetector for positron emission tomography
|
|
|
- Penelope Hoover
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 23 Readout of LYSO using a new silicon photodetector for positron emission tomography M. L. Lerch University of Wollongong, mlerch@uow.edu.au R. Ward University of Wollongong Philip E. Simmonds University of Wollongong, simmonds@uow.edu.au V. L. Perevertailo SPA-BIT "Detector", Kiev, Ukraine S. R. Meikle Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney See next page for additional authors Publication Details This article was originally published as: Lerch, MLF, Ward, R, Simmonds, PE et al, Readout of LYSO using a new silicon photodetector for positron emission tomography, IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, October 23, vol 2, Copyright IEEE 23. Research Online is the open access institutional repository for the University of Wollongong. For further information contact the UOW Library: research-pubs@uow.edu.au
2 Authors M. L. Lerch, R. Ward, Philip E. Simmonds, V. L. Perevertailo, S. R. Meikle, G. N. Taylor, and Anatoly B. Rosenfeld This conference paper is available at Research Online:
3 Readout of LYSO Using a New Silicon Photodetector for Positron Emission Tomography Michael L.F. Lerch, Member, IEEE, Robert Ward Student Member, IEEE, Phillip E. Simmonds, Vladimir L. Pervertailo, Steven R. Meikle, Geoffery N. Taylor and Anatoly B. Rosenfeld, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract--. This article focuses on the characterisation of three versions of a custom designed silicon photodetector using nuclear spectroscopy techniques. Room temperature gamma ray spectroscopy experiments have been performed using an LYSO excited by 137 Cs and 22 Na sources and read out by the new photodiodes. We have measured an energy resolution of 13.1% FWHM for the 511 kev gamma rays from a 22 Na source and 11.2% FWHM for the 662 kev gamma rays from a 137 Cs source. This is one of the best ever-reported energy resolutions for a lutetium based scintillator crystal read out by a silicon photodetector. I. INTRODUCTION urrent commercial PET scanners are general purpose C devices which are designed to support a wide range of clinical applications. These generally require a scanner with reasonably large detector ring diameter ( 8 cm) and the ability to image the whole body in incremental steps. Recently, new applications of PET have emerged which place different demands on PET instrumentation, requiring high spatial resolution and sensitivity, in particular for imaging small volumes. Such applications include small animal imaging, breast cancer imaging and high resolution brain imaging. With these emerging applications, a large ring diameter is not only not required but also limits the performance that can be achieved when imaging small volumes. Manuscript received October 7, 23. This work was supported in part by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council under Grant No , the Australian Institute for Nuclear Science and Engineering under grant number 884 and Insight Oceania Pty Ltd., Australia M.L.F. Lerch ( mlerch@uow.edu.au), R. Ward, P.E. Simmonds A.B. Rosenfeld are with the Centre for Medical Radiation Physics, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, NSW, 2522, Australia, Ph V.L.Pervertailo is with SPA-BIT, Kiev, Ukraine S.R. Meikle is with the PET and Nuclear Medicine Department, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney, NSW, Australia G.N. Taylor is with the High Energy Physics Department, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Vic, Australia Significant research has been undertaken in the development of read out schemes of scintillator crystal configurations in an attempt to improve the spatial resolution of PET scanners [1,2]. We are developing a new Positron Emission Tomography (PET) detection module with depth of interaction capability. Pixilated scintillation crystals read out by silicon 8x8 photodiode arrays form the basis of the new module. The new photodiode arrays were designed by the Centre for Medical Radiation Physics and produced by SPA Detector, Ukraine. Silicon photodiodes represent the relatively cheap and robust end of the silicon based photodetector (PD) market. Improvement in the photodiode quantum efficiency at wavelengths around 42 nm (the peak emission wavelength of LSO), whist maintaining good photogenerated charge collection times, represents one of the biggest challenges in the photodiode design. We have designed a silicon PD to improve the PD quantum efficiency near the emission wavelength of LSO. This article concentrates on comparison of the nuclear spectroscopic performance of the new PDs. In particular we are interested in measuring any quantitative improvement of the scintillation light collection efficiency of the diodes to see if it correlates with the measured improvement in the quantum efficiency. II. DETECTORS AND METHODS A. Detectors The photodiodes are of a planar design consisting of a 3x3 mm 2 active area and are 3 µm thick. The detectors were produced by SPA-BIT Detector, Ukraine on high resistivity n- Si (Resistivity 5 kωcm). Three versions of the diode were produced: SPAD1, SPAD2 and SPAD3. SPAD 2 and 3 are both structurally similar to SPAD1. However, SPAD2 includes p+ strips at the surface of the p- layer aimed at enhancing the charge collection time as shown in Fig. 1. SPAD3 includes an additional antireflective layer to improve photon detection near the 43 nm (peak emission wavelength of the LYSO scintillator)[3] /4/$2. 24 IEEE. 148
4 The LYSO scintillator crystals have an emission spectrum that nominally peaks at 43 nm [4]. The absorption length of light with a wavelength of 43 nm is.1-.2 µm in silicon. In order to improve the sensitivity of the new photodiodes at wavelengths in the region of 4nm we are using an (boron) ion implantation technique to produce the p - -layer that is optically coupled to the scintillator crystal. This technique allows the resulting electric field to extend very close to the p - active surface, which has the dimensions of 3x3 mm 2 for each pixel element in our array, when the PD is under bias while still maintaining the potential across the p - surface. In effect we are able to improve the sensitivity of the PD in the blue spectral region, by reducing the effect of Auger recombination, while maintaining good charge collection properties to ensure fast timing signals for coincident detection techniques. p - -layer SiO 2 (.1 µm ) SiO 2 (.5 µm ) Al passivation layer ( 1. µm ) C. Spectroscopy Experiments For gamma and X-ray spectroscopy experiments the spectroscopy readout arrangement comprised of an AMPTEK A25 preamplifier and a Canberra 221, spectroscopy amplifier. A PC, using software supplied with the MCA, collected the data via an AMPTEK TM 8A MCA. D. Scintillator Light Collection Efficiency The complicated nature of the optical transparent layers forming the entrance window of the PD leads to a complicated quantum efficiency (QE) curve as a function of incident optical photon angle (measured from the normal to the PD surface) [3]. The QE also varies with wavelength [3]. In order to compare one the gamma ray spectroscopy performance indicators of the different PD designs we have the SCLICE. SLICE is the scintillator light collection efficiency and is simply the deduced number of photons detected by the PD divided by the estimated absolute number of optical photons emitted within the scintillator per gamma ray event (~13,3 photons per 511 kev event for our LYSO). We have assumed here that each optical photon detected produces one electron hole pair in the PD. For SLICE deductions direct X-ray spectroscopy (no scintillator crystal attached) data is used and was obtained under identical experimental conditions. n-layer n + -layer p - -layer SiO 2 (.1 µm ) Fig. 1(a) SiO 2 (.5 µm ) Al p + -strips Al-layer passivation layer ( 1. µm ) III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. Quantum Efficiency Fig. 2 shows the external quantum efficiency (QE) of the SPAD3 relative to SPAD1 over the wavelength range of 38 nm to 6 nm. The experimental method used to obtain this data is outlined in ref. [5]. The quantum efficiency of the SPAD3 is also shown on the same graph. The absolute responses were measured carefully under the same experimental conditions n-layer n + Al-layer -layer Fig. 1(b) Fig. 1 Schematic cut-away view of SPAD1 and SPAD2. The two designs differ in that one has a uniform p - layer at the surface (Fig. 1a) and the other has p + strips embedded in the p - layer (Fig. 1b). B. Scintillators The LYSO scintillator material was purchased from Crystal Photonics Inc.(CPI), Sanford, Florida, USA. The material was subsequently cut into 3x3x3 mm 3 cubes and polished and the absolute light output determined by A&D Precision Co., Newton, MA, USA. The absolute light output was deduced to be ~26 photons/kev, which is 65% of that of NaI (~4 photons/kev). Relative quantum efficiency Wavelength (nm) Figure 2. Relative quantum efficiency (QE) of SPAD3 to SPAD1 together with the external QE of SPAD Quantum efficiency /4/$2. 24 IEEE. 149
5 The data indicates that the measured relative response and deduced quantum of SPAD3 is significantly enhanced compared to SPAD1 over the blue/violet spectral region. The enhancement in the blue/violet region reaches a maximum of 1.8x at 45 nm. The internal quantum efficiency of these diodes has also been measured by us and is the same [3]. The deduced quantum efficiency for SPAD3 shown in Fig. 2 peaks at 45 nm where it is 81%. Across several photodiodes the peak wavelength varied by ± 15 nm and the peak quantum efficiency varied by ± 5%. This result is quite significant in that it indicates that SPAD3 is performing to its design specifications and hence is well suited for use with the LYSO scintillator whose emission wavelength peaks in the blue/violet spectral region. B. Gamma Ray Spectroscopy In gamma ray spectroscopy experiments the SPAD PD was optically coupled to a 3x3x3mm 3 LYSO crystal. The crystal has the same dimensions as that to be used in our detector module that incorporates pixilated crystals. The best-measured energy resolution was 13.1% FWHM for the 511 kev gamma rays and 11.2% FWHM for the 662 kev gamma rays from the 22 Na and 137 Cs source respectively. This result is shown in Fig 3 and was achieved using the SPAD3 PD, biased at 5V, to readout the painted LYSO scintillator, with a shaping time of.5 µs. Also shown in Fig 3 is the contribution to the FWHM from the readout electronics and PD system. The measured 8.2 % is equivalent to ~2e - rms. A variation in the energy resolution of ± 1% was observed by reading out the same LYSO crystal with several copies of the SPAD3 PD made from different parts of the wafer also used to make the silicon 8x8 arrays in the PET module. ADC Counts FWHM = 8.2% FWHM = 13.1% SPAD3 + LYSO Bias 5 V.5 µs shaping time FWHM = 11.2% Cs-137 Series2 Na-22 Series1 Pulser Figure 3. Pulse height spectrum of 22 Na and 137 Cs. Table 1 shows the experimentally measured energy resolution (T = 298 K) as a function of shaping time using the SPAD 3 photodetector at 5 V bias to read out the 3x3x3 mm 3 painted LYSO scintillator crystal excited by a 22 Na source. The excellent energy resolution measured at short shaping times indicates that the PD can operate well under high count rate conditions if necessary, which is important in PET. Shaping Time (µs) E/E (SPAD3 + LYSO) 511 kev photopeak % % % % Table 1 Energy resolution as a function of shaping time. Fig. 4 shows the room temperature (298 K) pulse height spectrum when the LYSO crystal is excited by a 22 Na and 137 Cs source and read out by SPAD1 (top), SPAD2 (middle) and SPAD3 (bottom) PD respectively. In these experiments a 1. µs shaping time was used. Fig. 4 shows the ADC channel on the X- axis, which is proportional to the signal pulse from each detector. In this case the qualitative differences between each readout method is clearly observable. A quantitative comparison of the readout methods related to each PD is given in Table 2. C. Scintillator Light Collection Efficiency Fig. 4 shows the ADC channel on the X-axis and energy on the X2-axis. In this case the relative improvement in the scintillator light collection efficiency (SLICE) for each version of the SPAD PD is clear as all experiments were performed under the same conditions. A quantitative estimate of the number of e-h pairs created by the optical scintillator photons detected by the PD can be obtained using a direct X-ray spectrum measured under the same operating and measuring conditions as shown in Fig. 5. The 511 kev photopeak occurs at the same channel as a 24.8 kev X-ray event directly detected in the PD. Therefore effectively 685±7 optical photons are detected by the PD per 511 kev event in the LYSO crystal. Given that for our LYSO we expect 13,3±65 photons per 511 kev event the SLICE in this case is 53 ±.4%. A summary of the SLICE for each PD is shown in Table 2. Table 2 shows that an 18% improvement is observed in the scintillation light collection efficiency between the SPAD1 and SPAD3 readout scheme. This improvement is very significant in the application of these PDs for PET but is far less than the increase in measured external quantum efficiency. In order to understand this observation one must take into account the angular dependence and wavelength dependence of the optical response in combination with the angular distribution of the /4/$2. 24 IEEE. 141
6 optical photons incident on the PD surface. We are doing this work as part of a separate study [3]. Counts Counts SPAD1 + LYSO SPAD2 + LYSO scheme was less significant than expected. The reduction is due to the addition of p+ strips within the active layer of the SPAD2 PD effectively reducing the internal quantum efficiency of the PD. The p+ strips occupy approximately one third of the active area. The minor reduction in efficiency could be tolerated if a significant improvement in the timing properties of the PD is observed. This study is currently on going. ADC Counts kev 22 kev 27 kev Bias 5 V.5 µs shaping time Series2 SPAD3 + I -125 direct Series1 SPAD3 + LYSO + Na Fig. 5 Room temperature pulse height spectrum of an LYSO crystal excited by a 22 Na source and read out by SPAD3 overlayed with an 125 I spectrum directly detected in the same PD. All operating and measurement conditions are identical. 2 Counts SPAD3 + LYSO Fig. 4 Room temperature (298 K) pulse height spectrum when the LYSO crystal is excited by a 22 Na and 137 Cs source and read out by SPAD1 (top), SPAD2 (middle) and SPAD3 (bottom) PD respectively. The small decrease of 3±.3% in the scintillation light collection efficiency between the SPAD1 and SPAD2 readout PD E/E (LYSO) Scintillator Light Collection 511 kev peak Efficiency (SLICE) SPAD % 58 optical photons detected or 43.6 ±.4% SPAD % 58 optical photons detected or 42.1 ±.4% SPAD % 58 optical photons detected or 53. ±.4% Table 2 Comparison of the measured energy resolution (shaping time of.5 µs) and scintillator light collection efficiency (SLICE) for SPAD 1, SPAD2 and SPAD3. IV. CONCLUSION We have characterised the custom designed silicon photodiodes using nuclear spectroscopic techniques that will be used in the development of a new detector module for positron emission tomography. The SPAD3 PDs have a measured quantum efficiency of 81% at 45 nm. We have measured an energy resolution of 13.1% FWHM for the 511 kev gamma rays from a 22 Na source. The new photodiodes are well suited for the /4/$2. 24 IEEE. 1411
7 readout of scintillators whose emission wavelength peak in the blue/violet spectral region. V. REFERENCES [1] Pichler, B.J., Bernecker, F., Boning, G., Rafecas, M., Pimpl, W., Schwaiger, M., Lorenz, E., Ziegler, S.I., A 4x8 APD array, consisting of two monolithic silicon wafers, coupled to a 32- channel LSO matrix for high-resolution PET. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., Vol. 48 (4), , 21 [2] Levin, C.S., Design of a high resolution and high sensitivity scintillation crystal array with nearly perfect light collection Presented at 21 IEEE NSS and MIC Conference, San Diego, USA [3] R.D. Ward, M.L.F. Lerch, P.E. Simmonds, G. Takacs, V. Perevertailo, and A.B. Rosenfeld, Angular dependence of response in a New Silicon Photodiode for use in PET presenting at IEEE NSS/MIC conference 23. [4] Saoudi, A., Pepin, C., Pepin, C., Houde, D., and Lecomte, R., Scintillation light emission studies of LSO scintillators, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., Vol. 46 (6), , 1999 [5] M.L.F.Lerch, A.B.Rosenfeld, P.E. Simmonds, G.N.Taylor, S.R.Meikle, V.L. Perevertailo Spectral Characterization of blueenhanced silicon photodiode, IEEE Trans. on Nucl. Sci., NS-48, N-4, , /4/$2. 24 IEEE. 1412
Charge collection in PET detectors
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2007 Charge collection in PET detectors Tony Young University of
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2007 Charge collection in PET detectors Tony Young University of
A dual scintillator - dual silicon photodiode detector module for intraoperative gamma\beta probe and portable anti-compton spectrometer
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2008 A dual scintillator - dual silicon photodiode detector module for
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2008 A dual scintillator - dual silicon photodiode detector module for
Gamma ray coincidence and angular correlation
 University of Cape Town Department of Physics Course III laboratory Gamma ray coincidence and angular correlation Introduction Medical imaging based on positron emission tomography (PET) continues to have
University of Cape Town Department of Physics Course III laboratory Gamma ray coincidence and angular correlation Introduction Medical imaging based on positron emission tomography (PET) continues to have
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A () Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima The
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A () Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima The
A scintillation dual-detector system featuring active Compton suppression
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2007 A scintillation dual-detector system featuring active Compton
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2007 A scintillation dual-detector system featuring active Compton
Recent Advances of Planar Silicon APD Technology
 Recent Advances of Planar Silicon APD Technology M. McClish 1, R. Farrell 1, R. Myers 1, F. Olschner 2, G. Entine 1, K.S. Shah 1 1 Radiation Monitoring Devices Inc., Watertown, MA 2 Cremat Inc., Newton,
Recent Advances of Planar Silicon APD Technology M. McClish 1, R. Farrell 1, R. Myers 1, F. Olschner 2, G. Entine 1, K.S. Shah 1 1 Radiation Monitoring Devices Inc., Watertown, MA 2 Cremat Inc., Newton,
CHIPP Plenary Meeting University of Geneva, June 12, 2008 W. Lustermann on behalf of the AX PET Collaboration
 CHIPP Plenary Meeting University of Geneva, June 12, 2008 W. Lustermann on behalf of the AX PET Collaboration INFN Bari, Ohio State University, CERN, University of Michigan, University of Oslo, INFN Roma,
CHIPP Plenary Meeting University of Geneva, June 12, 2008 W. Lustermann on behalf of the AX PET Collaboration INFN Bari, Ohio State University, CERN, University of Michigan, University of Oslo, INFN Roma,
Detectors for High Resolution Gamma-ray Imaging Based on a Single CsI(Tl) Scintillator Coupled to an Array of Silicon Drift Detectors
 1 Detectors for High Resolution Gamma-ray Imaging Based on a Single CsI(Tl) Scintillator Coupled to an Array of Silicon Drift Detectors C. Fiorini, A. Longoni, F. Perotti, C. Labanti, E. Rossi, P. Lechner,
1 Detectors for High Resolution Gamma-ray Imaging Based on a Single CsI(Tl) Scintillator Coupled to an Array of Silicon Drift Detectors C. Fiorini, A. Longoni, F. Perotti, C. Labanti, E. Rossi, P. Lechner,
Gamma-ray Spectroscopy with LaBr 3 :Ce Scintillator Readout by a Silicon Drift Detector
 Gamma-ray Spectroscopy with LaBr 3 :Ce Scintillator Readout by a Silicon Drift Detector C. Fiorini, member, IEEE, A. Gola, M. Zanchi, A. Longoni, P. Lechner, H. Soltau, L. Strüder Abstract In this work
Gamma-ray Spectroscopy with LaBr 3 :Ce Scintillator Readout by a Silicon Drift Detector C. Fiorini, member, IEEE, A. Gola, M. Zanchi, A. Longoni, P. Lechner, H. Soltau, L. Strüder Abstract In this work
Investigation of Position Sensitive Avalanche Photodiodes for a New High Resolution PET Detector Design
 Investigation of Position Sensitive Avalanche Photodiodes for a New High Resolution PET Detector Design Craig S. Levin, Member, IEEE, Angela M. K. Foudray, Student Member, IEEE, Peter D. Olcott, Frezghi
Investigation of Position Sensitive Avalanche Photodiodes for a New High Resolution PET Detector Design Craig S. Levin, Member, IEEE, Angela M. K. Foudray, Student Member, IEEE, Peter D. Olcott, Frezghi
Development of a High Precision Axial 3-D PET for Brain Imaging
 Development of a High Precision Axial 3-D PET for Brain Imaging On behalf of the AX-PET Collaboration SIENA - IPRD08 October 1st 4th, 2008 1 Outline Basics of Positron Emission Tomography (PET); Principle
Development of a High Precision Axial 3-D PET for Brain Imaging On behalf of the AX-PET Collaboration SIENA - IPRD08 October 1st 4th, 2008 1 Outline Basics of Positron Emission Tomography (PET); Principle
Positron Emission Tomography
 Positron Emission Tomography Presenter: Difei Wang June,2018 Universität Bonn Contents 2 / 24 1 2 3 4 Positron emission Detected events Detectors and configuration Data acquisition Positron emission Positron
Positron Emission Tomography Presenter: Difei Wang June,2018 Universität Bonn Contents 2 / 24 1 2 3 4 Positron emission Detected events Detectors and configuration Data acquisition Positron emission Positron
Neutron Induced Nuclear Counter Effect in Hamamatsu Silicon APDs and PIN Diodes
 Neutron Induced Nuclear Counter Effect in Hamamatsu Silicon APDs and PIN Diodes Rihua Mao, Liyuan Zhang, Ren-yuan Zhu California Institute of Technology Introduction Because of its immunity to magnetic
Neutron Induced Nuclear Counter Effect in Hamamatsu Silicon APDs and PIN Diodes Rihua Mao, Liyuan Zhang, Ren-yuan Zhu California Institute of Technology Introduction Because of its immunity to magnetic
arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013](/thumbs/91/107598870.jpg) Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION arxiv:1302.0278v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013 Investigation of gamma ray detection performance of thin LFS scintillator with MAPD readout E.Guliyev a, F.Ahmadov
Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION arxiv:1302.0278v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013 Investigation of gamma ray detection performance of thin LFS scintillator with MAPD readout E.Guliyev a, F.Ahmadov
Key words: avalanche photodiode, soft X-ray detector, scintillation γ-ray detector, imaging device PACS: 07.85;95.55.A;85.60.D
 We have studied the performance of large area avalanche photodiodes (APDs) recently developed by Hamamatsu Photonics K.K, in high-resolution X-rays and γ- rays detections. We show that reach-through APD
We have studied the performance of large area avalanche photodiodes (APDs) recently developed by Hamamatsu Photonics K.K, in high-resolution X-rays and γ- rays detections. We show that reach-through APD
Stand-off Nuclear Radiation Detection
 Stand-off Nuclear Radiation Detection Peter E. Vanier Detector Development and Testing Div. Nonproliferation and National Security Dept. Brookhaven National Laboratory Brookhaven Science Associates U.S.
Stand-off Nuclear Radiation Detection Peter E. Vanier Detector Development and Testing Div. Nonproliferation and National Security Dept. Brookhaven National Laboratory Brookhaven Science Associates U.S.
Prospects for achieving < 100 ps FWHM coincidence resolving time in time-of-flight PET
 Prospects for achieving < 100 ps FWHM coincidence resolving time in time-of-flight PET, 28-Feb-2012, ICTR-PHE, Geneva, Switzerland 1 Time-of-flight PET Colon cancer, left upper quadrant peritoneal node
Prospects for achieving < 100 ps FWHM coincidence resolving time in time-of-flight PET, 28-Feb-2012, ICTR-PHE, Geneva, Switzerland 1 Time-of-flight PET Colon cancer, left upper quadrant peritoneal node
Energy resolution and absolute detection efficiency for LSO crystals: a comparison between Monte Carlo simulation and experimental data
 Energy resolution and absolute detection efficiency for LSO crystals: a comparison between Monte Carlo simulation and experimental data Harold Rothfuss a,b, Larry Byars c, Michael E. Casey a, Maurizio
Energy resolution and absolute detection efficiency for LSO crystals: a comparison between Monte Carlo simulation and experimental data Harold Rothfuss a,b, Larry Byars c, Michael E. Casey a, Maurizio
Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors. Tobias Eggert Ketek GmbH
 Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Tobias Eggert Ketek GmbH Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Part A Principles of Semiconductor Detectors 1. Basic Principles 2. Typical Applications 3. Planar Technology 4. Read-out
Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Tobias Eggert Ketek GmbH Semiconductor X-Ray Detectors Part A Principles of Semiconductor Detectors 1. Basic Principles 2. Typical Applications 3. Planar Technology 4. Read-out
Silicon Drift Detectors for gamma-ray detection: 15 years of research (and collaboration between Politecnico and INAF-Milano)
 Silicon Drift Detectors for gamma-ray detection: 15 years of research (and collaboration between Politecnico and INAF-Milano) Outline The Silicon Drift Detector (SDD) Gamma-ray detectors based on scintillators
Silicon Drift Detectors for gamma-ray detection: 15 years of research (and collaboration between Politecnico and INAF-Milano) Outline The Silicon Drift Detector (SDD) Gamma-ray detectors based on scintillators
Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection
 Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection R. Kreuger, C. W. E. van Eijk, Member, IEEE, F. A. F. Fraga, M. M. Fraga, S. T. G. Fetal, R. W. Hollander, Member, IEEE, L. M.
Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection R. Kreuger, C. W. E. van Eijk, Member, IEEE, F. A. F. Fraga, M. M. Fraga, S. T. G. Fetal, R. W. Hollander, Member, IEEE, L. M.
Time-of-Flight PET using Cherenkov Photons Produced in PbF 2
 Photons Produced in PbF 2 R. Dolenec a, S. Korpar b,a, P. Križan c,a, R. Pestotnik a, A. Stanovnik d,a a, Ljubljana, Slovenia b Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Maribor, Slovenia
Photons Produced in PbF 2 R. Dolenec a, S. Korpar b,a, P. Križan c,a, R. Pestotnik a, A. Stanovnik d,a a, Ljubljana, Slovenia b Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Maribor, Slovenia
Gamma-ray spectroscopy with the scintillator/photomultiplierand with the high purity Ge detector: Compton scattering, photoeffect, and pair production
 Experiment N2: Gamma-ray spectroscopy with the scintillator/photomultiplierand with the high purity Ge detector: Compton scattering, photoeffect, and pair production References: 1. Experiments in Nuclear
Experiment N2: Gamma-ray spectroscopy with the scintillator/photomultiplierand with the high purity Ge detector: Compton scattering, photoeffect, and pair production References: 1. Experiments in Nuclear
ISPA-Tubes with YAP:Ce Active Windows for X and Gamma Ray Imaging.
 PIXEL 2000 International Workshop on Semiconductor Pixel Detectors for Particles and X-Rays Genova - Porto Antico - Magazzini del Cotone (Sala Libeccio) June 5-8, 2000 ISPA-Tubes with YAP:Ce Active Windows
PIXEL 2000 International Workshop on Semiconductor Pixel Detectors for Particles and X-Rays Genova - Porto Antico - Magazzini del Cotone (Sala Libeccio) June 5-8, 2000 ISPA-Tubes with YAP:Ce Active Windows
Compton Camera. Compton Camera
 Diagnostic Imaging II Student Project Compton Camera Ting-Tung Chang Introduction The Compton camera operates by exploiting the Compton Effect. It uses the kinematics of Compton scattering to contract
Diagnostic Imaging II Student Project Compton Camera Ting-Tung Chang Introduction The Compton camera operates by exploiting the Compton Effect. It uses the kinematics of Compton scattering to contract
Scintillation Detectors
 Scintillation Detectors J.L. Tain Jose.Luis.Tain@ific.uv.es http://ific.uv.es/gamma/ Instituto de Física Corpuscular C.S.I.C - Univ. Valencia Scintillation detector: SCINTILLATION MATERIAL LIGHT-GUIDE
Scintillation Detectors J.L. Tain Jose.Luis.Tain@ific.uv.es http://ific.uv.es/gamma/ Instituto de Física Corpuscular C.S.I.C - Univ. Valencia Scintillation detector: SCINTILLATION MATERIAL LIGHT-GUIDE
GAMMA RAY SPECTROSCOPY
 GAMMA RAY SPECTROSCOPY Gamma Ray Spectroscopy 1 In this experiment you will use a sodium iodide (NaI) detector along with a multichannel analyzer (MCA) to measure gamma ray energies from energy level transitions
GAMMA RAY SPECTROSCOPY Gamma Ray Spectroscopy 1 In this experiment you will use a sodium iodide (NaI) detector along with a multichannel analyzer (MCA) to measure gamma ray energies from energy level transitions
hν' Φ e - Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous?
 Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous? 2. Briefly discuss dead time in a detector. What factors are important
Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous? 2. Briefly discuss dead time in a detector. What factors are important
X-ray spectrometry with Peltier-cooled large area avalanche photodiodes
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 213 (24) 267 271 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb X-ray spectrometry with Peltier-cooled large area avalanche photodiodes L.M.P. Fernandes, J.A.M. Lopes,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 213 (24) 267 271 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb X-ray spectrometry with Peltier-cooled large area avalanche photodiodes L.M.P. Fernandes, J.A.M. Lopes,
Application of Nuclear Physics
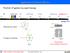 Application of Nuclear Physics Frontier of gamma-ray spectroscopy 0.1 IR visible light UV soft X-ray X-ray hard X-ray gamma-ray 1 10 100 1e3 1e4 1e5 1e6 energy [ev] Photoelectric effect e - Compton scattering
Application of Nuclear Physics Frontier of gamma-ray spectroscopy 0.1 IR visible light UV soft X-ray X-ray hard X-ray gamma-ray 1 10 100 1e3 1e4 1e5 1e6 energy [ev] Photoelectric effect e - Compton scattering
A monolithic array of silicon drift detectors coupled to a single scintillator for γ-ray imaging with sub-millimeter position resolution
 1 A monolithic array of silicon drift detectors coupled to a single scintillator for γ-ray imaging with sub-millimeter position resolution C.Fiorini a*, A.Longoni a, F.Perotti b, C.Labanti c, E.Rossi c,
1 A monolithic array of silicon drift detectors coupled to a single scintillator for γ-ray imaging with sub-millimeter position resolution C.Fiorini a*, A.Longoni a, F.Perotti b, C.Labanti c, E.Rossi c,
Geant4 simulation of SOI microdosimetry for radiation protection in space and aviation environments
 Geant4 simulation of SOI microdosimetry for radiation protection in space and aviation environments Dale A. Prokopovich,2, Mark I. Reinhard, Iwan M. Cornelius 3 and Anatoly B. Rosenfeld 2 Australian Nuclear
Geant4 simulation of SOI microdosimetry for radiation protection in space and aviation environments Dale A. Prokopovich,2, Mark I. Reinhard, Iwan M. Cornelius 3 and Anatoly B. Rosenfeld 2 Australian Nuclear
Detector technology. Aim of this talk. Principle of a radiation detector. Interactions of gamma photons (gas) Gas-filled detectors: examples
 Aim of this tal Detector technology WMIC Educational Program Nuclear Imaging World Molecular Imaging Congress, Dublin, Ireland, Sep 5-8, 202 You can now the name of a bird in all the languages of the world,
Aim of this tal Detector technology WMIC Educational Program Nuclear Imaging World Molecular Imaging Congress, Dublin, Ireland, Sep 5-8, 202 You can now the name of a bird in all the languages of the world,
Measurements of CsI(Tl) Crystals with PMT and APD. ipno.in2p3.fr Jean Peyré Milano - October 2006
 Measurements of I(Tl) Crystals with PMT and APD Jean Peyré Milano - Oct 2006 IPNO-RDD-Jean Peyré 1 1.Characteristics of I(Tl), PMT and APD 2.Measurements on I(Tl) a) I(Tl) /Teflon + XP5300B b) I(Tl) /VM2000
Measurements of I(Tl) Crystals with PMT and APD Jean Peyré Milano - Oct 2006 IPNO-RDD-Jean Peyré 1 1.Characteristics of I(Tl), PMT and APD 2.Measurements on I(Tl) a) I(Tl) /Teflon + XP5300B b) I(Tl) /VM2000
Large Area Avalanche Photodiodes in X-rays and scintillation detection
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 442 (2000) 230}237 Large Area Avalanche Photodiodes in X-rays and scintillation detection M. MoszynH ski *, M. Kapusta, M. Balcerzyk, M. Szawlowski,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 442 (2000) 230}237 Large Area Avalanche Photodiodes in X-rays and scintillation detection M. MoszynH ski *, M. Kapusta, M. Balcerzyk, M. Szawlowski,
Gamma-ray spectroscopy with the scintillator/photomultiplierand with the high purity Ge detector: Compton scattering, photoeffect, and pair production
 Experiment N2: Gamma-ray spectroscopy with the scintillator/photomultiplierand with the high purity Ge detector: Compton scattering, photoeffect, and pair production References: 1. Experiments in Nuclear
Experiment N2: Gamma-ray spectroscopy with the scintillator/photomultiplierand with the high purity Ge detector: Compton scattering, photoeffect, and pair production References: 1. Experiments in Nuclear
Design of a Lanthanum Bromide Detector for TOF PET
 Design of a Lanthanum Bromide Detector for TOF PET A. Kuhn, S. Surti, Member, IEEE, J. S. Karp, Senior Member, IEEE, P. S. Raby, K. S. Shah, A. E. Perkins, Member, IEEE, G. Muehllehner, Fellow Member,
Design of a Lanthanum Bromide Detector for TOF PET A. Kuhn, S. Surti, Member, IEEE, J. S. Karp, Senior Member, IEEE, P. S. Raby, K. S. Shah, A. E. Perkins, Member, IEEE, G. Muehllehner, Fellow Member,
Fast Neutron and Gamma-Ray Detectors for the CSIRO Air Cargo Scanner
 Fast Neutron and Gamma-Ray Detectors for the CSIRO Air Cargo Scanner J.E. Eberhardt, A.J. McEwan, D. Milinkovic, V. Sharp, * and J.R. Tickner CSIRO Minerals, Private Mail Bag 5, Menai NSW 2234 Australia
Fast Neutron and Gamma-Ray Detectors for the CSIRO Air Cargo Scanner J.E. Eberhardt, A.J. McEwan, D. Milinkovic, V. Sharp, * and J.R. Tickner CSIRO Minerals, Private Mail Bag 5, Menai NSW 2234 Australia
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #6 is assigned, due May 1 st Final exam May 8, 10:30-12:30pm
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #6 is assigned, due May 1 st Final exam May 8, 10:30-12:30pm
Light yield non-proportionality and energy resolution of Lu 1.95 Y 0.05 SiO 5 :Ce and Lu 2 SiO 5 :Ce scintillation crystals
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 32 (2012) 765 771 I-SEEC2011 Light yield non-proportionality and energy resolution of Lu 1.95 Y 0.05 SiO 5 :Ce and Lu 2 SiO 5 :Ce scintillation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 32 (2012) 765 771 I-SEEC2011 Light yield non-proportionality and energy resolution of Lu 1.95 Y 0.05 SiO 5 :Ce and Lu 2 SiO 5 :Ce scintillation
Sample Spectroscopy System Hardware
 Semiconductor Detectors vs. Scintillator+PMT Detectors Semiconductors are emerging technology - Scint.PMT systems relatively unchanged in 50 years. NaI(Tl) excellent for single-photon, new scintillation
Semiconductor Detectors vs. Scintillator+PMT Detectors Semiconductors are emerging technology - Scint.PMT systems relatively unchanged in 50 years. NaI(Tl) excellent for single-photon, new scintillation
Nuclear Lifetimes. = (Eq. 1) (Eq. 2)
 Nuclear Lifetimes Theory The measurement of the lifetimes of excited nuclear states constitutes an important experimental technique in nuclear physics. The lifetime of a nuclear state is related to its
Nuclear Lifetimes Theory The measurement of the lifetimes of excited nuclear states constitutes an important experimental technique in nuclear physics. The lifetime of a nuclear state is related to its
LET dependence of the charge collection efficiency of silicon microdosimeters
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2003 LET dependence of the charge collection efficiency of silicon microdosimeters
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2003 LET dependence of the charge collection efficiency of silicon microdosimeters
Energetic particles and their detection in situ (particle detectors) Part II. George Gloeckler
 Energetic particles and their detection in situ (particle detectors) Part II George Gloeckler University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI University of Maryland, College Park, MD Simple particle detectors Gas-filled
Energetic particles and their detection in situ (particle detectors) Part II George Gloeckler University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI University of Maryland, College Park, MD Simple particle detectors Gas-filled
Gamma and X-Ray Detection
 Gamma and X-Ray Detection DETECTOR OVERVIEW The kinds of detectors commonly used can be categorized as: a. Gas-filled Detectors b. Scintillation Detectors c. Semiconductor Detectors The choice of a particular
Gamma and X-Ray Detection DETECTOR OVERVIEW The kinds of detectors commonly used can be categorized as: a. Gas-filled Detectors b. Scintillation Detectors c. Semiconductor Detectors The choice of a particular
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW SILICON BASED DETECTOR MODULE FOR PET
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW SILICON BASED DETECTOR MODULE FOR PET A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree Master of Science (Honours) from UNIVERSITY OF WOLLONGONG By
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW SILICON BASED DETECTOR MODULE FOR PET A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree Master of Science (Honours) from UNIVERSITY OF WOLLONGONG By
Advances in PET technology
 Advances in PET technology Jostein Sæterstøl September 15th 2009 Outline Introduction Detectors Time-of-flight PET PET / MRI Conclusions Introduction Fluor-18; FDG β + decay p n + e + + ν Annihilation
Advances in PET technology Jostein Sæterstøl September 15th 2009 Outline Introduction Detectors Time-of-flight PET PET / MRI Conclusions Introduction Fluor-18; FDG β + decay p n + e + + ν Annihilation
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title Labr3:Ce scintillators for gamma ray spectroscopy Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/38f0c7zv Authors Shah, K.S.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title Labr3:Ce scintillators for gamma ray spectroscopy Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/38f0c7zv Authors Shah, K.S.
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon
 Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Dual Isotope Imaging with LaBr3:Ce Crystal and H8500 PSPMT
 Dual Isotope Imaging with LaBr3:Ce Crystal and H8500 PSPMT Dr. Andrea Fabbri, University of Rome Roma Tre I.N.F.N. (National Institue of Nuclear Physics) γ-ray imaging with scintillator and PSPMT γ-ray
Dual Isotope Imaging with LaBr3:Ce Crystal and H8500 PSPMT Dr. Andrea Fabbri, University of Rome Roma Tre I.N.F.N. (National Institue of Nuclear Physics) γ-ray imaging with scintillator and PSPMT γ-ray
SCI-O11. Design of a Compton Spectrometer Experiment for Studying Electron Response of a Scintillator
 88 The 1 st NPRU Academic Conference SCI-O11 Design of a Compton Spectrometer Experiment for Studying Electron Response of a Scintillator P. Limkitjaroenporn and W.Chewpraditkul Radiation Physics Laboratory,
88 The 1 st NPRU Academic Conference SCI-O11 Design of a Compton Spectrometer Experiment for Studying Electron Response of a Scintillator P. Limkitjaroenporn and W.Chewpraditkul Radiation Physics Laboratory,
Scintillators 1. YEAR, I. CYCLE. AUTHOR: BPhys. Manja Ščetinec ADVISOR/MENTOR: Prof. Boštjan Golob
 Scintillators SEMINAR 1. YEAR, I. CYCLE AUTHOR: BPhys. Manja Ščetinec ADVISOR/MENTOR: Prof. Boštjan Golob Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University in Ljubljana Ljubljana, October 2017 Abstract In
Scintillators SEMINAR 1. YEAR, I. CYCLE AUTHOR: BPhys. Manja Ščetinec ADVISOR/MENTOR: Prof. Boštjan Golob Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University in Ljubljana Ljubljana, October 2017 Abstract In
Gamma Spectroscopy. References: Objectives:
 Gamma Spectroscopy References: G.F. Knoll, Radiation Detection and Measurement (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2000) W. R. Leo, Techniques for Nuclear and Particle Physics Experiments: A How-to Approach,
Gamma Spectroscopy References: G.F. Knoll, Radiation Detection and Measurement (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2000) W. R. Leo, Techniques for Nuclear and Particle Physics Experiments: A How-to Approach,
SCINTILLATION DETECTORS & GAMMA SPECTROSCOPY: AN INTRODUCTION
 SCINTILLATION DETECTORS & GAMMA SPECTROSCOPY: AN INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE The primary objective of this experiment is to use an NaI(Tl) detector, photomultiplier tube and multichannel analyzer software system
SCINTILLATION DETECTORS & GAMMA SPECTROSCOPY: AN INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE The primary objective of this experiment is to use an NaI(Tl) detector, photomultiplier tube and multichannel analyzer software system
A POSITION SENSITIVE ALPHA PARTICLE DETECTOR BASED ON A LYSO CRYSTAL AND A MICRO-PIXEL AVALANCHE PHOTODIODE
 A POSITION SENSITIVE ALPHA PARTICLE DETECTOR BASED ON A LYSO CRYSTAL AND A MICRO-PIXEL AVALANCHE PHOTODIODE Ahmadov G.S. a,b,c, Ahmadov F.I. b,c, Kopatch Yu.N. a, Telezhnikov S.A. a, Nuriyev S.M. a,b,
A POSITION SENSITIVE ALPHA PARTICLE DETECTOR BASED ON A LYSO CRYSTAL AND A MICRO-PIXEL AVALANCHE PHOTODIODE Ahmadov G.S. a,b,c, Ahmadov F.I. b,c, Kopatch Yu.N. a, Telezhnikov S.A. a, Nuriyev S.M. a,b,
Scintillators: new ways to fast emission
 Scintillators: new ways to fast emission for Medical and High Energy Physics Applications Rosana Martinez Turtós Tutor: Marco Paganoni Co-tutor: Alessio Ghezzi Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Physics
Scintillators: new ways to fast emission for Medical and High Energy Physics Applications Rosana Martinez Turtós Tutor: Marco Paganoni Co-tutor: Alessio Ghezzi Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Physics
Introduction to Radiation Monitoring
 Introduction to Radiation Monitoring Iain Darby Honorary Research Fellow, University of Glasgow iain.darby@glasgow.ac.uk https://at.linkedin.com/in/idarby https://www.facebook.com/iain.darby.662 Outline
Introduction to Radiation Monitoring Iain Darby Honorary Research Fellow, University of Glasgow iain.darby@glasgow.ac.uk https://at.linkedin.com/in/idarby https://www.facebook.com/iain.darby.662 Outline
1 of :32
 Home Page Products Price List Links & PDFs DISCONTINUED: SEE GAMMA-RAD Gamma Ray & X-Ray Spectroscopy System Hand-Held, High Efficiency NaI(Tl) Detector The GAMMA-8000 is a powerful, portable instrument
Home Page Products Price List Links & PDFs DISCONTINUED: SEE GAMMA-RAD Gamma Ray & X-Ray Spectroscopy System Hand-Held, High Efficiency NaI(Tl) Detector The GAMMA-8000 is a powerful, portable instrument
Lecture 5: Tomographic nuclear systems: SPECT
 Lecture 5: Tomographic nuclear systems: SPECT Field trip this saturday at 11 AM at UWMC meet in main hospital lobby at 11 AM if you miss the 'boat', page me at 540-4950 should take ~1 to 1.5 hours, depending
Lecture 5: Tomographic nuclear systems: SPECT Field trip this saturday at 11 AM at UWMC meet in main hospital lobby at 11 AM if you miss the 'boat', page me at 540-4950 should take ~1 to 1.5 hours, depending
Chapter 4 Scintillation Detectors
 Med Phys 4RA3, 4RB3/6R03 Radioisotopes and Radiation Methodology 4-1 4.1. Basic principle of the scintillator Chapter 4 Scintillation Detectors Scintillator Light sensor Ionizing radiation Light (visible,
Med Phys 4RA3, 4RB3/6R03 Radioisotopes and Radiation Methodology 4-1 4.1. Basic principle of the scintillator Chapter 4 Scintillation Detectors Scintillator Light sensor Ionizing radiation Light (visible,
Alpha particle scintillation detector based on micro pixel avalanche photodiode and LYSO crystal
 Alpha particle scintillation detector based on micro pixel avalanche photodiode and LYSO crystal G.S. Ahmadov, F.I. Ahmadov Institute of Radiation Problems of ANAS, Baku, Azerbaijan C. Granja, S. Pospíšil
Alpha particle scintillation detector based on micro pixel avalanche photodiode and LYSO crystal G.S. Ahmadov, F.I. Ahmadov Institute of Radiation Problems of ANAS, Baku, Azerbaijan C. Granja, S. Pospíšil
Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors
 XENON Experiment - SAGENAP Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors Department of Physics Brown University Source at http://gaitskell.brown.edu Gaitskell Review WIMP
XENON Experiment - SAGENAP Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors Department of Physics Brown University Source at http://gaitskell.brown.edu Gaitskell Review WIMP
First Results and Realization Status of a Proton Computed Radiography Device
 First Results and Realization Status of a Proton Computed Radiography Device V. Sipala for the PRIMA collaboration V.Sipalaa,b, D.LoPrestia,b, N.Randazzob, M.Bruzzid,e, D.Menichellie,d, C.Civininid, M.Bucciolinic,d,
First Results and Realization Status of a Proton Computed Radiography Device V. Sipala for the PRIMA collaboration V.Sipalaa,b, D.LoPrestia,b, N.Randazzob, M.Bruzzid,e, D.Menichellie,d, C.Civininid, M.Bucciolinic,d,
Development of High-Z Semiconductor Detectors and Their Applications to X-ray/gamma-ray Astronomy
 Development of High-Z Semiconductor Detectors and Their Applications to X-ray/gamma-ray Astronomy Taka Tanaka (SLAC/KIPAC) 9/19/2007 SLAC Advanced Instrumentation Seminar Outline Introduction CdTe Diode
Development of High-Z Semiconductor Detectors and Their Applications to X-ray/gamma-ray Astronomy Taka Tanaka (SLAC/KIPAC) 9/19/2007 SLAC Advanced Instrumentation Seminar Outline Introduction CdTe Diode
Analysis of γ spectrum
 IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology LAB 26 Analysis of γ spectrum NAME PERSONAL NUMBER DATE APPROVED I. OBJECTIVES - To understand features of gamma spectrum and recall basic knowledge
IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology LAB 26 Analysis of γ spectrum NAME PERSONAL NUMBER DATE APPROVED I. OBJECTIVES - To understand features of gamma spectrum and recall basic knowledge
THE spectroscopic performance of large volume CdZnTe
 3098 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 51, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2004 Analysis of Detector Response Using 3-D Position-Sensitive CZT Gamma-Ray Spectrometers Feng Zhang, Student Member, IEEE, Zhong He,
3098 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 51, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2004 Analysis of Detector Response Using 3-D Position-Sensitive CZT Gamma-Ray Spectrometers Feng Zhang, Student Member, IEEE, Zhong He,
Maximum-Likelihood Deconvolution in the Spatial and Spatial-Energy Domain for Events With Any Number of Interactions
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 59, NO. 2, APRIL 2012 469 Maximum-Likelihood Deconvolution in the Spatial and Spatial-Energy Domain for Events With Any Number of Interactions Weiyi Wang, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 59, NO. 2, APRIL 2012 469 Maximum-Likelihood Deconvolution in the Spatial and Spatial-Energy Domain for Events With Any Number of Interactions Weiyi Wang, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 4, AUGUST /$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 4, AUGUST 2008 2425 Optical and Scintillation Properties of Inorganic Scintillators in High Energy Physics Rihua Mao, Member, IEEE, Liyuan Zhang, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 4, AUGUST 2008 2425 Optical and Scintillation Properties of Inorganic Scintillators in High Energy Physics Rihua Mao, Member, IEEE, Liyuan Zhang, Member,
Application Note. The Continuous Air Monitoring (CAM) PIPS Detector Properties and Applications
 Application Note The Continuous Air Monitoring (CAM) PIPS Detector Properties and Applications Introduction The increasing demand for safety in nuclear installations calls for continuous survey of airborne
Application Note The Continuous Air Monitoring (CAM) PIPS Detector Properties and Applications Introduction The increasing demand for safety in nuclear installations calls for continuous survey of airborne
Timing and Energy Response of Six Prototype Scintillators
 Timing and Energy Response of Six Prototype Scintillators CCM Kyba 1, J Glodo 2, EVD van Loef 2, JS Karp 1, KS Shah 2 1 University of Pennsylvania 2 Radiation Monitoring Devices SCINT 2007 June 7, 2007
Timing and Energy Response of Six Prototype Scintillators CCM Kyba 1, J Glodo 2, EVD van Loef 2, JS Karp 1, KS Shah 2 1 University of Pennsylvania 2 Radiation Monitoring Devices SCINT 2007 June 7, 2007
New trends in CdTe detectors for X and γ-ray applications
 New trends in CdTe detectors for X and γ-ray applications Olivier Limousin CEA Saclay / DSM / DAPNIA Service d Astrophysique France New developments in photodetection, Beaune 2002 / Solid state detectors
New trends in CdTe detectors for X and γ-ray applications Olivier Limousin CEA Saclay / DSM / DAPNIA Service d Astrophysique France New developments in photodetection, Beaune 2002 / Solid state detectors
A new timing model for calculating the intrinsic timing resolution of a scintillator detector
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Phys. Med. Biol. 5 (7) 3 7 PHYSICS IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY doi:.88/3-955/5/4/6 A new timing model for calculating the intrinsic timing resolution of a scintillator detector
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Phys. Med. Biol. 5 (7) 3 7 PHYSICS IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY doi:.88/3-955/5/4/6 A new timing model for calculating the intrinsic timing resolution of a scintillator detector
Inorganic Scintillators
 Inorganic Scintillators Inorganic scintillators are inorganic materials (usually crystals) that emit light in response to ionizing radiation NaI is the protypical example Scintillation mechanism is different
Inorganic Scintillators Inorganic scintillators are inorganic materials (usually crystals) that emit light in response to ionizing radiation NaI is the protypical example Scintillation mechanism is different
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps
 Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Single Photon detectors
 Single Photon detectors Outline Motivation for single photon detection Semiconductor; general knowledge and important background Photon detectors: internal and external photoeffect Properties of semiconductor
Single Photon detectors Outline Motivation for single photon detection Semiconductor; general knowledge and important background Photon detectors: internal and external photoeffect Properties of semiconductor
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 308 Angular dependence of 662 kev multiple backscattered gamma photons in Aluminium Ravindraswami K a, Kiran K U b, Eshwarappa K M b and Somashekarappa H M c* a St Aloysius College (Autonomous), Mangalore
308 Angular dependence of 662 kev multiple backscattered gamma photons in Aluminium Ravindraswami K a, Kiran K U b, Eshwarappa K M b and Somashekarappa H M c* a St Aloysius College (Autonomous), Mangalore
Recent advances and future perspectives of gamma imagers for scintimammography
 3rd International Conference on Imaging Technologies in Biomedical Sciences: ITBS2005 Innovation in Nuclear and Radiological Imaging: From Basic Research to Clinical Application Milos Conference Center,
3rd International Conference on Imaging Technologies in Biomedical Sciences: ITBS2005 Innovation in Nuclear and Radiological Imaging: From Basic Research to Clinical Application Milos Conference Center,
The Compton Effect. Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA (Dated: November 26, 2002)
 The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
Detection of X-Rays. Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics
 Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
A novel method to calibrate DOI function of a PET detector with a dual-ended-scintillator readout
 A novel method to calibrate DOI function of a PET detector with a dual-ended-scintillator readout Yiping Shao a Department of Imaging Physics, University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, 55 Holcombe
A novel method to calibrate DOI function of a PET detector with a dual-ended-scintillator readout Yiping Shao a Department of Imaging Physics, University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, 55 Holcombe
EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 5 Radiation Sensors
 EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 5 Radiation Sensors 5. Radiation Microsensors Radiation µ-sensors convert incident radiant signals into standard electrical out put signals. Radiant Signals Classification
EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 5 Radiation Sensors 5. Radiation Microsensors Radiation µ-sensors convert incident radiant signals into standard electrical out put signals. Radiant Signals Classification
List of Nuclear Medicine Radionuclides. Nuclear Medicine Imaging Systems: The Scintillation Camera. Crystal and light guide
 Nuclear Medicine Imaging Systems: The Scintillation Camera List of Nuclear Medicine Radionuclides Tc99m 140.5 kev 6.03 hours I-131 364, 637 kev 8.06 days I-123 159 kev 13.0 hours I-125 35 kev 60.2 days
Nuclear Medicine Imaging Systems: The Scintillation Camera List of Nuclear Medicine Radionuclides Tc99m 140.5 kev 6.03 hours I-131 364, 637 kev 8.06 days I-123 159 kev 13.0 hours I-125 35 kev 60.2 days
Performance of a Si PIN photodiode at low temperatures and in high magnetic fields
 Performance of a Si PIN photodiode at low temperatures and in high magnetic fields Frederik Wauters *, Ilya Kraev *, Nathal Severijns *, Sam Coeck *, Michael Tandecki *, Valentin Kozlov *, Dalibor Zákoucký
Performance of a Si PIN photodiode at low temperatures and in high magnetic fields Frederik Wauters *, Ilya Kraev *, Nathal Severijns *, Sam Coeck *, Michael Tandecki *, Valentin Kozlov *, Dalibor Zákoucký
Quality Assurance. Purity control. Polycrystalline Ingots
 Quality Assurance Purity control Polycrystalline Ingots 1 Gamma Spectrometry Nuclide Identification Detection of Impurity Traces 1.1 Nuclides Notation: Atomic Mass Atomic Number Element Neutron Atomic
Quality Assurance Purity control Polycrystalline Ingots 1 Gamma Spectrometry Nuclide Identification Detection of Impurity Traces 1.1 Nuclides Notation: Atomic Mass Atomic Number Element Neutron Atomic
LEC E T C U T R U E R E 17 -Photodetectors
 LECTURE 17 -Photodetectors Topics to be covered Photodetectors PIN photodiode Avalanche Photodiode Photodetectors Principle of the p-n junction Photodiode A generic photodiode. Photodetectors Principle
LECTURE 17 -Photodetectors Topics to be covered Photodetectors PIN photodiode Avalanche Photodiode Photodetectors Principle of the p-n junction Photodiode A generic photodiode. Photodetectors Principle
Mayneord-Phillips Summer School St Edmund Hall, University of Oxford July Proton decays to n, e +, ν
 Positron Emission Tomography Physics & Instrumentation Dimitra G. Darambara, Ph.D Multimodality Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Physics RMH/ICR Outline Introduction PET Physics overview Types of
Positron Emission Tomography Physics & Instrumentation Dimitra G. Darambara, Ph.D Multimodality Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Physics RMH/ICR Outline Introduction PET Physics overview Types of
NUCL 3000/5030 Laboratory 2 Fall 2013
 Lab #2: Passive Gamma Spec Measurements in Decoding Natural Radioactivity in SLC Area Objectives a. Learn basics of gamma spectroscopy b. Learn the equipment in Counting stations #4, #5 and #8 c. Apply
Lab #2: Passive Gamma Spec Measurements in Decoding Natural Radioactivity in SLC Area Objectives a. Learn basics of gamma spectroscopy b. Learn the equipment in Counting stations #4, #5 and #8 c. Apply
Ultra High Quantum Efficiency PMT for energy resolution measurements of LaBr 3 (Ce) scintillation crystals
 Ultra High Quantum Efficiency PMT for energy resolution measurements of LaBr 3 (Ce) scintillation crystals Roberto Pani INFN and Sapienza - University of Rome, Italy On behalf of ECORAD Collaboration Cinti
Ultra High Quantum Efficiency PMT for energy resolution measurements of LaBr 3 (Ce) scintillation crystals Roberto Pani INFN and Sapienza - University of Rome, Italy On behalf of ECORAD Collaboration Cinti
Keywords: mechanical property, polymer optical fibre, radiation, transmission.
 5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 27 1-12 December 27, Brisbane, Australia Radiation damage to polymer optical fibres C. Yan 1, S.H. Law 2, N. Suchowerska 3,4 and S.H. Hong 5 1 School
5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 27 1-12 December 27, Brisbane, Australia Radiation damage to polymer optical fibres C. Yan 1, S.H. Law 2, N. Suchowerska 3,4 and S.H. Hong 5 1 School
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 316 Effective atomic number of composite materials by Compton scattering - nondestructive evaluation method Kiran K U a, Ravindraswami K b, Eshwarappa K M a and Somashekarappa H M c* a Government Science
316 Effective atomic number of composite materials by Compton scattering - nondestructive evaluation method Kiran K U a, Ravindraswami K b, Eshwarappa K M a and Somashekarappa H M c* a Government Science
A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 364 371 TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 364 371 TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
PHOTODETECTORS AND SILICON PHOTO MULTIPLIER
 ESE seminar Photodetectors - Sipm, P. Jarron - F. Powolny 1 PHOTODETECTORS AND SILICON PHOTO MULTIPLIER ESE seminar Pierre Jarron, Francois Powolny OUTLINE 2 Brief history and overview of photodetectors
ESE seminar Photodetectors - Sipm, P. Jarron - F. Powolny 1 PHOTODETECTORS AND SILICON PHOTO MULTIPLIER ESE seminar Pierre Jarron, Francois Powolny OUTLINE 2 Brief history and overview of photodetectors
V. 3. Development of an Accelerator Beam Loss Monitor Using an Optical Fiber
 CYRIC Annual Report 2001 V. 3. Development of an Accelerator Beam Loss Monitor Using an Optical Fiber Kawata N. Baba M. Kato M.*, Miura T.**, and Yamadera A.***, Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center, Tohoku
CYRIC Annual Report 2001 V. 3. Development of an Accelerator Beam Loss Monitor Using an Optical Fiber Kawata N. Baba M. Kato M.*, Miura T.**, and Yamadera A.***, Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center, Tohoku
Review of Semiconductor Drift Detectors
 Pavia October 25, 2004 Review of Semiconductor Drift Detectors Talk given by Pavel Rehak following a presentation on 5 th Hiroshima Symposium of Semiconductor Tracking Detectors Outline of the Review Principles
Pavia October 25, 2004 Review of Semiconductor Drift Detectors Talk given by Pavel Rehak following a presentation on 5 th Hiroshima Symposium of Semiconductor Tracking Detectors Outline of the Review Principles
A Study On Radioactive Source Imaging By Using A Pixelated CdTe Radiation Detector
 ISSN: 1791-4469 Copyright 2012 Hellenic Naval Academy A Study On Radioactive Source Imaging By Using A Pixelated CdTe Radiation Detector K. Zachariadou a,c, K. Karafasoulis b,c, S. Seferlis c, I. Papadakis
ISSN: 1791-4469 Copyright 2012 Hellenic Naval Academy A Study On Radioactive Source Imaging By Using A Pixelated CdTe Radiation Detector K. Zachariadou a,c, K. Karafasoulis b,c, S. Seferlis c, I. Papadakis
CCD readout of GEM-based neutron detectors
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 478 (2002) 357 361 CCD readout of GEM-based neutron detectors F.A.F. Fraga a, *, L.M.S. Margato a, S.T.G. Fetal a, M.M.F.R. Fraga a, R. Ferreira Marques
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 478 (2002) 357 361 CCD readout of GEM-based neutron detectors F.A.F. Fraga a, *, L.M.S. Margato a, S.T.G. Fetal a, M.M.F.R. Fraga a, R. Ferreira Marques
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na. Ellen Simmons
 Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/20/09
 Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/20/09 Radiation Detection and Measurement Semiconductor Detectors The electrons in a sample of silicon are each bound to specific silicon atoms (occupy the valence band). If
Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/20/09 Radiation Detection and Measurement Semiconductor Detectors The electrons in a sample of silicon are each bound to specific silicon atoms (occupy the valence band). If
PET scan simulation. Meysam Dadgar. UMSU, Iran. IFMP, Elbasan, Fig 1: PET camera simulation in gate by cylindrical phantom
 PET scan simulation Meysam Dadgar UMSU, Iran IFMP, Elbasan, 2016 Meysamdadgar10@gmail.com 1 Fig 1: PET camera simulation in gate by cylindrical phantom 2 What is PET? Positron emission tomography (PET),
PET scan simulation Meysam Dadgar UMSU, Iran IFMP, Elbasan, 2016 Meysamdadgar10@gmail.com 1 Fig 1: PET camera simulation in gate by cylindrical phantom 2 What is PET? Positron emission tomography (PET),
XENON Dark Matter Search. Juliette Alimena Columbia University REU August 2 nd 2007
 XENON Dark Matter Search Juliette Alimena Columbia University REU August 2 nd 2007 Evidence of Dark Matter Missing mass in Coma galaxy cluster (Fritz Zwicky) Flat rotation curves of spiral galaxies (Vera
XENON Dark Matter Search Juliette Alimena Columbia University REU August 2 nd 2007 Evidence of Dark Matter Missing mass in Coma galaxy cluster (Fritz Zwicky) Flat rotation curves of spiral galaxies (Vera
