Name Date Period Answer Key change font to white CHAPTER 4/5 THE PERIODIC TABLE/ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS: WARM-UP
|
|
|
- Ezra Lamb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Date Period Answer Key change font to white CHAPTER 4/5 THE PERIODIC TABLE/ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS: WARM-UP 1. What is the periodic law? (These questions are from Chapter 5 The Periodic Table) When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic #, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. 2. What is a group, or family of the periodic table? The vertical columns are called groups of the periodic table 3. What is a period of the periodic table? The horizontal rows are called periods 4. Give the names of at least four families, or groups of the periodic table. Alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the Noble Gases. 5. There are three types of elements on the periodic table, fill in the table below for each Name Properties Location on the periodic table a. Metals Shiny, good conductors, typically room temp, left of the staircase line malleable & ductile b. Non-metals not shiny, most are poor conductors, not malleable or Right of the staircase ductile, many are gases. c. Semi-metals or metalloids Have some properties of metals and some properties of non-metals or properties in between. Touching The Staircase 6. Where are the transition metals on the Periodic Table? Middle section (the d-block) 7. Where are the post-transition metals on the Periodic Table? Under the stair case 8. There are three states that the elements can exist in, list all three. State How can you tell what state they are in on the periodic table? a. Solid They are black on the periodic table b. Liquid They are blue on the periodic table c. Gas They are red on the periodic table. 9. Describe the general differences between elements on the left side of the periodic table and those on the right. The right side contains non-metals, while the left side contains metals. 10. In the rest of this chapter, 3 periodic trends will be discussed. They are listed below. Define them and explain how they will be seen on the periodic table. Property Definition How the Trend is seen a. Atomic radius c. d. Ionization Energy (IE) Electronegativity (EN) distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost electron energy needed to remove one of the electrons. an atoms ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond 11. Why do elements within a group have similar properties? They have the same # of valence electrons. As you go down, the atoms get bigger, as you go left to right the atoms get smaller. As you go down I.E. decreases, increases as you move left to right. Increases as you move from the bottom to the top, and increases as you move left to right. 12. What are valence electrons? Electrons in the outermost energy level 13. What is the trend in valence electrons across the Periodic Table? 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 Last Updated: 10/12/11 Page 1/12
2 14. The technical definition of the octet rule is atoms tend to gain/lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of valence electrons. a. What does oct- mean? eight b. What are valence electrons? the electrons in the outermost energy level c. What does a full set of valence electrons mean for most atoms? 8 electrons in the outermost enery level d. Write a definition of the octet rule in your own words. elements try to get 8 outermost electrons by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons e. Would it be OK to call it the noble gas rule instead of the octet rule. EXPLAIN. Yes, everyones electrons end up looking like a noble gas. 15. What does it mean when an atom has become an ion? It has gained or lost electrons 16. Explain the difference between Na which explodes when put in water and Na + which we eat everyday. Na is a sodium atom which has not given away it s electrons yet. Na + has already given away it s electrons and is therefore much more stable and less dangerous. 17. Explain the trend across the Periodic Table in the typical charges of the ions. 1,2 3,4,5,6,7,8 18. Define atomic radius. Atomic radius is the distance from the center of atom s nucleus to its outermost electron. 19. Why do atoms get smaller as you move across a period of the periodic table? The increasing positive charge on the nucleus exerts a stronger pull on the electrons, shrinking their orbitals and making the atom smaller. Contrast ionization energy and electronegativity. In general, what can you say about these values for metals and 20. nonmetals? In general what can you say about the types of ions they form? Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. Electronegativity is an atoms ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. In general, metals have both lower ionization energies and electronegativities than nonmetals. Therefore, metals tend to form positive ions while nonmetals tend to form negative ions. 21. Explain why noble gases are inert (do not react) and do not form ions. Noble gases have a full set of valence electrons and do not need to gain or lose electrons to acquire and octet 22. Define the term electronegativity. What is the periodic trend for electronegativity? Electronegativity is a measure of an atom s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group. 23. What information is presented in each square of the periodic table? The elements name and symbol. The atomic #. The atomic mass. Whether the element is a liquid or a solid. 24. A chemistry experiment calls for a compound that supplies ions of bromine, but unfortunately this compound is not available. Pacey substitutes a compound that supplies ions of chlorine. Dawson uses a compound that contains selenium. From what you know about the periodic table, predict whether Dawson or Pacey will run a more successful experiment. Pacey s experiment will be more successful because bromine and chlorine are in the same family (Halogens). Selenium, although next to bromine probably does not have properties that are as similar as chlorine. Last Updated: 10/12/11 Page 2/12
3 DETERMINING HOW THE TRENDS FOLLOW THE PERIODIC TABLE (TAKE NOTES) 25. Atomic Radius (size of the atom) The 1 st criterion is: Up Down The 2 nd criterion is: Left Right st Ionization Energy (IE) The 1 st criterion is: Up Down The 2 nd criterion is: Left Right 27. Electronegativity (EN) fluorine is the most electronegative element on the periodic table. The 1 st criterion is: Up Down The 2 nd criterion is: Left Right 28. For all 3 trends above (size, IE, EN), what causes a more significant change, going across a period or down a group? WHY? Up Down because change by entire energy level of e-, not just be 1 e- Last Updated: 10/12/11 Page 3/12
4 SECTION 5-3 PROBLEMS Complete the table. Column 1 and 2 tell the number or protons and electrons in the atom/ion. Column 3 write the elements state (sol, liq, or gas). Column 4 write the type of element (metal, semi-, or non-metal). Column 5 write number of electron shells each atom has. Column 6, 7, & 8 rank each group as LO for smallest/lowest, HI for biggest/largest, & MID for in between. Column 9 write the symbol of most common ion Element Protons Electrons State Type # of e- Shells Atomic Radius Ionization Energy EN # of valence e- Common Ion Chlorine Gas Non 3 LO HI HI 7 Cl - (-1) Selenium Solid Non 4 HI LO LO 6 Se -2 (-2) Bromine Liquid Non 4 MID MID MID 7 Br - (-1) Phosphorus Solid Non 3 MID MID MID 5 P -3 (-3) Sulfur Solid Non 3 LO HI HI 6 S -2 (-2) Selenium Solid Non 4 HI LO LO 6 Se -2 (-2) Scandium Solid Metal 4 LO HI HI 2 Sc +2 (+2) Yttrium Solid Metal 5 MID MID MID 2 Y +2 (+2) Lutetium Solid Metal 6 HI LO LO 2 Lu +2 (+2) Vanadium Solid Metal 4 MID MID MID 2 V +2 (+2) Chromium Solid Metal 4 LO HI HI 2 Cr +2 (+2) Tungsten Solid Metal 6 HI LO LO 2 W +2 (+2) Nitrogen 7 7 Gas Non 2 LO HI HI 5 N -3 (-3) Phosphorus Solid Non 3 MID MID MID 5 P -3 (-3) Arsenic Solid Semi 4 HI LO LO 5 As -3 (-3) K Solid Metal 4 1 K+1 K Rb Solid Metal 5 1 Rb+1 Cl Gas Non 3 7 Cl-1 Cl Br Liquid Non 4 7 Br-1 Li 3 3 Solid Metal 2 1 Li+1 Li Na Solid Metal 3 1 Na+1 Te I Xe Gas Non 5 8 Aluminum Solid Metal 3 LO LO 3 Al +3 (+3) Silicon Solid Semi 3 MID MID 4 Si +4 (+4) Phosphorus Solid Non 3 HIGH HI 5 P -3 (-3) Last Updated: 10/12/11 Page 4/12
5 Which atom in each pair has the larger atomic radius? 39. Li or K 40. O or C 41. Si or S K C Si 42. Ca or Ni 43. Cl or Br 44. Fe or Au Ca Br Au 45. Ga or B 46. Be or Ba Ga Ba Which atom in each pair has the larger ionization energy? 47. Na or O 48. Cu or Ra 49. Ca or Fr O Cu Ca 50. Be or Ba 51. I or Ne 52. W or Se Be Ne Se 53. Ar or F 54. K or V Ar V Which atom in each pair has the smaller electronegativity? 55. Na or O 56. Cu or Ra 57. Ca or Fr Na Ra Fr 58. B or Be 59. Fe or Rh 60. C or Ge Be Rh Ge 61. N or S 62. Ca or Na S Ca Write the charge that each of the following atoms will acquire when it has a complete set of valence electrons. 63. O 64. F 65. Ca O -2 (-2) F - (-1) Ca +2 (+2) 66. Na 67. N 68. Ar Na + (+1) N -3 (-3) No Charge Last Updated: 10/12/11 Page 5/12
6 CHAPTER 4 LIGHT & ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS 69. Quickly sketch the electromagnetic spectrum and label the general areas. Below the spectrum indicate whether the energy is increasing or decreasing left to right. (These Questions are now from Chapter 4 Electron Configurations) Gamma Rays X-rays UV Visible Infrared Microwaves TV Radio ENERGY IS DECREASING What is the photoelectric effect? Einstein took different colored lights and shone them on two charged plates that were about to spark, he found that red light would not make them spark, but blue light would. (Do the phosphorescent screen.) 71. What did Einstein call these particles that make up light? Photons 72. What is a (bright) line spectrum? When certain elements are excited and the light the emit is passed through a prism, only certain frequencies of light(colors) are visible. 73. How can you get a (bright) line spectrum? By exciting gas samples of pure elements. 74. Sketch a quick model of the atom. 75. Draw a sketch of an atom showing what happens when an electron gets excited. 76. What must have happened for the electron in the sketch above to have gotten excited? Energy in, either heat or electricity 77. Draw a sketch of an atom showing what happens when an electron returns from an excited state to a lower energy state. 78. What happens when that electron falls to the lower energy state in the sketch above? light emitted 79. If the electron falls further in energy, what will be different? bluer light 80. What is the difference between the ground state and the excited state? Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 6/12
7 The ground state is when all the electrons in an atom are in the lowest possible orbital, the excited state is when one or more of the electrons have jumped to a higher energy level. 81. In your own words describe Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle. You can t know where an electron is and where it is headed at the same time. Knowing one changes the other. 82. Bohr s model is the 4 th model of the atom, what is the name of the currently accepted model? Quantum mechanical model (electron cloud model) 83. What are the letters associated with the 4 different shapes? s, p, d, f 84. Quickly sketch the general shape of an s, p and a d orbital. 85. Every principal energy level (n) can be divided into how many sublevels? The 1 st principal energy level (n=1) can be divided into one sublevel (s). The 2 nd (n=2) can be divided into 2(s, p). The 3 rd can be divided into 3(s, p, d). The 4 th can be divided into 4(s, p, d, f) Fill in the following chart Quantum Numbers and Number of Electrons Electron Shells, Sublevels, & Orbitals Electron Shell or Principal Quantum Number (n) Number of Sublevels (shapes) Name of Sublevels Max Number of electrons in each sublevel Maximum # Electrons possible in the n th shell 1 1 1s 2 2 2s p 6 3s p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 4d 10 4f Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 7/12
8 SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION Decreasing energy You work in a factory and your boss is mad that some chemicals have been mixed together. Being the bright chemistry student (and employee) that you are, you remember hearing that every element gives of its own unique bright line specta, which is almost like a fingerprint on a human, no two elements have the same one. So you take your Stevie Wonder glasses, then take the mixture and vaporize it in a flame. Above is the bright line spectrum that you see. So you grab a chemical reference and look up a bunch of spectra (shown on the back). Can you tell me what elements have been mixed The chemicals are argon and sodium Decreasing energy Decreasing energy Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 8/12
9 SECTION 4-5 TABLE #1 Fill in the following table: Element Electron Configuration Noble Gas Configuration Last e - Configuration 86. Potassium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 [Ar]4s 1 4s Cobalt 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 7 [Ar]4s 2 3d 7 3d Nitrogen 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3 [He]2s 2 2p 3 2p Silicon 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 2 [Ne]3s 2 3p 2 3p Lithium 1s 2 2s 1 [He]2s 1 2s Phosphorus 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3 [Ne]3s 2 3p 3 3p Iridium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 7 [Xe]6s 2 4f 14 5d 7 5d Selenium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 4 [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 4p 4 4p Scandium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 1 [Ar]4s 2 3d 1 3d Bismuth 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 3 [Xe]6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 3 6p Vanadium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 3 [Ar]4s 2 3d 3 3d Cadmium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 [Kr]5s 2 4d 10 4d Sulfur 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4 [Ne]3s 2 3p 4 3p Mercury 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 [Xe]6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 5d Osmium 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 6 [Xe]6s 2 4f 14 5d 6 5d 6 2 # of Valence Electrons Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 9/12
10 Element Noble gas notation # Valence electrons Most common ion Group Name 101. N [He]2s 2 2p 3 5 N S [Ne]3s 2 3p 4 6 S Ti [Ar] 4s 2 3d 2 2 Ti Na + [He] 2s 2 2p Sr [Kr] 5s 2 2 Sr Tc [Kr] 5s 2 4d 5 2 Tc Fr + [Rn] W [Xe] 6s 2 4f 14 5d 4 2 W K + [Ne]3s 2 3p Co [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7 2 Co Ge [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p or Cl - [Ne]3s 2 3p Br [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5 7 Br In [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 5p 1 3 In Pb [Xe] 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p or Xe [Kr] 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 8 Xe or No Ion formed Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 10/12
11 117. TABLE #2 Fill in the following table Element Noble Gas Configuration Last e - # Valence e - N -3 (Nitride) [He]2s 2 2p K + [Ar] or [Ne]3s 2 3p 6 3p S -2 (Sulfide) [Ne] 3s 2 3p 2 3p Co +2 [Ar]3d 7 3d Ti [Ar]4s 2 3d 2 3d Ge [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 4p 2 4p Na + [Ne] or [He]2s 2 2p 6 2p Cl - (Chloride) [Ar] or [Ne]3s 2 3p 6 3p Sr [Kr]5s 2 5s Se -2 (Selenide) [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 4p 2 4p Tc [Kr]5s 2 4d 5 4d In [Kr]5s 2 4d 10 5p 1 5p Fr +1 [Rn] 7s Pb [Xe]6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2 6p W +4 [Xe]4f 14 5d 2 5d 4 2 Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 11/12
12 Ch 4 Electron Configurations Radiant Energy Waves (Amplitude, Frequency, Wavelength, Speed of Light) Visible Sectrum Quantum Theory (Quantum, Planck s constant, photoelectrics effect, photons) Line Spectra, energy level numbers (1st quantum number), ground versus excited states, Uncertainty Principle Quantum Mechanical Model, electron density, orbitals, principle energy level, sublevels Electron Configurations Orbital Diagrams Ch 5 The Periodic Table Periodic Law Groups/Families, Periods Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Halogens, Noble Gases Metals, Non-Metals, Semi-Metals Transition Metals & Post-Transition Metals Valence electrons Octet Rule (not in book until Chap 7) Abbreviated electron configurations Noble gas inner core electron configurations Periodic Trends Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionization Energy ElectronAffinity Electronegativity Valence e- Ion Charges Last Updated: 10/12/11 Electron Configurations: Page 12/12
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
Periodic Table Workbook
 Key Ideas: The placement or location of elements on the Periodic Table gives an indication of physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order
Key Ideas: The placement or location of elements on the Periodic Table gives an indication of physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order
Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE
 Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE What Makes Red Light Red? (4.1) Electromagnetic Radiation: energy that travels in waves (light) Waves Amplitude: height
Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE What Makes Red Light Red? (4.1) Electromagnetic Radiation: energy that travels in waves (light) Waves Amplitude: height
Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element.
Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element.
Unit 5. The Periodic Table
 Unit 5 The Periodic Table I. Development of Periodic Table Periodic law: when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern.
Unit 5 The Periodic Table I. Development of Periodic Table Periodic law: when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern.
Note that the protons and neutrons are each almost 2,000 times more massive than an electron; What is the approximate diameter of an atom?
 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Organizing the Periodic Table
 Organizing the Periodic Table How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? Chemists used the properties of the elements to sort them into groups. The Organizers JW Dobereiner grouped the elements
Organizing the Periodic Table How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? Chemists used the properties of the elements to sort them into groups. The Organizers JW Dobereiner grouped the elements
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6)
 Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6) All answers and work on a separate sheet of paper! Classify the following as always true (AT), sometimes true (ST), or never true (NT) 1. Atoms of
Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6) All answers and work on a separate sheet of paper! Classify the following as always true (AT), sometimes true (ST), or never true (NT) 1. Atoms of
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on
 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the number of oxidation states 2.
1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the number of oxidation states 2.
MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 C10 04/19/2013 13:34:14 Page 114 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is
C10 04/19/2013 13:34:14 Page 114 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-5A 6 S S S
 Chemistry: Form TR4-5A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass,
Chemistry: Form TR4-5A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass,
Chapter 4 Atoms Practice Problems
 Chapter 4 Atoms Practice Problems 1) The primary substances of which all other things are composed are A) molecules. B) compounds. C) elements. D) electrons. E) protons. 2) Which of the following is a
Chapter 4 Atoms Practice Problems 1) The primary substances of which all other things are composed are A) molecules. B) compounds. C) elements. D) electrons. E) protons. 2) Which of the following is a
Made the FIRST periodic table
 Made the FIRST periodic table 1869 Mendeleev organized the periodic table based on the similar properties and relativities of certain elements Later, Henri Moseley organized the elements by increasing
Made the FIRST periodic table 1869 Mendeleev organized the periodic table based on the similar properties and relativities of certain elements Later, Henri Moseley organized the elements by increasing
Mr. Dolgos Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET. Unit 3: Periodic Table
 *STUDENT* *STUDENT* Mr. Dolgos Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET Unit 3: Periodic Table 2 3 It s Elemental DIRECTIONS: Use the reading below to answer the questions that follow. We all know by now that
*STUDENT* *STUDENT* Mr. Dolgos Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET Unit 3: Periodic Table 2 3 It s Elemental DIRECTIONS: Use the reading below to answer the questions that follow. We all know by now that
How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas?
 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine to moles chlorine using formula weight 2 - Convert moles
EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine to moles chlorine using formula weight 2 - Convert moles
Full file at
 16 Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element. a.
16 Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element. a.
CHAPTER 2. Atoms,Elements, Periodic Table
 CHAPTER Atoms,Elements, Periodic Table 1 Vocabulary Chemistry Science that describes matter its properties, the changes it undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany those processes Matter Anything
CHAPTER Atoms,Elements, Periodic Table 1 Vocabulary Chemistry Science that describes matter its properties, the changes it undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany those processes Matter Anything
Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table
 Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table Focus Questions for the unit... How has the modern view of the atom changed over time? How does a chemist use symbols and notation to communicate
Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table Focus Questions for the unit... How has the modern view of the atom changed over time? How does a chemist use symbols and notation to communicate
Chemistry Chapter 9 Review. 2. Calculate the wavelength of a photon of blue light whose frequency is 6.3 x s -1.
 Chemistry Chapter 9 Review 1. What is the frequency of radiation that has a wavelength of 4.7 x 10-5 cm? 2. Calculate the wavelength of a photon of blue light whose frequency is 6.3 x 10 14 s -1. 3. The
Chemistry Chapter 9 Review 1. What is the frequency of radiation that has a wavelength of 4.7 x 10-5 cm? 2. Calculate the wavelength of a photon of blue light whose frequency is 6.3 x 10 14 s -1. 3. The
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-9A
 Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
CDO AP Chemistry Unit 5
 1. a. Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 5.56 MHz. b. Calculate the frequency of electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength equal to 667 nm. 2. Electromagnetic
1. a. Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 5.56 MHz. b. Calculate the frequency of electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength equal to 667 nm. 2. Electromagnetic
Electronic Structure and Bonding Review
 Name: Band: Date: Electronic Structure and Bonding Review 1. For electrons: a. What is the relative charge? b. What is the relative mass? c. What is the symbol? d. Where are they located in the modern
Name: Band: Date: Electronic Structure and Bonding Review 1. For electrons: a. What is the relative charge? b. What is the relative mass? c. What is the symbol? d. Where are they located in the modern
Valence electron- Energy sublevel- Transition element- Period 10. Electronegativity- Alkaline earth metal- 11. Ion- Halogen- 12.
 Mrs. Hilliard 1. Valence electron 2. Period 3. Alkaline earth metal 4. Halogen 5. Metalloid 6. Hund s Rule 7. Representative element 8. Energy sublevel 9. Transition element 10. Electronegativity 11. Ion
Mrs. Hilliard 1. Valence electron 2. Period 3. Alkaline earth metal 4. Halogen 5. Metalloid 6. Hund s Rule 7. Representative element 8. Energy sublevel 9. Transition element 10. Electronegativity 11. Ion
Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table
 Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table 1 VOCABULARY For each word, provide a short but specific definition from YOUR OWN BRAIN! No boring textbook definitions. Write something to help
Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table 1 VOCABULARY For each word, provide a short but specific definition from YOUR OWN BRAIN! No boring textbook definitions. Write something to help
Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET
 *KEY* *KEY* Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET Unit 3: Periodic Table 1 Copyright 2015 Tim Dolgos 2 Copyright 2015 Tim Dolgos 3 Copyright 2015 Tim Dolgos It s Elemental DIRECTIONS: Use the reading below
*KEY* *KEY* Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET Unit 3: Periodic Table 1 Copyright 2015 Tim Dolgos 2 Copyright 2015 Tim Dolgos 3 Copyright 2015 Tim Dolgos It s Elemental DIRECTIONS: Use the reading below
Unit 4 - Periodic Table Exam Name: PRACTICE QUESTIONS Date: 2/23/2016
 Name: PRACTICE QUESTIONS Date: 2/23/2016 1. Which pair of symbols represents a metalloid and a noble gas? 1) Si and Bi 2) As and Ar 3) Ge and Te 4) Ne and Xe 2. What determines the order of placement of
Name: PRACTICE QUESTIONS Date: 2/23/2016 1. Which pair of symbols represents a metalloid and a noble gas? 1) Si and Bi 2) As and Ar 3) Ge and Te 4) Ne and Xe 2. What determines the order of placement of
Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass
 Elemental Properties Review Worksheet Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass Periodic Table 1. List the element symbols for the following
Elemental Properties Review Worksheet Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass Periodic Table 1. List the element symbols for the following
Unit 02 Review: Atomic Theory and Periodic Table Review
 Practice Multiple Choice Questions Unit 02 Review: Atomic Theory and Periodic Table Review 1. The number of neutrons in an atom of radioactive C 14 is: a) 6 c) 8 b) 12 d) 14 2. When a radioactive nucleus
Practice Multiple Choice Questions Unit 02 Review: Atomic Theory and Periodic Table Review 1. The number of neutrons in an atom of radioactive C 14 is: a) 6 c) 8 b) 12 d) 14 2. When a radioactive nucleus
Duncan. Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3
 Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Light Calculation Notes Here s how the type/form of EM radiation can be determined The amount
Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Light Calculation Notes Here s how the type/form of EM radiation can be determined The amount
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide The Periodic Table, Chapter 5
 Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide The Periodic Table, Chapter 5 Terms, definitions, and people Dobereiner Newlands Mendeleev Moseley Periodic table Periodic Law group family period Page 1 of 38 alkali
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide The Periodic Table, Chapter 5 Terms, definitions, and people Dobereiner Newlands Mendeleev Moseley Periodic table Periodic Law group family period Page 1 of 38 alkali
EM SPECTRUM, WAVELENGTH, FREQUENCY, AND ENERGY WORKSHEET
 EM SPECTRUM, WAVELENGTH, FREQUENCY, AND ENERGY WORKSHEET 1.) Look at the EM spectrum below to answer this question. As you move across the visible light spectrum from red to violet (A) Does the wavelength
EM SPECTRUM, WAVELENGTH, FREQUENCY, AND ENERGY WORKSHEET 1.) Look at the EM spectrum below to answer this question. As you move across the visible light spectrum from red to violet (A) Does the wavelength
KWL CHART--ELECTRONS
 KWL CHART--ELECTRONS WHAT DO I ALREADY KNOW ABOUT ELECTRONS? WHAT DO I WANT TO KNOW CONCERNING ELECTRONS? WHAT HAVE I LEARNED TODAY ABOUT ELECTRONS? GPS STANDARD SC3. Students will use the modern atomic
KWL CHART--ELECTRONS WHAT DO I ALREADY KNOW ABOUT ELECTRONS? WHAT DO I WANT TO KNOW CONCERNING ELECTRONS? WHAT HAVE I LEARNED TODAY ABOUT ELECTRONS? GPS STANDARD SC3. Students will use the modern atomic
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior
 Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior Models of the Atom I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior Models of the Atom I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The
Periodic Trends. 1. Why is it difficult to measure the size of an atom? 2. What does the term atomic radius mean? 3. What is ionization energy?
 Periodic Trends 1. Why is it difficult to measure the size of an atom? 2. What does the term atomic radius mean? 3. What is ionization energy? 4. What periodic trends exist for ionization energy? 5. What
Periodic Trends 1. Why is it difficult to measure the size of an atom? 2. What does the term atomic radius mean? 3. What is ionization energy? 4. What periodic trends exist for ionization energy? 5. What
The Atom. The Atom and The Periodic Table of Elements. Evolution of Atomic Theory
 The Atom The Atom and The Periodic Table of Elements An atom is the smallest particle of matter. It cannot be divided chemically An atom is very small: A sheet of paper is about a million atoms thick Because
The Atom The Atom and The Periodic Table of Elements An atom is the smallest particle of matter. It cannot be divided chemically An atom is very small: A sheet of paper is about a million atoms thick Because
Periodic Table Practice 11/29
 Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
Periodic Table of Elements
 Name: Periodic Table of Elements Block: The periodic table is a scientific work of art, hidden within it are multiple trends, groups, families, and patterns It took a few tries to get to this current masterpiece
Name: Periodic Table of Elements Block: The periodic table is a scientific work of art, hidden within it are multiple trends, groups, families, and patterns It took a few tries to get to this current masterpiece
1. Draw a wave below and label the following parts: peak, trough, wavelength and amplitude
 Wave Nature of Light 1. Draw a wave below and label the following parts: peak, trough, wavelength and amplitude 2. Draw two waves with different frequencies and circle the wave that has a higher frequency.
Wave Nature of Light 1. Draw a wave below and label the following parts: peak, trough, wavelength and amplitude 2. Draw two waves with different frequencies and circle the wave that has a higher frequency.
Unit 2: The Periodic Table
 Unit 2: The Periodic Table The following pages are practice questions for this unit, and will be submitted for homework! You must complete: Unit Vocabulary ALL QUESTIONS What Group Am I? ALL QUESTIONS
Unit 2: The Periodic Table The following pages are practice questions for this unit, and will be submitted for homework! You must complete: Unit Vocabulary ALL QUESTIONS What Group Am I? ALL QUESTIONS
Part I Assignment: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 11 The Periodic Table Part I Assignment: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Use your periodic table and your new knowledge of how it works with electron configurations to write complete
Chapter 11 The Periodic Table Part I Assignment: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Use your periodic table and your new knowledge of how it works with electron configurations to write complete
Atoms with More than One Electron
 Activity 6 Atoms with More than One Electron GOALS In this activity you will: View the spectra of various materials. Graphically analyze patterns in the amounts of energy required to remove electrons from
Activity 6 Atoms with More than One Electron GOALS In this activity you will: View the spectra of various materials. Graphically analyze patterns in the amounts of energy required to remove electrons from
Electrons and Periodic Table (Ch. 4 & 5) OTHS Academic Chemistry
 Name Objectives: Per. Electrons and Periodic Table (Ch. 4 & 5) OTHS Academic Chemistry Express the arrangement of electrons in atoms through electron configurations Understand the electromagnetic spectrum
Name Objectives: Per. Electrons and Periodic Table (Ch. 4 & 5) OTHS Academic Chemistry Express the arrangement of electrons in atoms through electron configurations Understand the electromagnetic spectrum
The Periodic Table of the Elements
 The Periodic Table of the Elements All matter is composed of elements. All of the elements are composed of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
The Periodic Table of the Elements All matter is composed of elements. All of the elements are composed of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
Advanced Chemistry. Mrs. Klingaman. Chapter 5: Name:
 Advanced Chemistry Mrs. Klingaman Chapter 5: The Periodic Law Name: _ Mods: Chapter 5: The Periodic Law Reading Guide 5.1 History of the Periodic Table (pgs. 125-129) 1) What did Dimitri Mendeleev notice
Advanced Chemistry Mrs. Klingaman Chapter 5: The Periodic Law Name: _ Mods: Chapter 5: The Periodic Law Reading Guide 5.1 History of the Periodic Table (pgs. 125-129) 1) What did Dimitri Mendeleev notice
Ch. 3 Answer Key. O can be broken down to form two atoms of H and 1 atom of O. Hydrogen and oxygen are elements.
 Ch. 3 Answer Key 1. The Greeks believed that all matter is made of elements. We currently believe the same thing. However, the Greeks believed that there were 4 elements: earth, water, air and fire. Instead,
Ch. 3 Answer Key 1. The Greeks believed that all matter is made of elements. We currently believe the same thing. However, the Greeks believed that there were 4 elements: earth, water, air and fire. Instead,
PERIODIC TRENDS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 PERIODIC TRENDS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE THE PERIODIC TABLE The row tells us how many energy levels are in that atom The row is also the group The column tells us how many electrons are in the outer energy
PERIODIC TRENDS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE THE PERIODIC TABLE The row tells us how many energy levels are in that atom The row is also the group The column tells us how many electrons are in the outer energy
CHAPTER 6 The Periodic Table
 CHAPTER 6 The Periodic Table 6.1 Organizing the Elements Mendeleev: listed the elements in order of increasing atomic mass and in vertical columns according to their properties. Left blank spaces for undiscovered
CHAPTER 6 The Periodic Table 6.1 Organizing the Elements Mendeleev: listed the elements in order of increasing atomic mass and in vertical columns according to their properties. Left blank spaces for undiscovered
Regan & Johnston Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period
 Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Periodic Table Practice Questions
 Periodic Table Practice Questions 1. Elements in the Periodic Table are arranged according to their (1) atomic number (3) relative activity (2) atomic mass (4) relative size 2. Elements in a given period
Periodic Table Practice Questions 1. Elements in the Periodic Table are arranged according to their (1) atomic number (3) relative activity (2) atomic mass (4) relative size 2. Elements in a given period
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 4 (2017-2018) Families (research and present) Metals/nonmetals Trends o Atomic radius o Electronegativity o Ionization energy o Metallic and nonmetallic character Review Ions Oxidation
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 (2017-2018) Families (research and present) Metals/nonmetals Trends o Atomic radius o Electronegativity o Ionization energy o Metallic and nonmetallic character Review Ions Oxidation
2. Why do all elements want to obtain a noble gas electron configuration?
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Do Now: 1. Complete the table based on the example given Location Element Electron Configuration Metal, Nonmetal or Semi-metal Metalloid)? Group 1, Period 1 Group 11,
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Do Now: 1. Complete the table based on the example given Location Element Electron Configuration Metal, Nonmetal or Semi-metal Metalloid)? Group 1, Period 1 Group 11,
2 e. 14 e. # e # orbitals. 10 e 5. sublevel. shape of orbital. Orbital Shapes. Notes Orbital Notation; e Config; NGN.
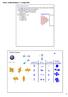 How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table
 Chapter 6: The Periodic Table Name: Per: Test date: In-Class Quiz: Moodle Quiz: preap Learning Objectives Trace the historical development of the periodic table Identify the major groups and key features
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table Name: Per: Test date: In-Class Quiz: Moodle Quiz: preap Learning Objectives Trace the historical development of the periodic table Identify the major groups and key features
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5)
 The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) I. History of the Periodic Table About 70 elements were known by 1850 (no noble gases) but there didn t appear to be a good way of arranging or relating them to study.
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) I. History of the Periodic Table About 70 elements were known by 1850 (no noble gases) but there didn t appear to be a good way of arranging or relating them to study.
Test Review # 5. Chemistry: Form TR5-8A. Average Atomic Mass. Subatomic particles.
 Chemistry: Form TR5-8A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 5 Subatomic particles. Type of Particle Location Mass Relative Mass Charge Proton Center 1.67 10-27 kg 1 +1 Electron Outside 9.11 10-31 kg 0-1
Chemistry: Form TR5-8A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 5 Subatomic particles. Type of Particle Location Mass Relative Mass Charge Proton Center 1.67 10-27 kg 1 +1 Electron Outside 9.11 10-31 kg 0-1
Unit 2 Part 2: Periodic Trends
 Unit 2 Part 2: Periodic Trends Outline Classification of elements using properties Representative elements, transition elements Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Classification of elements using electron
Unit 2 Part 2: Periodic Trends Outline Classification of elements using properties Representative elements, transition elements Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Classification of elements using electron
Periods: horizontal rows (# 1-7) 2. Periodicity the of the elements in the same group is explained by the arrangement of the around the nucleus.
 The Modern Periodic Table 1. An arrangement of the elements in order of their numbers so that elements with properties fall in the same column (or group). Groups: vertical columns (#1-18) Periods: horizontal
The Modern Periodic Table 1. An arrangement of the elements in order of their numbers so that elements with properties fall in the same column (or group). Groups: vertical columns (#1-18) Periods: horizontal
Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory
 Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
The Periodic Table & Formation of Ions
 The Periodic Table & Formation of Ions Development of the Periodic Table Mendeleev: Considered to be the father of the periodic table Arranged elements by increasing atomic mass Placed elements with similar
The Periodic Table & Formation of Ions Development of the Periodic Table Mendeleev: Considered to be the father of the periodic table Arranged elements by increasing atomic mass Placed elements with similar
Unit 3 Periodic Table and Quantum HW Packet Name Date. Periodic Table Concepts. 1. In what family are the most active metals located?
 Directions: Answer the following questions. Periodic Table Concepts 1. In what family are the most active metals located? 2. In what family are the most active non-metals located? 3. What family on the
Directions: Answer the following questions. Periodic Table Concepts 1. In what family are the most active metals located? 2. In what family are the most active non-metals located? 3. What family on the
CHAPTER 6. Table & Periodic Law. John Newlands
 CHAPTER 6 Table & Periodic Law 6.1 Developing a Periodic Table The periodic table was developed to show the properties of an element by simply looking at it's location. In 1860, chemists agreed on a way
CHAPTER 6 Table & Periodic Law 6.1 Developing a Periodic Table The periodic table was developed to show the properties of an element by simply looking at it's location. In 1860, chemists agreed on a way
A bit of review. Atoms are made of 3 different SUB-ATOMIC PARTICLES: 1. ELECTRONS 2. PROTONS 3. NEUTRONS
 Chemistry in Action A bit of review Chemistry is the study of MATTER and ENERGY. Matter is anything that has MASS. All matter is made of super small particles called ATOMS. Atoms are made of 3 different
Chemistry in Action A bit of review Chemistry is the study of MATTER and ENERGY. Matter is anything that has MASS. All matter is made of super small particles called ATOMS. Atoms are made of 3 different
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table
 Chapter 6 The Periodic Table Section 6.1 Organizing the Elements OBJECTIVES: Explain how elements are organized in a periodic table. Section 6.1 Organizing the Elements OBJECTIVES: Compare early and modern
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table Section 6.1 Organizing the Elements OBJECTIVES: Explain how elements are organized in a periodic table. Section 6.1 Organizing the Elements OBJECTIVES: Compare early and modern
Practice Periodic Table Review
 Practice Periodic Table Review Name 1. An electron will emit energy in quanta when its energy state changes from 4p to A) 5s B) 5p C) 3s D) 6p 2. Which electron configuration represents an atom in the
Practice Periodic Table Review Name 1. An electron will emit energy in quanta when its energy state changes from 4p to A) 5s B) 5p C) 3s D) 6p 2. Which electron configuration represents an atom in the
Using the Periodic Table
 MATH SKILLS TRANSPARENCY WORKSHEET Using the Periodic Table 6 Use with Chapter 6, Section 6.2 1. Identify the number of valence electrons in each of the following elements. a. Ne e. O b. K f. Cl c. B g.
MATH SKILLS TRANSPARENCY WORKSHEET Using the Periodic Table 6 Use with Chapter 6, Section 6.2 1. Identify the number of valence electrons in each of the following elements. a. Ne e. O b. K f. Cl c. B g.
Electron Configurations
 Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Name PRACTICE Unit 3: Periodic Table
 1. Compared to the atoms of nonmetals in Period 3, the atoms of metals in Period 3 have (1) fewer valence electrons (2) more valence electrons (3) fewer electron shells (4) more electron shells 2. On the
1. Compared to the atoms of nonmetals in Period 3, the atoms of metals in Period 3 have (1) fewer valence electrons (2) more valence electrons (3) fewer electron shells (4) more electron shells 2. On the
Honors Chemistry - Unit 4 Bonding Part I
 Honors Chemistry - Unit 4 Bonding Part I Unit 4 Packet - Page 1 of 8 Vocab Due: Quiz Date(s): Test Date: UT Quest Due: Bonding Vocabulary: see separate handout assignment OBJECTIVES: Chapters 4-8 Be able
Honors Chemistry - Unit 4 Bonding Part I Unit 4 Packet - Page 1 of 8 Vocab Due: Quiz Date(s): Test Date: UT Quest Due: Bonding Vocabulary: see separate handout assignment OBJECTIVES: Chapters 4-8 Be able
Searching for an Organizing Principle. Searching for an Organizing Principle. How did chemists begin to organize the known elements?
 Searching for an Organizing Principle Searching for an Organizing Principle How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? Searching for an Organizing Principle A few elements, including copper,
Searching for an Organizing Principle Searching for an Organizing Principle How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? Searching for an Organizing Principle A few elements, including copper,
Name: Teacher: Gerraputa
 Name: Teacher: Gerraputa 1. Which list of elements contains a metal, a metalloid, and a nonmetal? 1. Ag, Si, I 2 3.K, Cu, Br 2 2. Ge, As, Ne 4.S, Cl 2, Ar 2. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged
Name: Teacher: Gerraputa 1. Which list of elements contains a metal, a metalloid, and a nonmetal? 1. Ag, Si, I 2 3.K, Cu, Br 2 2. Ge, As, Ne 4.S, Cl 2, Ar 2. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged
Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14
 Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14 1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms We need to further develop our understanding of atomic structure to help us understand how atoms bond to
Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14 1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms We need to further develop our understanding of atomic structure to help us understand how atoms bond to
Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table
 1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above are metals. 3. Which element is
1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above are metals. 3. Which element is
How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas?
 146 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine gas to moles. Use formula weight. 2 - Convert moles
146 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine gas to moles. Use formula weight. 2 - Convert moles
Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table 1. What are the three primary particles found in an atom? A) neutron, positron, and electron B) electron, neutron, and proton C) electron, proton,
Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table 1. What are the three primary particles found in an atom? A) neutron, positron, and electron B) electron, neutron, and proton C) electron, proton,
Chapter 3: Elements and Compounds. 3.1 Elements
 Chapter 3: Elements and Compounds 3.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical or physical methods to simpler substances. The 118 known elements are nature
Chapter 3: Elements and Compounds 3.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical or physical methods to simpler substances. The 118 known elements are nature
Frequency and wavelength are mathematically related to each other by the equation: c = λν.
 Chemistry I Unit 3: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Properties of Light The Wave Description of Light Electromagnetic radiation- a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels
Chemistry I Unit 3: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Properties of Light The Wave Description of Light Electromagnetic radiation- a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels
Modern Atomic Theory CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Chapter 3B Modern Atomic Theory 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Waves Electromagnetic Radiation Dual Nature of Light Bohr Model of Atom Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Electron Configuration Electron Configuration
Chapter 3B Modern Atomic Theory 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Waves Electromagnetic Radiation Dual Nature of Light Bohr Model of Atom Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Electron Configuration Electron Configuration
- Atomic line spectra are UNIQUE to each element. They're like atomic "fingerprints".
 - Atomic line spectra are UNIQUE to each element. They're like atomic "fingerprints". - Problem was that the current model of the atom completely failed to explain why atoms emitted these lines. An orbit
- Atomic line spectra are UNIQUE to each element. They're like atomic "fingerprints". - Problem was that the current model of the atom completely failed to explain why atoms emitted these lines. An orbit
The Periodic Table. Unit 4
 The Periodic Table Unit 4 I. History A. Dmitir Mendeleev Russian chemist, 19th century Arranged elements by their properties Arranged by increasing atomic mass Groups: vertical groups-elements have similar
The Periodic Table Unit 4 I. History A. Dmitir Mendeleev Russian chemist, 19th century Arranged elements by their properties Arranged by increasing atomic mass Groups: vertical groups-elements have similar
Assessment Chapter 5 Pre-Test Chapter: The Periodic Law Use the periodic table below to answer the questions in this Chapter Test.
 Assessment Chapter 5 Pre-Test Chapter: The Periodic Law Use the periodic table below to answer the questions in this Chapter Test. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best
Assessment Chapter 5 Pre-Test Chapter: The Periodic Law Use the periodic table below to answer the questions in this Chapter Test. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best
HSVD Ms. Chang Page 1
 Name: Chemistry, PERIODIC TABLE 1. A solid element that is malleable, a good conductor of electricity, and reacts with oxygen is classified as a (1) noble gas (2) metalloid (3) metal (4) nonmetal 2. Which
Name: Chemistry, PERIODIC TABLE 1. A solid element that is malleable, a good conductor of electricity, and reacts with oxygen is classified as a (1) noble gas (2) metalloid (3) metal (4) nonmetal 2. Which
Exam Electrons and Periodic Table
 1-20 multiple choice. Answer on scantron. 21-25 short response. Answer on exam paper. All questions are 4 points each. 1. Which term is defined as the region in an atom where an electron is most likely
1-20 multiple choice. Answer on scantron. 21-25 short response. Answer on exam paper. All questions are 4 points each. 1. Which term is defined as the region in an atom where an electron is most likely
- Some properties of elements can be related to their positions on the periodic table.
 186 PERIODIC TRENDS - Some properties of elements can be related to their positions on the periodic table. ATOMIC RADIUS - The distance between the nucleus of the atoms and the outermost shell of the electron
186 PERIODIC TRENDS - Some properties of elements can be related to their positions on the periodic table. ATOMIC RADIUS - The distance between the nucleus of the atoms and the outermost shell of the electron
Regan & Johnston Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period
 Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
 The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends The properties of the elements exhibit trends and these trends can be predicted with the help of the periodic table. They can also be explained and understood by
The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends The properties of the elements exhibit trends and these trends can be predicted with the help of the periodic table. They can also be explained and understood by
Unit 2 Periodic Table
 2-1 Unit 2 Periodic Table At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Describe the origin of the periodic table State the modern periodic law Key the periodic table according to metals vs. nonmetals and
2-1 Unit 2 Periodic Table At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Describe the origin of the periodic table State the modern periodic law Key the periodic table according to metals vs. nonmetals and
There are 7 trends on the periodic table that we will follow. Using your periodic table, answer all of the questions in the packet. Think hard.
 Trends Handout ANSWERS There are 7 trends on the periodic table that we will follow. Using your periodic table, answer all of the questions in the packet. Think hard. The periodic table has 18 groups that
Trends Handout ANSWERS There are 7 trends on the periodic table that we will follow. Using your periodic table, answer all of the questions in the packet. Think hard. The periodic table has 18 groups that
The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. orbital 3s 3p 3d. Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n.
 Shells and Subshells The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. n=3 orbital 3s 3p 3d Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n n=3 3s 3p 3d Subshell: all orbitals with the same value
Shells and Subshells The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. n=3 orbital 3s 3p 3d Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n n=3 3s 3p 3d Subshell: all orbitals with the same value
Name Unit 4: Periodic Table Period. Unit 4 Vocabulary.Due Test Day
 Name Unit 4: Periodic Table Period 1. History and Language of the Periodic Table 2. Identifying PROPERTIES OF METALS, METALLOIDS, & NONMETALS 3. Identifying GROUP PROPERTIES 4. Classifying elements 5.
Name Unit 4: Periodic Table Period 1. History and Language of the Periodic Table 2. Identifying PROPERTIES OF METALS, METALLOIDS, & NONMETALS 3. Identifying GROUP PROPERTIES 4. Classifying elements 5.
- Some properties of elements can be related to their positions on the periodic table.
 179 PERIODIC TRENDS - Some properties of elements can be related to their positions on the periodic table. ATOMIC RADIUS - The distance between the nucleus of the atoms and the outermost shell of the electron
179 PERIODIC TRENDS - Some properties of elements can be related to their positions on the periodic table. ATOMIC RADIUS - The distance between the nucleus of the atoms and the outermost shell of the electron
Elements are the building blocks of matter. Chapter 2
 Elements are the building blocks of matter. Chapter 2 S In this chapter we will be covering S ELEMENTS!!! S The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties!!! S The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory! What is
Elements are the building blocks of matter. Chapter 2 S In this chapter we will be covering S ELEMENTS!!! S The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties!!! S The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory! What is
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
Discovery of Elements. Dmitri Mendeleev Stanislao Canizzaro (1860) Modern Periodic Table. Henry Moseley. PT Background Information
 Discovery of Elements Development of the Periodic Table Chapter 5 Honors Chemistry 412 At the end of the 1700 s, only 30 elements had been isolated Included most currency metals and some nonmetals New
Discovery of Elements Development of the Periodic Table Chapter 5 Honors Chemistry 412 At the end of the 1700 s, only 30 elements had been isolated Included most currency metals and some nonmetals New
Homework Chapter 03 Chemistry 51 Los Angeles Mission College Answer the following questions: a. What electron sublevel starts to fill after
 3.93 Give the period and group number for each of the following elements: a. bromine b. argon c. potassium d. radium 3.94 Give the period and group number for each of the following elements: a. radon b.
3.93 Give the period and group number for each of the following elements: a. bromine b. argon c. potassium d. radium 3.94 Give the period and group number for each of the following elements: a. radon b.
5E Essential Lesson-SC.8.P.8.6. Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1. Number of valence electrons: 2
 Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5
 Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 DO NOW - Finish coloring your periodic tables! (5 min) State at Room Temperature Appearance Conductivity Malleability and Ductility Metals - solid except for mercury
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 DO NOW - Finish coloring your periodic tables! (5 min) State at Room Temperature Appearance Conductivity Malleability and Ductility Metals - solid except for mercury
Mendeleev s Table (1871) While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the
 Periodic Table Mendeleev s Table (1871) While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the very stable copper, in the same family.
Periodic Table Mendeleev s Table (1871) While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the very stable copper, in the same family.
