Application of He-Ne laser to study the variation of refractive index of liquid solutions with the concentration
|
|
|
- Sophia Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Integr. Sci. Technol, 2013, 1, 1, Article Application of He-Ne laser to study the variation of refractive index of liquid solutions with the concentration Vivek Kumar Singh a, Brij Bir Singh Jaswal a, Vinay Kumar a, Ram Prakash a, and Priyanka Rai b a School of Physics, Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University, Katra , J&K, India b Department of Mathematics, Patna Science College, Patna University, Patna , Bihar, India Received: Accepted: Available Online: ABSTRACT In the present paper, we have presented the variation of the refractive index of liquid solutions with the concentration at the He-Ne laser wavelength nm. The measurements of the present experiment were carried out using the conventional minimum deviation method of an equilateral hollow glass prism. We measured the refractive indices of sugar solutions, sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions, and sodium (Na) for a range of density varying from distilled water to a saturated condition and their variation with the concentration is presented. Our results reveal that the refractive index of liquid solutions varies linearly with the concentration of sugar and sodium chloride at low concentrations. For the higher concentrations of sugar solution we found a slight curvature from the plot of refractive index vs concentration of solution. For the quantitative measurements of sugar, NaCl and Na present in different kinds of samples we drew the calibration curves. We have verified our results with the results reported and obtained from atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). We have also used this method to determine the salinity of the water sample of Adriatic Sea. Keywords: Sugar, Salt, Sodium, He-Ne laser, Minimum deviation Introduction The refractive index or indices of a substance describe an important part of its interaction with electromagnetic radiation. The refractive index is a basic optical property of materials. Its accurate measurement is often needed in many branches of physics and chemistry and it has several applications to many industries and materials. Refractive index is measured for many reasons. It is clearly important to know the refractive index of materials used for their clarity, such as glasses and solid plastics. In complex fluids such as drinks or foods, the refractive index is a measure of dissolved or submicronic material. The Brix scale relates refractive index to sugar concentration. Common industrial applications are to microemulsions to measure their oil/water ratio, to antifreeze to check the glycol/water ratio, and to inaccessible liquids such as the electrolyte of rechargeable cells 1. Address: Dr. Vivek Kumar Singh School of Physics, Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University, Katra , Jammu and Kashmir, India. Tel: , Ext (O) singh_vivekkumar2005@yahoo.com Cite as: VK Singh et. al. J Integr. Sci. Technol., 2013, 1(1), IS Publications JIST ISSN Numerous methods for measuring the refractive index of a liquid solution are well documented in textbooks 2, however the most suitable and easiest method was also reported 3, 4. The authors have reported that the use of an equilateral hollow prism would allow measurement of the refractive index of most ordinary liquids. It opens the possibility of studying small variations in the refractive index of a solution with concentration. In the present paper, we have discussed an experimental technique using He-Ne laser to determine the refractive index of transparent liquid samples making the use of Snell s law. We have utilized He-Ne laser as a light source to measure the refractive index of different kinds of standard and unknown sample solutions and hence to determine the concentrations of the sugar and salt in unknown samples. Materials and Methods Experimental Setup The theory and method have been discussed in well manner in the reported literature and textbooks 3-6. However, in brief we have discussed the method to measure the minimum deviation to measure the refractive index of liquid solutions making use of Snell s law. Regarding Fig. 1, a collimated light beam AB is incident on a prism of apex angle α. The angle of deviation is found to be minimum ( ) if and are equal. In this position the refracted ray is parallel to the base of the prism. Then the refractive index of the material filled inside the prism or solid prism can be determined by using Snell s law which is given by: = sin( + )/2 (1) 13
2 To derive Equation (1), the value α = 60 and n air = is being used. Figure 1: Refraction through prism at the position of minimum deviation ( ) To perform the experiment, an equilateral hollow prism is fixed on a spectrometer table. A 2 mw He-Ne laser at nm was used as the light source. A schematic representation of the apparatus setup is shown in Fig. 2. At first we have set the laser pointer in such a way so that the laser beam (light ray AD) fall perpendicularly to a nearby wall. We have attached a big piece of paper to the wall for marking and measuring where the beam hits. We have also adjusted the height of the laser pointer so that it hits about half-way up the side of the prism. The laser pointer is fixed and in place and we have checked periodically to make sure that the beam is still hitting its original spot. When the prism was empty (filled only with air), then we placed it in the path of the laser beam. We marked the laser spot on the wall when the prism was empty. When we filled the prism with liquid, the laser beam refracted within the prism. To find the angle of minimum deviation the position of minimum deviation is required. To find this position we changed the angle of incident by rotating the prism table in that direction where the deviated laser beam spot move towards the undeviated laser spot. Figure 2: Experimental setup to measure the angle of minimum deviation ( ) At a particular incident angle the laser beam spot stops and the laser spots reverse its direction. At that point where the laser spot stops is the position of minimum deviation. By theory and experiments, it is proved that at this position the angle of incident and the angle of emergence are equal and the refracted ray (light ray AB) is parallel to the base of the prism which can be seen in Photographs 3. The emerging beam (light ray BC) hits the wall some distance away from the original spot (point D) of the undiverted beam. Thus, the angle of minimum deviation can be measured easily using the formula: = ( / ) (2) Finally, the index of refraction is calculated using Equation (1). To check the validity of this experimental setup we calculated the index of distilled water which came and validate our experimental setup and procedure. Figure 3: Photographs of the experimental setup in the laboratory at the position of minimum deviation Preparation of standard samples of varying concentration of sugar and sodium chloride for calibration For the quantitative analysis of sugar and NaCl present in the unknown sample solutions, we have to draw proper calibration curves. Thus, for the calibration curve (a graph between refractive index and the concentration of sugar or NaCl in the matrix), different liquid samples having a known concentration of sugar and NaCl are required. In this work, a standard solution method 7 was preferred for the preparation of the standard samples, to maintain the homogeneity of the liquid samples. The standard sugar solutions having sugar concentration of 2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 30%, 40%, and 60% were prepared. A 2% sugar solution is meant by 2 gm of sugar is dissolved in 100 ml of distilled water i.e. (2% = 2 gm 100 ml). In the present experiment, distilled water is used to avoid any type of contamination error. Similarly, the standard solutions having different concentrations of sodium chloride (NaCl) i.e. 2%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% were prepared. A 2% NaCl solution is meant by 2 gm of NaCl is dissolved in 100 ml of distilled water. Since the percentage equivalent of Na in NaCl is %, then 1 gm of NaCl contains 0.39 gm of Na. Thus, the equivalent percentage of Na in these standard NaCl 14
3 solutions is given by 0.78% ( 0.78% = 0.78 gm 100 ml), 1.95%, 3.9%, 5.85%, and 7.8% respectively. These solutions have been used to calculate the refractive index of the solutions. Collections of different types of samples containing Sugar and Salt We have collected different types of samples containing sugar and different kinds of salt samples. We have also collected the water from an Adriatic Sea to analyze their salinity. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. Its coasts are part of (in decreasing order of coastline length without islands) Croatia, Italy, Albania, Montenegro, Slovenia and Bosnia Herzegovina 8. These solutions then finally used to determine their refractive index and hence to determine the sugar content, salt content and the concentration of Na in these samples. Results and Discussion Study of the Variation of of Sugar Solution with the Concentration of Sugar Using Equation (1) we have calculated refractive index of sugar solutions of varying concentrations and the variation of the refractive index of the sugar solution with the concentration sugar is plotted and shown in Fig Concentration (gm/100ml) Figure 4: Variation of index of refraction with concentration of sugar All the data points on the graphs represent five independent measurements carried out at a particular concentration of solution. From the Fig. 4 it is clear that the variation of refractive index with sugar concentration is linear for lower concentration but at higher concentrations a slight curvature can be seen. For the sugar solutions containing sugar upto 30% one can figure on a linear relationship between the refraction and sugar concentration. Our result is very close to the results reported by W. Mahmood bin Mat Yunus 9. They have found the linear part of the graph for the solution concentration upto 24 gm/100 ml which is 24%. From the literature 10 the report says that the linear relationship was found upto 40% y = x ; R = Concentration (gm/100 ml) Figure 5: Calibration plot for the variation of index of refraction with concentration of sugar solution up to 20% For more accuracy, we drew the calibration curves for different concentration of sugar solutions by plotting refractive index vs concentration of sugar upto 20% only, using ORIGIN software. It is because that the linear regression coefficient of the linear fitted data for the concentration upto 20% is much more better than that of the linear fitted data concentration upto 30% (Figure not shown here). Therefore, the calibration plot as shown by Fig. 5 is better than that of obtained from the concentration upto 30%. Five measurements were carried out separately to determine the refractive index of the solution and, finally, the mean relative standard deviation (RSD) of the refractive index is calculated and shown as ± error bar. We obtained the slopes of these calibration curves by fitting data in the linear regression functions concentrations upto 20%. Using this calibration curve we have determined the sugar content of different payable liquids of different brands available in the markets. The refractive index of these liquids has been determined using the calibration curve and tabulated in Table 1. From the Table 1 it is clear that the calculated sugar content is in good agreement with the sugar contents reported in these liquids. Thus, we can explore the possibility of using this method to determine the sugar content in complex fluids like orange juice, apple juice etc. We have also used this calibration curve to determine the sugar content in sugar cane juice. The calculated value of the sugar in sugar cane liquid was approximately 22% for the particular sugar cane juice which is good agreement with the reported literature 11. High quality cane has a good juice content with high sugar levels (20% plus) 11. Poor quality cane or cane that has been harvested early may have similar juice content but the sugar levels will be reduced. From the literature, it is clear that our result is in close agreement with the results reported in literature. From the above results it is clear that the present method is very useful to determine the refractive index of transparent liquids and finally to determine the sugar content in complex fluids. 15
4 Study of the Variation of of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Solution with the Concentration of NaCl Using Equation (1) we hav e calculated refractive index of NaCl solutions having different concentrations of NaCl and the variation of the refractive index with the concentration is plotted and shown in Fig. 6. the solution concentration less than 10 gm/100 ml which is 10%. y = x ; R = Concentration of Na (gm/100 ml) Figure 6: Variation of index of refraction with the concentration of NaCl Concentration (gm/100 ml) y = x ; R = Concentration (gm/100 ml) Figure 7: Calibration plot for the variation of index of refraction with concentration of NaCl upto 15% From this plot (Fig. 5) it is clear that the refractive index varies linearly with the concentration of NaCl. For better accuracy, we drew the calibration plots upto the concentrations 15%. We obtained the slopes of these calibration curves by fitting data in the linear regression functions for the concentrations upto 15%. We have seen that at low concentration less than 20%, the variation of the refractive index is linear with the concentration. This is in good agreement with the results reported by W. Mahmood bin Mat Yunus 9. They have found the linear part of the graph for Figure 8: Calibration plot for the variation of index of refraction with concentration of Na We have used this calibration curve to determine the salinity of the water collected from Adriatic Sea. The content of NaCl is determined which was approximately 4%. Generally, the salinity of sea water is reported 12 from 3%-5%. Quantitative Study of Na in different kinds of Salts Using Calibration Curve There are several types of salts that are easily available in the market place for daily use and they contain different proportions of Na. The Na contents in the salts are directly related to high blood pressure and kidney diseases. The levels of Na in these salts can help to make the choice of low Na, which are the requirement to manage these diseases. So it is very important to know the Na concentration in these salts. To know the Na content in different kinds of salts four different types of common edible salts taken in the present study are described below. (i) Black salt: Black salt, containing Na, is available in purified form in the Indian markets. (ii) Tata salt: This is a refined iodinated salt widely used as a table salt and easily available in the Indian markets. (iii) Saindha salt: It is commonly known as rock salt 13. (iv) Ordinary salt: This is an ordinary type of salt, which is not refined and can be obtained easily in the Indian markets. The solutions of these salt samples were prepared which are finally used to determine the refractive index and hence to calculate the concentration of Na in the salt samples. To prepare the solution we dissolve 10 gm of Tata salt, Saindha salt, Ordinary salt and 8 gm of Black salt in 100 ml of distilled water and filled these solutions in hollow prism to calculate the refractive index of these solution. The refractive indices of these solutions were measured and finally the concentrations of Na in these salt samples are given in Table 2. The calculated value of the concentration of Na is 16
5 in good agreement with the results reported. We have also determined the concentration of Na in Ordinary Salt and Saindha Salt using atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) which is in good agreement with our results reported here. Table 1: Concentration of sugar content in different liquids Salt Samples Calculated concentration of Na (gm/100gm of salt) Reported concentration of Na (gm/100gm of salt) Black Salt Tata Salt Saindha Salt (Results of AAS) Ordinary Salt (Results of AAS) Table 2: Concentration of Na content in different kinds of salts In the Saindha salt, the concentration of Na is in Common Calculated Concentration drinks concentration reported of sugar (gm/100 ml) (gm/100 ml) Brand A Brand B Brand C comparable to Black salt but is lower than that of Tata salt and Ordinary salt (Table 2). It is difficult to use daily Black salt in daily food so keeping this point in view Saindha salt is more beneficial to use especially for the blood pressure and kidney patients. The presence of a reasonable amount of Na in the human body helps with nerve activity, muscle contraction, and fluid balance. Thus, one needs some sodium, but since Na is found naturally in foods, most people consume more Na than they need. When kidneys fail to work properly, the extra Na is not removed from the body. With extra sodium in the body one will feel thirsty and drink more fluids. Drinking a lot of fluids is dangerous for chronic kidney disease patients. Too much fluid can also cause high blood pressure, difficulties in breathing, and swelling of hands, feet and legs. Thus, the best way to control thirst is to limit Na. This means that one need to select the proper use of salt containing low Na, thus, Saindha salt is suitable for this purpose. Thus, we can say that the present experimental setup is very useful to calculate the concentration of Na and other minerals of the salt which affects the human being directly like K, Ca, and Mg etc. Conclusion and Further Prospects of the Research In the present paper, we have studied the variation of refractive index of liquid solutions with the concentration dissolve in the liquid at He-Ne laser wavelength µm. We have successfully determined the sugar content in common drinks. We have also determined the concentration of Na in some different kinds of salts. In summary, we have demonstrated that this method is quite capable to determine the solute content dissolved in a solvent which is transparent. Our results reveal that this method can also be application for the determination of the content of the other major and minor elements like Ca, Mg, Na and K which directly affects the human health. References and notes 1. Geake, J. E.; Smalley, C. A; Simple linear hand-held refractometer. J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 1983, 16, Longhurst, R. S. Geometrical and Physical Optics, Wiley: New York, Grange, B. W.; Stevenson, W. H.; Viskanta, R.; of Liquid Solutions at Low Temperatures: An Accurate Measurement. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, Jenkin, D. D.; of Solution. Phys. Educ. 1982, 17, Cariou, J. M.; Dugas, J.; Martin, L.; Michel, P.; Refractive-Index Variations with Temperature of PMMA and Polycarbonate. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, Bass, J. D.; Weidner, D. J.; Method for Measuring the of Transparent Solids. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1984, 55, The article can be found at: tm. 8. The article can be found at: 9. Yunus, W. M. B. M.; Rahman, A. B. A.; Refractive index of solutions at high concentrations. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, Lide, D. R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry & Physics, 90 th Edition, CRC, The article can be found at: uction_from_cane.pdf. 12.The article can be found at: 13.The article can be found at: Dr. Vivek Kumar Singh obtained his M.Sc. (Physics) and D. Phil. Degree from the University of Allahabad, Allahabad, India in 2004 and 2010 respectively. Currently, Dr. Singh is an Assistant Professor of Physics at the Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University (SMVDU), Katra, J&K, India. His research interests are in the field of Lasers and Spectroscopy. Dr. Singh is currently working in the field of Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for the study of biological samples like gallstones, kidney stones, teeth, bones etc. He has published more than 15 International research papers. He is also working in the field of Theoretical Physics and published several article in the field of Cosmology. He is also life member of Indian Laser Association, Modular Labs, BARC, Bombay; Laser and Spectroscopy Society of India, BHU, Varanasi, Indian Science Congress Association, Kolkata, Indian Society of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Ahmedabad, and Indian Association of Physics Teachers, Kanpur. 17
6 Dr. Priyanka Rai has completed her M.Sc. degree in 2007 from Patna University, Patna, India and received several University Gold Medals. She completed her Ph.D. degree from Veer Kunwar Singh University, Ara, Bihar, India in Her research interests are in the field of Cosmological Models in Scalar-Tensor Theories of Gravitation. She has published her research work in the Journal of International repute like International Journal of Theoretical Physics. Currently, she is involved in theoretical as well as experimental Physics. Mr. Brij Bir Singh Jaswal has completed his M.Sc. (Physics) degree in 2012 from Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University (SMVDU), Katra, J&K, India. His research interests are in the field of Laser and Spectroscopy. He has attended National level conferences to present his research work. Dr. Vinay Kumar received his M. Sc. Degree in Physics from Jiwaji University Gwalior in He obtained his Ph.D. from K.U., Kurukshetra in His research interests are in fluorescent nanomaterials in powder and thin film forms, and their applications in lighting, displays, and latent finger-print development. He did his first Post- Doctoral Research from UFS, South Africa and second PDF from Panjab University, Chandigarh, India. He has published more than 38 international research articles. Currently, Dr. V. Kumar is an Assistant Professor of Physics at the Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University, Katra (J&K) India. He is also a Life member of Luminescence Society of India. He is also a recipient of DST-Young Scientist Award in Dr. Ram Prakash received his Ph.D. Degree in Physics from DAVV, Indore. He has also post doctoral experiences from IIT Kanpur and South Korea. His areas of Specialization are Magnetic oxide thin films, DMS, Materials science, Experimental Techniques and area of Interest are Materials Science, thin film & nanostructures, spintronic materials and optical materials. He has published more than 20 International research papers. Currently, He is an Assistant Professor of Physics at the Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University, Katra, J&K, India. He is also a Life member of Indian Science Congress Association, Kolkata, MRSI, and Indian Association of Physics Teachers, Kanpur. 18
Optical Characterization of Sucrose (C 12 H 21 O 11 ) at Different Temperatures
 Optical Characterization of Sucrose (C 12 H 21 O 11 ) at Different Temperatures N. K. Wagholikar 1, S. B. Jagtap 2 * Asst. Professor, Dept. of Physics, Sir Parashurambhau College, Pune, Maharashtra State,
Optical Characterization of Sucrose (C 12 H 21 O 11 ) at Different Temperatures N. K. Wagholikar 1, S. B. Jagtap 2 * Asst. Professor, Dept. of Physics, Sir Parashurambhau College, Pune, Maharashtra State,
Surface plasmon resonance based refractive index sensor for liquids
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 43, November 005, pp. 854-858 Surface plasmon resonance based refractive index sensor for liquids Navina Mehan, Vinay Gupta, K Sreenivas & Abhai Mansingh Department
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 43, November 005, pp. 854-858 Surface plasmon resonance based refractive index sensor for liquids Navina Mehan, Vinay Gupta, K Sreenivas & Abhai Mansingh Department
Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) From Aqueous Solution
 Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) From Aqueous Solution U.V. Biradar 1, S.M. Dongarge 2 and N.V.Wani 3 1 Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya, Latur, Maharashtra (India) 2 Department of
Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) From Aqueous Solution U.V. Biradar 1, S.M. Dongarge 2 and N.V.Wani 3 1 Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya, Latur, Maharashtra (India) 2 Department of
Chapter 4. Dispersion of Glass. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Apparatus
 Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy A. Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Objective The single feature that contributes most to making atomic
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission Spectroscopy A. Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Objective The single feature that contributes most to making atomic
RESEARCH ON STUDY OF CONCENTRATION DEPENDENCE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX OF OIL USING A NOVEL TECHNIQUE
 RESEARCH ON STUDY OF CONCENTRATION DEPENDENCE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX OF OIL USING A NOVEL TECHNIQUE Department of Physics, Mid Western University, Campus of Science and Technology email:dhakaldharma605@gmail.com
RESEARCH ON STUDY OF CONCENTRATION DEPENDENCE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX OF OIL USING A NOVEL TECHNIQUE Department of Physics, Mid Western University, Campus of Science and Technology email:dhakaldharma605@gmail.com
Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aquous Solution
 Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aquous Solution Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya Latur 413512 (M.S.)INDIA. ABSTRACT There are different methods to determine the refractive index
Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aquous Solution Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya Latur 413512 (M.S.)INDIA. ABSTRACT There are different methods to determine the refractive index
Which of the following statements could explain this process?
 Name Date Mark: /65 = % PRETEST ON CHAPTER 2 MOLECULES AND SOLUTIONS Part 1 MULTIPLE CHOICES Answer all the questions on the multiple choice sheet provided 1) Jamie is a very curious student. She has just
Name Date Mark: /65 = % PRETEST ON CHAPTER 2 MOLECULES AND SOLUTIONS Part 1 MULTIPLE CHOICES Answer all the questions on the multiple choice sheet provided 1) Jamie is a very curious student. She has just
Crystals! Table of Contents. Vocabulary 2. Word Search 6. What is a Crystal? 7. Atoms, Ions, Molecules. and the Unit Cell 13.
 Crystals! Table of Contents Vocabulary 2 Word Search 6 What is a Crystal? 7 Atoms, Ions, Molecules and the Unit Cell 13 Crystal Shapes 15 X-Ray Crystallography 17 Recipes for Making A Booklet for Elementary
Crystals! Table of Contents Vocabulary 2 Word Search 6 What is a Crystal? 7 Atoms, Ions, Molecules and the Unit Cell 13 Crystal Shapes 15 X-Ray Crystallography 17 Recipes for Making A Booklet for Elementary
Speed of Light in Glass
 Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION
 FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION Atomic spectroscopy is based on the absorption, emission or fluorescence process of light by atoms or elementary ions. Information for atomic scale is obtained in two
FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION Atomic spectroscopy is based on the absorption, emission or fluorescence process of light by atoms or elementary ions. Information for atomic scale is obtained in two
Study of concentration dependence of Refractive index of Sugar and Salt Solution
 KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE (PHYSICS) Study of concentration dependence of Refractive index of Sugar and Salt Solution A 2 nd Year 1 st Semester Project Report
KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE (PHYSICS) Study of concentration dependence of Refractive index of Sugar and Salt Solution A 2 nd Year 1 st Semester Project Report
Mixtures & Solutions. What is matter? What is a mixture? What is a mechanical mixture? What is a solution? What is a pure substance?
 R. ROSS BEATTIE SCIENCE CLASS KEY WORDS: Matter Solid, liquid, gas Pure substance Mixture Mechanical Mixture Solution Solute Solvent Dissolving Solubility Concentrated Diluted Saturated Unsaturated Can
R. ROSS BEATTIE SCIENCE CLASS KEY WORDS: Matter Solid, liquid, gas Pure substance Mixture Mechanical Mixture Solution Solute Solvent Dissolving Solubility Concentrated Diluted Saturated Unsaturated Can
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Waves Atoms & Space
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Waves Atoms & Space Moulsham High School 1 1. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown below. gamma rays X-rays A visible light infra-red
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Waves Atoms & Space Moulsham High School 1 1. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown below. gamma rays X-rays A visible light infra-red
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1. Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry. Accuracy vs Precision
 Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Dispersion of Glass Introduction Apparatus Theory
 Dispersion of Glass Introduction This experiment will develop skills in aligning and using a spectrometer to measure dispersion of glass, and choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting
Dispersion of Glass Introduction This experiment will develop skills in aligning and using a spectrometer to measure dispersion of glass, and choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting
Chiroptical Spectroscopy
 Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings. Abstract
 Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
DISPERSION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS. Two identical prisms made of the same material placed with their based on opposite sides (of the
 DISPERSION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. What will be the spectrum of sun during a total solar eclipse? Q-2. Why the secondary rainbow is always fainter than the primary rainbow? Q-3. Two identical
DISPERSION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. What will be the spectrum of sun during a total solar eclipse? Q-2. Why the secondary rainbow is always fainter than the primary rainbow? Q-3. Two identical
PHY 192 Optical Activity 1
 PHY 192 Optical Activity 1 Optical Activity Introduction The electric (E) and magnetic (B) vectors in a traveling electromagnetic wave (such as light for example) oscillate in directions perpendicular
PHY 192 Optical Activity 1 Optical Activity Introduction The electric (E) and magnetic (B) vectors in a traveling electromagnetic wave (such as light for example) oscillate in directions perpendicular
Solutions and Concentrations
 A02 Solutions and Concentration.notebook Solutions and Concentrations What is concentration? 1 The difference between concentrated solutions and dilute solutions can be determined qualitatively and quantitatively.
A02 Solutions and Concentration.notebook Solutions and Concentrations What is concentration? 1 The difference between concentrated solutions and dilute solutions can be determined qualitatively and quantitatively.
How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks)
 Q1. The diagram shows an atom. How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks) Page 1 of 53 Q2. The picture shows a man at work in a factory
Q1. The diagram shows an atom. How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks) Page 1 of 53 Q2. The picture shows a man at work in a factory
Study of Interdiffusion of Calcium Chloride-Water system Using Laser Beam Deflection Sensor
 STUDENT JOURNAL OF PHYSICS Study of Interdiffusion of Calcium Chloride-Water system Using Laser Beam Deflection Sensor T.M. Sreedevi 1, N.P. Dhanya 2, P.R. Sasikumar 3 1 M Sc (Physics, Fourth Semester)
STUDENT JOURNAL OF PHYSICS Study of Interdiffusion of Calcium Chloride-Water system Using Laser Beam Deflection Sensor T.M. Sreedevi 1, N.P. Dhanya 2, P.R. Sasikumar 3 1 M Sc (Physics, Fourth Semester)
Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time.
 L e c t u r e 8 1 Polarization Polarized light Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time. Imagine two harmonic, linearly polarized light
L e c t u r e 8 1 Polarization Polarized light Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time. Imagine two harmonic, linearly polarized light
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry
 Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagrams show the sub-atomic particles in four different atoms.
 2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagrams show the sub-atomic particles in four different atoms. Atom A Atom B Atom C Atom D Use the Chemistry Data Sheet to help you to answer these
2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagrams show the sub-atomic particles in four different atoms. Atom A Atom B Atom C Atom D Use the Chemistry Data Sheet to help you to answer these
Variation of Refractive Index of PMMA with temperature and different doping % of Tio 2
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 10 Pages 3626-3631 2015 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Variation of Refractive Index of PMMA with temperature
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 10 Pages 3626-3631 2015 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Variation of Refractive Index of PMMA with temperature
LIQUID LIGTH GUIDE. Una Pale
 LIQUID LIGTH GUIDE Una Pale XV gymnasium, Faculty of electrical engineering and computing, University of Zagreb, Croatia 1. Introduction Light guide is a fiber-optic cable which is used to transfer signal
LIQUID LIGTH GUIDE Una Pale XV gymnasium, Faculty of electrical engineering and computing, University of Zagreb, Croatia 1. Introduction Light guide is a fiber-optic cable which is used to transfer signal
R R CH. Some reactions of alcohols vary depending on their classification as 1º, 2º, or 3º alcohols.
 Experiment: Alcohol Reactions Alcohols are important organic molecules characterized by an alkyl group covalently bonded to a hydroxyl group. They may be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary,
Experiment: Alcohol Reactions Alcohols are important organic molecules characterized by an alkyl group covalently bonded to a hydroxyl group. They may be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary,
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
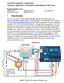 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
Required Items. ACTIVE PARTICIPATION in class and lab. Use of iclicker
 Welcome to Chem103 Required Items Textbook: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, Martin S. Silberberg, 5 th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2009 iclicker Scientific calculator ACTIVE PARTICIPATION
Welcome to Chem103 Required Items Textbook: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, Martin S. Silberberg, 5 th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2009 iclicker Scientific calculator ACTIVE PARTICIPATION
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION
 Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Optical properties of a laser dye in a solid-state polymeric host
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 91, NUMBER 12 15 JUNE 2002 Optical properties of a laser dye in a solid-state polymeric host Dhiraj K. Sardar and Felipe S. Salinas Department of Physics and Astronomy,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 91, NUMBER 12 15 JUNE 2002 Optical properties of a laser dye in a solid-state polymeric host Dhiraj K. Sardar and Felipe S. Salinas Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Concentrations that absorb. Measuring percentage transmittance of solutions at different concentrations
 Measuring percentage transmittance of solutions at different Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 Concentrations that
Measuring percentage transmittance of solutions at different Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 Concentrations that
Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY
 Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Subject Area(s) Chemistry, Physical Science, Science & Technology Associated Unit Nanotechnology Activity Title: A DNA biosensor Grade Level: 11th-12th Time Required: 3 hours
Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Subject Area(s) Chemistry, Physical Science, Science & Technology Associated Unit Nanotechnology Activity Title: A DNA biosensor Grade Level: 11th-12th Time Required: 3 hours
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications
 Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Lab 4: Spectrometer Tuesday and Wednesday, April 12, 13 Due: Friday, April 22, 2011
 Introduction MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Spectrometer measurements Lab
Introduction MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Spectrometer measurements Lab
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer
 Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4817934472* PHYSICS 0625/32 Paper 3 Extended February/March 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4817934472* PHYSICS 0625/32 Paper 3 Extended February/March 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
Classification of Matter
 Classification of Matter All the objects that we see in the world around us are made of matter. Matter makes up the air we breathe, the ground we walk on, the food we eat and the animals and plants that
Classification of Matter All the objects that we see in the world around us are made of matter. Matter makes up the air we breathe, the ground we walk on, the food we eat and the animals and plants that
Study Guide Chemistry. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
 Study Guide Chemistry Name Period 1. What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. List 3 examples of matter and 3 non-examples of matter. EXAMPLES NN-EXAMPLES 1. _air 1. time
Study Guide Chemistry Name Period 1. What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. List 3 examples of matter and 3 non-examples of matter. EXAMPLES NN-EXAMPLES 1. _air 1. time
CARBON NANOTUBE ANALYSIS USING THE TSI LIBS DESKTOP ANALYZER
 CARBON NANOTUBE ANALYSIS USING THE TSI LIBS DESKTOP ANALYZER APPLICATION NOTE LIBS-019 Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are used in an ever increasing number of applications, from engineering applications (lighter,
CARBON NANOTUBE ANALYSIS USING THE TSI LIBS DESKTOP ANALYZER APPLICATION NOTE LIBS-019 Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are used in an ever increasing number of applications, from engineering applications (lighter,
UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs. Eman Mousa Alhajji
 UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Double-Slit Interference
 Double-Slit Interference 1. Objectives. The objective of this laboratory is to verify the double-slit interference relationship. 2. Theory. a. When monochromatic, coherent light is incident upon a double
Double-Slit Interference 1. Objectives. The objective of this laboratory is to verify the double-slit interference relationship. 2. Theory. a. When monochromatic, coherent light is incident upon a double
Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions
 1 Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions Part 1. Acid and Base Chemistry A. Introduction BIO 105 Summer 2013 Name One of the most important concepts in biology is acid/base chemistry. We are familiar
1 Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions Part 1. Acid and Base Chemistry A. Introduction BIO 105 Summer 2013 Name One of the most important concepts in biology is acid/base chemistry. We are familiar
Concentrations. 3. A total of 60 g of sodium chloride (NaCl) are dissolved in 240 g water. Give the NaCl concentration in mass percent.
 Concentrations Most chemical reactions take place in solutions. We therefore have no pure substances but certain amounts of them in a certain amount of a solvent. Thus, the important thing is the ratio
Concentrations Most chemical reactions take place in solutions. We therefore have no pure substances but certain amounts of them in a certain amount of a solvent. Thus, the important thing is the ratio
Lesson 1: The Organization of Matter
 Atoms and Molecules Lesson 1: The rganization of Matter All matter regardless of its size, shape or color is made of atoms air, water, humans, dogs, shoes etc are all made up of atoms An atom is the smallest
Atoms and Molecules Lesson 1: The rganization of Matter All matter regardless of its size, shape or color is made of atoms air, water, humans, dogs, shoes etc are all made up of atoms An atom is the smallest
Experiment 6: Interferometers
 Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
The Hand Warmer Design Challenge: Where Does the Heat Come From?
 The Hand Warmer Design Challenge: Where Does the Heat Come From? LSNED Learn Something New Every Day About Sharing and Contributions Interesting Facts Science In Your Mittens: The Chemistry Of Hand Warmers
The Hand Warmer Design Challenge: Where Does the Heat Come From? LSNED Learn Something New Every Day About Sharing and Contributions Interesting Facts Science In Your Mittens: The Chemistry Of Hand Warmers
Brief Bio Data of Dr. Vivek Kr. Singh
 Brief Bio Data of Dr. Vivek Kr. Singh *************************************************************************** Dr. Vivek Kr. Singh (D.Phil., Raman Fellow) Assistant Professor School of Physics Shri
Brief Bio Data of Dr. Vivek Kr. Singh *************************************************************************** Dr. Vivek Kr. Singh (D.Phil., Raman Fellow) Assistant Professor School of Physics Shri
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL
 ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY SPECIMEN PAPER NAME: FORM 3 CLASS: TIME: 2 hrs Directions to Candidates: Answer ALL Questions in Section 1 and Section 2. Write your answers
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY SPECIMEN PAPER NAME: FORM 3 CLASS: TIME: 2 hrs Directions to Candidates: Answer ALL Questions in Section 1 and Section 2. Write your answers
AP Physics 2 Sample Syllabus 3
 Syllabus 066439v Curricular Requirements CR Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including college-level textbooks and reference materials in print or electronic format. CRa The
Syllabus 066439v Curricular Requirements CR Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including college-level textbooks and reference materials in print or electronic format. CRa The
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
UNIT-5 EM WAVES UNIT-6 RAY OPTICS
 UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
AP Physics 2 Sample Syllabus 3
 Curricular Requirements CR CRa CRb CRc CRd CRe CRf CRg CR3 CR4 CR CR6a CR6b CR7 CR8 Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including collegelevel textbooks and reference materials
Curricular Requirements CR CRa CRb CRc CRd CRe CRf CRg CR3 CR4 CR CR6a CR6b CR7 CR8 Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including collegelevel textbooks and reference materials
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *1331047203* CHEMISTRY 5070/42 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2011 1 hour Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *1331047203* CHEMISTRY 5070/42 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2011 1 hour Candidates
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 6: Polarization Original: Professor McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the basics of polarization and learn to use common optical elements
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 6: Polarization Original: Professor McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the basics of polarization and learn to use common optical elements
Research Article. A r t i c l e I n f o. Received 11/5/2016. Accepted 5/10/2016
 Al-Mustansiriyah Journal of Science ISSN: 84-635X (print), ISSN: 5-35 (online) Volume 8, Issue, 7 DOI: http://doi.org/.385/mjs.v8i.37 Research Article Asrar A. Saeed, Nadia M. Sloomi Department of Physics,
Al-Mustansiriyah Journal of Science ISSN: 84-635X (print), ISSN: 5-35 (online) Volume 8, Issue, 7 DOI: http://doi.org/.385/mjs.v8i.37 Research Article Asrar A. Saeed, Nadia M. Sloomi Department of Physics,
UV Spectroscopy Determination of Aqueous Lead and Copper Ions in Water
 UV Spectroscopy Determination of Aqueous Lead and Copper Ions in Water C. H. Tan a, Y. C. Moo a, M. Z. Matjafri a and H. S. Lim a a School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 118 Pulau Pinang, Malaysia.
UV Spectroscopy Determination of Aqueous Lead and Copper Ions in Water C. H. Tan a, Y. C. Moo a, M. Z. Matjafri a and H. S. Lim a a School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 118 Pulau Pinang, Malaysia.
The table shows the average background radiation dose from various sources that a person living in Britain receives in one year.
 ## The table shows the average background radiation dose from various sources that a person living in Britain receives in one year. Source of background radiation Average amount each year in dose units
## The table shows the average background radiation dose from various sources that a person living in Britain receives in one year. Source of background radiation Average amount each year in dose units
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Map - Norwell Middle School SUBJECT: Science Grade Level: 7
 Grade 7 Science Curriculum Map - Norwell Middle School SUBJECT: Science Grade Level: 7 Unit: Physical Science (Chemistry) ~ 10 Weeks Ending Near Thanksgiving Science Standard 2: Differentiate between volume
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Map - Norwell Middle School SUBJECT: Science Grade Level: 7 Unit: Physical Science (Chemistry) ~ 10 Weeks Ending Near Thanksgiving Science Standard 2: Differentiate between volume
Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. diffraction reflection refraction
 Q1. Light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. (a) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. diffraction reflection refraction The change of direction when light
Q1. Light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. (a) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. diffraction reflection refraction The change of direction when light
2. What characteristic of water makes it the universal solvent? Nonpolar large molecules long-chain hydrocarbon molecules polar
 PS Chemistry Chapter 22 & 23 Review Test Date Chapter 22 Suggestions for Studying Section 1 Know that a solution is made up of a solute and solvent. Be able to provide an example of a solute and a solvent.
PS Chemistry Chapter 22 & 23 Review Test Date Chapter 22 Suggestions for Studying Section 1 Know that a solution is made up of a solute and solvent. Be able to provide an example of a solute and a solvent.
General Chemistry I CHEM-1030 Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Physical Separation Techniques
 General Chemistry I CHEM-1030 Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Physical Separation Techniques Introduction When two or more substances that do not react chemically are blended together, the components of the
General Chemistry I CHEM-1030 Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Physical Separation Techniques Introduction When two or more substances that do not react chemically are blended together, the components of the
PHY 192 Optical Activity Spring
 PHY 192 Optical Activity Spring 2017 1 Optical Activity Introduction The electric (E) and magnetic (B) vectors in a traveling electromagnetic wave (such as light for example) oscillate in directions perpendicular
PHY 192 Optical Activity Spring 2017 1 Optical Activity Introduction The electric (E) and magnetic (B) vectors in a traveling electromagnetic wave (such as light for example) oscillate in directions perpendicular
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13318-2 Second edition 2007-09-15 Determination of particle size distribution by centrifugal liquid sedimentation methods Part 2: Photocentrifuge method Détermination de la distribution
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13318-2 Second edition 2007-09-15 Determination of particle size distribution by centrifugal liquid sedimentation methods Part 2: Photocentrifuge method Détermination de la distribution
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6608480670* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6608480670* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. Part A: Solutions That Conduct Electricity
 Chemical Dominoes Activity 6 Electrochemical Cells GALS In this activity you will: Determine if a substance will conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Construct a galvanic cell and explain the function
Chemical Dominoes Activity 6 Electrochemical Cells GALS In this activity you will: Determine if a substance will conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Construct a galvanic cell and explain the function
Republic of Somaliland. Somaliland National Examination Board. Form Four. Physics Examination. June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS
 Name..... Total Score School... Roll No... Republic of Somaliland Form Four Physics Examination June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS Plus 10 minutes for reading through the paper Total time 2 Hours and 10 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS
Name..... Total Score School... Roll No... Republic of Somaliland Form Four Physics Examination June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS Plus 10 minutes for reading through the paper Total time 2 Hours and 10 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS
Instruction Manual HI Refractometer for Sodium Chloride Measurements
 Instruction Manual HI 96821 Refractometer for Sodium Chloride Measurements www.hannainst.com 1 Dear Customer, Thank you for choosing a Hanna Instruments product. Please read this instruction manual carefully
Instruction Manual HI 96821 Refractometer for Sodium Chloride Measurements www.hannainst.com 1 Dear Customer, Thank you for choosing a Hanna Instruments product. Please read this instruction manual carefully
LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I
 OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
March 30, Chapter 22 Notes.notebook. Section 1: How Solutions form
 Thursday, March 23 rd 1) No QOTD 2) Finish presentations 3) Intro to Chapter 22: Solutions Section 1: How Solutions form A. Solution a mixture that appears the same throughout and is mixed at the molecular
Thursday, March 23 rd 1) No QOTD 2) Finish presentations 3) Intro to Chapter 22: Solutions Section 1: How Solutions form A. Solution a mixture that appears the same throughout and is mixed at the molecular
n(λ) = c/v(λ). Figure 1: Dispersion curves for some common optical glass types.
 Physics 2310 Lab 2: The Dispersion of Optical Glass Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Based on a lab by Dr. M. Kruger (Univ. of Missouri, Kansas City) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce
Physics 2310 Lab 2: The Dispersion of Optical Glass Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Based on a lab by Dr. M. Kruger (Univ. of Missouri, Kansas City) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce
A.Thakur. et. al./ 2(4) pp December-2014
 Development and Validation of UV spectrophotometric method for determination of levofloxacin hemihydrate in marketed tablet dosage formulations Abhimanyu Thakur 1*, Rakesh Kumar 2, 1,2 Department of Pharmaceutical
Development and Validation of UV spectrophotometric method for determination of levofloxacin hemihydrate in marketed tablet dosage formulations Abhimanyu Thakur 1*, Rakesh Kumar 2, 1,2 Department of Pharmaceutical
COMMON ENTRANCE STYLE EXAMINATION AT 13+ CHEMISTRY Practice Paper 2
 COMMON ENTRANCE STYLE EXAMINATION AT 13+ CHEMISTRY Practice Paper 2 1. Underline the option which best completes each of the following: (a) A substance which only contains one sort of atom is magnesium
COMMON ENTRANCE STYLE EXAMINATION AT 13+ CHEMISTRY Practice Paper 2 1. Underline the option which best completes each of the following: (a) A substance which only contains one sort of atom is magnesium
(2) (1) Describe how beta radiation is produced by a radioactive isotope (1) (Total 4 marks)
 1 (a) (i) Describe the structure of alpha particles. (ii) What are beta particles? (b) Describe how beta radiation is produced by a radioactive isotope....... (Total 4 marks) Page 1 of 25 2 Atoms are very
1 (a) (i) Describe the structure of alpha particles. (ii) What are beta particles? (b) Describe how beta radiation is produced by a radioactive isotope....... (Total 4 marks) Page 1 of 25 2 Atoms are very
Nanosphere Lithography
 Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Review for solution, electrolyte and ph test. 1. Which of the following has the highest concentration? A) 22% B) 200 g/l C) 550 ppm D) 15 mg/l
 Review for solution, electrolyte and ph test 1. Which of the following has the highest concentration? A) 22% B) 200 g/l C) 550 ppm D) 15 mg/l 2. Convert the following units to ppm: A) 15 % B) 150 g/l C)
Review for solution, electrolyte and ph test 1. Which of the following has the highest concentration? A) 22% B) 200 g/l C) 550 ppm D) 15 mg/l 2. Convert the following units to ppm: A) 15 % B) 150 g/l C)
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
MANIPAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SCHEME OF EVAUATION MANIPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOOGY MANIPA UNIVERSITY, MANIPA SECOND SEMESTER B.Tech. END-SEMESTER EXAMINATION - MAY SUBJECT: ENGINEERING PHYSICS (PHY/) Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 5 Note: Answer
SCHEME OF EVAUATION MANIPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOOGY MANIPA UNIVERSITY, MANIPA SECOND SEMESTER B.Tech. END-SEMESTER EXAMINATION - MAY SUBJECT: ENGINEERING PHYSICS (PHY/) Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 5 Note: Answer
Gold Nanoparticles-Electrolyte Experiment Worksheet
 Gold NanoparticlesElectrolyte Experiment Worksheet Background Since ancient times, gold and silver nanoparticles have been used for staining glass with intense colors. In fact, it is recorded that ancient
Gold NanoparticlesElectrolyte Experiment Worksheet Background Since ancient times, gold and silver nanoparticles have been used for staining glass with intense colors. In fact, it is recorded that ancient
Water Hardness and Softening (Bring a water sample from home) Minneapolis Community and Technical College Principles of Chemistry II, C1152 v.2.
 Water Hardness and Softening (Bring a water sample from home) Minneapolis Community and Technical College Principles of Chemistry II, C1152 v.2.16 I. Introduction Hard Water and Water Softening Water that
Water Hardness and Softening (Bring a water sample from home) Minneapolis Community and Technical College Principles of Chemistry II, C1152 v.2.16 I. Introduction Hard Water and Water Softening Water that
On Determining the Specific Rotation of the Given Solution
 On Determining the Specific Rotation of the Given Solution Manual as a Part of B.Tech Part One Physics Laboratory August 13, 2016 Figure 1: Left-panel : Polarimeter instrument and its set-up. Right-panel
On Determining the Specific Rotation of the Given Solution Manual as a Part of B.Tech Part One Physics Laboratory August 13, 2016 Figure 1: Left-panel : Polarimeter instrument and its set-up. Right-panel
From Which Planet is the Soil Sample From?
 Teacher From Which Planet is the Soil Sample From? NGSSS: SC.912.P.8.2: Differentiate between physical and chemical properties and physical and chemical changes of matter. Purpose of Lab/Activity: To separate
Teacher From Which Planet is the Soil Sample From? NGSSS: SC.912.P.8.2: Differentiate between physical and chemical properties and physical and chemical changes of matter. Purpose of Lab/Activity: To separate
Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 2: Spectroscopy
 Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 2: Spectroscopy 1. Which color of visible light has the longest wavelength? Name Date Section 2. List the colors of visible light from highest frequency to lowest frequency. 3. Does
Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 2: Spectroscopy 1. Which color of visible light has the longest wavelength? Name Date Section 2. List the colors of visible light from highest frequency to lowest frequency. 3. Does
Dependence Of Gamma Ray Attenuation On Concentration Of Manganese (II) Chloride Solution
 Dependence Of Gamma Ray Attenuation On Concentration Of Manganese (II) Chloride Solution Chikkappa Udagani Abstract: This paper presents the precise method to estimate the dependence of linear and mass
Dependence Of Gamma Ray Attenuation On Concentration Of Manganese (II) Chloride Solution Chikkappa Udagani Abstract: This paper presents the precise method to estimate the dependence of linear and mass
PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL
 *B16* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2011 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from section A and five questions from section B. Page 1 of 10 SECTION A (120 marks) Answer three
*B16* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2011 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from section A and five questions from section B. Page 1 of 10 SECTION A (120 marks) Answer three
MEASUREMENT OF THE FRICTION AND LUBRICITY PROPERTIES OF CONTACT LENSES
 Proceedings of ANTEC `95, Boston, MA, May 7-11, 1995. MEASUREMENT OF THE FRICTION AND LUBRICITY PROPERTIES OF CONTACT LENSES John A. Nairn, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA Tong-bi Jiang,
Proceedings of ANTEC `95, Boston, MA, May 7-11, 1995. MEASUREMENT OF THE FRICTION AND LUBRICITY PROPERTIES OF CONTACT LENSES John A. Nairn, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA Tong-bi Jiang,
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
Proper&es of Water. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 2.2 Properties of Water
 Lesson Overview Proper&es of Water Lesson Overview 2.2 Properties of Water THINK ABOUT IT Looking back at Earth from space, an astronaut called it the blue planet, referring to the oceans of water that
Lesson Overview Proper&es of Water Lesson Overview 2.2 Properties of Water THINK ABOUT IT Looking back at Earth from space, an astronaut called it the blue planet, referring to the oceans of water that
2011 Assessment Report. Physics Level 1
 National Certificate of Educational Achievement 2011 Assessment Report Physics Level 1 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 90938 Demonstrate understanding of aspects
National Certificate of Educational Achievement 2011 Assessment Report Physics Level 1 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 90938 Demonstrate understanding of aspects
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CHAPTER-2 NCERT SOLUTION
 CHAPTER-2 NCERT SOLUTION Page no. 15 Question 1: What is meant by a pure substance? Answer 1: A pure substance is the one that consists of a single type of particles, i.e., all constituent particles of
CHAPTER-2 NCERT SOLUTION Page no. 15 Question 1: What is meant by a pure substance? Answer 1: A pure substance is the one that consists of a single type of particles, i.e., all constituent particles of
Applying Understanding Hinge Point Question Exemplars What A Good One Looks Like Example 1 Secondary Science
 This is a good hinge point question as there are multiple correct answers. Applying Understanding Hinge Point Question Exemplars What A Good One Looks Like Example 1 Secondary Science Which of these is/are
This is a good hinge point question as there are multiple correct answers. Applying Understanding Hinge Point Question Exemplars What A Good One Looks Like Example 1 Secondary Science Which of these is/are
Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mixtures 2 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Pure and impure substances 3 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 All materials can be classified as either a pure substance or an impure
Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mixtures 2 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Pure and impure substances 3 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 All materials can be classified as either a pure substance or an impure
