ESTABLISHMENT OF HIGHLY EFFICIENT AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES-MEDIATED TRANSFORMATION
|
|
|
- Karin Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACTA BIOLOGICA CRACOVIENSIA Series Botanica 58/1: , 2016 DOI: /abcsb ESTABLISHMENT OF HIGHLY EFFICIENT AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES-MEDIATED TRANSFORMATION FOR STEVIA REBAUDIANA BERTONI EXPLANTS Z ANETA MICHALEC-WARZECHA 1, LAURA PISTELLI 2, FRANCESCA D ANGIOLILLO 2 AND MARTA LIBIK-KONIECZNY 1* 1 Franciszek Górski Institute of Plant Physiology, Polish Academy of Sciences, ul. Niezapominajek 21, Krakow, Poland 2 University of Pisa, Department of Agriculture, Food and Environment, Via del Borghetto 80, I Pisa, Italy November 10, 2015; revision accepted February 14, 2016 Leaves and internodes from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni plants growing in different conditions were used for transformation with two strains of Agrobacterium rhizogenes: ATCC and LBA Hairy roots formation was observed and the percentage of the transformed explants depended on the type of explant, time of inoculation and inoculum concentration. Inoculation of explants from ex vitro and in vitro plants with LBA 9402 strain led to higher efficiency of transformation than inoculation with ATCC strain. Growth rate of hairy roots in liquid culture was assessed under light and dark conditions. It was found that the growth of hairy roots decreased significantly under light conditions. Transformation of hairy roots growing in different culture conditions was confirmed at the molecular level using PCR method with primers constructed against rolb and rolc genes from A. rhizogenes. Keywords: Agrobacterium rhizogenes, transformation, steviol glycosides INTRODUCTION Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni is a perennial herb of the Asteraceae family. It is native to certain regions of South America. Leaves of S. rebaudiana accumulate large quantities of steviol glycosides. These secondary metabolites belong to two groups of compounds: stevioside which appear 300 times sweeter than sucrose (0.4% solution) and rebaudioside (especially rebaudioside A) which could be 400 times sweeter than sucrose (Sreedhar et al., 2008). In addition to this, steviol glycosides are non-caloric and clinical studies suggest that they can reduce blood glucose and blood pressure (Hsieh et al., 2003; Gregersen et al., 2004). Because of the mentioned facts, purified steviol glycosides are increasingly used in food industry as sweeteners and food additives. An important feature of steviol glycosides composition in S. rebaudiana plants used in industry is the ratio of stevioside to rebaudioside A. This is because rebaudioside A reduces the feeling of bitterness that is the aftertaste of stevioside. Steviol glycosides are accumulated in leaves of S. rebaudiana at concentrations as high as 20% of the dry weight (Brandle et al., 1998), depending on the climate in which the plants are grown. Different quantitative compositions of rebaudiosides and steviosides in samples of leaves of S. rebaudiana are presented by Kovylyaeva et al., Clearly, smaller accumulation of these compounds is noted in moderate climate regions. Moreover, in such conditions, the ratio of rebaudioside A to stevioside is less favorable, compared to plants of tropical and subtropical climates. Furthermore, classical plant propagation is limited due to very poor seed germination and, consequently, production of seedlings. For that reason propagation of stevia is usually done by stem cuttings; however, the number of stems present on a single plant also limits the vegetative multiplication through cuttings. Clonal propagation in in vitro conditions is useful for small scale production because it is asso- * Corresponding author, libik@ifr-pan.krakow.pl PL ISSN Polish Academy of Sciences and Jagiellonian University, Cracow 2016
2 114 Michalec-Warzecha et al. ciated with large economical costs (Singh and Rao, 2005). Agrobacterium rhizogenes transformation of plant explants could be an alternative method for obtaining steviol glycosides by hairy roots (HR) cultures. After infection, T-DNA from the Ri plasmid of bacteria is integrated with the plant genome, changing the plant metabolism and thus causing proliferation of hairy roots on the infected explants. Transformed roots are able to produce secondary metabolites at levels that are comparable or greater than in uninfected plants (Giri and Narasu, 2000). Moreover, the possibility to regenerate stevia plants in in vitro conditions opens a new perspective concerning the genetic manipulation based on establishment of an efficient transformation method. The aim of our work was to obtain hairy root cultures of S. rebaudiana after transformation of different kinds of explants with two strains of A. rhizogenes: ATCC and LBA 9402 for further manipulation to produce secondary metabolites. MATERIAL AND METHODS PLANT MATERIAL Experiments were performed on S. rebaudiana plants which originated from: 1) in vitro conditions: in vitro plants were micropropagated from nodes of explants cultured on MS (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) medium supplemented with 1.0 mg/l NAA (1-naphthaleneacetic acid), 0.5 mg/l BAP (6-benzylaminopurine), 2) ex vitro conditions: ex vitro plants were micropropagated from in vitro micropropagation and then transferred to greenhouse conditions, 3) in vivo conditions: in vivo plants originated from standard vegetative propagation and were cultured in field conditions. Two types of explants: leaves and internodes, collected from each group of plants, were used for transformation. Explants from in vivo and ex vitro plants were sterilized using two different protocols: a) Explants from ex vitro plants were surface sterilized with 70% (v/v) ETOH for 30 seconds, then rinsed 3 times with distilled, sterile water and transferred to solution of 10% (v/v) NaClO for 5 minutes. After this time they were rinsed carefully with sterile distilled water. b) Explants from in vivo plants were first shaken for 20 minutes in 0.1% (v/v) Tween 20 solution, then they were rinsed 3 times with distilled, sterile water. Later, they were surface sterilized with 70% ETOH for 30 seconds, rinsed 3 times with distilled, sterile water and then kept in the solution of 10% NaClO for 5 minutes followed rinsing with sterile distilled water. BACTERIA STRAINS Two different strains of A. rhizogenes were used for transformation: 1) the wild-type hyper-virulent strain LBA 9402 (a gift from Dr. David Tepfer, INRA Versailles, France) 2) agropine strain ATCC (American Type Culture Collection). A single colony of each strain was grown for 48 h at 28 C on the following media: Yeast Mannitol Broth medium for LBA 9402 strain (Hooykaas et al., 1977), and Nutrient Broth medium for ATCC strain (Downes and Ito, 2001). TRANSFORMATION AND ESTABLISHMENT OF HAIRY ROOTS CULTURES Fragments of leaves (10 20 mm²) and internodes (5 10 mm) were co-cultured with freshly grown A. rhizogenes strains with optical density (OD) as follows: A 600 = 0.1 for 10 min, A for 30 min, or A for 10 min. Control explants were soaked in sterile distilled water for the same time. After co-culture the explants were placed on hormone-free MS medium (MS) for three days and then they were transferred to MS medium supplemented with cefotaxime (100 mg/l MSCX medium). Inoculated explants were kept in darkness at 26 C throughout the experimental period. The transformation frequency expressed as the percentage of inoculated explants producing roots and the number of roots per explant were studied 30 days after inoculation. The hairy roots length was measured at 10 and 30 days after appearance. Roots (about 1 cm long) formed on the infected explants were excised and transferred on fresh MSCX and incubated in the dark. After four passages, the concentration of cefotaxime was reduced to 50 mg and after next four weeks cefotaxime was omitted from the medium. Some of new lines, which showed good growth, were selected and used for establishment of a liquid culture. CONFIRMATION OF TRANSFORMATION Transformation was confirmed by PCR analysis. RNA was extracted according to Chomczyński (1987) from two putative hairy roots lines (100 mg) and from leaf tissues of ex vitro plants (100 mg, control). RNA purity was determined by measuring the ratio of absorbance at two wavelengths: OD 260 nm and OD 280 nm. A given sample of RNA was considered pure (free from proteins and DNA) when the value A (260) / A (280) ranged between Then, cdna was obtained with the use of iscript cdna Synthesis Kit (BioRad, USA) and reverse transcription reaction. Each PCR reaction was performed in a final volume
3 Transfomation of Stevia rebaudiana explants 115 of 50 μl using DreamTaq Green PCR Master Mix (ThermoScientific) containing: DreamTaq DNA polymerase, 2X DreamTaq Green buffer, datp, dctp, dgtp and dttp, 0.4 mm each, and 4 mm MgCl 2. For each reaction we used 25 μl DreamTaq Green Master Mix, 0.5 μm each forward and reverse primer and 1 μg template DNA, all complemented with water nucleasefree to 50 μl. PCR conditions for rolc and rolb gene (rolb 5 -GCTCTTGCAGTGCTAGATTT-3 and 5 -GAAGGTGCAAGCTACCTCTC-3 ; rolc 5 -CTCCTGACATCAAACTCGTC-3 and 5 -TGCTTCGAGTTATGGGTACA-3, Królicka et al., 2001) were as follows: 40 cycles, initial denaturation at 95 C for 3 min, denaturation at 95 C for 30 s, primer annealing at 53 C for 30 s, elongation at 72 C for 1 min, followed by final elongation for 5 min (C1000 Thermal Cycler, Bio-Rad). Amplification products were resolved by electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel in TE buffer, stained with ethidium bromide and observed under UV light. GROWTH STUDIES For determination of the growth rate root lines called SRY (internodes) and SRL (leaves) transformed by A. rhizogenes LBA9402 were chosen among the rolc gene positives. Hairy roots (0.5 g of fresh weight) were cultured in 50 ml of MS liquid medium in 300-ml Erlenmeyer flasks. The cultures were incubated on a rotary shaker (80 rpm) in a growth chamber at 26 C in the dark or under light from cool white fluorescent lamps (16 h light/8 h dark period; 40 μm m -2 s -1 ). The cultures were grown for 30 days and fresh weight was recorded at 0, 10, 20, 30 day of culture. Each result was based on 3 replicates and the experiment was repeated three times. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Hairy roots production was achieved after infection of different explants from S. rebaudiana with two strains of A. rhizogenes: ATCC and LBA The efficiency of transformation was influenced by the type of the bacteria strain, concentration of inoculum, the time of inoculation and the type of explant (Tab. 1.). The explants inoculated with ATTCC strain (OD ) for 10 min, exhibited hairy roots formation after 30 days only on the infected internodes from in vitro plants. The percentage of transformed explants was poor (only 2%). On the other hand, the inoculation with LBA 9402 strain led to efficient transformation of both S. rebaudiana leaves and internodes (Fig. 1a). Hairy roots were formed 13 days after inoculation of leaves explants from ex vitro plants for 30 min with LBA9402 strain with OD (Fig. 1b). The percentage of transformed explants was 40%. Even greater efficiency of transformation (50%) was demonstrated for the same explants but inoculated for a shorter time (10 min) with more concentrated bacterial strain OD (Tab. 1, Fig. 1c) Hairy roots were also formed from internodes of explants from ex vitro and in vitro plants inoculated with LBA9402 strain (Fig. 1d); however, the efficiency of their transformation was significantly lower than in the case of leaves (Tab. 1). Bacterial cells were removed from the hairy root cultures by the use of cefotaxime in the MS medium (Fig. 1e). After a few passages hairy roots free of bacteria were transferred in liquid medium (Fig. 1f) without antibiotics and plant growth regulators and incubated in light and dark conditions. Previously, it had been observed that hairy roots cultured in light exhibited the potential to produce certain secondary metabolites that were mainly found in aerial organs and never in hairy root cultures normally incubated in the dark. These hairy root cultures also show development of chlorophyll, causing greening of these cultures; therefore, the roots are called green hairy roots (Sharma et al., 2013). A similar effect was found in our experiment where greenish hairy roots were produced when cultured in light conditions. Fresh weight of the cultured hairy roots was recorded after 0, 10, 20, 30 days of culture. The increase of fresh weight was noted for both types of the culture but these from the dark conditions increased their weight seven times while the fresh weight of hairy roots cultured in the light increased only three times (Tab. 2). Integration of the T-DNA into S. rebaudiana genome was confirmed at the molecular level by the PCR with cdna obtained after reverse transcription on the base of RNA isolated from hairy roots from light and dark conditions and primers constructed on the sequences of rolb and rolc genes of A. rhizogenes. The PCR reaction was also conducted for control explants, incubated in water instead of bacteria strain and grown in the same conditions as hairy roots. PCR products were absent in the nontransformed tissue. However, transcripts of rolb and rolc were presented in both light (Fig. 2a) and dark culture (Fig. 2b) of hairy roots. PCR product of 383 bp DNA for rolb gene as well as PCR product of 586 bp DNA for rolc gene were obtained from RNA isolated from hairy root tissues. In literature there is only one publication concerning an attempt at S. rebaudiana transformation where the authors showed only 2% efficiency of transformation after application of leaf explants and A. rhizogenes (Yamazaki et al., 1991). Lately, the information concerning A. tumefaciens mediated infiltration of S. rebaudiana leaves as a gene silencing approach was published (Guleria and
4 116 Michalec-Warzecha et al. TABLE 1. Parameters of S. rebaudiana explants transformation. Percentage of transformed explants (%) Mean no. of HR 1 per dish/ per explant 10 days after root appearance 10 days [mm] 30 days [cm] HR appearancedays after inoculation Percentage of transformed explants (%) Mean no. of HR 1 per dish/ per explant 10 days after root appearance 10 days [mm] 30 days [cm] HR appearancedays after inoculation Agrobacterium rhizogenes strain ATCC LBA 9402 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 T1 T2 T3 Leaves in vivo Leaves in vitro Leaves ex vitro /3 99/ Internodes in vivo Internodes in vitro 3 20/ / Internodes ex vitro 20 30/ HR: Hairy roots. T1: optical density OD ; inoculation time 10 min. T2: optical density OD ; inoculation time 30 min. T3: optical density OD ; inoculation time 10 min.
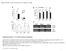
5 Transfomation of Stevia rebaudiana explants 117 a b c d e f Fig. 1. Transformation of S. rebaudiana. (a) Different explants on MS medium after inoculation with A. rhizogenes LBA9402; (b) Formation of hairy roots on ex vitro leaf explant; (c) Formation of hairy roots on ex vitro internode explant; (d) Growth of hairy root culture on ex vitro leaf explant; (e) Growth of hairy roots separated from the explant on MS solid medium; (f) Growth of hairy roots in MS liquid medium. TABLE 2. Growth rate of hairy roots in liquid MS medium. The values are means of three experiments ± SD. Values within the rows followed by a different letter are statistically different at P 0.05 (Duncan s test) Hairy roots weight (g of FW±SD) Type of culture 0 10 days 20 days 30 days Culture in light 0.55 ± 0.06d 0.68 ± 0.06c 1.49 ± 0.12b 1.79 ± 0.16a Culture in dark 0.62 ± 0.08d 0.83 ± 0.11c 2.20 ± 0.36b 4.43 ± 0.87a a b Fig. 2. Identification of rolb and rolc gene fragments in hairy roots grown after S. rebaudiana transformation with A. rhizogenes LBA9402 strain. PCR reactions was performed using as a target DNA isolated from: (a) dark conditions, (b) light conditions. Actin (Act) was used as a reference gene. Gene ruler DNA Ladder Mix (Life Technologies) was applied for quantification of visualized bands.
6 118 Michalec-Warzecha et al. Yadav, 2013). However, there is still lack of studies carried out on transformed stevia plants (Singh et al., 2009). It is probably due not only to lack of good plant regeneration system but also to lack of an efficient transformation protocol. In our studies we achieved, for the first time, highly effective transformation of different explants from S. rebaudiana plants with A. rhizogenes strains. It is worth mentioning that all the investigated explants from in vivo plants did not respond positively to the infection with both A. rhizogenes strains. Plants which originate in the natural environment are exposed to many stress factors, including pathogens. In order to survive, they are equipped with more efficient defense system than plants which grow in controlled, sterile conditions and, therefore, are more resistant to the infection. Thus, for future experiments we recommend use of plants under controlled conditions. Moreover, we found that the best strain for transformation of S. rebaudiana is the wild-type hyper virulent strain LBA Liquid cultures of hairy roots achieved after transformation of S. rebaudiana explants allow us to continue the studies concerning the influence of different factors on steviol glycosides biosynthesis. AUTHORS CONTRIBUTIONS Ż. Michalec-Warzecha and F. D Angiolillo performed the experiments, analyzed the achieved data and participated in writing the paper. M. Libik-Konieczny and L. Pistelli designed the experiments and wrote the paper. M. Libik-Konieczny has primary responsibility for the final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We would like to thank Jarmila Skružná from Botanical Garden in Praque, Czech Republic for sharing the plant material. This work was supported in part by projects funded by the National Science Center (no. 2012/05/B/NZ9/01035 and no. 2013/09/N/NZ9/01650). REFERENCES BRANDLE JE, STARRAT AN, and GIJZEN M Stevia rebaudiana: its agricultural, biological, and chemical properties. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 78: CHOMCZYŃSKI P, and SACCHI N Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Analytical Biochemistry 162: DOWNES FP, and ITO K Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods, 4th Ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C. GIRI A, and NARASA ML Transgenic hairy roots: recent trends and applications. Biotechnology Advances 18: GREGERSEN S, JEPPENSEN PB, HOLST JJ, and HERNANSEN K Antihyperglycemic effects of stevioside in type 2 diabetic subjects. Metabolism 53: GULERIA P and YADAV SK Agrobacterium mediated transient gene silencing (AMTS) in Stevia rebaudiana: insights into steviol glycoside biosynthesis pathway. Plos One 8: HOOKAAS PJJ, KLAPWIJK PM, NUTI MP, SCHILPEROORT RA, and RÖRSCH A Transfer of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid to avirulent agrobacteria and to rhizobium ex planta. Microbiology 98 (2): HSIEH MH, CHAN P, SUE YM, LIU JC, LIANG TH, HUANG TY, TOMA- LINSON B, CHOW MS, KAO PF, and CHEN YJ Efficacy and tolerability of oral stevioside in patients with mild essential hypertension: a two-year, randomized, placebocontrolled study. Clinical Therapeutics 25: KOVYLYAEVA GI, BAKALEININ GA, STRABYKINA IY, GUBSKAVA VI, SHARIPOVA RR, AL FONSOV VA, KATAEV VE, and TOLS- TIKOV AG Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana. Chemis try of Natural Compounds 43: KRÓLICKA A, STANISZEWSKA I, BIELAWSKI K, MALIŃSKI E, SZAFRANEK J, and ŁOJKOWSKA E Establishment of hairy root cultures of Ammi majus. Plant Science 160: MURASHIGE T, and SKOOG F A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia Plantarum 15: SHARMA P, PADH H, SHRIVASTAVA N Hairy root cultures: A suitable biological system for studying secondary metabolic pathways in plants. Engeneering in Life Science 13: SHREEDHAR RV, VENNKATACHALAM L, THIMMARAJU R, BHAGYALAK- SHMI N, NARAYAN MS, and RAVISHANKAR GA Direct organogenesis from leaf explants of Stevia rebaudiana and cultivation in bioreactor. Biologia Plantarum 52: SINGH HP, DHIR SK, and DHIR S Stevia. Part 7. Transgenic Sugar, Tuber and Fiber Crops. In: Kole Ch and Hall TC (eds) Compendium of Transgenic Crop Plants October 2008, Wiley-Blackwell SINGH SD, and RAO GP Stevia: The herbal sugar of 21 st Century. Sugar Technology 7: YAMAZAKI T, and FLORES H Examination of steviol glucosides production by hairy roots and shoot cultures of Stevia rebaudiana. Journal of Natural Products 54:
Received 23 July 2014; received in revised form 25 October 2014; accepted 14 November 2014.
 Journal of Tropical Agriculture 52 (2) : 149-153, 2014 149 Short Communication Genetic transformation in Artemesia annua L. for hairy root induction and enhancement of secondary metabolites V.M. Shaneeja*,
Journal of Tropical Agriculture 52 (2) : 149-153, 2014 149 Short Communication Genetic transformation in Artemesia annua L. for hairy root induction and enhancement of secondary metabolites V.M. Shaneeja*,
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES
 PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES GABRIELA POPA', AURELIA BREZEANU~, C. PETRUTA CORNEA', J.P. BOE The effects of inoculation with wild type of Agrobacterium
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES GABRIELA POPA', AURELIA BREZEANU~, C. PETRUTA CORNEA', J.P. BOE The effects of inoculation with wild type of Agrobacterium
IN VITRO RHIZOGENESIS IN PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.)
 J. Plant Develop. 20(2013): 51 55 IN VITRO RHIZOGENESIS IN PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) Jaime A. TEIXEIRA DA SILVA 1,2 Abstract: The seeds of two papaya (Carica papaya L.) cultivars ('Rainbow' and 'Sunrise
J. Plant Develop. 20(2013): 51 55 IN VITRO RHIZOGENESIS IN PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) Jaime A. TEIXEIRA DA SILVA 1,2 Abstract: The seeds of two papaya (Carica papaya L.) cultivars ('Rainbow' and 'Sunrise
Expression of Viral Resistance in Transformed Petunia Plants Regenerated in Vitro
 Expression of Viral Resistance in Transformed Petunia Plants Regenerated in Vitro Meira Ziv and Mirit Gandelman The RH Smith Institute of Plant Science The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Rehovot, PO Box
Expression of Viral Resistance in Transformed Petunia Plants Regenerated in Vitro Meira Ziv and Mirit Gandelman The RH Smith Institute of Plant Science The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Rehovot, PO Box
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated
 Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium L.
 Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in Jow Haw rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2016 Vol. 12(2):241-248 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2016 Vol. 12(2):241-248 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL
 GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
Journal of Agricultural Technology
 Study on the growth patterns of transformed carrot hairy roots in an optimized system Y.R. Danesh *, E. Mohammadi Goltapeh and A. Alizadeh Department of Plant Pathology, College of Agriculture, Tarbiat
Study on the growth patterns of transformed carrot hairy roots in an optimized system Y.R. Danesh *, E. Mohammadi Goltapeh and A. Alizadeh Department of Plant Pathology, College of Agriculture, Tarbiat
Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach
 Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO JAMIA MILLIA ISLAMIA NEW DELHI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO JAMIA MILLIA ISLAMIA NEW DELHI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
AMADEPA Association Martiniquaise pour le Developpement des Plantes Alimentaires
 AMADEPA Association Martiniquaise pour le Developpement des Plantes Alimentaires 29eme CONGRES ANNUEL ANNUAL MEETING REUNION ANNUAL Agriculture Intensive dans les Iles de la Caraibe : enjeux, contraintes
AMADEPA Association Martiniquaise pour le Developpement des Plantes Alimentaires 29eme CONGRES ANNUEL ANNUAL MEETING REUNION ANNUAL Agriculture Intensive dans les Iles de la Caraibe : enjeux, contraintes
Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis
 Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis BOM-11: 10.9 Plasmids: General Principles (review) p. 274 10.11 Conjugation: Essential Features (review) p. 278 19.21 Agrobacterium
Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis BOM-11: 10.9 Plasmids: General Principles (review) p. 274 10.11 Conjugation: Essential Features (review) p. 278 19.21 Agrobacterium
Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum Leaf Disks
 JARQ 51 (4), 351-355 (2017) https://www.jircas.go.jp Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation
JARQ 51 (4), 351-355 (2017) https://www.jircas.go.jp Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation
** * * * Col-0 cau1 CAU1. Actin2 CAS. Actin2. Supplemental Figure 1. CAU1 affects calcium accumulation.
 Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Prereq: Concurrent 3 CH
 0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.) Blume
 ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
Introduction. Phylogeny. Taxonomy
 jim_3-1-4.fm Page 91 Thursday, October 6, 2005 5:19 PM CHAPTER 3.1.4 eth sun Ge um i retcabor Ag The Genus Agrobacterium ANN G. MATTHYSSE Introduction The genus Agrobacterium is a group of Gramnegative
jim_3-1-4.fm Page 91 Thursday, October 6, 2005 5:19 PM CHAPTER 3.1.4 eth sun Ge um i retcabor Ag The Genus Agrobacterium ANN G. MATTHYSSE Introduction The genus Agrobacterium is a group of Gramnegative
AGROBACTERIUM. First described by Smith and Townsend (1907) Responsible for crown gall. Performed Koch's postulates
 AGROBACTERIUM First described by Smith and Townsend (1907) Responsible for crown gall Performed Koch's postulates The disease is worldwide in distribution Speciation was based on pathogenicity Agrobacterium
AGROBACTERIUM First described by Smith and Townsend (1907) Responsible for crown gall Performed Koch's postulates The disease is worldwide in distribution Speciation was based on pathogenicity Agrobacterium
RNA-Solv Reagent. R preps R preps R preps
 RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
Identification of factors involved in Xylem Cell Differentiation Aarush Mohit Mittal 1, 2
 Identification of factors involved in Xylem Cell Differentiation Aarush Mohit Mittal 1, 2 1 Department of Biological Sciences and Bio-Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India 2 Department
Identification of factors involved in Xylem Cell Differentiation Aarush Mohit Mittal 1, 2 1 Department of Biological Sciences and Bio-Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India 2 Department
RNA-Solv Reagent. R preps R preps R preps
 RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
23-. Shoot and root development depend on ratio of IAA/CK
 Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY. Screening of Chemical Libraries in Search of Inhibitors of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis. A Thesis Submitted to the
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Screening of Chemical Libraries in Search of Inhibitors of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Screening of Chemical Libraries in Search of Inhibitors of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials
 Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Establishment of rapid propagation cultures of Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated transgenic hairy roots in sugarbeet
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 12/ March 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Establishment of rapid propagation cultures of Agrobacterium
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 12/ March 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Establishment of rapid propagation cultures of Agrobacterium
Establishment of root to root culture and evaluation of phytochemicals in Rhizobium rhizogenes transformed roots of Stevia rebaudiana
 2017; SP1: 49-54 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2017; SP1: 49-54 Shweta Singh Department of Bio-Engineering, Birla institute of Technology, Mesra, Sunita Murmu Anath Bandhu Das Department of Botany,
2017; SP1: 49-54 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2017; SP1: 49-54 Shweta Singh Department of Bio-Engineering, Birla institute of Technology, Mesra, Sunita Murmu Anath Bandhu Das Department of Botany,
Plants are some of nature s best chemists
 Outline: Alkaloids: Function and biosynthesis Secondary metabolites of plants are naturally occurring products that appear to have no direct function to growth and development. Physiological Role: They
Outline: Alkaloids: Function and biosynthesis Secondary metabolites of plants are naturally occurring products that appear to have no direct function to growth and development. Physiological Role: They
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Phenol-Chloroform reagents. Selection guide. OH ; MW : High quality reagents for use in nucleic acid purification.
 Phenol-Chloroform reagents Extraction with phenol and phenol/chloroform mixtures is a universal method for purification of DNA and RNA. Proteins and restriction enzymes are removed by phenol and chloroform
Phenol-Chloroform reagents Extraction with phenol and phenol/chloroform mixtures is a universal method for purification of DNA and RNA. Proteins and restriction enzymes are removed by phenol and chloroform
Development of a protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Brassica oleraceae L var botrytis cv Early kunwari
 204; (3): 34-38 ISSN 232-922 EJBB 204; (3): 34-38 Received 20-0-204 Accepted: **--204 Development of a protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Brassica oleraceae L var botrytis cv Early kunwari
204; (3): 34-38 ISSN 232-922 EJBB 204; (3): 34-38 Received 20-0-204 Accepted: **--204 Development of a protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Brassica oleraceae L var botrytis cv Early kunwari
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
 INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
BEMS Reports A multifaceted post peer review journal in the field of Biology, Engineering, Medicine and Allied Sciences
 BEMS Reports A multifaceted post peer review journal in the field of Biology, Engineering, Medicine and Allied Sciences SCIENCE Induction and Growth Optimisation of hairy root culture of Chlorophytum species
BEMS Reports A multifaceted post peer review journal in the field of Biology, Engineering, Medicine and Allied Sciences SCIENCE Induction and Growth Optimisation of hairy root culture of Chlorophytum species
State Forest Research Institute, Post Box No. 159, Itanagar , India 1 Department of Botany, Rajiv Gandhi University, Itanagar , India
 Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Transformation of Hypericum tomentosum L. and Hypericum tetrapterum Fries.
 Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Transformation of Hypericum tomentosum L. and Hypericum tetrapterum Fries. Hedviga Komarovská a, Annalisa Giovannini b, Ján Košuth a, and Eva Čellárová a, * a P. J. Šafárik
Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Transformation of Hypericum tomentosum L. and Hypericum tetrapterum Fries. Hedviga Komarovská a, Annalisa Giovannini b, Ján Košuth a, and Eva Čellárová a, * a P. J. Šafárik
Hairy root and tissue cultures of Leucojum aestivum L. relationships to galanthamine content
 DOI 10.1007/s11101-006-9043-z Hairy root and tissue cultures of Leucojum aestivum L. relationships to galanthamine content M. F. Diop Æ A. Hehn Æ A. Ptak Æ F. Chrétien Æ S. Doerper Æ E. Gontier Æ F. Bourgaud
DOI 10.1007/s11101-006-9043-z Hairy root and tissue cultures of Leucojum aestivum L. relationships to galanthamine content M. F. Diop Æ A. Hehn Æ A. Ptak Æ F. Chrétien Æ S. Doerper Æ E. Gontier Æ F. Bourgaud
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE- DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY. STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE PROCEDURE NO: GLP 021 MOD: 1st Issue Page: 1 of 6
 Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
(DMB 01) M.Sc. (Previous) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER First Year. Microbiology. Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 wk 7 (DMB 01) Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS PART A (5 8 = 40 marks) 1. Explain the growth of microbiology in the twentieth century. 2. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cell with a neat-labeled
wk 7 (DMB 01) Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS PART A (5 8 = 40 marks) 1. Explain the growth of microbiology in the twentieth century. 2. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cell with a neat-labeled
INFECTION OF PINUS RADIATA WITH AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES AND LONG-TERM GROWTH OF DETACHED HAIRY ROOTS IN VITRO
 11 INFECTION OF PINUS RADIATA WITH AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES AND LONG-TERM GROWTH OF DETACHED HAIRY ROOTS IN VITRO B. A. BERGMANN*, J. DUKES, and A-M. STOMP Department of Forestry, North Carolina State
11 INFECTION OF PINUS RADIATA WITH AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES AND LONG-TERM GROWTH OF DETACHED HAIRY ROOTS IN VITRO B. A. BERGMANN*, J. DUKES, and A-M. STOMP Department of Forestry, North Carolina State
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines
 Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
ydci GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC
 Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
PHYLOGENETIC GROUPING BY PCR ANALYSES OF Sinorhizobium meliloti STRAINS ISOLATED FROM EUTROPHIC SOIL. Abstract
 ID # 15-01 PHYLOGENETIC GROUPING BY PCR ANALYSES OF Sinorhizobium meliloti STRAINS ISOLATED FROM EUTROPHIC SOIL. W.S. Oliveira 1, P.P.A. Oliveira 2, C.M. Bellato 1, F.R.S. Duarte 1, S.M. Tsai 1 1 Universidade
ID # 15-01 PHYLOGENETIC GROUPING BY PCR ANALYSES OF Sinorhizobium meliloti STRAINS ISOLATED FROM EUTROPHIC SOIL. W.S. Oliveira 1, P.P.A. Oliveira 2, C.M. Bellato 1, F.R.S. Duarte 1, S.M. Tsai 1 1 Universidade
Snow Algae Powder Key to skin s longevity
 Snow Algae Powder Key to skin s longevity Michal Rössler Snow Algae Powder Key to skin s longevity Repairing the Effects of Time by Mimicking Calorie Restriction With Snow Algae Powder, Mibelle Biochemistry
Snow Algae Powder Key to skin s longevity Michal Rössler Snow Algae Powder Key to skin s longevity Repairing the Effects of Time by Mimicking Calorie Restriction With Snow Algae Powder, Mibelle Biochemistry
Part II. Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Gene Transfer
 Part II Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Gene Transfer Introduction II Agrobacterium rhizogenes, a Natural Transformation System D. TEPFER Plant-microorganism interactions are based on exchanges of nutritional
Part II Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Gene Transfer Introduction II Agrobacterium rhizogenes, a Natural Transformation System D. TEPFER Plant-microorganism interactions are based on exchanges of nutritional
Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222
 Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Chapter 2 Introduction to the Biology of Plant Propagation -A review- 1 5. Plant Hormones and Plant development Phytohormones Nt Naturally
Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Chapter 2 Introduction to the Biology of Plant Propagation -A review- 1 5. Plant Hormones and Plant development Phytohormones Nt Naturally
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang Chen, Qiang Dong, Jiangqi Wen, Kirankumar S. Mysore and Jian Zhao
 New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
The involvement of photosynthesis in inducing bud formation on excised leaf segments of Heloniopsis orientalis (Liliaceae)
 Plant & Cell Physiol. 19(5): 791-799 (1978) The involvement of photosynthesis in inducing bud formation on excised leaf of Heloniopsis orientalis (Liliaceae) Yukio Kato Biological Laboratory, Fukui University,
Plant & Cell Physiol. 19(5): 791-799 (1978) The involvement of photosynthesis in inducing bud formation on excised leaf of Heloniopsis orientalis (Liliaceae) Yukio Kato Biological Laboratory, Fukui University,
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 5 115
 Chapter 5 Genetic transformation of peanut with Agrobacterium rhizogenes INTRODUCTION Genetic engineering has opened new avenues to modify crops, and provided new solutions to satisfy specific needs for
Chapter 5 Genetic transformation of peanut with Agrobacterium rhizogenes INTRODUCTION Genetic engineering has opened new avenues to modify crops, and provided new solutions to satisfy specific needs for
1( ) 5, dist. 4 5, dist. 3 5, dist. 5 5, dist
 and plant regeneration protocols for Brassica napus // International Journal of agriculture & Biology. 2011. Vol. 13. P. 83 88. 10. Gamborg O. L., Miller R. A, Ojima K. Nutrient requirements of suspension
and plant regeneration protocols for Brassica napus // International Journal of agriculture & Biology. 2011. Vol. 13. P. 83 88. 10. Gamborg O. L., Miller R. A, Ojima K. Nutrient requirements of suspension
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Factors Affecting the Infection of Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Transformed Root Culture
 Factors Affecting the Infection of Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Transformed Root Culture Poonpilai Suwanaritl, Savitri Ascharakul2, Omsub Nopamornbodi3 and Malee Suwana-adth4 I Department
Factors Affecting the Infection of Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Transformed Root Culture Poonpilai Suwanaritl, Savitri Ascharakul2, Omsub Nopamornbodi3 and Malee Suwana-adth4 I Department
INDUCTION OF HAIRY ROOTS IN ATROPA KOMAROVII USING AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES
 INDUCTION OF HAIRY ROOTS IN ATROPA KOMAROVII USING AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES Ofelia Banihashemi 1, Ramazan-Ali Khavari-Nejad 1, * NarguessYassa 2 and FarzanehNajafi 3 1 Department of Biology, Science and
INDUCTION OF HAIRY ROOTS IN ATROPA KOMAROVII USING AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES Ofelia Banihashemi 1, Ramazan-Ali Khavari-Nejad 1, * NarguessYassa 2 and FarzanehNajafi 3 1 Department of Biology, Science and
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER NO. TITLE PAGE NO. LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES 1 INTRODUCTION AIM AND SCOPE OF THE PRESENT INVESTIGATION 7
 viii TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES iii xxiii xxviii 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 AIM AND SCOPE OF THE PRESENT INVESTIGATION 7 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 8 2.1 AN OVERVIEW OF TEA 8 2.2 TEA
viii TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES iii xxiii xxviii 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 AIM AND SCOPE OF THE PRESENT INVESTIGATION 7 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 8 2.1 AN OVERVIEW OF TEA 8 2.2 TEA
Changes of alkaloids in Tibetan medicine Przewalskia tangutica during tissue culture and differentiation of its stem rapid propagation system
 386 1, 2, 3 1 1, 2, 3 1, 2, 3* 4 4 1 1. 818 2. 818 3. 149 4. 8116 Przewalskia tangutica 3 d 2 3 cm HPLC 4 MS 6-BA 2. mg/l NAA.5 mg/l 96.67% MS NAA.5 mg/l 71.67% HPLC 4 141.25 μg/g R282.21 A 253-267(215)2-386
386 1, 2, 3 1 1, 2, 3 1, 2, 3* 4 4 1 1. 818 2. 818 3. 149 4. 8116 Przewalskia tangutica 3 d 2 3 cm HPLC 4 MS 6-BA 2. mg/l NAA.5 mg/l 96.67% MS NAA.5 mg/l 71.67% HPLC 4 141.25 μg/g R282.21 A 253-267(215)2-386
Applying crown gall research-based knowledge to orchard management. E. Fichtner, UCCE Tulare County
 Applying crown gall research-based knowledge to orchard management E. Fichtner, UCCE Tulare County Paradox: Juglans hindsii x Juglans regia Crown Gall Common in walnut Paradox rootstock susceptible Less
Applying crown gall research-based knowledge to orchard management E. Fichtner, UCCE Tulare County Paradox: Juglans hindsii x Juglans regia Crown Gall Common in walnut Paradox rootstock susceptible Less
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Effect of some root associative bacteria on germination of seeds, nitrogenase activity and dry matter production by rice plants
 Journal of crop and weed 2(2) : 47-51 (2006) Effect of some root associative bacteria on germination of seeds, nitrogenase activity and dry matter production by rice plants A. C. DAS AND S. C. KOLE Department
Journal of crop and weed 2(2) : 47-51 (2006) Effect of some root associative bacteria on germination of seeds, nitrogenase activity and dry matter production by rice plants A. C. DAS AND S. C. KOLE Department
Ethylene is critical to the maintenance of primary root growth and Fe. homeostasis under Fe stress in Arabidopsis
 Ethylene is critical to the maintenance of primary root growth and Fe homeostasis under Fe stress in Arabidopsis Guangjie Li, Weifeng Xu, Herbert J. Kronzucker, Weiming Shi * Supplementary Data Supplementary
Ethylene is critical to the maintenance of primary root growth and Fe homeostasis under Fe stress in Arabidopsis Guangjie Li, Weifeng Xu, Herbert J. Kronzucker, Weiming Shi * Supplementary Data Supplementary
Impact of Ozone on Plant Competition and Structural Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Grassland Mesocosms
 Phyton (Austria) Special issue: "Global change" Vol. 42 Fasc. 3 (7)-(12) 1.10.2002 Impact of Ozone on Plant Competition and Structural Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Grassland Mesocosms
Phyton (Austria) Special issue: "Global change" Vol. 42 Fasc. 3 (7)-(12) 1.10.2002 Impact of Ozone on Plant Competition and Structural Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Grassland Mesocosms
09/07/16 12/07/16: 14/07/16:
 09/07/16 Transformation of DH5 alpha with the InterLab transformation protocol : DNA constructions were dried, so we resuspended them into 100µL nuclease-free water. We took 5µL of the product for 25µL
09/07/16 Transformation of DH5 alpha with the InterLab transformation protocol : DNA constructions were dried, so we resuspended them into 100µL nuclease-free water. We took 5µL of the product for 25µL
Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1
 Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1 D. Skálová *, B. Navrátilová, and A. Lebeda * Palacký University, Faculty of Science, Department
Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1 D. Skálová *, B. Navrátilová, and A. Lebeda * Palacký University, Faculty of Science, Department
FAMILY AND CLONAL VARIATION IN SUSCEPTIBILITY OF PINUS RADIATA TO AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS IN RELATION TO IN VITRO SHOOT GROWTH RATE
 3 FAMILY AND CLONAL VARIATION IN SUSCEPTIBILITY OF PINUS RADIATA TO AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS IN RELATION TO IN VITRO SHOOT GROWTH RATE B. A. BERGMANN and A.-M. STOMP Department of Forestry, North Carolina
3 FAMILY AND CLONAL VARIATION IN SUSCEPTIBILITY OF PINUS RADIATA TO AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS IN RELATION TO IN VITRO SHOOT GROWTH RATE B. A. BERGMANN and A.-M. STOMP Department of Forestry, North Carolina
New Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates: collection, identification and screening of efficiency in symbiosis with clover
 New Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates: collection, identification and screening of efficiency in symbiosis with clover T. Šimon Research Institute of Crop Production, Prague-Ruzyne, Czech Republic
New Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates: collection, identification and screening of efficiency in symbiosis with clover T. Šimon Research Institute of Crop Production, Prague-Ruzyne, Czech Republic
Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset
 583 Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset Fatemeh Rezaee, Faezeh Ghanati* and Laleh Yusefzadeh Boroujeni Department of Plant Biology, Faculty
583 Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset Fatemeh Rezaee, Faezeh Ghanati* and Laleh Yusefzadeh Boroujeni Department of Plant Biology, Faculty
GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS OF PSEUDOMONAS PUTIDA STRAINS AND EFFECT OF HUMIC SUBSTANCES ON CELL DENSITY DURING BATCH CULTIVATION
 8 T. Georgieva, D. Nikolova, Y. Evstatieva, Ts. Licheva and V. Savov ulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, (Supplement 1) 14, 8 86 Agricultural Academy GROWTH HARATERISTIS OF PSEUDOMONAS PUTIDA STRAINS
8 T. Georgieva, D. Nikolova, Y. Evstatieva, Ts. Licheva and V. Savov ulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, (Supplement 1) 14, 8 86 Agricultural Academy GROWTH HARATERISTIS OF PSEUDOMONAS PUTIDA STRAINS
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard. Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard
 Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
LEDStorm Grow Spectrum Light (with EMS Technology) Light Comparison Testing Spokane, WA. A New Natural Approach to Lighting.
 Grow Spectrum Light 1.0 Light Comparison Testing Spokane, WA April 12-15th 2016 This was a test to show that the LEDStorm PL11, 75w (Grow Spectrum Light w/ems Technology), with its special array, can be
Grow Spectrum Light 1.0 Light Comparison Testing Spokane, WA April 12-15th 2016 This was a test to show that the LEDStorm PL11, 75w (Grow Spectrum Light w/ems Technology), with its special array, can be
Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated hairy root induction in Oxystelma esculentum (L.f) R.Br.
 Journal of Biological Research-Thessaloniki 8: 207 212, 2007 J. Biol. Res.-Thessalon. is available online at http://www.jbr.gr Indexed in: WoS (Web of Science, ISI Thomson), CAS (Chemical Abstracts Service)
Journal of Biological Research-Thessaloniki 8: 207 212, 2007 J. Biol. Res.-Thessalon. is available online at http://www.jbr.gr Indexed in: WoS (Web of Science, ISI Thomson), CAS (Chemical Abstracts Service)
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Bacterial Growth and Ste111 Water Relations in Cut Flowers
 Bacterial Growth and Ste111 Water Relations in Cut Flowers Porntip Sae Jeang Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Agricultural Science UNIVERSITY OF TASMANIA HOBART FEBRUARY
Bacterial Growth and Ste111 Water Relations in Cut Flowers Porntip Sae Jeang Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Agricultural Science UNIVERSITY OF TASMANIA HOBART FEBRUARY
EXPRESSION AND STABILITY OF TRANSGENES IN ASPEN-POPULUS
 EXPRESSION AND STABILITY OF TRANSGENES IN ASPEN-POPULUS M.R. Ahuja and M. Fladung Abstract:-- We have employed Populus as a model system to investigate questions regarding stability and expression of foreign
EXPRESSION AND STABILITY OF TRANSGENES IN ASPEN-POPULUS M.R. Ahuja and M. Fladung Abstract:-- We have employed Populus as a model system to investigate questions regarding stability and expression of foreign
E.Z.N.A. MicroElute Clean-up Kits Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. MicroElute Clean-up Kits Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Kit Contents... 3 Preparing Reagents/Storage and Stability... 4 Guideline for Vacuum Manifold... 5 MicroElute Cycle-Pure - Spin Protocol...
E.Z.N.A. MicroElute Clean-up Kits Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Kit Contents... 3 Preparing Reagents/Storage and Stability... 4 Guideline for Vacuum Manifold... 5 MicroElute Cycle-Pure - Spin Protocol...
Electronic Journal of Plant Breeding, 7(4): (December 2016) ISSN X
 Research Article Pflp gene transformation in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) resistance to bacterial blight disease (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae) Akshata Hosamani *, Sukhada Mohandas, V. Manjula,
Research Article Pflp gene transformation in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) resistance to bacterial blight disease (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae) Akshata Hosamani *, Sukhada Mohandas, V. Manjula,
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
TOPIC 9.3 GROWTH IN PLANTS
 TOPIC 9.3 GROWTH IN PLANTS 9.3 A Growth INTRO http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/18130/social-suggested-images/plant_growing.jpeg IB BIO 9.3 3 In general, plants are able to grow indeterminately. This means
TOPIC 9.3 GROWTH IN PLANTS 9.3 A Growth INTRO http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/18130/social-suggested-images/plant_growing.jpeg IB BIO 9.3 3 In general, plants are able to grow indeterminately. This means
Reduction of Exudates (Browning) in Sugarcane Micro Propagation
 Nig J. Biotech. Vol. 23 (2011) 40-44 ISSN: 0189 17131 Available online at www.biotechsocietynigeria.org. Reduction of Exudates (Browning) in Sugarcane Micro Propagation Ishaq M.N. and Ehirim Bernard O.
Nig J. Biotech. Vol. 23 (2011) 40-44 ISSN: 0189 17131 Available online at www.biotechsocietynigeria.org. Reduction of Exudates (Browning) in Sugarcane Micro Propagation Ishaq M.N. and Ehirim Bernard O.
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids
 Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Heavy metal uptake from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Single and mix-metal exposure
 15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Heavy metal uptake from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Single and mix-metal
15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Heavy metal uptake from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Single and mix-metal
Major Plant Hormones 1.Auxins 2.Cytokinins 3.Gibberelins 4.Ethylene 5.Abscisic acid
 Plant Hormones Lecture 9: Control Systems in Plants What is a Plant Hormone? Compound produced by one part of an organism that is translocated to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells
Plant Hormones Lecture 9: Control Systems in Plants What is a Plant Hormone? Compound produced by one part of an organism that is translocated to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells
NAD + /NADH Assay [Colorimetric]
![NAD + /NADH Assay [Colorimetric] NAD + /NADH Assay [Colorimetric]](/thumbs/91/105496846.jpg) G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name NAD + /NADH Assay [Colorimetric] (Cat. #786 1539, 786 1540) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name NAD + /NADH Assay [Colorimetric] (Cat. #786 1539, 786 1540) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Performance of Bradyrhizobial isolates under drought conditions
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 5 (2013) pp. 228-232 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Performance of Bradyrhizobial isolates under drought conditions C. Uma*, P. Sivagurunathan and D. Sangeetha
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 5 (2013) pp. 228-232 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Performance of Bradyrhizobial isolates under drought conditions C. Uma*, P. Sivagurunathan and D. Sangeetha
Is that artificial turf or real grass? Its thicker than Bermuda!
 Is that artificial turf or real grass? Its thicker than Bermuda! 1 Using Plant Growth Regulators Growth regulators DO NOT interfere with plant respiration, photosynthesis, or other internal plant functions
Is that artificial turf or real grass? Its thicker than Bermuda! 1 Using Plant Growth Regulators Growth regulators DO NOT interfere with plant respiration, photosynthesis, or other internal plant functions
NATURAL VARIATION IN THE CYTOKININ METABOLIC NETWORK IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 NATURAL VARIATION IN THE CYTOKININ METABOLIC NETWORK IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA PŘÍRODNÍ VARIACE METABOLISMU CYTOKININŮ U ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Samsonová Z. 1, 2, 3, Kuklová A. 1, 2, Mazura P. 1, 2, Rotková
NATURAL VARIATION IN THE CYTOKININ METABOLIC NETWORK IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA PŘÍRODNÍ VARIACE METABOLISMU CYTOKININŮ U ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Samsonová Z. 1, 2, 3, Kuklová A. 1, 2, Mazura P. 1, 2, Rotková
The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match the part of the plant (A, B, C or D) to its function by writing the letters in the table.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name:
 Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name: Section 1. In the space to the left of the statements below, write the word(s) that best fit the definition or description. (20 pts) Vegetative reproduction
Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name: Section 1. In the space to the left of the statements below, write the word(s) that best fit the definition or description. (20 pts) Vegetative reproduction
Data Sheet. Azide Cy5 RNA T7 Transcription Kit
 Cat. No. Size 1. Description PP-501-Cy5 10 reactions à 40 µl For in vitro use only Quality guaranteed for 12 months Store all components at -20 C. Avoid freeze and thaw cycles. DBCO-Sulfo-Cy5 must be stored
Cat. No. Size 1. Description PP-501-Cy5 10 reactions à 40 µl For in vitro use only Quality guaranteed for 12 months Store all components at -20 C. Avoid freeze and thaw cycles. DBCO-Sulfo-Cy5 must be stored
Life Science Journal 2014;11(9) Cryptochrome 2 negatively regulates ABA-dependent seed germination in Arabidopsis
 Cryptochrome 2 negatively regulates ABA-dependent seed germination in Arabidopsis Sung-Il Kim 1, Sang Ik Song 3, Hak Soo Seo 1, 2, 4 * 1 Department of Plant Science and Research Institute of Agriculture
Cryptochrome 2 negatively regulates ABA-dependent seed germination in Arabidopsis Sung-Il Kim 1, Sang Ik Song 3, Hak Soo Seo 1, 2, 4 * 1 Department of Plant Science and Research Institute of Agriculture
In vitro fruit trees rooting by Agrobacterium rhizogenes wild type infection
 EJB Electronic Journal of Biotechnology ISSN: 0717-345 Vol.1 No.2, Issue of August 15, 1998. 1998 by Universidad Católica de Valparaíso - Chile Invited review paper/ Received 20 October, 1998. RESEARCH
EJB Electronic Journal of Biotechnology ISSN: 0717-345 Vol.1 No.2, Issue of August 15, 1998. 1998 by Universidad Católica de Valparaíso - Chile Invited review paper/ Received 20 October, 1998. RESEARCH
CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS FROM MAIZE MATURE EMBRYOS (ZEA MAYS L.)
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 13(1) 3565-3569 (2013) (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) ISSN: 0973-0028; E-ISSN: 0974-0910 Original Article CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 13(1) 3565-3569 (2013) (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) ISSN: 0973-0028; E-ISSN: 0974-0910 Original Article CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS
Rapid, Efficient Production of Homozygous Transgenic Tobacco Plants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Seed to Seed Protocol.
 1 Rapid, Efficient Production of Homozygous Transgenic Tobacco Plants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Seed to Seed Protocol. Dane K. Fisher and Mark J. Guiltinan* Department of Horticulture, Intercollegiate
1 Rapid, Efficient Production of Homozygous Transgenic Tobacco Plants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Seed to Seed Protocol. Dane K. Fisher and Mark J. Guiltinan* Department of Horticulture, Intercollegiate
Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus. Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008
 Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008 Jude Grosser University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center,
Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008 Jude Grosser University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center,
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102. Getting to Know Plants
 The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
By Jonathan I. Watkinson. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. Doctor of Philosophy Horticulture
 Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with
Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with
Comparative Artemisinin analysis in Artemisia dubia transformed with two different Agrobacteria harbouring rol ABC genes
 POJ 5(4):386-391 (2012) ISSN:1836-3644 Comparative Artemisinin analysis in Artemisia dubia transformed with two different Agrobacteria harbouring rol ABC genes Bushra Hafeez Kiani 1, Naila Safdar 1, Abdul
POJ 5(4):386-391 (2012) ISSN:1836-3644 Comparative Artemisinin analysis in Artemisia dubia transformed with two different Agrobacteria harbouring rol ABC genes Bushra Hafeez Kiani 1, Naila Safdar 1, Abdul
