Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I 26 September 2002 NAME
|
|
|
- Bertha Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 437 EXAM1.DOC Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I 26 September 2002 NAME 0. When you gaze at the stars, why do you have to look slightly away from the really faint ones in order to be able to see them? (1 pt.) True or False (write true or false ; 9 points total; 1 point each) 1. A slow chemical synapse usually utilizes a ligand-gated ion channel in the postsynaptic membrane. 2. When an ion species moves across the membrane through open channels, changing the membrane potential, the concentration gradient for that ion is abolished and needs to be reestablished later using ATP. 3. Because of the existence of an absolute refractory period for voltage-gated Na + channels, if you were to artificially stimulate a resting axon to threshold somewhere in the middle of its entire length, the resultant AP would move only down toward the axon terminals. 4. Lateral inhibition can function in olfaction to help identify a specific type of odorant molecule even if that odorant molecule binds, at least somewhat, to several different receptor types. 5. Rhodopsins are the more common visual pigments in freshwater vertebrates. 6. The log 10 of afferent action potential frequency is linearly related to the incoming stimulus intensity. 7. Glomerular convergence means that the many cell receptors for a specific type of molecular odor in the nasal epithelium tend to synapse on to the same glomerulus. 8. Thermoreceptors in snakes are sometimes bimodal. When they are bimodal they usually detect both heat and odor. 9. During smolting of Atlantic Salmon, these fish become more tolerant of seawater because of increased levels of Na + -K + -2Cl - cotransporter, Na + -K + -ATPase, and numbers of chloride cells in the gills.
2 Really Short Answer (maybe a few words or a sentence; 25 points total; 2.5 points each) 1. How do both krait (a type of snake) venom and curare (used by native South Americans on blow darts) work to incapacitate their victims? 2. With respect to changing membrane potentials, what is special about the endolymph within the cochlea of the ear. 3. Give two examples of species of vertebrates that have vomeronasal organs. 4. List three properties of molecules such as ions that allow ion channels to be selective. 5. What is the equilibrium potential (E x ) for an imaginary ion X 2- given the following information: [X 2- ] outside = 75 mm and [X 2- ] inside = 15 mm (please show your work). 6. What is the absolute value of the electromotive force (emf) acting on the above ion if V m = -50 mv? 7. How might the following statement be false: An unmyelinated axon cannot transmit an action potential as fast as a myelinated axon. 8. List two ways that electrical synapses differ from chemical ones.
3 9. If both Na + and K + move through open cholinergic receptor channels, why does the cell membrane depolarize? 10. Which of these transmitters (A or B) leads to an EPSP and which to an IPSP? Is there evidence of temporal or spatial summation in these graphs? membrane potential (mv) -70 current A A B Short Answer (CHOOSE 6 (SIX) of the following 8 questions; ~ 2 or 3 sentence answers; 30 points total; 5 points each) 1. Which graph (A or B) shows competitive inhibition? Why? A B
4 2. On the diagram, clearly label three phases of the action potential and indicate which ion(s) is primarily responsible for each of the phases identified. 0 V m (mv) ms 3. Provide an example of an electrochemical gradient that is commonly established in cells. How is it established and what are some potential uses of that electrochemical gradient for the organism? 4. Briefly describe the voltage clamping method and its utility in studying physiology.
5 5. In nerve signal transmission, what does it mean to alternate between graded and all-or-none potentials? 6. Several examples of the conservation of proteins consisting of 7-transmembrane helices have been presented in lecture and in your text. Please list two. How does evolutionary biology explain the similar protein structures seen in several different physiological contexts? 7. Describe similarities between receptor cells for hearing and equilibrium (other than that they are often both in the ear). 8. How are salty taste and bitter taste receptor transduction different?
6 Longer Essay Answer (20 pts; ~a few well-organized paragraphs). 1. Explain the transduction of light into electrical signals from the point of photons hitting the cornea up to the point where signals are sent toward the central nervous system. Please be sure to touch on the following topics in your discussion: anatomy, acuity, sensitivity, amplification, membrane potential, etc.
7 Long Essay Answer (15 pts; ~a few well-organized paragraphs). 2. Choose one of the readings from your discussion section thus far this semester. Describe the methods used (generally), the important findings, and how the paper informs your knowledge of vertebrate physiology in a whole-animal context.
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes.
 1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
Control and Integration. Nervous System Organization: Bilateral Symmetric Animals. Nervous System Organization: Radial Symmetric Animals
 Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
لجنة الطب البشري رؤية تنير دروب تميزكم
 1) Hyperpolarization phase of the action potential: a. is due to the opening of voltage-gated Cl channels. b. is due to prolonged opening of voltage-gated K + channels. c. is due to closure of the Na +
1) Hyperpolarization phase of the action potential: a. is due to the opening of voltage-gated Cl channels. b. is due to prolonged opening of voltage-gated K + channels. c. is due to closure of the Na +
Nerve Signal Conduction. Resting Potential Action Potential Conduction of Action Potentials
 Nerve Signal Conduction Resting Potential Action Potential Conduction of Action Potentials Resting Potential Resting neurons are always prepared to send a nerve signal. Neuron possesses potential energy
Nerve Signal Conduction Resting Potential Action Potential Conduction of Action Potentials Resting Potential Resting neurons are always prepared to send a nerve signal. Neuron possesses potential energy
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
BIOLOGY 11/10/2016. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Concept 48.1: Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
Information processing. Divisions of nervous system. Neuron structure and function Synapse. Neurons, synapses, and signaling 11/3/2017
 Neurons, synapses, and signaling Chapter 48 Information processing Divisions of nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Brain and a nerve cord Integration center Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Nerves
Neurons, synapses, and signaling Chapter 48 Information processing Divisions of nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Brain and a nerve cord Integration center Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Nerves
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.
 Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
Chapter 9. Nerve Signals and Homeostasis
 Chapter 9 Nerve Signals and Homeostasis A neuron is a specialized nerve cell that is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neural signaling communication by neurons is the process by which an animal
Chapter 9 Nerve Signals and Homeostasis A neuron is a specialized nerve cell that is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neural signaling communication by neurons is the process by which an animal
Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function
 Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function Integration An animal needs to function like a coherent organism, not like a loose collection of cells. Integration = refers to processes such as summation
Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function Integration An animal needs to function like a coherent organism, not like a loose collection of cells. Integration = refers to processes such as summation
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Biology September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY
 Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY
 Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Responses, Nervous System & Muscles
 thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Responses, Nervous System & Muscles 1 Response Mechanism tropism Definition A growth movement of part of plant in response to a directional stimulus examples Positive:
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Responses, Nervous System & Muscles 1 Response Mechanism tropism Definition A growth movement of part of plant in response to a directional stimulus examples Positive:
Organization of the nervous system. Tortora & Grabowski Principles of Anatomy & Physiology; Page 388, Figure 12.2
 Nervous system Organization of the nervous system Tortora & Grabowski Principles of Anatomy & Physiology; Page 388, Figure 12.2 Autonomic and somatic efferent pathways Reflex arc - a neural pathway that
Nervous system Organization of the nervous system Tortora & Grabowski Principles of Anatomy & Physiology; Page 388, Figure 12.2 Autonomic and somatic efferent pathways Reflex arc - a neural pathway that
BIOLOGY. 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Communication in Neurons
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
Neurons and Nervous Systems
 34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Housekeeping, 26 January 2009
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
Neurons. 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan Finish Solutes + Water. 2. Neurons. Chapter 11
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
MEMBRANE POTENTIALS AND ACTION POTENTIALS:
 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical students, 2017/2018 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Review: Membrane physiology
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical students, 2017/2018 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Review: Membrane physiology
Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers.
 The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) innervate Divisions: a. Afferent
 Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Lines of Communication
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Lines of Communication
Universality of sensory-response systems
 excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
Action Potentials & Nervous System. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials & Nervous System Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review: Membrane potentials exist due to unequal distribution of charge across the membrane Concentration gradients drive ion
Action Potentials & Nervous System Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review: Membrane potentials exist due to unequal distribution of charge across the membrane Concentration gradients drive ion
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
Neuron Structure. Why? Model 1 Parts of a Neuron. What are the essential structures that make up a neuron?
 Why? Neuron Structure What are the essential structures that make up a neuron? Cells are specialized for different functions in multicellular organisms. In animals, one unique kind of cell helps organisms
Why? Neuron Structure What are the essential structures that make up a neuron? Cells are specialized for different functions in multicellular organisms. In animals, one unique kind of cell helps organisms
Neurophysiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
The Nervous System. Nerve Impulses. Resting Membrane Potential. Overview. Nerve Impulses. Resting Membrane Potential
 The Nervous System Overview Nerve Impulses (completed12/03/04) (completed12/03/04) How do nerve impulses start? (completed 19/03/04) (completed 19/03/04) How Fast are Nerve Impulses? Nerve Impulses Nerve
The Nervous System Overview Nerve Impulses (completed12/03/04) (completed12/03/04) How do nerve impulses start? (completed 19/03/04) (completed 19/03/04) How Fast are Nerve Impulses? Nerve Impulses Nerve
Transmission of Nerve Impulses (see Fig , p. 403)
 How a nerve impulse works Transmission of Nerve Impulses (see Fig. 12.13, p. 403) 1. At Rest (Polarization) outside of neuron is positively charged compared to inside (sodium ions outside, chloride and
How a nerve impulse works Transmission of Nerve Impulses (see Fig. 12.13, p. 403) 1. At Rest (Polarization) outside of neuron is positively charged compared to inside (sodium ions outside, chloride and
BIOLOGY. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Lines of Communication The
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Lines of Communication The
Bio 449 Fall Exam points total Multiple choice. As with any test, choose the best answer in each case. Each question is 3 points.
 Name: Exam 1 100 points total Multiple choice. As with any test, choose the best answer in each case. Each question is 3 points. 1. The term internal environment, as coined by Clause Bernard, is best defined
Name: Exam 1 100 points total Multiple choice. As with any test, choose the best answer in each case. Each question is 3 points. 1. The term internal environment, as coined by Clause Bernard, is best defined
What are neurons for?
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes Water 2. Neurons Neurons Chapter 11
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes Water 2. Neurons Neurons Chapter 11
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34
 NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
Neural Conduction. biologyaspoetry.com
 Neural Conduction biologyaspoetry.com Resting Membrane Potential -70mV A cell s membrane potential is the difference in the electrical potential ( charge) between the inside and outside of the cell. The
Neural Conduction biologyaspoetry.com Resting Membrane Potential -70mV A cell s membrane potential is the difference in the electrical potential ( charge) between the inside and outside of the cell. The
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK IT 0469 NEURAL NETWORKS
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK IT 0469 NEURAL NETWORKS Elementary Neuro Physiology Neuron: A neuron nerve cell is an electricallyexcitable cell that processes and transmits information
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK IT 0469 NEURAL NETWORKS Elementary Neuro Physiology Neuron: A neuron nerve cell is an electricallyexcitable cell that processes and transmits information
The Neuron - F. Fig. 45.3
 excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling The Neuron - F. Fig. 45.3 Today s lecture we ll use clickers Review today 11:30-1:00 in 2242 HJ Patterson Electrical signals Dendrites: graded post-synaptic potentials
excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling The Neuron - F. Fig. 45.3 Today s lecture we ll use clickers Review today 11:30-1:00 in 2242 HJ Patterson Electrical signals Dendrites: graded post-synaptic potentials
Ch 7. The Nervous System 7.1 & 7.2
 Ch 7 The Nervous System 7.1 & 7.2 SLOs Describe the different types of neurons and supporting cells, and identify their functions. Identify the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the CNS and
Ch 7 The Nervous System 7.1 & 7.2 SLOs Describe the different types of neurons and supporting cells, and identify their functions. Identify the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the CNS and
Electrical Signaling. Lecture Outline. Using Ions as Messengers. Potentials in Electrical Signaling
 Lecture Outline Electrical Signaling Using ions as messengers Potentials in electrical signaling Action Graded Other electrical signaling Gap junctions The neuron Using Ions as Messengers Important things
Lecture Outline Electrical Signaling Using ions as messengers Potentials in electrical signaling Action Graded Other electrical signaling Gap junctions The neuron Using Ions as Messengers Important things
Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works
 Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works Essential Knowledge Statement 3.E.2 Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and
Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works Essential Knowledge Statement 3.E.2 Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and
1. Neurons & Action Potentials
 Lecture 6, 30 Jan 2008 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2008 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Intro Nervous System Fxn (slides 32-60 from Mon 28 Jan; Ch10) 2. Neurons
Lecture 6, 30 Jan 2008 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2008 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Intro Nervous System Fxn (slides 32-60 from Mon 28 Jan; Ch10) 2. Neurons
Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005
 Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY POWERPOINT
 POWERPOINT LECTURE SLIDE PRESENTATION by LYNN CIALDELLA, MA, MBA, The University of Texas at Austin Additional text by J Padilla exclusively for physiology at ECC UNIT 2 8 Neurons: PART A Cellular and
POWERPOINT LECTURE SLIDE PRESENTATION by LYNN CIALDELLA, MA, MBA, The University of Texas at Austin Additional text by J Padilla exclusively for physiology at ECC UNIT 2 8 Neurons: PART A Cellular and
Neurophysiology. Review from 12b. Topics in neurophysiology 7/08/12. Lecture 11b BIOL241
 Neurophysiology Lecture 11b BIOL241 Review from 12b. CNS brain and spinal cord PNS nerves SNS (somatic) ANS (autonomic) Sympathetic NS Parasympathetic NS Afferent vs efferent (SAME) Cells of the nervous
Neurophysiology Lecture 11b BIOL241 Review from 12b. CNS brain and spinal cord PNS nerves SNS (somatic) ANS (autonomic) Sympathetic NS Parasympathetic NS Afferent vs efferent (SAME) Cells of the nervous
Lecture 2. Excitability and ionic transport
 Lecture 2 Excitability and ionic transport Selective membrane permeability: The lipid barrier of the cell membrane and cell membrane transport proteins Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular
Lecture 2 Excitability and ionic transport Selective membrane permeability: The lipid barrier of the cell membrane and cell membrane transport proteins Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular
Sensory Transduction
 Sensory Transduction Gordon L. Fain University of California, Los Angeles with illustrations by Margery J. Fain Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Contents Chapter
Sensory Transduction Gordon L. Fain University of California, Los Angeles with illustrations by Margery J. Fain Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Contents Chapter
Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1
 Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1 Objectives: Describe the Cells of the NS Explain the creation and propagation of an electrical signal in a nerve
Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1 Objectives: Describe the Cells of the NS Explain the creation and propagation of an electrical signal in a nerve
The sense of smell Outline Main Olfactory System Odor Detection Odor Coding Accessory Olfactory System Pheromone Detection Pheromone Coding
 The sense of smell Outline Main Olfactory System Odor Detection Odor Coding Accessory Olfactory System Pheromone Detection Pheromone Coding 1 Human experiment: How well do we taste without smell? 2 Brief
The sense of smell Outline Main Olfactory System Odor Detection Odor Coding Accessory Olfactory System Pheromone Detection Pheromone Coding 1 Human experiment: How well do we taste without smell? 2 Brief
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11 Part B Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 11.4 Membrane
Chapter 11 Part B Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 11.4 Membrane
SENSORY PROCESSES PROVIDE INFORMATION ON ANIMALS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND INTERNAL STATUS 34.4
 SENSORY PROCESSES PROVIDE INFORMATION ON ANIMALS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND INTERNAL STATUS 34.4 INTRODUCTION Animals need information about their external environments to move, locate food, find mates,
SENSORY PROCESSES PROVIDE INFORMATION ON ANIMALS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND INTERNAL STATUS 34.4 INTRODUCTION Animals need information about their external environments to move, locate food, find mates,
NOTES: CH 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 NOTES: CH 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling A nervous system has three overlapping functions: 1) SENSORY INPUT: signals from sensory receptors to integration centers 2) INTEGRATION: information from
NOTES: CH 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling A nervous system has three overlapping functions: 1) SENSORY INPUT: signals from sensory receptors to integration centers 2) INTEGRATION: information from
The Nervous System. Nervous System Organization. Nerve Tissue. Two parts to the nervous system 11/27/2016
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
Introduction to electrophysiology. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of the
Introduction to electrophysiology Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of the
Biosciences in the 21st century
 Biosciences in the 21st century Lecture 1: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Dr. Michael Burger Outline: 1. Why neuroscience? 2. The neuron 3. Action potentials 4. Synapses 5. Organization of the nervous
Biosciences in the 21st century Lecture 1: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Dr. Michael Burger Outline: 1. Why neuroscience? 2. The neuron 3. Action potentials 4. Synapses 5. Organization of the nervous
Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina
 Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina September 27, 2017 The retina is part of the CNS Calloway et al., 2009) 1 Retinal circuits: neurons and synapses Rods and Cones Bipolar cells Horizontal
Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina September 27, 2017 The retina is part of the CNS Calloway et al., 2009) 1 Retinal circuits: neurons and synapses Rods and Cones Bipolar cells Horizontal
Sensory Systems (con t)
 10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 Housekeeping, Fri 06
10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 Housekeeping, Fri 06
Sensory Processing II Chapter 13
 10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
Sensory Processing II
 10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. The Nervous System and Muscle
 The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
Converting energy into nerve impulses, resting potentials and action potentials Sensory receptors
 D 1.3 s Converting energy into nerve impulses, resting potentials and action potentials Sensory receptors A receptor converts an external or internal stimulus into an electrical signal. Sensory receptors
D 1.3 s Converting energy into nerve impulses, resting potentials and action potentials Sensory receptors A receptor converts an external or internal stimulus into an electrical signal. Sensory receptors
Nervous system. 3 Basic functions of the nervous system !!!! !!! 1-Sensory. 2-Integration. 3-Motor
 Nervous system 3 Basic functions of the nervous system 1-Sensory 2-Integration 3-Motor I. Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord I. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 2) Afferent towards afferent
Nervous system 3 Basic functions of the nervous system 1-Sensory 2-Integration 3-Motor I. Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord I. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 2) Afferent towards afferent
Curtis et al. Il nuovo Invito alla biologia.blu BIOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS KEYS
 BIOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS KEYS Watch the videos and download the transcripts of this section at: online.scuola.zanichelli.it/curtisnuovoinvitoblu/clil > THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 2. WARM UP a) The structures that
BIOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS KEYS Watch the videos and download the transcripts of this section at: online.scuola.zanichelli.it/curtisnuovoinvitoblu/clil > THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 2. WARM UP a) The structures that
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary
 2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
Neurochemistry 1. Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906
 Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 9. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 9 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS The Dynamic Nature of the Plasma Membrane SEM of human erythrocytes
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 9 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS The Dynamic Nature of the Plasma Membrane SEM of human erythrocytes
Nerves and their impulses. Biology 12 C-11
 Nerves and their impulses Biology 12 C-11 Nerves and their impulses Nerves are designed to transmit electrical impulses from the dendrites, over the cell body and through the axon. The impulse will then
Nerves and their impulses Biology 12 C-11 Nerves and their impulses Nerves are designed to transmit electrical impulses from the dendrites, over the cell body and through the axon. The impulse will then
Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
 Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials Nerve and muscle cells: Excitable Capable of generating rapidly changing electrochemical impulses at their membranes
Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials Nerve and muscle cells: Excitable Capable of generating rapidly changing electrochemical impulses at their membranes
Neurons. The Molecular Basis of their Electrical Excitability
 Neurons The Molecular Basis of their Electrical Excitability Viva La Complexity! Consider, The human brain contains >10 11 neurons! Each neuron makes 10 3 (average) synaptic contacts on up to 10 3 other
Neurons The Molecular Basis of their Electrical Excitability Viva La Complexity! Consider, The human brain contains >10 11 neurons! Each neuron makes 10 3 (average) synaptic contacts on up to 10 3 other
Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission. Membrane Potential
 Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
Ch 33. The nervous system
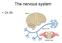 Ch 33 The nervous system AP bio schedule Tuesday Wed Thursday Friday Plant test Animal behavior lab Nervous system 25 Review Day (bring computer) 27 Review Day (bring computer) 28 Practice AP bio test
Ch 33 The nervous system AP bio schedule Tuesday Wed Thursday Friday Plant test Animal behavior lab Nervous system 25 Review Day (bring computer) 27 Review Day (bring computer) 28 Practice AP bio test
Membrane Protein Channels
 Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes
 Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neurons and Models Lecture 1 Topics Membrane (Nernst) Potential Action potential/voltage-gated
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neurons and Models Lecture 1 Topics Membrane (Nernst) Potential Action potential/voltage-gated
Nervous System AP Biology
 Nervous System 2007-2008 Why do animals need a nervous system? What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? fast accurate reset quickly Remember Poor think bunny! about the bunny signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 Why do animals need a nervous system? What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? fast accurate reset quickly Remember Poor think bunny! about the bunny signal direction
QUESTION? Communication between neurons depends on the cell membrane. Why is this so?? Consider the structure of the membrane.
 QUESTION? Communication between neurons depends on the cell membrane Why is this so?? Consider the structure of the membrane. ECF ICF Possible ANSWERS?? Membrane Ion Channels and Receptors: neuron membranes
QUESTION? Communication between neurons depends on the cell membrane Why is this so?? Consider the structure of the membrane. ECF ICF Possible ANSWERS?? Membrane Ion Channels and Receptors: neuron membranes
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump
 The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of
Neurons. General neuron anatomy. BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 7 Neurons. Nervous system:
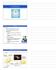 BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 7 Neurons Nervous system: Neurons Integrates and coordinates the body s ac3vi3es Provides rapid and brief responses to s3muli Major divisions: Central nervous system (CNS) brain
BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 7 Neurons Nervous system: Neurons Integrates and coordinates the body s ac3vi3es Provides rapid and brief responses to s3muli Major divisions: Central nervous system (CNS) brain
Action Potential Propagation
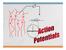 Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Questions: Properties of excitable tissues Transport across cell membrane Resting potential Action potential Excitability change at excitation
 Questions: Properties of excitable tissues Transport across cell membrane Resting potential Action potential Excitability change at excitation EXCITABLE TISSUES The tissues can change the properties under
Questions: Properties of excitable tissues Transport across cell membrane Resting potential Action potential Excitability change at excitation EXCITABLE TISSUES The tissues can change the properties under
Purpose: Perception, Movement, Learning, Memory, Thinking, Communication Functions:
 Nervous System Purpose: Perception, Movement, Learning, Memory, Thinking, Communication Functions: Sensory Input: Obtaining stimulation from the environment (light, heat, pressure, vibration, chemical,
Nervous System Purpose: Perception, Movement, Learning, Memory, Thinking, Communication Functions: Sensory Input: Obtaining stimulation from the environment (light, heat, pressure, vibration, chemical,
Channels can be activated by ligand-binding (chemical), voltage change, or mechanical changes such as stretch.
 1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p.
 Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Intro and Homeostasis
 Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
General Physics. Nerve Conduction. Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power. Fluids. Direct Current (DC)
 Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
1. Control a. In a negative feedback system, a is a device that measures the current value of the.
 031804 Quiz Questions Week #1 1. Control a. In a negative feedback system, a is a device that measures the current value of the. b. Define an effector? c. What does it mean when a negative feedback system
031804 Quiz Questions Week #1 1. Control a. In a negative feedback system, a is a device that measures the current value of the. b. Define an effector? c. What does it mean when a negative feedback system
Some sensory receptors are specialized neurons while others are specialized cells that regulate neurons Figure 50.4
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms Chapter 50 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system Sensory Pathways Sensory pathways have four basic
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms Chapter 50 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system Sensory Pathways Sensory pathways have four basic
Housekeeping, 06 February 2008
 Lecture 9, 06 Feb 2008 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2008 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Synapses (Ch12) 2. Sensory Systems (Ch13) http://eebweb.arizona.edu/eeb_course_websites.htm
Lecture 9, 06 Feb 2008 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2008 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Synapses (Ch12) 2. Sensory Systems (Ch13) http://eebweb.arizona.edu/eeb_course_websites.htm
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 6 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Action Potentials NeuroPhysiology TextBook Readings Pages 400 through 408 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words!
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 6 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Action Potentials NeuroPhysiology TextBook Readings Pages 400 through 408 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words!
SUMMARY OF THE EVENTS WHICH TRIGGER AN ELECTRICAL IMPUSLE IN NERVE CELLS (see figures on the following page)
 Anatomy and Physiology/AP Biology ACTION POTENTIAL SIMULATION BACKGROUND: The plasma membrane of cells is a selectively permeable barrier, which separates the internal contents of the cell from the surrounding
Anatomy and Physiology/AP Biology ACTION POTENTIAL SIMULATION BACKGROUND: The plasma membrane of cells is a selectively permeable barrier, which separates the internal contents of the cell from the surrounding
