Neuron Structure. Why? Model 1 Parts of a Neuron. What are the essential structures that make up a neuron?
|
|
|
- Hope Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why? Neuron Structure What are the essential structures that make up a neuron? Cells are specialized for different functions in multicellular organisms. In animals, one unique kind of cell helps organisms survive by collecting information and sending messages throughout the body. The shapes and features of neurons, which are the primary cells in the nervous system, enable animals to experience all of the five senses; find food, mates, and shelter; and to survive in their diverse environments. Model 1 Parts of a Neuron 1. Model 1 is an illustration of two neurons. Label one of the neurons in the diagram with the following structures: Cell body or soma Cell nucleus Axon Synapse Dendrites 2. Which structure(s) on the neuron in Model 1 would receive a signal from either a sensory cell (taste bud, touch receptor, retinal cell) or from another neuron? 3. Draw an arrow through the two cells in Model 1 to show the path of a nerve impulse if a message was being sent through the two neurons. Neuron Structure 1
2 Model 2 Membrane Potential Area of detail K + Na + Outside of cell Sodium/ potassium pump 70 mv Inside of cell ATP ADP P 4. Describe the cellular structure shown in detail in Model Identify each of these symbols in Model Consider Model 2. a. Which side of the membrane has more sodium ions when the neuron is at rest? b. Briefly explain why sodium ions cannot cross the membrane without the use of a protein channel. c. Which direction should sodium ions flow naturally if a channel is provided? 2 POGIL Activities for AP* Biology
3 7. Consider Model 2. a. Which side of the membrane has more potassium ions when the neuron is at rest? b. Which direction should potassium ions flow naturally if a channel is provided? 8. The embedded proteins in Model 2 illustrate both active and passive transport. What evidence from Model 2 supports the idea that one of the types of embedded proteins use active transport? 9. Does the sodium/potassium ion pump move sodium ions into or out of the cell when activated? 10. Does the sodium/potassium ion pump move potassium ions into or out of the cell when activated? 11. What is the ratio of sodium ions to potassium ions that are moved through the sodium/ potassium ion pump each cycle? 12. If the sodium/potassium ion pump were to stop functioning, what would eventually happen to the concentration gradients of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane? Justify your answer with evidence from Model The diagram in Model 2 shows a voltage or potential across the membrane. a. What is the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (Be sure to include units.) b. Propose an explanation for why there is an uneven distribution of charge across the membrane, resulting in a potential. Neuron Structure 3
4 Read This! When a neuron is at rest, it is constantly pumping sodium ions out and potassium ions in to maintain a potential across the membrane of about 70 millivolts. The outside of the neuron has a slightly positive charge, the inside a slightly negative charge. The potassium/sodium ion pump process must be continuous as the ions will leak back in or out in the direction of the concentration gradient. The resulting membrane potential is caused by a combination of factors including the relative number of positive and negative ions on each side of the membrane and the properties of the ion channels themselves. In this state the neuron is always ready to quickly respond to a stimulus. Model 3 Membrane Potential Gradient K + Na + Outside of cell +40 mv 20 mv 70 mv Inside of cell Ligand 14. The protein channel illustrated in Model 3 is a ligand-gated channel. What must occur for the gate to open and allow movement of ions across the membrane? 15. Consider Model 3. a. What type of ions, sodium or potassium, are moving through the ligand-gated protein channel when it is open? b. Are the ions moving against the original concentration gradient or with the original concentration gradient? c. Is the transport of ions across the membrane active or passive transport? Justify your reasoning. 4 POGIL Activities for AP* Biology
5 16. When the gated channel is open and ions flood through, does the concentration of that ion species inside of the cell increase, decrease or stay the same a. in the immediate vicinity of the protein channel? b. in the area further away from the protein channel? 17. What will happen to the ions that entered the cell through the gated channel in the time that follows the closing of the channel? (Recall this is the same membrane that contains the embedded proteins from Model 2.) 18. Examine the voltage readings across the membrane in Model 3. How does the flood of ions through the gated channel affect the membrane potential a. in the immediate vicinity of the protein channel? b. in the area further away from the protein channel? 19. What will happen to the membrane potential in the time that follows the closing of the channel? 20. The shapes of some proteins are dependent on the electrical potential in the surrounding area. Predict what might happen to such a protein if it was near one of the gated protein channels as it opened. Neuron Structure 5
6 Extension Questions 21. Extreme athletes use sports drinks not only to hydrate but also to replenish the electrolytes (ions) in their body that are lost through sweat. Propose some reasons why this would be necessary to keep an athlete healthy and in top condition. 22. How long is the longest neuron in the human body, and where is it located? 6 POGIL Activities for AP* Biology
Transmission of Nerve Impulses (see Fig , p. 403)
 How a nerve impulse works Transmission of Nerve Impulses (see Fig. 12.13, p. 403) 1. At Rest (Polarization) outside of neuron is positively charged compared to inside (sodium ions outside, chloride and
How a nerve impulse works Transmission of Nerve Impulses (see Fig. 12.13, p. 403) 1. At Rest (Polarization) outside of neuron is positively charged compared to inside (sodium ions outside, chloride and
Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers.
 The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
Neurons and Nervous Systems
 34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals?
 LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
Intro and Homeostasis
 Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
The Nervous System. Nerve Impulses. Resting Membrane Potential. Overview. Nerve Impulses. Resting Membrane Potential
 The Nervous System Overview Nerve Impulses (completed12/03/04) (completed12/03/04) How do nerve impulses start? (completed 19/03/04) (completed 19/03/04) How Fast are Nerve Impulses? Nerve Impulses Nerve
The Nervous System Overview Nerve Impulses (completed12/03/04) (completed12/03/04) How do nerve impulses start? (completed 19/03/04) (completed 19/03/04) How Fast are Nerve Impulses? Nerve Impulses Nerve
Converting energy into nerve impulses, resting potentials and action potentials Sensory receptors
 D 1.3 s Converting energy into nerve impulses, resting potentials and action potentials Sensory receptors A receptor converts an external or internal stimulus into an electrical signal. Sensory receptors
D 1.3 s Converting energy into nerve impulses, resting potentials and action potentials Sensory receptors A receptor converts an external or internal stimulus into an electrical signal. Sensory receptors
Curtis et al. Il nuovo Invito alla biologia.blu BIOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS KEYS
 BIOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS KEYS Watch the videos and download the transcripts of this section at: online.scuola.zanichelli.it/curtisnuovoinvitoblu/clil > THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 2. WARM UP a) The structures that
BIOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS KEYS Watch the videos and download the transcripts of this section at: online.scuola.zanichelli.it/curtisnuovoinvitoblu/clil > THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 2. WARM UP a) The structures that
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34
 NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
Action Potentials & Nervous System. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials & Nervous System Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review: Membrane potentials exist due to unequal distribution of charge across the membrane Concentration gradients drive ion
Action Potentials & Nervous System Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review: Membrane potentials exist due to unequal distribution of charge across the membrane Concentration gradients drive ion
The Nervous System. Nervous System Organization. Nerve Tissue. Two parts to the nervous system 11/27/2016
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
Nerves and their impulses. Biology 12 C-11
 Nerves and their impulses Biology 12 C-11 Nerves and their impulses Nerves are designed to transmit electrical impulses from the dendrites, over the cell body and through the axon. The impulse will then
Nerves and their impulses Biology 12 C-11 Nerves and their impulses Nerves are designed to transmit electrical impulses from the dendrites, over the cell body and through the axon. The impulse will then
Particles with opposite charges (positives and negatives) attract each other, while particles with the same charge repel each other.
 III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
Nerve Signal Conduction. Resting Potential Action Potential Conduction of Action Potentials
 Nerve Signal Conduction Resting Potential Action Potential Conduction of Action Potentials Resting Potential Resting neurons are always prepared to send a nerve signal. Neuron possesses potential energy
Nerve Signal Conduction Resting Potential Action Potential Conduction of Action Potentials Resting Potential Resting neurons are always prepared to send a nerve signal. Neuron possesses potential energy
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump
 The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
Membrane Potentials. Why are some cells electrically active? Model 1: The Sodium/Potassium pump. Critical Thinking Questions
 Membrane Potentials Model 1: The Sodium/Potassium pump Why are some cells electrically active? 1. What ion is being moved out of the cell according to model 1? a. How many of these are being moved out?
Membrane Potentials Model 1: The Sodium/Potassium pump Why are some cells electrically active? 1. What ion is being moved out of the cell according to model 1? a. How many of these are being moved out?
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) innervate Divisions: a. Afferent
 Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Neurochemistry 1. Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906
 Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
Control and Integration. Nervous System Organization: Bilateral Symmetric Animals. Nervous System Organization: Radial Symmetric Animals
 Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons
< Eyes < Ears < Skin < And elsewhere Ú And commands are sent out to response unitsl
 Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Dr. Van Cantfort Neural Communication Neural Communication Nerve cells are specialized for generating and moving information around in the nervous system. These two simple
Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Dr. Van Cantfort Neural Communication Neural Communication Nerve cells are specialized for generating and moving information around in the nervous system. These two simple
Membrane Structure and Function POGIL
 Why? Membrane Structure and Function POGIL Advertisements for sports drinks, such as Gatorade, Powerade, and Vitaminwater seem to be everywhere. All of these drinks are supposed to help your body recover
Why? Membrane Structure and Function POGIL Advertisements for sports drinks, such as Gatorade, Powerade, and Vitaminwater seem to be everywhere. All of these drinks are supposed to help your body recover
Biology September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY
 Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY
 Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
General Physics. Nerve Conduction. Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power. Fluids. Direct Current (DC)
 Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Neurophysiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Chapter 9. Nerve Signals and Homeostasis
 Chapter 9 Nerve Signals and Homeostasis A neuron is a specialized nerve cell that is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neural signaling communication by neurons is the process by which an animal
Chapter 9 Nerve Signals and Homeostasis A neuron is a specialized nerve cell that is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neural signaling communication by neurons is the process by which an animal
ACTION POTENTIAL. Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil
 ACTION POTENTIAL Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil DEFINITIONS: Stimulus: A stimulus is an external force or event which when applied to an excitable tissue produces a characteristic response. Subthreshold
ACTION POTENTIAL Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil DEFINITIONS: Stimulus: A stimulus is an external force or event which when applied to an excitable tissue produces a characteristic response. Subthreshold
Ch 33. The nervous system
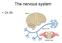 Ch 33 The nervous system AP bio schedule Tuesday Wed Thursday Friday Plant test Animal behavior lab Nervous system 25 Review Day (bring computer) 27 Review Day (bring computer) 28 Practice AP bio test
Ch 33 The nervous system AP bio schedule Tuesday Wed Thursday Friday Plant test Animal behavior lab Nervous system 25 Review Day (bring computer) 27 Review Day (bring computer) 28 Practice AP bio test
Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1
 Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1 Objectives: Describe the Cells of the NS Explain the creation and propagation of an electrical signal in a nerve
Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1 Objectives: Describe the Cells of the NS Explain the creation and propagation of an electrical signal in a nerve
SUMMARY OF THE EVENTS WHICH TRIGGER AN ELECTRICAL IMPUSLE IN NERVE CELLS (see figures on the following page)
 Anatomy and Physiology/AP Biology ACTION POTENTIAL SIMULATION BACKGROUND: The plasma membrane of cells is a selectively permeable barrier, which separates the internal contents of the cell from the surrounding
Anatomy and Physiology/AP Biology ACTION POTENTIAL SIMULATION BACKGROUND: The plasma membrane of cells is a selectively permeable barrier, which separates the internal contents of the cell from the surrounding
Nimble Nerve Impulses OO-005-DOWN
 Nimble Nerve Impulses OO-005-DOWN We d love to hear any feedback, comments or questions you have! Please email us: info@ Find us on Facebook: facebook.com/origamiorganelles Thanks for purchasing an Origami
Nimble Nerve Impulses OO-005-DOWN We d love to hear any feedback, comments or questions you have! Please email us: info@ Find us on Facebook: facebook.com/origamiorganelles Thanks for purchasing an Origami
Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works
 Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works Essential Knowledge Statement 3.E.2 Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and
Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works Essential Knowledge Statement 3.E.2 Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and
Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Neural Conduction. biologyaspoetry.com
 Neural Conduction biologyaspoetry.com Resting Membrane Potential -70mV A cell s membrane potential is the difference in the electrical potential ( charge) between the inside and outside of the cell. The
Neural Conduction biologyaspoetry.com Resting Membrane Potential -70mV A cell s membrane potential is the difference in the electrical potential ( charge) between the inside and outside of the cell. The
Channels can be activated by ligand-binding (chemical), voltage change, or mechanical changes such as stretch.
 1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics. Eileen Nugent
 Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11 Part B Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 11.4 Membrane
Chapter 11 Part B Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 11.4 Membrane
Nervous System: Part III How the Neuron Works: RESTING VS. ACTION POTENTIAL
 Nervous System: Part III How the Neuron Works: RESTING VS. ACTION POTENTIAL 1 RESTING VS. ACTION POTENTIAL 2 How does a neuron cause the transmission of informa4on? 3 Cells: surrounded by charged ions
Nervous System: Part III How the Neuron Works: RESTING VS. ACTION POTENTIAL 1 RESTING VS. ACTION POTENTIAL 2 How does a neuron cause the transmission of informa4on? 3 Cells: surrounded by charged ions
Nervous System AP Biology
 Nervous System 2007-2008 Why do animals need a nervous system? What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? fast accurate reset quickly Remember Poor think bunny! about the bunny signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 Why do animals need a nervous system? What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? fast accurate reset quickly Remember Poor think bunny! about the bunny signal direction
Biology I Photosynthesis. O + sunlight energy C 6. Outer membrane. Inner membrane
 Name: Why? Biology I Photosynthesis How do light-dependent and light-independent reactions provide food for a plant? Plants are the original solar panels. Through photosynthesis a plant is able to convert
Name: Why? Biology I Photosynthesis How do light-dependent and light-independent reactions provide food for a plant? Plants are the original solar panels. Through photosynthesis a plant is able to convert
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
NOTES: CH 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 NOTES: CH 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling A nervous system has three overlapping functions: 1) SENSORY INPUT: signals from sensory receptors to integration centers 2) INTEGRATION: information from
NOTES: CH 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling A nervous system has three overlapping functions: 1) SENSORY INPUT: signals from sensory receptors to integration centers 2) INTEGRATION: information from
Neuron Func?on. Principles of Electricity. Defini?ons 2/6/15
 Neuron Func?on 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part B Neurons are highly Respond to adequate s?mulus by genera?ng an ac?on poten?al (nerve impulse) Impulse is always the regardless
Neuron Func?on 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part B Neurons are highly Respond to adequate s?mulus by genera?ng an ac?on poten?al (nerve impulse) Impulse is always the regardless
Neurons. General neuron anatomy. BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 7 Neurons. Nervous system:
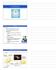 BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 7 Neurons Nervous system: Neurons Integrates and coordinates the body s ac3vi3es Provides rapid and brief responses to s3muli Major divisions: Central nervous system (CNS) brain
BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 7 Neurons Nervous system: Neurons Integrates and coordinates the body s ac3vi3es Provides rapid and brief responses to s3muli Major divisions: Central nervous system (CNS) brain
QUESTION? Communication between neurons depends on the cell membrane. Why is this so?? Consider the structure of the membrane.
 QUESTION? Communication between neurons depends on the cell membrane Why is this so?? Consider the structure of the membrane. ECF ICF Possible ANSWERS?? Membrane Ion Channels and Receptors: neuron membranes
QUESTION? Communication between neurons depends on the cell membrane Why is this so?? Consider the structure of the membrane. ECF ICF Possible ANSWERS?? Membrane Ion Channels and Receptors: neuron membranes
Lecture 2. Excitability and ionic transport
 Lecture 2 Excitability and ionic transport Selective membrane permeability: The lipid barrier of the cell membrane and cell membrane transport proteins Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular
Lecture 2 Excitability and ionic transport Selective membrane permeability: The lipid barrier of the cell membrane and cell membrane transport proteins Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I 26 September 2002 NAME
 437 EXAM1.DOC Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I 26 September 2002 NAME 0. When you gaze at the stars, why do you have to look slightly away from the really faint ones in order to be able to see them? (1
437 EXAM1.DOC Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I 26 September 2002 NAME 0. When you gaze at the stars, why do you have to look slightly away from the really faint ones in order to be able to see them? (1
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Responses, Nervous System & Muscles
 thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Responses, Nervous System & Muscles 1 Response Mechanism tropism Definition A growth movement of part of plant in response to a directional stimulus examples Positive:
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Responses, Nervous System & Muscles 1 Response Mechanism tropism Definition A growth movement of part of plant in response to a directional stimulus examples Positive:
Universality of sensory-response systems
 excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
BIOLOGY 11/10/2016. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Concept 48.1: Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
Information processing. Divisions of nervous system. Neuron structure and function Synapse. Neurons, synapses, and signaling 11/3/2017
 Neurons, synapses, and signaling Chapter 48 Information processing Divisions of nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Brain and a nerve cord Integration center Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Nerves
Neurons, synapses, and signaling Chapter 48 Information processing Divisions of nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Brain and a nerve cord Integration center Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Nerves
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
Nervous & Endocrine System
 3/19 HW Day 1 Read pages 897-900 Complete Vocab. on pg 897 Aim: What is Regulation? Do Now: What 2 organ systems are involved in regulation? Nervous & Endocrine System Regulation: The control and coordination
3/19 HW Day 1 Read pages 897-900 Complete Vocab. on pg 897 Aim: What is Regulation? Do Now: What 2 organ systems are involved in regulation? Nervous & Endocrine System Regulation: The control and coordination
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Membrane Protein Channels
 Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
 Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials Nerve and muscle cells: Excitable Capable of generating rapidly changing electrochemical impulses at their membranes
Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials Nerve and muscle cells: Excitable Capable of generating rapidly changing electrochemical impulses at their membranes
Cells have an unequal distribution of charge across their membrane: more postiive charges on the outside; more negative charges on the inside.
 Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary
 2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function
 Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function Integration An animal needs to function like a coherent organism, not like a loose collection of cells. Integration = refers to processes such as summation
Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function Integration An animal needs to function like a coherent organism, not like a loose collection of cells. Integration = refers to processes such as summation
Nervous system. 3 Basic functions of the nervous system !!!! !!! 1-Sensory. 2-Integration. 3-Motor
 Nervous system 3 Basic functions of the nervous system 1-Sensory 2-Integration 3-Motor I. Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord I. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 2) Afferent towards afferent
Nervous system 3 Basic functions of the nervous system 1-Sensory 2-Integration 3-Motor I. Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord I. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 2) Afferent towards afferent
Chapter 7-3 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter 7-3 Cells and Their Environment 7-3 Passive Transport Passive transport-the movement of substances across the cell membrane without using NRG Concentration Gradient-difference in concentration
Chapter 7-3 Cells and Their Environment 7-3 Passive Transport Passive transport-the movement of substances across the cell membrane without using NRG Concentration Gradient-difference in concentration
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Action Potential Propagation
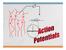 Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
The Nervous System. What did you learn at school today? Neurophysiology!
 The Nervous System What did you learn at school today? Neurophysiology! The Nervous System Controls heart rate, emotions, memories, consciousness, and much more. The most intricate and beautifully complex
The Nervous System What did you learn at school today? Neurophysiology! The Nervous System Controls heart rate, emotions, memories, consciousness, and much more. The most intricate and beautifully complex
Electrical Signaling. Lecture Outline. Using Ions as Messengers. Potentials in Electrical Signaling
 Lecture Outline Electrical Signaling Using ions as messengers Potentials in electrical signaling Action Graded Other electrical signaling Gap junctions The neuron Using Ions as Messengers Important things
Lecture Outline Electrical Signaling Using ions as messengers Potentials in electrical signaling Action Graded Other electrical signaling Gap junctions The neuron Using Ions as Messengers Important things
BIOLOGY. 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Communication in Neurons
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
Biomedical Instrumentation
 ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Membrane Physiology. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Oct-18 1
 Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Chapt. 12, Movement Across Membranes. Chapt. 12, Movement through lipid bilayer. Chapt. 12, Movement through lipid bilayer
 Chapt. 12, Movement Across Membranes Two ways substances can cross membranes Passing through the lipid bilayer Passing through the membrane as a result of specialized proteins 1 Chapt. 12, Movement through
Chapt. 12, Movement Across Membranes Two ways substances can cross membranes Passing through the lipid bilayer Passing through the membrane as a result of specialized proteins 1 Chapt. 12, Movement through
Questions: Properties of excitable tissues Transport across cell membrane Resting potential Action potential Excitability change at excitation
 Questions: Properties of excitable tissues Transport across cell membrane Resting potential Action potential Excitability change at excitation EXCITABLE TISSUES The tissues can change the properties under
Questions: Properties of excitable tissues Transport across cell membrane Resting potential Action potential Excitability change at excitation EXCITABLE TISSUES The tissues can change the properties under
Ch 7. The Nervous System 7.1 & 7.2
 Ch 7 The Nervous System 7.1 & 7.2 SLOs Describe the different types of neurons and supporting cells, and identify their functions. Identify the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the CNS and
Ch 7 The Nervous System 7.1 & 7.2 SLOs Describe the different types of neurons and supporting cells, and identify their functions. Identify the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the CNS and
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 12, PAGE 1 of 7
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 12, 2009 -- PAGE 1 of 7 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 12, 2009 -- PAGE 1 of 7 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Lines of Communication
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 37 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Lines of Communication
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.
 Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 6 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Action Potentials NeuroPhysiology TextBook Readings Pages 400 through 408 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words!
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 6 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Action Potentials NeuroPhysiology TextBook Readings Pages 400 through 408 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words!
BIOL Week 5. Nervous System II. The Membrane Potential. Question : Is the Equilibrium Potential a set number or can it change?
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System II 1 The Membrane Potential Question : Is the Equilibrium Potential a set number or can it change? Let s look at the Nernst Equation again.
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System II 1 The Membrane Potential Question : Is the Equilibrium Potential a set number or can it change? Let s look at the Nernst Equation again.
Unit 5: Cells Mr. Nagel Meade High School
 Unit 5: Cells Mr. Nagel Meade High School Hierarchy of Biology Organize the following from smallest to greatest: Tissue, atom, organism, organelle, organ, population, cell, community, ecosystem, organ
Unit 5: Cells Mr. Nagel Meade High School Hierarchy of Biology Organize the following from smallest to greatest: Tissue, atom, organism, organelle, organ, population, cell, community, ecosystem, organ
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes.
 1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
Neurons and the membrane potential. N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016
 Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p.
 Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Test 2: Cell Structure and Function
 Name Test 2: Cell Structure and Function Date 1. Our bodies are made of, which are made up of many different parts and are the basic units of life. 1. a. cells b. organelles c. molecules d. proteins 2.
Name Test 2: Cell Structure and Function Date 1. Our bodies are made of, which are made up of many different parts and are the basic units of life. 1. a. cells b. organelles c. molecules d. proteins 2.
Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY POWERPOINT
 POWERPOINT LECTURE SLIDE PRESENTATION by LYNN CIALDELLA, MA, MBA, The University of Texas at Austin Additional text by J Padilla exclusively for physiology at ECC UNIT 2 8 Neurons: PART A Cellular and
POWERPOINT LECTURE SLIDE PRESENTATION by LYNN CIALDELLA, MA, MBA, The University of Texas at Austin Additional text by J Padilla exclusively for physiology at ECC UNIT 2 8 Neurons: PART A Cellular and
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Hodgkin-Huxley Model for Nerve Cell Action Potential Part 1 Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 References Hoppensteadt-Peskin Ch. 3 for all the mathematics. Cooper s The Cell
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Hodgkin-Huxley Model for Nerve Cell Action Potential Part 1 Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 References Hoppensteadt-Peskin Ch. 3 for all the mathematics. Cooper s The Cell
Purpose: Perception, Movement, Learning, Memory, Thinking, Communication Functions:
 Nervous System Purpose: Perception, Movement, Learning, Memory, Thinking, Communication Functions: Sensory Input: Obtaining stimulation from the environment (light, heat, pressure, vibration, chemical,
Nervous System Purpose: Perception, Movement, Learning, Memory, Thinking, Communication Functions: Sensory Input: Obtaining stimulation from the environment (light, heat, pressure, vibration, chemical,
MEMBRANE POTENTIALS AND ACTION POTENTIALS:
 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical students, 2017/2018 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Review: Membrane physiology
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical students, 2017/2018 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Review: Membrane physiology
7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 4
 MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel NAME TA 7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 4 FRIDAY April 8th,
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel NAME TA 7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 4 FRIDAY April 8th,
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
