A Specialized Version of the HD Hydrolase Domain Implicated in Signal Transduction
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(2): JMMB Correspondence The HD Hydrolase Domain in Signal Transduction 303 A Specialized Version of the HD Hydrolase Domain Implicated in Signal Transduction Michael Y. Galperin*, Darren A. Natale, L. Aravind, and Eugene V. Koonin National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20894, USA Recently, a superfamily of proteins containing a previously undetected domain with predicted metal-dependent phosphohydrolase activity has been described and designated the HD superfamily, after the principal conserved residues implicated in catalysis (Aravind and Koonin, 1998). In the course of our analysis of ancient conserved regions in microbial genomes (Koonin et al., 1998), we found a distinct version of this domain which is encoded in one to three copies in the genomes of Aquifex aeolicus, Borrelia burgdorferi, Synechocystis sp. and Treponema pallidum, but is dramatically expanded in the genomes of Thermotoga maritima and Clostridium acetobutylicum (Figure 1). Compared with the consensus HD domain (Aravind and Koonin, 1998), this version contains a number of additional highly conserved residues; hereinafter we refer to it as the HD-GYP domain, after the characteristic sequence signatures (Figure 1). This domain was also detected in previously uncharacterized proteins from Wolinella succinogenes (Kreis-Kleinschmidt et al., 1995), Bacillus halodurans (Takami et al., 1999), Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bordetella pertussis (Figure 1). The HD- GYP domain is missing in E. coli and B. subtilis. Remarkably, however, in other γ-proteobacteria, such as Shewanella putrefaciens and Vibrio cholerae, it is present in up to 8 copies (data not shown). While none of the proteins that contain the HD-GYP domain has ever been characterized experimentally, the spectrum of the domains that are associated with HD-GYP in multidomain proteins (Figure 2) suggests that it is probably involved in signal transduction. In Synechocystis sp., both copies of the HD-GYP domain are found in proteins that also contain CheY-like receiver domains of the twocomponent signal transduction system (Pao and Saier, 1995; Volz and Matsumura, 1991). A similar CheY HD- GYP domain organization is found in two T. maritima proteins, TM0186 and TM1147 (Figure 2). Two other proteins from T. maritima, TM1170 and TM1682, combine the HD- GYP domain with extracytoplasmic ligand-binding domains, which are closely related, respectively, to periplasmic solute-binding protein components of the ATP-dependent transport systems (Tam and Saier, 1993) and the extracytoplasmic part of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Bacillus subtilis, such as McpA and McpB (Hanlon and Ordal, 1994). Such a combination of an Received October 4, 1999; accepted October 4, *For correspondence. galperin@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov; Tel ; Fax extracytoplasmic ligand-binding domain and a cytoplasmic HD-GYP domain, connected by a transmembrane segment, has the same topology as methyl-accepting proteins and many sensor kinases, which further supports the participation of the HD-GYP domain in signal transduction. Finally, in the Aq_2027 protein from A. aeolicus, the HD-GYP domain is found together with the GGDEF domain (Figure 2). The latter domain has been recently identified in diguanylate cyclases and phosphodiesterases involved in the regulation of cellulose synthesis in Acetobacter xylinum (Tal et al., 1998) and in a variety of bacterial signalling proteins in combination with CheY, PAS, and HAMP domains (Hecht and Newton, 1995; Aravind and Ponting, 1999). The GGDEF domain is often associated with another uncharacterized domain, EAL, in particular, in diguanylate cyclases and phosphodiesterases (Tal et al., 1998; Aravind and Ponting, 1999). Remarkably, however, the combination of the HD-GYP and EAL domains is not seen in any of the currently available microbial genomes. Moreover, the number of copies of the HD-GYP domain in complete genomes generally correlates with prevalence of the GGDEF domain over the EAL domain (Table 1). Furthermore, the HD-GYP family of HD proteins so far is lacking in archaea and eukaryotes and so are the GGDEF and EAL domains. This suggests that HD-GYP domain might be also involved in cyclic diguanylate-mediated signaling. The HD superfamily is related to the camp/ cgmp phosphodiesterases that are involved in eukaryotic signalling (Aravind and Koonin, 1998). Therefore is seems plausible that the HD-GYP family proteins are likely to possess a diguanylate phosphodiesterase activity and complement the function that, in the characterized diguanylate phosphodiesterases, is performed by the EAL domain. Table 1. Distribution of Three Domains Implicated in Signal Transduction in Complete Microbial Genomes Species a Domains GGDEF EAL HD-GYP Escherichia coli Rickettsia prowazekii Bacillus subtilis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Synechocystis sp Borellia burgdorferi Treponema pallidum 1-3 Aquifex aeolicus Thermotoga maritima 9-9 Clostridium acetobutylicum b a Genomes of bacteria Haemophilus influenzae, Helicobacter pylori, Chlamydia trachomatis, C. pneumoniae, Mycoplasma genitalium, M. pneumoniae, and archaea Methanococcus jannaschii, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Pyrococcus horikoshii, and Aeropyrum pernix do not contain any of these domains. b Preliminary data based on unfinished genome sequence ( Horizon Scientific Press
2 Further Reading Caister Academic Press is a leading academic publisher of advanced texts in microbiology, molecular biology and medical research. Full details of all our publications at caister.com MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in Microbiology Edited by: M Kostrzewa, S Schubert (2016) Aspergillus and Penicillium in the Post-genomic Era Edited by: RP Vries, IB Gelber, MR Andersen (2016) The Bacteriocins: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects Edited by: RL Dorit, SM Roy, MA Riley (2016) Omics in Plant Disease Resistance Edited by: V Bhadauria (2016) Acidophiles: Life in Extremely Acidic Environments Edited by: R Quatrini, DB Johnson (2016) Climate Change and Microbial Ecology: Current Research and Future Trends Edited by: J Marxsen (2016) Biofilms in Bioremediation: Current Research and Emerging Technologies Edited by: G Lear (2016) Microalgae: Current Research and Applications Edited by: MN Tsaloglou (2016) Gas Plasma Sterilization in Microbiology: Theory, Applications, Pitfalls and New Perspectives Edited by: H Shintani, A Sakudo (2016) Virus Evolution: Current Research and Future Directions Edited by: SC Weaver, M Denison, M Roossinck, et al. (2016) Arboviruses: Molecular Biology, Evolution and Control Edited by: N Vasilakis, DJ Gubler (2016) Shigella: Molecular and Cellular Biology Edited by: WD Picking, WL Picking (2016) Aquatic Biofilms: Ecology, Water Quality and Wastewater Treatment Edited by: AM Romaní, H Guasch, MD Balaguer (2016) Alphaviruses: Current Biology Edited by: S Mahalingam, L Herrero, B Herring (2016) Thermophilic Microorganisms Edited by: F Li (2015) Flow Cytometry in Microbiology: Technology and Applications Edited by: MG Wilkinson (2015) Probiotics and Prebiotics: Current Research and Future Trends Edited by: K Venema, AP Carmo (2015) Epigenetics: Current Research and Emerging Trends Edited by: BP Chadwick (2015) Corynebacterium glutamicum: From Systems Biology to Biotechnological Applications Edited by: A Burkovski (2015) Advanced Vaccine Research Methods for the Decade of Vaccines Edited by: F Bagnoli, R Rappuoli (2015) Antifungals: From Genomics to Resistance and the Development of Novel Agents Edited by: AT Coste, P Vandeputte (2015) Bacteria-Plant Interactions: Advanced Research and Future Trends Edited by: J Murillo, BA Vinatzer, RW Jackson, et al. (2015) Aeromonas Edited by: J Graf (2015) Antibiotics: Current Innovations and Future Trends Edited by: S Sánchez, AL Demain (2015) Leishmania: Current Biology and Control Edited by: S Adak, R Datta (2015) Acanthamoeba: Biology and Pathogenesis (2nd edition) Author: NA Khan (2015) Microarrays: Current Technology, Innovations and Applications Edited by: Z He (2014) Metagenomics of the Microbial Nitrogen Cycle: Theory, Methods and Applications Edited by: D Marco (2014) Order from caister.com/order
3 304 Galperin et al. Figure 1. Multiple alignment of HD GYP domains. The proteins are listed under their names in complete genomes (left column) and their unique gene identification (gi) numbers in the GenBank protein database (right column); the numbers indicate positions of the first and the last residues in each protein, where available, and the distances between the aligned segments. Species name abbreviations are as follows: Aq, Aquifex aeolicus; Bb, Borrelia burgdorferi; Bhal, Bacillus halodurans; Cl.acetobut., Clostridium acetobutylicum; Sy, Synechocystis sp., Tma, Thermotoga maritima; Tpa, Treponema pallidum; Vcho, Vibrio cholerae; Wsuc, Wolinella succinogenes. Reverse shading indicates most conserved amino acid residues that are probably involved in metal and/or substrate binding. Grey shading indicates conserved uncharged amino acid residues, other conserved residues are in bold. The secondary structure of the HD domain is as predicted by PHDsec program (Rost and Sander, 1993); H indicates predicted α-helical segments, dash indicates a loop or the absence of confident prediction.
4 The HD Hydrolase Domain in Signal Transduction 305 Figure 2. Association of HD-GYP domain with other signaling domains. CheY domain (Pao and Saier, 1995; Volz and Matsumura, 1991) and the periplasmic ligand-binding domain of TM1170 (Vyas et al., 1988) are well characterized; GGDEF domain (Hecht and Newton, 1995; Tal et al., 1998) and the MCP-like extracellular ligand-binding domain of TM1682 (Hanlon and Ordal, 1994) are less studied. The transmembrane portion of TM1467 does not show significant similarity to any characterized membrane protein. Such a function is compatible with the high sequence conservation of this domain as well as its unusual expansion in certain genomes. Indeed, cyclic diguanylate stimulates cellulose synthesis in Acetobacter xylinum in response to the lack of oxygen (Ross et al., 1991). Similarly, multiple HD-GYP domains in T. maritima, C. acetobutylicum, S. putrefaciens and V. cholerae might be involved in signalling the availability of various electron acceptors, including iron and sulfur (Nealson and Saffarini, 1994; Vargas et al., 1998). Remarkably, sugar metabolism in Thermotoga neapolitana has been found to be subject to catabolite repression (Galperin et al., 1997; Vargas and Noll, 1996), although this organism is devoid of the PTS system (Galperin et al., 1996; Nelson et al., 1999) and contains negligible amounts of camp (Vargas and Noll, 1996). Thus preferential utilization of certain sugars (e.g., glucose) in Thermotoga should be regulated by an elaborate regulatory system different from those found in, for example, E. coli or B. subtilis. Whatever its exact function, the HD-GYP domain is likely to play a crucial role in this novel regulatory mechanism. Acknowledgements Analysis of unfinished genome sequences was made possible by generous submission to the public databases of preliminary sequence data by Genome Therapeutics (C. acetobutylicum), the Sanger Centre (B. pertussis), The Institute for Genome Research (S. putrefaciens, V. cholerae) and the Pseudomonas sequencing project (P. aeruginosa). References Aravind, L., and E. V. Koonin The HD domain defines a new superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23: Aravind, L., and Ponting, C.P The cytoplasmic helical linker domain of receptor histidine kinase and methyl-accepting proteins is common to many prokaryotic signalling proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 176: Galperin, M. Y., K. M. Noll, and A. H. Romano The glucose transport system of the hyperthermophilic anaerobic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: Galperin, M. Y., K. M. Noll, and A. H. Romano Coregulation of betagalactoside uptake and hydrolysis by the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: Hanlon, D. W., and G. W. Ordal Cloning and characterization of genes encoding methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem. 269: Hecht, G. B., and A. Newton Identification of a novel response regulator required for the swarmer- to-stalked-cell transition in Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 177: Koonin, E. V., R. L. Tatusov, and M. Y. Galperin Beyond the complete genomes: from sequences to structure and function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8: Kreis-Kleinschmidt, V., F. Fahrenholz, E. Kojro, and A. Kroger Periplasmic sulphide dehydrogenase (Sud) from Wolinella succinogenes: isolation, nucleotide sequence of the sud gene and its expression in Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 227: Nealson, K. H., and D. Saffarini Iron and manganese in anaerobic respiration: environmental significance, physiology, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 48: Nelson, K. E., R. A. Clayton, S. R. Gill, M. L. Gwinn, R. J. Dodson, D. H. Haft, E. K. Hickey, J. D. Peterson, W. C. Nelson, K. A. Ketchum, L. McDonald, T. R. Utterback, J. A. Malek, K. D. Linher, M. M. Garrett, A. M. Stewart, M. D. Cotton, M. S. Pratt, C. A. Phillips, D. Richardson, J. Heidelberg, G. G. Sutton, R. D. Fleischmann, J. A. Eisen, and C. M. Fraser Evidence for lateral gene transfer between Archaea and bacteria from genome sequence of Thermotoga maritima. Nature. 399: Pao, G. M., and M. H. Saier, Jr Response regulators of bacterial signal transduction systems: selective domain shuffling during evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 40: Ponting, C. P., J. Schultz, F. Milpetz, and P. Bork SMART: identification and annotation of domains from signalling and extracellular protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 27: Ross, P., Mayer, R., and Benziman, M Cellulose biosynthesis and function in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 55: Rost, B., and C. Sander Prediction of protein secondary structure at better than 70% accuracy. J. Mol. Biol. 232: Takami, H., N. Masui, K. Nakasone, and K. Horikoshi Replication origin region of the chromosome of alkaliphilic Bacillus halodurans C Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63: Tal, R., H. C. Wong, R. Calhoon, D. Gelfand, A. L. Fear, G. Volman, R. Mayer, P. Ross, D. Amikam, H. Weinhouse, A. Cohen, S. Sapir, P. Ohana, and M. Benziman Three cdg operons control cellular turnover of cyclic di-gmp in Acetobacter xylinum: genetic organization and occurrence of conserved domains in isoenzymes. J. Bacteriol. 180: Tam, R., and M. H. Saier, Jr Structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships among extracellular solute-binding receptors of bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 57: Vargas, M., K. Kashefi, E. L. Blunt-Harris, and D. R. Lovley Microbiological evidence for Fe(III) reduction on early Earth. Nature. 395: Vargas, M., and K. M. Noll Catabolite repression in the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana is independent of camp. Microbiology. 142: Volz, K., and P. Matsumura Crystal structure of Escherichia coli CheY refined at 1.7-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 266: Vyas, N. K., M. N. Vyas, and F. A. Quiocho Sugar and signal-transducer binding sites of the Escherichia coli galactose chemoreceptor protein. Science. 242:
5 306 Galperin et al.
A Novel Ubiquitous Family of Putative Efflux Transporters
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(2): 195-198. JMMB Communication Putative Efflux Transporters 195 A Novel Ubiquitous Family of Putative Efflux Transporters Kevin T. Harley and Milton H. Saier, Jr.*
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(2): 195-198. JMMB Communication Putative Efflux Transporters 195 A Novel Ubiquitous Family of Putative Efflux Transporters Kevin T. Harley and Milton H. Saier, Jr.*
Bacterial Homologs of the Small Subunit of Eukaryotic DNA Primase
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 509-512. JMMB Communication Primases 509 Bacterial Homologs of the Small Subunit of Eukaryotic DNA Primase Eugene V. Koonin*, Yuri I. Wolf, Alexy S. Kondrashov
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 509-512. JMMB Communication Primases 509 Bacterial Homologs of the Small Subunit of Eukaryotic DNA Primase Eugene V. Koonin*, Yuri I. Wolf, Alexy S. Kondrashov
ABCdb: an ABC Transporter Database
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 501-504. JMMB Bioinformatics Corner ABCdb: an ABC Transporter Database 501 ABCdb: an ABC Transporter Database Yves Quentin* and Gwennaele Fichant Laboratoire
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 501-504. JMMB Bioinformatics Corner ABCdb: an ABC Transporter Database 501 ABCdb: an ABC Transporter Database Yves Quentin* and Gwennaele Fichant Laboratoire
Prediction of Two- and Three-Amino-Acid Sequences of Citrobacter Freundii ß-Lactamase from its Amino Acid Composition
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(3): 277-281. JMMB Prediction Research and ß-Lactamase Article 277 Prediction of Two- and Three-Amino-Acid Sequences of Citrobacter Freundii ß-Lactamase from its
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(3): 277-281. JMMB Prediction Research and ß-Lactamase Article 277 Prediction of Two- and Three-Amino-Acid Sequences of Citrobacter Freundii ß-Lactamase from its
Regulation of Galactoside Transport by the PTS
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 381-384. JMMB Symposium PTS Regulation of Galactoside Transport 381 Regulation of Galactoside Transport by the PTS Masayuki Kuroda 1,2, Thomas H. Wilson 3, and
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 381-384. JMMB Symposium PTS Regulation of Galactoside Transport 381 Regulation of Galactoside Transport by the PTS Masayuki Kuroda 1,2, Thomas H. Wilson 3, and
Sensory Transduction to the Flagellar Motor of Sinorhizobium meliloti
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 183 186. JMMB Symposium Sensory Transduction to the Flagellar Motor of Sinorhizobium meliloti Birgit Scharf and Rüdiger Schmitt* Lehrstuhl für Genetik, Universität
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 183 186. JMMB Symposium Sensory Transduction to the Flagellar Motor of Sinorhizobium meliloti Birgit Scharf and Rüdiger Schmitt* Lehrstuhl für Genetik, Universität
The Ostensible Paradox of Multidrug Recognition
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 151-154. JMMB Symposium Multidrug Recognition 151 The Ostensible Paradox of Multidrug Recognition Alex A. Neyfakh* Center for Pharmaceutical Biotechnology (M/C
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 151-154. JMMB Symposium Multidrug Recognition 151 The Ostensible Paradox of Multidrug Recognition Alex A. Neyfakh* Center for Pharmaceutical Biotechnology (M/C
AcrAB and Related Multidrug Efflux Pumps of Escherichia coli
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 215-218. JMMB Symposium Multidrug Efflux Pumps of E. coli 215 AcrAB and Related Multidrug Efflux Pumps of Escherichia coli Hiroshi Nikaido* and Helen I. Zgurskaya
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 215-218. JMMB Symposium Multidrug Efflux Pumps of E. coli 215 AcrAB and Related Multidrug Efflux Pumps of Escherichia coli Hiroshi Nikaido* and Helen I. Zgurskaya
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil PHY498BIO, HW 3
 The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
Pressure Response in Deep-sea Piezophilic Bacteria
 J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 87-92. JMMB Symposium Pressure Response in Piezophilic Bacteria 87 Pressure Response in Deep-sea Piezophilic Bacteria Chiaki Kato*, and Mohammad Hassan Qureshi
J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 87-92. JMMB Symposium Pressure Response in Piezophilic Bacteria 87 Pressure Response in Deep-sea Piezophilic Bacteria Chiaki Kato*, and Mohammad Hassan Qureshi
2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission
 2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission Berend Snel, Peer Bork and Martijn A. Huynen Trends in Genetics 16 (2000) 9-11 13 Chapter 2 Introduction With the advent of complete genome sequencing,
2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission Berend Snel, Peer Bork and Martijn A. Huynen Trends in Genetics 16 (2000) 9-11 13 Chapter 2 Introduction With the advent of complete genome sequencing,
JMMB Communication. Susanne Behrens 2, Uta Meyer 1, Holger Schankin 1, Michael A. Lonetto 3,4, Ralf-Jörg Fischer 1, and Hubert Bahl 1 * Introduction
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(3): 265-269. JMMB Communication ECF Sigma Factors of Clostridium acetobutylicum 265 Identification of Two Genes Encoding Putative New Members of the ECF Subfamily
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(3): 265-269. JMMB Communication ECF Sigma Factors of Clostridium acetobutylicum 265 Identification of Two Genes Encoding Putative New Members of the ECF Subfamily
Antibacterial Activity of 4,5-Dihydroxy-2-cyclopentan-1-one (DHCP) and Cloning of a Gene Conferring DHCP Resistance in Escherichia coli
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 461-465. JMMB Communication E. coli DHCP Efflux Protein 461 Antibacterial Activity of 4,5-Dihydroxy-2-cyclopentan-1-one (DHCP) and Cloning of a Gene Conferring
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 461-465. JMMB Communication E. coli DHCP Efflux Protein 461 Antibacterial Activity of 4,5-Dihydroxy-2-cyclopentan-1-one (DHCP) and Cloning of a Gene Conferring
Regulation of Succinoglycan and Galactoglucan Biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 187 190. JMMB Symposium Regulation of Succinoglycan and Galactoglucan Biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti Anke Becker*, Silvia Rüberg, Birgit Baumgarth, Peter
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 187 190. JMMB Symposium Regulation of Succinoglycan and Galactoglucan Biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti Anke Becker*, Silvia Rüberg, Birgit Baumgarth, Peter
Conserved hypothetical proteins: new hints and new puzzles
 Comparative and Functional Genomics Comp Funct Genom 2001; 2: 14 18. Conference Paper Conserved hypothetical proteins: new hints and new puzzles Michael Y. Galperin* National Center for Biotechnology Information,
Comparative and Functional Genomics Comp Funct Genom 2001; 2: 14 18. Conference Paper Conserved hypothetical proteins: new hints and new puzzles Michael Y. Galperin* National Center for Biotechnology Information,
Evolutionary Use of Domain Recombination: A Distinction. Between Membrane and Soluble Proteins
 1 Evolutionary Use of Domain Recombination: A Distinction Between Membrane and Soluble Proteins Yang Liu, Mark Gerstein, Donald M. Engelman Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University,
1 Evolutionary Use of Domain Recombination: A Distinction Between Membrane and Soluble Proteins Yang Liu, Mark Gerstein, Donald M. Engelman Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University,
Comparative Genomics of Microbial Drug Efflux Systems
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 145-150. JMMB Symposium Genomic Analysis of Drug Efflux 145 Comparative Genomics of Microbial Drug Efflux Systems Ian T. Paulsen*,1, Joan Chen 1, Karen E. Nelson
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 145-150. JMMB Symposium Genomic Analysis of Drug Efflux 145 Comparative Genomics of Microbial Drug Efflux Systems Ian T. Paulsen*,1, Joan Chen 1, Karen E. Nelson
Evolutionary Analysis by Whole-Genome Comparisons
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 2260 2272 Vol. 184, No. 8 0021-9193/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 184.8.2260 2272.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evolutionary Analysis
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 2260 2272 Vol. 184, No. 8 0021-9193/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 184.8.2260 2272.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evolutionary Analysis
ABSTRACT. As a result of recent successes in genome scale studies, especially genome
 ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation / Thesis: COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSES OF MICROBIAL GENOMES OPERONS, PROTEIN FAMILIES AND LATERAL GENE TRANSFER. Yongpan Yan, Doctor of Philosophy, 2005 Dissertation / Thesis Directed
ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation / Thesis: COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSES OF MICROBIAL GENOMES OPERONS, PROTEIN FAMILIES AND LATERAL GENE TRANSFER. Yongpan Yan, Doctor of Philosophy, 2005 Dissertation / Thesis Directed
Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05
 1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
# shared OGs (spa, spb) Size of the smallest genome. dist (spa, spb) = 1. Neighbor joining. OG1 OG2 OG3 OG4 sp sp sp
 Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
Whole Genome Analyses of Transporters in Spirochetes: Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 393-399. Whole Genome Analyses of Transporters in Spirochetes: Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum JMMB Symposium on Spirochete Physiology Analysis of
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 393-399. Whole Genome Analyses of Transporters in Spirochetes: Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum JMMB Symposium on Spirochete Physiology Analysis of
Assessing evolutionary relationships among microbes from whole-genome analysis Jonathan A Eisen
 475 Assessing evolutionary relationships among microbes from whole-genome analysis Jonathan A Eisen The determination and analysis of complete genome sequences have recently enabled many major advances
475 Assessing evolutionary relationships among microbes from whole-genome analysis Jonathan A Eisen The determination and analysis of complete genome sequences have recently enabled many major advances
The Hydrogen-Sensing Apparatus in Ralstonia eutropha
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 255 262. JMMB Symposium The Hydrogen-Sensing Apparatus in Ralstonia eutropha Oliver Lenz, Michael Bernhard, Thorsten Buhrke, Edward Schwartz, and Bärbel Friedrich*
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 255 262. JMMB Symposium The Hydrogen-Sensing Apparatus in Ralstonia eutropha Oliver Lenz, Michael Bernhard, Thorsten Buhrke, Edward Schwartz, and Bärbel Friedrich*
Correlations between Shine-Dalgarno Sequences and Gene Features Such as Predicted Expression Levels and Operon Structures
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 2002, p. 5733 5745 Vol. 184, No. 20 0021-9193/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.20.5733 5745.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Correlations
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 2002, p. 5733 5745 Vol. 184, No. 20 0021-9193/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.20.5733 5745.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Correlations
Routes for Fructose Utilization by Escherichia coli
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 355-359. JMMB Symposium Routes for Fructose Utilization by E. coli 355 Routes for Fructose Utilization by Escherichia coli Hans L. Kornberg* Department of Biology,
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 355-359. JMMB Symposium Routes for Fructose Utilization by E. coli 355 Routes for Fructose Utilization by Escherichia coli Hans L. Kornberg* Department of Biology,
Structure-Function Relationship and Regulation of Two Bacillus subtilis DNA-Binding Proteins, HBsu and AbrB
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 323 329. JMMB Symposium Structure-Function Relationship and Regulation of Two Bacillus subtilis DNA-Binding Proteins, HBsu and AbrB Wolfgang Klein 1,2,andMohamed
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 323 329. JMMB Symposium Structure-Function Relationship and Regulation of Two Bacillus subtilis DNA-Binding Proteins, HBsu and AbrB Wolfgang Klein 1,2,andMohamed
Heme-based NO sensors. HNOX: Heme-nitric oxide/oxygen binding domain/protein Bacterial
 Heme-based sensors HX: Heme-nitric oxide/oxygen binding domain/protein Bacterial 1 J. Inorg. Biochem. 99, 892 (2005). Soluble guanylate cyclase (sgc) is a nitric oxide () sensing hemoprotein that has been
Heme-based sensors HX: Heme-nitric oxide/oxygen binding domain/protein Bacterial 1 J. Inorg. Biochem. 99, 892 (2005). Soluble guanylate cyclase (sgc) is a nitric oxide () sensing hemoprotein that has been
Base Composition Skews, Replication Orientation, and Gene Orientation in 12 Prokaryote Genomes
 J Mol Evol (1998) 47:691 696 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 1998 Base Composition Skews, Replication Orientation, and Gene Orientation in 12 Prokaryote Genomes Michael J. McLean, Kenneth H. Wolfe, Kevin
J Mol Evol (1998) 47:691 696 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 1998 Base Composition Skews, Replication Orientation, and Gene Orientation in 12 Prokaryote Genomes Michael J. McLean, Kenneth H. Wolfe, Kevin
Chapter 16 Lecture. Concepts Of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Chapter 16 Lecture Concepts Of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Chapter Contents 16.1 Prokaryotes Regulate Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Conditions 16.2
Chapter 16 Lecture Concepts Of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Chapter Contents 16.1 Prokaryotes Regulate Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Conditions 16.2
The use of gene clusters to infer functional coupling
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 2896 2901, March 1999 Genetics The use of gene clusters to infer functional coupling ROSS OVERBEEK*, MICHAEL FONSTEIN, MARK D SOUZA*, GORDON D. PUSCH*, AND NATALIA
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 2896 2901, March 1999 Genetics The use of gene clusters to infer functional coupling ROSS OVERBEEK*, MICHAEL FONSTEIN, MARK D SOUZA*, GORDON D. PUSCH*, AND NATALIA
Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis in Leptospira
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 375-380. Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis in Leptospira JMMB Symposium Leptospiral LPS on 375 Spirochete Physiology Dieter M. Bulach*, Thareerat Kalambaheti,
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2000) 2(4): 375-380. Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis in Leptospira JMMB Symposium Leptospiral LPS on 375 Spirochete Physiology Dieter M. Bulach*, Thareerat Kalambaheti,
MHYT, a new integral membrane sensor domain
 FEMS Microbiology Letters 205 (2001) 17^23 www.fems-microbiology.org a d MHYT, a new integral membrane sensor domain Michael Y. Galperin a; *, Tatiana A. Gaidenko b, Armen Y. Mulkidjanian c, Michiko Nakano
FEMS Microbiology Letters 205 (2001) 17^23 www.fems-microbiology.org a d MHYT, a new integral membrane sensor domain Michael Y. Galperin a; *, Tatiana A. Gaidenko b, Armen Y. Mulkidjanian c, Michiko Nakano
HOBACGEN: Database System for Comparative Genomics in Bacteria
 Resource HOBACGEN: Database System for Comparative Genomics in Bacteria Guy Perrière, 1 Laurent Duret, and Manolo Gouy Laboratoire de Biométrie et Biologie Évolutive, Unité Mixte de Recherche Centre National
Resource HOBACGEN: Database System for Comparative Genomics in Bacteria Guy Perrière, 1 Laurent Duret, and Manolo Gouy Laboratoire de Biométrie et Biologie Évolutive, Unité Mixte de Recherche Centre National
Multifractal characterisation of complete genomes
 arxiv:physics/1854v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 21 Multifractal characterisation of complete genomes Vo Anh 1, Ka-Sing Lau 2 and Zu-Guo Yu 1,3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland
arxiv:physics/1854v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 21 Multifractal characterisation of complete genomes Vo Anh 1, Ka-Sing Lau 2 and Zu-Guo Yu 1,3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Microbial Gene Transfer: An Ecological Perspective
 J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 45-50. JMMB Microbial Symposium Gene Transfer 45 Microbial Gene Transfer: An Ecological Perspective John H. Paul* Department of Marine Science, University
J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 45-50. JMMB Microbial Symposium Gene Transfer 45 Microbial Gene Transfer: An Ecological Perspective John H. Paul* Department of Marine Science, University
Midterm Exam #1 : In-class questions! MB 451 Microbial Diversity : Spring 2015!
 Midterm Exam #1 : In-class questions MB 451 Microbial Diversity : Spring 2015 Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Signed : Name : Date : TOTAL = 45 points 1.
Midterm Exam #1 : In-class questions MB 451 Microbial Diversity : Spring 2015 Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Signed : Name : Date : TOTAL = 45 points 1.
TER 26. Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny. Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains. Nitrogen cycle
 Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Correlation property of length sequences based on global structure of complete genome
 Correlation property of length sequences based on global structure of complete genome Zu-Guo Yu 1,2,V.V.Anh 1 and Bin Wang 3 1 Centre for Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland University
Correlation property of length sequences based on global structure of complete genome Zu-Guo Yu 1,2,V.V.Anh 1 and Bin Wang 3 1 Centre for Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland University
Genome reduction in prokaryotic obligatory intracellular parasites of humans: a comparative analysis
 International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2004), 54, 1937 1941 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.63090-0 Genome reduction in prokaryotic obligatory intracellular parasites of humans: a comparative
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2004), 54, 1937 1941 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.63090-0 Genome reduction in prokaryotic obligatory intracellular parasites of humans: a comparative
MxdA modulates intracellular c-di-gmp level in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. indirectly
 AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 28 January 2011 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.01985-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 28 January 2011 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.01985-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
An Evolutionary Alternative System for Aryl β-glucosides Assimilation in Bacteria
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 467-470. JMMB Communication Aryl ß-Glucosides 467 An Evolutionary Alternative System for Aryl β-glucosides Assimilation in Bacteria Denis Faure 1,2 *, Milton
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 467-470. JMMB Communication Aryl ß-Glucosides 467 An Evolutionary Alternative System for Aryl β-glucosides Assimilation in Bacteria Denis Faure 1,2 *, Milton
Sequence Motifs Determine Structure and Ca ++ -binding by EF-hand Proteins
 J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 175-182. JMMB Article EF-hand Proteins 175 Sequence Motifs Determine Structure and Ca ++ -binding by EF-hand Proteins Hooman H. Rashidi, Margarethe Bauer,
J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 175-182. JMMB Article EF-hand Proteins 175 Sequence Motifs Determine Structure and Ca ++ -binding by EF-hand Proteins Hooman H. Rashidi, Margarethe Bauer,
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
JMMB Research Article
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(2): 327-336. JMMB Research Article Topology of LysE and a Novel Superfamily of Exporters 327 The LysE Superfamily: Topology of the Lysine Exporter LysE of Corynebacterium
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(2): 327-336. JMMB Research Article Topology of LysE and a Novel Superfamily of Exporters 327 The LysE Superfamily: Topology of the Lysine Exporter LysE of Corynebacterium
Essentiality in B. subtilis
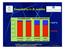 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Introduction to Microbiology. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 031903 Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes Zu-Guo Yu, 1,2, * Vo Anh, 1 and Ka-Sing Lau 3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 031903 Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes Zu-Guo Yu, 1,2, * Vo Anh, 1 and Ka-Sing Lau 3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics,
Regulation of Gas Vesicle Formation in Halophilic Archaea
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 175 181. JMMB Symposium Regulation of Gas Vesicle Formation in Halophilic Archaea Felicitas Pfeifer*, DagmarGregor, Annette Hofacker, Petra Plößer and Peter
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 175 181. JMMB Symposium Regulation of Gas Vesicle Formation in Halophilic Archaea Felicitas Pfeifer*, DagmarGregor, Annette Hofacker, Petra Plößer and Peter
The Multiple Identities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
 J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 51-57. JMMB Symposium Multiple Identities of V. parahaemolyticus 51 The Multiple Identities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Linda McCarter* Microbiology Department,
J. Molec. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(1): 51-57. JMMB Symposium Multiple Identities of V. parahaemolyticus 51 The Multiple Identities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Linda McCarter* Microbiology Department,
The EcoCyc Database. January 25, de Nitrógeno, UNAM,Cuernavaca, A.P. 565-A, Morelos, 62100, Mexico;
 The EcoCyc Database Peter D. Karp, Monica Riley, Milton Saier,IanT.Paulsen +, Julio Collado-Vides + Suzanne M. Paley, Alida Pellegrini-Toole,César Bonavides ++, and Socorro Gama-Castro ++ January 25, 2002
The EcoCyc Database Peter D. Karp, Monica Riley, Milton Saier,IanT.Paulsen +, Julio Collado-Vides + Suzanne M. Paley, Alida Pellegrini-Toole,César Bonavides ++, and Socorro Gama-Castro ++ January 25, 2002
Carbon Catabolite Repression by the Catabolite Control Protein CcpA in Staphylococcus xylosus
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 309 314. JMMB Symposium Carbon Catabolite Repression by the Catabolite Control Protein CcpA in Staphylococcus xylosus Ivana Jankovic 1 and Reinhold Brückner*
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2002) 4(3): 309 314. JMMB Symposium Carbon Catabolite Repression by the Catabolite Control Protein CcpA in Staphylococcus xylosus Ivana Jankovic 1 and Reinhold Brückner*
Origin of Eukaryotic Cell Nuclei by Symbiosis of Archaea in Bacteria supported by the newly clarified origin of functional genes
 Genes Genet. Syst. (2002) 77, p. 369 376 Origin of Eukaryotic Cell Nuclei by Symbiosis of Archaea in Bacteria supported by the newly clarified origin of functional genes Tokumasa Horiike, Kazuo Hamada,
Genes Genet. Syst. (2002) 77, p. 369 376 Origin of Eukaryotic Cell Nuclei by Symbiosis of Archaea in Bacteria supported by the newly clarified origin of functional genes Tokumasa Horiike, Kazuo Hamada,
Bacterial histidine kinase as signal sensor and transducer
 The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology xxx (2005) xxx xxx Molecules in focus Bacterial histidine kinase as signal sensor and transducer Ahmad Khorchid, Mitsuhiko Ikura Division of Molecular
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology xxx (2005) xxx xxx Molecules in focus Bacterial histidine kinase as signal sensor and transducer Ahmad Khorchid, Mitsuhiko Ikura Division of Molecular
Bacterial Signal Transduction Modules: from Genomics to Biology
 Bacterial Signal Transduction Modules: from Genomics to Biology Bacterial signaling proteins consist of modular domains that combine to yield arrays of sensors, transducers, and responders Michael Y. Galperin
Bacterial Signal Transduction Modules: from Genomics to Biology Bacterial signaling proteins consist of modular domains that combine to yield arrays of sensors, transducers, and responders Michael Y. Galperin
Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters
 Ph.D thesis Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters Presented by Attila Szvetnik Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Kálmán Biology Ph.D School University of Szeged Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research
Ph.D thesis Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters Presented by Attila Szvetnik Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Kálmán Biology Ph.D School University of Szeged Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
MicroGenomics. Universal replication biases in bacteria
 Molecular Microbiology (1999) 32(1), 11±16 MicroGenomics Universal replication biases in bacteria Eduardo P. C. Rocha, 1,2 Antoine Danchin 2 and Alain Viari 1,3 * 1 Atelier de BioInformatique, UniversiteÂ
Molecular Microbiology (1999) 32(1), 11±16 MicroGenomics Universal replication biases in bacteria Eduardo P. C. Rocha, 1,2 Antoine Danchin 2 and Alain Viari 1,3 * 1 Atelier de BioInformatique, UniversiteÂ
Common Extracellular Sensory Domains in Transmembrane Receptors for Diverse Signal Transduction Pathways in Bacteria and Archaea
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Jan. 2003, p. 285 294 Vol. 185, No. 1 0021-9193/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.1.285 294.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Common Extracellular
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Jan. 2003, p. 285 294 Vol. 185, No. 1 0021-9193/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.1.285 294.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Common Extracellular
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
 CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Genomic analysis of the histidine kinase family in bacteria and archaea
 Microbiology (2001), 147, 1197 1212 Printed in Great Britain Genomic analysis of the histidine kinase family in bacteria and archaea Dong-jin Kim and Steven Forst Author for correspondence: Steven Forst.
Microbiology (2001), 147, 1197 1212 Printed in Great Britain Genomic analysis of the histidine kinase family in bacteria and archaea Dong-jin Kim and Steven Forst Author for correspondence: Steven Forst.
Genetic Organization and Regulation of Antimicrobial Efflux Systems Possessed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 219-224. JMMB Symposium Neisserial Efflux Pumps 219 Genetic Organization and Regulation of Antimicrobial Efflux Systems Possessed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(2): 219-224. JMMB Symposium Neisserial Efflux Pumps 219 Genetic Organization and Regulation of Antimicrobial Efflux Systems Possessed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and
Welcome to Class 21!
 Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Novel Phosphotransferase Systems Revealed by Bacterial Genome Analysis: The Complete Repertoire of pts Genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(2): 289-293. JMMB Minireview pts Genes in P. aeruginosa 289 Novel Phosphotransferase Systems Revealed by Bacterial Genome Analysis: The Complete Repertoire of pts
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (1999) 1(2): 289-293. JMMB Minireview pts Genes in P. aeruginosa 289 Novel Phosphotransferase Systems Revealed by Bacterial Genome Analysis: The Complete Repertoire of pts
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters
 Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
The genomic tree of living organisms based on a fractal model
 Physics Letters A 317 (2003) 293 302 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla The genomic tree of living organisms based on a fractal model Zu-Guo Yu a,b,,voanh a, Ka-Sing Lau c, Ka-Hou Chu d a Program in Statistics
Physics Letters A 317 (2003) 293 302 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla The genomic tree of living organisms based on a fractal model Zu-Guo Yu a,b,,voanh a, Ka-Sing Lau c, Ka-Hou Chu d a Program in Statistics
The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome
 Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Subsystem: Succinate dehydrogenase
 Subsystem: Succinate dehydrogenase Olga Vassieva Fellowship for Interpretation of Genomes The super-macromolecular respiratory complex II (succinate:quinone oxidoreductase) couples the oxidation of succinate
Subsystem: Succinate dehydrogenase Olga Vassieva Fellowship for Interpretation of Genomes The super-macromolecular respiratory complex II (succinate:quinone oxidoreductase) couples the oxidation of succinate
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Bio Microbiology - Spring 2014 Learning Guide 04.
 Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2014 Learning Guide 04 http://pessimistcomic.blogspot.com/ Cell division is a part of a replication cycle that takes place throughout the life of the bacterium A septum
Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2014 Learning Guide 04 http://pessimistcomic.blogspot.com/ Cell division is a part of a replication cycle that takes place throughout the life of the bacterium A septum
Phosphotransfer Functions of Mutated Bacillus subtilis HPr-Like Protein Crh Carrying a Histidine in the Active Site
 J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 439-444. JMMB Symposium Phosphotransfer Activity of CrhQ15H 439 Phosphotransfer Functions of Mutated Bacillus subtilis HPr-Like Protein Crh Carrying a Histidine
J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2001) 3(3): 439-444. JMMB Symposium Phosphotransfer Activity of CrhQ15H 439 Phosphotransfer Functions of Mutated Bacillus subtilis HPr-Like Protein Crh Carrying a Histidine
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
BCH 400/600 Introductory Biochemistry
 BCH 400/600 Introductory Biochemistry Instructor: David Shintani Office: 311C Fleischmann Ag. Lab: 308 Fleischmann Ag. E-mail: shintani@unr.edu Phone: (775) 784-4631 Before BCH 400 BCH 400 is heavy on
BCH 400/600 Introductory Biochemistry Instructor: David Shintani Office: 311C Fleischmann Ag. Lab: 308 Fleischmann Ag. E-mail: shintani@unr.edu Phone: (775) 784-4631 Before BCH 400 BCH 400 is heavy on
Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
 Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON
 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 2001
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 2001 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 2001](/thumbs/77/75258851.jpg) Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes Zu-Guo Yu,2, Vo Anh and Ka-Sing Lau 3 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland University of Technology,
Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes Zu-Guo Yu,2, Vo Anh and Ka-Sing Lau 3 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland University of Technology,
Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair. 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination.
 Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Nucleotide Second Messenger Signaling in Bacteria
 Nucleotide Second Messenger Signaling in Bacteria SPP 1879 Kick-off Meeting 16-17 September, 2016, Harnack-Haus, Berlin-Dahlem, Germany Organizers: Regine Hengge, Mihaela Pruteanu & Christine Kanow-Scheel
Nucleotide Second Messenger Signaling in Bacteria SPP 1879 Kick-off Meeting 16-17 September, 2016, Harnack-Haus, Berlin-Dahlem, Germany Organizers: Regine Hengge, Mihaela Pruteanu & Christine Kanow-Scheel
Grade Level: AP Biology may be taken in grades 11 or 12.
 ADVANCEMENT PLACEMENT BIOLOGY COURSE SYLLABUS MRS. ANGELA FARRONATO Grade Level: AP Biology may be taken in grades 11 or 12. Course Overview: This course is designed to cover all of the material included
ADVANCEMENT PLACEMENT BIOLOGY COURSE SYLLABUS MRS. ANGELA FARRONATO Grade Level: AP Biology may be taken in grades 11 or 12. Course Overview: This course is designed to cover all of the material included
SYLLABUS. Meeting Basic of competence Topic Strategy Reference
 SYLLABUS Faculty : Mathematics and science Study Program : Biology education Lecture/Code : Microbiology/BIO 236 Credits : 2 unit of semester credit Semester : 5 Prerequisites lecture : Biochemistry, Cell
SYLLABUS Faculty : Mathematics and science Study Program : Biology education Lecture/Code : Microbiology/BIO 236 Credits : 2 unit of semester credit Semester : 5 Prerequisites lecture : Biochemistry, Cell
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity
 Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. Genome sequencing Assembly. Gene prediction. Protein targeting.
 Genome Annotation Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Genome Annotation Frank Oliver Glöckner 1 Genome Analysis Roadmap Genome sequencing Assembly Gene prediction Protein targeting trna prediction
Genome Annotation Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Genome Annotation Frank Oliver Glöckner 1 Genome Analysis Roadmap Genome sequencing Assembly Gene prediction Protein targeting trna prediction
RNA Synthesis and Processing
 RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis
 Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis Xiuying Liu 1,3, Yan Yin 1,2,3, Jinjun Wu 1 and Zhenfeng Liu 1 1 National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules,
Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis Xiuying Liu 1,3, Yan Yin 1,2,3, Jinjun Wu 1 and Zhenfeng Liu 1 1 National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules,
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Chapter 19. Microbial Taxonomy
 Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
Additional file 1 for Structural correlations in bacterial metabolic networks by S. Bernhardsson, P. Gerlee & L. Lizana
 Additional file 1 for Structural correlations in bacterial metabolic networks by S. Bernhardsson, P. Gerlee & L. Lizana Table S1 The species marked with belong to the Proteobacteria subset and those marked
Additional file 1 for Structural correlations in bacterial metabolic networks by S. Bernhardsson, P. Gerlee & L. Lizana Table S1 The species marked with belong to the Proteobacteria subset and those marked
A thermophilic last universal ancestor inferred from its estimated amino acid composition
 CHAPTER 17 A thermophilic last universal ancestor inferred from its estimated amino acid composition Dawn J. Brooks and Eric A. Gaucher 17.1 Introduction The last universal ancestor (LUA) represents a
CHAPTER 17 A thermophilic last universal ancestor inferred from its estimated amino acid composition Dawn J. Brooks and Eric A. Gaucher 17.1 Introduction The last universal ancestor (LUA) represents a
Physiological diversity
 Physiological diversity Principles Energetic considerations Biochemical pathways Organisms Ecological relevance Physiological diversity Sulfate- and nitrate reducers (5. Nov.) Methanogens and homoacetogens
Physiological diversity Principles Energetic considerations Biochemical pathways Organisms Ecological relevance Physiological diversity Sulfate- and nitrate reducers (5. Nov.) Methanogens and homoacetogens
Chapter 1. Basics of Microbiology
 Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
How many potentially secreted proteins are contained in a bacterial genome?
 Gene 237 (1999) 113 121 www.elsevier.com/locate/gene How many potentially secreted proteins are contained in a bacterial genome? Gisbert Schneider * F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Pharmaceuticals Division,
Gene 237 (1999) 113 121 www.elsevier.com/locate/gene How many potentially secreted proteins are contained in a bacterial genome? Gisbert Schneider * F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Pharmaceuticals Division,
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS
 CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
The two daughter cells are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.
 Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
