CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION
|
|
|
- Reginald Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION paracrine & juxtacrine signalling autocrine & intracrine signalling methods to study cell-cell communication: attraction & repulsion chemotaxis & chemokinesis substrate preference bidirectional signalling
2 How to study chemotaxis and chemochinesis? time lapse video wound healing transwell assay/boyden s chambers turning assay explant migration
3 How to study chemotaxis and chemochinesis? time lapse video wound healing transwell assay/boyden s chambers turning assay explant migration
4
5 Methods to study chemotaxis and chemochinesis time lapse video wound healing transwell assay/boyden s chambers turning assay explant migration
6 Neuron migration and axon guidance (Mei and Xiong, 2008)
7 ErbB4 lox/+ hgfap-cre ErbB4 lox/- hgfap-cre ErbB4 ErbB4 lox/- nestin-cre RMS (Anton et al., 2004) ErbB4 lox/+ hgfap-cre ErbB4 lox/- hgfap-cre
8 in vivo ErbB4 expressing neurons are attracted by soluble NRG1 ErbB4 How can you obtain cell aggregates expressing a ligand? (Anton et al, 2004)
9 HANGING DROP TECHNIQUE Cells are previously transiently transfected to obtain expression and release of the soluble factor that must be tested.
10 HANGING DROP TECHNIQUE
11 in vivo ErbB4 expressing neurons are attracted by soluble NRG1 ErbB4 What is blind analysis? (Flames et al, 2004)
12 ????? How can you define the behaviour of these explants?
13
14 ErbB4 stable expression in neural progenitor cells JMa-cyt1 JMb-cyt1 JMa-cyt2 JMb-cyt2 mock mock A1.1 - A1.2 B B1.7 A A2.1 B2.1 - B2.16
15 (Fornasari et al., 2016)
16 CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION paracrine & juxtacrine signalling autocrine & intracrine signalling methods to study cell-cell communication: attraction & repulsion chemotaxis & chemokinesis substrate preference bidirectional signalling
17 Stripe choice assay Cells expressing the receptor are plated on alternating stripes expressing or not the ligand Ligand+ Mock Ligand+ Receptor+ Mock Receptor+ Receptor+ Cells expressing the ligand are plated on alternating stripes expressing or not the receptor Ligand+
18 in vivo ErbB4 expressing neurons adhere preferentially on a substrate expressing transmembrane NRG1 NRG1-III (Flames et al, 2004)
19 in vitro analysis of substrate preference mediated by different ErbB4 isoforms following interaction with transmembrane NRG1 Nrg1-III-β3 Mock Nrg1-III-β3 ErbB4/ mock +RFP 24h (Fregnan et al., 2013)
20 Stripe Choice Assay N7 NRG1 NRG1 (Fregnan et al., 2013)
21 in vitro analysis of substrate preference mediated by different ErbB4 isoforms following interaction with transmembrane NRG1 Nrg1-III-β3 Mock Nrg1-III-β3 ErbB4/ mock +RFP 24h NRG1-III-β3 CTR (Fregnan et al., 2013)
22 CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION paracrine & juxtacrine signalling autocrine & intracrine signalling methods to study cell-cell communication: attraction & repulsion chemotaxis & chemokinesis substrate preference bidirectional signalling
23 Cell-cell comunication: how to study bidirectional signalling??
24 Eph-ephrin as a model to study cell-cell communication
25 Bidirectional communication
26
27 Steps in cell-contact-dependent Eph bidirectional signalling a,b - Eph receptors and ephrins on opposed cell surfaces mediate cell adhesion on cell contact.
28 Steps in cell-contact-dependent Eph bidirectional signalling c - tetramerization leads to tyrosine phosphorylation and signalling. d - the tetrameric complexes can further grow into larger clusters that, in the Eph receptor-expressing cells, can extend beyond the region of contact through homophilic interactions between Eph receptors. The degree of clustering might regulate signal intensity and the nature of the signals.
29 Eph INTERACTION ephrin? How can two cells separate after ligand-receptor interaction?
30 Mechanisms of Eph signal attenuation and termination Cleavage of the ephrin by a protease allows cell separation following Eph ephrin engagement.
31 Proteolytic cleavage ectodomain shedding cell separation
32 Eph INTERACTION ephrin ephrin A PROTEOLYSIS REPULSION
33 Eph INTERACTION ephrin ephrin A PROTEOLYSIS ephrin B
34 Eph INTERACTION ephrin ephrin A PROTEOLYSIS ephrin B TRANS-ENDOCITOSYS? reverse forward? REPULSION
35 Which method to study cell-cell interaction did we already see?
36 signal transduction is usually studied by stimulating the target cells with a recombinant soluble ligand or with a recombinant soluble receptor Stimulation of cells expressing the receptor with soluble ligand ephrin-fc Eph Stimulation of cells expressing the ligand with soluble receptor Eph-Fc ephrin
37 sometime this approach is deeply different from the physiological process of intercellular communication, in part because the proteins that act as ligands for certain receptors are themselves anchored to the cell membrane
38 Methods to study cell-cell communication - stimulation of cells expressing the receptor with the ligand - stimulation of cells expressing the ligand with the receptor - stimulation of cells expressing the receptor with cells expressing the ligand - stimulation of cells expressing the ligand with cells expressing the receptor
39 Stimulation of recipient cells expressing the receptor with cells expressing the ligand NIH3T3 ephrin stimulator cells NIH3T3 EphB2 recipient cells
40 Stimulation of recipient cells expressing the ligand with cells expressing the receptor NIH3T3 ephrinb1 recipient cells NIH3T3 EphB2 stimulator cells
41 A sparse monolayer of recipient cells, is first cultured on glass cover slips. Next, stimulator cells are taken in suspension by a mild treatment and added onto the recipient cells. After 10 min, all cells are fixed and stained.
42 A sparse monolayer of recipient cells, is first cultured on glass cover slips. Next, stimulator cells are taken in suspension by a mild treatment and added onto the recipient cells. After 10 min, all cells are fixed and stained. Cells are fixed in the absence of detergents and immunolabelled for ephrin on the cell surface. Then, cells are permeabilized with detergents and stained for total ephrin using a different primary antibody. Staining that appears exclusively after permeabilization represents the intracellular pool of ephrin
43 Methods to study cell-cell communication - stimulation of cells expressing the receptor with the ligand - stimulation of cells expressing the ligand with the receptor - stimulation of cells expressing the receptor with cells expressing the ligand - stimulation of cells expressing the ligand with cells expressing the receptor - time lapse analysis of the interactions between cells expressing the receptor with cells expressing the ligand
44 Time lapse analysis of the interactions between cells expressing the receptor with cells expressing the ligand (I added new slides to this lesson, to better explain this part, that we will see next time)
45 to determine whether bi-directional trans-endocytosis affects repulsive cell migration, an in vitro assay was developed in which cells expressing fluorescently tagged EphB2 receptor (EphB2 YFP) were co-cultured with cells expressing fluorescently tagged ephrinb1 (CFP ephrinb1) HeLa cells were chosen because they express low levels of endogenous ephrinb and EphB proteins and high levels of transfected proteins; they are also very motile, which makes them ideal for fluorescence time-lapse imaging.
46 Bi-directional trans-endocytosis regulates repulsion response and cell detachment * * * a. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with full-length EphB2 YFP and fulllength CFP ephrinb1 and then cocultured before time-lapse imaging. Left, selected fluorescence images with EphB2 YFP in red and CFP ephrinb1 in green. Right, phase contrast images. Intense clustering of EphB2 and ephrinb1 is seen in yellow at the contact site between the two cells at 20 min, the EphB2 YFP cell retracts a lamellipodium from the ephrinb1 cell (indicated by the distance between the two stippled lines).
47 in almost all observed cases, when a ruffling lamellipodium of an EphB2 YFP cell collides with an CFP ephrinb1 cell, strong coclustering of receptor with ligand occurs within 1 min and the initial clusters always appear in filopodia-like protrusions. during the retraction of EphB2 YFP positive lamellipodia, receptor ligand complexes endocytose bi-directionally contacts of EphB2 YFP- or CFP ephrinb1-transfected cells with untransfected cells in the same culture do not result in clustering nor cell retraction (asterisks in the figure)
48 * * * * b. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with full length EphB2 YFP and C-terminally truncated CFP ephrinb1- C then cocultured before time-lapse imaging. Left, selected fluorescence images with EphB2 YFP in red and CFP ephrinb1- C in green. Right, phase contrast images. EphB2 YFP clusters (in yellow) are uni-directionally endocytosed into the EphB2 YFP expressing cell. Strong repulsion and rounding of EphB2 YFP expressing cell is observed. * *
49 when ephrinb1 endocytosis was blocked by a C-terminal truncation (CFP ephrinb1- C), markedly different cell behaviour was observed rapid co-clustering with EphB2 YFP occurs after contact, but these clusters remain in part localized to the surface of the ligand expressing cell, where they grow to much larger complexes the EphB2 YFP cell engulfs the clusters vigorously, retracts strongly, and in most cases even rounds up, a behaviour rarely observed with wild-type ephrinb1 therefore, a mutation that blocks ephrinb1 endocytosis results in a stronger EphB2 cell retraction response
50 * * * c. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with C-terminally truncated EphB2 YFP- C and full length CFP ephrinb1 then cocultured before time-lapse imaging. Left, selected fluorescence images with EphB2 YFP- C in red and CFP ephrinb1 in green. Right, phase contrast images. EphB2 YFP clusters (in yellow) are strongly uni-directionally endocytosed into the CFP ephrinb1 expressing cell. Otherwise normal cell behaviour similar to un-transfected cells is observed.
51 How do cells react to unidirectional ephrinb reverse signalling? as expected, CFP ephrinb1 cells strongly endocytose receptor ligand clusters, whereas EphB2 YFP- C cells fail to endocytose these complexes however, the cells neither retract nor adhere to each other cell behaviour is indistinguishable from non-transfected cells ephrinb1 reverse trans-endocytosis is sufficient to terminate adhesion and to cause cell detachment
52 c. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with C-terminally truncated EphB2 YFP- C and CFP ephrinb1- C then cocultured before time-lapse imaging. Left, selected fluorescence images with EphB2 YFP- C in red and CFP ephrinb1- C in green. Right, phase contrast images. Cells strongly adhere to each other forming large fascicles filled with EphB2 YFP- C and CFP ephrinb1- C yellow complexes.
53 when both ephrinb1 and EphB2 are truncated at the C-terminal (EphB2 YFP- C and CFP ephrinb1- C ), the cells strongly adhere to each other and large receptor-and ligand-bearing fascicles are formed at the contact zone ephrinb and EphB proteins can function as adhesion molecules if endocytosis and other signalling events are blocked.
1- Eph- ephrin. Eph receptors and ephrin ligands. *glycosylphosphatidylinositol. anchored
 1- Eph- ephrin Eph receptors and ephrin ligands * *glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchored 1 Midline guidance in the visual system In animals with binocular vision, most retinal axons (red) cross
1- Eph- ephrin Eph receptors and ephrin ligands * *glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchored 1 Midline guidance in the visual system In animals with binocular vision, most retinal axons (red) cross
ADAM FAMILY. ephrin A INTERAZIONE. Eph ADESIONE? PROTEOLISI ENDOCITOSI B A RISULTATO REPULSIONE. reverse. forward
 ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin
 5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune
5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune
Axon guidance I. Paul Garrity March 15, /9.013
 Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
Neurite initiation. Neurite formation begins with a bud that sprouts from the cell body. One or several neurites can sprout at a time.
 Neurite initiation. Neuronal maturation initiation f-actin polarization and maturation tubulin stage 1: "spherical" neuron stage 2: neurons extend several neurites stage 3: one neurite accelerates its
Neurite initiation. Neuronal maturation initiation f-actin polarization and maturation tubulin stage 1: "spherical" neuron stage 2: neurons extend several neurites stage 3: one neurite accelerates its
Axon Guidance. Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues:
 Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization
 Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 An immature neuron in cell culture first sprouts
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 An immature neuron in cell culture first sprouts
Avoidance of posterior tectal membranes by temporal retinal axons
 Development 101. 909-913 (1987) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 909 Avoidance of posterior tectal membranes by temporal retinal axons JOCHEN WALTER, SIGRID HENKE-FAHLE and
Development 101. 909-913 (1987) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 909 Avoidance of posterior tectal membranes by temporal retinal axons JOCHEN WALTER, SIGRID HENKE-FAHLE and
Chapter 16. Cellular Movement: Motility and Contractility. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Cellular Movement: Motility and Contractility Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Two eukaryotic motility systems 1. Interactions between motor proteins and microtubules
Chapter 16 Cellular Movement: Motility and Contractility Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Two eukaryotic motility systems 1. Interactions between motor proteins and microtubules
Endocytosis of EphA receptors is essential for the proper development of the retinocollicular topographic map
 The EMBO Journal (2011) 30, 1593 1607 & 2011 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 0261-4189/11 www.embojournal.org Endocytosis of EphA receptors is essential for the proper development
The EMBO Journal (2011) 30, 1593 1607 & 2011 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 0261-4189/11 www.embojournal.org Endocytosis of EphA receptors is essential for the proper development
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
targets. clustering show that different complex pathway
 Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
RANK. Alternative names. Discovery. Structure. William J. Boyle* SUMMARY BACKGROUND
 RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
Conclusions. The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights
 C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization. The cytoskeletal components of neurons have characteristic distributions and associations
 Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Types of Cell Movement passive: active: cell sheets flow cilia or flagella ameboid adhesion
Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Types of Cell Movement passive: active: cell sheets flow cilia or flagella ameboid adhesion
Supplemental Information. The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51. Requires ADP as a Cofactor
 Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
BE 159: Signal Transduction and Mechanics in Morphogenesis
 BE 159: Signal Transduction and Mechanics in Morphogenesis Justin Bois Caltech Winter, 2018 2018 Justin Bois. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License CC-BY 4.0. 5 Delta-Notch
BE 159: Signal Transduction and Mechanics in Morphogenesis Justin Bois Caltech Winter, 2018 2018 Justin Bois. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License CC-BY 4.0. 5 Delta-Notch
Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts
 Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts - Integrins as central adhesion receptors - - Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) as a central signal molecule - Structure of Cell/Cell and Cell/Matrix
Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts - Integrins as central adhesion receptors - - Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) as a central signal molecule - Structure of Cell/Cell and Cell/Matrix
Supplemental table S7.
 Supplemental table S7. GO terms significantly enriched in significantly up-regulated genes of the microarray. K: number of genes from the input cluster in the given category. F: number of total genes in
Supplemental table S7. GO terms significantly enriched in significantly up-regulated genes of the microarray. K: number of genes from the input cluster in the given category. F: number of total genes in
6 Mechanotransduction
 6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
EphA/ephrin A reverse signaling promotes the migration of cortical interneurons from the medial ganglionic eminence
 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd (2014) 141, 460-471 doi:10.1242/dev.101691 RESEARCH ARTICLE EphA/ephrin A reverse signaling promotes the migration of cortical interneurons from the medial
2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd (2014) 141, 460-471 doi:10.1242/dev.101691 RESEARCH ARTICLE EphA/ephrin A reverse signaling promotes the migration of cortical interneurons from the medial
Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
 Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells 7.16 2-10-05 Apoptosis is an important factor in many human diseases Cancer malignant cells evade death by suppressing apoptosis (too little apoptosis) Stroke damaged neurons
Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells 7.16 2-10-05 Apoptosis is an important factor in many human diseases Cancer malignant cells evade death by suppressing apoptosis (too little apoptosis) Stroke damaged neurons
return in class, or Rm B
 Last lectures: Genetic Switches and Oscillators PS #2 due today bf before 3PM return in class, or Rm. 68 371B Naturally occurring: lambda lysis-lysogeny decision lactose operon in E. coli Engineered: genetic
Last lectures: Genetic Switches and Oscillators PS #2 due today bf before 3PM return in class, or Rm. 68 371B Naturally occurring: lambda lysis-lysogeny decision lactose operon in E. coli Engineered: genetic
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
ADAMS: KEY COMPONENTS IN EGFR SIGNALLING AND DEVELOPMENT
 ADAMS: KEY COMPONENTS IN EGFR SIGNALLING AND DEVELOPMENT Carl P. Blobel Abstract ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease) proteins are membrane-anchored metalloproteases that process and shed the ectodomains
ADAMS: KEY COMPONENTS IN EGFR SIGNALLING AND DEVELOPMENT Carl P. Blobel Abstract ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease) proteins are membrane-anchored metalloproteases that process and shed the ectodomains
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Hierarchical Organization of Guidance Receptors: Silencing of Netrin Attraction by Slit Through a Robo/DCC Receptor Complex
 Hierarchical Organization of Guidance Receptors: Silencing of Netrin Attraction by Slit Through a Robo/DCC Receptor Complex Elke Stein and Marc Tessier-Lavigne* Axonal growth cones that cross the nervous
Hierarchical Organization of Guidance Receptors: Silencing of Netrin Attraction by Slit Through a Robo/DCC Receptor Complex Elke Stein and Marc Tessier-Lavigne* Axonal growth cones that cross the nervous
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Modeling of magnetic field In this study, the magnetic field was generated with N52 grade nickel-plated neodymium block magnets (K&J Magnetics). The residual flux density of the magnets
Supplementary Methods Modeling of magnetic field In this study, the magnetic field was generated with N52 grade nickel-plated neodymium block magnets (K&J Magnetics). The residual flux density of the magnets
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 KEY
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 KEY May 2, 2006 This is an OPEN BOOK exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes BUT NOT computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 KEY May 2, 2006 This is an OPEN BOOK exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes BUT NOT computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Multiple Effects of Ephrin-A5 on Cortical Neurons Are Mediated by Src Family Kinases
 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 23, 2007 27(21):5643 5653 5643 Development/Plasticity/Repair Multiple Effects of Ephrin-A5 on Cortical Neurons Are Mediated by Src Family Kinases Geraldine Zimmer, 1 Bettina
The Journal of Neuroscience, May 23, 2007 27(21):5643 5653 5643 Development/Plasticity/Repair Multiple Effects of Ephrin-A5 on Cortical Neurons Are Mediated by Src Family Kinases Geraldine Zimmer, 1 Bettina
WD Repeat Domain of Dictyostelium Myosin Heavy Chain Kinase C Functions in both Substrate Targeting and Cellular Localization,
 WD Repeat Domain of Dictyostelium Myosin Heavy Chain Kinase C Functions in both Substrate Targeting and Cellular Localization, By: Atiya Franklin, Linzi Hyatt, Alyssa Chowdhury, and Paul A. Steimle* Franklin,
WD Repeat Domain of Dictyostelium Myosin Heavy Chain Kinase C Functions in both Substrate Targeting and Cellular Localization, By: Atiya Franklin, Linzi Hyatt, Alyssa Chowdhury, and Paul A. Steimle* Franklin,
Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Commissural Axon Guidance: The Role of Intracellular Tyrosine Kinases in Netrin-Dcc/Frazzled Axon Attraction
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Commissural Axon Guidance: The Role of Intracellular Tyrosine Kinases in Netrin-Dcc/Frazzled
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Commissural Axon Guidance: The Role of Intracellular Tyrosine Kinases in Netrin-Dcc/Frazzled
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, an expert on cell adhesion and AFM (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, an expert on cell adhesion and AFM (Remarks to the Author): Understanding how cells adhere to extracellular matrix proteins is a very important, yet not fully understood
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, an expert on cell adhesion and AFM (Remarks to the Author): Understanding how cells adhere to extracellular matrix proteins is a very important, yet not fully understood
Introduction to Cellular Communication *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
MIT 9.14 Class The growth of the long extensions of neurons and related topics
 9.14 - Brain Structure and its Origins Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2005
9.14 - Brain Structure and its Origins Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2005
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Delivery. Delivery Processes. Delivery Processes: Distribution. Ultimate Toxicant
 Delivery Ultimate Toxicant The chemical species that reacts with the endogenous target. Toxicity depends on the concentration (dose) of the ultimate toxicant at the target site Delivery Processes Absorption
Delivery Ultimate Toxicant The chemical species that reacts with the endogenous target. Toxicity depends on the concentration (dose) of the ultimate toxicant at the target site Delivery Processes Absorption
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Reference: Forscher, P., Kaczmarek, L.K., Buchanan, J. and Smith, S.J. (1987) Cyclic AMP induces changes in distribution and transport of organelles
 Reference: Forscher, P., Kaczmarek, L.K., Buchanan, J. and Smith, S.J. (1987) Cyclic AMP induces changes in distribution and transport of organelles within growth cones of Aplysia bag cell neurons. J.
Reference: Forscher, P., Kaczmarek, L.K., Buchanan, J. and Smith, S.J. (1987) Cyclic AMP induces changes in distribution and transport of organelles within growth cones of Aplysia bag cell neurons. J.
Self-assembled Peptides as Drug Delivery Molecules for transport across the Biological Barriers
 Self-assembled Peptides as Drug Delivery Molecules for transport across the Biological Barriers Porter, S., McCarthy, H., & Laverty, G. (2017). Self-assembled Peptides as Drug Delivery Molecules for transport
Self-assembled Peptides as Drug Delivery Molecules for transport across the Biological Barriers Porter, S., McCarthy, H., & Laverty, G. (2017). Self-assembled Peptides as Drug Delivery Molecules for transport
RabGDI controls axonal midline crossing by regulating Robo1 surface expression
 Philipp et al. Neural Development 2012, 7:36 RESEARCH ARTICLE RabGDI controls axonal midline crossing by regulating Robo1 surface expression Open Access Melanie Philipp 1, Vera Niederkofler 2, Marc Debrunner
Philipp et al. Neural Development 2012, 7:36 RESEARCH ARTICLE RabGDI controls axonal midline crossing by regulating Robo1 surface expression Open Access Melanie Philipp 1, Vera Niederkofler 2, Marc Debrunner
Published in Physical Review E: 99, (2019)
 Role of geometrical cues in neuronal growth Joao Marcos Vensi Basso 1, Ilya Yurchenko 1, Marc Simon 1, Daniel J. Rizzo 1,2, Cristian Staii 1,* 1. Department of Physics and Astronomy, Center for Nanoscopic
Role of geometrical cues in neuronal growth Joao Marcos Vensi Basso 1, Ilya Yurchenko 1, Marc Simon 1, Daniel J. Rizzo 1,2, Cristian Staii 1,* 1. Department of Physics and Astronomy, Center for Nanoscopic
Endocytosis Regulates Cell Soma Translocation and the Distribution of Adhesion Proteins in Migrating Neurons
 Endocytosis Regulates Cell Soma Translocation and the Distribution of Adhesion Proteins in Migrating Neurons Jennifer C. Shieh 1,2, Bruce T. Schaar 3, Karpagam Srinivasan 1, Frances M. Brodsky 4, Susan
Endocytosis Regulates Cell Soma Translocation and the Distribution of Adhesion Proteins in Migrating Neurons Jennifer C. Shieh 1,2, Bruce T. Schaar 3, Karpagam Srinivasan 1, Frances M. Brodsky 4, Susan
Computational Model Of Axon Guidance
 Mestrado em Engenharia Informática Dissertação Relatório Final arxiv:1508.01537v1 [q-bio.nc] 6 Aug 2015 Computational Model Of Axon Guidance Rui André Ponte Costa racosta@student.dei.uc.pt Orientadores:
Mestrado em Engenharia Informática Dissertação Relatório Final arxiv:1508.01537v1 [q-bio.nc] 6 Aug 2015 Computational Model Of Axon Guidance Rui André Ponte Costa racosta@student.dei.uc.pt Orientadores:
FLRT Structure: Balancing Repulsion and Cell Adhesion in Cortical and Vascular Development
 Article FLRT Structure: Balancing Repulsion and Cell Adhesion in Cortical and Vascular Development Elena Seiradake, 1,7 Daniel del Toro, 2,7 Daniel Nagel, 2,5 Florian Cop, 3,4 Ricarda Härtl, 3,4 Tobias
Article FLRT Structure: Balancing Repulsion and Cell Adhesion in Cortical and Vascular Development Elena Seiradake, 1,7 Daniel del Toro, 2,7 Daniel Nagel, 2,5 Florian Cop, 3,4 Ricarda Härtl, 3,4 Tobias
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins
 13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION
 PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION PART-A 1. What is prokaryotic cell 2. Explain Eukaryotic cell 3. Major difference of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 4. Role of lipid
PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION PART-A 1. What is prokaryotic cell 2. Explain Eukaryotic cell 3. Major difference of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 4. Role of lipid
Report. Functional Diversity of Robo Receptor Immunoglobulin Domains Promotes Distinct Axon Guidance Decisions
 Current Biology 20, 567 572, March 23, 2010 ª2010 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.021 Functional Diversity of Robo Receptor Immunoglobulin Domains Promotes Distinct Axon Guidance
Current Biology 20, 567 572, March 23, 2010 ª2010 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.021 Functional Diversity of Robo Receptor Immunoglobulin Domains Promotes Distinct Axon Guidance
The molecular genetics of chemotaxis: sensing and responding to chemoattractant gradients
 The molecular genetics of chemotaxis: sensing and responding to chemoattractant gradients Richard A. Firtel* and Chang Y. Chung Summary Chemotaxis plays a central role in various biological processes,
The molecular genetics of chemotaxis: sensing and responding to chemoattractant gradients Richard A. Firtel* and Chang Y. Chung Summary Chemotaxis plays a central role in various biological processes,
How does a cell communicate? AP Biology Curriculum Framework
 Enduring Understanding 3.D Cells communicate by generating, transmitting and receiving chemical signals. 1 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part I: Introduction to Communication You may wish to print a copy
Enduring Understanding 3.D Cells communicate by generating, transmitting and receiving chemical signals. 1 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part I: Introduction to Communication You may wish to print a copy
Amneh Auben. Abdulrahman Jabr. Diala Abu-Hassan
 21 Amneh Auben Abdulrahman Jabr Diala Abu-Hassan Matrix polysaccharides Extracellular matrix (ECM): It s a collection of components that fills the spaces outside the cell or between the cells. ---------
21 Amneh Auben Abdulrahman Jabr Diala Abu-Hassan Matrix polysaccharides Extracellular matrix (ECM): It s a collection of components that fills the spaces outside the cell or between the cells. ---------
< Eyes < Ears < Skin < And elsewhere Ú And commands are sent out to response unitsl
 Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Dr. Van Cantfort Neural Communication Neural Communication Nerve cells are specialized for generating and moving information around in the nervous system. These two simple
Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Dr. Van Cantfort Neural Communication Neural Communication Nerve cells are specialized for generating and moving information around in the nervous system. These two simple
Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy I: Fluorescence (Foster) Resonance Energy Transfer
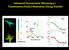 Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy I: Fluorescence (Foster) Resonance Energy Transfer 3.0 Pax 2.5 2.0 1200 800 400 GFP- Pax GFP-Pax + FATmCherry FAT FAT 1.5 Lifetime (ns) 0 1500 2000 2500 3000 Average lifetime
Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy I: Fluorescence (Foster) Resonance Energy Transfer 3.0 Pax 2.5 2.0 1200 800 400 GFP- Pax GFP-Pax + FATmCherry FAT FAT 1.5 Lifetime (ns) 0 1500 2000 2500 3000 Average lifetime
Cells to Tissues. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
The Molecular Biology of Axon Guidance
 Thursday, January 25, 2001 Science -- Tessier-Lavigne and Goodman 274 (5290): 1123 Page: 1 Institution: HARVARD UNIVERSITY Sign In as Individual FAQ The Molecular Biology of Axon Guidance Marc Tessier-Lavigne
Thursday, January 25, 2001 Science -- Tessier-Lavigne and Goodman 274 (5290): 1123 Page: 1 Institution: HARVARD UNIVERSITY Sign In as Individual FAQ The Molecular Biology of Axon Guidance Marc Tessier-Lavigne
Full-length GlpG sequence was generated by PCR from E. coli genomic DNA. (with two sequence variations, D51E/L52V, from the gene bank entry aac28166),
 Supplementary Methods Protein expression and purification Full-length GlpG sequence was generated by PCR from E. coli genomic DNA (with two sequence variations, D51E/L52V, from the gene bank entry aac28166),
Supplementary Methods Protein expression and purification Full-length GlpG sequence was generated by PCR from E. coli genomic DNA (with two sequence variations, D51E/L52V, from the gene bank entry aac28166),
Any protein that can be labelled by both procedures must be a transmembrane protein.
 1. What kind of experimental evidence would indicate that a protein crosses from one side of the membrane to the other? Regions of polypeptide part exposed on the outside of the membrane can be probed
1. What kind of experimental evidence would indicate that a protein crosses from one side of the membrane to the other? Regions of polypeptide part exposed on the outside of the membrane can be probed
Cardiac cell-cell Communication Part 1 Alonso P. Moreno D.Sc. CVRTI, Cardiology
 Bioengineering 6003 Cellular Electrophysiology and Biophysics Cardiac cell-cell Communication Part 1 Alonso P. Moreno D.Sc. CVRTI, Cardiology moreno@cvrti.utah.edu November 2010 poster Physiological Relevance
Bioengineering 6003 Cellular Electrophysiology and Biophysics Cardiac cell-cell Communication Part 1 Alonso P. Moreno D.Sc. CVRTI, Cardiology moreno@cvrti.utah.edu November 2010 poster Physiological Relevance
S1 Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the network alignment results
 1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
Cell Adhesion and Signaling
 Cell Adhesion and Signaling mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology 1 Transactivation NATURE REVIEWS CANCER VOLUME 7 FEBRUARY 2007 85 2 Functions of Cell Adhesion cell cycle proliferation
Cell Adhesion and Signaling mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology 1 Transactivation NATURE REVIEWS CANCER VOLUME 7 FEBRUARY 2007 85 2 Functions of Cell Adhesion cell cycle proliferation
Protein dynamics and conformational selection in bidirectional signal transduction
 CO M M E N TA RY Open Access Protein dynamics and conformational selection in bidirectional signal transduction Ruth Nussinov* 1,2 and Buyong Ma 1 See research article http://www.biomedcentral.com/2046-1682/5/2
CO M M E N TA RY Open Access Protein dynamics and conformational selection in bidirectional signal transduction Ruth Nussinov* 1,2 and Buyong Ma 1 See research article http://www.biomedcentral.com/2046-1682/5/2
Domain 6: Communication
 Domain 6: Communication 6.1: Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. (EK3.D.1) 1. Introduction to Communication Communication requires the generation,
Domain 6: Communication 6.1: Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. (EK3.D.1) 1. Introduction to Communication Communication requires the generation,
Role of Unc51.1 and its binding partners in CNS axon outgrowth
 Role of Unc51.1 and its binding partners in CNS axon outgrowth Toshifumi Tomoda, Jee Hae Kim, Caixin Zhan, and Mary E. Hatten 1 Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology, The Rockefeller University, New
Role of Unc51.1 and its binding partners in CNS axon outgrowth Toshifumi Tomoda, Jee Hae Kim, Caixin Zhan, and Mary E. Hatten 1 Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology, The Rockefeller University, New
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
The neuron as a secretory cell
 The neuron as a secretory cell EXOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS The secretory pathway. Transport and sorting of proteins in the secretory pathway occur as they pass through the Golgi complex before reaching the
The neuron as a secretory cell EXOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS The secretory pathway. Transport and sorting of proteins in the secretory pathway occur as they pass through the Golgi complex before reaching the
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
with%dr.%van%buskirk%%%
 with%dr.%van%buskirk%%% How$to$do$well?$ Before$class:$read$the$corresponding$chapter$ Come$to$class$ready$to$par9cipate$in$Top$Hat$ Don t$miss$an$exam!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!$ But$I m$not$good$with$science
with%dr.%van%buskirk%%% How$to$do$well?$ Before$class:$read$the$corresponding$chapter$ Come$to$class$ready$to$par9cipate$in$Top$Hat$ Don t$miss$an$exam!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!$ But$I m$not$good$with$science
Sarah Bashiruddin Georgina Lopez Jillian Merica Sarah Wardlaw
 Sarah Bashiruddin Georgina Lopez Jillian Merica Sarah Wardlaw Introduction: Dr. Carol Erickson and her lab study the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which neural crest cells differentiate and migrate
Sarah Bashiruddin Georgina Lopez Jillian Merica Sarah Wardlaw Introduction: Dr. Carol Erickson and her lab study the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which neural crest cells differentiate and migrate
Intercellular Communication. Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara
 Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
Pioneer midbrain longitudinal axons navigate using a balance of Netrin attraction and Slit repulsion
 Pioneer midbrain longitudinal axons navigate using a balance of Netrin attraction and Slit repulsion Kim et al. Kim et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:17 Kim et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:17 RESEARCH
Pioneer midbrain longitudinal axons navigate using a balance of Netrin attraction and Slit repulsion Kim et al. Kim et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:17 Kim et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:17 RESEARCH
The cis side of juxtacrine signaling: a new role in the development of the nervous system
 Review The cis side of juxtacrine signaling: a new role in the development of the nervous system Avraham Yaron 1 and David Sprinzak 2 1 Department of Biological Chemistry, Weizmann Institute of Science,
Review The cis side of juxtacrine signaling: a new role in the development of the nervous system Avraham Yaron 1 and David Sprinzak 2 1 Department of Biological Chemistry, Weizmann Institute of Science,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1237 a b retinol retinal RA OH RDH (retinol dehydrogenase) O H Raldh2 O R/R.6.4.2 (retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) RA retinal retinol..1.1 1 Concentration (nm)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1237 a b retinol retinal RA OH RDH (retinol dehydrogenase) O H Raldh2 O R/R.6.4.2 (retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) RA retinal retinol..1.1 1 Concentration (nm)
Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective
 Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective H. Steven Wiley January 22nd, 2002 What is a Systems Approach in the Context of Biological Organisms? Looking at cells as integrated systems and not as
Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective H. Steven Wiley January 22nd, 2002 What is a Systems Approach in the Context of Biological Organisms? Looking at cells as integrated systems and not as
REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
active site Region of an enzyme surface to which a substrate molecule binds in order to undergo a catalyzed reaction.
 Glossary acetyl Chemical group derived from acetic acid. Acetyl groups are important in metabolism and are added covalently to some proteins as a posttranslational modification. actin Abundant protein
Glossary acetyl Chemical group derived from acetic acid. Acetyl groups are important in metabolism and are added covalently to some proteins as a posttranslational modification. actin Abundant protein
Supplementary Table 3. Membrane/Signaling/Neural Genes of the DmSP. FBgn CG5265 acetyltransferase amino acid metabolism
 Supplementary Table 3 Membrane/Signaling/Neural Genes of the DmSP FlyBase ID Gene Name Molecular function summary Membrane Biological process summary FBgn0038486 CG5265 acetyltransferase amino acid metabolism
Supplementary Table 3 Membrane/Signaling/Neural Genes of the DmSP FlyBase ID Gene Name Molecular function summary Membrane Biological process summary FBgn0038486 CG5265 acetyltransferase amino acid metabolism
Supplementary Figure 1-10 with Figure legends
 332 coordinates mechanotransduction and growth cone bifurcation in sensory neurons Li Yang Chiang 1, Kate Poole, Beatriz E. Oliveira, Neuza Duarte,Yinth Andrea Bernal Sierra, Leena Bruckner Tuderman, Manuel
332 coordinates mechanotransduction and growth cone bifurcation in sensory neurons Li Yang Chiang 1, Kate Poole, Beatriz E. Oliveira, Neuza Duarte,Yinth Andrea Bernal Sierra, Leena Bruckner Tuderman, Manuel
Src Family Kinases Are Involved in EphA Receptor-Mediated Retinal Axon Guidance
 6248 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 14, 2004 24(28):6248 6257 Development/Plasticity/Repair Src Family Kinases Are Involved in EphA Receptor-Mediated Retinal Axon Guidance Bernd Knöll and Uwe Drescher
6248 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 14, 2004 24(28):6248 6257 Development/Plasticity/Repair Src Family Kinases Are Involved in EphA Receptor-Mediated Retinal Axon Guidance Bernd Knöll and Uwe Drescher
C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance
 C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance Biorad Lihsia Chen Dept. of Genetics, Cell Biology & Development Developmental Biology Center C. elegans embryogenesis Goldstein lab, UNC-Chapel
C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance Biorad Lihsia Chen Dept. of Genetics, Cell Biology & Development Developmental Biology Center C. elegans embryogenesis Goldstein lab, UNC-Chapel
The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi Cisternal Stacking and Cell Cycle Progression
 Traffic 2010; 11: 827 842 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01055.x The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi Cisternal Stacking and Cell Cycle Progression Danming Tang, Hebao Yuan and Yanzhuang
Traffic 2010; 11: 827 842 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01055.x The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi Cisternal Stacking and Cell Cycle Progression Danming Tang, Hebao Yuan and Yanzhuang
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals?
 LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
CL T123 PKA? Possible Cx26deaf mutation: T123N 2,3 EL2 T177 Intracellular kinases or ecto-kinases 2 EL2/TM4 border
 Name AA MW (Da) Cx26 =GJB2 Cx31 =GJB3 BIP Region P-site Modifying enzyme 226 26,215 9.11 NT D2, T5 or S8 1 # Functional consequences Deafness mutation at S8 1 CL T123 PKA Possible Cx26deaf mutation: T123N
Name AA MW (Da) Cx26 =GJB2 Cx31 =GJB3 BIP Region P-site Modifying enzyme 226 26,215 9.11 NT D2, T5 or S8 1 # Functional consequences Deafness mutation at S8 1 CL T123 PKA Possible Cx26deaf mutation: T123N
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
Localized Ras signaling at the leading edge regulates PI3K, cell polarity, and directional cell movement
 JCB: ARTICLE Localized Ras signaling at the leading edge regulates PI3K, cell polarity, and directional cell movement Atsuo T. Sasaki, Cheryl Chun, Kosuke Takeda, and Richard A. Firtel Section of Cell
JCB: ARTICLE Localized Ras signaling at the leading edge regulates PI3K, cell polarity, and directional cell movement Atsuo T. Sasaki, Cheryl Chun, Kosuke Takeda, and Richard A. Firtel Section of Cell
Eph, a Protein Family Coming of Age: More Confusion, Insight, or Complexity? Martin Lackmann and Andrew W. Boyd (15 April 2008)
 Eph, a Protein Family Coming of Age: More Confusion, Insight, or Complexity? Martin Lackmann and Andrew W. Boyd (15 April 2008) Science Signaling 1 (15), re2. [DOI: 10.1126/stke.115re2] The following resources
Eph, a Protein Family Coming of Age: More Confusion, Insight, or Complexity? Martin Lackmann and Andrew W. Boyd (15 April 2008) Science Signaling 1 (15), re2. [DOI: 10.1126/stke.115re2] The following resources
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 30, Please print your name:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 30, 2014 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 30, 2014 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Neurophysiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Development of Drosophila
 Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Monday, 27 June, 9.30 am 12.30 pm Answer
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Monday, 27 June, 9.30 am 12.30 pm Answer
FRET 1 FRET CFP YFP. , resonance energy transfer, FRET), , CFP, (green fluorescent protein, GFP) ). GFP ]. GFP GFP, YFP. , GFP , CFP.
![FRET 1 FRET CFP YFP. , resonance energy transfer, FRET), , CFP, (green fluorescent protein, GFP) ). GFP ]. GFP GFP, YFP. , GFP , CFP. FRET 1 FRET CFP YFP. , resonance energy transfer, FRET), , CFP, (green fluorescent protein, GFP) ). GFP ]. GFP GFP, YFP. , GFP , CFP.](/thumbs/92/108070919.jpg) 980 Prog Biochem Biophys FRET 2 3 33 (, 510631) FRET 2,, 2,, 2 (fluorescence resonance energy transfer, FRET),, 2, ( FRET), 2, Q6 ( ) GFP CFP YFP : CFP : ( fluorescence YFP, resonance energy transfer,
980 Prog Biochem Biophys FRET 2 3 33 (, 510631) FRET 2,, 2,, 2 (fluorescence resonance energy transfer, FRET),, 2, ( FRET), 2, Q6 ( ) GFP CFP YFP : CFP : ( fluorescence YFP, resonance energy transfer,
