5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin
|
|
|
- Gervase Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1
2 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune function -tumor progression cell guidance control by semaphorins requires plexins the functional receptor for secreted semaphorins is a complex including neuropilins and plexins semaphorins have multiple functions in morphogenesis and tissue remodeling by mediating cell-repelling cues through plexin receptors SEMAPHORIN SUBFAMILIES Class 1 and 2 contain transmembrane and secreted semaphorins from invertebrates, respectively. Secreted semaphorins of vertebrates fall into class 3. The other vertebrate semaphorins are membrane bound, either transmembrane (class 4, 5, and 6) or GPI anchored (class 7). The Sema domain is the hallmark of this protein family, and it includes a Met-related sequence (MRS motif). Other conserved domains are immunoglobulin domains (in classes 2, 3, 4, and 7), domains rich in basic amino acids (class 3), and thrombospondin repeats (class 5). 2
3 THE SEMAPHORIN RECEPTORS PLEXINS Nine human plexins are currently known, which fall into four homology groups (A, B, C, and D subfamilies), based on sequence similarity, structural features, and tissue distribution. All plexins include a conserved cytoplasmic domain (sex-plexin domain, SP, blue) and a Sema domain (yellow). Repeated MRS motifs (orange) are found in the extracellular domain. Plexin-B subfamily members include potential cleavage sites for furin-like convertases (also found in plexin-b of Drosophila, here marked in red). The prototype member of the plexin-c subfamily (Vespr) is shorter, including only two MRS motifs. Plexin-D1 includes an atypical sequence in its third MRS (stippled). Evolution of semaphorins and their receptors 3
4 Semaphorins and plexins Both semaphorins and plexins are characterized by Sema domains. Additional domains that are present in semaphorins include PSI (plexin, semaphorin and integrin) domains, immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, thrombospondin domains and PDZ domain-binding sites, both putative and described. Additional domains present in plexins include PSI domains, IPT (Ig-like, plexins and transcription factors) domains, a GTPase-binding domain and a segment GAP (GTPase-activating protein) domain. Some plexins also have PDZ-domain binding sites, and convertase-cleavage sites. Arrows indicate binding interactions detected between semaphorins and plexins. Labels on the arrows indicate which specific semaphorin has been shown to interact with which plexin. Blue labels indicate the necessity for neuropilin-1 (dark blue) or neuropilin-2 (light blue) as coreceptors. Semaphorin signals can act in different modes Short range (juxtacrine) Autocrine Long range (paracrine) 4
5 Semaphorin plexin interactions semaphorins can be both membrane-bound and secreted, plexins can functionally interact with semaphorins on adjacent cells and with semaphorins in the extracellular environment semaphorin binding relieves plexin autoinhibition, as Plexin-A1 lacking its Sema domain is constitutively active. An intramolecular interaction between the Sema domain and the rest of the plexin extracellular domain probably inhibits receptor activity in the unbound state most plexin semaphorin interactions are mediated through the Sema domains of both proteins, except for class 3 semaphorins, which, with one exception, require neuropilins as essential semaphorin binding co-receptors to signal through class A plexins neuropilins are transmembrane proteins of ~900 amino acids with short intracellular domains that lack intrinsic enzymatic activity. They function as the ligand-binding partner in co-receptor complexes for both plexins and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs). Receptors for secreted or membrane-bound semaphorins Secreted (subclass 3) semaphorins are dimeric and bind to receptor complexes that include neuropilins (homo or heterodimeric) and plexins (dimeric?). Membrane-bound semaphorins bind directly to plexins and transduce intracellular signals through the sex-plexin (SP) domain. Transmembrane semaphorins might generate bidirectional signals by associating with cytoplasmic transducers. 5
6 Semaphorin signalling is mediated by Receptor Complexes Secreted SEMAs GPI-SEMAs Ig-CAMs (e.g. L1) NP-1/2 OTK Integrins TM-SEMAs VEGFs CD72 SFs VEGF-Rs VEGF-Rs PLEXINS Erb-B2 cyto-tks SF-Rs (e.g. Met) Semaphorins Regulate a Variety of Functions stop or go Axon guidance Immune response Cell migration e.g. Neural Crest cells Oligodendrocytes Endothelial cells Epithelial cells Cancer cells 6
7 Semaphorins Regulate a Variety of Functions stop or go Axon guidance Cell migration SEMAPHORIN + Sema Cellular collapse Sema PLEXIN + Sema Axon turning Growth cone collapse Sema4D-induced collapse of neuronal growth cones is abrogated in PlexinB1-deficient neurons nt Sema4D PlexinB1 Sema 4D Collapsed neuronal growth cones 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% WT PlexB1 KO con Sema4D Phalloidin-FITC α-vinculin hippocampal neurons growth cones 7
8 Plexin signalling and the collapsing response can inhibit cell migration + Sema 4D + Sema 4D Transwell insert Adhering cells Upper chamber Microporous membrane (8 µm) Lower chamber SKBR3 mammary carcinoma cells NIH-3T3 fibroblasts Axons and cells retract in response to semaphorins (the collapsing response) 8
9 Cellular collapse upon Plexin-B1 activation control + Sema4D Cellular collapse upon Plexin activation control + Sema4D time: 0 time: 15 9
10 What are the molecular mechanisms mediating semaphorin signals? Molecular mechanisms controlling cell migration Rear retraction 1. Integrin-based adhesion 2. Cytoskeletal remodeling (Rho GTPases) 10
11 Cell-substrate adhesive complexes Epithelial cell Fibroblast Sema4D triggers the disassambly of adhesive structures in epithelial cells expressing endogenous Plexin-B1 nt Sema4D 30 Sema4D 60 SKBR3 cells 11
12 Plexin activation elicits the disassembly of focal adhesions FA+ : 92 % SF+ : 100 % 31% 16% 2% 80% 21% 2% NIH-3T3 fibroblasts expressing Plexin-B1 Barberis et al., 2004 Plexin signalling inhibits cell migration Adhering cells Transwell insert Upper chamber Microporous membrane (8 µm) Lower chamber NIH-3T3 fibroblasts SKBR3 epithelial cells 12
13 Semaphorin signalling on activation by semaphorins, plexins become phosphorylated on tyrosine residues in their cytoplasmic domain the mechanisms of tyrosine phosphorylation and the role of kinases in plexin signalling are now being unveiled for both class A and B plexins Plexins have GAP activity towards R-Ras the intracellular domain of plexins has two highly conserved regions (C1 and C2) that are similar to a GAP (GTPase-activating protein) domain divided in two by a linker region the conserved regions contain two arginine residues that are necessary for catalytic activity in GAPs. They are essential in Plexin-A1 signalling and mutating them in Plexin-B1 abolishes the Sema4D induced collapse of COS-7 cells consequently, it has been suggested that plexins could be Ras GAPs, but until recently these ideas were only speculative, as efforts to establish GAP activity proved difficult it has recently been established that both Plexin-B1 and Plexin-A1 are GAPs for the Ras-family GTPase R-Ras this finding establishes a new mechanism of GAP regulation and promotes plexins to the pantheon of transmembrane receptors with intrinsic enzymatic activity 13
14 Plexin A1 signalling no ligand - without ligand, R-Ras is active, resulting in integrin-mediated attachment to the extracellular matrix (ECM). Plexin A1 signalling + Sema3A 14
15 Plexin B1 signalling no ligand without bound semaphorin, active Rac promotes the activation of p21- activated kinase (PAK). + Sema4D Plexin B1 signalling 15
16 Semaphorins repel axonal growth cones 16
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
ADAM FAMILY. ephrin A INTERAZIONE. Eph ADESIONE? PROTEOLISI ENDOCITOSI B A RISULTATO REPULSIONE. reverse. forward
 ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology
 Cell Adhesion 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology 1 Cell-Cell Adhesion and Cell-Matrix Adhesion actin filaments adhesion belt (cadherins) cadherin Ig CAMs integrin
Cell Adhesion 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology 1 Cell-Cell Adhesion and Cell-Matrix Adhesion actin filaments adhesion belt (cadherins) cadherin Ig CAMs integrin
CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION
 CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION paracrine & juxtacrine signalling autocrine & intracrine signalling methods to study cell-cell communication: attraction & repulsion chemotaxis & chemokinesis substrate preference
CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION paracrine & juxtacrine signalling autocrine & intracrine signalling methods to study cell-cell communication: attraction & repulsion chemotaxis & chemokinesis substrate preference
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization
 Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 An immature neuron in cell culture first sprouts
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 An immature neuron in cell culture first sprouts
Axon Guidance. Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues:
 Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Cell Adhesion and Signaling
 Cell Adhesion and Signaling mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology 1 Transactivation NATURE REVIEWS CANCER VOLUME 7 FEBRUARY 2007 85 2 Functions of Cell Adhesion cell cycle proliferation
Cell Adhesion and Signaling mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology 1 Transactivation NATURE REVIEWS CANCER VOLUME 7 FEBRUARY 2007 85 2 Functions of Cell Adhesion cell cycle proliferation
Biol403 - Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases
 Biol403 - Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases The TGFβ (transforming growth factorβ) family of growth factors TGFβ1 was first identified as a transforming factor; however, it is a member of a family of structurally
Biol403 - Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases The TGFβ (transforming growth factorβ) family of growth factors TGFβ1 was first identified as a transforming factor; however, it is a member of a family of structurally
Neurite initiation. Neurite formation begins with a bud that sprouts from the cell body. One or several neurites can sprout at a time.
 Neurite initiation. Neuronal maturation initiation f-actin polarization and maturation tubulin stage 1: "spherical" neuron stage 2: neurons extend several neurites stage 3: one neurite accelerates its
Neurite initiation. Neuronal maturation initiation f-actin polarization and maturation tubulin stage 1: "spherical" neuron stage 2: neurons extend several neurites stage 3: one neurite accelerates its
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization. The cytoskeletal components of neurons have characteristic distributions and associations
 Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
Semaphorins as signals for cell repulsion and invasion
 PERSPECTIVE SERIES Invasive growth Paolo Comoglio, Series Editor Semaphorins as signals for cell repulsion and invasion Yoshio Goshima, 1,3 Takaaki Ito, 2 Yukio Sasaki, 1 and Fumio Nakamura 1 1 Department
PERSPECTIVE SERIES Invasive growth Paolo Comoglio, Series Editor Semaphorins as signals for cell repulsion and invasion Yoshio Goshima, 1,3 Takaaki Ito, 2 Yukio Sasaki, 1 and Fumio Nakamura 1 1 Department
Mechanisms of Human Health and Disease. Developmental Biology
 Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Amneh Auben. Abdulrahman Jabr. Diala Abu-Hassan
 21 Amneh Auben Abdulrahman Jabr Diala Abu-Hassan Matrix polysaccharides Extracellular matrix (ECM): It s a collection of components that fills the spaces outside the cell or between the cells. ---------
21 Amneh Auben Abdulrahman Jabr Diala Abu-Hassan Matrix polysaccharides Extracellular matrix (ECM): It s a collection of components that fills the spaces outside the cell or between the cells. ---------
Reading. Lecture VI. Making Connections 9/17/12. Bio 3411 Lecture VI. Making Connections. Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012
 Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Supplemental table S7.
 Supplemental table S7. GO terms significantly enriched in significantly up-regulated genes of the microarray. K: number of genes from the input cluster in the given category. F: number of total genes in
Supplemental table S7. GO terms significantly enriched in significantly up-regulated genes of the microarray. K: number of genes from the input cluster in the given category. F: number of total genes in
Conclusions. The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights
 C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts
 Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts - Integrins as central adhesion receptors - - Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) as a central signal molecule - Structure of Cell/Cell and Cell/Matrix
Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts - Integrins as central adhesion receptors - - Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) as a central signal molecule - Structure of Cell/Cell and Cell/Matrix
C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance
 C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance Biorad Lihsia Chen Dept. of Genetics, Cell Biology & Development Developmental Biology Center C. elegans embryogenesis Goldstein lab, UNC-Chapel
C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance Biorad Lihsia Chen Dept. of Genetics, Cell Biology & Development Developmental Biology Center C. elegans embryogenesis Goldstein lab, UNC-Chapel
Axon guidance I. Paul Garrity March 15, /9.013
 Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
RANK. Alternative names. Discovery. Structure. William J. Boyle* SUMMARY BACKGROUND
 RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation
 Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Varicose and cheerio collaborate with pebble to mediate semaphorin-1a reverse signaling in Drosophila
 Varicose and cheerio collaborate with pebble to mediate semaphorin-1a reverse signaling in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong a,1, Da-som Yang a, Young Gi Hong a, Sarah P. Mitchell b,c, Matthew P. rown b,c, and
Varicose and cheerio collaborate with pebble to mediate semaphorin-1a reverse signaling in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong a,1, Da-som Yang a, Young Gi Hong a, Sarah P. Mitchell b,c, Matthew P. rown b,c, and
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation
 Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Types of Cell Movement passive: active: cell sheets flow cilia or flagella ameboid adhesion
Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Types of Cell Movement passive: active: cell sheets flow cilia or flagella ameboid adhesion
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Migration of Neurons During Embryonic Development. Christine Simmons Saint Louis University April 15 th, 2008
 Migration of Neurons During Embryonic Development Christine Simmons Saint Louis University April 15 th, 2008 Embryonic Development of the CNS Central Nervous System (CNS) arises from Surface ectoderm Skin,
Migration of Neurons During Embryonic Development Christine Simmons Saint Louis University April 15 th, 2008 Embryonic Development of the CNS Central Nervous System (CNS) arises from Surface ectoderm Skin,
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
The EGF Signaling Pathway! Introduction! Introduction! Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3. EGF promotes cell growth
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
S1 Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the network alignment results
 1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
targets. clustering show that different complex pathway
 Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Chapter 16. Cellular Movement: Motility and Contractility. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Cellular Movement: Motility and Contractility Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Two eukaryotic motility systems 1. Interactions between motor proteins and microtubules
Chapter 16 Cellular Movement: Motility and Contractility Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Two eukaryotic motility systems 1. Interactions between motor proteins and microtubules
The Molecular Biology of Axon Guidance
 Thursday, January 25, 2001 Science -- Tessier-Lavigne and Goodman 274 (5290): 1123 Page: 1 Institution: HARVARD UNIVERSITY Sign In as Individual FAQ The Molecular Biology of Axon Guidance Marc Tessier-Lavigne
Thursday, January 25, 2001 Science -- Tessier-Lavigne and Goodman 274 (5290): 1123 Page: 1 Institution: HARVARD UNIVERSITY Sign In as Individual FAQ The Molecular Biology of Axon Guidance Marc Tessier-Lavigne
Plexins: axon guidance and signal transduction
 CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62 (2005) 1363 1371 1420-682X/05/121363-09 DOI 10.1007/s00018-005-5018-2 Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2005 CMLS Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Review Plexins: axon guidance
CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62 (2005) 1363 1371 1420-682X/05/121363-09 DOI 10.1007/s00018-005-5018-2 Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2005 CMLS Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Review Plexins: axon guidance
b. The maximum binding will decrease.
 Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular
Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 04
 01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Signal Transduction Phosphorylation Protein kinases. Misfolding diseases. Protein Engineering Lysozyme variants
 Signal Transduction Phosphorylation Protein kinases Misfolding diseases Protein Engineering Lysozyme variants Cells and Signals Regulation The cell must be able to respond to stimuli Cellular activities
Signal Transduction Phosphorylation Protein kinases Misfolding diseases Protein Engineering Lysozyme variants Cells and Signals Regulation The cell must be able to respond to stimuli Cellular activities
The Control of Semaphorin-1a-Mediated Reverse Signaling by Opposing Pebble and RhoGAPp190 Functions in Drosophila
 Article The Control of Semaphorin-1a-Mediated Reverse Signaling by Opposing Pebble and RhoGAPp190 Functions in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong, 1 Katarina Juhaszova, 1 and Alex L. Kolodkin 1, 1 Solomon H. Snyder
Article The Control of Semaphorin-1a-Mediated Reverse Signaling by Opposing Pebble and RhoGAPp190 Functions in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong, 1 Katarina Juhaszova, 1 and Alex L. Kolodkin 1, 1 Solomon H. Snyder
Chemical aspects of the cell. Shape and structure of the cell
 Chemical aspects of the cell Shape and structure of the cell Cellular composition https://www.studyblue.com/ 2 Cellular composition Set of videos with basic information: Cell characteristics: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=urujd5nexc8
Chemical aspects of the cell Shape and structure of the cell Cellular composition https://www.studyblue.com/ 2 Cellular composition Set of videos with basic information: Cell characteristics: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=urujd5nexc8
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
CHAPTER 1 THE STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY OF THE FGF19 SUBFAMILY
 CHAPTER 1 THE STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY OF THE FGF19 SUBFAMILY Andrew Beenken and Moosa Mohammadi* Department of Pharmacology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA. *Corresponding Author:
CHAPTER 1 THE STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY OF THE FGF19 SUBFAMILY Andrew Beenken and Moosa Mohammadi* Department of Pharmacology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA. *Corresponding Author:
 Cell-cell communication in development Review of cell signaling, paracrine and endocrine factors, cell death pathways, juxtacrine signaling, differentiated state, the extracellular matrix, integrins, epithelial-mesenchymal
Cell-cell communication in development Review of cell signaling, paracrine and endocrine factors, cell death pathways, juxtacrine signaling, differentiated state, the extracellular matrix, integrins, epithelial-mesenchymal
Cells to Tissues. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Supplementary Table 3. Membrane/Signaling/Neural Genes of the DmSP. FBgn CG5265 acetyltransferase amino acid metabolism
 Supplementary Table 3 Membrane/Signaling/Neural Genes of the DmSP FlyBase ID Gene Name Molecular function summary Membrane Biological process summary FBgn0038486 CG5265 acetyltransferase amino acid metabolism
Supplementary Table 3 Membrane/Signaling/Neural Genes of the DmSP FlyBase ID Gene Name Molecular function summary Membrane Biological process summary FBgn0038486 CG5265 acetyltransferase amino acid metabolism
1- Eph- ephrin. Eph receptors and ephrin ligands. *glycosylphosphatidylinositol. anchored
 1- Eph- ephrin Eph receptors and ephrin ligands * *glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchored 1 Midline guidance in the visual system In animals with binocular vision, most retinal axons (red) cross
1- Eph- ephrin Eph receptors and ephrin ligands * *glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchored 1 Midline guidance in the visual system In animals with binocular vision, most retinal axons (red) cross
1. Introduction. 1. Introduction. 1.1 Signal transduction
 1. Introduction 1.1 Signal transduction During the evolution of multicellular organisms, highly complex and integrative communication networks have evolved to coordinate growth, differentiation and metabolism
1. Introduction 1.1 Signal transduction During the evolution of multicellular organisms, highly complex and integrative communication networks have evolved to coordinate growth, differentiation and metabolism
MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways
 MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways Lisa Stalheim and Gary L. Johnson Abstract SAPK/JNK members of the MAPK family are regulated by at least fourteen known MAPK kinase kinases (MKKKs). In
MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways Lisa Stalheim and Gary L. Johnson Abstract SAPK/JNK members of the MAPK family are regulated by at least fourteen known MAPK kinase kinases (MKKKs). In
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Visual pigments. Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019
 Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology
 Department of Biology Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology Academic contact during examination: Per Winge Phone: 99369359 Examination date: 20 th December 2017 Examination time (from-to):
Department of Biology Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology Academic contact during examination: Per Winge Phone: 99369359 Examination date: 20 th December 2017 Examination time (from-to):
PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION
 PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION PART-A 1. What is prokaryotic cell 2. Explain Eukaryotic cell 3. Major difference of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 4. Role of lipid
PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION PART-A 1. What is prokaryotic cell 2. Explain Eukaryotic cell 3. Major difference of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 4. Role of lipid
This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository:
 This is an pen Access document downloaded from RCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/5576/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted for
This is an pen Access document downloaded from RCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/5576/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted for
Raghuram et al PNAS 100:9620
 ION CHANNL MACROMOLCULAR COMPLXS A V I R W c g I S L S R d L L LLL I VA S f L LS HP a b D G C S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 I e V N S6 COOH NH 2 PDZ domains; recognition of short peptides with a COOH terminal hydrophobic
ION CHANNL MACROMOLCULAR COMPLXS A V I R W c g I S L S R d L L LLL I VA S f L LS HP a b D G C S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 I e V N S6 COOH NH 2 PDZ domains; recognition of short peptides with a COOH terminal hydrophobic
Receptors and Ion Channels
 Receptors and Ion Channels Laurie Kellaway Senior Lecturer Department of Human Biology Laurie@curie.uct.ac.za Tel. +27 +21 4066 271 What are the two types of Neurotransmitter receptors Ionotropic receptors
Receptors and Ion Channels Laurie Kellaway Senior Lecturer Department of Human Biology Laurie@curie.uct.ac.za Tel. +27 +21 4066 271 What are the two types of Neurotransmitter receptors Ionotropic receptors
Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Manning et al. 1.173/pnas.8131415 SI Text RM1 Motif. This Monosiga-specific motif of 22 aa is repeated 8 13 times in the extracellular regions of two RTKA s, one RTKG, and 4 other
Supporting Information Manning et al. 1.173/pnas.8131415 SI Text RM1 Motif. This Monosiga-specific motif of 22 aa is repeated 8 13 times in the extracellular regions of two RTKA s, one RTKG, and 4 other
10/2/2015. Chapter 4. Determination and Differentiation. Neuroanatomical Diversity
 Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Visual pigments. Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2015
 Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2015 References Photoreceptors and visual pigments Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a127)
Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2015 References Photoreceptors and visual pigments Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a127)
6 Mechanotransduction
 6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1)
 Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1) The most important properties of an ion channel Intrinsic properties of the channel (Selectivity and Mode of Gating) + Location Physiological Function Types
Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1) The most important properties of an ion channel Intrinsic properties of the channel (Selectivity and Mode of Gating) + Location Physiological Function Types
The sense of smell Outline Main Olfactory System Odor Detection Odor Coding Accessory Olfactory System Pheromone Detection Pheromone Coding
 The sense of smell Outline Main Olfactory System Odor Detection Odor Coding Accessory Olfactory System Pheromone Detection Pheromone Coding 1 Human experiment: How well do we taste without smell? 2 Brief
The sense of smell Outline Main Olfactory System Odor Detection Odor Coding Accessory Olfactory System Pheromone Detection Pheromone Coding 1 Human experiment: How well do we taste without smell? 2 Brief
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p
 Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
FARP1 Promotes the Dendritic Growth of Spinal Motor Neuron Subtypes through Transmembrane Semaphorin6A and PlexinA4 Signaling
 Article FARP1 Promotes the Dendritic Growth of Spinal Motor Neuron Subtypes through Transmembrane Semaphorin6A and PlexinA4 Signaling BinQuan Zhuang, 1 YouRong Sophie Su, 1 and Shanthini Sockanathan 1,
Article FARP1 Promotes the Dendritic Growth of Spinal Motor Neuron Subtypes through Transmembrane Semaphorin6A and PlexinA4 Signaling BinQuan Zhuang, 1 YouRong Sophie Su, 1 and Shanthini Sockanathan 1,
Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Commissural Axon Guidance: The Role of Intracellular Tyrosine Kinases in Netrin-Dcc/Frazzled Axon Attraction
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Commissural Axon Guidance: The Role of Intracellular Tyrosine Kinases in Netrin-Dcc/Frazzled
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Commissural Axon Guidance: The Role of Intracellular Tyrosine Kinases in Netrin-Dcc/Frazzled
Cell Biology Review. The key components of cells that concern us are as follows: 1. Nucleus
 Cell Biology Review Development involves the collective behavior and activities of cells, working together in a coordinated manner to construct an organism. As such, the regulation of development is intimately
Cell Biology Review Development involves the collective behavior and activities of cells, working together in a coordinated manner to construct an organism. As such, the regulation of development is intimately
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, an expert on cell adhesion and AFM (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, an expert on cell adhesion and AFM (Remarks to the Author): Understanding how cells adhere to extracellular matrix proteins is a very important, yet not fully understood
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1, an expert on cell adhesion and AFM (Remarks to the Author): Understanding how cells adhere to extracellular matrix proteins is a very important, yet not fully understood
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
The Protein Ontology: An Evolution
 The rotein Ontology: An Evolution 251 st ACS National Meeting & Exposition Chemistry, Data & the Semantic Web: An Important Triple to Advance Science San Diego, CA Darren A. Natale, h.d. rotein Science
The rotein Ontology: An Evolution 251 st ACS National Meeting & Exposition Chemistry, Data & the Semantic Web: An Important Triple to Advance Science San Diego, CA Darren A. Natale, h.d. rotein Science
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
The plexin PLX-2 and the ephrin EFN-4 have distinct roles in MAB-20/Semaphorin
 The plexin PLX-2 and the ephrin EFN-4 have distinct roles in MAB-20/Semaphorin 2A signaling in C. elegans morphogenesis Fumi Nakao *,1, Martin L. Hudson,1, Motoshi Suzuki *, Zachary Peckler, Rie Kurokawa
The plexin PLX-2 and the ephrin EFN-4 have distinct roles in MAB-20/Semaphorin 2A signaling in C. elegans morphogenesis Fumi Nakao *,1, Martin L. Hudson,1, Motoshi Suzuki *, Zachary Peckler, Rie Kurokawa
Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
AXON GUIDANCE MECHANISMS AND MOLECULES: LESSONS FROM INVERTEBRATES
 AXON GUIDANCE MECHANISMS AND MOLECULES: LESSONS FROM INVERTEBRATES Sofia J. Araújo and Guy Tear Vertebrates and invertebrates share the formidable task of accurately establishing the elaborate connections
AXON GUIDANCE MECHANISMS AND MOLECULES: LESSONS FROM INVERTEBRATES Sofia J. Araújo and Guy Tear Vertebrates and invertebrates share the formidable task of accurately establishing the elaborate connections
Domain 6: Communication
 Domain 6: Communication 6.1: Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. (EK3.D.1) 1. Introduction to Communication Communication requires the generation,
Domain 6: Communication 6.1: Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. (EK3.D.1) 1. Introduction to Communication Communication requires the generation,
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-2016 FUNDAMENTALS OF CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY BIO-4004B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-2016 FUNDAMENTALS OF CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY BIO-4004B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section
Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition
 Supplementary Information to Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition Nadine Czudnochowski 1,2, *, Christian A. Bösken 1, * & Matthias Geyer 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Supplementary Information to Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition Nadine Czudnochowski 1,2, *, Christian A. Bösken 1, * & Matthias Geyer 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs), HAESA, ERECTA-family
 Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs), HAESA, ERECTA-family GENES & DEVELOPMENT (2000) 14: 108 117 INTRODUCTION Flower Diagram INTRODUCTION Abscission In plant, the process by which a plant
Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs), HAESA, ERECTA-family GENES & DEVELOPMENT (2000) 14: 108 117 INTRODUCTION Flower Diagram INTRODUCTION Abscission In plant, the process by which a plant
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins
 13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
The neuron as a secretory cell
 The neuron as a secretory cell EXOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS The secretory pathway. Transport and sorting of proteins in the secretory pathway occur as they pass through the Golgi complex before reaching the
The neuron as a secretory cell EXOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS The secretory pathway. Transport and sorting of proteins in the secretory pathway occur as they pass through the Golgi complex before reaching the
Inhibitors of neuronal regeneration: mediators and signaling mechanisms
 Neurochemistry International 42 (2003) 189 203 Review Inhibitors of neuronal regeneration: mediators and signaling mechanisms Bor Luen Tang a,b, a NCA Laboratory, Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology,
Neurochemistry International 42 (2003) 189 203 Review Inhibitors of neuronal regeneration: mediators and signaling mechanisms Bor Luen Tang a,b, a NCA Laboratory, Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology,
1. The plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells is supported by a. actin filaments. b. microtubules. c. lamins. d. intermediate filaments.
 ANALYSIS AND MODELING OF CELL MECHANICS Homework #2 (due 1/30/13) This homework involves comprehension of key biomechanical concepts of the cytoskeleton, cell-matrix adhesions, and cellcell adhesions.
ANALYSIS AND MODELING OF CELL MECHANICS Homework #2 (due 1/30/13) This homework involves comprehension of key biomechanical concepts of the cytoskeleton, cell-matrix adhesions, and cellcell adhesions.
Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers.
 The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
Semiotic modelling of biological processes: Semiotic processes in the immune system João Queiroz a,b,c & Charbel El-Hani b,c,d
 Semiotic modelling of biological processes: Semiotic processes in the immune system João Queiroz a,b,c & Charbel El-Hani b,c,d a. Institute of Arts and Design, Federal University of Juiz de Fora, Brazil.
Semiotic modelling of biological processes: Semiotic processes in the immune system João Queiroz a,b,c & Charbel El-Hani b,c,d a. Institute of Arts and Design, Federal University of Juiz de Fora, Brazil.
Old FINAL EXAM BIO409/509 NAME. Please number your answers and write them on the attached, lined paper.
 Old FINAL EXAM BIO409/509 NAME Please number your answers and write them on the attached, lined paper. Gene expression can be regulated at several steps. Describe one example for each of the following:
Old FINAL EXAM BIO409/509 NAME Please number your answers and write them on the attached, lined paper. Gene expression can be regulated at several steps. Describe one example for each of the following:
Introduction to Cellular Communication *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
A Monte Carlo study of ligand-dependent integrin signal initiation
 A Monte Carlo study of ligand-dependent integrin signal initiation Federico Felizzi and Dagmar Iber 1 D-BSSE, ETH Zurich, Mattenstrasse 26, CH-4058 Basel, Switzerland 1 Author for correspondance, Dagmar.Iber@bsse.ethz.ch
A Monte Carlo study of ligand-dependent integrin signal initiation Federico Felizzi and Dagmar Iber 1 D-BSSE, ETH Zurich, Mattenstrasse 26, CH-4058 Basel, Switzerland 1 Author for correspondance, Dagmar.Iber@bsse.ethz.ch
Epithelial Polarity. Gerard Apodaca Luciana I. Gallo. Colloquium series on Building BloCks of the Cell: Cell structure and function
 Colloquium series on Building BloCks of the Cell: Cell structure and function Series Editor: Ivan Robert Nabi Epithelial Polarity Gerard Apodaca Luciana I. Gallo life sciences Morgan & Claypool life SCIEnCES
Colloquium series on Building BloCks of the Cell: Cell structure and function Series Editor: Ivan Robert Nabi Epithelial Polarity Gerard Apodaca Luciana I. Gallo life sciences Morgan & Claypool life SCIEnCES
BE 159: Signal Transduction and Mechanics in Morphogenesis
 BE 159: Signal Transduction and Mechanics in Morphogenesis Justin Bois Caltech Winter, 2018 2018 Justin Bois. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License CC-BY 4.0. 5 Delta-Notch
BE 159: Signal Transduction and Mechanics in Morphogenesis Justin Bois Caltech Winter, 2018 2018 Justin Bois. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License CC-BY 4.0. 5 Delta-Notch
16 The Cell Cycle. Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization
 The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
Supplementary Figures
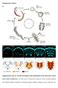 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Does Rac GTPase Play a Role in EphA4 Signaling in Xenopus Embryos?
 Eastern Michigan University DigitalCommons@EMU Senior Honors Theses Honors College 2009 Does Rac GTPase Play a Role in EphA4 Signaling in Xenopus Embryos? Ashley Durand Follow this and additional works
Eastern Michigan University DigitalCommons@EMU Senior Honors Theses Honors College 2009 Does Rac GTPase Play a Role in EphA4 Signaling in Xenopus Embryos? Ashley Durand Follow this and additional works
