A Case Study -- Chu et al. The Transcriptional Program of Sporulation in Budding Yeast. What is Sporulation? CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 1
|
|
|
- Lily Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Case Study -- Chu et al. An interesting early microarray paper My goals Show arrays used in a real experiment Show where computation is important Start looking at analysis techniques The Transcriptional Program of Sporulation in Budding Yeast S. Chu, * J. DeRisi, * M. Eisen, J. Mulholland, D. Botstein, P. O. Brown, I. Herskowitz Science, 282 (Oct 1998) What is Sporulation? Under adverse conditions, one yeast cell transforms itself into spores -- tetrad of cells with tough cell wall, goes dormant Yeast is ordinarily diploid; spores are haploid. I.e., genetically, sporulation is analogous to formation of egg/sperm in most sexual organisms -- 2 rounds of meiotic (not mitotic) cell division. And many of the genes/proteins involved in this are recognizably similar to human genes/proteins 3 4 CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 1
2 The Chu et al. Experiment Measure mrna expression levels of all 6200 yeast genes in 7 time points (0-11 hours) in a (loosely synchronized) sporulating yeast culture Compare level at time t to level at time 0 on 2-color cdna array Plus some more standard tests as controls Measures of Sporulation NB: < 20% spores, so data are mixtures of cell stages 5 6 Standard Test (Northern) vs Array Prototype Expression Profiles 7 8 CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 2
3 "Sporulation" Summary, I What they did: measured mrna expression levels of all 6200 yeast genes in 7 time points in a (loosely synchronized) sporulating yeast culture plus some more standard tests as controls What they learned: 3-10x increase in number of genes implicated in various subprocesses several subsequently verified by direct knockouts further evidence for significance of some known transcription factors and/or binding motifs several potential new ones evidence for existence of others 9 "Sporulation" Summary, II More on Computation Where computation fits in 10 automated sample handling image analysis data storage, retrieval, integration visualization clustering More on these sequence analysis topics later in similarity search the course motif discovery Similarity Search -- given a loosely defined sequence motif, e.g. a transcription factor binding site, scan genome for matches structure prediction Motif discovery -- given a collection of sequences presumed to contain a common pattern, e.g. a transcription factor binding site, find it & characterize it 11 CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo Which genes have an MSE element? E.g., weight matrix models, Markov models What motifs are common to Early Middle genes? E.g., MEME, Gibbs Sampler, Footprinter, 12 3
4 More on Computation Finding groups of sequences that plausibly contain common sequence motifs E.g., clustering (co-varying because coregulated?) Chu s Supervised Clustering Hand picked ~ 40 prototype genes With significant variation in data set With known function Hand-segregated into 7 groups ( Early, ) Assign all others to nearest group Based on Pearson correlation to per-group averages of prototypes For visualization, order within groups by correlation to neighboring groups Critique warnings about arrays & clusters Warning 1: expression data often do not separate into nice, compact, well-separated clusters Cf Raychaudhuri et al. (next 2 slides) CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 4
5 warnings about arrays & clusters Warning 2: it s hard to visualize high-dimensional data & inadequate visualization may obscure as well as enlighten Cf Next 2 slides CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 5
6 21 CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 6
Modelling Gene Expression Data over Time: Curve Clustering with Informative Prior Distributions.
 BAYESIAN STATISTICS 7, pp. 000 000 J. M. Bernardo, M. J. Bayarri, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, D. Heckerman, A. F. M. Smith and M. West (Eds.) c Oxford University Press, 2003 Modelling Data over Time: Curve
BAYESIAN STATISTICS 7, pp. 000 000 J. M. Bernardo, M. J. Bayarri, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, D. Heckerman, A. F. M. Smith and M. West (Eds.) c Oxford University Press, 2003 Modelling Data over Time: Curve
Unit 6 : Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Unit 6 : Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2006-2007 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same number of chromosomes
Unit 6 : Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2006-2007 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same number of chromosomes
Topographic Independent Component Analysis of Gene Expression Time Series Data
 Topographic Independent Component Analysis of Gene Expression Time Series Data Sookjeong Kim and Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology San 31 Hyoja-dong,
Topographic Independent Component Analysis of Gene Expression Time Series Data Sookjeong Kim and Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology San 31 Hyoja-dong,
Bioinformatics. Transcriptome
 Bioinformatics Transcriptome Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgique Laboratoire de Bioinformatique des Génomes et des Réseaux (BiGRe) http://www.bigre.ulb.ac.be/ Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics Transcriptome Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgique Laboratoire de Bioinformatique des Génomes et des Réseaux (BiGRe) http://www.bigre.ulb.ac.be/ Bioinformatics
Clustering & microarray technology
 Clustering & microarray technology A large scale way to measure gene expression levels. Thanks to Kevin Wayne, Matt Hibbs, & SMD for a few of the slides 1 Why is expression important? Proteins Gene Expression
Clustering & microarray technology A large scale way to measure gene expression levels. Thanks to Kevin Wayne, Matt Hibbs, & SMD for a few of the slides 1 Why is expression important? Proteins Gene Expression
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains a fool forever.
 CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles AP Biology 2005-2006 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA
CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles AP Biology 2005-2006 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA
Principal component analysis (PCA) for clustering gene expression data
 Principal component analysis (PCA) for clustering gene expression data Ka Yee Yeung Walter L. Ruzzo Bioinformatics, v17 #9 (2001) pp 763-774 1 Outline of talk Background and motivation Design of our empirical
Principal component analysis (PCA) for clustering gene expression data Ka Yee Yeung Walter L. Ruzzo Bioinformatics, v17 #9 (2001) pp 763-774 1 Outline of talk Background and motivation Design of our empirical
11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Slide 1 of 35
 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
6.047 / Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.047 / 6.878 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.047 / 6.878 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
Statistics 246 Spring 2006
 Statistics 246 Spring 2006 Meiosis and Recombination Week 3, Lecture 1 1 - the process which starts with a diploid cell having one set of maternal and one of paternal chromosomes, and ends up with four
Statistics 246 Spring 2006 Meiosis and Recombination Week 3, Lecture 1 1 - the process which starts with a diploid cell having one set of maternal and one of paternal chromosomes, and ends up with four
Name Class Date. Term Definition How I m Going to Remember the Meaning
 11.4 Meiosis Lesson Objectives Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. Summarize the events of meiosis. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. Describe how alleles from different genes
11.4 Meiosis Lesson Objectives Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. Summarize the events of meiosis. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. Describe how alleles from different genes
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
9-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35
 9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
Lecture 5: November 19, Minimizing the maximum intracluster distance
 Analysis of DNA Chips and Gene Networks Spring Semester, 2009 Lecture 5: November 19, 2009 Lecturer: Ron Shamir Scribe: Renana Meller 5.1 Minimizing the maximum intracluster distance 5.1.1 Introduction
Analysis of DNA Chips and Gene Networks Spring Semester, 2009 Lecture 5: November 19, 2009 Lecturer: Ron Shamir Scribe: Renana Meller 5.1 Minimizing the maximum intracluster distance 5.1.1 Introduction
Fuzzy Clustering of Gene Expression Data
 Fuzzy Clustering of Gene Data Matthias E. Futschik and Nikola K. Kasabov Department of Information Science, University of Otago P.O. Box 56, Dunedin, New Zealand email: mfutschik@infoscience.otago.ac.nz,
Fuzzy Clustering of Gene Data Matthias E. Futschik and Nikola K. Kasabov Department of Information Science, University of Otago P.O. Box 56, Dunedin, New Zealand email: mfutschik@infoscience.otago.ac.nz,
THINK ABOUT IT. Lesson Overview. Meiosis. As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located.
 Notes THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Notes THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis
 Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the
Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the
Inferring Transcriptional Regulatory Networks from Gene Expression Data II
 Inferring Transcriptional Regulatory Networks from Gene Expression Data II Lectures 9 Oct 26, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday
Inferring Transcriptional Regulatory Networks from Gene Expression Data II Lectures 9 Oct 26, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday
Improving the identification of differentially expressed genes in cdna microarray experiments
 Improving the identification of differentially expressed genes in cdna microarray experiments Databionics Research Group University of Marburg 33 Marburg, Germany Alfred Ultsch Abstract. The identification
Improving the identification of differentially expressed genes in cdna microarray experiments Databionics Research Group University of Marburg 33 Marburg, Germany Alfred Ultsch Abstract. The identification
Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read
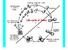 Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read chapter 22 and chapter 10 [section on MATing type gene
Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read chapter 22 and chapter 10 [section on MATing type gene
4/6/2014. Chromosome Number
 Meiosis 1of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just
Meiosis 1of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13)
 Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
CLUSTER, FUNCTION AND PROMOTER: ANALYSIS OF YEAST EXPRESSION ARRAY
 CLUSTER, FUNCTION AND PROMOTER: ANALYSIS OF YEAST EXPRESSION ARRAY J. ZHU, M. Q. ZHANG Cold Spring Harbor Lab, P. O. Box 100 Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724 Gene clusters could be derived based on expression
CLUSTER, FUNCTION AND PROMOTER: ANALYSIS OF YEAST EXPRESSION ARRAY J. ZHU, M. Q. ZHANG Cold Spring Harbor Lab, P. O. Box 100 Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724 Gene clusters could be derived based on expression
MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
 MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Why do kids look different from the parents? How are they similar to their parents? Why aren t brothers or sisters more alike? Meiosis A process where the number
MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Why do kids look different from the parents? How are they similar to their parents? Why aren t brothers or sisters more alike? Meiosis A process where the number
Meiosis. What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation
 Meiosis What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation Reproduction Asexual reproduction resulting from mitosis (or a similar process) that involves only one parent; the offspring
Meiosis What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation Reproduction Asexual reproduction resulting from mitosis (or a similar process) that involves only one parent; the offspring
Almost all human cells contain 46 chromosomes, and are diploid (2n). Q: If a sperm cell has 46 chromosomes (2n) & an egg cell has 46 chromosomes
 Almost all human cells contain 46 chromosomes, and are diploid (2n). Q: If a sperm cell has 46 chromosomes (2n) & an egg cell has 46 chromosomes (2n), when they combine during fertilization, how many chromosomes
Almost all human cells contain 46 chromosomes, and are diploid (2n). Q: If a sperm cell has 46 chromosomes (2n) & an egg cell has 46 chromosomes (2n), when they combine during fertilization, how many chromosomes
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
Bellwork. Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically?
 Bellwork Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically? SC.912.L.16.17 Meiosis Functions in Sexual Reproduction Other Standards Addressed:
Bellwork Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically? SC.912.L.16.17 Meiosis Functions in Sexual Reproduction Other Standards Addressed:
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall
 Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
Tree-Dependent Components of Gene Expression Data for Clustering
 Tree-Dependent Components of Gene Expression Data for Clustering Jong Kyoung Kim and Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology San 31 Hyoja-dong, Nam-gu Pohang
Tree-Dependent Components of Gene Expression Data for Clustering Jong Kyoung Kim and Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology San 31 Hyoja-dong, Nam-gu Pohang
networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber
 networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber networks in molecular biology Regulatory networks: components = gene products interactions = regulation of transcription, translation, phosphorylation... Metabolic
networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber networks in molecular biology Regulatory networks: components = gene products interactions = regulation of transcription, translation, phosphorylation... Metabolic
Lecture 9: Readings: Chapter 20, pp ;
 Lecture 9: Meiosis i and heredity Readings: Chapter 20, pp 659-686; skim through pp 682-3 & p685 (but just for fun) Chromosome number: haploid, diploid, id polyploid l Talking about the number of chromosome
Lecture 9: Meiosis i and heredity Readings: Chapter 20, pp 659-686; skim through pp 682-3 & p685 (but just for fun) Chromosome number: haploid, diploid, id polyploid l Talking about the number of chromosome
Inferring Transcriptional Regulatory Networks from High-throughput Data
 Inferring Transcriptional Regulatory Networks from High-throughput Data Lectures 9 Oct 26, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20
Inferring Transcriptional Regulatory Networks from High-throughput Data Lectures 9 Oct 26, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20
Analyzing Microarray Time course Genome wide Data
 OR 779 Functional Data Analysis Course Project Analyzing Microarray Time course Genome wide Data Presented by Xin Zhao April 29, 2002 Cornell University Overview 1. Introduction Biological Background Biological
OR 779 Functional Data Analysis Course Project Analyzing Microarray Time course Genome wide Data Presented by Xin Zhao April 29, 2002 Cornell University Overview 1. Introduction Biological Background Biological
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over
 Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS ANALYSIS TO SUMMARIZE MICROARRAY EXPERIMENTS: APPLICATION TO SPORULATION TIME SERIES
 PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS ANALYSIS TO SUMMARIZE MICROARRAY EXPERIMENTS: APPLICATION TO SPORULATION TIME SERIES Soumya Raychaudhuri *, Joshua M. Stuart *, and Russ B. Altman Ψ Stanford Medical Informatics Stanford
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS ANALYSIS TO SUMMARIZE MICROARRAY EXPERIMENTS: APPLICATION TO SPORULATION TIME SERIES Soumya Raychaudhuri *, Joshua M. Stuart *, and Russ B. Altman Ψ Stanford Medical Informatics Stanford
Roles of Cell Division. Reproduction - Like begets like, more or less. Examples of Cell Numbers. Outline Cell Reproduction
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Chapter 2 Lecture. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Lecture Mitosis Click to and edit Meiosis Master tit Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 2.1 Cell Structure Is Closely Tied to Genetic Function Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright
Chapter 2 Lecture Mitosis Click to and edit Meiosis Master tit Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 2.1 Cell Structure Is Closely Tied to Genetic Function Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright
11.4 Meiosis. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary
 11.4 Meiosis Lesson Objectives Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. Summarize the events of meiosis. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. Describe how alleles from different genes
11.4 Meiosis Lesson Objectives Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. Summarize the events of meiosis. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. Describe how alleles from different genes
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Meiosis * OpenStax. This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0.
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45466 1 Meiosis * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m45466 1 Meiosis * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
De novo identification of motifs in one species. Modified from Serafim Batzoglou s lecture notes
 De novo identification of motifs in one species Modified from Serafim Batzoglou s lecture notes Finding Regulatory Motifs... Given a collection of genes that may be regulated by the same transcription
De novo identification of motifs in one species Modified from Serafim Batzoglou s lecture notes Finding Regulatory Motifs... Given a collection of genes that may be regulated by the same transcription
Segregation and the Principle of independent assortment
 . Segregation and the Principle of independent assortment The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop.
. Segregation and the Principle of independent assortment The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop.
Kingdom Fungi. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Activity1: Zygomycota. Revised Fall 2017
 Kingdom Fungi Revised Fall 2017 ** You will require your text book Biological Science during this lab ** Learning Objectives Building on the learning objectives from your lab syllabus, you will be expected
Kingdom Fungi Revised Fall 2017 ** You will require your text book Biological Science during this lab ** Learning Objectives Building on the learning objectives from your lab syllabus, you will be expected
Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true?
 11.4 Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true? An organism with two parents must inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent When that organism produces gametes,
11.4 Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true? An organism with two parents must inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent When that organism produces gametes,
Cluster Analysis of Gene Expression Microarray Data. BIOL 495S/ CS 490B/ MATH 490B/ STAT 490B Introduction to Bioinformatics April 8, 2002
 Cluster Analysis of Gene Expression Microarray Data BIOL 495S/ CS 490B/ MATH 490B/ STAT 490B Introduction to Bioinformatics April 8, 2002 1 Data representations Data are relative measurements log 2 ( red
Cluster Analysis of Gene Expression Microarray Data BIOL 495S/ CS 490B/ MATH 490B/ STAT 490B Introduction to Bioinformatics April 8, 2002 1 Data representations Data are relative measurements log 2 ( red
Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab
 Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab Objectives: - Explain how meiosis and crossing over result in the different arrangements of ascospores within asci. - Learn how to calculate the map distance between a gene
Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab Objectives: - Explain how meiosis and crossing over result in the different arrangements of ascospores within asci. - Learn how to calculate the map distance between a gene
SI Materials and Methods
 SI Materials and Methods Gibbs Sampling with Informative Priors. Full description of the PhyloGibbs algorithm, including comprehensive tests on synthetic and yeast data sets, can be found in Siddharthan
SI Materials and Methods Gibbs Sampling with Informative Priors. Full description of the PhyloGibbs algorithm, including comprehensive tests on synthetic and yeast data sets, can be found in Siddharthan
Three different fusions led to three basic ideas: 1) If one fuses a cell in mitosis with a cell in any other stage of the cell cycle, the chromosomes
 Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology Volume 4, Issue 1 2005 Article 10 Prediction of Missing Values in Microarray and Use of Mixed Models to Evaluate the Predictors Guri Feten Trygve
Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology Volume 4, Issue 1 2005 Article 10 Prediction of Missing Values in Microarray and Use of Mixed Models to Evaluate the Predictors Guri Feten Trygve
Name: Test date: Per:
 Name: Test date: Per: Cell Cycle/Protein Synthesis Unit 1 Study Guide Always remember to use your notes/lectures first, then book, then other sources to help you find the right answers. Be as thorough
Name: Test date: Per: Cell Cycle/Protein Synthesis Unit 1 Study Guide Always remember to use your notes/lectures first, then book, then other sources to help you find the right answers. Be as thorough
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
11.4 Meiosis. Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad
 11.4 Meiosis Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad Key Concept: What happens during the process of meiosis? How is MEIOSIS different than mitosis? Blast from the past What
11.4 Meiosis Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad Key Concept: What happens during the process of meiosis? How is MEIOSIS different than mitosis? Blast from the past What
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Sperm & Eggs & Variation..OH MY!
 Sperm & Eggs & Variation..OH MY! 1 What if a new individual was formed through mitosis? 2 allele amniocentesis asexual reproduction autosome binary fission chorionic villi sampling crossing over diploid
Sperm & Eggs & Variation..OH MY! 1 What if a new individual was formed through mitosis? 2 allele amniocentesis asexual reproduction autosome binary fission chorionic villi sampling crossing over diploid
1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals.
 1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals. Which statement best explains how these processes often produce offspring that have traits not
1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals. Which statement best explains how these processes often produce offspring that have traits not
CELL REPRODUCTION. Unit 20 LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 Unit 20 CELL REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to distinguish the differences between mitotic and meiotic cell division. 2. Learn the role that both mitotic and meiotic types of cell division
Unit 20 CELL REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to distinguish the differences between mitotic and meiotic cell division. 2. Learn the role that both mitotic and meiotic types of cell division
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Cell Division. Mitosis 11/8/2016
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Variable Selection in Structured High-dimensional Covariate Spaces
 Variable Selection in Structured High-dimensional Covariate Spaces Fan Li 1 Nancy Zhang 2 1 Department of Health Care Policy Harvard University 2 Department of Statistics Stanford University May 14 2007
Variable Selection in Structured High-dimensional Covariate Spaces Fan Li 1 Nancy Zhang 2 1 Department of Health Care Policy Harvard University 2 Department of Statistics Stanford University May 14 2007
Chapter 5: Microarray Techniques
 Chapter 5: Microarray Techniques 5.2 Analysis of Microarray Data Prof. Yechiam Yemini (YY) Computer Science Department Columbia University Normalization Clustering Overview 2 1 Processing Microarray Data
Chapter 5: Microarray Techniques 5.2 Analysis of Microarray Data Prof. Yechiam Yemini (YY) Computer Science Department Columbia University Normalization Clustering Overview 2 1 Processing Microarray Data
Which of these best predicts the outcome of the changes illustrated in the diagrams?
 1. The diagrams below show two different scenarios for a pair of homologous chromosomes, known as a tetrad, undergoing a change where segments of DNA switch on parts of the chromosomes. In each scenario,
1. The diagrams below show two different scenarios for a pair of homologous chromosomes, known as a tetrad, undergoing a change where segments of DNA switch on parts of the chromosomes. In each scenario,
Introduction to clustering methods for gene expression data analysis
 Introduction to clustering methods for gene expression data analysis Giorgio Valentini e-mail: valentini@dsi.unimi.it Outline Levels of analysis of DNA microarray data Clustering methods for functional
Introduction to clustering methods for gene expression data analysis Giorgio Valentini e-mail: valentini@dsi.unimi.it Outline Levels of analysis of DNA microarray data Clustering methods for functional
The development and application of DNA and oligonucleotide microarray
 Dynamic modeling of gene expression data Neal S. Holter*, Amos Maritan, Marek Cieplak*, Nina V. Fedoroff, and Jayanth R. Banavar* *Department of Physics and Center for Materials Physics, 104 Davey Laboratory,
Dynamic modeling of gene expression data Neal S. Holter*, Amos Maritan, Marek Cieplak*, Nina V. Fedoroff, and Jayanth R. Banavar* *Department of Physics and Center for Materials Physics, 104 Davey Laboratory,
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: SIMULATION OF MEIOSIS EVOLUTION. Activity #9
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
Intro Gene regulation Synteny The End. Today. Gene regulation Synteny Good bye!
 Today Gene regulation Synteny Good bye! Gene regulation What governs gene transcription? Genes active under different circumstances. Gene regulation What governs gene transcription? Genes active under
Today Gene regulation Synteny Good bye! Gene regulation What governs gene transcription? Genes active under different circumstances. Gene regulation What governs gene transcription? Genes active under
Human Biology Chapter 13.4: Meiosis and Genetic Variation
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58013 1 Human Biology Chapter 13.4: Meiosis and Genetic Variation Willy Cushwa Based on Meiosis by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58013 1 Human Biology Chapter 13.4: Meiosis and Genetic Variation Willy Cushwa Based on Meiosis by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Clustering gene expression data using graph separators
 1 Clustering gene expression data using graph separators Bangaly Kaba 1, Nicolas Pinet 1, Gaëlle Lelandais 2, Alain Sigayret 1, Anne Berry 1. LIMOS/RR-07-02 13/02/2007 - révisé le 11/05/2007 1 LIMOS, UMR
1 Clustering gene expression data using graph separators Bangaly Kaba 1, Nicolas Pinet 1, Gaëlle Lelandais 2, Alain Sigayret 1, Anne Berry 1. LIMOS/RR-07-02 13/02/2007 - révisé le 11/05/2007 1 LIMOS, UMR
T contained in a sac and usually originate from the reduction of a single
 ASCI IN SACCHAROMYCES WITH MORE THAN FOUR SPORES CARL C. LINDEGREN AND GERTRUDE LINDEGREN Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IIlinois Received March 18. 1952 HE ascomycetes are characterized by
ASCI IN SACCHAROMYCES WITH MORE THAN FOUR SPORES CARL C. LINDEGREN AND GERTRUDE LINDEGREN Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IIlinois Received March 18. 1952 HE ascomycetes are characterized by
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
Chapter 8 Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida
 Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of
GSBHSRSBRSRRk IZTI/^Q. LlML. I Iv^O IV I I I FROM GENES TO GENOMES ^^^H*" ^^^^J*^ ill! BQPIP. illt. goidbkc. itip31. li4»twlil FIFTH EDITION
 FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
Clustering and Network
 Clustering and Network Jing-Dong Jackie Han jdhan@picb.ac.cn http://www.picb.ac.cn/~jdhan Copy Right: Jing-Dong Jackie Han What is clustering? A way of grouping together data samples that are similar in
Clustering and Network Jing-Dong Jackie Han jdhan@picb.ac.cn http://www.picb.ac.cn/~jdhan Copy Right: Jing-Dong Jackie Han What is clustering? A way of grouping together data samples that are similar in
Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring
 In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, Take Home Final. Topic 1
 Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
The Transcriptional Program of Sporulation in Budding Yeast
 The Transcriptional Program of Sporulation in Budding Yeast S. Chu,* J. DeRisi,* M. Eisen, J. Mulholland, D. Botstein, P. O. Brown, I. Herskowitz Diploid cells of budding yeast produce haploid cells through
The Transcriptional Program of Sporulation in Budding Yeast S. Chu,* J. DeRisi,* M. Eisen, J. Mulholland, D. Botstein, P. O. Brown, I. Herskowitz Diploid cells of budding yeast produce haploid cells through
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT
 November 27, 2002 Bio251 Dr. Calhoon Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT The experiment was conducted to verify the
November 27, 2002 Bio251 Dr. Calhoon Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT The experiment was conducted to verify the
Meiosis. Section 8-3
 Meiosis Section 8-3 Meiosis process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number in the original cell For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive
Meiosis Section 8-3 Meiosis process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number in the original cell For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive
A. Changes in the New Biology Curriculum
 A. Changes in the New Biology Curriculum The changes made in the Biology curriculum for 2003 and afterwards are summarized in the table below. They include additions, deletions or rewriting of topics in
A. Changes in the New Biology Curriculum The changes made in the Biology curriculum for 2003 and afterwards are summarized in the table below. They include additions, deletions or rewriting of topics in
Advance Organizer. Topic: Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis
 Name: Row Unit 8 - Chapter 11 - Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis Advance Organizer Topic: Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis 1. Objectives (What should I be able to do?) a. Summarize the outcomes of Gregor Mendel's
Name: Row Unit 8 - Chapter 11 - Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis Advance Organizer Topic: Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis 1. Objectives (What should I be able to do?) a. Summarize the outcomes of Gregor Mendel's
Describe the process of cell division in prokaryotic cells. The Cell Cycle
 The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS
 Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Learning Objectives:
 Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Modeling Genetic Variation in Gametes PSI AP Biology
 Modeling Genetic Variation in Gametes PSI AP Biology Name: Objective Students will model the processes of gamete formation that increase genetic variation: independent assortment, crossing-over, and fertilization.
Modeling Genetic Variation in Gametes PSI AP Biology Name: Objective Students will model the processes of gamete formation that increase genetic variation: independent assortment, crossing-over, and fertilization.
Lesson 11. Functional Genomics I: Microarray Analysis
 Lesson 11 Functional Genomics I: Microarray Analysis Transcription of DNA and translation of RNA vary with biological conditions 3 kinds of microarray platforms Spotted Array - 2 color - Pat Brown (Stanford)
Lesson 11 Functional Genomics I: Microarray Analysis Transcription of DNA and translation of RNA vary with biological conditions 3 kinds of microarray platforms Spotted Array - 2 color - Pat Brown (Stanford)
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Chromosome Chr Duplica Duplic t a ion Pixley
 Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
