The April 1982 "Big SurVtorm: An Example of Extreme Rainfall in California
|
|
|
- Anastasia Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The April 1982 "Big SurVtorm: An Example of Extreme Rainfall in California Richard Grotjahn and Su-Tzai Soong Dept. of Land, Air, and Water Resources Univ. of California, Davis, modumon During the wi.nter of 1982 there were two periods of unusually heavy rainfall in California. In January a major storm dumped a lot of snow in the central Sierra Nevada mountains. This storm closed interstate highway 80 for nearly 3 days! In April, the second stormy period was punctuated by an intense low of subtropical origin which brought heavy rain along a diagonal band from the central California coast to the northern Sierras. This talk focusses upon this second system. We have referred to the April storm as the "Big Sur" storm because the heavy rainfall it brought (on top of saturated soils) led to numerous landslides along the California coast. A particularly massive slide closed California highway 1, along the big sur coast, for more than a year. Two-day rainfall totals for some representative California stations are shown in figure 1. The diagonal orientation of the precipitation, southwest to northeast, is apparent in figure 1. This is also consistent with the orientation during some other recent heavy rainfalls, most notably the february 1986 storm. The 1986 storm is the subject of the next talk, and its diagonal band of precipitation was located about 100 km to the north. What can cause the high amounts of precipitation? It is widely believed that higher topography causes higher rainfall amounts, but that is only partly true. One might make that case for Sierra City, which sits at 1290 m elevation in a broad mountain valley. However, the higher rainfall amounts reported at Ben Lommond (elevation 137 m) and Pfeiffer Big Sur State Park (elevation 72 m) are not caused by these stations being at higher elevation. However, there are steep-sided mountains to the lee of these stations which rise to km elevation. Such high ridgelines may lead to convergence on their windward side which enhances the precipitation there. The presentation by Soong and Kim may address this issue of upstream convergence. In this case, and most cases of widespread heavy rainfall, the topography acts to'modulate the rainfall distribution. What creates the larger scale, widespread nature of the precipitation is the focus of this talk. We shall see that several rather uncommon events must come together in just the right way in order for an event like the big sur storm to happen. This is probably obvious, since such events are rare. What is interesting is to identify just what those events are. To identify those events, we use a good set of observational analyses prepared by the European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). These data are provided at equally spaced latitude and longitude grid intervals of degrees. The period we show is 25 March through 14 April. During these three weeks we find two storms which form in same part of the subtropics. The former storm does not develop much strength. The latter storm becomes intense. Rainfall amounts from the latter storm are about 10 times those of the first storm. Hence, these two storms help highlight what is needed to produce a storm capable of heavy rainfall.
2 Richarson Grove S. P. 3.43" I* Eureka 1.14" * Redding 0.63" I Sierra City 7.82" Fort Bragg.0.92" * 1 Echo Summit 2.45" Davis 3.35" Santa Rosa 2.05" * * *\ Calaverras Big Trees S. P. 4.76" San Francisco 1.50" ft Stockton 1.26" \ Half h4oon Bay 2.15" City 1.38" Ben Lommond " b Santa Cruz 3.04" Monferey 1.65" 4 * Fresno 0.71" I 3-4 Pfeiffer Big Sur S. P. 6.37" g Coalinga 0.84" \ \ * Morro Bay 2.62" Bakersfield 0.32" I * San Luis Obispo U " I Santa Barbara 1.77" (Los Angeles 0.7") Figure 1. Two-day rainfall totals on 10 and 11 April for selected California stations. The heaviest rainfall occurs mainly on 11 April.
3 SYNOPTIC SUMMARY An 11 minute film has been prepared which shows these fields at these levels: Segment 1: 850 mb level, relative humidity > 85% (shaded), isobaric trajectories (arrows), geopotential height (contours, with 1470 m dashed). Segment 2: 850 mb level, isotherms (contours, with dashed line for 273 K), isobaric trajectories (arrows). Segment 3: 850 mb level, isotherms (contours), eddy horizontal heat flux (arrows). Segment 4: 300 mb level, relative humidity > 60% (shaded), isobaric trajectories (arrows), and geopotential height (contours, 9120 m dashed). Similar format as segment 1. Segment 5: 300 mb level, geopotential height (contours), eddy horizontal momentum fluxes (arrows). Segment 6: 1000 mb level, specific humidity > 10 gmkg (shaded) and > 15 gmkg (double shading), isobaric trajectories (arrows), and geopotential height (contours, 9120 m dashed). There are many features that one can examine in the segments, but we highlight the following uncommon events which happened prior to and during the big sur storm. 1. The subtropical high is well to the west of its normal location. This has several implications upon the atmospheric flow. (a) On the west side of this ridge is warm advection which strengthens the ridge at upper levels and helps to block flow from the west. By blocking the flow, the big sur low is able to stall just off the California coast (for an extra day or so) which increased the total rainfall for the storm. (b) On the east side of this ridge occurred cold advection which allowed an upper level low to develop as well as a strengthening of the meridional temperature gradient upstream of the low. Both provide support to the developing low. Also, the baroclinic energy conversion is fostered this way, unlike the first low which never develops. (c) The presence of the long wave ridge fosters the development of the deep upper level low which in turn steers the big sur low in an unusual track: from southwest to northeast. The track therefore parallels the orientation of the cold front. Hence the line of precipitation is dragged across California in the direction of its longest dimension. 2. A short wave travels across the subtropics well to the south of the ridge. (a) This short wave provides the initial boost that forms a cyclonic circulation in the subtropics at lower levels. It continues to propagate past the lower level features and does not play a role in the final intensification of the big sur storm. (b) By initiating a low in the subtropics, very moist air in a deep layer is "capturedn by the developing system. The earlier storm forms in the same location as the big sur storm. Hence, the upper and lower level troughs (in height patterns) look superficially similar during the early stages. The first storm also taps into the subtropical moisture, though perhaps not quite as much. Two things are most notably different for the first storm: the ridge in the west side of the domain is much weaker and the meridional gradient of temperature near the surface low is much weaker. Both of these differences foster the development of the low by baroclinic means. The presence of the strong ridge also allows the big sur low to stall, extending the time period of rain. (Both lows follow similar tracks.) ' Illustrative figures (2-4) follow which are drawn from the film.
4 60' N JOOmb 60 Z and above 9120m dashed - 50 m/s JOOmb 60 X and above 912Om dashad - 50 m/a 50. N 40. N SO' N 20. N lwomb 8Om dashad MIXING RATIO (DOTS) $hadlnp o bw 10 ond 15 pm/kg 40 m sonlour In1~nol loodmb 8Om d0sh.d MIXING RATIO (DOTS) shadlng abwa 10 ond 15 gm/kg 40 m contour Intawal 850mb 273K dashad EODY HEAT FLUX (ARROWS) TEMPERATURE (CONTOURS) mk/a 4 K sonlour lntawal 60 ' 85Omb 273K doshad EDDY HEAT FLUX (ARROWS) TEMPERATURE (CONTOURS)- 200 mk/a 4 K contour inlarval 50 ' 40 ' SO. 20 Figure 2. Left column shows film segments for the first storm, which has weak development. The right column shows the big sur storm. The patterns of height and moisture at 300 mb (top charts) and 1000 mb (middle charts) are quite similar. The temperature pattern (850 mb, bottom charts) has much stronger meridional gradient for the big sur storm.
5 SOOmb 60 Z and abc 9lZOm dashad - 50 m/s ond above - 25 m/s April SOOmb 9120m dashmd 60 X and abo,.- 50 m/s 850mb 85 X and obore 1470m dashed - 25 m/s April ' N 300mb 60 X and above 912Om dashed - SO m/s REUTIVE HUMIDITY (SHADED) 850mb 85 Z and above 1470m dashed - 25 m/s 50- N 40. N SO. N 20. N Figure 3..Left column shows time sequence of 300 mb height contours. The corresponding height contours at 850 mb are shown in the right column. Upper trough (labelled "Aw) has entered the domain at the southwest corner 4 days earlier; it has initiated a low at 850 on 3 April (top charts). In the middle charts, upper trough "A" is now east of the 850 mb trough. Trough "B" eventually intensifies and provides the support that helps intensify the big sur low.
6 1000mb 80m dashed MIXING RATIO (DOTS) shading above 10 and 15 gm/kg 40 m contour Interval 242 April April Figure 4. Time sequence showing the big sur storm over 3 days. The storm moves from the. subtropics in a direction parallel to the orientation'of the cold front, and therefore parallel to the 'band of precipitation. The band of precipitation would lie approximately where to the shaded area is near California.
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY. Metr Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts. Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak
 Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Synoptic Meteorology
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone
 Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex
 Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex SWAC Jan 2014 AKA Circumpolar Vortex Science or Hype? Will there be one this year? Today s objectives Pre and Post exams What is the Polar Vortex
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex SWAC Jan 2014 AKA Circumpolar Vortex Science or Hype? Will there be one this year? Today s objectives Pre and Post exams What is the Polar Vortex
Observation Homework Due 11/24. Previous Lecture. Midlatitude Cyclones
 Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones Mid-Latitude Cyclones
 Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones Mid-Latitude Cyclones Mid-latitude cyclones form along a boundary separating polar air from warmer air to the south. Life Cycle of Cyclone Cyclone Structures Steering
Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones Mid-Latitude Cyclones Mid-latitude cyclones form along a boundary separating polar air from warmer air to the south. Life Cycle of Cyclone Cyclone Structures Steering
Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones
 Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones Life Cycle of Cyclone Cyclone Structures Steering of Cyclone Mid-Latitude Cyclones Mid-latitude cyclones form along a boundary separating polar air from warmer air to
Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones Life Cycle of Cyclone Cyclone Structures Steering of Cyclone Mid-Latitude Cyclones Mid-latitude cyclones form along a boundary separating polar air from warmer air to
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples Figure 1
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps
 Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars
 Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
The number of events satisfying the heat wave definition criteria varies widely
 1 III. Discussion of Results A. Event Identification The number of events satisfying the heat wave definition criteria varies widely between stations. For the unfiltered data following the definition requiring
1 III. Discussion of Results A. Event Identification The number of events satisfying the heat wave definition criteria varies widely between stations. For the unfiltered data following the definition requiring
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
MET Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16)
 MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
PLOTTING WEATHER DATA to perform a SURFACE ANALYSIS
 PLOTTING WEATHER DATA to perform a SURFACE ANALYSIS The surface analysis permits one to identify and locate the large scale features of the sea level pressure field and the surface fronts. Isobars with
PLOTTING WEATHER DATA to perform a SURFACE ANALYSIS The surface analysis permits one to identify and locate the large scale features of the sea level pressure field and the surface fronts. Isobars with
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3) What is the difference between latitude and longitude and what is their affect on local and world weather and climate?
 www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
Mesoscale predictability under various synoptic regimes
 Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics (2001) 8: 429 438 Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics c European Geophysical Society 2001 Mesoscale predictability under various synoptic regimes W. A. Nuss and D. K. Miller
Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics (2001) 8: 429 438 Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics c European Geophysical Society 2001 Mesoscale predictability under various synoptic regimes W. A. Nuss and D. K. Miller
2. Methods and data. 1 NWS Reno, NV report circulated in the LA Times story maximum wind was observed at 0900 AM 8 January 2017.
 The California Extreme Precipitation Event of 8-10 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction A strong Pacific jet and a surge of
The California Extreme Precipitation Event of 8-10 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction A strong Pacific jet and a surge of
Climate. Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) January Temperature. July Temperature. Average Precipitation (Last 30 Years)
 Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Chapter 12 Fronts & Air Masses
 Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points
 ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017
 Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Earth Science. Lab 21: Weather Patterns
 Name: Lab 21: Weather Patterns Earth Science Date: Introduction: A basic principle in Earth Science is that energy is constantly bringing about changes. In order to understand the changing Earth, we must
Name: Lab 21: Weather Patterns Earth Science Date: Introduction: A basic principle in Earth Science is that energy is constantly bringing about changes. In order to understand the changing Earth, we must
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
(April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2
 Lecture #17 (April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2 Hurricane Katrina August 2005 All tropical cyclone tracks (1945-2006). Hurricane Formation While moving westward, tropical disturbances
Lecture #17 (April 7, 2010, Wednesday) Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Part 2 Hurricane Katrina August 2005 All tropical cyclone tracks (1945-2006). Hurricane Formation While moving westward, tropical disturbances
Quasi-Geostrophic Implications
 Chapter 10 Quasi-Geostrophic Implications When you look at a weather chart with all its isolines and plotted data, you need a framework upon which to interpret what you see. Quasi-geostrophic theory provides
Chapter 10 Quasi-Geostrophic Implications When you look at a weather chart with all its isolines and plotted data, you need a framework upon which to interpret what you see. Quasi-geostrophic theory provides
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Pre-Christmas Warm-up December 2013-Draft
 Pre-Christmas Warm-up 21-23 December 2013-Draft By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A large ridge over the west-central Atlantic (Fig.1) and trough moving into eastern
Pre-Christmas Warm-up 21-23 December 2013-Draft By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A large ridge over the west-central Atlantic (Fig.1) and trough moving into eastern
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
PRACTICAL ACTIVITY: DRAWING ISOLINES OR CONTOURS
 COME RAIN OR SHINE PRACTICAL ACTIVITY: DRAWING ISOLINES OR CONTOURS Ideally you would need a pencil for this activity (rather than a pen) and coloured pencils are useful too. These activities maybe a little
COME RAIN OR SHINE PRACTICAL ACTIVITY: DRAWING ISOLINES OR CONTOURS Ideally you would need a pencil for this activity (rather than a pen) and coloured pencils are useful too. These activities maybe a little
Elementary Social Studies Content Area Assessment Task. Winter 2010 EDUC 203
 1 Elementary Social Studies Content Area Assessment Task Winter 2010 EDUC 203 Students: Fourth grade class in Watsonville, CA. Approximately 90% Latino, primarily of Mexicandescent. About 80% participate
1 Elementary Social Studies Content Area Assessment Task Winter 2010 EDUC 203 Students: Fourth grade class in Watsonville, CA. Approximately 90% Latino, primarily of Mexicandescent. About 80% participate
Application of microwave radiometer and wind profiler data in the estimation of wind gust associated with intense convective weather
 Application of microwave radiometer and wind profiler data in the estimation of wind gust associated with intense convective weather P W Chan 1 and K H Wong 2 1 Hong Kong Observatory, 134A Nathan Road,
Application of microwave radiometer and wind profiler data in the estimation of wind gust associated with intense convective weather P W Chan 1 and K H Wong 2 1 Hong Kong Observatory, 134A Nathan Road,
PREDICTING THE WEATHER
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) PREDICTING THE WEATHER How well does your local weatherman do in predicting the weather? Is he or she more accurate for the next day or for a week in the future? Why do you think that
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) PREDICTING THE WEATHER How well does your local weatherman do in predicting the weather? Is he or she more accurate for the next day or for a week in the future? Why do you think that
COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Weather and Climate Review
 Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns. Meteorology
 Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework. 5-7 May 2015
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions. Magnitudes are measured differently for different hazard types:
 Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Department of Geosciences San Francisco State University Spring Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points)
 Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains
 Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Presented by Ertan TURGU*
 Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs Turkish State Meteorological Service A Case Study: Analysis of Flash Flood Using FFGS Products on 17 January 2016 in Çeşme, Dikili, Izmir and Manisa. Presented by
Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs Turkish State Meteorological Service A Case Study: Analysis of Flash Flood Using FFGS Products on 17 January 2016 in Çeşme, Dikili, Izmir and Manisa. Presented by
3. As warm, moist air moves into a region, barometric pressure readings in the region will generally 1. decrease 2. increase 3.
 Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Middle-Latitude Cyclone
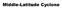 Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Evidence for Weakening of Indian Summer Monsoon and SA CORDEX Results from RegCM
 Evidence for Weakening of Indian Summer Monsoon and SA CORDEX Results from RegCM S K Dash Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Based on a paper entitled Projected Seasonal
Evidence for Weakening of Indian Summer Monsoon and SA CORDEX Results from RegCM S K Dash Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Based on a paper entitled Projected Seasonal
CW3E Atmospheric River Outlook Update on Atmospheric River Forecast to Impact California This Week - Light to moderate precipitation has begun
 CW3E Atmospheric River Outlook Update on Atmospheric River Forecast to Impact California This Week - Light to moderate precipitation has begun falling over portions of California - GFS Ensemble members
CW3E Atmospheric River Outlook Update on Atmospheric River Forecast to Impact California This Week - Light to moderate precipitation has begun falling over portions of California - GFS Ensemble members
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
 Identification of Predictors for Nowcasting Heavy Rainfall In Taiwan --------------------- Part II: Storm Characteristics and Nowcasting Applications Challenges in Developing Nowcasting Applications for
Identification of Predictors for Nowcasting Heavy Rainfall In Taiwan --------------------- Part II: Storm Characteristics and Nowcasting Applications Challenges in Developing Nowcasting Applications for
RR#5 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. The table shows the area, in million square kilometers, of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice from
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. The table shows the area, in million square kilometers, of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice from
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall ERTH FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts
 Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Forecasting Challenges
 Forecasting Challenges 2017-18 Alex Tardy- NWS San Diego Alexander.Tardy@noaa.gov CW3E meetings April 2018 Atmospheric Rivers Climate Forecast System by NOAA 100-h fuel moisture all-time low for South
Forecasting Challenges 2017-18 Alex Tardy- NWS San Diego Alexander.Tardy@noaa.gov CW3E meetings April 2018 Atmospheric Rivers Climate Forecast System by NOAA 100-h fuel moisture all-time low for South
AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Topics for today: Air Masses. Fronts. Lecture 19 Apr
 Air Masses AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Air Masses Fronts Lecture 19 Apr 11 2019 1 Today s Weather Map http://www.wpc.ncep.noaa.gov/#page=sfc
Air Masses AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Air Masses Fronts Lecture 19 Apr 11 2019 1 Today s Weather Map http://www.wpc.ncep.noaa.gov/#page=sfc
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Earth Science final exam study guide (Semester 2)
 Earth Science final exam study guide (Semester 2) Chapter 22: astronomy, sun-earth-moon system Define the following vocabulary and answer the questions that follow Earth-Sun-Moon 1. Define nebula: 2. Identify
Earth Science final exam study guide (Semester 2) Chapter 22: astronomy, sun-earth-moon system Define the following vocabulary and answer the questions that follow Earth-Sun-Moon 1. Define nebula: 2. Identify
Chapter 9. Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones
 Chapter 9 Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones Frontal Weather Fronts are boundary surfaces between different air masses. Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Drylines Frontal Weather
Chapter 9 Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones Frontal Weather Fronts are boundary surfaces between different air masses. Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Drylines Frontal Weather
ANSWERS TO EXAMPLE ASSIGNMENT (For illustration only)
 ANSWERS TO EXAMPLE ASSIGNMENT (For illustration only) In the following answer to the Example Assignment, it should be emphasized that often there may be no right answer to a given question. Data are usually
ANSWERS TO EXAMPLE ASSIGNMENT (For illustration only) In the following answer to the Example Assignment, it should be emphasized that often there may be no right answer to a given question. Data are usually
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
WEATHER PATTERNS NAME DATE. VOCABULARY: Synoptic weather map- Isotherm- Barometric Pressure- Isobar- Convergence- Divergence- Cyclone- Anticyclone-
 NAME DATE VOCABULARY: Synoptic weather map- WEATHER PATTERNS Isotherm- Barometric Pressure- Isobar- Convergence- Divergence- Cyclone- Anticyclone- Air mass- Source region- Front- OBJECTIVE: Construct a
NAME DATE VOCABULARY: Synoptic weather map- WEATHER PATTERNS Isotherm- Barometric Pressure- Isobar- Convergence- Divergence- Cyclone- Anticyclone- Air mass- Source region- Front- OBJECTIVE: Construct a
LAB 19. Lab 19. Differences in Regional Climate: Why Do Two Cities Located at the Same Latitude and Near a Body of Water Have Such Different Climates?
 Lab Handout Lab 19. Differences in Regional Climate: Why Do Two Cities Located at the Same Latitude and Near a Body of Water Have Such Different Climates? Introduction Weather describes the current atmospheric
Lab Handout Lab 19. Differences in Regional Climate: Why Do Two Cities Located at the Same Latitude and Near a Body of Water Have Such Different Climates? Introduction Weather describes the current atmospheric
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Weather Practice Test
 Name: Weather Practice Test 1. The diagram below shows weather instruments A and B. Which table correctly indicates the name of the weather instrument and the weather variable that it measures? A) B) C)
Name: Weather Practice Test 1. The diagram below shows weather instruments A and B. Which table correctly indicates the name of the weather instrument and the weather variable that it measures? A) B) C)
Weather Basics. Challenges of Winter Weather Forecasting Along the East Coast North American Snow Conference 5/23/16
 Challenges of Winter Weather Forecasting Along the East Coast Sara Croke sara@weatherornot.com Sullivan Brown sully@weatherornot.com @WeatherorNotInc /WeatherOrNotInc 913.722.3955 Weather Basics Moisture
Challenges of Winter Weather Forecasting Along the East Coast Sara Croke sara@weatherornot.com Sullivan Brown sully@weatherornot.com @WeatherorNotInc /WeatherOrNotInc 913.722.3955 Weather Basics Moisture
CLIMATE. UNIT TWO March 2019
 CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California
 A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
Earth s Environmental System: Climate V2100. Midterm Exam. Wednesday March 12, 2003
 Earth s Environmental System: Climate V2100 Midterm Exam Wednesday March 12, 2003 Please put your name at the top of each page If you sketch something, make it big and clear and label your axes Explain
Earth s Environmental System: Climate V2100 Midterm Exam Wednesday March 12, 2003 Please put your name at the top of each page If you sketch something, make it big and clear and label your axes Explain
California OES Weather Threat Briefing
 California OES Weather Threat Briefing Wednesday, January 16, 2019 9:00 AM PST Day 1: Strong winds, heavy mountain snow and heavy rain with isolated thunderstorms across much of the state through Thursday
California OES Weather Threat Briefing Wednesday, January 16, 2019 9:00 AM PST Day 1: Strong winds, heavy mountain snow and heavy rain with isolated thunderstorms across much of the state through Thursday
Charles Jones ICESS University of California, Santa Barbara CA Outline
 The Influence of Tropical Variations on Wintertime Precipitation in California: Pineapple express, Extreme rainfall Events and Long-range Statistical Forecasts Charles Jones ICESS University of California,
The Influence of Tropical Variations on Wintertime Precipitation in California: Pineapple express, Extreme rainfall Events and Long-range Statistical Forecasts Charles Jones ICESS University of California,
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Maximization of Historical Severe Precipitation Events over American, Yuba and Feather River Basins
 Maximization of Historical Severe Precipitation Events over merican, Yuba and Feather River Basins M. L. Kavvas 1, K. Ishida 1, S. Jang 1, N. Ohara 2, Z.Q.Chen 3, and M. nderson 3 1 University Of California,
Maximization of Historical Severe Precipitation Events over merican, Yuba and Feather River Basins M. L. Kavvas 1, K. Ishida 1, S. Jang 1, N. Ohara 2, Z.Q.Chen 3, and M. nderson 3 1 University Of California,
Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday. Air Masses & Fronts
 Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday Air Masses & Fronts General definitions air masses source regions fronts Air masses formation types Fronts formation types Air Masses General Definitions a large body
Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday Air Masses & Fronts General definitions air masses source regions fronts Air masses formation types Fronts formation types Air Masses General Definitions a large body
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
California 120 Day Precipitation Outlook Issued Tom Dunklee Global Climate Center
 California 120 Day Precipitation Outlook Issued 11-01-2008 Tom Dunklee Global Climate Center This is my second updated outlook for precipitation patterns and amounts for the next 4 s of the current rainy
California 120 Day Precipitation Outlook Issued 11-01-2008 Tom Dunklee Global Climate Center This is my second updated outlook for precipitation patterns and amounts for the next 4 s of the current rainy
10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN
 10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN Andrew L. Hulme* and Jonathan E. Martin University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN Andrew L. Hulme* and Jonathan E. Martin University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
CW3E Atmospheric River Outlook
 CW3E Atmospheric River Outlook Update on Atmospheric River Forecast to Impact California This Week - Precipitation continues to fall across portions of California - The AR will begin to propagate southward
CW3E Atmospheric River Outlook Update on Atmospheric River Forecast to Impact California This Week - Precipitation continues to fall across portions of California - The AR will begin to propagate southward
Natural Disasters and Storms in Philadelphia. What is a storm? When cold, dry air meets warm, moist (wet) air, there is a storm.
 Natural Disasters and Storms in Philadelphia 1. What is a natural disaster? 2. Does Philadelphia have many natural disasters? o Nature (noun) everything in the world not made No. Philadelphia does not
Natural Disasters and Storms in Philadelphia 1. What is a natural disaster? 2. Does Philadelphia have many natural disasters? o Nature (noun) everything in the world not made No. Philadelphia does not
1. INTRODUCTION: 2. DATA AND METHODOLOGY:
 27th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 24-28 April 2006, Monterey, CA 3A.4 SUPERTYPHOON DALE (1996): A REMARKABLE STORM FROM BIRTH THROUGH EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION TO EXPLOSIVE REINTENSIFICATION
27th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 24-28 April 2006, Monterey, CA 3A.4 SUPERTYPHOON DALE (1996): A REMARKABLE STORM FROM BIRTH THROUGH EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION TO EXPLOSIVE REINTENSIFICATION
Arizona Climate Summary February 2012
 Arizona Climate Summary February 2012 Summary of conditions for January 2012 January 2012 Temperature and Precipitation Summary January 1 st 20 th : The New Year has started on a very dry note. The La
Arizona Climate Summary February 2012 Summary of conditions for January 2012 January 2012 Temperature and Precipitation Summary January 1 st 20 th : The New Year has started on a very dry note. The La
CW3E Atmospheric River Summary
 CW3E Atmospheric River Summary A strong AR made landfall over southern California this week - The atmospheric river made initial landfall over Big Sur around 1800 UTC Wednesday, 20 March 2018 - AR conditions
CW3E Atmospheric River Summary A strong AR made landfall over southern California this week - The atmospheric river made initial landfall over Big Sur around 1800 UTC Wednesday, 20 March 2018 - AR conditions
