Overview of All 5 HIPPO Missions November 19, 2012
|
|
|
- Laureen Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview of All 5 HIPPO Missions November 19, 2012 More Detailed Research Flight Descriptions follow these Mission overview tables. Mission Flight Path Notes Features of Interest HIPPO-1 Northern polar flight #1 reached 80º N. Sampling Dates January 8 to January 30, 2009 Vertical Profiles Flown 138 Southbound Pacific flights followed the typical central flight path. Southern ocean flight reached 67º S, 175º W The northbound flights followed an Eastern Pacific Route over Central and Southern North America. HIPPO-1 was only mission to not return to the Arctic a second time. CO2: High CO2 at low altitude and high latitude, reaching 2 km at 75º N, reflecting respiration and industrial emissions from late autumn / early winter. Small decreases in CO2 at low altitude over the Southern Ocean. O2 and APO: Hemispheric-scale plume of high O2 and APO emanating from the Southern Ocean during austral summer, starting near the surface at 20º S and growing to 10 km at 67º S. In the Northern Hemisphere, low O2 and APO concentrated between 40º and 60º N. Black Carbon: Southbound results characterize background BC mass concentrations over the central Pacific. Northbound results showed enhanced BC loadings in the lower troposphere over Central and Southern North America. 1
2 Mission Flight Path Notes Features of Interest HIPPO-2 Northern polar flight #1 reached 80º N. Sampling Dates October 31 to November 22, 2009 Vertical Profiles Flown 148 Both southbound and northbound Pacific flights followed a central flight path. Southern ocean flight reached 66º S, 174º W Northern polar flight #2 reached 83º N. CO2: Several plumes of high CO2 (and aerosols) at high altitude over the arctic, 2 6 km at 80º N reflecting Asian emission sources. Low CO2 on approach / departure from New Zealand but otherwise fairly homogenous CO2 from 60º N to 67º S at this time of seasonal transition. O2 and APO: Mainly homogeneous O2 throughout N-S slice but with plumes of low O2 at high altitude over Arctic matching CO2 and aerosols. Several plumes of low APO over the Southern Ocean. Black Carbon: During RF02, at 80º N there were stratified aerosol plumes in the middle and upper troposphere likely pollution from Asia--the atmosphere was full of dark material, with high concentrations of CO. Diluted long-range biomass burning plumes were encountered in the southern hemisphere. Results for two pre-mission training/research flights are also included. 2
3 Mission Flight Path Notes Features of Interest HIPPO-3 Northern polar flight #1 reached 84.75º N. Sampling Dates March 24 to April 16, 2010 Vertical Profiles Flown 136 Both southbound and northbound Pacific flights followed a central flight path. Southbound RF04 reached 41,000 feet over the equator allowing insight into the atmospheric cross section near the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Northbound RF09 was coordinated to track with the NASA Global Hawk (50,000 feet higher) and both intercepted the track of the NASA Aura satellite, which carries the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS). Southern ocean flight reached 66.8º S, 170º E. Northern polar flight #2 reached 85º N. Polar flight RF10 flew three 500 feet altitude by 5 minute legs crossing extensive networks of fractures in ice CO2: High CO2 permeated the entire Northern Hemisphere troposphere from the surface to 8 km near the end of the winter build-up. Between 50º N and 10º N much stronger horizontal than vertical gradients. Low CO2 throughout the Southern Hemisphere extratropics for the greatest N-S CO2 difference observed. O2 and APO: The remains of the high O2 and APO over the Southern Hemisphere during late austral summer. Low O2 throughout Northern Hemisphere matching CO2 buildup from terrestrial and industrial processes, but also showing low in APO indicating additional ocean contribution to O2 signals. Black Carbon: BC from Asian sources was extremely high and well stratified in the Arctic. During RF03, from Alaska to Hawaii, the highest BC mass loadings in the free troposphere during HIPPO were observed in biomass burning plumes from SE Asia between the ITCZ and ~40 N. BC mass varied by as much as 4 orders of magnitude between northern and southern hemispheres. Results for 2 pre-mission training/research flights are also included. 3
4 Mission Flight Path Notes Features of Interest HIPPO-4 Northern polar flight #1 reached 84º N. Sampling Dates June 14 to July 11, 2011 Vertical Profiles Flown 175 Southbound Pacific flights followed the typical central flight path. In the Southern Pacific, a Chilean volcanic ash cloud caused a schedule change. Flights were delayed to allow ash-free air masses to move in to permit safe sampling. High latitude air masses were also pushed south, which limited GV access to Polar air. Southern ocean flight reached 58º S, 145º E. The northbound flights followed a Western Pacific route but the earthquake and tsunami in Japan necessitated a less westerly return than was planned. Northern polar flight #2 reached 82º N. Polar flight RF11 flew over Point Hope, AK and traversed open ocean, scattered ice, flooded ice, and ice with melt ponds with a low altitude transect ranging from 500 to 5,000 feet. Solid ice was not reach by turnaround at 82N. CO2: Rapid seasonal changes observed between southbound and northbound legs. Southbound still had remains of high CO2 in Northern Hemisphere but Northbound showed regions of strongly lower CO2 north of 50º N, especially at high altitude over the Arctic. Low CO2 at low altitude over the Southern Ocean. O2 and APO: Increasing O2 in Northern Hemisphere between southern and northern legs in N matching CO2. Mostly homogeneous APO, but with low APO near surface over Southern Ocean and signs of strong O2 production from algae blooms over the North Pacific and Arctic Oceans. Black Carbon: Moderate loadings in both the northern and southern hemispheres. This was the closest flight to Asia although no significant enhancements in BC were observed. Results for two pre-mission training/research flights are also included. 4
5 Mission Flight Path Notes Features of Interest HIPPO-5 Northern polar flight #1 reached 82º N. Sampling Dates August 9 to September 8, 2011 Vertical Profiles Flown 190 Both southbound and northbound Pacific flights followed a central flight path. Southern ocean flight reached 67º S, 164º E. Flight RF09 reached the ice edge; one profile crossed the edge and another profile was over solid ice. Northern polar flight #2 reached 87º N. CO2: Deepest CO2 drawdown and strongest vertical gradients seen on southbound leg starting at 2 km depth at 30º N and growing to 10 km at 60º N. On northbound leg, CO2 drawdown permeates more broadly, to 8 km at 40º N, but with weaker gradients. Very homogeneous CO2 over the Southern Hemisphere. O2 and APO: High O2 in the Northern Hemisphere with greater stratification on southbound leg, matching CO2. Moderately low O2, and very low APO permeating the Southern Hemisphere south of 5º S to 8 km reflecting ventilation of O2 depleted waters. Black Carbon: Observed lowest northern hemisphere BC mass loadings. Well defined biomass burning plumes were encountered in the middle troposphere between 50º and 25º S. Results for two pre-mission North American research flights are also included. 5
6 Detailed Mission Research Flight Descriptions November 19, 2012 All missions began and ended at NCAR's Earth Observing Laboratory, Research Aviation Facility (RAF), located at the Rocky Mountain Metropolitan Airport (KBJC), Broomfield, CO. [Profiles (1 Count Count Count Count Count 190 Grand Count 787) ] HIPPO-1 Mission Segments HIPPO Initiation Northern Polar Region #1 Pacific Southbound Flight Descriptions Billings, MO to Anchorage, AK >> RF01, Broomfield, CO to Billings, MT turned into an overnight stop due to GV maintenance issue. No data reported for RF01. Anchorage to 80º N and return From Anchorage, to Honolulu, HI, to Pago Pago, American Samoa, and to Christchurch, NZ. >> This was the only mission that stopped in Honolulu, with subsequent missions using Kona. Research Flight Number(s) Vertical Profile Numbers RF RF RF04 - RF Southern Ocean Christchurch to 67º S, 175º W and return RF Pacific Northbound Eastern Pacific Route: From Christchurch to Papeete, Tahiti, to Easter Island, Chile, and to San Jose, Costa Rica >> Air traffic control limited profile flight frequency approaching Central America. RF08 - RF Northern Polar HIPPO-1 was also the only mission to not return to the Arctic a Region #2 second time. Return San Jose, Costa Rica to Broomfield, CO RF
7 HIPPO-2 Mission Segments Flight Descriptions Test fight for instrument checks from Broomfield, CO to Ponca City, OK and return. >> Missed approach at Ponca City, OK Test fight for instrument checks from Broomfield, CO to Northern Wisconsin and return. >> Low approach near WLEF tall tower* Research Flight Vertical Profile Number(s) Numbers RF RF HIPPO Initiation Broomfield, CO to Anchorage, AK RF Northern Polar RF Region #1 Pacific Southbound Southern Ocean Pacific Northbound Anchorage to 80º N and return >> Profiles down to 500 ft were conducted over the sea ice and open leads to sample the shallow Arctic boundary layer for the first time. From Anchorage, to Kona, HI to Rarotonga, Cook Islands, and to Christchurch, NZ. >> Only a fly-by of American Samoa en route to Rarotonga due to recent tsunami. Christchurch to 66º S, 174º W and to Honiara, Solomon Islands >> GV flew a profile over the TCCON site in Wollongong, Australia en route to Honiara, Solomon Islands RF03 - RF RF Central Pacific Route: From Honiara, Solomon Islands to Kona, RF07 - RF HI, and to Anchorage, AK. Anchorage to 83º N and return RF Northern Polar Region #2 Return Anchorage, AK to Broomfield, CO RF *Park Falls, WI, and WLEF tall tower is an AmeriFlux site ( and a Total Carbon Column Observing Network (TCCON) site ( 7
8 HIPPO-3 Mission Research Flight Vertical Profile Flight Descriptions Segments Number(s) Numbers Test fights for instrument checks from Broomfield, CO around CO RF and return. Test fights for instrument checks from Broomfield, CO to OK and RF return HIPPO Initiation Broomfield, CO to Anchorage, AK RF Northern Polar Anchorage to 84.75º N and return RF Region #1 Pacific Southbound From Anchorage, to Kona, HI, to Pago Pago, American Samoa, RF03 - RF and to Christchurch, NZ. Southern Ocean Christchurch to 66.8º S, 170º E and return RF Pacific Northbound Central Pacific Route: From Christchurch, NZ, to Pago Pago, RF07 - RF American Samoa, to Kona, HI, and to Anchorage, AK. Northern Polar Anchorage to 85º N and return RF Region #2 Return Anchorage, AK to Broomfield, CO RF
9 HIPPO-4 Mission Segments Flight Descriptions Test fight for instrument checks from Broomfield, CO to southwest Colorado and Farmington, NM and return. >> With low approach and overfly of Los Alamos TCCON site. Test fight for instrument checks from Broomfield, CO to TX, LA, OK and return. >> Flight in series to investigate the emissions of CH4, CO2 and other gases from the intensive natural gas extraction operations in Texas (conventional and shale) and Northwestern Louisiana (shale gas only). Research Flight Vertical Profile Number(s) Numbers RF RF HIPPO Initiation Broomfield, CO to Anchorage, AK RF (23-24 gap) Northern Polar Anchorage to 84º N and return RF Region #1 Pacific Southbound From Anchorage, to Kona, HI, to Rarotonga, Cook Islands, and to Christchurch, NZ. >> In the Southern Pacific, a Chilean volcanic ash cloud caused a schedule change. Flights were delayed to allow ash-free air masses to move in to permit safe sampling. High latitude air masses were also pushed South, which limited GV access to Polar air. >> After delaying in Rarotonga, the GV flew to Christchurch with restricted profiling. RF03 - RF Southern Ocean Pacific Northbound Christchurch to 58º S, 145º E and to Hobart (Tasmania), Australia. >> Polar air masses were at the margin of the GV flight track that landed in Hobart, Tasmania Western Pacific Route: Hobart to Darwin, Australia, to Saipan, Northern Mariana Islands, to Midway Island, and to Anchorage, AK. RF RF07 - RF Northern Polar Anchorage to 82º N and return RF Region #2 Return Anchorage, AK to Broomfield, CO RF (175 total) 9
10 HIPPO-5 Mission Segments Flight Descriptions Research Flight Number(s) Vertical Profile Number(s) North American Research Flight #1 Broomfield, CO to Northern Wisconsin WLEF tall tower*, and conducted three low approaches in the US corn belt, and return. RF (11-18 gap) North American Broomfield, CO to TX, LA, AR, OK and return RF Research Flight #2 >> Test flight in series to investigate the emissions of CH4, CO2 and other gases from the intensive natural gas extraction operations in Texas (conventional and shale) and Northwestern Louisiana (shale gas only). HIPPO Initiation Broomfield, CO to Anchorage, AK RF Northern Polar RF04 was cut short because of research instrumentation issues. RF Region Anchorage return Northern Polar Anchorage to 82º N and return RF Region #1 Pacific From Anchorage, to Kona, HI to Rarotonga, Cook Islands, and to RF06 - RF Southbound Christchurch, NZ. Southern Ocean Christchurch to 67º S, 164º E and return RF Pacific Central Pacific Route: From Christchurch, NZ, to Rarotonga, Cook RF10 - RF Northbound Islands, to Kona, HI, and to Anchorage, AK. Northern Polar Anchorage to 87º N and return RF Region #2 Return Anchorage, AK to Broomfield, CO >> Limited measurements. RF (190 total) *Park Falls, WI, and WLEF tall tower is an AmeriFlux site ( and a Total Carbon Column Observing Network (TCCON) site ( 10
San Jose State University. From the SelectedWorks of Minghui Diao
 San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Minghui Diao November 14, 2012 Water Vapor and Temperature Comparisons Between AIRS/AMSU-A and In Situ Aircraft Observations From 87 N to 67 S and Sensitivities
San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Minghui Diao November 14, 2012 Water Vapor and Temperature Comparisons Between AIRS/AMSU-A and In Situ Aircraft Observations From 87 N to 67 S and Sensitivities
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: May 15, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: May 15, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com APRIL 2014 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature for
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: May 15, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com APRIL 2014 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature for
Figure 1. Carbon dioxide time series in the North Pacific Ocean (
 Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
 Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
THE ATMOSPHERE IN MOTION
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE IN MOTION Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey Factor 1: Our Energy Source Hi, I m the Sun! I provide 99.9999+
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE IN MOTION Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey Factor 1: Our Energy Source Hi, I m the Sun! I provide 99.9999+
Weather Outlook 2016: Cycles and Patterns Influencing Our Growing Season
 Weather Outlook 2016: Cycles and Patterns Influencing Our Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor of Atmospheric Sciences University of North Dakota Cycle of El Niño Events
Weather Outlook 2016: Cycles and Patterns Influencing Our Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor of Atmospheric Sciences University of North Dakota Cycle of El Niño Events
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones
 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Methane Sensing Flight of Scanning HIS over Hutchinson, KS, 31 March 2001
 Methane Sensing Flight of Scanning HIS over Hutchinson, KS, 31 March 2001 Hank Revercomb, Chris Moeller, Bob Knuteson, Dave Tobin, Ben Howell University of Wisconsin, Space Science and Engineering Center
Methane Sensing Flight of Scanning HIS over Hutchinson, KS, 31 March 2001 Hank Revercomb, Chris Moeller, Bob Knuteson, Dave Tobin, Ben Howell University of Wisconsin, Space Science and Engineering Center
Baseline Ozone in Western North America: Measurements and Models. David Parrish
 Baseline Ozone in Western North America: Measurements and Models David Parrish CIRES University of Colorado NOAA/ESRL Chemical Sciences Division Boulder, Colorado USA Consultant with David.D.Parrish, LLC
Baseline Ozone in Western North America: Measurements and Models David Parrish CIRES University of Colorado NOAA/ESRL Chemical Sciences Division Boulder, Colorado USA Consultant with David.D.Parrish, LLC
Winter. Here s what a weak La Nina usually brings to the nation with tempseraures:
 2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire
 Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Pacific Decadal Oscillation ( PDO ):
 Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2015-2016. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2015-2016. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) Why has the weather been so violent?
 WEATHER TOPICS Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) 2009 Why has the weather been so violent? As can be seen by the following forecast map, the Fall Transition and early Winter Season of
WEATHER TOPICS Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) 2009 Why has the weather been so violent? As can be seen by the following forecast map, the Fall Transition and early Winter Season of
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Chapter 1 Climate in 2016
 Chapter 1 Climate in 2016 1.1 Global climate summary Extremely high temperatures were frequently observed in many regions of the world, and in particular continued for most of the year in various places
Chapter 1 Climate in 2016 1.1 Global climate summary Extremely high temperatures were frequently observed in many regions of the world, and in particular continued for most of the year in various places
Match (one-to-one) the following (1 5) from the list (A E) below.
 GEO 302C EXAM 1 Spring 2009 Name UID You may not refer to any other materials during the exam. For each question (except otherwise explicitly stated), select the best answer for that question. Read all
GEO 302C EXAM 1 Spring 2009 Name UID You may not refer to any other materials during the exam. For each question (except otherwise explicitly stated), select the best answer for that question. Read all
Tropical Moist Rainforest
 Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Hadley Circulation in Action. MET 200 Lecture 12! Global Winds: The General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Scales of Motion
 Hadley Circulation in Action MET 200 Lecture 12! Global Winds: The General Circulation of the Atmosphere 1 2 Previous Lecture Local Winds cales of Motion Eddies ea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook
Hadley Circulation in Action MET 200 Lecture 12! Global Winds: The General Circulation of the Atmosphere 1 2 Previous Lecture Local Winds cales of Motion Eddies ea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for January 2018 1.1 The prevailing Northeast monsoon conditions over Southeast Asia strengthened in January
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for January 2018 1.1 The prevailing Northeast monsoon conditions over Southeast Asia strengthened in January
Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere
 Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere Permafrost Permafrost Ground that is at a temperature of 0 or below for
Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere Permafrost Permafrost Ground that is at a temperature of 0 or below for
EPIC2001 was conceived as an intensive process study along and near 95 o W during September and October 2001 used to make measurements of the atmosphe
 EPIC2001 was conceived as an intensive process study along and near 95 o W during September and October 2001 used to make measurements of the atmosphere and ocean in this region. Two aircraft, the National
EPIC2001 was conceived as an intensive process study along and near 95 o W during September and October 2001 used to make measurements of the atmosphere and ocean in this region. Two aircraft, the National
Level 3 Earth and Space Science, 2017
 91414 914140 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Earth and Space Science, 2017 91414 Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system 2.00 p.m. Monday 27 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement
91414 914140 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Earth and Space Science, 2017 91414 Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system 2.00 p.m. Monday 27 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: September 2008
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land.
 The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Website Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1
 Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Aircra&/Satellite comparisons from the HIPPO and GloPac campaigns
 Aircra&/Satellite comparisons from the HIPPO and GloPac campaigns Karen Rosenlof 1 and Eric Ray 2 1 NOAA ESRL CSD 2 CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, CO HIPPO Workshop March 16-18, 2011 NCAR Instruments
Aircra&/Satellite comparisons from the HIPPO and GloPac campaigns Karen Rosenlof 1 and Eric Ray 2 1 NOAA ESRL CSD 2 CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, CO HIPPO Workshop March 16-18, 2011 NCAR Instruments
CDR Phil Hall Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research
 CDR Phil Hall Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research 23 June 2011 Tools for Building UAS Capacity Requirements Documentation and Trade Studies Observing System Simulation Experiments and Information
CDR Phil Hall Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research 23 June 2011 Tools for Building UAS Capacity Requirements Documentation and Trade Studies Observing System Simulation Experiments and Information
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline. Heating the Atmosphere
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Heating the Atmosphere They are still here! Focus on the Atmosphere Weather Occurs over a short period of time Constantly changing Climate Averaged over a long period of time
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Heating the Atmosphere They are still here! Focus on the Atmosphere Weather Occurs over a short period of time Constantly changing Climate Averaged over a long period of time
LAB G - ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE LAB I TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE PRESSURE PORTION
 LAB G - ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE LAB I TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE PRESSURE PORTION Introduction This lab will provide the student with the opportunity to become familiar with the concepts introduced in Chapter
LAB G - ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE LAB I TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE PRESSURE PORTION Introduction This lab will provide the student with the opportunity to become familiar with the concepts introduced in Chapter
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
IMPACTS OF A WARMING ARCTIC
 The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
Brita Horlings
 Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
Current and future climate of the Cook Islands. Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program
 Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Penrhyn Pukapuka Nassau Suwarrow Rakahanga Manihiki N o r t h e r n C o o k I s l a nds S o u t h e Palmerston r n C o o k I s l
Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Penrhyn Pukapuka Nassau Suwarrow Rakahanga Manihiki N o r t h e r n C o o k I s l a nds S o u t h e Palmerston r n C o o k I s l
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty
 Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Major climate change triggers
 Major climate change triggers Variations in solar output Milankovitch cycles Elevation & distribution of continents Ocean interactions Atmospheric composition change (CO 2 and other volcanic gasses) Biological
Major climate change triggers Variations in solar output Milankovitch cycles Elevation & distribution of continents Ocean interactions Atmospheric composition change (CO 2 and other volcanic gasses) Biological
OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor
 OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor Hypsometric Curve for Earth s solid surface Note histogram Hypsometric curve of Earth shows two modes. Hypsometric curve of Venus shows only one! Why? Ocean Depth vs.
OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor Hypsometric Curve for Earth s solid surface Note histogram Hypsometric curve of Earth shows two modes. Hypsometric curve of Venus shows only one! Why? Ocean Depth vs.
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
World Geography Chapter 3
 World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest
 Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Oct 15, 2012)
 ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Oct 15, 2012) Elif Soyer Ecosystem and Physical Environment Atmosphere, Ocean, Weather & Climate, Internal Planetary Processes Atmospheric Circulation Different
ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Oct 15, 2012) Elif Soyer Ecosystem and Physical Environment Atmosphere, Ocean, Weather & Climate, Internal Planetary Processes Atmospheric Circulation Different
Transparency: Redoubt ash cloud
 Module 1 Investigation 3 Transparency: Redoubt ash cloud Aerial view of Redoubt Volcano during a continuous, low-level eruption of steam and ash December 18, 1989 Source: photo by W. White, USGS, http://www.avo.alaska.edu/avo3/volc/redou/photo.htm
Module 1 Investigation 3 Transparency: Redoubt ash cloud Aerial view of Redoubt Volcano during a continuous, low-level eruption of steam and ash December 18, 1989 Source: photo by W. White, USGS, http://www.avo.alaska.edu/avo3/volc/redou/photo.htm
Mediterranean Climates (Csa, Csb)
 Climatic Zones & Types Part II I've lived in good climate, and it bores the hell out of me. I like weather rather than climate. 1 John Steinbeck Mediterranean Climates (Csa, Csb) Main locations Western
Climatic Zones & Types Part II I've lived in good climate, and it bores the hell out of me. I like weather rather than climate. 1 John Steinbeck Mediterranean Climates (Csa, Csb) Main locations Western
Global Atmospheric Circulation
 Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight,
 The air that we breathe comes from the atmosphere, a thin gaseous layer that surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight, but this weight varies
The air that we breathe comes from the atmosphere, a thin gaseous layer that surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight, but this weight varies
ttp://news.discovery.com/earth/iceland-volcano-aurora.html
 ttp://news.discovery.com/earth/iceland-volcano-aurora.html Outline Role of volcanism on the climate system Distribution of Arctic volcanoes Types of eruptions Frequency of Arctic eruptions Influence on
ttp://news.discovery.com/earth/iceland-volcano-aurora.html Outline Role of volcanism on the climate system Distribution of Arctic volcanoes Types of eruptions Frequency of Arctic eruptions Influence on
Climate.tgt, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Choose the letter of the best answer. (5 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Date: A city located in the middle of North America experiences extreme temperature changes during
Name: Key Concepts Choose the letter of the best answer. (5 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Date: A city located in the middle of North America experiences extreme temperature changes during
Variations of atmospheric electric field and meteorological parameters in Kamchatka in
 Variations of atmospheric electric field and meteorological parameters in Kamchatka in 1997-2016 Sergey Smirnov 1, 1 Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Radio Wave Propagation FEB RAS, Paratunka, Russia
Variations of atmospheric electric field and meteorological parameters in Kamchatka in 1997-2016 Sergey Smirnov 1, 1 Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Radio Wave Propagation FEB RAS, Paratunka, Russia
The Impacts on Air Traffic of Volcanic Ash from the Okmok and Kasatochi Eruptions During the Summer of 2008
 The Impacts on Air Traffic of Volcanic Ash from the Okmok and Kasatochi Eruptions During the Summer of 2008 Lauren A. Hudnall Christopher Newport University, Newport News, VA A.J. Krueger University of
The Impacts on Air Traffic of Volcanic Ash from the Okmok and Kasatochi Eruptions During the Summer of 2008 Lauren A. Hudnall Christopher Newport University, Newport News, VA A.J. Krueger University of
Atmospheric CO2 Observations
 ATS 760 Global Carbon Cycle Atmospheric CO2 Observations (in-situ) BRW MLO Point Barrow, Alaska Scott Denning CSU ATS Mauna Loa, Hawaii 1 ATS 760 Global Carbon Cycle SPO SMO American Samoa South Pole Interannual
ATS 760 Global Carbon Cycle Atmospheric CO2 Observations (in-situ) BRW MLO Point Barrow, Alaska Scott Denning CSU ATS Mauna Loa, Hawaii 1 ATS 760 Global Carbon Cycle SPO SMO American Samoa South Pole Interannual
South & South East Asian Region:
 Issued: 15 th December 2017 Valid Period: January June 2018 South & South East Asian Region: Indonesia Tobacco Regions 1 A] Current conditions: 1] El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) ENSO Alert System
Issued: 15 th December 2017 Valid Period: January June 2018 South & South East Asian Region: Indonesia Tobacco Regions 1 A] Current conditions: 1] El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) ENSO Alert System
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION AND WIND
 ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION AND WIND The source of water for precipitation is the moisture laden air masses that circulate through the atmosphere. Atmospheric circulation is affected by the location on the
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION AND WIND The source of water for precipitation is the moisture laden air masses that circulate through the atmosphere. Atmospheric circulation is affected by the location on the
A B C D PROBLEMS Dilution of power plant plumes. z z z z
 69 PROBLEMS 4. Dilution of power plant plumes Match each power plant plume (-4) to the corresponding atmospheric lapse rate (A-D, solid lines; the dashed line is the adiabatic lapse rate Γ). Briefly comment
69 PROBLEMS 4. Dilution of power plant plumes Match each power plant plume (-4) to the corresponding atmospheric lapse rate (A-D, solid lines; the dashed line is the adiabatic lapse rate Γ). Briefly comment
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study
 The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
MOZAIC-IAGOS : Its role in the satellite validation and in assessing the ozone trends.
 MOZAIC-IAGOS : Its role in the satellite validation and in assessing the ozone trends. MOZAIC Aug. 1994 Jun. 2009 http://mozaic.aero.obs-mip.fr 32 000 flights 230 000 Hours http://www.iagos.org V. Thouret,
MOZAIC-IAGOS : Its role in the satellite validation and in assessing the ozone trends. MOZAIC Aug. 1994 Jun. 2009 http://mozaic.aero.obs-mip.fr 32 000 flights 230 000 Hours http://www.iagos.org V. Thouret,
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Arctic Oxidation Chemistry
 19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Chapter 7 Projections Based on Downscaling
 Damage caused by Tropical Cyclone Pat, Cook Islands, February 2010. Photo: National Environment Service, Government of the Cook Islands Chapter 7 Projections Based on Downscaling 181 Summary Downscaled
Damage caused by Tropical Cyclone Pat, Cook Islands, February 2010. Photo: National Environment Service, Government of the Cook Islands Chapter 7 Projections Based on Downscaling 181 Summary Downscaled
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
). It is a gas produced naturally in the stratosphere where it strongly absorbs incoming
 Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction Chapter Overview The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction Chapter Overview The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
MDA WEATHER SERVICES AG WEATHER OUTLOOK. Kyle Tapley-Senior Agricultural Meteorologist May 22, 2014 Chicago, IL
 MDA WEATHER SERVICES AG WEATHER OUTLOOK Kyle Tapley-Senior Agricultural Meteorologist May 22, 2014 Chicago, IL GLOBAL GRAIN NORTH AMERICA 2014 Agenda Spring Recap North America Forecast El Niño Discussion
MDA WEATHER SERVICES AG WEATHER OUTLOOK Kyle Tapley-Senior Agricultural Meteorologist May 22, 2014 Chicago, IL GLOBAL GRAIN NORTH AMERICA 2014 Agenda Spring Recap North America Forecast El Niño Discussion
Answer Key for Practice Test #2
 Answer Key for Practice Test #2 Section 1. Multiple-choice questions. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark your choice on the optical scan sheet. 1.
Answer Key for Practice Test #2 Section 1. Multiple-choice questions. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark your choice on the optical scan sheet. 1.
Sudan Seasonal Monitor
 Sudan Seasonal Monitor Sudan Meteorological Authority Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Issue 5 August 2010 Summary Advanced position of ITCZ during July to most north of Sudan emerged wide
Sudan Seasonal Monitor Sudan Meteorological Authority Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Issue 5 August 2010 Summary Advanced position of ITCZ during July to most north of Sudan emerged wide
RR#5 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. The table shows the area, in million square kilometers, of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice from
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. The table shows the area, in million square kilometers, of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice from
The Atmospheric Circulation
 The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity?
 Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
An assessment of the risk of aerial transport of rust pathogens to the Western Hemisphere and within North America
 An assessment of the risk of aerial transport of rust pathogens to the Western Hemisphere and within North America Scott A. Isard Departments of Plant Pathology and Meteorology Pennsylvania State University
An assessment of the risk of aerial transport of rust pathogens to the Western Hemisphere and within North America Scott A. Isard Departments of Plant Pathology and Meteorology Pennsylvania State University
Bugs in JRA-55 snow depth analysis
 14 December 2015 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency Bugs in JRA-55 snow depth analysis Bugs were recently found in the snow depth analysis (i.e., the snow depth data generation process)
14 December 2015 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency Bugs in JRA-55 snow depth analysis Bugs were recently found in the snow depth analysis (i.e., the snow depth data generation process)
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH
 L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
Science Results Based on Aura OMI-MLS Measurements of Tropospheric Ozone and Other Trace Gases
 Science Results Based on Aura OMI-MLS Measurements of Tropospheric Ozone and Other Trace Gases J. R. Ziemke Main Contributors: P. K. Bhartia, S. Chandra, B. N. Duncan, L. Froidevaux, J. Joiner, J. Kar,
Science Results Based on Aura OMI-MLS Measurements of Tropospheric Ozone and Other Trace Gases J. R. Ziemke Main Contributors: P. K. Bhartia, S. Chandra, B. N. Duncan, L. Froidevaux, J. Joiner, J. Kar,
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Overview: Students will learn about global climate change, what causes global warming, and scientific projections about climate change in the near future. Levels V-VI Grades 9-12
Global Climate Change Overview: Students will learn about global climate change, what causes global warming, and scientific projections about climate change in the near future. Levels V-VI Grades 9-12
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Colorado CoCoRaHS. Colorado CoCoRaHS. Because Every Drop Counts! October 2014 Volume 2, Issue 10
 U.S. PRECIPITATION (% OF AVERAGE) LOOKING BACK AT SEPTEMBER 2014 September was dry for much of the nation with a few exceptions; one of those being the central Rockies. In Colorado, it was wetter-than-average
U.S. PRECIPITATION (% OF AVERAGE) LOOKING BACK AT SEPTEMBER 2014 September was dry for much of the nation with a few exceptions; one of those being the central Rockies. In Colorado, it was wetter-than-average
Impacts of Climate on the Corn Belt
 Impacts of Climate on the Corn Belt Great Lakes Crop Summit 2015 2015 Evelyn Browning Garriss Conclusions Climate change is not linear. It ebbs and flows. Recent polar volcano eruptions created a cool
Impacts of Climate on the Corn Belt Great Lakes Crop Summit 2015 2015 Evelyn Browning Garriss Conclusions Climate change is not linear. It ebbs and flows. Recent polar volcano eruptions created a cool
FLOODING. Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system.
 CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
A Living Planet. The Earth Inside and Out
 A Living Planet The Earth Inside and Out Planet Earth Earth s Rotation, Revolution, and Tilt Most of Earth s energy comes from the Sun, which we call solar energy. Imagine that the Earth has an imaginary
A Living Planet The Earth Inside and Out Planet Earth Earth s Rotation, Revolution, and Tilt Most of Earth s energy comes from the Sun, which we call solar energy. Imagine that the Earth has an imaginary
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Mathematics and Statistics Level 3
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Mathematics and Statistics for Achievement Standard 91580 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Mathematics and Statistics Level 3 This exemplar supports
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Mathematics and Statistics for Achievement Standard 91580 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Mathematics and Statistics Level 3 This exemplar supports
Satellite techniques for timely detection and near real-time monitoring of volcanic ash clouds for aviation safety
 Satellite techniques for timely detection and near real-time monitoring of volcanic ash clouds for aviation safety N. Pergola A. Falconieri F. Marchese V. Tramutoli Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche Istituto
Satellite techniques for timely detection and near real-time monitoring of volcanic ash clouds for aviation safety N. Pergola A. Falconieri F. Marchese V. Tramutoli Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche Istituto
What is wind? Moving air... Friday, 21 November, 14
 What is wind? Moving air... Why does air move? To create atmospheric equilibrium There are always regions of high air pressure and regions of low air pressure on in the troposphere. Or......to fill in
What is wind? Moving air... Why does air move? To create atmospheric equilibrium There are always regions of high air pressure and regions of low air pressure on in the troposphere. Or......to fill in
Intensive porpoising with a research aircraft to determine atmospheric structure during the SALLJEX and NAME programs
 Intensive porpoising with a research aircraft to determine atmospheric structure during the SALLJEX and NAME programs Michael Douglas National Severe Storms Laboratory Norman, Oklahoma John Mejia CIMMS/University
Intensive porpoising with a research aircraft to determine atmospheric structure during the SALLJEX and NAME programs Michael Douglas National Severe Storms Laboratory Norman, Oklahoma John Mejia CIMMS/University
Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak
 Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Climate Change Impacts in Alaska: the Weather Perspective
 Climate Change Impacts in Alaska: the Weather Perspective September 18, 2007 NOAA s National Weather Service, Alaska Region James Partain, Chief Environmental and Scientific Services Division NOAA NWS
Climate Change Impacts in Alaska: the Weather Perspective September 18, 2007 NOAA s National Weather Service, Alaska Region James Partain, Chief Environmental and Scientific Services Division NOAA NWS
Global Temperature Report: December 2018
 Jan 2, 2019 Vol. 28, No. 9 For Additional Information: Dr. John Christy, (256) 961-7763 christy@nsstc.uah.edu Dr. Roy Spencer, (256) 961-7960 spencer@nsstc.uah.edu Global Temperature Report: December 2018
Jan 2, 2019 Vol. 28, No. 9 For Additional Information: Dr. John Christy, (256) 961-7763 christy@nsstc.uah.edu Dr. Roy Spencer, (256) 961-7960 spencer@nsstc.uah.edu Global Temperature Report: December 2018
Future Climate Change
 Future Climate Change How do you know whether to trust a prediction about the future? All predictions are based on global circulation models (GCMs, AOGCMs) - model accuracy is verified by its ability to
Future Climate Change How do you know whether to trust a prediction about the future? All predictions are based on global circulation models (GCMs, AOGCMs) - model accuracy is verified by its ability to
The Distribution of Cold Environments
 The Distribution of Cold Environments Over 25% of the surface of our planet can be said to have a cold environment, but defining what we actually mean by that can be very challenging. This is because cold
The Distribution of Cold Environments Over 25% of the surface of our planet can be said to have a cold environment, but defining what we actually mean by that can be very challenging. This is because cold
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past
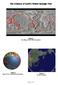 The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
