Questions. Making Better Weather-Based Management Decisions. Dual Polarization 5/1/2018
|
|
|
- Vanessa Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Making Better Weather-Based Management Decisions Brad Jakubowski, Questions Should I irrigate? Should I be scouting for diseases? Can I spray today? Should I syringe? Should we start later in the morning? Are we going to have a frost delay? Should I tarp or will I be ok if I don t? What do I do about lightning? Radar Imaging 450,000 Watts Dual Polarization Doppler radar sends the energy in pules and listens for any returned signal. Signal is measured in decibals DBz Value of 20 dbz is typically the point at which light rain begins. 60 to 65 dbz is about the level where 1" diameter hail can occur. 1
2 Base Reflectivity At increasing distance, the radar is viewing higher and higher in storms and the beam may overshoot the most intense parts. Base Reflectivity Composite Reflectivity Looks at ALL elevation scans in order to create an image. Composite Reflectivity Composite Reflectivity So, if the storm is traveling 16 mph, that 16 mile stretch might potentially receive 1 of rain. 2
3 Composite Reflectivity Base Reflectivity Composite Reflectivity What Do We Do About Lightning? Brrr! 3
4 NOT SAFE!! 4
5 50,000 Degrees NOT SAFE!! NOT SAFE!! 100 Million Volts SAFE!! NOT SAFE!! SAFE!! Lightning can strike long distances, even outside of rain and cloud cover If Thunder Roars, Get Indoors Obey the 30/30 rule 5
6 Weather Safety for Organized Outdoor Athletic Events Another good lightning safety motto is: Weatherbug Spark "If you can see it (lightning) flee it; if you can hear it (thunder), clear it." NWS Mobile NWS Mobile Can I Spray Today? 6
7 Unstable Air Stable Air Isobars and Wind 7
8 Predicting Weather with Lows Predicting Weather with Lows H H H H L L L L 8
9 High: 83ºF High: 84ºF High: 82ºF It s all about Weather Heat 2 hrs High: 111ºF High: 111ºF High: 108ºF Why such a difference in temps? Water Water s Changes of State Should I Syringe? Ice melting absorbs HEAT Anyone make ice cream? 80 calories per gram Evaporation absorbs HEAT Anyone syringe their turf? 600 calories per gram 9
10 The amount of water air holds depends on temperature Cooler Air holds less moisture Warmer air holds more moisture Moisture Holding Capacity of Air Relative Humidity (%Humidity): Is a Ratio Amount of H 2 O in air How much H 2 O air can hold Indicates how near air is to being 100% saturated with water NOT actual amount of water in the air Total Water Vapor Air can Hold Actual Amount of Water 50% Relative Humidity Relative Humidity Changes with Temperature Actual Humidity Does Not Dew Point or Dew Point Temperature The temperature at which dew, clouds or frost forms Occurs when the air temp and dewpoint meet Dewpoint is a direct indicator of how much moisture is in the air Total Water Vapor Air can Hold Actual Amount of Water So: High dew point temps = moist air Low dew point temps = dry air 10
11 Do We Consider 100% Relative Humidity Humid? Dewpoint / Moisture Content Should We Consider 70% Relative Humidity Humid? Which city Which has is in city a greater is more need disease humid? of irrigation? potential? A A B B Air Temp 37ºF 11
12 What conditions can we expect overnight Monday/Tuesday? What conditions can we expect overnight Tuesday/Wednesday? What conditions can we expect overnight Friday/Saturday? 12
13 Temps are below freezing Can we expect frost on either night? Which day would a have greater need for irrigation? Monday, June 11 Today s high will be 96º F, with 15 mph winds out of the south. Friday, June 15 Today s high will be 93º F, with 6 mph winds out of the southwest. Which days may have greater disease potential? IPM Example Pest Management Log Date 7/16/17 Current Time 7:00 am Sunrise / Sunset 5:52 / 9:32 Wind Speed / Direction SW 5-8 mph; shifting NW mph Current Temperature 79 F (yesterday s high: 95) Dewpoint 70 Relative Humidity 84% Target Pest ID Pythium alert? Product Used Total Amount Amount ai Management Decisions Based on Weather Information You have a cold front coming through the night before a 3 pm Softball Championship game. The forecast is ¾ - 1 inch of rain overnight, 28 dewpoints, sunny, breezy: What will you do? People are traveling long distances, what calls do you make? Maybe nothing! The dewpoints are low enough to allow the water to evaporate What about a 65 degree dewpoint forecast? Management Decisions Based on Weather Information You have a warm front coming through in 4 days, you were planning to deep-tine aerify during that time. How does it affect your plans? 13
14 Thank You!! 14
Weather 101 Brad Jakubowski Doane College Water
 Weather 101 Fundamental Meteorology for Turf Managers Brad Jakubowski Doane College Do Baseballs Really Fly Farther at Coors Field? In theory, A well struck baseball should travel 10 percent farther at
Weather 101 Fundamental Meteorology for Turf Managers Brad Jakubowski Doane College Do Baseballs Really Fly Farther at Coors Field? In theory, A well struck baseball should travel 10 percent farther at
Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know
 The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1st Annual Southwest Ohio Snow Conference April 8, 2010 Abner F. Johnson, Office of Maintenance - RWIS Coordinator
 1st Annual Southwest Ohio Snow Conference April 8, 2010 Abner F. Johnson, Office of Maintenance - RWIS Coordinator The Ohio Department of Transportation ODOT has approximately 5500 full-time employees
1st Annual Southwest Ohio Snow Conference April 8, 2010 Abner F. Johnson, Office of Maintenance - RWIS Coordinator The Ohio Department of Transportation ODOT has approximately 5500 full-time employees
Weather Maps. Name:& & &&&&&Advisory:& & 1.! A&weather&map&is:& & & & 2.! Weather&fronts&are:& & & & & &
 Name: Advisory: Weather Maps 1. Aweathermapis: 2. Weatherfrontsare: a. Labelthefrontsbelow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Clovercoversymbols 4. Precipitationsymbols 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. RadarEchoIntensityshows 6. Isobarsare
Name: Advisory: Weather Maps 1. Aweathermapis: 2. Weatherfrontsare: a. Labelthefrontsbelow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Clovercoversymbols 4. Precipitationsymbols 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. RadarEchoIntensityshows 6. Isobarsare
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Guided Notes Weather. Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation
 Guided Notes Weather Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the
Guided Notes Weather Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
Mr. P s Science Test!
 WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
TFS WEATHER BRIEF. Monday, March 25
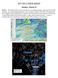 TFS WEATHER BRIEF Monday, March 25 Review: The leading edge of cooler and drier air was pushing through Central and East TX this morning. A few lingering thunderstorms were in progress south of I-20 in
TFS WEATHER BRIEF Monday, March 25 Review: The leading edge of cooler and drier air was pushing through Central and East TX this morning. A few lingering thunderstorms were in progress south of I-20 in
MOISTURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE MEGA PACKET
 NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
3 Severe Weather. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns. Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Issued by: National Weather Service San Joaquin Valley - Hanford CA. Issue time: 409 AM PST Wed Jan
 Forecast Information Location: New_Exchequer_Dam Updated: January 16, 2019, 11:45 am NWS Weather Discussion: Issued by: National Weather Service San Joaquin Valley - Hanford CA Issue time: 409 AM PST Wed
Forecast Information Location: New_Exchequer_Dam Updated: January 16, 2019, 11:45 am NWS Weather Discussion: Issued by: National Weather Service San Joaquin Valley - Hanford CA Issue time: 409 AM PST Wed
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
latent heat/humidity
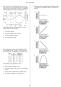 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
Key Concept Weather results from the movement of air masses that differ in temperature and humidity.
 Section 2 Fronts and Weather Key Concept Weather results from the movement of air masses that differ in temperature and humidity. What You Will Learn Differences in pressure, temperature, air movement,
Section 2 Fronts and Weather Key Concept Weather results from the movement of air masses that differ in temperature and humidity. What You Will Learn Differences in pressure, temperature, air movement,
Name Date Hour Table. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One
 Name Date Hour Table 1. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Name Date Hour Table Directions: Answer each question to create your word bank.
Name Date Hour Table 1. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Name Date Hour Table Directions: Answer each question to create your word bank.
2. What are the four most common gasses in the atmosphere and their percentages?
 Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Severe Weather. Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb
 Severe Weather People need to know what the weather is going to do. Sometimes severe weather can happen. Severe weather can cause property damage, injuries to people and animals, and even loss of life.
Severe Weather People need to know what the weather is going to do. Sometimes severe weather can happen. Severe weather can cause property damage, injuries to people and animals, and even loss of life.
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather
 Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Post-Show. Weather. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Weather After the Show We recently presented a Weather show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The following
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Weather After the Show We recently presented a Weather show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The following
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume.
 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Elementary Science Department TERM 4 GRADE 4. Revision. 1. Weather ( ) 1. Is too little precipitation.
 EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Elementary Science Department TERM 4 GRADE 4 A. Match using letters: Revision 1. Weather ( ) 1. Is too little precipitation. 2. Humidity ( ) 2. Is the condition of
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Elementary Science Department TERM 4 GRADE 4 A. Match using letters: Revision 1. Weather ( ) 1. Is too little precipitation. 2. Humidity ( ) 2. Is the condition of
Weather. All photos, graphics, and text copyright 2007 Kris Light
 Weather All photos, graphics, and text copyright 2007 Kris Light http://www.easttennesseewildflowers.com www.easttennesseewildflowers.com/ Weather is a Child of the Sun, Atmosphere, and Water The 3 elements
Weather All photos, graphics, and text copyright 2007 Kris Light http://www.easttennesseewildflowers.com www.easttennesseewildflowers.com/ Weather is a Child of the Sun, Atmosphere, and Water The 3 elements
above the land to be warmer, causing convection currents because of the difference in air pressure.
 Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Air Mass. 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types
 Air Mass 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types A. Continental-relatively dry air masses that form over land. B. Maritime: relatively humid air masses
Air Mass 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types A. Continental-relatively dry air masses that form over land. B. Maritime: relatively humid air masses
The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1%
 The Atmosphere 18.1 The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1% Layers of the Atmosphere made made up of 5 layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Ionosphere
The Atmosphere 18.1 The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1% Layers of the Atmosphere made made up of 5 layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Ionosphere
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
Name Class Date. 3. In what part of the water cycle do clouds form? a. precipitation b. evaporation c. condensation d. runoff
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
78% : component of atmosphere! 21% : 1% : Changes depending on origin of air: - originated over - originated over Ozone = O 3 Definition:
 Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
2016 EXPLANATION OF OBSERVATIONS BY REFERENCE NUMBER
 S 2016 EXPLANATION OF OBSERVATIONS BY REFERENCE NUMBER tation was moved to 10905 Virginia Forest Court Glen Allen, Virginia in Henrico County on June 10, 2008. Latitude 37 39' 18.87" (37.65537) Longitude
S 2016 EXPLANATION OF OBSERVATIONS BY REFERENCE NUMBER tation was moved to 10905 Virginia Forest Court Glen Allen, Virginia in Henrico County on June 10, 2008. Latitude 37 39' 18.87" (37.65537) Longitude
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
Unit 5 Lesson 3 How is Weather Predicted? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Tracking the Weather Warm up 1 Why is it important to watch the weather forecast before traveling to another country? Tracking the Weather A meteorologist is a scientist who studies weather. Meteorologists
Tracking the Weather Warm up 1 Why is it important to watch the weather forecast before traveling to another country? Tracking the Weather A meteorologist is a scientist who studies weather. Meteorologists
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall ERTH FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms
 ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms Before Lab: Review pages 244-324 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Pay special attention to the sections entitled Fronts, Life Cyclone of a Midlatitude
ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms Before Lab: Review pages 244-324 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Pay special attention to the sections entitled Fronts, Life Cyclone of a Midlatitude
Three things necessary for weather are Heat, Air, Moisture (HAM) Weather takes place in the Troposphere (The lower part of the atmosphere).
 Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
25.1 Air Masses. Section 25.1 Objectives
 Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Weather and Energy Review
 Weather and Energy Review Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere Which type
Weather and Energy Review Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere Which type
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida
4. Which map best represents the type of fronts and direction of movement of these fronts in relation to the low-pressure center?
 1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere
 14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
Road Weather: Pavement Forecasting
 Road Weather: Pavement Forecasting By Jon Tarleton Marketing Development Manager Meteorologist Surface Systems, Inc. (SSI ) QTT Quixote Transportation Technologies 314-872-0509 jdt@surface.com 2006 APWA
Road Weather: Pavement Forecasting By Jon Tarleton Marketing Development Manager Meteorologist Surface Systems, Inc. (SSI ) QTT Quixote Transportation Technologies 314-872-0509 jdt@surface.com 2006 APWA
CLIMATE. UNIT TWO March 2019
 CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER EARTH SCIENCE
 EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
according to and water. High atmospheric pressure - Cold dry air is other air so it remains close to the earth, giving weather.
 EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
12/22/2018. Water and the Atmosphere. 8 th Grade. Lesson 1 (Water in the Atmosphere) Chapter 4: Weather. Lesson 2 (Clouds) Clouds
 Lesson 1 (Water in the Atmosphere) Water cycle the continual movement of water among Earth s atmosphere, oceans, and land surface through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation Water and the Atmosphere
Lesson 1 (Water in the Atmosphere) Water cycle the continual movement of water among Earth s atmosphere, oceans, and land surface through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation Water and the Atmosphere
May 17, earthsciencechapter24.notebook. Apr 8 10:54 AM Review. Grade:9th. Subject:Earth Science. Date:4/8.
 Apr 8 10:54 AM 24.1 Review Grade:9th Subject:Earth Science Date:4/8 Apr 8 9:29 AM 1 1 As lower layers of air are warmed... A the air rises B winds form C the air dries D the air sinks Apr 8 9:49 AM 2 What
Apr 8 10:54 AM 24.1 Review Grade:9th Subject:Earth Science Date:4/8 Apr 8 9:29 AM 1 1 As lower layers of air are warmed... A the air rises B winds form C the air dries D the air sinks Apr 8 9:49 AM 2 What
Chapter Introduction. Weather. Patterns. Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
What do you think of when someone says weather?
 Weather Our World: What is Weather? video What do you think of when someone says weather? Questions from Bill Nye video 1. What causes wind? 2. What are two things that were mentioned by Bill Nye that
Weather Our World: What is Weather? video What do you think of when someone says weather? Questions from Bill Nye video 1. What causes wind? 2. What are two things that were mentioned by Bill Nye that
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts
 Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Weather Practice. 4. As wind velocity decreases, the distance between isobars on a weather map will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
 1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CH.15 practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a) climate. c) water cycle. b) weather.
CH.15 practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a) climate. c) water cycle. b) weather.
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
Meteorology Unit Study Guide
 Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
Vantage Pro Technical Reference
 Vantage Pro Technical Reference Davis Instruments 3465 Diablo Ave. Hayward, CA 94545 Created: 9/11/01 Calculations of Derived Variables The following parameters do not have any sensors or circuitry. They
Vantage Pro Technical Reference Davis Instruments 3465 Diablo Ave. Hayward, CA 94545 Created: 9/11/01 Calculations of Derived Variables The following parameters do not have any sensors or circuitry. They
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at different times in August.
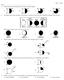 Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Weather Unit Part 2: Meteorology
 Name: Earth Science Date: Period: Weather Unit Part 2: Meteorology 1 The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the map, label the following locations:
Name: Earth Science Date: Period: Weather Unit Part 2: Meteorology 1 The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the map, label the following locations:
WEATHER. rain. thunder. The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning.
 WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
Page 1. Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period.
 Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time
 WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT
 Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT Standard 1: Air Masses Air Mass An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude When an air mass
Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT Standard 1: Air Masses Air Mass An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude When an air mass
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
Weather: Air Patterns
 Weather: Air Patterns Weather: Air Patterns Weather results from global patterns in the atmosphere interacting with local conditions. You have probably experienced seasonal shifts, such as winter in New
Weather: Air Patterns Weather: Air Patterns Weather results from global patterns in the atmosphere interacting with local conditions. You have probably experienced seasonal shifts, such as winter in New
a. Air is more dense b. Associated with cold air (more dense than warm air) c. Associated with sinking air
 Meteorology 1. Air pressure the weight of air pressing down on Earth 2. Temperature and altitude determine air pressure 3. The more air particles are present, the more air density or pressure exists 4.
Meteorology 1. Air pressure the weight of air pressing down on Earth 2. Temperature and altitude determine air pressure 3. The more air particles are present, the more air density or pressure exists 4.
Counselor s Name: Counselor s Ph #: 1) Define meteorology. Explain how the weather affects farmers, sailors, aviators,
 Weather Merit Badge Workbook This workbook is not required but is designed to help you with this merit badge. No one can add or subtract from the Boy Scout Requirements #33215. Use page backs & add pages
Weather Merit Badge Workbook This workbook is not required but is designed to help you with this merit badge. No one can add or subtract from the Boy Scout Requirements #33215. Use page backs & add pages
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 5 Content: Weather Maps Notes
 Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid. Clouds form by this process.
 CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
Introduction. Sunny Partly Cloudy Cloudy. Flurries Snow Ice. Showers Thunderstorms Rain. High Pressure Low Pressure FRONTS. Cold Warm Stationary
 Introduction Weather can change from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day, or season to season. Meteorologists are scientists who study Earth s atmosphere in order to predict these changes. Meteorologists
Introduction Weather can change from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day, or season to season. Meteorologists are scientists who study Earth s atmosphere in order to predict these changes. Meteorologists
Unit 8: Meteorology. How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather?
 Unit 8: Meteorology How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Weather Structure of Earth s atmosphere Air Temperature
Unit 8: Meteorology How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Weather Structure of Earth s atmosphere Air Temperature
Forecasting Local Weather
 Forecasting Local Weather Sea/Land Breeze Temperature Dew Fog Frost Snow Thunderstorms Tropical Cyclones Temperatures: Radiation Balance Typical Diurnal Variation of Temperature Min soon after dawn Temp
Forecasting Local Weather Sea/Land Breeze Temperature Dew Fog Frost Snow Thunderstorms Tropical Cyclones Temperatures: Radiation Balance Typical Diurnal Variation of Temperature Min soon after dawn Temp
Chapter 15: Weather and Climate
 Chapter 15: Weather and Climate Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a. climate. c. water cycle.
Chapter 15: Weather and Climate Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a. climate. c. water cycle.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters
 Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
General Physical Science
 General Physical Science Chapter 20 Atmospheric Effects Condensation and Precipitation Supercooled (supersaturated) air Cooled below dewpoint without condensation Condensation will occur rapidly in the
General Physical Science Chapter 20 Atmospheric Effects Condensation and Precipitation Supercooled (supersaturated) air Cooled below dewpoint without condensation Condensation will occur rapidly in the
Introduction. Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere. How Much Heat Is Brought Upward By Water Vapor?
 Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Weather Maps. The Sun s radiation produces weather on Earth.
 Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6)
 Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6) Temperature is the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere. Air pressure is due to the weight of the air and is determined by several factors including
Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6) Temperature is the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere. Air pressure is due to the weight of the air and is determined by several factors including
West Henrico Co. - Glen Allen Weather Center N W. - Koontz
 PAGE #1 Oct 2017 West Henrico Co. - Glen Allen Weather Center 37.6554 N. 77.5692 W. - Koontz 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Oct Week TEMPERATURE F TEMPERATURE F SKY PRECIPITATION FROZ.
PAGE #1 Oct 2017 West Henrico Co. - Glen Allen Weather Center 37.6554 N. 77.5692 W. - Koontz 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Oct Week TEMPERATURE F TEMPERATURE F SKY PRECIPITATION FROZ.
Marine Weather Primer
 1 of 73 Marine Weather Primer Mark A. Thornton LakeErieWX: Marine Weather Education and Forecasting Resources Mark@LakeErieWX.com 2 of 73 3 of 73 Marine Weather Seminars & Workshops Learn a little meteorology
1 of 73 Marine Weather Primer Mark A. Thornton LakeErieWX: Marine Weather Education and Forecasting Resources Mark@LakeErieWX.com 2 of 73 3 of 73 Marine Weather Seminars & Workshops Learn a little meteorology
Air stability. About. Precipitation. air in unstable equilibrium will move--up/down Fig. 5-1, p.112. Adiabatic = w/ no exchange of heat from outside!
 Air stability About clouds Precipitation A mass of moist, stable air gliding up and over these mountains condenses into lenticular clouds. Fig. 5-CO, p.110 air in unstable equilibrium will move--up/down
Air stability About clouds Precipitation A mass of moist, stable air gliding up and over these mountains condenses into lenticular clouds. Fig. 5-CO, p.110 air in unstable equilibrium will move--up/down
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
