United States Patent (19) Rex
|
|
|
- Dana Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.: 751, Filed: Dec. 16, Foreign Application Priority Data Dec. 19, 1975 (DE Fed. Rep. of Germany ) Int. Cl.... H01, 31/04 52 U.S. C /89 PC; 350/294 58) Field of Search /206, 89 PC; 126/270, 271; 62/2; 350/294 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,023,257 2/1962 Fritts /206 3,350,234 10/1967 Ule /89 PC 3,929,510 12/1975 Kitti /206 3,982,527 9/1976 Cheng et al /270 (11) (45 May 8, ,999,283 12/1976 Dean et al /89 PC 4,023,368 5/1977 Kelly /89 PC 4,045,246 8/1977 Mlavsky et al /89 PC FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1961 France /270 Primary Examiner-Maynard R. Wilbur Assistant Examiner-Lawrence Goodwin Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Smyth, Pavitt, Siegemund, Jones & Martella 57 ABSTRACT A solar panel is constructed from plural parabolic-cylin drical mirrors arranged side by side, and each mirror has three functions. Its concave ground focusses solar energy, its convex rear carries a strip-like solar cell being thereby disposed close to the focal line of the adjacent mirror, while the rest of the rear surface and possibly also the ground surface dissipates thermal en ergy. 10 Claims, 4 Drawing Figures Tsota as tecrow ressive laws
2 U.S. Patent May 8, 1979 Sheet 1 of * as a smo ongs oup wou us an ump me sens
3 U.S. Patent May 8, 1979 Sheet 2 of 2 TA - Ih I O Fig
4 1. SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to the collection of solar energy by means of mirrors which direct solar radiation onto solar cells for purposes of generating electrical energy. Satellites, space probes, space stations or other space vehicles are frequently equipped with so-called solar panels wherein solar radiation is converted into electri cal energy by means of solar cells, and the generated electric energy is used to furnish the vehicle with oper ating power. These solar panels are, for example, con structed in that a frame made of metal or fiber re inforced plastic holds a substrate constructed as honey comb plate or as a glass fiber re-inforced foil. The sub strate carries the solar cells which may be bonded thereto. The panels are oriented to intercept the solar radiation as close as possible to a right angle for receiv ing as much radiation power as is possible per unit area. In outer space, the maximum amount is 1.4 kilowatts per square meter. The cells have a particular mass or weight per unit area of exposure to the sun and they exhibit a particular efficiency. Also, these cells have a cost basis which can be expressed as per unit area of captured radiation (as sumed to be the maximum in each instance). One can, therefore, calculate a particular power output per unit weight factor or parameter, and one can also calculate particular cost amount per unit power output under consideration of complete coverage of a radiation re ceiving area by solar cells. These values or factors are presently about 9.9 kilogram per kilowatt and about $600,000 per kilowatt at a price of a little under $60,000 per square meter for solar cells. It has been proposed to improve these parameters in that the power yield per unit area is increased through concentration of the solar radiation. For example, plane mirrors are arranged on two opposite sides of a large solar panel. These mirrors are inclined by 60 to the solar panel plane and direct thereto additional radiation. The yield was doubled in that fashion as far as captured radiation is concerned. However, the value of mass per unit power and the cost on a per unit power basis could not be correspondingly improved in that manner, because the increased radia tion intensity raises the temperature of the solar cells to such an extent that their efficiency drops considerably. In other words, the larger area used for capturing solar radiation did not increase the effective output because the efficiency of producing energy was reduced in the cells on account of raised temperature. ESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to provide a new and improved solar energy collector construction in which the mass or weight per kilowatt as well as the cost per power unit for the same from which radiation is collected and converted into electrical energy, is reduced. in accordance with the preferred embodiment of the present invention, it is suggested to use a plurality of mirrors, each having a reflecting front and a rear Sur face; the mirrors being so arranged that the focal area of the reflecting front of one mirror is close to a portion of the rear surface of a mirror next to it, and that portion carries a solar cell receiving the focussed radiation of the first mentioned mirror while the mirror carrying the 5 O cell serves as heat dissipator. Most mirrors in the assem bly, thus, serve triple purposes and functions: (a) focussing radiation, (b) carrying a solar cell, (c) dissipating thermal energy. In the preferred form of practicing the invention, the mirrors have concave cylindrical reflecting surfaces with parabolic or near parabolic cross-section. The respective solar cell is affixed either to an outer edge or in the middle of the rear surface of the respective mir ror. That rear surface, to the extent that it is not covered by solar cell material, should carry a layer of high ther mal emissivity. Each mirror together with the edge of the mirror next to it, defines a particular aperture area for captying solar radiation. That area over the actual surface area of the solar cell onto which that radiation is focussed, is a ratio that can be made larger than unity. It should certainly be larger than two possible higher than five. Since the cells are quite effectively cooled, their efficiency is hardly impaired by the use of concentrated radiation. Thus, all factors based on unit area of cap tured radiation are improved accordingly. Particularly the sofar cell weight per kilowatt factor is drastically increased, and the cost of such a generator (for a given output of needed electrical power) is reduced accord ingly. A parabolic contour is desirable but an approxi mation suffices because too strong a concentration of radiation is not needed nor desirable for reasons of avoiding the generation of hot spots. If the reflecting surface is covered by a layer that is transparent to solar radiation but emits thermal radiation, dissipation of thermal energy is improved further. OESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS While the specification concludes with claims partic ularly pointing out and distinctly claiming the subject matter which is regarded as the invention, it is believed that the invention, the objects and features of the inven tion and further objects, features and advantages thereof will be better understood from the following description taken in connection with the accompanying drawings in which: FIG. 1 is a somewhat schematic cross-section view through a solar energy collector constructed in accor dance with the preferred embodiment of the invention; F.G. 2 is a top elevation of the collector shown in F.G. 1; F.G. 3 shows a detail for a modification of the struc ture shown in FGS. 1 and 2; and FIG. 4 is a schematic overall front view of a solar panel that incorporates the structure of FIGS. 1, 2 and Mor 3. Proceeding now to the detailed description of the drawings, the figures show a plurality of mirror strips 1 which are cylindrical mirrors with parabolic cross-sec tion. The parabola is defined by the equation y2=2px wherein the ordinate x runs in the direction of the in coming radiation 5. p is a constant of e.g. 6 cm and y, of course, is the coordinate direction transversely to the axis x as well as to the cylinder axis of the mirrors, that latter axis extending transversely to the plane of the drawing of FIG. 1. The edge 1a of a mirror just about coincides with the apex of the parabola and, therefore, can be regarded as x=0 point. The edge 1b is located at a point given by x = -(p+sv2) wherein S is a particular width dimen sion. Specifically, the rear side 4 of each mirror is pro vided with a solar cell strip 2 extending for the length of
5 3 the mirror in the direction of the cylinder axis and hav ing a width S. Each solar cell 2 is affixed to the respective mirror for good thermal conduction particularly from the cell to the mirror material. The back surface 4 of each mirror strip 1 is preferably provided with a layer which has a very high coefficient of emissivity particularly for the expected temperature of the strip 1 so that, in fact, each such strip serves as a cooling vane for the respective solar cell. Solar energy not converted into electrical energy is, thus, radiated out of the system. Each mirror has a concave reflecting surface 3 which has as high a reflectivity as possible. However, that reflecting layer may be covered by a layer that is trans parent to solar radiation, but has a high emissivity for the expected temperature of the mirror, so that also this surface serves for heat dissipation through radiation. The arrangement, therefore, is constituted by a set of such mirrors which are all directed and oriented to receive solar radiation 5, each mirror capturing a por tion and focusses that portion in a focal area, i.e. a line 7 (extending parallel to the cylinder). Diverging radia tion from each such focal line is fully intercepted by the solar cell on the back surface of the next mirror in the assembly. It can be seen that direct placement of the solar cell into the focal line is not desirable because radiation is concentrated too much. Thus, the cells 2 are slightly out-of-focus. Since such strict focussing is, therefore, not used, one does not need a parabolic mirror, but a spherical or other curved approximation may suffice. However, it should be noted that the radiation field edges as intercepted and redirected by the reflector onto cell 2 should be sharply delineated to fully use the surface of that cell 2 as uniformly as possible. For this reason, a parabolic mirror or close approximation is indeed preferred. FIG. 2 demonstrates how the concentration of solar radiation can be expressed as the ratio of the geometric receiver width D and of the width S of the respective solar cell strip. In view of the double function of each mirror strip as focussing reflector and as a cooling vane, the solar cells are maintained quite cool in spite of the concentration of radiation upon them. Thus, their efficiency remains (as compared with use for intercepting unfocussed solar radiation) almost unimpaired. The amount of the solar cell material per unit area of intercepted radiation is actually reduced by the ratio of S/D. Due to the fact that the efficiency of each cell is hardly reduced, the weight per kilowatt parameter is increased accordingly by that ratio. In other words, for a given needed kilo watt output the weight in solar cell material is reduced, not quite by the ratio S/D because of other facts, but the reduction is quite closely related to the S/D ratio. Since the cost of the solar cell material is the dominating cost component in the price of the solar panel as a whole; the cost is reduced accordingly. That cost is the price of needed solar cells per unit area of captured radiation or it can be expressed in cost per kilowatt output. In the specific example of FIG. 1, the ratio D/S may be about 5.5. The temperature of the solar cells can be maintained at about 370 Kelvin and the weight per power factor was only 6.1 kg/kw while the cost was reduced to about $145,000 per kilowatt (or less than one fourth of the per kilowatt price when the area of cap tured radiation equals the area covered by solar cells) In the modification shown in FIG, 3, the location of the solar cell, here denoted by 32, has been changed. The cross-sectional contour of the mirror strip 31 is again a portion of a parabolay2=2px. One edge, 31a, is located at a point x=p/8, the other edge, 31b, is located at a point x=p. The cell32 is affixed to about the middle of the rear surface of strip 31. The depth of the arrange ment in the y-direction is somewhat larger than in the case of FIG. 1, but the cooling function of the strip 31 is improved because heat can flow from solar cell strip 32 in both directions. It was found to be advantageous to reduce the thickness of the mirror 1 or 31 slightly toward the outer edges 1a or 31a and 31b. FIG. 4 illustrates the front view of a solar panel con structed in accordance with the invention. A frame 48 contains a large plurality of mirror strips 4 of the type shown in FIGS. 1 to 3, whereby the respective solar cells can be situated as shown in FIGS., 2 or in FIG. 3. The panel is divided into frame portions whereby cross bars 49 hold the mirror strips. It will be under stood further that the first mirror of each row does not carry a solar cell strip, while a solar strip must be appro priately affixed to the frame adjacent to the last one of these mirrors. The mirrors 41 should be mounted to the frame and cross bars so that any dimensional changes due to heating be duly compensated. Thin bars 50 pro vide additional support for the mirror strips. The frame 48 is affixed to a holder 51 which is con nected to a turning shaft for purposes of orienting the panel. The mounting may include an articulated joint to permit greater freedom in the adjustment of the panel. Reference numeral 53 represents schematically the space vehicle. The invention has been explained with reference to utilizing solar energy on a space vehicle, as that poses the most stringent environment. Of course, the inven tion can also be practiced for generating solar energy on earth. The invention is not limited to the embodiments de scribed above but all changes and modifications thereof not constituting departures from the spirit and scope of the invention are intended to be included. I claim: 1. Collector of solar energy for generating electrical energy without requiring convective cooling, compris Ing: a plurality of concave mirrors each having a concave reflecting surface and a conversely curved rear surface, not being in heat exchange relation with a cooling fluid, said mirrors arranged side by side so that a portion of the convex rear surface of a first mirror of the plurality is adjacent a focal area of a second mirror of the plurality next to the first mir ror; and a strip-shaped photoelectric solar energy cell affixed to said surface portion of said first mirror receiving. radiation as focussed by the second mirror for di rectly generating electrical energy, a flat side of the cell being in thermal conductive relation with said first mirror said mirror having a thermal emissive surface so that the first mirror serves as radiation vane to dissipate thermal energy exclusively by radiation. 2. Collector as in claim 1, wherein said mirrors have parabolic cross-section. 3. Collector as in claim 2, wherein the parabola fol lows an equation y2=2px, whereinx is a direction of the incoming radiation energy, y is a transverse direction,
6 5 also transverse to a cylinder axis of the respective mir ror and p is a geometric parameter. 4. Collector as in claim3, whereby an edge of the first mirror is located at a position x = :-(p+sv2), wherein S is the width of the solar cell, the cell is disposed along said edge. 5. Collector as in claim 3, wherein a first edge of the first mirror is located at a position x=p/8 and a second edge is located at a position about x=p, and the solar cell is disposed in about the middle between the first and second edges, along a cylinder axis, 6. Collector as in claim 1, wherein said mirrors are Collector as in claim 1, said rear surface being provided with a layer to enhance radiation emissivity. 8. Collector as in claim 1, the solar cell having a particular width in a direction extending transversely to the axial extension of the cell, the second mirror defin ing an effective aperture given by dimension in the direction of axial extension and by a dimension in the direction transversely thereto, the ratio of the latter dimension over said width being larger than two. 9. Collector as in claim 1, said reflecting surface being covered by layer that is transparent to solar radiation but having a large emissivity at the temperature of the mirror. 10. Collector as in claim 1, said mirrors being thinner cylindrical mirrors, the focal areas being line-shaped 15 towards a respective outer edge. accordingly. is is
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
AA. *alt24& DS. (12) United States Patent US 6,607,370 B2. Aug. 19, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Fukamachi et al.
 (12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB 3,187,583. ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION SPACE SIMULATOR A. IMAGE OF LIGHT SOURCE (C)
 June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION Filed Nov. 9, 196 4 SheetsSheet 1 RADIATION SOURCE (C) SPHERCA REFLECTOR EPICA REFLECTOR R 2 A. IMAGE OF LIGHT
June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION Filed Nov. 9, 196 4 SheetsSheet 1 RADIATION SOURCE (C) SPHERCA REFLECTOR EPICA REFLECTOR R 2 A. IMAGE OF LIGHT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
refore z 19, COMAU7AR f7 Sg 26 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT 3,464,770 Horst Schmidt LASER TRANSM/TTER AT TORNEYS NVENTOR
 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Filed Oct. 21, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet l LASER TRANSM/TTER 19, f7 Sg 26 COMAU7AR ------- V. 7 29 8 NVENTOR Horst Schmidt refore z
Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Filed Oct. 21, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet l LASER TRANSM/TTER 19, f7 Sg 26 COMAU7AR ------- V. 7 29 8 NVENTOR Horst Schmidt refore z
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
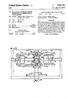 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Eizenhoefer et al.
 United States Patent (19) Eizenhoefer et al. (54) PIEZOELECTRICSHOCKWAVE GENERATOR 75 Inventors: Harald Eizenhoefer, Johannesberg: Ernst Marlinghaus, Germering, both 73 Assignee: 21) Appl. No.: 779,113
United States Patent (19) Eizenhoefer et al. (54) PIEZOELECTRICSHOCKWAVE GENERATOR 75 Inventors: Harald Eizenhoefer, Johannesberg: Ernst Marlinghaus, Germering, both 73 Assignee: 21) Appl. No.: 779,113
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
April 26, J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604
 April 26, 1932- J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet l 43 00009600 2/ 22 ' April 26, 1932. J'. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 46 l? wag Patented Apr. 26,
April 26, 1932- J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet l 43 00009600 2/ 22 ' April 26, 1932. J'. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 46 l? wag Patented Apr. 26,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,167,752 B1. Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001
 USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
100-N. (12) United States Patent N 2 Q US 7,234,334 B1. Jun. 26, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: SZZ
 USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O157111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0157111A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL CELL (76) Inventors: Shigeru Sakamoto, Osaka (JP); Yasunori
(19) United States US 2004O157111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0157111A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL CELL (76) Inventors: Shigeru Sakamoto, Osaka (JP); Yasunori
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent
 US007540229B2 (12) United States Patent Seo et al. (54) EXPLOSIVE REACTIVE ARMOR WITH MOMENTUMITRANSFER MECHANISM (75) Inventors: Yongseok Seo, Seongnam (KR): Jeong-Tae Kim, Daejeon (KR); Chang Choi, Daejeon
US007540229B2 (12) United States Patent Seo et al. (54) EXPLOSIVE REACTIVE ARMOR WITH MOMENTUMITRANSFER MECHANISM (75) Inventors: Yongseok Seo, Seongnam (KR): Jeong-Tae Kim, Daejeon (KR); Chang Choi, Daejeon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0256036A1 NAKAMURA US 20150256036A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) LAMINATED IRON CORE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD FOR LAMINATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0256036A1 NAKAMURA US 20150256036A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) LAMINATED IRON CORE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD FOR LAMINATED
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
(19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
United States Patent (19) Schrader
 United States Patent (19) Schrader US005534997A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 54 RAMAN SPECTROMETER USING A REMOTE PROBE WITHENHANCED EFFICIENCY 75 Inventor: Bernhard Schrader, Essen-Heisingen,
United States Patent (19) Schrader US005534997A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 54 RAMAN SPECTROMETER USING A REMOTE PROBE WITHENHANCED EFFICIENCY 75 Inventor: Bernhard Schrader, Essen-Heisingen,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS 22. 8a 1. United States Patent (19) Maru et al. 11 4,365,007 45) Dec. 21, 1982
 United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki
United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
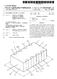 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO6108491A Patent Number: Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2000 54) DUAL SURFACE REFLECTOR 5,556.275 9/1996 Sakata et al.. 5,595,241 1/1997 Jelinek. (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO6108491A Patent Number: Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2000 54) DUAL SURFACE REFLECTOR 5,556.275 9/1996 Sakata et al.. 5,595,241 1/1997 Jelinek. (75) Inventor:
Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
United States Patent (19) Murdoch
 33.245 4M28/8 SR XR 4, 263,719 United States Patent (19) Murdoch (54) OPTICAL SIGHTING DEVICES 76 Inventor: Colin A. Murdoch, 14a Hassall St., Timaru, New Zealand 21 Appl. No.: 824,960 22 Filed: Aug. 15,
33.245 4M28/8 SR XR 4, 263,719 United States Patent (19) Murdoch (54) OPTICAL SIGHTING DEVICES 76 Inventor: Colin A. Murdoch, 14a Hassall St., Timaru, New Zealand 21 Appl. No.: 824,960 22 Filed: Aug. 15,
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
s 2. (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,009,796 B2 Popescu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 30, 2011 s % s
 USO08009796B2 (12) United States Patent Popescu et al. (54) X-RAY CTSYSTEM TO GENERATE TOMOGRAPHC PHASE CONTRAST OR DARK FIELD EXPOSURES (75) Inventors: Stefan Popescu, Erlangen (DE); Christian David,
USO08009796B2 (12) United States Patent Popescu et al. (54) X-RAY CTSYSTEM TO GENERATE TOMOGRAPHC PHASE CONTRAST OR DARK FIELD EXPOSURES (75) Inventors: Stefan Popescu, Erlangen (DE); Christian David,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
Thermal conversion of solar radiation. c =
 Thermal conversion of solar radiation The conversion of solar radiation into thermal energy happens in nature by absorption in earth surface, planetary ocean and vegetation Solar collectors are utilized
Thermal conversion of solar radiation The conversion of solar radiation into thermal energy happens in nature by absorption in earth surface, planetary ocean and vegetation Solar collectors are utilized
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,261,710 B1
 USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
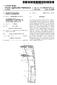 (19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
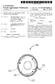 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
- X. (bka III IIII. United States Patent (19) Sobata et al e (2. o
 United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
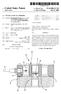 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,765 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING. Filed Aug. 19, 1965 (,,,,, SR-33-R-N
 May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
FLOW-THROUGH CAPACITOR ASSEMBLY FOR THE TREATMENT OF A. Field of application
 FLOW-THROUGH CAPACITOR ASSEMBLY FOR THE TREATMENT OF A FLUID Field of application The present invention regards a flow-through capacitor assembly for the treatment of a fluid, according to the preamble
FLOW-THROUGH CAPACITOR ASSEMBLY FOR THE TREATMENT OF A FLUID Field of application The present invention regards a flow-through capacitor assembly for the treatment of a fluid, according to the preamble
IIIHIIIHIII. United States Patent (19) Chew et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, Patent Number: 5,417,389
 United States Patent (19) Chew et al. 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) METHOD OF, AND APPARATUS FOR, DE-CING AN AIRCRAFT BY NFRARED RADATION Inventors: Charles J. Chew, Ellicottville; Timothy P. Seel, Tonawanda,
United States Patent (19) Chew et al. 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) METHOD OF, AND APPARATUS FOR, DE-CING AN AIRCRAFT BY NFRARED RADATION Inventors: Charles J. Chew, Ellicottville; Timothy P. Seel, Tonawanda,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2
 USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1
 USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) United States Patent
 USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120275180A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0275180 A1 Button et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2012 (54) LIGHT DIFFUSING FIBERS AND METHODS (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20120275180A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0275180 A1 Button et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2012 (54) LIGHT DIFFUSING FIBERS AND METHODS (52) U.S. Cl....
TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T (11) EP 2 618 130 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.07.13 Bulletin 13/30 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/ (06.01) G01N 21/77 (06.01) G01N 33/43 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T (11) EP 2 618 130 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.07.13 Bulletin 13/30 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/ (06.01) G01N 21/77 (06.01) G01N 33/43 (06.01) (21) Application
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
TEPZZ 95785_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
Ndiaga MBODJI and Ali Hajji
 January 22 nd to 24 th, 2018 Faro Portugal 22/01/2018 Ndiaga MBODJI and Ali Hajji Process Engineering and Environment Research Unit Institut Agronomique et Vétérinaire Hassan II 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 1. 3 Solar
January 22 nd to 24 th, 2018 Faro Portugal 22/01/2018 Ndiaga MBODJI and Ali Hajji Process Engineering and Environment Research Unit Institut Agronomique et Vétérinaire Hassan II 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 1. 3 Solar
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
