(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
|
|
|
- Cornelius Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority Data SEMCONDUCTOR DEVICE Mar. 19, 1999 (TW) (76) Inventors: Ming-Dou Ker, Hsinchu (TW); Publication Classification Hsin-Chin Jiang, Taipei (TW) (51) Int. Cl."... H01L 23/48; H01L 23/52; Correspondence Address: HO1L 29/40 J.C. Patents (52) U.S. Cl /781; 257/786 Suite 114 (57) ABSTRACT 1340 Reynolds Ave. Irvine, CA (US) A low-capacitance bonding pad for a Semiconductor device. A diffusion region is formed in a Substrate, and a bonding pad is formed on the substrate and aligned with the diffusion (21) Appl. No.: 09/818,449 region. The bonding pad is made from a Stacked metal layer and a metal layer. The Stacked metal layer is made from a (22) Filed: Mar. 27, 2001 plurality of metal layers and a plurality of dielectric layers, and the metal layers and the dielectric layers are Stacked Related U.S. Application Data alternately. The metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer are formed with Small areas. Each of the metal layers (62) Division of application No. 09/329,648, filed on Jun. Stacked in the Stacked metal layer is coupled with the 9, adjacent metal layer by via plugs.
2
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 12 US 2001/ A O8 < O 212 FIG. 4
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 12 US 2001/ A FIG. 6
5 Patent Application Publication Sheet 4 of 12 US 2001/ A1 FIG. 7 FIG. 8
6 Patent Application Publication Sheet 5 of 12 US 2001/ A ,
7 Patent Application Publication Sheet 6 of 12 US 2001/ A /22/22/24.544; s 2. 4 % sial?ta ba a
8 Patent Application Publication Sheet 7 of 12 US 2001/ A1 FIG. 13 FIG. 14
9 Patent Application Publication Sheet 8 of 12 US 2001/ A1 210, FIG , ,
10 Patent Application Publication Sheet 9 of 12 US 2001/ A1 FIG ,220 FIG. 18
11 Patent Application Publication Sheet 10 of 12 US 2001/ A1 FIG. 20
12 Patent Application Publication Sheet 11 of 12 US 2001/ A1 FIG. 21 FIG. 22
13 Patent Application Publication Sheet 12 of 12 US 2001/ A1 FIG. 23
14 US 2001/ A1 LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR SEMCONDUCTOR DEVICE 0001 CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICA TION 0002 This application claims the priority benefit of Tai wan application Ser. No , filed Mar. 19, 1999, the full disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0003) 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a semiconductor device. More particularly, the present invention relates to a bonding pad with low capacitance for a Semiconductor device Description of the Related Art 0006 Trends for electrical products are light, short, Small, and thin. Usually, the chips manufacturing technology and the packaging technology are rapidly developed to meet these trends. However, due to a limitation of bonding machines, a size of a bonding pad for a Semiconductor device is not reduced as well as a line width of a chip is greatly reduced. Because the size of the bonding pad is insufficiently Small, an area of a Substrate overlapped by the bonding pad is large. As a result, a parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad remains high. Additionally, a peel-off effect often occurs while forming the bonding wire, So that bond ing reliability is decreased FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view, Schematically illustrating a conventional bonding pad Referring to FIG. 1, a dielectric layer 12 is formed on a substrate 10, and a metal layer 14 is formed on the dielectric layer 12. A passivation layer 16 having a bonding pad opening 18 is formed on the metal layer 14. A bonding pad wire 19 is formed on the metal layer 14 within the bonding pad opening 18. A parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad maybe Small if the distance between the substrate 10 and the metal layer 14 is large. But if the bonding pad is only formed by the uppermost metal layer to increase the distance between the Substrate 10 and the metal layer 14, the peel-off effect, denoted as a region 17, often occurs during formation of the bonding wire 19 and chip packaging. The bonding reliability is therefore reduced due to the peel-off effect. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention provides a low-capacitance bonding pad for a Semiconductor device So as to avoid a peel-off effect and reduce a parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad To achieve these and other advantages and in accordance with the purpose of the invention, as embodied and broadly described herein, the invention provides a low-capacitance bonding pad for a Semiconductor device. A diffusion region is formed in a Substrate at a region on which a bonding pad is to be formed. The bonding pad includes a Stacked metal layer and a metal layer, in which the metal layer is on the Stacked metal layer. The Stacked metal layer includes Several metal layers and Several dielectric layers, in which the metal layers are isolated by the dielectric layers in between by alternately Stacking them up. The metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer are formed with Small areas. Each of the metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer is coupled with an adjacent metal layer by a via plug Since the bonding pad includes several metal layers and buried deeply in the dielectric layer, the peel-off effect is effectively avoided. An area of the substrate overlapped by the metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer is Small because the areas of the metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer are Small. As a result, the parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is also effectively reduced. Moreover, the parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is further reduced due to the diffusion region in the Substrate, which Serves as an additional capacitor coupled in Series to the capacitor induced by the metal layers. The metal layers in the Stacked metal layer can include various geometry Structures. For example, the metal layer includes Several metal bars in one layer and crosses to each other in different layer in different bar direction So as to form a geometric Structure, Such as a net Structure or any other overlapping structure To achieve these and other advantages and in accordance with the purpose of the invention, as embodied and broadly described herein, the invention provides another low-capacitance bonding pad for a Semiconductor device. A device is formed under a bonding pad which is made from a Stacked metal layer and an uppermost metal layer. The metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer are formed with Small area and each area of the metal layer in the Stacked metal layer is Smaller than the uppermost metal layer The device is formed on a substrate. Several metal layers close to the device Serve as Signal lines. Several metal layers Stacked on the metal layers as Signal lines Serve as power lines, and other metal layers Stacked on the power lines Serve as the bonding pad which consists of a Stacked metal layer and an uppermost metal layer. The metal layers in the Stacked metal layer can include various geometry Structures. For example, the metal layer includes Several metal bars in one layer and crosses to each other in different layer in different bar direction So as to form a geometric Structure, Such as a net Structure or any other overlapping Structure Because the device is formed between the bonding pad and the Substrate, an area of the integrated circuits layout is reduced. The area of the Substrate overlapped by the metal layers Stacked in the Stacked metal layer is Small Since areas of the metal layers are Small, So that the parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is reduced. The peel-off effect is avoided and the bonding reliability increases because the bonding pad includes the Stacked metal layers which are buried deeply in the dielectric layer. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0015 The accompanying drawings are included to pro vide a further understanding of the invention, and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this specification. The drawings illustrate embodiments of the invention and, together with the description, Serve to explain the principles of the invention. In the drawings, 0016 FIG. 1 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross Sectional view of a conventional bonding pad;
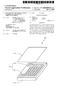
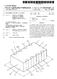
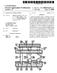
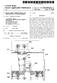
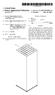
15 US 2001/ A FIG. 2 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a top View of a bonding pad layout according to the invention; FIG. 3 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross sectional view of FIG. 2 taken along a line III-III; FIG. 4 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross sectional view of FIG. 2 taken along a line IV-IV; 0020 FIG. 5 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross sectional view of FIG. 2 taken along a line V-V; 0021 FIG. 6 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross sectional view of FIG. 2 taken along a line VI-VI; 0022 FIG. 7 is another schematic drawing, illustrating a top view of a bonding pad layout according to the invention; 0023 FIG. 8 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross sectional view of FIG. 7 taken along a line VIII-VIII; 0024 FIG. 9 is another schematic drawing, illustrating a top view of a bonding pad to layout according to the invention; FIG. 10 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross-sectional view of FIG. 9 taken along a line X-X; FIG. 11 is another schematic drawing, illustrating a top view of a bonding pad layout according to the invention; FIG. 12 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross-sectional view of FIG. 11 taken along a line XII-XII; 0028 FIGS. 13 through 16 are schematic drawings, illustrating cross-sectional views of bonding pad layouts according to the invention; 0029 FIGS. 17 through 22 are schematic drawings, illustrating cross-sectional views of bonding pad layouts according to the invention; and 0030 FIG. 23 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a cross-sectional view of another bonding pad layout accord ing to the invention. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Reference will now be made in detail to the present preferred embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings Wherever possible, the same reference numbers are used in the drawings and the description to refer to the same or like parts. EXAMPLE FIG. 2 is a schematic drawing, illustrating a top View of a bonding pad layout according to the invention. FIGS. 3, 4, 5 and 6 are schematic drawings, illustrating cross-sectional views of FIG. 2 taken along lines III-III, IV-IV, V-V and VI-VI, respectively. 0034) Referring to FIGS. 2 and 4, a p-type substrate 200 having an n-well 202 is provided. A p-type doped region 204 is formed as a diffusion region in the n-well 202. Abonding pad includes a stacked metal layer 208 and a metal layer 250 lies located on the p-type substrate 200 and is aligned with the p-type doped region 204. The stacked metal layer 208 includes several metal layers 210, 220, 230, 240 and several dielectric layers 212, 222, 232, 242, 252. Additionally, the metal layers 210, 220, 230, 240 and the dielectric layers 212, 222, 232, 242, 252 are stacked alternately on the p-type substrate 200. The metal layer 250 is formed on the dielec tric layer 252. In this structure as described above, a junction capacitance C occurs between the n-well 202 and the p-type doped region 204. A junction capacitance CN occurs between the n-well 202 and the p-type substrate 200. A total equivalent capacitance CM also occurs due to contribution from the metal layers 210, 220, 230, 240, 250. All the capacitance Of C, CN, and CMs are coupled in Series So that a parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is effectively reduced. 0035) The metal layers 210, 220, 230, and 240 are all designed, for example, to have a bar Structures in this embodiment but the metal layer 250 is a planar layer. Each width of the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 is designed to be as Small as possible, So that an area of the p-type substrate 200 overlapped by the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 is reduced. This is significantly helpful to reduce the parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad. 0036) The metal layers 210 and 240 are parallel to a row direction 400 shown in FIG. 2, and the metal layer 240 is aligned with the metal layer 210. Additionally, the metal layers 220 and 230 are parallel to a column direction 300 shown in FIG. 2 and perpendicular to the row direction 400. Similarly, the metal layer 230 is aligned with the metal layer 220. As a result, the metal layers 210 and 240 are shown as a layer structure in FIG. 4 but not shown in FIG. 3 due to the different cross-sectional line III-III. In FIGS. 5 and 6, the metal layers 210 and 240 are shown like bars which are not connected to each other, and the metal layer 210 is aligned with the metal layer 240. Similarly, the metal layers 220 and 230 are shown as bars in FIG. 6 and not shown in FIG. 5. In FIGS. 3 and 4, the metal layers 220 and 230 are shown as bars that are not connected to each other, and the metal layer 230 is aligned with the metal layer 220. A layout of the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 resembles a mesh or a net as shown in FIG In the invention, each of the metal layers 210, 220, 230, 240 and 250 are connected with the adjacent metal layers by via plugs 214,224, 234,244 in the dielectric layers 222, 232,242, and 252. In order to avoid the peel-off effect, the via plugs are alternately positioned in the adjacent dielectric layers 222, 232, 242, and 252 so as to achieve a uniform distribution of the via plugs 214, 224, 234,244. For example, the via plug 244 is not aligned with the via plug 234 as shown in FIG. 4. Similarly, the via plug 234 and the via plug 224 are not aligned and the Via plug 224 and the Via plug 214 are also not aligned as shown in FIG. 2. This structure can effectively avoid the peel-off effect due to a uniform StreSS. The via plug 224 connecting the metal layers 220 and 230 is only shown in FIGS. 3 and 6. The via plug 214 connecting the metal layers 210 and 220 and the via plug 234 connecting the metal layers 230 and 240 are only shown in FIGS. 4 and 6 due to different cross-sectional views. The via plug 244 connecting the metal layers 240 and 250 is only shown in FIGS. 4 and 5. Furthermore, the via plug 214 is aligned with the via plug 234 and is not aligned with the via plugs 224 and 244, as shown in FIGS. 4 and A passivation layer 262 is formed on the metal layer 250 with a bonding pad opening 270 used for a Subsequent bonding process.
16 US 2001/ A The bonding pad according to the invention includes the stacked metal layer 208 and the metal layer 250. The peel-off effect is effectively avoided by this structure. The area of the p-type substrate 200 overlapped by the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 is decreased by about 50% comparing with the conventional bonding pad. Because of the diffusion region, that is, the p-type doped region 204 in the invention, the junction capacitance C between the n-well 202 and the p-type doped region 204, the junction capacitance CN between the n-well 202 and the p-type Substrate 200 and the total equivalent capacitance CM between the Substrate 200 and the metal layers 210, 220, 230, 240,250 are series connected. As a result, the parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is about 50% less than that of the conventional bonding pad A layout of the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 mentioned above is not the only way to reduce the area of the p-type substrate 200 overlapped by the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 according to the invention FIG. 7 is a top view of a portion of a substrate, Schematically illustrating a bonding pad layout according to the invention, and FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view, Sche matically illustrating the bonding pad taken along a line VIII-VIII of FIG. 7. In FIGS. 7 and 8, the metal layers are referred in numerals 710, 720,730, 740 and 750. Each of the metal layers 710,720,730 and 740 are designed as a bar, and the metal layer 750 is a planar layer. The metal layers 710, 720, 730 and 740 are aligned with each other and are isolated by several dielectric layers 212, 222, 232,242 in between. A top dielectric layer 252 covers the metal layer 740. The metal layer 750 is located on the dielectric layer 252. Additionally, a direction of the metal layers 710, 720, 730 and 740 deviates from the direction 400 (FIG. 2) with an angle, which preferably is 45 degrees in this embodiment Referring to FIGS. 7 and 8, each of the metal layers 710, 720, 730, 740 and 750 are coupled with the adjacent metal layers by via plugs 714, 724, 734, 744 in the dielectric layers 212, 222, 232, 242. Positions of the via plugs are not aligned for two adjacent layers. In this manner, the via plug 714 and the via plug 724 are not aligned, the via plug 724 and the via plug 734 are not aligned, and also the via plug 734 and the via plug 744 are not aligned. The via plug 714 and the via plug 734 may be aligned and the via plug 724 and the via plug 744 may be aligned. As a result, the position of the via plug 724 connecting the metal layers 720 and 730 is not superimposed on the position of the via plug 714 used to connect the metal layers 710 and 720 as shown in FIG.8. The position of the via plug 734 connect ing the metal layers 730 and 740 is not superimposed on the position of the via plug 724. However, the via plug 734 is aligned with the via plug 714, and the via plug 744 is aligned with the via plug Based on a concept of reducing the area of the Substrate overlapped by the metal layers, other layouts of the metal layers are also Suitable for the invention FIGS. 9 and 11 are top views of a portion of a Substrate, Schematically illustrating another two bonding pad layouts according to the invention, and FIGS. 10 and 12 are cross-sectional views, Schematically illustrating the bonding pad layouts respectively taken along lines X-X and XII-XII in FIG. 9 and FIG. 10. A layout of the metal layers in FIG. 9 includes, for example, several concentric circles, and a layout of the metal layers in FIG. 11 is concentric polygons, Such as Squares In FIGS. 9 and 10, the metal layers are referred in numerals 910, 920, 930, 940 and 950. Each of the metal layers 910, 920, 930 and 940 are designed as concentric circles, and the metal layer 950 is a planar layer. Referring to FIGS. 9 and 10, the metal layers 910, 920,930 and 940 are aligned with each other, and each of the metal layers 910, 920,930, 940, 950 are coupled by via plugs 914,924,934, 944, which are formed in several isolation layers, such as the dielectric layers 212, 222, 232, 242, 252 as shown in the previous examples. Again, the via plugs 914, 924,934, 944 are alternately distributed for the two adjacent layers. The design concept of this layout is the same as the previous designs. 0046) In FIGS. 11 and 12, the metal layers are referred to by numerals 1110, 1120, 1130, 1140 and The metal layers 1110, 1120, 1130 and 1140 are designed as concentric Squares, and the metal layer 1150 is a plane. Referring to FIGS. 11 and 12, the metal layers 1110, 1120, 1130 and 1140 are aligned with each other, and each of the metal layers 1110, 1120, 1130, 1140 and 1150 are coupled with the adjacent metal layers by via plugs 1114, 1124, 1134 and The design concept of this layout is the same as the previous designs FIGS. 13, 14, 15 and 16 are top views of a portion of a Substrate, Schematically illustrating other bonding pad layouts for the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 according to the invention. Layouts of the metal layers in FIGS. 13, 14, 15 and 16 respectively are concentric pentagons, concentric hexagons, concentric heptagons and concentric octagons. The design concept of these layouts is the same as the previous examples. According to the concept, other kinds of polygons are also acceptable in the invention In FIGS. 17 and 18, the layouts of the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 resemble meshes. The layout shown in FIG. 17 is a honeycombed type mesh, and the layout shown in FIG. 18 is a mesh composed of adjacent octagonal units arranged in rows. The mesh in the invention comprises a mesh composed of a unit shape as seen in FIGS. 17 and 18. However, a mesh composed of various unit shapes is suitable for the invention. In FIG. 19, the layout of the metal layers 210, 220, 230 and 240 is a mesh composed of rows of pentagonal Structures connected by a line, with each pentagonal unit connected to the pentagon in the row above or below by a line. Each unit shape of the mesh is changed to a heptagon, an octagon and a circle in FIGS. 20, 21 and 22, respectively. Also, other kinds of polygons are accept able Although only a few layouts for the metal layers are disclosed in the embodiment. An implementation of the layout is not limited by the disclosed examples because the concept disclosed in the invention is to reduce the area of the Substrate overlapped by the metal layers. By this concept, the parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is reduced and the peel-off effect is avoided. As a result, any kind of layout that meets the concept is suitable for the invention. The bonding pad layout can be designed with many types of unit shape that meet the concept, So that any kind of geometry is Suitable for use in the invention.
17 US 2001/ A1 EXAMPLE In a conventional semiconductor device, the bond ing pad is not formed above an active device region or circuit region because a Subsequent bonding wire process could damage the formed device This issue can also be solved by the invention. Since the bonding pad of the invention include a top metal layer 250 of FIG. 4 and the stacked metal layer 208. The bonding pad opening 270 can be adjusted at the location above the device region. As a result, the available Substrate Surface can be more efficiently used FIG. 23 is a cross-sectional view, Schematically illustrating a bonding pad layout with a device, according to the invention. In this example 2, devices are formed on the Substrate just under the bonding pad. 0053) Referring to FIG. 23, a device 32, such as a field effect transistor, is formed on a substrate 30. Metal layers 51, 52,53,54, 55 and 56 are formed in a dielectric layer 60 over the device 32, in which the dielectric layer 60 serves as an isolation and a frame to stack the metal layers 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56. The dielectric layer 60 can also further include Several Sub-layers to hold and isolate the metal layers. A bonding pad includes the metal layers 55 and 56 and is covered by the a passivation layer 80. The passivation layer 80 includes a bonding pad opening 82, which exposes a portion of the metal layer 56. The metal layers 51 and 52 near the Substrate 30 are used to Serve as, for example, Signal lines, and the metal layers 53 and 54 are designed to be planar layers and used to serve as, for example, power lines. A passivation layer 80 is formed on a dielectric layer 60, and the bonding pad opening 82 is formed in the passivation layer 80 to expose the metal layer 56. A bonding wire 84 is attached to the metal layer 56 within the bonding pad opening 84. Each pair of the metal layers 51, 52, 53, 54, 55 and 56 is isolated by the dielectric layer 60. The metal layers 55, 56 are coupled by a via plug 75 and the metal layers 51, 52 are coupled by a via plug 71. The metal layers 52, 53 and 54 Serving as Signal lines and power lines are also coupled by via plugs (not shown), and the metal layers 54 and 55 are similar. However, these via plugs should not be formed under the bonding pad opening 82. Thus, the metal layers 53, 54 can be used to be the buffer layers, and the bonding stress borne on the active devices can be reduced through these buffer layers. 0054) In the invention, the device 32, such as a CMOS device, is formed on the Substrate 30 or an n-well 34 in the substrate 30. The metal layer 56 is a plane, and the metal layer 55 is designed as applying one of the layouts shown in example 1 for the metal layer 55 so that the parasitic capacitance and the bonding reliability of the bonding pad are effectively reduced and increased, respectively According to the foregoing, the advantages of the invention include the following: The bonding pad in the invention is formed by multiple metal layers and buried deeply in the dielectric layer, so that the peel-off effect is avoided and the bonding reliability effectively increases In the invention, the overlapping area of between the Substrate and the metal layers is greatly reduced. The parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is reduced A diffusion region is formed in the substrate So that the contact capacitance of the diffusion region and the capacitance of the bonding pad are connected in Series. The parasitic capacitance of the bonding pad is reduced The invention is compatible with the cur rent conventional processes. Only the layout design of the bonding pad is changed to meet the require ment of a Semiconductor device. Manufactures can achieve the bonding pad structure of the invention without modifying their fabrication processes The device can be formed under the bond ing pad So that the Substrate Surface is more effi ciently used for compact circuit layout It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made to the Structure of the present invention without departing from the Scope or Spirit of the invention. In View of the foregoing, it is intended that the present invention cover modifications and variations of this invention provided they fall within the Scope of the following claims and their equivalents. What is claimed is: 1. A low-capacitance bonding pad structure for a Semi conductor device, the Structure comprising: a Substrate; a Stacked metal layer positioned on the Substrate, wherein the Stacked metal layer further comprises a plurality of metal layers and a plurality of dielectric layers, which are alternately Stacked up, and the metal layers are coupled by a plurality of via plugs in the dielectric layers, an uppermost metal layer positioned on the Stacked metal layer, wherein an area of each metal layer in the Stacked metal layer is Smaller than that of the uppermost metal layer; and a passivation layer having a bonding pad opening posi tioned on the uppermost metal layer, wherein the bonding pad opening exposes a portion of the upper most metal layer. 2. The structure of claim 1, wherein the metal layers in the Stacked metal layer are in the shape of bars. 3. The structure of claim 2, wherein the bar direction of each layer of the metal layers is across to each other for the different metal layers. 4. The structure of claim 2, wherein the metal layers are Stacked and aligned with each other. 5. The structure of claim 1, wherein the metal layers in the Stacked metal layer comprises concentric polygons. 6. The structure of claim 1, wherein the metal layers in the Stacked metal layer comprises concentric circles. 7. The structure of claim 1, wherein the metal layers in the Stacked metal layer comprises a mesh Structure. 8. The structure of claim 7, wherein the metal layers in the Stacked metal layer are aligned with each other. 9. The structure of claim 7, wherein the mesh is composed of a unit geometric shape. 10. The structure of claim 9, wherein the unit shape is a polygon. 11. The structure of claim 9, wherein the unit shape is a circle.
18 US 2001/ A1 12. The structure of claim 1, wherein the mesh is com posed of various unit shapes. 13. The structure of claim 1, wherein locations of the via plugs in two adjacent layers of the dielectric layers are shifted with a proper distance. 14. A Semiconductor Structure, the Structure comprising: a Substrate; a bonding pad over the Substrate, wherein the bonding pad comprises a Stacked metal layer and an uppermost metal layer; and a device located on the Substrate just under the bonding pad. 15. The structure of claim 14, wherein the stacked metal layer comprises a plurality of metal layers and a plurality of dielectric layers, which are altematingly Stacked up, and the metal layers are coupled by a plurality of via plugs in the dielectric layers. 16. The structure of claim 14, wherein an area of each metal layer in the Stacked metal layer is Smaller than that of the uppermost metal layer. 17. The structure of claim 14, wherein the structure further comprises a signal line and a power line between the device and the bonding pad. 18. The structure of claim 17, wherein the stacked metal layer comprises a plurality of metal layers and a plurality of dielectric layers, which are altematingly Stacked up, and the metal layers are coupled by a plurality of via plugs in the dielectric layers. 19. The structure of claim 17, wherein an area of each metal layer in the Stacked metal layer is Smaller than that of the uppermost metal layer. 20. The structure of claim 14, wherein the device on the Substrate just under the bonding pad is an active device. 21. The structure of claim 14, wherein the device on the Substrate just under the bonding pad is a passive device. 22. A low-capacitance bonding pad structure for a Semi conductor device, the Structure comprising: a Substrate having a well; a doped region as a diffusion region formed in the well; and a bonding pad over the Substrate and aligned with the doped region, wherein the bonding pad comprises a Stacked metal layer and an uppermost metal layer. 23. The structure of claim 22, wherein ions doped in the doped region is opposite to those in the well. 24. The structure of claim 22, wherein the stacked metal layer comprises a plurality of metal layers and a plurality of dielectric layers, which are altematingly Stacked up, and the metal layers are coupled by a plurality of via plugs in the dielectric layers. 25. The structure of claim 22, wherein an area of each metal layer in the Stacked metal layer is Smaller than that of the uppermost metal layer. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1
 USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
(19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160284659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0284659 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE (52) U.S. Cl. STRUCTURE,
(19) United States US 20160284659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0284659 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE (52) U.S. Cl. STRUCTURE,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
(22) Filed: Feb. 22, 2000 Primary Examiner-Carl Whitehead, Jr. 30 F Application O O P tv Dat. ASSistant Examiner Toniae M. Thomas
 (12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(ΐ2) United States Patent Ramaswamy et al.
 US009281044B2 US009281044B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Ramaswamy et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: US 9,281,044 Β2 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) APPARATUSES
US009281044B2 US009281044B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Ramaswamy et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: US 9,281,044 Β2 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) APPARATUSES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,853,818 B2
 USOO8853.818B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,853,818 B2 Lue (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 2014 (54) 3D NAND FLASH MEMORY OTHER PUBLICATIONS (71) Applicant: Hang-Ting Lue, Zhubei (TW) Jung
USOO8853.818B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,853,818 B2 Lue (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 2014 (54) 3D NAND FLASH MEMORY OTHER PUBLICATIONS (71) Applicant: Hang-Ting Lue, Zhubei (TW) Jung
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction q Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip q Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! q Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction q Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip q Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! q Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
NNNS 2NNN 30NYO VC2 C 28N 30. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States 4. N
 (19) United States US 2008O1924.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0192452 A1 Randall et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PASSIVE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (76) Inventors: Michael S. Randall,
(19) United States US 2008O1924.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0192452 A1 Randall et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PASSIVE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (76) Inventors: Michael S. Randall,
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
TEPZZ 89955_A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2
 USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
III M
 III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0164247 A1 Riehle et al. US 2004O164247A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) PROCESS FOR MONITORING AND
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0164247 A1 Riehle et al. US 2004O164247A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) PROCESS FOR MONITORING AND
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
EE382M-14 CMOS Analog Integrated Circuit Design
 EE382M-14 CMOS Analog Integrated Circuit Design Lecture 3, MOS Capacitances, Passive Components, and Layout of Analog Integrated Circuits MOS Capacitances Type of MOS transistor capacitors Depletion capacitance
EE382M-14 CMOS Analog Integrated Circuit Design Lecture 3, MOS Capacitances, Passive Components, and Layout of Analog Integrated Circuits MOS Capacitances Type of MOS transistor capacitors Depletion capacitance
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
The below identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO 31 October 2018 The below identified patent application is available
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO 31 October 2018 The below identified patent application is available
Circuits. L5: Fabrication and Layout -2 ( ) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
 EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L5: Fabrication and Layout -2 (12.8.2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 44 Passive Components: Resistor Besides MOS transistors, sometimes one requires to implement passive
EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L5: Fabrication and Layout -2 (12.8.2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 44 Passive Components: Resistor Besides MOS transistors, sometimes one requires to implement passive
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8680443B2 (12) United States Patent McMillin et al. (54) COMBINED MATERIAL LAYERING TECHNOLOGES FOR ELECTRICHEATERS (75) Inventors: James McMillin, Algonquin, IL (US); Louis P. Steinhauser, St. Louis,MO
USOO8680443B2 (12) United States Patent McMillin et al. (54) COMBINED MATERIAL LAYERING TECHNOLOGES FOR ELECTRICHEATERS (75) Inventors: James McMillin, Algonquin, IL (US); Louis P. Steinhauser, St. Louis,MO
Jinx UDX. (12) United States Patent. 2a2b se 2e2f (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, a2b 2c2d2.
 (12) United States Patent Tadokoro et al. USOO6365894B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) ELECTROMAGNET AND MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventors: Masahiro
(12) United States Patent Tadokoro et al. USOO6365894B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) ELECTROMAGNET AND MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventors: Masahiro
Wafer Charging in Process Equipment and its Relationship to GMR Heads Charging Damage
 Wafer Charging in Process Equipment and its Relationship to GMR Heads Charging Damage Wes Lukaszek Wafer Charging Monitors, Inc. 127 Marine Road, Woodside, CA 94062 tel.: (650) 851-9313, fax.: (650) 851-2252,
Wafer Charging in Process Equipment and its Relationship to GMR Heads Charging Damage Wes Lukaszek Wafer Charging Monitors, Inc. 127 Marine Road, Woodside, CA 94062 tel.: (650) 851-9313, fax.: (650) 851-2252,
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01J 5/62 ( ) G01J 3/28 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
(19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review
UK Patent Application 9 >GB
 UK Patent Application 9 >GB 2 055 465 A (21) (22) (30) (31) (32) (33) (43) (51) (52) (56) (58) (71) (72) (74) Application No 8018366 Date of filing 4 Jun 1980 Priority data 79/20667 14Jun1979 United Kingdom
UK Patent Application 9 >GB 2 055 465 A (21) (22) (30) (31) (32) (33) (43) (51) (52) (56) (58) (71) (72) (74) Application No 8018366 Date of filing 4 Jun 1980 Priority data 79/20667 14Jun1979 United Kingdom
FIG.1. Form organic light emitting. Coat the encapsulation. encapsulation substrate. Prepare an. Prepare a substrate
 (19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,882,745 B2
 USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130269420A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0269420 A1 VALENZA, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 (54) METHODS OF MEASURING POROSITY ON Publication
(19) United States US 20130269420A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0269420 A1 VALENZA, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 (54) METHODS OF MEASURING POROSITY ON Publication
III. United States Patent (19) Alcon. 11 Patent Number: 5,319,336 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Alcon (54) LEVITATIN DEVICE 76) Inventor: Andrew R. Alcon, 7432 Yolanda Dr., Fort Worth, Tex. 76112 (21) Appl. No.: 605,574 22 Filed: ct. 29, 1990 (51) Int. Cl.... H01F 3/00;
United States Patent (19) Alcon (54) LEVITATIN DEVICE 76) Inventor: Andrew R. Alcon, 7432 Yolanda Dr., Fort Worth, Tex. 76112 (21) Appl. No.: 605,574 22 Filed: ct. 29, 1990 (51) Int. Cl.... H01F 3/00;
Characteristics of Passive IC Devices
 008/Oct 8 esistors Characteristics of Passive IC Devices Poly esistance Diffusion esistance Well esistance Parasitic esistance Capacitors Poly Capacitors MOS Capacitors MIM Capacitors Parasitic Capacitors
008/Oct 8 esistors Characteristics of Passive IC Devices Poly esistance Diffusion esistance Well esistance Parasitic esistance Capacitors Poly Capacitors MOS Capacitors MIM Capacitors Parasitic Capacitors
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060070371A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0070371 A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT PROPULSION (22) Filed: Oct.
US 20060070371A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0070371 A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT PROPULSION (22) Filed: Oct.
