(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Damian Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant: GLOBALFOUNDRIES Inc., Grand Cayman (KY) Inventor: Ajey Poovannummoottil Jacob, Watervliet, NY (US) Assignee: GLOBALFOUNDRIES Inc., Grand Cayman (KY) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 15 days. Appl. No.: 14/608,337 Filed: Jan. 29, 2015 Prior Publication Data US 2016/ A1 Aug. 4, 2016 Int. C. HOIL 2L/20 ( ) HOIL 2.3/532 ( ) HOIL 23/528 ( ) HOIL 23/522 ( ) HOIL 2/768 ( ) U.S. C. CPC. H0IL 23/53276 ( ); HOIL 21/7682 ( ); HOIL 21/76843 ( ); HOIL 21/76879 ( ); HOIL 23/5226 ( ); HOIL 23/5283 ( ); HOIL 23/53238 ( ); HOIL 222 1/1094 ( ) (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... H01L 51/0048; H01L 23/49827; H01L 23/49877; H01L 23/5384; H01L 51/057; H01L 23/53276; H01L 51/444 USPC /734, 773, 784, 776 See application file for complete search history. (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,792,790 A * 12/1988 Reeb... GO6K 19, /E ,015,142 B2 * 3/2006 DeHeer... HOL 21/ E21,041 7,772,059 B2* 8/2010 Parikh... HOL 29, ,142 8, B2 * 4/2014 Jain... HO1L 29, /317 * cited by examiner Primary Examiner S. V. Clark (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Amerson Law Firm, PLLC (57) ABSTRACT A method includes forming a folding template in a first dielectric layer. The folding template has a plurality of surfaces that are positioned in different planes. A ballistic conductor line is formed on the plurality of surfaces of the folding template. A device includes a first dielectric layer and a vertically folded line disposed in the first dielectric layer, the vertically folded line including a ballistic conduc tor material. 21 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets ?ail 7 // : M. : : 125
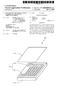
2 U.S. Patent Apr. 25, 2017 Sheet 1 of 3 Figure 1A 1 -- Figure 1B Figure 1C
3 U.S. Patent Apr. 25, 2017 Sheet 2 of [ 50?-( )()()()()()()()()()()()()()()(); }} Figure 1 F
4 U.S. Patent Apr. 25, 2017 Sheet 3 of Figure 1G Figure 1H
5 1. FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The disclosed subject matter relates generally to the fabrication of semiconductor devices and, more particularly, to forming a folded ballistic conductor interconnect line. 2. Description of the Related Art In modern integrated circuits, minimum feature sizes, such as the channel length of field effect transistors, have reached the deep Sub-micron range, thereby steadily increas ing performance of these circuits in terms of speed and/or power consumption and/or diversity of circuit functions. As the size of the individual circuit elements is significantly reduced, thereby improving, for example, the Switching speed of the transistor elements, the available floor space for interconnect lines electrically connecting the individual cir cuit elements is also decreased. Consequently, the dimen sions of these interconnect lines and the spaces between the metal lines have to be reduced to compensate for a reduced amount of available floor space and for an increased number of circuit elements provided per unit area. Interconnect lines can be generally categorized into three groups: signal, clock and power lines. These interconnect types have different and, in some cases, opposing require ments. Signal lines require Small capacitance and are less sensitive to resistance especially for short interconnects. Signal lines are almost immune from electromigration because they pass bidirectional currents. Thus, for signal lines, low aspect ratio lines are favored. Clock lines, which have an activity factor of 1, require low resistance and Small capacitance. Clock lines, however, can fail due to electro migration because of the large currents they pass and because, in Some cases, the current path is different in charge and discharge durations. Power lines are particularly sus ceptible to electromigration failure due to large currents flowing mainly in one direction. In integrated circuits, one limiting factor as it related to device performance is the signal propagation delay caused by the switching speed of the transistor elements. However, as the channel length of these transistor elements has now reached 50 nm and less on more modern integrated circuits, the signal propagation delay is no longer limited by the switching speed of the field effect transistors. Rather, the signal propagation delay is limited in large part, owing to the increased circuit density, by the interconnect lines, since the line-to-line capacitance (C) is increased and also the resis tance (R) of the lines is increased due to their reduced cross-sectional area. The parasitic RC time constants for signal lines tends to limit the performance of the semicon ductor devices. Conventional dual damascene interconnect techniques typically result in lines having the same aspect ratio in a particular metallization layer. Hence, it is difficult to opti mize the constructs of the lines depending on their intended function: signal, clock or power. The present application is directed to various methods for forming folded ballistic conductor interconnect lines so as to eliminate or reduce the effects of one or more of the problems identified above. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The following presents a simplified summary of the invention in order to provide a basic understanding of some aspects of the invention. This Summary is not an exhaustive overview of the invention. It is not intended to identify key or critical elements of the invention or to delineate the scope of the invention. Its sole purpose is to present some concepts in a simplified form as a prelude to the more detailed description that is discussed later. Generally, the present disclosure is directed to various methods of forming conductive lines. One illustrative method includes, among other things, forming a folding template in a first dielectric layer. The folding template has a plurality of Surfaces that are positioned in different planes. A ballistic conductor line is formed on the plurality of Surfaces of the folding template. An illustrative device includes, among other things, a first dielectric layer and a vertically folded line disposed in the first dielectric layer, the vertically folded line including a ballistic conductor material. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The disclosure may be understood by reference to the following description taken in conjunction with the accom panying drawings, in which like reference numerals identify like elements, and in which: FIGS. 1A-1H are cross-sectional diagrams depicting illus trative techniques for forming folded ballistic conductor lines in an interconnect structure. While the subject matter disclosed herein is susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, specific embodiments thereof have been shown by way of example in the drawings and are herein described in detail. It should be understood, however, that the description herein of spe cific embodiments is not intended to limit the invention to the particular forms disclosed, but on the contrary, the intention is to cover all modifications, equivalents, and alternatives falling within the spirit and scope of the inven tion as defined by the appended claims. DETAILED DESCRIPTION Various illustrative embodiments of the invention are described below. In the interest of clarity, not all features of an actual implementation are described in this specification. It will of course be appreciated that in the development of any Such actual embodiment, numerous implementation specific decisions must be made to achieve the developers specific goals, such as compliance with system-related and business-related constraints, which will vary from one implementation to another. Moreover, it will be appreciated that such a development effort might be complex and time-consuming, but would nevertheless be a routine under taking for those of ordinary skill in the art having the benefit of this disclosure. The present subject matter will now be described with reference to the attached figures. Various structures, systems and devices are schematically depicted in the drawings for purposes of explanation only and so as to not obscure the present disclosure with details that are well known to those skilled in the art. Nevertheless, the attached drawings are included to describe and explain illustrative examples of the present disclosure. The words and phrases used herein should be understood and interpreted to have a meaning consistent with the understanding of those words and phrases by those skilled in the relevant art. No special definition of a term or phrase, i.e., a definition that is different from the ordinary and customary meaning as understood by those skilled in the art, is intended to be
6 3 implied by consistent usage of the term or phrase herein. To the extent that a term or phrase is intended to have a special meaning, i.e., a meaning other than that understood by skilled artisans, such a special definition will be expressly set forth in the specification in a definitional manner that directly and unequivocally provides the special definition for the term or phrase. The present disclosure is directed to various methods of forming an interconnect structure. With reference to the attached drawings various illustrative embodiments of the methods and devices disclosed herein will now be described in more detail. FIGS. 1A-1G are cross-sectional diagrams illustrating one illustrative method disclosed herein for forming folded ballistic conductor lines in a semiconductor device 100, which, in the present embodiment, may be represented by an integrated circuit including circuit elements, such as tran sistors, capacitors, resistors and the like. FIG. 1A illustrates the device 100 including a substrate 105 having a device layer 110 formed in and above the substrate 105 in which semiconductor-based circuit ele ments, such as transistors, resistors and the like, may be provided. For convenience, any such circuit elements are not shown in FIG. 1A. The substrate 105 may also include any appropriate microstructure features, such as micromechani cal components, optoelectronic components and the like, wherein at least Some of these components may require a conductive inter-connect structure. In highly complex inte grated circuits, a very large number of electrical connections may be required and, thus, a plurality of metallization layers may typically be formed in the metallization system. The device layer 110 includes contacts 115 (e.g., tungsten) for contacting underlying devices, such as transistors (not shown). A first metallization layer 120 (sometimes referred to in the industry as the M1 or metal 1' layer), including a first dielectric layer 125 and an embedded via 130, is formed above the device layer 110. In the illustrated embodi ment, the dielectric layer 125 may be a low-k dielectric material having a dielectric constant of approximately 3.0 or lower or an ultra-low-k (ULK) material having a dielectric constant of approximately 2.5 or lower. FIG. 1B illustrates the device 100 after a first deposition process was performed to form a second dielectric layer 135, a second deposition process was performed to form a mask layer 140 (e.g., silicon nitride), and a photolithography process was performed to pattern the mask layer 140 to define openings 145. The dielectric layers 125, 130 may be the same or different materials. FIG. 1C illustrates the device 100 after an etch process was performed through the openings 145 to pattern the second dielectric layer 135 to define a folding template 150 therein above the via 130. The folding template 150 exposes one or more portions of the underlying via 130 and runs into and out of the page to provide a linear path for Subsequently forming a conductive line. For example, the folding template 150 may engage an additional via (not shown) in a different portion of the device 100. FIG. 1D illustrates a close-up view of the device 100 showing the folding template 150 of FIG. 1C after a con formal deposition process was performed to deposit a clad ding layer 155 (e.g., copper or boron nitride, etc.) above the second dielectric layer 135 and covering the folding tem plate 150. In some embodiments, the cladding layer 155 may include multiple layers. For example, in an embodiment where copper is employed in the cladding layer 155, a barrier layer (e.g., Ta, TaN. TiN, etc.) (not separately shown) may be formed beneath a copper layer (not separately shown) FIG. 1E illustrates the device 100 after a patterned mask layer 160 (e.g., photoresist) was formed above the folding template 150 and an etch process was performed to remove portions of the cladding layer 155 not covered by the patterned mask layer 160. Forming the cladding layer 155 over the folding template 150 increases the effective width of the cladding layer 155 if it were to be unfolded. The lateral width of the patterned mask layer 160 may be varied to change the effective unfolded width of the cladding layer 155 by modulating the size of the portion of the cladding layer 155 disposed on horizontal surfaces of the second dielectric layer 135 after the cladding layer 155 is patterned. FIG.1F illustrates the device 100 after the patterned mask layer 160 was removed and after a ballistic conductor layer 165 was formed using the cladding layer 155 as a deposition template to define a ballistic conductor line 170 (e.g., the ballistic conductor material is formed selectively on the cladding material). The manner in which the ballistic con ductor material is formed is well known to those skilled in the art. FIG. 1G illustrates a perspective view of the ballistic conductor line 170. In general, the ballistic conductor line 170 has a vertically serpentine cross-section along its length 172 resulting from the planar surfaces of the folding tem plate 150 being oriented in different planes (e.g., horizontal and vertical). The effective width of the ballistic conductor line 170 depends on the number of folds defined by the surfaces of the folding template 150. The ballistic conductor layer 165 is formed from a material that exhibits ballistic conduction, also referred to as ballistic transport, where the transport of electrons occurs in a medium having negligible electrical resistivity caused by scattering. In contrast, a conventional Ohmic conductor material has a resistivity value that is in large part defined by the degree of Scattering within the material. In some embodiments, the ballistic conductor layer 165 may include a plurality of layers of ballistic conductor material formed in a stack. In other embodiments, a stack may be formed by alternating layers of ballistic conductor material and cladding material. Exemplary ballistic conductor materials include gra phene, carbon nanotubes, silicon nanowires, Samarium hexaboride, stanene, silicene, boronene and topolocial insu lators, such as mercury telluride, cadmium telluride, bismuth antimonide, pure antimony, bismuth selenide, bismuth tel luride and antimony telluride. In general, ballistic conductor materials provide low-capacitance signal paths with very thin material layers. In general, ballistic conductor materials may be formed in very thin sheets, sometime as thin as the thickness of a single atom. The manner in which Such ballistic conductor materials may be formed is known to those skilled in the art. In some embodiments, the patterning of the cladding layer 155 illustrated in FIG. 1E may occur after the ballistic conductor layer 165 is formed, such that exposed portions of both the cladding layer 155 and the ballistic conductor layer 165 are selectively removed using the patterned mask layer 160. FIG. 1H illustrates the device 100 after a third dielectric layer 175 is formed above the second dielectric layer 135. The dielectric layers 125, 135, 175 may be the same or different materials. In some embodiments, the third dielec tric layer may be a thin layer that only makes up for the height offset due to the portion of the ballistic conductor line 170 above the horizontal surface of the second dielectric layer 135. In some embodiments, the third dielectric layer 175 may not completely fill the space between the folds, leaving air gaps 180. Such air gaps 180 may be beneficial for
7 5 reducing capacitance of the ballistic conductor line 170, thereby improving performance. In other embodiments, the third dielectric layer 175 may substantially fill the recesses between the folds in the ballistic conductor line 170. Addi tional processing steps may be performed to complete the fabrication of the device 100, such as the formation of additional metallization layers. The use of folded ballistic conductor lines 170 within the metallization layer 120 allows the RC characteristics of the line 170 to be controlled depending on the length of the line 170 and the amount of current required to be carried by the line 170. To increase the current-carrying capacity of the ballistic conductor line 170, the effective line width may be increased by including additional folds in the folding tem plate 150 or by increasing the portion of the cladding layer 155 and the ballistic conductor layer 165 that is disposed on the horizontal surface of the second dielectric layer 135 (see FIG. 1E). The folded ballistic conductor lines 170 may be used in conjunction with other conductive lines (not shown), Such as copper lines. For example, a folded ballistic con ductor line 170 may be used to connect two relatively closely spaced devices, such as transistors, and a copper line (not shown) may connect to the folded ballistic conductor line 170 through a via for a longer interconnect (not shown). The particular embodiments disclosed above are illustra tive only, as the invention may be modified and practiced in different but equivalent manners apparent to those skilled in the art having the benefit of the teachings herein. For example, the process steps set forth above may be performed in a different order. Furthermore, no limitations are intended to the details of construction or design herein shown, other than as described in the claims below. It is therefore evident that the particular embodiments disclosed above may be altered or modified and all such variations are considered within the scope and spirit of the invention. Accordingly, the protection sought herein is as set forth in the claims below. What is claimed: 1. A method, comprising: forming a folding template in a first dielectric layer, said folding template having a plurality of Surfaces that are positioned in different planes; and forming a ballistic conductor line on said plurality of Surfaces of said folding template, said ballistic conduc tor line having a vertical serpentine cross section along its length corresponding to said plurality of Surfaces of said folding template. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein forming said ballistic conductor line comprises: forming a cladding layer above said first dielectric layer and said folding template; forming a patterned mask layer covering a portion of said cladding layer disposed above said folding template: and performing an etch process to remove portions of said cladding layer not covered by said patterned mask layer. 3. The method of claim 2, wherein forming said ballistic conductor line further comprises forming a ballistic conduc tor layer on said cladding layer. 4. The method of claim 1, wherein forming said ballistic conductor line comprises: forming a cladding layer above said first dielectric layer and said folding template; forming a ballistic conductor layer on said cladding layer; forming a patterned mask layer covering a portion of said ballistic conductor layer and said cladding layer dis posed above said folding template; and performing an etch process to remove portions of said ballistic conductor layer and said cladding layer not covered by said patterned mask layer. 5. The method of claim 1, wherein said ballistic conductor line comprises a cladding layer and a ballistic conductor layer. 6. The method of claim 5, wherein said cladding layer comprises a barrier layer formed on said plurality of Surfaces and a copper layer formed above said barrier layer. 7. The method of claim 1, further comprising forming a conductive feature in a second dielectric layer disposed beneath said first dielectric layer, wherein said folding template exposes at least one portion of said conductive feature, and said ballistic conductor line contacts said at least one exposed portion. 8. The method of claim 7, wherein said conductive feature comprises a via. 9. The method of claim 1, further comprising forming a second dielectric layer above said first dielectric layer and above said ballistic conductor line. 10. The method of claim 1, wherein said plurality of Surfaces comprises at least two adjacent vertical Surfaces, the method further comprising forming a second dielectric layer above said first dielectric layer and above said ballistic conductor line without filling a space between said at least two adjacent vertical Surfaces to define an air gap between said at least two adjacent vertical Surfaces. 11. The method of claim 1, wherein said ballistic con ductor line comprises graphene. 12. A device, comprising: a first dielectric layer; and a vertically folded line having a vertical serpentine cross section along its length disposed in said first dielectric layer, said vertically folded line comprising a ballistic conductor material. 13. The device of claim 12, wherein a portion of said vertically folded line is disposed above a horizontal surface of said first dielectric layer. 14. The device of claim 12, wherein said vertically folded line comprises a ballistic conductor layer and a cladding layer. 15. The device of claim 14, wherein said cladding layer comprises a barrier layer and a copper layer formed above said barrier layer. 16. The device of claim 12, further comprising forming a conductive feature in a second dielectric layer disposed beneath said first dielectric layer, wherein said vertically folded line contacts said conductive feature. 17. The device of claim 16, wherein said conductive feature comprises a via. 18. The device of claim 12, wherein said vertically folded line comprises at least two adjacent vertical Surfaces, further comprising a second dielectric layer disposed above said first dielectric layer and above said vertically folded line without filling a space between said at least two adjacent vertical Surfaces to define an air gap between said at least two adjacent vertical Surfaces. 19. The device of claim 12, wherein said ballistic con ductor material comprises graphene. 20. A device, comprising: a first dielectric layer; and a vertically folded line disposed in said first dielectric layer, said vertically folded line comprising a ballistic conductor material, wherein a portion of said vertically folded line is disposed above a horizontal surface of said first dielectric layer.
8 7 21. The device of claim 20, wherein said vertically folded line comprises a ballistic conductor layer and a cladding layer, wherein said cladding layer comprises a barrier layer and a copper layer formed above said barrier layer. k k k k k
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1
 USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
' ' ' - see see 24. (12) United States Patent US 8, B2. Jan. 17, (45) Date of Patent: A. zrrara (10) Patent No.
 USO08097536B2 (12) United States Patent Schuehrer et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,097.536 B2 Jan. 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) REDUCING METAL VOIDS INA
USO08097536B2 (12) United States Patent Schuehrer et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,097.536 B2 Jan. 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) REDUCING METAL VOIDS INA
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(22) Filed: Feb. 22, 2000 Primary Examiner-Carl Whitehead, Jr. 30 F Application O O P tv Dat. ASSistant Examiner Toniae M. Thomas
 (12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 0320422A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0320422 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) FINFET CONTACTING A CONDUCTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. STRAP
(19) United States US 2013 0320422A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0320422 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) FINFET CONTACTING A CONDUCTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. STRAP
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,202,177 B2
 USOO7202177B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,202,177 B2 Zhu et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Apr. 10, 2007 (54) NITROUS OXIDE STRIPPING PROCESS FOR (56) References Cited ORGANOSILICATE GLASS
USOO7202177B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,202,177 B2 Zhu et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Apr. 10, 2007 (54) NITROUS OXIDE STRIPPING PROCESS FOR (56) References Cited ORGANOSILICATE GLASS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,882,745 B2
 USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,853,818 B2
 USOO8853.818B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,853,818 B2 Lue (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 2014 (54) 3D NAND FLASH MEMORY OTHER PUBLICATIONS (71) Applicant: Hang-Ting Lue, Zhubei (TW) Jung
USOO8853.818B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,853,818 B2 Lue (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 2014 (54) 3D NAND FLASH MEMORY OTHER PUBLICATIONS (71) Applicant: Hang-Ting Lue, Zhubei (TW) Jung
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160284659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0284659 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE (52) U.S. Cl. STRUCTURE,
(19) United States US 20160284659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0284659 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE (52) U.S. Cl. STRUCTURE,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,994,072 B2. Hohage et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 9, 2011
 US007994.072B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,994,072 B2 Hohage et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 9, 2011 (54) STRESSTRANSFER BY SEQUENTIALLY 2006, OO27924 A1 2/2006 Chen et al.... 257/751
US007994.072B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,994,072 B2 Hohage et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 9, 2011 (54) STRESSTRANSFER BY SEQUENTIALLY 2006, OO27924 A1 2/2006 Chen et al.... 257/751
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2 Geng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2007
 United States Patent USOO7235478B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,235.478 B2 Geng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2007 (54) POLYMER SPACER FORMATION 6,537.866 B1* 3/2003 Shields et al.... 438, 183 6,562,696
United States Patent USOO7235478B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,235.478 B2 Geng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2007 (54) POLYMER SPACER FORMATION 6,537.866 B1* 3/2003 Shields et al.... 438, 183 6,562,696
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2
 USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7419,867 B2
 USOO7419867B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7419,867 B2 Wieczorek et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2008 (54) CMOS GATESTRUCTURE COMPRISING (58) Field of Classification Search... 438/232,
USOO7419867B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7419,867 B2 Wieczorek et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2008 (54) CMOS GATESTRUCTURE COMPRISING (58) Field of Classification Search... 438/232,
(ΐ2) United States Patent Ramaswamy et al.
 US009281044B2 US009281044B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Ramaswamy et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: US 9,281,044 Β2 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) APPARATUSES
US009281044B2 US009281044B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Ramaswamy et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: US 9,281,044 Β2 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) APPARATUSES
USPC / 295. See application file for complete search history. Tso - Ping Ma, Branford, CT ( US )
 THI NA MATU U U U UTAWA DINI US009818848B2 ( 12 ) United States Patent Sun et al. ( 54 ) THREE - DIMENSIONAL FERROELECTRIC FET - BASED STRUCTURES ( 71 ) Applicant : Yale University, New Haven, CT ( US
THI NA MATU U U U UTAWA DINI US009818848B2 ( 12 ) United States Patent Sun et al. ( 54 ) THREE - DIMENSIONAL FERROELECTRIC FET - BASED STRUCTURES ( 71 ) Applicant : Yale University, New Haven, CT ( US
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
- o. ( 12 ) United States Patent. ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2. ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, Wang
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
S A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,503,962 Caldwell (45. Date of Patent: Apr. p 2, 1996
 IIIllull III S005503962A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,503,962 Caldwell (45. Date of Patent: Apr. p 2, 1996 54 CHEMICAL-MECHANICALALIGNMENT 5,294,556 3/1994 Kawamura... 437/924 MARKAND
IIIllull III S005503962A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,503,962 Caldwell (45. Date of Patent: Apr. p 2, 1996 54 CHEMICAL-MECHANICALALIGNMENT 5,294,556 3/1994 Kawamura... 437/924 MARKAND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,519 B1
 USOO6462519 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,519 B1 McDaniel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC POWER FACTOR 4,771,225. A 9/1988 Nishikawa... 323/211 CORRECTION
USOO6462519 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,519 B1 McDaniel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC POWER FACTOR 4,771,225. A 9/1988 Nishikawa... 323/211 CORRECTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,716,763 B2
 USOO6716763B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,716,763 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF CONTROLLING STRIATIONS 5.242,536 A 9/1993 Schoenborn AND CD LOSS IN CONTACT
USOO6716763B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,716,763 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF CONTROLLING STRIATIONS 5.242,536 A 9/1993 Schoenborn AND CD LOSS IN CONTACT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8680443B2 (12) United States Patent McMillin et al. (54) COMBINED MATERIAL LAYERING TECHNOLOGES FOR ELECTRICHEATERS (75) Inventors: James McMillin, Algonquin, IL (US); Louis P. Steinhauser, St. Louis,MO
USOO8680443B2 (12) United States Patent McMillin et al. (54) COMBINED MATERIAL LAYERING TECHNOLOGES FOR ELECTRICHEATERS (75) Inventors: James McMillin, Algonquin, IL (US); Louis P. Steinhauser, St. Louis,MO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1
 USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,153,764 B2. Colli (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 6, 2015
 US009 153764B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,153,764 B2 Colli (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 6, 2015 (54) APPARATUS FORTRANSDUCING A 386 A. ck 33. Sarah al..............3s. aghloul et al....
US009 153764B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,153,764 B2 Colli (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 6, 2015 (54) APPARATUS FORTRANSDUCING A 386 A. ck 33. Sarah al..............3s. aghloul et al....
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O133638A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0133638A1 Simsek-Ege et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 12, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) MEMORY CELL, PLLAR INCLUDING
(19) United States US 2016O133638A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0133638A1 Simsek-Ege et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 12, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) MEMORY CELL, PLLAR INCLUDING
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2. Hung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 2015
 USOO9048222B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.048.222 B2 Hung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 2015 (54) METHOD OF FABRICATING 23/5386 (2013.01); HOIL 25/105 (2013.01); INTERCONNECT
USOO9048222B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.048.222 B2 Hung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 2015 (54) METHOD OF FABRICATING 23/5386 (2013.01); HOIL 25/105 (2013.01); INTERCONNECT
() -10 to. (12) United States Patent ATF. (10) Patent No.: US 7.925,614 B2. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, WAVELENGTH. Burkard et al.
 USOO7925.614B2 (12) United States Patent Burkard et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND STRUCTURE TO SOLATEA QUBIT FROM THE ENVIRONMENT Inventors: Guido Burkard, Irvington,
USOO7925.614B2 (12) United States Patent Burkard et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND STRUCTURE TO SOLATEA QUBIT FROM THE ENVIRONMENT Inventors: Guido Burkard, Irvington,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0103105 A1 Nakama et al. US 201601031 05A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0103105 A1 Nakama et al. US 201601031 05A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
NNNS 2NNN 30NYO VC2 C 28N 30. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States 4. N
 (19) United States US 2008O1924.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0192452 A1 Randall et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PASSIVE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (76) Inventors: Michael S. Randall,
(19) United States US 2008O1924.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0192452 A1 Randall et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PASSIVE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (76) Inventors: Michael S. Randall,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130269420A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0269420 A1 VALENZA, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 (54) METHODS OF MEASURING POROSITY ON Publication
(19) United States US 20130269420A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0269420 A1 VALENZA, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 (54) METHODS OF MEASURING POROSITY ON Publication
(12) United States Patent
 US00751.5454B2 (12) United States Patent Symanczyk (54) CBRAM CELL AND CBRAM ARRAY. AND METHOD OF OPERATING THEREOF (75) Inventor: Ralf Symanczyk, Tuntenhausen (DE) (73) Assignees: Infineon Technologies
US00751.5454B2 (12) United States Patent Symanczyk (54) CBRAM CELL AND CBRAM ARRAY. AND METHOD OF OPERATING THEREOF (75) Inventor: Ralf Symanczyk, Tuntenhausen (DE) (73) Assignees: Infineon Technologies
Alkali Metal-Cathode Solution Battery
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Alkali Metal-Cathode Solution Battery 11-11-2014 Pyoungho Choi University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Alkali Metal-Cathode Solution Battery 11-11-2014 Pyoungho Choi University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9427.946B2 (12) United States Patent Winer () Patent No.: US 9.427,946 B2 (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 30, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR TRANSFER
USOO9427.946B2 (12) United States Patent Winer () Patent No.: US 9.427,946 B2 (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 30, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR TRANSFER
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2. Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013
 US008517600B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2 Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) DEPOSITION SENSORBASED ON 4.595,297 A 6/1986 Liu et al. DIFFERENTAL, HEAT TRANSFER
US008517600B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2 Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) DEPOSITION SENSORBASED ON 4.595,297 A 6/1986 Liu et al. DIFFERENTAL, HEAT TRANSFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 14, 2006
 US 20060202272A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0202272 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIDE BANDGAPTRANSISTORS WITH Publication Classification GATE-SOURCE
US 20060202272A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0202272 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIDE BANDGAPTRANSISTORS WITH Publication Classification GATE-SOURCE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO868.4738B2 (12) United States Patent Wade (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) METHOD AND TOOL FOR FIREARM SIGHT TRAINING Inventor: Christian
USOO868.4738B2 (12) United States Patent Wade (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) METHOD AND TOOL FOR FIREARM SIGHT TRAINING Inventor: Christian
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
s N NS NRAIN (12) United States Patent US 8,748,976 B1 Jun. 10, 2014 (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 US008748976B1 (12) United States Patent KOcOn et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,748,976 B1 Jun. 10, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) DUAL RESURF TRENCH FIELD PLATE
US008748976B1 (12) United States Patent KOcOn et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,748,976 B1 Jun. 10, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) DUAL RESURF TRENCH FIELD PLATE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,064,634 B2
 USOO9064634B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,064,634 B2 Nakamura (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) CAPACITOR HOLDER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Tatsuya Nakamura, Nagoya
USOO9064634B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,064,634 B2 Nakamura (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) CAPACITOR HOLDER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Tatsuya Nakamura, Nagoya
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
100-N. (12) United States Patent N 2 Q US 7,234,334 B1. Jun. 26, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: SZZ
 USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,765 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING. Filed Aug. 19, 1965 (,,,,, SR-33-R-N
 May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,515,339 B2
 USOO6515339B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,515,339 B2 Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 4, 2003 (54) METHOD OF HORIZONTALLY GROWING CARBON NANOTUBES AND FIELD EFFECT 6,423,583 B1
USOO6515339B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,515,339 B2 Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 4, 2003 (54) METHOD OF HORIZONTALLY GROWING CARBON NANOTUBES AND FIELD EFFECT 6,423,583 B1
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
III M
 III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
