United States Patent (19)
|
|
|
- Moses Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl. No.: 874, Filed: Feb. 2, Int. Cl... H01, 21/ U.S.C /186; 148/187; 48/ Field of Search /186, 187, References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTs 2,827,436 3/1958 Bernski /186 2,937,963 5/1960 Pelfrey /186 X 3,340,598 9/1967 Hatcher /1.5 3,349,474 /1967 Rauscher /89 X 3,3,4 7/1969 Wyclislak /186 3,602,778 8/1971 Ura et al /1.5 X 3,6,773 3,878,001 3,933,527 4,013,483 4,046,608 1/1972 4/1975 1/1976 3/1977 9/1977 (11) ) Feb. 6, 1979 Thire /186X Olk /186 Tarneja et al /186X Nuzillat et al / Iseghem et al /188 Primary Examiner-G. Ozaki Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Ostrolenk, Faber, Gerb & Soffen 57 ABSTRACT A method of manufacture of a zener diode with a given breakdown voltage is disclosed wherein the resistivity of the initial wafer is measured before diffusion of a junction in the wafer, and a diffusion operation is then performed to diffuse the junction at a fixed diffusion temperature and for a time which is determined such that the desired breakdown voltage is proportional to the product of the square root of the initial resistivity and the fourth root of the diffusion time. Claims, 5 Drawing Figures 2% NYNY YNNN SYYYNYNNY NNNNNNNNNNNNfn,
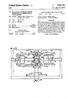
2 U.S. Patent Feb. 6, 1979 Az Z.Z. ZZZ.A. 4\ 2-7 7% Az Z. A 2. /2 // a 7-yaa a/aa-z/us/02/v Azi A4 v 2%-e LZ775. At NNNNaNNaNNNNA Syxxas A.Nxxxxxx
3 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to the manufacture of semicon ductor devices such that a given reverse avalance bulk breakdown voltage across a p-n junction can be accu rately reproduced in the manufacturing process, and more specifically relates to a novel process for the man ufacture of a zener diode wherein the reverse break down voltage of the device can be held within narrow tolerances during the manufacturing operation. Processes for the manufacture of Zener diodes are well known, and are described in numerous prior publi cations including, for example, U.S. Pat. No. 3,378,9, dated Apr. 23, Zener diodes have an accurately defined reverse breakdown voltage and this characteristic is widely used in various electrical circuits. Zener diodes are normally sold with a given reverse voltage breakdown to within a tolerance of plus or minus 5%. Thus, the manufacturing operation must be closely controlled to avoid too high a rejection rate. The actual breakdown voltage of a given device will be determined by the depth of the junction, and by the resistivity of the wafer materials. These characteristics in turn are controlled by the initial resistivity of the wafer, the diffusion temperature, and the diffusion time for a given diffusion system using given n-type or p type conductivity materials. Consequently, the break down voltage of devices being produced will vary with changes in any of the above parameters. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION In accordance with the invention, a novel manufac turing process is provided for zener-type junctions, in which diffusion temperature is fixed and the diffusion time is very accurately controlled in accordance with a fourth root law wherein: V = Zener breakdown voltage; k = constant; p = resistivity of the wafer prior to diffusion; T = total diffusion time. The above relationship, which is newly discovered, reveals that the ultimate breakdown voltage produced is proportional to the fourth root of diffusion time dur ing the manufacturing process. The relation also reveals that if one tries to change both diffusion temperature (which is contained in the constant k in the novel rela tion of the invention, and is held constant in accordance with the invention) and diffusion time during the pro cess, the process becomes virtually uncontrollable. The relation also reveals that if the resistivity of the initial wafer material varies only slightly, the diffusion time must be greatly changed to obtain a given break down voltage. This is particularly important since semi conductor crystals are commonly sold to device manu facturers with resistivity tolerances of plus or minus %. For example, the process may begin with p-type monocrystalline silicon wafers having a resistivity in the range of 0.07 to ohm cm. An n-type region is then diffused into the p-type wafer. The final breakdown voltage, however, will vary widely if the same process 2 parameters are used for initial 0.07 ohm cm. material as for the ohm cm. material; and will vary uncontrol lably if one tries to control the process by modifying diffusion temperature and other parameters. In carrying out the invention, the resistivity of one or more pilot wafers is measured, and the devices are dif fused under fixed temperature conditions until a device is made with the requisite breakdown voltage, say 34 volts. This then allows the determination of the con stant k in the novel relationship: v - kvp WT. For example, if, after hours of diffusion at a given time and under given diffusion conditions, and using a material measured to be ohm cm., one produces a device with a volt reverse-voltage breakdown, then from the above equation: - kv0,079 W. If the next wafers to be diffused to form volt Zeners have a resistivity of ohm cm., the diffusion time T needed for the wafer can be calculated from: k\oog \ss - -, 3 - k\oos \t. or NT. - No.079 x N and T at hours. Thus, the single process variable of diffusion time T. can now be calculated from the initial wafer resistivity, and the process will produce devices with reproducible reverse bulk avalance breakdown characteristics within a tolerance of plus or minus 5%. Note in the above example that a drastically different diffusion time is needed for ohm cm. material than the hours for the ohm cm. material to obtain the same break down voltage.... Stated differently, and in accordance with the inven tion, if the resistivity of the initial wafer is changed from p1 to p2, the diffusion time T of the initial wafer at constant temperature must change from T1 to T2, where T = (p1/p).t. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a plan view of a monocrystalline silicon wafer which is to be processed to produce a zener di ode. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of FIG. 1 taken across section line 2-2 in FIG. I. FIG. 3 shows the wafer of FIG. 2 after a diffusion step, FIG. 4 shows the wafer of FIG. 3 after the bottom surface has been lapped. FIG. 5 shows the wafer of FIG. 4 after electrodes have been attached thereto. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS Referring first to FIGS. 1 and 2, there is shown a monocrystalline silicon wafer which may have a thick y
4 3 ness of 13 mils and a diameter of 1 inch. One or more devices are to be made from this wafer. In the follow ing, the invention is illustrated for the case of a zener diode having a reverse voltage of volts, plus or minus 1.5 volts. However, the invention will be under stood to be applicable to the reproducible production of any given bulk avalanche breakdown voltage (in the range from approximately volts to 0 volts) for any junction in a silicon semiconductor body. The wafer of FIGS. 1 and 2 is typically available with any required resistivity within about a % range and with any desired impurity type. For the example described herein the wafer is a p-type wafer having a resistivity in the range of 0.07 ohm cm. to ohm C. In order to form the zener diode, the wafer is placed in a suitable diffusion furnace and an n-type impurity, such as phosphorus, is diffused into the wafer to form the thin n-type conductivity shell 11 of FIG. 3 which creates the p-n junction 12. Any other diffusion process could be used, including but not limited to vapor phase deposition processes. After the Zener diode is completed, it is provided with suitable electrodes 13 and 14, as shown in FIG. 5. The present invention is directed to a novel process for producing the junction in a plurality of devices 12 such that they have highly reproducible reverse-voltage breakdown characteristics. In particular, the present invention is based on the discovery that if diffusion temperature is held constant, the breakdown voltage can be described with high accuracy, by the following relation: V = k Vp WT (1) V is breakdown voltage; p is the resistivity of wafer of FIGS. 1 and 2 before the diffusion step; T is the total diffusion time; k is the constant. This approximate equation holds very well for break down voltages in the range of volts to 0 volts. Equation (1) is derived as follows: The breakdown voltage V is known to be (for a grad ual junction): t 1 s \ grad N/X, where N is the concentration of donor atoms in the semiconductor body, and X1 is the depth of the junction 12 into body. The following approximation is used for the concen tration of donor atoms at any depth in the wafer Na(x): Na = Ne Wor N is the surface concentration of donor atoms; X is the distance into the surface of the semiconduc tor body; D is the diffusivity of the donor atoms; and T is the total diffusion time. (2) (3) 5 60 The concentration of acceptor atoms at the depth X1 is Na(x1) and is: - Na(x) = No e \ or. It follows from equation (4) that - (5) grad N/X = - e \ or a/4 \r DT and therefore from equations (4) and (5): N (6) grad N/X = - \ror Combining equations (2) and (6), (7) Vast re o N Since p at 1/N (8) and since D is a constant if diffusion temperature is constant, combining (7) and (8) gives equation (1): In accordance with the present invention, the diffu sion temperature is kept constant, for example, 12 C, for the total diffusion time T. Note that diffusion time is measured from the time the wafers enter the diffusion furnace until the temperature starts to decline with a cooling rate about 2 C./min. The warm-up and cool down times need not be considered if they are not con sidered in the calibrating procedure which is used to account for the proportionality factor k. When using the process of the invention, and in order to take into account the proportionality factork, wafers of a measured resistivity p are processed in the equip ment, using a fixed diffusion temperature and using a given diffusion process. The apparatus can then be used to process subsequent wafers, changing only the diffusion time T in accor dance with the measured resistivity p of the wafers being processed. Thus, in one example, it was found that a wafer having a resistivity of ohm cm. pro duced a volt junction after hours of diffusion. A new wafer sample having a resistivity of ohm cm., but being otherwise similar to the original wafer can then be directly processed in the same diffusion appara tus, where, however, the diffusion time T is changed by the amount determined from: 34 is k Noong N 34 - k\oo96 NT T = ( ) at 37.2 In the above example, a typical wafer having the resistivity ohm cm. may have an initial thickness of 13 to 14 mils. This wafer is etched to remove about 3 (4)
5 5 mils and to polish the surface. Thereafter, a layer of phosphorus is deposited on the surface of the wafer until the sheet resistance of the surface is about 0.3 ohms. Thereafter, the temperature is increased to 12 C. and is maintained at that temperature for hours. The final device has a zener voltage of volts. In carrying out the present invention, it will be under stood that the processing of the devices is conventional, except that the diffusion temperature is calculated as described above, and diffusion temperature is kept con stant. The process can also be applied to multiple junc tion devices having at least one zener diode junction therein and any desired donor and acceptor atom can be used. Although a preferred embodiment of this invention has been described, many variations and modifications will now be apparent to those skilled in the art, and it is preferred therefore that the instant invention be limited not by the specific disclosure herein but only by the appended claims. I claim: 1. The process of manufacture of a zener diode hav ing a predetermined reverse voltage (V) comprising the steps of measuring the resistivity (p) of a semiconduct ing body which is to receive a zener diode junction therein, and diffusing impurity atoms into said body at a constant temperature and for a time (T) where said time (T) is determined from the relation: where k is a constant. 2. The process of claim 1 wherein said body is ini tially of a p-type conductivity and wherein said impu rity atoms diffused into said body are donor type atoms. 3. The process of making a p-n junction in a semicon ductor body, which junction has a predetermined breakdown voltage within plus or minus about 5%, comprising the steps of measuring the resistivity of the semiconducting body before the formation of said p-n junction; and then diffusing impurity atoms into said body at a constant temperature for a controlled length of time such that said predetermined breakdown volt age is proportional to the product of the square root of the measured resistivity and the fourth root of the diffu sion time. The process of making a p-n junction in a semicon ductor body which has a predetermined breakdown voltage within plus or minus about 5%, comprising the steps of measuring the resistivity of the semiconducting body before the formation of said p-n junction; and then diffusing impurity atoms into said body at a constant temperature and varying the diffusion time such that: 6 where T is diffusion time, V is said predetermined breakdown voltage, p is said resistivity, and k is a con stant. 5. The process of claim 1 wherein said constant k is determined by processing semiconducting bodies of pre-measured resistivities for measured times T until a device is produced having said predetermined reverse voltage V wherein said last-mentioned device had an initial measured resistivity p1 and was diffused for a measured time T1. 6. The process of claim 5 wherein the diffusion time T for subsequently produced wafers made by the same process apparatus which produced said device is deter mined by measuring their resistivities p and by deter mining their diffusion time T from the relation: 7. The process of claim 4 wherein said constant k is determined by processing semiconducting bodies of pre-measured resistivities for measured times T until a device is produced having said predetermined reverse voltage V and which had an initial resistivity p1 and was diffused for a time T1. 8. The process of claim 7 wherein the diffusion time T. for subsequently produced wafers is determined by measuring their resistivities p and by determining their diffusion times T from the relation: 9. The process of producing a zener diode having a given reverse breakdown voltage V within a given tolerance range; said process comprising the steps of measuring the resistivity p1 of a first wafer of monocrys talline semiconductor material, and diffusing a junction into said first wafer at a constant temperature and for a time T sufficient to produce the reverse breakdown voltage V; and thereafter measuring the resistivity p2 of a second wafer of monocrystalline material, and diffus ing a junction into said second wafer at said constant temperature and for a time T2 to produce said reverse breakdown voltage V in said second wafer, where the time T2 is determined by: T2 = (p/p2) T.. The process of manufacture of a zener diode hav ing a given breakdown voltage wherein a junction is diffused into wafers of semiconductor material at con stant temperature for a given diffusion time and wherein, when the initial resistivity of wafers being diffused is changed from p1 to p2, the diffusion time T used to diffuse wafers of resistivity p1 is changed to a time T, wherein: T = (p1/p2) T. k t
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7419,867 B2
 USOO7419867B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7419,867 B2 Wieczorek et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2008 (54) CMOS GATESTRUCTURE COMPRISING (58) Field of Classification Search... 438/232,
USOO7419867B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7419,867 B2 Wieczorek et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2008 (54) CMOS GATESTRUCTURE COMPRISING (58) Field of Classification Search... 438/232,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,882,745 B2
 USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,765 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING. Filed Aug. 19, 1965 (,,,,, SR-33-R-N
 May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki
United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1
 USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9033892B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. (54) PREDICTIVE DROWSINESSALARM METHOD (75) Inventors: Yu Jen Su, Kaohsiung (TW); Yen Hsien Lee, Taoyuan County (TW); Kuang I Chang, Taoyuan County (TW)
USOO9033892B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. (54) PREDICTIVE DROWSINESSALARM METHOD (75) Inventors: Yu Jen Su, Kaohsiung (TW); Yen Hsien Lee, Taoyuan County (TW); Kuang I Chang, Taoyuan County (TW)
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
United States Patent (19) Namba et al.
 United States Patent (19) Namba et al. 54 PIEZOELECTRIC DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Akihiko Namba; Tetsuyoshi Ogura; Yoshihiro Tomita, all of Osaka; Kazuo Eda. Nara, all
United States Patent (19) Namba et al. 54 PIEZOELECTRIC DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Akihiko Namba; Tetsuyoshi Ogura; Yoshihiro Tomita, all of Osaka; Kazuo Eda. Nara, all
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(12) United States Patent
 US009 147855B2 (12) United States Patent Zhang et al. (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (71) Applicant: BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing (CN) (72) Inventors: Feng Zhang,
US009 147855B2 (12) United States Patent Zhang et al. (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (71) Applicant: BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing (CN) (72) Inventors: Feng Zhang,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(22) Filed: Feb. 22, 2000 Primary Examiner-Carl Whitehead, Jr. 30 F Application O O P tv Dat. ASSistant Examiner Toniae M. Thomas
 (12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
Lecture (02) Introduction to Electronics II, PN Junction and Diodes I
 Lecture (02) Introduction to Electronics II, PN Junction and Diodes I By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda Current in semiconductors/conductors N type, P type semiconductors N Type Semiconductor P Type Semiconductor
Lecture (02) Introduction to Electronics II, PN Junction and Diodes I By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda Current in semiconductors/conductors N type, P type semiconductors N Type Semiconductor P Type Semiconductor
Jinx UDX. (12) United States Patent. 2a2b se 2e2f (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, a2b 2c2d2.
 (12) United States Patent Tadokoro et al. USOO6365894B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) ELECTROMAGNET AND MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventors: Masahiro
(12) United States Patent Tadokoro et al. USOO6365894B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) ELECTROMAGNET AND MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventors: Masahiro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,716,763 B2
 USOO6716763B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,716,763 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF CONTROLLING STRIATIONS 5.242,536 A 9/1993 Schoenborn AND CD LOSS IN CONTACT
USOO6716763B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,716,763 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF CONTROLLING STRIATIONS 5.242,536 A 9/1993 Schoenborn AND CD LOSS IN CONTACT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2. Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013
 US008517600B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2 Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) DEPOSITION SENSORBASED ON 4.595,297 A 6/1986 Liu et al. DIFFERENTAL, HEAT TRANSFER
US008517600B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2 Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) DEPOSITION SENSORBASED ON 4.595,297 A 6/1986 Liu et al. DIFFERENTAL, HEAT TRANSFER
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Unit 1
 ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Unit 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 2, Sections 2.1-2.4 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Analog Circuits Recall ET115 & ET145 Ohms Law I = V/R If voltage across a resistor increases
ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Unit 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 2, Sections 2.1-2.4 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Analog Circuits Recall ET115 & ET145 Ohms Law I = V/R If voltage across a resistor increases
A SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE. P-N Junction
 A SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE P-N Junction Analog Electronics Pujianto Department of Physics Edu. State University of Yogyakarta A Semiconductor Devices A Semiconductor devices can be defined as a unit which consists,
A SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE P-N Junction Analog Electronics Pujianto Department of Physics Edu. State University of Yogyakarta A Semiconductor Devices A Semiconductor devices can be defined as a unit which consists,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
Lecture (02) PN Junctions and Diodes
 Lecture (02) PN Junctions and Diodes By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ I Agenda N type, P type semiconductors N Type Semiconductor P Type Semiconductor PN junction Energy Diagrams of the PN Junction and Depletion
Lecture (02) PN Junctions and Diodes By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ I Agenda N type, P type semiconductors N Type Semiconductor P Type Semiconductor PN junction Energy Diagrams of the PN Junction and Depletion
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007 O190148A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0190148A1 Cronin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) GEL COMPOSITIONS, APPARATUSES AND Publication Classification
US 2007 O190148A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0190148A1 Cronin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) GEL COMPOSITIONS, APPARATUSES AND Publication Classification
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,746,934 B2
 USOO6746934B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sandhu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2004 (54) ATOMIC LAYER DOPING APPARATUS AND 5,527,733 A 6/1996 Nishizawa et al. METHOD 5,793,109 A 8/1998
USOO6746934B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sandhu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2004 (54) ATOMIC LAYER DOPING APPARATUS AND 5,527,733 A 6/1996 Nishizawa et al. METHOD 5,793,109 A 8/1998
United States Patent (19) Amiet
 United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
- X. (bka III IIII. United States Patent (19) Sobata et al e (2. o
 United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
FIG.1. Form organic light emitting. Coat the encapsulation. encapsulation substrate. Prepare an. Prepare a substrate
 (19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
Wide-Acceptance-Angle Circular Polarizers (DIV)
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Wide-Acceptance-Angle Circular Polarizers (DIV) 12-11-2012 Shin-Tson Wu University of Central Florida Qi Hong University of Central Florida Ruibo Lu University
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Wide-Acceptance-Angle Circular Polarizers (DIV) 12-11-2012 Shin-Tson Wu University of Central Florida Qi Hong University of Central Florida Ruibo Lu University
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
...S(&S (& N 2%3.22:24, 2. United States Patent (9) Walden. 11, 3,852,799 (45) Dec. 3, Physics and Applications of Charge-Coupled De
 United States Patent (9) Walden 54 BUREED CHANNEL CHARGE COUPLED APPARATUS 75) Inventor: Robert Henry Walden, Warren, N.J. 73) Assignee: Bell Telephone Laboratories Incorporated, Murray Hill, N.J. 22 Filed:
United States Patent (9) Walden 54 BUREED CHANNEL CHARGE COUPLED APPARATUS 75) Inventor: Robert Henry Walden, Warren, N.J. 73) Assignee: Bell Telephone Laboratories Incorporated, Murray Hill, N.J. 22 Filed:
III. United States Patent (19) Hyman, Jr. et al. 5,572,314 Nov. 5, Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Cambridge, Mass ; Cornelius S.
 United States Patent (19) Hyman, Jr. et al. 54 BREWSTER ANGLE REFRACTOMETER (76 Inventors: Mark Hyman, Jr., 1010 Memorial Dr., Cambridge, Mass. 02138; Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1010 Waltham St., Lexington,
United States Patent (19) Hyman, Jr. et al. 54 BREWSTER ANGLE REFRACTOMETER (76 Inventors: Mark Hyman, Jr., 1010 Memorial Dr., Cambridge, Mass. 02138; Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1010 Waltham St., Lexington,
L:. l._l_. J. United States Patent c191 4,447,779. May 8, Gelinas [ "1 rr: f60 ~
 United States Patent c191 Gelinas [11] [45] May 8, 1984 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF A RECEIVING DEVICE RELATIVE TO A TRANSMITTING DEVICE UTILIZING A CURL-FREE MAGNETIC VECTOR POTENTIAL
United States Patent c191 Gelinas [11] [45] May 8, 1984 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF A RECEIVING DEVICE RELATIVE TO A TRANSMITTING DEVICE UTILIZING A CURL-FREE MAGNETIC VECTOR POTENTIAL
() -10 to. (12) United States Patent ATF. (10) Patent No.: US 7.925,614 B2. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, WAVELENGTH. Burkard et al.
 USOO7925.614B2 (12) United States Patent Burkard et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND STRUCTURE TO SOLATEA QUBIT FROM THE ENVIRONMENT Inventors: Guido Burkard, Irvington,
USOO7925.614B2 (12) United States Patent Burkard et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND STRUCTURE TO SOLATEA QUBIT FROM THE ENVIRONMENT Inventors: Guido Burkard, Irvington,
75 Inventors: St.Ste's 't Stanley 3, /1976 Fletcher et al... 73/432 R s s a wa a 4,158,395 6/1979 Brown /210
 USOO5902964A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Solberg, Jr. et al. () Date of Patent: *May 11, 1999 54 MEASUREMENT OF MASS USING SIMPLE 3,323,370 6/1967 Green et al.... 73/432 HARMONIC MOTION
USOO5902964A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Solberg, Jr. et al. () Date of Patent: *May 11, 1999 54 MEASUREMENT OF MASS USING SIMPLE 3,323,370 6/1967 Green et al.... 73/432 HARMONIC MOTION
United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,186,745 Maniar (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 16, CA107(6): 50440s, Fairchild Semiconductor Corp.
 III US5186745A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,186,745 Maniar (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 16, 1993 (54. TES BASED SPIN-N-GLASS AND PRCESSES FR MAKING AND USNG THE SAME 75 Inventor: Papu D.
III US5186745A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,186,745 Maniar (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 16, 1993 (54. TES BASED SPIN-N-GLASS AND PRCESSES FR MAKING AND USNG THE SAME 75 Inventor: Papu D.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
Introduction to Semiconductor Devices
 Physics 233 Experiment 48 Introduction to Semiconductor Devices References 1. G.W. Neudeck, The PN Junction Diode, Addison-Wesley MA 1989 2. Background notes (Appendix A) 3. Specification sheet for Diode
Physics 233 Experiment 48 Introduction to Semiconductor Devices References 1. G.W. Neudeck, The PN Junction Diode, Addison-Wesley MA 1989 2. Background notes (Appendix A) 3. Specification sheet for Diode
He'? United States Patent (19) Foer. 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 NOOH /6. PRODUCT NaCl + H2O FEED (54)
 United States Patent (19) Foer 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 (54) I75 (73) 21 22 63 (51) (52) 58 ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF GASEOUS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE AND AOUEOUS
United States Patent (19) Foer 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 (54) I75 (73) 21 22 63 (51) (52) 58 ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF GASEOUS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE AND AOUEOUS
