FIG.1. Form organic light emitting. Coat the encapsulation. encapsulation substrate. Prepare an. Prepare a substrate
|
|
|
- Samantha Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE USING THE SAME (76) Inventors: Seung-Yong Song, Yongin-City (KR); Young-Seo Choi, Yongun-City (KR): Oh-June Kwon, Yongin-city (KR); Ji-Hun Ryu, Yongin-city (KR); Sun-Young Jung, Yongin-city (KR); Young-Cheol Joo, Yongin-city (KR) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. HOIL 5/52 ( ) C08G 77/04 ( ) C08G 77/4 ( ) HOIL 5/56 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /40:528/10,528/33; 438/28; 257/E (57) ABSTRACT A sealing filler for an organic light emitting device display includes a siloxane polymer having a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less. The siloxane polymer may be represented by (21) Appl. No.: 12/636,393 (22) Filed: Jan. 28, 2010 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 9, 2009 (KR) O12 where each of R' to R' is independently a non-polar sub stituent, and n ranges from 20 to N N 230 % N
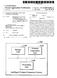
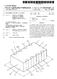
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 2 US 2011/ A1 FIG.1 Prepare a substrate Form organic light emitting diode on the substrate Prepare an encapsulation substrate Coat the encapsulation substrate with a filler S103 S104 Laminate the two substrates S105
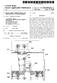
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 2 US 2011/ A1 FIG H N 2 N %
4 FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE ORGANIC LIGHT EMIMITING DEVICE USING THE SAME BACKGROUND Field 0002 Example embodiments relate to a filler for sealing an organic light emitting device display and a method of manufacturing the organic light emitting device display Description of the Related Art 0004 An organic light emitting device is a self-light emit ting display that emits light by electrically exciting an organic compound. The organic light emitting device may be oper able at a low Voltage and may exhibit high visibility and quick response rate. Since the organic light emitting device is light and thin, it is drawing attention as the next-generation display The organic compound of the organic light emitting device, however, may deteriorate when exposed to moisture and/or oxygen. Therefore, the organic light emitting device may include an encapsulating member, e.g., an encapsulation substrate, thereon to provide protection from moisture and/or oxygen. A conventional encapsulation Substrate, however, may be easily damaged by external impact or pressure. SUMMARY 0006 Embodiments are therefore directed to a filler for sealing an organic light emitting device and a method of manufacturing the same, which Substantially overcome one or more of the problems due to the limitations and disadvan tages of the related art It is therefore a feature of an embodiment to provide a filler for hermetically sealing an organic light emitting device display to protect the organic light emitting device display from external impact or pressure It is another feature of an embodiment to provide a method for manufacturing an organic light emitting device display having a filler for hermetically sealing the organic light emitting device display At least one of the above and other features and advantages may be realized by providing a filler for hermeti cally sealing an organic light emitting device display, includ ing a siloxane polymer with a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less. The siloxane polymer may be represented by the following In, each of R' to R' may be 20 to 50. Each of R' to R' may be independently one of an alkyl, an aryl, and ether. The alkyl may be a C4 to C20 alkyl, the aryl may be a C6 to C20 aryl, and the ether may be a C4 to C20 ether. The siloxane polymer may have a surface tension of about 18 dyn/cm or less At least one of the above and other features and advantages may also be realized by providing a method for manufacturing an organic light emitting device display, including forming an organic light emitting diode array on a Substrate, coating an encapsulation Substrate with a filler, the filler including a siloxane polymer having a Surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less, laminating the encapsulation Sub strate with the Substrate. Such that the organic light emitting diode and filler are sealed between the encapsulation sub strate and the substrate. The lamination may be performed at a pressure ranging from about 0 torr to about 760 torr. The siloxane polymer may be represented by the following. (0012. In the, each of R' to R' may be 20 to 50. Each of R' to R' may be independently one of an alkyl, an aryl, and ether. The alkyl may be to a C4 to C20 alkyl, the aryl may be C6 to C20 aryl, and the ether may be a C4 to C20 ether. The siloxane polymer may have surface tension of about 18 dyn/cm or less. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0013 The above and other features and advantages will become more apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art by describing in detail exemplary embodiments with reference to the attached drawings, in which: 0014 FIG. 1 illustrates a flowchart of a method for manu facturing an organic light emitting device display according to an embodiment; and 0015 FIG. 2 illustrates an organic light emitting device display with a filler according to an embodiment. DETAILED DESCRIPTION (0016 Korean Patent Application No , filed on Sep. 9, 2009, in the Korean Intellectual Property Office, and entitled: Filler for Sealing Organic Light Emit ting Device and Method for Manufacturing the Organic Light Emitting Device Using the Same is incorporated by refer ence herein in its entirety Example embodiments will now be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying draw ings; however, they may be embodied in different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art In the drawing figures, the dimensions of layers and regions may be exaggerated for clarity of illustration. It will also be understood that when a layer or element is referred to as being on another layer or substrate, it can be directly on the other layer or Substrate, or intervening layers may also be present. In addition, it will also be understood that when a layer is referred to as being between two layers, it can be the only layer between the two layers, or one or more intervening layers may also be present. Like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout.
5 0019. According to example embodiments, an organic light emitting device display, i.e., an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display device, may include an organic light emitting diode array sealed between a Substrate and an encap Sulation Substrate, and a filler Surrounding the organic light emitting diode array and filling a space between the Substrate and the encapsulation substrate. The filler may hermetically seal the organic light emitting device display, and may include a siloxane polymer having a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less. For example, the siloxane polymer may have a surface tension of about 18 dyn/cm or less When the filler has a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm, it may be possible to apply the filler to the organic light emitting device display, i.e., fill the organic light emit ting device display, under atmospheric or Substantial atmo spheric pressure conditions. When the surface tension of the filler is higher than 20 dyn/cm, the filler may not be properly, e.g., uniformly, applied to active pixel regions of the organic light emitting device display under atmospheric pressure con ditions because of the attraction among the filler particles, thereby reducing a desired effect of the filler in the organic light emitting device display. While a conventional filler with a high Surface tension may be applied to an organic light emitting device display under vacuum condition, Such con ditions may increase manufacturing time and costs, e.g., requiring acquisition of a separate vacuum chamber. There fore, since the filler according to an embodiment includes a siloxane polymer with a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less, it may be possible to apply the filler to the organic light emitting device display under atmospheric pressure condi tions, i.e., without using a separate vacuum chamber. As such, manufacturing costs and time may be substantially reduced The siloxane polymer may be represented by the following i-o-i-o-i-o- pi In the, each of R' to R' may be 20 to 50. The polymer characteristic as a filler may be achieved when n ranges from 20 to In order to minimize the attraction between mol ecules of the filler, i.e., in order to reduce surface tension, the substituents R' to R' are non-polar substituents. For the non-polar substituent, each of R' to R' may be indepen dently one of an alkyl, an aryl, and an ether Proximity, e.g., affinity, between the siloxane poly mers in the filler may be adjusted, e.g., restricted, in order to reduce the surface tension of the filler. For example, the substituents R' to R' may have a high molecular weight. For example, the molecular weight of each of the substituents R' to R' may range from about 16,000 to about 162, For example, an alkyl substituent may be a C4 to C20 alkyl, an aryl substituent may be a C6 to C20 aryl, and an ether substituent may be a C4 to C20 ether. With the number of carbon atoms falling in the above range, a desired Surface tension for the filler, i.e., a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less, may be acquired Examples of the alkyl substituents may include butyl, pentyl, hexyl, 3-ethylhexyl, and the like. Examples of the aryl Substituent may include phenyl, naphthyl, tri-phenyl, and the like. Examples of the ether substituent may include ethyl propyl ether, ethylbutyl ether, and the like A method for manufacturing an organic light emit ting device display according to an embodiment will be described hereinafter with reference to FIG. 1. FIG. 1 illus trates a flowchart describing a method for manufacturing an organic light emitting device display according to an embodi ment First, referring to FIG. 1, a substrate may be pre pared in operation S101, and an organic light emitting diode array including at least one organic light emitting diode may be formed on the substrate in operation S102. The organic light emitting diode may include a first electrode, an emission layer, and a second electrode The substrate may be formed, e.g., of glass and/or a transparent plastic material. The organic light emitting diode array may include at least one organic light emitting diode with the first electrode, the emission layer, and the second electrode formed therein. The first electrode may have a plu rality of thin film transistors in a lower portion, and the first electrode may be electrically connected to a drain of a thin film transistor. Any one of the first electrode and the second electrode may be an anode, and the other may be a cathode. In the organic light emitting diode, when a predetermined Volt age is applied to the anode and the cathode, holes implanted in the anode are transferred to the emission layer through a hole transport layer (HTL), and electrons implanted in the cathode are transferred to the emission layer through an elec tron transport layer (ETL). The electrons and the holes are re-combined in the emission layer to produce excitons, and as the state of the excitons is changed from an excited State to a base state, the organic material of the emission layer emits light to realize an image. A color of the emitted light may vary according to the organic material in the emission layer of the organic light emitting diode, and lights of various grayscales may be realized using organic materials representing red, green, and blue colors The encapsulation substrate maybe prepared in operation S103. The encapsulation substrate may be coated with a filler including a siloxane polymer having a Surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less in operation S104. Then, the encapsulation Substrate may be attached to the Substrate, i.e., to hermetically seal the organic light emitting diode, in operation S105. Operations S104 and S105 may be per formed at atmospheric pressure, e.g., about 760 torr or Sub stantially close to about 760, so special equipment or manu facturing conditions, e.g., for providing vacuum, may not be required for manufacturing the organic light emitting device display according to an embodiment The encapsulation substrate may be formed, e.g., of glass, metal, plastic, and/or silicon oxide. The filler may include the siloxane polymer having a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less, as described previously When a filler having a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less is used, a device may be filled with the filler under atmospheric pressure conditions. In contrast, when the filler has a high Surface tension, e.g., above 20 dyn/cm, active pixel regions may be hardly filled due to the affinity between the filler molecules at atmospheric pressure. Thus, the effect of the filler may not be sufficiently acquired. Further, filling a conventional filler with a high Surface tension under vacuum
6 conditions may be costly due to costs associated with acqui sition and/or manufacturing of a separate a vacuum chamber The siloxane polymer according to example embodiments may have a Surface tension of about 18 dyn/cm or less. The siloxane polymer may be represented by the following. --i-o-i-o-i-o-i-o-i-o- R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 pi In the, each of R' to R' may be 20 to 50. The substituents R' to R' may be non-polar sub stituents in order to minimize the attraction between the mol ecules. Each of the non-polar substituents R' to R' may be independently one of an alkyl, an aryl, and an ether The proximity between the polymers in the filler may be restricted to reduce the surface tension of the filler by having Substituents with a high molecular weight. For example, the molecular weight of each Substituent may range from about 16,000 to about 162, The alkyl substituent may be a C4 to C20 alkyl, the aryl substituent may be a C6 to C20 aryl, and the ether substituent may be a C4 to C20 ether. The filler may have the desired surface tension when the number of carbon atoms falls in the above range Examples of the alkyl substituent may include butyl, pentyl, hexyl, 3-ethylhexyl, and the like. Examples of the aryl Substituent may include phenyl, naphthyl, tri-phenyl, and the like. Examples of the ether substituent may include ethyl propyl ether, ethylbutyl ether, and the like Referring back to FIG.1, before, during, or after the encapsulation substrate is coated with the filler in operation S104, a sealing member may be formed on the encapsulation Substrate to correspond to the edge portion of the organic light emitting diode array. The sealing member may laminate the substrate with the encapsulation substrate in operation S105. For example, the sealing member may include fit, e.g., one or more of K2O, Fe2O, Sb2O, ZnO, P.O.V.O.s, TiO, Al2O, WO, SnO, PbO, MgO, CaO, BaO, LiO, NaO, B.O.Te0, SiO, Ru-O, Rb2O, RhC), CuO, and BiO The sealing member may be formed to be spaced apart from the filler inwardly, e.g., by a distance of about 100 um to about 300 um. Since the sealing member is spaced apart from the filler, it may be possible to prevent the filler from being deformed due to the heat generated when the sealing member is cured. For example, the sealing member and the filler may be formed on the encapsulation Substrate through a deposition method, printing, or dripping The sealing member of the laminated organic light emitting device display may be cured by irradiating a laser or ultraviolet rays (UV). Next, the organic light emitting device display may be put into a heat chamber to cure the filler FIG. 2 illustrates a cross-sectional view of an organic light emitting device display with a filler according to an embodiment. Referring to FIG. 2, the organic light emit ting device display may include a substrate 200, an organic light emitting diode array 210 formed on the substrate 200 and including at least one organic light emitting diode, an encapsulation substrate 220, a sealing member 230 for lami nating the substrate 200 with the encapsulation substrate 220, and a filler 240 filling the space between the substrate 200 and the encapsulation substrate 220. The filler 240 may be the siloxane polymer having a Surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less, as described previously The filler 240 may cover the organic light emitting device array 210, e.g., the organic light emitting device array 210 may be completely encapsulated between the filler 240 and the substrate 200. The filler 240 may fill the space between the substrate 200 and the encapsulation substrate 220, e.g., completely fill a space between the organic light emitting device array 210 and the encapsulation Substrate 220. The filler 240 may protect the organic light emitting device display from external impact and/or pressure Exemplary embodiments have been disclosed herein, and although specific terms are employed, they are used and are to be interpreted in a generic and descriptive sense only and not for purpose of limitation. Accordingly, it will be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that various changes in form and details may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention as set forth in the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. A sealing filler for an organic light emitting device display comprising a siloxane polymer having a surface ten sion of about 20 dyn/cm or less. 2. The sealing filler as claimed in claim 1, wherein the siloxane polymer is represented by the following formula: wherein in the formula, each of R' to R' is independently a non-polar Substituent, and n ranges from 20 to The sealing filler as claimed in claim 2, wherein each of R" to R' is independently one of an alkyl, an aryl, and ether. 4. The sealing filler as claimed in claim3, wherein the alkyl is a C4 to C20 alkyl, the aryl is a C6 to C20 aryl, and the ether is a C4 to C20 ether. 5. The sealing filler as claimed in claim 2, wherein the siloxane polymer has surface tension of about 18 dyn/cm or less. 6. A method for manufacturing an organic light emitting device display, comprising: forming an organic light emitting diode array on a Sub Strate; coating an encapsulation Substrate with a filler, the filler including a siloxane polymer having a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less; and laminating the encapsulation Substrate with the Substrate, Such that the organic light emitting diode array and filler are sealed between the encapsulation Substrate and the Substrate. 7. The method as claimed in claim 6, wherein laminating the encapsulation substrate with the substrate is performed at a pressure range from about 0 torr to about 760 torr.
7 8. The method as claimed in claim 7, wherein laminating the encapsulation substrate with the substrate is performed at an atmospheric pressure. 9. The method of as claimed in claim 6, wherein the silox ane polymer is represented by the following formula: pi wherein in the formula, each of R' to R' is independently a non-polar Substituent, and n ranges from 20 to The method as claimed in claim 9, wherein each of R' to R' is independently one of an alkyl, an aryl, and ether. 11. The method as claimed in claim 10, wherein the alkyl is a C4 to C20 alkyl, and the aryl is a C6 to C20 aryl, and the ether is a C4 to C20 ether. 12. The method as claimed in claim 9, wherein the siloxane polymer has a surface tension of about 18 dyn/cm or less. 13. An organic light emitting device display, comprising: an organic light emitting diode array on a Substrate; an encapsulation Substrate on the Substrate, the organic light emitting diode array being between the encapsula tion Substrate and the Substrate; and a filler between the substrate and the encapsulation sub strate, the filler including a siloxane polymer having a surface tension of about 20 dyn/cm or less. 14. An organic light emitting device display claimed in claim 13, wherein the siloxane polymer is represented by the following formula: pi wherein in the formula, each of R to R' is independently a non-polar Substituent, and n ranges from 20 to 50. c c c c c
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070199.109A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0199109 A1 Y et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2007 (54) NANOCOMPOSITE MATERIAL AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20070199.109A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0199109 A1 Y et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2007 (54) NANOCOMPOSITE MATERIAL AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(12) United States Patent
 US009 147855B2 (12) United States Patent Zhang et al. (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (71) Applicant: BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing (CN) (72) Inventors: Feng Zhang,
US009 147855B2 (12) United States Patent Zhang et al. (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (71) Applicant: BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing (CN) (72) Inventors: Feng Zhang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O157111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0157111A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL CELL (76) Inventors: Shigeru Sakamoto, Osaka (JP); Yasunori
(19) United States US 2004O157111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0157111A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL CELL (76) Inventors: Shigeru Sakamoto, Osaka (JP); Yasunori
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O170331A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0170331 A1 Bertram et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTROLUMNESCENT DEVICE WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2006O170331A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0170331 A1 Bertram et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTROLUMNESCENT DEVICE WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0256036A1 NAKAMURA US 20150256036A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) LAMINATED IRON CORE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD FOR LAMINATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0256036A1 NAKAMURA US 20150256036A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) LAMINATED IRON CORE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD FOR LAMINATED
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020027416A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0027416A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2002 (54) ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICE INCLUDING CHARGE
(19) United States US 20020027416A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0027416A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2002 (54) ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICE INCLUDING CHARGE
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2 Geng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2007
 United States Patent USOO7235478B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,235.478 B2 Geng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2007 (54) POLYMER SPACER FORMATION 6,537.866 B1* 3/2003 Shields et al.... 438, 183 6,562,696
United States Patent USOO7235478B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,235.478 B2 Geng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2007 (54) POLYMER SPACER FORMATION 6,537.866 B1* 3/2003 Shields et al.... 438, 183 6,562,696
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,206,350 B2
 US9206B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,206,3 B2 Choi et al. () Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 20 (54) CMPSITIN CMPRISING QUANTUM DT, AND DEVICE USING SAME (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... C09K II/0 (2013.01);
US9206B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,206,3 B2 Choi et al. () Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 20 (54) CMPSITIN CMPRISING QUANTUM DT, AND DEVICE USING SAME (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... C09K II/0 (2013.01);
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001610121A1* (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158(3) EPC (43) Date of publication:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001610121A1* (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158(3) EPC (43) Date of publication:
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,013,525 B2
 USO0801B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2011 (54) FLEXIBLE OLED DISPLAY WITH CHIPLETS FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WO 20/O19185 A1 2, 20 (75) Inventors: Ronald
USO0801B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2011 (54) FLEXIBLE OLED DISPLAY WITH CHIPLETS FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WO 20/O19185 A1 2, 20 (75) Inventors: Ronald
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 2005OO18526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0018526A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) PHASE-CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
(12) United States Patent
 US009691.853B2 (12) United States Patent He0 et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,691,853 B2 Jun. 27, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE INCLUDING GRAPHENE AND QUANTUM DOTS (71) Applicant: Samsung
US009691.853B2 (12) United States Patent He0 et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,691,853 B2 Jun. 27, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE INCLUDING GRAPHENE AND QUANTUM DOTS (71) Applicant: Samsung
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,619,222 B2
 US8619222B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,619,222 B2 Nakamura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND (56) References Cited MANUFACTURING METHD
US8619222B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,619,222 B2 Nakamura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND (56) References Cited MANUFACTURING METHD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160284659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0284659 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE (52) U.S. Cl. STRUCTURE,
(19) United States US 20160284659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0284659 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE (52) U.S. Cl. STRUCTURE,
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160149157A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2016/014.9157 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2016 (54) ORGAIC LIGHT EMITTIG DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY ICLUDIG
(19) United States US 20160149157A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2016/014.9157 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2016 (54) ORGAIC LIGHT EMITTIG DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY ICLUDIG
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0131955 A1 Bennett et al. US 2015O131955A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) LIGHT OFFUSING FIBER WITH LOW
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0131955 A1 Bennett et al. US 2015O131955A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) LIGHT OFFUSING FIBER WITH LOW
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(22) Filed: Feb. 22, 2000 Primary Examiner-Carl Whitehead, Jr. 30 F Application O O P tv Dat. ASSistant Examiner Toniae M. Thomas
 (12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) United States Patent Hwang et al. USOO6479343B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) DRAM CELL CAPACITOR AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: Yoo-Sang Hwang, Suwon;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
US 20160358915A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0358915 A1 Flachowsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FERROELECTRIC FINFET HOIL 29/5 (2006.01) HOIL 29/78 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O140452A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2015/0140452 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 21, 2015 (54) METAL-AIR BATTERY HAVIG FOLDED HOLM 6/18 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 2015O140452A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2015/0140452 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 21, 2015 (54) METAL-AIR BATTERY HAVIG FOLDED HOLM 6/18 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2
 USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
NAV A. Attorney Docket No Date: 4 February 2008
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 NAV A Attorney Docket No. 96813 Date: 4 February
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 NAV A Attorney Docket No. 96813 Date: 4 February
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.252,397 B2
 US009252397 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.252,397 B2 Harikrishna Mohan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) OVJP FOR PRINTING GRADED/STEPPED (56) References Cited ORGANIC
US009252397 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.252,397 B2 Harikrishna Mohan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) OVJP FOR PRINTING GRADED/STEPPED (56) References Cited ORGANIC
Robert A. Meger Richard F. Fernster Martin Lampe W. M. Manheimer NOTICE
 Serial Number Filing Date Inventor 917.963 27 August 1997 Robert A. Meger Richard F. Fernster Martin Lampe W. M. Manheimer NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests
Serial Number Filing Date Inventor 917.963 27 August 1997 Robert A. Meger Richard F. Fernster Martin Lampe W. M. Manheimer NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Hauge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2011
 US 20110262772A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0262772 A1 Hauge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING ALIGNED NEAR Publication Classification
US 20110262772A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0262772 A1 Hauge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING ALIGNED NEAR Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices
 Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1
 USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 201701 40924A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0140924 A1 Suzuki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FORMATION OF SIOCN THIN FILMS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H0IL 21/02126
US 201701 40924A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0140924 A1 Suzuki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FORMATION OF SIOCN THIN FILMS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H0IL 21/02126
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0126359 A1 DEGUCH et al. US 2013 0126359A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 23, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0126359 A1 DEGUCH et al. US 2013 0126359A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 23, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,261,710 B1
 USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. s y % V SS SS - 93 O ZZZ zaz 52 SE E 35,61 " 34,61 15 N 42
 (19) United States US 2016O2993.76A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/02993.76 A1 ISHIKAWA et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE, RADATION-SENSITIVE RESN COMPOSITION,
(19) United States US 2016O2993.76A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/02993.76 A1 ISHIKAWA et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE, RADATION-SENSITIVE RESN COMPOSITION,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 06390A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0106390 A1 Elmeguenni (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 20, 2017 (54) BOTTLE AND METHOD FOR A61O 13/00 (2006.01) MANUFACTURING
(19) United States US 201701 06390A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0106390 A1 Elmeguenni (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 20, 2017 (54) BOTTLE AND METHOD FOR A61O 13/00 (2006.01) MANUFACTURING
(12) United States Patent
 USO08035559B2 (12) United States Patent Yu et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2011 (54) GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM RECEIVER (75) Inventors: Xiaoguang Yu, Wuhan (CN); Haiquan Huang, Chengdu
USO08035559B2 (12) United States Patent Yu et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2011 (54) GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM RECEIVER (75) Inventors: Xiaoguang Yu, Wuhan (CN); Haiquan Huang, Chengdu
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O234.809A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2004/0234809 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: ov. 25, 2004 (54) OXAZOLE-, THIAZOLE-, AD (21) Appl. o.: 10/441,164
US 2004O234.809A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2004/0234809 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: ov. 25, 2004 (54) OXAZOLE-, THIAZOLE-, AD (21) Appl. o.: 10/441,164
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 14, 2006
 US 20060202272A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0202272 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIDE BANDGAPTRANSISTORS WITH Publication Classification GATE-SOURCE
US 20060202272A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0202272 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIDE BANDGAPTRANSISTORS WITH Publication Classification GATE-SOURCE
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
UK Patent Application 9 >GB
 UK Patent Application 9 >GB 2 055 465 A (21) (22) (30) (31) (32) (33) (43) (51) (52) (56) (58) (71) (72) (74) Application No 8018366 Date of filing 4 Jun 1980 Priority data 79/20667 14Jun1979 United Kingdom
UK Patent Application 9 >GB 2 055 465 A (21) (22) (30) (31) (32) (33) (43) (51) (52) (56) (58) (71) (72) (74) Application No 8018366 Date of filing 4 Jun 1980 Priority data 79/20667 14Jun1979 United Kingdom
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150272278A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0272278 A1 Jeong (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) ADHESION FOR SHOE SOLE BONDING (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A43D
(19) United States US 20150272278A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0272278 A1 Jeong (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) ADHESION FOR SHOE SOLE BONDING (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A43D
ENCODED EXCITATION SOURCE RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY METHODS AND SYSTEMS
 ( 3 of 11 ) United States Patent Application 20050254047 Kind Code A1 Brady, David J. ; et al. November 17, 2005 ENCODED EXCITATION SOURCE RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY METHODS AND SYSTEMS Abstract Selected combinations
( 3 of 11 ) United States Patent Application 20050254047 Kind Code A1 Brady, David J. ; et al. November 17, 2005 ENCODED EXCITATION SOURCE RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY METHODS AND SYSTEMS Abstract Selected combinations
III M
 III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
Koshikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, (54) PHOTOEMISSION ELECTRON 6,671,398 B1* 12/2003 Reinhorn et al ,145. be carried out.
 (12) United States Patent US007034295B2 () Patent No.: US 7,034.295 B2 Koshikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2006 (54) PHOTOEMISSION ELECTRON 6,671,398 B1* 12/2003 Reinhorn et al.... 382,145 MCROSCOPY
(12) United States Patent US007034295B2 () Patent No.: US 7,034.295 B2 Koshikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2006 (54) PHOTOEMISSION ELECTRON 6,671,398 B1* 12/2003 Reinhorn et al.... 382,145 MCROSCOPY
Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
