United States Patent [19]
|
|
|
- Allen Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
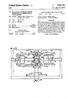
1 United States Patent [19] Murphy US A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE BASED GRAVITY SENSOR [7S] Inventor: Michael E. Murphy, Ann Arbor, Mich. [73] Assignee: Design & Test Technology, Inc., Ann Arbor, Mich. [21] Appl. No.: 273,793 [22] Filed: Jul. 12, 1994 [SI] Int. Cl GOIC 9/06 [52] U.S. CI /366 [58] Field of Search... 33/366, 312; 340/689 [56] References Cited u.s. PATENT DOCUMENTS 2,620,571 12/1952 Varian. 2,711,590 6/1955 Wilcol(. 3,946,494 3/1976 Wells... 33/366 4,521,973 6/1985 Wiklund et al.. 4,528,760 7/1985 Plummer. 4,628,612 12/1986 Hori et al.. 4,641,434 2/1987 Engler... 33/366 4,644,662 2/1987 Anderson et al /366 4,846,954 7/1989 Ryan et al... 33/366 4,912,662 3/1990 Butler et al.. 4,937,518 6/1990 Donati et al... 33/312 5,170,567 12/1992 Davis et al /366 5,237,753 8/1993 Carlson et al /366 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1993 European Pat. Off... 33/ / / /1990 Japan... 33/366 Japan... 33/366 Japan... 33/366 United Kingdom... 33/366 WIPO... 33/366 Primary Examiner-Thomas B. Will Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Harness, Dickey & Pierce [S7] ABSTRACT An improved inclination sensor in which electrically conductive elements are fabricated onto one or both surfaces of a flat plate. The plate comprising discrete, isolated sector sections having a distinct electrically conductive regions is oriented in a substantially vertical plane. The plate has an axis which lies in a horizontal plane and which is substantially perpendicular to the plate so that the plate may tilt about the axis. The plate is encased within a sealed chamber occupied by a fluid having electrical properties. In one embodiment a dielectric fluid oecupies a first portion of a chamber and has a dielectric constant greater than that of a gas which occupies a second portion of the sealed chamber. The fluid flows in response to a change in the tilt of the sealed chamber and In a second embodiment a capacitive fluid changes the capacitance between the distinct electrically conductive regions of each section of By determining the capacitance between the electrically conductive regions in one or more of the sections, the tilt of the inclinometer may be determined. 21 Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets 16c 14
2 u.s. Patent Jan. 2, 1996 Sheet 1 of 2 5,479,716 Fig-l 20~ 125 i8 Fig-2 14 ~ ~, IL II ".,-- 20a 20b
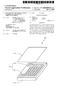
3 u.s. Patent Jan. 2, 1996 Sheet 2 of 2 5,479, Fig ~-30 Fig-4
4 1 CAPACITIVE BASED GRAVITY SENSOR BACKGROUND AND SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to a sensor for detecting inclination of an object, and morc particularly, to a sensor having capacitive sectors within which the capacitance varies in accordance with the inclination of the sensor. There are currently a number of leveling sensors in the art which may be used to measure the tilt of an object with respect to a vertical plane. In their simplest form, a carpenter's level having a transparent tube partially filled with fluid 5,479,716 2 with the variance in fluid position due to the tilt of the sensor, a quantitative measurement of the horizontal tilt of the sensor may be determined. In general, a number of tilt sensors exist which depend on 5 varying the capacitance between sections comprising substantial portions of separate plate sections of the sensor according to the percentage of area covered by a fluid, either dielectric or electrolytic. They generally rely on a capacitance between conductive areas located on separate sub- 10 strates as in multiple plates around a bubble in a vile or tube, multiple plates around a sphere, or multiple plates on the same axis. Such sensor assemblies tend to be difficult to construct, align, and are rather sensitive to rolling moveto leave a bubble which travels within the tube as the angle 15 of tilt of the tube varies. Typically, this tube has two lines scribed onto it between which the bubble must rest to indicate that the sensor is level horizontally. When one side of the sensor tilts downward from a horizontal plane, the bubble moves in a direction opposite the downward motion outside of the scribed lines. Carpenter levels and the like indicate qualitative measurements of a vertical orientation of the sensing device or a deviation from vertical in a particular direction. Other than through visual inspection of the position of the bubble within the transparent tube, these levels do not indicate with specificity the angular measurement from a horizontal plane through which the sensor has tilted. For a number of applications, such qualitative measurements are sufficient, but for other applications, specificity of the angle onto the substrate using known methods such as etching in foil or other printed circuit board techniques. This provides a sensor having mechanical characteristics such as rigidity, coefficient of expansion, and sensitivity to temperature which are significantly related to the meehanical properties of the substrate assembly and less so to mechanical propof inclination is required. A number of inclination sensing instruments based on the properties of the fluid and transparent tube level may be employed to determine deviations from the horizontal. In one such inclinometer, the tilt indication occurs through the use of gravity-type potentiometers. Electrical conductors are placed in a conical or circular tube containing fluid to a predetermined level. Two equal length segments of electrical conductor extend from the conducting fluid so that when the device is level, equal segments of the wire are submerged in the electrical conducting fluid. When the tube is tilted from a horizontal reference, the tube rotates, creating unequal length segments of electrical conductor within the resistance fluid. The variance in resistance between the wires is used to determine qualitatively the tilt of the sensor. This device is extremely sensitive to the resistance of the wire which varies in accordance with the temperature coefficient of resistivity of the wire and the temperature coefficient of expansion of the fluid. In another variety of electrical inclination sensing instruments, variations in capacitance caused by variations in the displacement of fluid partially filling a sealed cavity indicate inclination. The fluid typically has a dielectric constant which is greater than that of the dielectric constant of the atmosphere of the cavity not occupied by fluid. This fluid, having a different dielectric constant, allows the variance of 55 capacitance between sections of electrical conductors in the sensor. In a number of capacitance-type sensors, a circular plate is divided into a number of sections each having an electrode. As the position of the fluid varies covering different sections, the capacitance between each section varies. 60 By measuring the differences in the section-to-section capacitance, the amount of tilt of the instrument may be determined. Other inclinometers employ two plates between which is established a capacitance by either a dielectric fluid (or an electrolytic fluid if the electrical conductors on the 65 plate are covered by a dielectric coating). By determining the capacitance between the parallel plates, in accordance ments and to changes in temperature. This invention is directed towards an improved inclination sensor in which electrically conductive elements are fabricated onto one or both flat surfaces of a plate shaped substrate. Fabrication onto a single flat substrate enables the manufacture of the electrically conductive elements directly erties dictated by the overall sensor assembly operation, as is encountered in any number of parallel plate designs. The precision of the mechanical construction of the capacitive elements is a function of, for example, photolithographic 30 etching processes for applying the pattern onto the substrate which can be done with great precision. A plate comprising discrete, isolated sections each spanning a portion of the circumference of the sensor having a 35 distinct electrically conductive regions is oriented in a substantially vertical plane. The plate has an axis which lies in a horizontal plane and which is substantially perpendicular to the plate so that the plate may tilt about the axis. The plate is encased within a sealed chamber occupied by a fluid 40 having electrical properties having a higher specific gravity than the outer fluid which may be a gas which occupy the chamber. In one embodiment of the invention, the fluid is a dielectric fluid having a dielectric constant greater than that of a gas which occupies a second portion of the sealed 45 chamber. The fluid flows in response to a change in the tilt of the sealed chamber and The capacitive fluid changes the capacitance between the distinct electrically conductive regions of each section of By determining the capacitance between the electrically conductive 50 regions of each section, the tilt of the inclinometer may be determined. In a second embodiment of this invention, the fluid is an electrolytic fluid, and the electrically conductive regions of each section are coated with a dielectric so that a capacitance may be established between the electrolytic fluid and the electrically conductive regions via the dielectric coating. With such a configuration, it is possible to vary the capacitance between the electrically conductive regions in a manner similar to that described above. When the inclinometer tilts about the axis, the position of the fluid varies in response to the change in tilt. By determining the capacitance between the electrically conductive regions of each section, the tilt of the sensor may be determined. Further objects, features and advantages of the invention will become apparent from a consideration of the following description and the appended claims when taken in connection with the aeeompanying drawings.
5 3 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a first exploded view of the inclinometer sensor according to this invention; FIG. 2 is a second exploded view of the inclinometer sensor according to this invention; FIG. 3 depicts a partial section inclinometer sensor substrate having three sections each of which has electrically conductive regions interdigitated or interleaved so that a capacitance between the electrically conductive regions may be established; and FIG. 4 depicts a partial cut away view of the inclinometer sensor assembly. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION Referring generally to FIGS. 1 and 2, two exploded views of the inclinometer 10 according to this invention are shown. In FIG. 1 a sensor substrate 12 is inserted into sensor body 14. Sensor substrate 12 may be made from conventional printed circuit board material and is a flat plate subdivided into three arcuate segment sections 1OO-c. Each section 16a-c has electrically conductive regions such that a capacitance may be determined between each electrically conductive region of a particular section, to be explained further with respect to FIG. 3. Plate 12 engages sensor body 14 at lip 18, and is connected so that sensor plate 12 moves in accordance with sensor body 14. Terminal connections 20a-c enable the application of electrical signals to conductors on plate 12, Sensor body 14 also contains a fluid having electrical properties which interacts with the electrically conductive regions of each section 16a-16c of sensor plate 12. The fluid may be either a dieleetric fluid or an electrolytic fluid. If the fluid is an electrolytic fluid, the electrically conductive regions of plate 12 are also coated with a dielectric material 5,479,716 in order to establish capacitance between various electrically conductive region of sensor plate 12. Sensor body 14 is then 40 sealed with cover plate 20 to seal sensor body 14 against fluid leakage. The effectiveness of the seal may be enhanced by a O-ring (not shown) or any other type of material which would maintain a suitable seal. Referring to FIG. 3, a front view of one face of plate is shown. Plate 12 is divided into three arcuate segment sections 1OO-c, each section having electrically conductive regions 22a-c and 22a'-c', respectively which are arranged in an interdigitated fashion and trace concentric arcuate pathes. The electrically conductive regions 22a-c and 50 22a'-c' span actually radially from the innermost segment to the outermost segments which are shown. The radially intermediate segments are left out in the drawing figure to leave space for the element numbers and lead lines. For each section 1OO-c, the electrically conductive regions 22a-c and 55 22a'-c' are energized so that a capacitance may be established between each pair of conductive regions 22a-a', 22b-b', and 22c-c'. Thus, each pair of electrically conductive regions on a specified section 16a-c on plate 12 may have a capacitance between them which is dependant upon 60 the conductor spacing and dielectric betwcen them. The electrically conductive regions for a particular section are energized via a pair of terminals connected to a source of energization (not shown). For example, electrically conductive regions 22a and 22a' are energized via terminal con- 65 nection 200 and 26a', respectively. In a similar manner, electrically conductive regions 22b and 22b' are energized 4 via a pair of terminal 24b and 24b', respectively. Finally. electrically conductive regions 22c and 22c' are energized via terminal connections 26c and 26c'. Thus, three sources of energization, or one source of energization and switching 5 means for applying energization signals to each of the terminal pairs 26a-a', 24b b', or 26c-c' must be provided. Several inventive aspects of inclinometer 10 using sensor plate 12 as shown in FIG. 3 will now be discussed. This sensor utilizes the capacitance created between the clectri- 10 cally conductive regions within one of the sections 16a-16c of sensor plate 12. The capacitance occurs in this embodiment by interdigitating the electrically conductive regions 22a-c and 22a'-c', respectively, to yield a pattern of eoncentric rings as shown in FIG. 3. In this manner, only one 15 sensor plate 12 is required to determine the tilt of inclinometer 10. Moreover, at least one of the sections 16a-c is partially immersed in the fluid within the inclinometer 10. The capacitance between a respective pair of conductive regions 22a-a', 22b-b', or 22c-c' varies in accordance 20 with the percentage of surface area of one or more section 16a-c covered by the liquid occupying the inclinometer 10 which has a higher specific gravity (density) than the gas above the liquid. In a related aspect of this invention, sensor plate 12 may be constructed as a substrate onto which the 25 electrically conductive regions may be deposited using any one of a number of printed circuit board techniques known in the art. Thus, sensor plate 12 acquires the mechanical properties of a printed circuit board. The positioning of each conductive region 22a-c in relation to its paired conductive 30 region 22a'-c'. respectively, varies in accordance with the accuracy in resolution of the printed circuit board manufacturing process, which is extremely accurate and repeatable. By comparison, the accuracy of current inclinometers varies in accordance with assembly and alignment techniques of 35 multiple substrates and other assembly components. The sensitivity of inclinometer 10 may be increased by duplicating the pattern of the conductive regions 16a-c of FIG. 3 onto the opposite face of sensor plate 12, creating a mirrored pattern on the other side of the sensor plate 12. A dual sided sensor provides the added feature of reduced sensitivity to roll. If sensor plate 12 is normal to a horizontal plane and immersed approximately half way in the fluid, as the sensor body is rotated about an axis located in a horizontal plane and normal to the tilt axis, the increased surface covered by the fluid on one side of sensor plate 12 is offset by an equal decrease in coverage of the fluid on the opposite side of sensor plate 12. This offset may be used to compensate for roll of the sensor. FIG. 4 depicts a partial sectional view of inclinometer 10 in a preferred orientation. The sensor plate 12, sensor body 14, and sensor top 20 of FIGS. 1 and 2 are shown positioned in a substantially vertical plane. Inclinometer 10 measures rotation in the vertical plane about central axis 28. Also shown in FIG. 4 is a dielectric fluid 30. Dielectric fluid is employed when sensor plate 12 is not covered with a dielectric coating. Dielectric fluid 30 occupics approximately 50% of the volume of sensor body 14 excluding that volume occupied by sensor plate 12 and sensor top 20. The residual volume is occupied generally by a gaseous medium 32 having a dielectric constant lower than that of dielectric fluid 30. Should the vertical orientation of inclinometer 10 vary, the sensor is said to roll. Such inclinometer roll 10 may be compensated if both faces of sensor plate 12 possess electrically conductive regions. The increase in fluid on one side of sensor plate 12 is offset by a decrease of fluid on the opposing face of sensor plate 12, effectuating compensation for roll by the sensor.
6 5,479, A sensor as described above offers several advantages over the prior art sensors. First, because the electrically conductive regions are positioned on one sensor plate 12 using known printed circuit board techniques, the electrically conductive regions may be positioned more accurately 5 and consistently. Second, the accuracy of inclinometer 10 is enhanced because the separation between the electrically conductive regions does not vary in accordance with the mechanical assembly of the sensor, but is a function of the accuracy of printed circuit board manufacturing techniques which is highly controllable. Third, because the electrically conductive regions lie within the same plane, the inclinometer 10 is less effected by roll. Finally, if electrically conductive regions 22a-c and 22a'-c' are located in mirror image positions on both faces of sensor plate 12, some quantitative measure of the amount of roll may be made. The teachings of this invention could be implemented in a multiple plate version which might be desired for higher output or enhanced roll sensitivity. However, in such an embodiment, the plates would be separated or isolated such that capacitance is not affected by minor deviations in plate 20 spacing, unlike present sensors. It is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the exact construction illustrated and described above, but that various changes and modifications may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as 25 defined in the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. An inclinometer for measuring tilt about a predetermined axis located in substantially in a horizontal plane: a plate oriented in a plane substantially normal to the 30 predetermined axis and having discreet, isolated sector sections arranged about the axis, the sections each having electrically conductive regions between which a capacitance may be established; a sealed chamber in which the plate is placed; 35 a fluid having electrical properties occupying a first portion of the sealed chamber, the fluid contacting the electrically conductive regions of at least one of the isolated sections of the plate when the inclinometer is oriented in a first tilted position about the predeter- 40 mined axis, and contacting differing portions of at least one section of the plate when the inclinometer is oriented in a second titled position about the predetermined axis wherein the capacitance of at least one section varies in accordance with the orientation of the 45 plate about the predetermined axis. 2. The inclinometer as defined in claim 1 further comprising: the fluid occupying the first portion of the sealed chamber having dielectric properties in accordance with a first dielectric constant; and a medium having dielectric properties in accordance with a second dielectric constant occupying a second portion of the chamber. 3. The inclinometer as defined in claim 2 wherein the plate electricall y conductive regions comprises interdigitated electrical conductors. 4. The inclinometer as defined in claim 2 wherein the single plate is a printed circuit board and the electrically conductive regions comprise traces on said printed circuit 60 board. 5. The inclinometer as defined in claim 2 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on one face of 6. The inclinometer as claimed in claim 2 wherein the 65 electrically conductive regions are arranged on both major sides of 7. The inclinometer as defined in claim 1 further comprising: the fluid having electrolytic properties; and a dielectric coating covering the electrically conductive regions of 8. The inclinometer as defined in claim 7 wherein the plate electrically conductive regions comprises interdigitated electrical conductors. 9. The inclinometer as defined in claim 7 wherein the plate 10 is a printed circuit board and the electrically conductive regions comprise traces on said printed circuit board. 10. The inclinometer as defined in claim 7 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on one side of The inclinometer as defined in claim 7 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on both sides of 12. An inclinometer for measuring tilt about a predetermined axis located in substantially in a horizontal plane: a plate oriented in a plane substantially normal to the predetermined axis and having discreet, isolated sector sections arranged about the axis, the sections each having electrically conductive regions between which a capacitance may be established; a sealed chamber in which the plate is placed; a fluid occupying a first portion of the sealed chamber having dielectric properties in accordance with a first dielectric constant and a medium having dielectric properties in accordance with a second dielectric constant, the second dielectric constant differing from the first dielectric constant, the fluid contacting the electrically conductive regions of atleast one of the isolated sections of the plate when the inclinometer is oriented in a first tilted position about the predetermined axis, and contacting differing portions of at least one section of the plate when the inclinometer is oriented in a second titled position about the predetermined axis wherein the capacitance of at least one section varies in accordance with the orientation of the plate about the predetermined axis. 13. The inclinometer as defined in claim 12 wherein the plate electrically conductive regions comprises interdigitated electrical conductors. 14. The inclinometer as defined in claim 12 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on one face of 15. The inclinometer as claimed in claim 14 wherein the plate is a printed circuit board and the electrically conductive regions are formed by traces on said printed circuit 50 board. 16. The inclinometer as claimed in claim 12 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on both sides of 17. An inclinometer for measuring tilt about a predeter- 55 mined axis located in substantially in a horizontal plane: a plate oriented in a plane substantially normal to the predetermined axis and having discreet, isolated sector sections arranged about the axis, the sections each having electrically conductive regions between which a capacitance may be established; a coating covering the electrically conductive regions of the plate; a sealed chamber in which the plate is placed; an electrolytic fluid occupying a first portion of the sealed chamber, the fluid contacting the electrically conductive regions of at least one of the isolated sections of the
7 5,479,716 7 plate when the inclinometer is oriented in a first tilted position about the predetermined axis, and contacting differing portions of at least one section of the plate when the inclinometer is oriented in a second titled position about the predetermined axis wherein the 5 capacitance of at least one section varies in accordance with the orientation of the plate about the predetermined axis. 18. The inclinometer as defined in claim 17 wherein the plate electrically conductive regions comprises interdigi- 10 tated electrical conductors The inclinometer as defined in claim 18 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on one face of 20. The inclinometer as claimed in claim 17 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on one side of 21. The inclinometer as claimed in claim 17 wherein the electrically conductive regions are arranged on both sides of * * * * *
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1
 USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
TEPZZ 89955_A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
Elizabethtown College Department of Physics and Engineering PHY104
 Elizabethtown College Department of Physics and Engineering PHY104 Lab #7- Capacitors 1. Introduction The capacitor is one of the essential elements of analog circuitry. It is highly useful for its energy
Elizabethtown College Department of Physics and Engineering PHY104 Lab #7- Capacitors 1. Introduction The capacitor is one of the essential elements of analog circuitry. It is highly useful for its energy
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
TEPZZ 6_Z6_ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6_Z6_ A_T (11) EP 2 6 612 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/27 (51) Int Cl.: G01N 27/333 (2006.01) G01N 27/416 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6_Z6_ A_T (11) EP 2 6 612 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/27 (51) Int Cl.: G01N 27/333 (2006.01) G01N 27/416 (2006.01) (21) Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,167,752 B1. Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001
 USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
Physics 196 Final Test Point
 Physics 196 Final Test - 120 Point Name You need to complete six 5-point problems and six 10-point problems. Cross off one 5-point problem and one 10-point problem. 1. Two small silver spheres, each with
Physics 196 Final Test - 120 Point Name You need to complete six 5-point problems and six 10-point problems. Cross off one 5-point problem and one 10-point problem. 1. Two small silver spheres, each with
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060070371A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0070371 A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT PROPULSION (22) Filed: Oct.
US 20060070371A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0070371 A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT PROPULSION (22) Filed: Oct.
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
(19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,882,745 B2
 USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
United States Patent (19) Hughes et al. 54 (75) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR LINEAR SCAN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Inventors: John L. Hughes, Rodeo; Gary A. Davis, Fremont; Robert J. Kolenkow, Berkeley; Carl T.
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001610121A1* (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158(3) EPC (43) Date of publication:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001610121A1* (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158(3) EPC (43) Date of publication:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
SCB10H Series Pressure Elements PRODUCT FAMILY SPEFICIFATION. Doc. No B
 PRODUCT FAMILY SPEFICIFATION SCB10H Series Pressure Elements SCB10H Series Pressure Elements Doc. No. 82 1250 00 B Table of Contents 1 General Description... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 General Description...
PRODUCT FAMILY SPEFICIFATION SCB10H Series Pressure Elements SCB10H Series Pressure Elements Doc. No. 82 1250 00 B Table of Contents 1 General Description... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 General Description...
TEPZZ 95785_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
100-N. (12) United States Patent N 2 Q US 7,234,334 B1. Jun. 26, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: SZZ
 USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
2014 F 2014 AI. 1. Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason.
 2014 F 1. Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason. 2. Figure shows the field lines on a positive charge. Is the work done
2014 F 1. Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason. 2. Figure shows the field lines on a positive charge. Is the work done
Method of modifying weather
 Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
NAV A. Attorney Docket No Date: 4 February 2008
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 NAV A Attorney Docket No. 96813 Date: 4 February
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 NAV A Attorney Docket No. 96813 Date: 4 February
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2
 USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
P202 Practice Exam 2 Spring 2004 Instructor: Prof. Sinova
 P202 Practice Exam 2 Spring 2004 Instructor: Prof. Sinova Name: Date: (5)1. How many electrons flow through a battery that delivers a current of 3.0 A for 12 s? A) 4 B) 36 C) 4.8 10 15 D) 6.4 10 18 E)
P202 Practice Exam 2 Spring 2004 Instructor: Prof. Sinova Name: Date: (5)1. How many electrons flow through a battery that delivers a current of 3.0 A for 12 s? A) 4 B) 36 C) 4.8 10 15 D) 6.4 10 18 E)
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
Capacitors. Charging a Capacitor. Charge and Capacitance. L05: Capacitors and Inductors
 L05: Capacitors and Inductors 50 Capacitors 51 Outline of the lecture: Capacitors and capacitance. Energy storage. Capacitance formula. Types of capacitors. Inductors and inductance. Inductance formula.
L05: Capacitors and Inductors 50 Capacitors 51 Outline of the lecture: Capacitors and capacitance. Energy storage. Capacitance formula. Types of capacitors. Inductors and inductance. Inductance formula.
(12) United States Design Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomlinson et al. US D701,634 S (45) Date of Patent: *1, Mar. 25, (21) Appl.No.
 USOOD701634S (12) United States Design Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomlinson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *1, (54) LIGHTING FIXTURE (75) Inventors: J oel Tomlinson, Westlake, OH (US); Rick Wiedemer, Rocky River,
USOOD701634S (12) United States Design Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomlinson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *1, (54) LIGHTING FIXTURE (75) Inventors: J oel Tomlinson, Westlake, OH (US); Rick Wiedemer, Rocky River,
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
Transducers. ME 3251 Thermal Fluid Systems
 Transducers ME 3251 Thermal Fluid Systems 1 Transducers Transform values of physical variables into equivalent electrical signals Converts a signal from one form to another form 2 Types of Transducers
Transducers ME 3251 Thermal Fluid Systems 1 Transducers Transform values of physical variables into equivalent electrical signals Converts a signal from one form to another form 2 Types of Transducers
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,261,710 B1
 USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
UNIT 102-2: ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE Approximate time two 100-minute sessions
 Name St.No. Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 1022: ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE Approximate time two 100minute sessions I get a real charge out of capacitors. P. W. Laws OBJECTIVES 1. To understand
Name St.No. Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 1022: ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE Approximate time two 100minute sessions I get a real charge out of capacitors. P. W. Laws OBJECTIVES 1. To understand
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
FIG.1. Form organic light emitting. Coat the encapsulation. encapsulation substrate. Prepare an. Prepare a substrate
 (19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
Office de la Propriete Canadian CA Al 2006/09/14 PI Intellectuelle Intellectual Property du Canada Office (21)
 1+1 F Office de la Propriete Canadian CA 2600414 Al 2006/09/14 PI Intellectuelle Intellectual Property du Canada Office (21) 2 600 414 Un organisme d'industrie Canada An agency of Industry Canada (12)
1+1 F Office de la Propriete Canadian CA 2600414 Al 2006/09/14 PI Intellectuelle Intellectual Property du Canada Office (21) 2 600 414 Un organisme d'industrie Canada An agency of Industry Canada (12)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1
 USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
Electro - Principles I
 Electro - Principles I Capacitance The Capacitor What is it? Page 8-1 The capacitor is a device consisting essentially of two conducting surfaces separated by an insulating material. + Schematic Symbol
Electro - Principles I Capacitance The Capacitor What is it? Page 8-1 The capacitor is a device consisting essentially of two conducting surfaces separated by an insulating material. + Schematic Symbol
CVD Method of Producing and Doping Fullerenes
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent CVD Method of Producing and Doping Fullerenes 4-23-1996 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent CVD Method of Producing and Doping Fullerenes 4-23-1996 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,104,270 Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000
 USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000 54) LIFTER WITH ELECTROPERMANENT 4.956,625 9/1990 Cardone et al.... 335/290 MAGNETS PROVIDED WITH A SAFETY
USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000 54) LIFTER WITH ELECTROPERMANENT 4.956,625 9/1990 Cardone et al.... 335/290 MAGNETS PROVIDED WITH A SAFETY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
Casse Study Toy ball. Belgrade, October Jörg Machek Director, Cluster Computers European Patent Office
 Casse Study Toy ball Belgrade, October 2010 Director, Cluster Computers European Patent Office The invention A ball that is fun to use, easy to catch and looks nice. How can you protect it from imitation?
Casse Study Toy ball Belgrade, October 2010 Director, Cluster Computers European Patent Office The invention A ball that is fun to use, easy to catch and looks nice. How can you protect it from imitation?
Wide-Acceptance-Angle Circular Polarizers (DIV)
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Wide-Acceptance-Angle Circular Polarizers (DIV) 12-11-2012 Shin-Tson Wu University of Central Florida Qi Hong University of Central Florida Ruibo Lu University
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Wide-Acceptance-Angle Circular Polarizers (DIV) 12-11-2012 Shin-Tson Wu University of Central Florida Qi Hong University of Central Florida Ruibo Lu University
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
