refore z 19, COMAU7AR f7 Sg 26 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT 3,464,770 Horst Schmidt LASER TRANSM/TTER AT TORNEYS NVENTOR
|
|
|
- Herbert Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
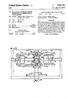
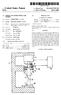
1 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Filed Oct. 21, Sheets-Sheet l LASER TRANSM/TTER 19, f7 Sg 26 COMAU7AR V NVENTOR Horst Schmidt refore z AT TORNEYS
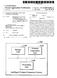
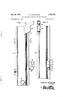
2 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Fied Oct. 2, Sheets-Sheet 2 Afg ea' f5 LASER TRANSMITTER t 2Zzzzzzzzz COMPUTER IN VENTOR Horst Schmidt AT TO R N E YS
3 United States Patent Office Patented Sept. 2, COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Horst Schmidt, Nauborn, Kreis, Wetzlar, Germany, as signor to Ernst Leitz GmbH, Optische Werke, Wetzlar, Germany Filed Oct. 21, 1965, Ser. No. 499,346 Claims priority, application Germany, Nov. 7, 1964, L 49,2; Sept. 3, 1965, IL 51,552 Int. Cl. G01c3/08; F41g 3/06; G02b 23/10 U.S. C Claims ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE Arrangement combining a laser range finder, including transmitter and receiver, with a sighting mechanism, in cluding an ocular, for determining the distance of a target and for adjusting the angle of elevation required to fire a projectile at the target. The laser range finder and the sighting mechanism have partially coextensive beam paths. A divider mirror in the beam path of the sighting mechanism directs received rays to the laser re ceiver and sighting mechanism ocular. A reticle plate ar ranged in front of the mirror is connected to an element of an optical system provided in front of the laser trans mitter. The reticle plate and such element are displaceable transversely to the optical axis of such optical system. Means provided in the beam path to the laser receiver block the rays reflected from the target to which the laser receiver is sensitive, except for rays, which correspond to the transmitted beam in divergence and direction and which are within the visible portion of the spectrum; the former being passed to the laser receiver and the latter to the ocular of the sighting mechanism via the divider mirror. Means are also coupled between the laser re ceiver and the reticle plate for displacing the reticle plate and such element in response to signals from the laser re ceiver. By this arrangement, adjustments can be made in the elevation angle required for a projectile to reach the target. -amaucreuaum The present invention relates to an arrangement where in a visual sighting mechanism is coupled with a laser range finder and wherein the arrangement is provided with a device which adjusts for the angle of elevation required, e.g. for a weapon associated with the arrangement to fire a projectile at a target. A device of this type is known wherein the angle of elevation for a weapon associated with the device is de termined by adjusting a rotating pair of prisms provided in the beam path of both the sighting mechanism and the laser transmitter. Since the rotating prisms must receive each beam path in contradistinction to a single beam path, the diameter of the optical systems for the pair of rotat ing prisms and also for the associated optical components positioned in front thereof must necessarily be corre spondingly larger. It has therefore been suggested that this disadvantage may be overcome by directing the beam of rays of the laser transmitter within the region of the beam path of the sighting mechanism. However, this is impossible without limiting the field of a portion of the beam required for the visual sighting device. Aside there from, the use of a rotating prism pair represents a sub stantial increase in the cost of the device because the prisms, of necessity, must be made of a complicated con struction in order that the prisms have good optical and mechanical properties. Another disadvantage of the prior arrangements is that when the mechanism is incorporated into armored ve hicles, it is particularly difficult to provide a gear con O nection between the adjusting device in the interior of the vehicle and the rotating prisms located on the outside of the vehicle. Additionally, there is a further disadvantage in that rotating prisms generally produce astigmatic distortions and Secondary chromatic aberrations. Furthermore, the components can not be cemented together because of the intense laser radiation and the resulting glass-air areas cause disturbing reflections. It is an object of the present invention to provide an ar rangement of a sighting mechanism coupled with a laser range finder which is of simple construction and economi cal to produce. It is another object of the present invention to provide a combined sighting mechanism and laser range finder having a common optical system for a portion of the beam paths. It is a further object to provide a combined sighting mechanism and laser range finder having an optical sys tem which is relatively free of distortions. In accordance with the present invention, the afore described disadvantages of the prior arrangements are overcome by providing in front of a chromatic divider mirror mounted in a conventional manner in the beam path of a sighting mechanism, a reticle plate, and connect ing the plate with an element of the optical system ar ranged in front of a laser transmitter, with the plate being mounted for displacement transverse to the optical axis. There is further provided in the beam path of a laser receiver, optical means which block the rays to which the laser receiver is sensitive, except for the rays which are reflected from the target and correspond to the trans mitted beam in divergence and direction and for the rays Within the visible portion of the spectrum which are fed to the ocular of the sighting mechanism via the divider mirror. According to a feature of the invention, the blocking may be accomplished by providing a coating on the re ticle plate, except for a small central surface portion, for blocking the rays lying beyond the visible portion of the Spectrum to which the laser receiver is sensitive. Thus the coating forms a diaphragm for limiting the beam of rays used for measuring and which is united with the reticle plate. Although the arrangement including a coating as a dia phragm for blocking the rays is more economical than prior arrangements, the coating increases the expense of the arrangement. Therefore, according to another feature of the invention, the diaphragm is separated from the re ticle plate and is mounted in a plane that is optically re lated to the plane of the reticle plate. There is further provided means which ensure that the received rays that are used for measuring and which are parallel to the transmitted rays always enter through the center of the diaphragm regardless of the position of the reticle plate. The diaphragrm may be adjusted to correspond to the dif ferent positions of the reticle plate by means of a com plicated gear arrangement. However, the present inven tion provides a simplified arrangement wherein a two member optical system having a parallel beam path be tween the two-members is arranged in front of the fixed diaphragm of the laser receiver. The reticle plate image is then produced in the diaphragm plane, and the member of the system which is adjacent the reticle plate is connected to the reticle plate and is displaceable with the plate in a plane transverse to the optical axis. The beam divider is suitably arranged between the reticle plate and the mem ber of the two-member system which is arranged in front of the laser receiver.
4 3. According to a further feature of the present invention, there is provided a pancratic or zoom lens telescopic sight as the sighting mechanism, wherein the sight may be used with the laser range finder or as an auxiliary system in place of the laser range finder. Additional objects and advantages of the present in vention will become apparent upon consideration of the following description when taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings in which: FIGURE 1 is a schematic view of the combined sight ing and laser beam measuring device having the reticle plate coupled with the device for blocking rays. FIGURE 2 is a front view of the recticle plate of FIG URE 1 with a target indicated thereon in dash-dot lines. FIGURE 3 is a schematic view of another embodiment of the present invention having a pancratic telescope sight and a deflection device. FIGURE 4 is a further embodiment of a combined sighting and laser beam measuring device according to the present invention having a reticle plate and a dia phragm that are arranged in different planes. Referring now to the drawings, there is shown in FIG. URE 1 a reticle plate 9 arranged in front of a chromatic divider or semi-reflecting mirror 1 which directs a portion 2a of the rays 4 coming from an objective 3 of the sight ing mechanism to a laser receiver 5 and reflects a por tion 2b via a field lens 6 and a mirror 7 to an ocular 8 with the field of view plane 29 being arranged in the ocu lar image plane. As can be seen, a plane parallel plate 1a supports the mirror 1. As shown in FIGURE 2, the reticle plate 9 which is fully permeable for the visible portion of the spectrum carries the line configuration 10 and is provided, outside of the central portion 11, with a coating 12 which is impermeable to laser rays, the size of the central portion 1 being determined by the scattere ing angle of the laser transmitter and by the focal length of the optical system of the sighting mechanism provided in front of the reticle plate. The coating may be of any suitable type such as a reflective coating effective only for laser rays. The reticle plate is connected with the nega tive optical member 13 of a two optical member Galilean system 14 and is displaceable with the member 13 in the direction of arrow A transverse to the optical axis of the two member optical system. The Galilean system has an axis 15 which extends in parallel with the center line of the objectives 3 and is arranged in front of a laser transmitter 16, whereby the negative member 13 which is connected to the reticle plate causes a deflection of the transmitted laser rays. The dis placement of the negative element has the same optical effect as the displacement of the reticle plate. The dis placement can be done in two coordinates at right angles to the optical axis of the laser transmitter and at right angles to the optical axis of the optical system provided in front of the divider mirror, respectively, i.e., in a plane transverse to the optical axis. A computer 17 is connected via a cable 18, with the laser beam measuring device and transmits its commands to the reticle plate 9 via the con nection. 19. The mechanical means for adjusting the sight ing mechanism are not illustrated in the drawing. The mode of operation of the arrangement shown in FIGURE 1 is essentially as follows: At first, the sighting procedure is carried out in the conventional manner through use of the visual sighting mechanism with the en tire system including a weapon coupled thereto, being set on the target with respect to height and direction. There after, the range finding process is carried out by means of the leaser beam device. In this process, the rays 15 emitted by the laser transmitter 16 are received by the objective 3 after reflection at the target and pass through the central aperture 11 of the reticle plate 9 to the divider mirror 1 and to the receiver 5. The sighting mechanism is provided with conventional protective devices which are actuated during the laser range finding. The divider mir ror may be supported by a plane parallel plate or, as 5 O shown in FIGURE 3, a prismatic cube. The reflective coating 12 prevents undesired rays from passing through the reticle plate for these would otherwise impair the measuring result. The laser beam range finding process is similar to a radar distance measuring process in that the time interval between the emission and reception of the transmitted beam is an indication of the distance of the target. The distance information is then fed to the computer 17, to gether with other values such as wind speed and direction, target speed, etc. The computer processes this data and determines the elevation and lead angle for the target and transmits the result to the plate 9 via the connection 19. The reticle plate 9 and the lens 13 are then shifted in accordance with the computer calculation to compensate for the elevation angle necessary for a projectile to reach the target. However, the shifting of the plate and the lens 13 results in the target no longer being centered in the cross-hairs 10 of the plate 9 since the line of sight is no longer directed at the target and therefore the entire sight ing arrangement and the weapon coupled thereto are shifted to again center the target. The movement of the weapon and the sighting arrangement thereby provide the required elevation angle necessary for a projectile to reach the target. The laser beam range finding process may then be repeated to check the target range without having to return the entire arrangement to a basic set ting. However, any further changes causing a further shift ing of the reticle plate will also have to be compensated for by a corresponding movement of the entire apparatus. In FIGURE 3, which is another embodiment according to the present invention, there is shown a movable mirror 20 provided behind the objective 3; whereby in case of inoperativeness or non-use of the laser device, the re ceived rays are directed to a pancratic or zoom lens range finder 21 combined with the sighting mechanism. For this purpose, a further deflection mirror 22 and an additional field lens 23 are provided in the beam path. Further more, the mirror 7 in this embodiment must be collap sible, i.e., capable of being swung out of the axis of the pancratic System. The deflection system also includes a range finding mark 24, arranged in the ocular 8. In the arrangement of FIGURE 3, the range finding procedure can be carried out by means of the pancratic System 2 in case the laser device is inoperative, or as a Supplement to the laser measuring process. However, in order to use the pancratic system for range finding, the mirrors 20 and 7 must be moved into the position shown in solid line in FIGURE 3. This range finding is then accomplished by changing the enlargement scale of the pancratic System until the target configuration on the range finding mark 24 is adjusted to the size of the target So that the mark is rendered congruent with the target. The adjustment path for changing the magnification which is an indication of the range, can then be used to Set the elevation angle of the weapon or the movement of the lens System can be transferred to the reticle plate 9 via means which are not illustrated, and the elevation of the Weapon carried out as discussed in connection with FIGURE 1. Thus, the Zoom lens system may be used with the laser arrangement as a complementary system, or as an auxiliary System in place of the laser arrangement for the purpose of range finding. Furthermore, it is also possible to obtain an auxiliary range finding without using a pancratic optic by provid ing in the ray path of the visual sighting mechanism a conventional range finder comprising two mutually dis placeable sections. In this conventional arrangement, as Well as in the arrangement using a pancratic system, the range finding mark is positioned in the image plane of an intermediate image producing system included in the auxiliary System. In order that only this measuring mark be visible in the field of vision, it is advantageous to cir cumvent the index plate located in a different image plane
5 5 by means of a mirror arrangement similar to that of FIGURE 3. However, if the range finding marks are ad vantageously arranged, for example in such a manner that they do not overlap one another, the feature of eliminating the reticle plate by deflection mirrors can be omitted. In the arrangement shown in FIGURE 4, which is a further embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a further two-member optical system compris ing lens 25a and lens 25b, a diaphragm 26 and a lens 27 arranged in front of the laser receiver 5. Reflected rays are directed to the beam divided mirror via the ob jective 3 arranged in the optical axis 4 of the laser re ceiver, after passing through the reticle plate 9. The beam divider 1 splits the received rays so that a portion of the rays is fed to the ocular 8 of the sighting device via the deflection mirror 7 and the other portion passes through the beam divider to the laser receiver via the two member system 25, the diaphragm 26 and the lens 27, with diaphragm 26 corresponding to the coating 12 as shown in FIGURE 1 for limiting the beam of rays used for measuring the range. The reticle plate 9 is arranged in the front focal plane of the lens 25a and the diaphragm 26 in the back focal plane of the lens 25b of the system 25 which is con structed to provide collimated rays between the two lens members, whereby the image of the reticle plate is produced in the diaphragm plane. The lens 25a is fixedly connected with the reticle plate 9 through a connecting member and together with the plate is displaceable in a plane transverse to the optical axis of the system. The negative member 13 of the Galilean system 14, which is arranged in the beam path 15 of the laser transmitter 16, is also coupled with the reticle plate and is displace able therewith. The reticle plate 9 is controlled via the cable 19 from the computer 17 which evaluates the measuring results fed to it from the laser beam range finder via cable 18. The mode of operation of the device shown in FIG URE 4 is as follows: As in the operation of the ar rangement of FIGURE 1, the range finding process is first performed in a conventional manner by using the sighting device, whereby the entire arrangement includ ing the coupled weapons is set on the target in height and direction. The target line of the telescope, the trans mitted laser beam, the received laser beam and the bore axis of the weapons are then arranged parallel to each other. The measuring of the range is then performed by means of the laser range finding device. The rays 15 transmitted by the transmitter 16 are in a conventional way received by the objective 3 after having been re flected by the target and then reach the chromatic di vided mirror 1 after having entered through the reticle plate 9. The divided mirror separate the visible portion of the rays and directs that portion to the ocular 8 of the sighting device with the laser beams being passed to receiver 5 via the system 25 and the lens 27. The results of the receiver are fed to the computer 17 for calcula tion of the angle of lead and elevation which is then transferred to the reticle plate 9 by displacing the same. The displacement of the negative member 13 and the lens 25a with the reticle plate results in the target line of the telescope as well as the transmitted and received laser beam being maintained parallel to each other, but forming as desired, an angle relative to the weapon cou pled therewith. The shifting of the reticle plate 9 and the sight line toward the target is then compensated for by counter-steering the entire sighting arrangement and the weapons, thereby providing the elevation angle re quired for a projectile to reach the target. The operation of the present embodiment is depend ent upon the displacement of the lens 25a with the reticle plate. Due to the afore-described construction of the system 25, it is provided that in any angular position existing between the transmitted beams and the bore axis of the weapons coupled to the sighting arrangement only those received rays that enter parallel to the trans mitted rays are directed in the desired way through the center of the diaphragm 26 to the laser receiver 5 for a true determination of the range. Thus, it is seen from the afore-described embodiments that the present invention provides arrangements includ ing laser beam range finders which directly adjust for the angle of elevation by movement of the reticle plate. These arrangements are economical to produce and are relative ly free of distortion since the need for additional optical components of complicated structure is eliminated. As shown, the present invention also provides means for limiting the rays passed to the laser receiver, such as the coating on the reticle plate and the separate diaphragm in a different plane from that of the reticle plate, in order to provide a true measurement of the target range. It will be understood that the above description of the present invention is susceptible to various modifications, changes, and adaptations. What is claimed is: 1. A combined sighting mechanism and laser range finder arrangement for determining the distance of a target from the arrangement and for adjusting for the angle of elevation required for a weapon associated with the arrangement to fire a projectile at the target, the ar rangement comprising, in combination: a laser range finder including a laser transmitter for transmitting laser rays to a target along a beam path and a laser receiver for receiving reflected rays from the target along a beam path; sighting mechanism optical system having a beam path and including an ocular, said beam path of the sighting mechanism optical system and said beam path of the laser receiver being at least partially co extensive; divider mirror mounted in the beam path of said laser receiver for transmitting received rays from the target to said laser receiver and for reflecting received rays from the target for direction to said ocular of said sighting mechanism optical system; a. two-member optical system arranged in the beam path of said laser transmitter; a reticle plate mounted in front of said divider mirror in the beam path of the laser receiver and the sight ing mechanism optical system and coupled to one member of said two-member optical system for dis placement in a plane transverse to the optical axis of such two-member optical system, such displacement adjusting the elevation angle required for a projec tile to reach the target; means for passing to said laser receiver that portion of the rays reflected from the target which correspond in direction and divergence to the transmitted rays and to which said laser receiver is responsive, and for passing to said ocular of the sighting mechanism op tical system that portion of the rays reflected from the target which fall within the visible spectrum by way of said mirror, and for blocking the other rays to which said laser receiver is responsive; and means coupled between the laser receiver and the ret icle plate and responsive to signals from said laser receiver for displacing the reticle plate and said one member of the two-member optical system in said transverse plane thereby to adjust for the elevation angle required for a projectile to reach the target. 2. An arrangement as defined in claim 1 wherein said reticle plate is fully permeable for the visible portion of the spectrum and said means for passing and for blocking the rays is a coating impermeable to laser rays provided on said reticle plate having a small open portion of a pre determined size at the center of said reticle plate for pass ing the rays to which the laser receiver is responsive, the
6 7 size of said open portion being determined by the Scatter ing angle of said laser transmitter and by the focal length of the optical system of said sighting mechanism. 3. An arrangement as defined in claim 2 wherein the coating provided on said reticle plate outside of the cen tral open portion reflects rays to which the laser receiver is responsive. 4. An arrangement as defined in claim 1 wherein said two member optical system is a Galilean System, said member connected with said reticle plate being the nega tive lens thereof. 5. An arrangement as defined in claim wherein said sighting mechanism is a pancratic telescopic sight. 6. An arrangement as defined in claim 5 wherein said pancratic telescopic sight is provided with a range finding mark for auxiliary range finding in addition to the laser range finder. 7. An arrangement as defined in claim 6 wherein said pancratic telescopic sight includes an image-reproduc ing system and said range finding mark is provided in the image plane of said system. 8. An arrangement as defined in claim wherein said divider mirror is a chromatic mirror and a plane parallel plate Supports said mirror. 9. A combined sighting mechanism and laser range finder arrangement for determining the distance of a target from the arrangement and for adjusting for the angle of elevation required for a weapon associated with the ar rangement to fire a projectile at the target, the arrange ment comprising, in combination: a laser range finder including a laser transmitter for transmitting laser rays to a target along a beam path and a laser receiver for receiving reflected rays from the target along a beam path; a sighting mechanism optical system having a beam path and including an ocular, said beam path of the sight ing mechanism optical System and said beam path of the laser receiver being at least partially coextensive; a divider mirror mounted in the beam path of said laser receiver for transmitting received rays from the tar get to said laser receiver and for reflecting received rays from the target for direction to said ocular of said sighting mechanism optical system; a two-member optical System arranged in the beam path of said laser transmitter; O a reticle plate mounted in front of said divider mirror in the beam path of the laser receiver and the sight ing mechanism optical system and coupled to one member of said two-member optical system for dis placement in a plane transverse to the optical axis of such two-member optical system, such displacement adjusting the elevation angle required for a projectile to reach the target; means for passing to said laser receiver that portion of the rays reflected from the target which correspond in direction and divergence to the transmitted rays and to which said laser receiver is responsive, and for blocking the other rays to which said laser receiver is responsive, said means for passing and for blocking the rays being a fixed diaphragm mounted in front of said laser receiver; means coupled between the laser receiver and the reticle plate and responsive to signals from said laser re ceiver for displacing the reticle plate and said one member of the two-member optical system in said transverse plane thereby to adjust for the elevation angle required for a projectile to reach the target; and a further two-member optical system arranged in front of said fixed diaphragm, one member of said further two-member optical system being adjacent to said reticle plate and connected therewith for displacement transverse to the optical axis of a portion of the sight ing mechanism optical system, said further two-mem ber optical system providing a parallel beam path. therebetween and producing the image of said reticle plate in the diaphragm plane. References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 3,339,457 9/1967 Pun. RONALD L. WILBERT, Primary Examiner F. L. EVANS, Assistant Examiner U.S. C. X.R.
United States Patent (19) Murdoch
 33.245 4M28/8 SR XR 4, 263,719 United States Patent (19) Murdoch (54) OPTICAL SIGHTING DEVICES 76 Inventor: Colin A. Murdoch, 14a Hassall St., Timaru, New Zealand 21 Appl. No.: 824,960 22 Filed: Aug. 15,
33.245 4M28/8 SR XR 4, 263,719 United States Patent (19) Murdoch (54) OPTICAL SIGHTING DEVICES 76 Inventor: Colin A. Murdoch, 14a Hassall St., Timaru, New Zealand 21 Appl. No.: 824,960 22 Filed: Aug. 15,
June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB 3,187,583. ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION SPACE SIMULATOR A. IMAGE OF LIGHT SOURCE (C)
 June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION Filed Nov. 9, 196 4 SheetsSheet 1 RADIATION SOURCE (C) SPHERCA REFLECTOR EPICA REFLECTOR R 2 A. IMAGE OF LIGHT
June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION Filed Nov. 9, 196 4 SheetsSheet 1 RADIATION SOURCE (C) SPHERCA REFLECTOR EPICA REFLECTOR R 2 A. IMAGE OF LIGHT
United States Patent (19) Rex
 United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.:
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
U.S. Cl /251; 356/252 Int. Cl... G02B /254, 255; 350/174
 -- -174. SR 39942.90. United States Patent Ekstrand 19 l l ) Mar. 9, 1976 54 PTICAL SIGHTING INSTRUMENT WITH MEANS FR PRDUCING ASIGHTING MARK 76 Inventor: John Arne Ingemund Ekstrand, Drottninggatan 72
-- -174. SR 39942.90. United States Patent Ekstrand 19 l l ) Mar. 9, 1976 54 PTICAL SIGHTING INSTRUMENT WITH MEANS FR PRDUCING ASIGHTING MARK 76 Inventor: John Arne Ingemund Ekstrand, Drottninggatan 72
2,479,673. Aug. 23, HTTO/P/VZY. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE. 2 Sheets~Sheet 1
 Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL MICROWAVE TRANSMISSION ' SYSTEM HAVING DIELECTRIC LENS 2 Sheets~Sheet 1 HTTO/P/VZY Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL
Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL MICROWAVE TRANSMISSION ' SYSTEM HAVING DIELECTRIC LENS 2 Sheets~Sheet 1 HTTO/P/VZY Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
IIIHHHHHHHHIIIHIII 5,184,176. United States Patent (19) Unino et al. ARITHMETIC. Feb. 2, mined magnification to form a pattern image on the
 United States Patent (19) Unino et al. (54) PROJECTION EXPOSURE APPARATUS WITH AN ABERRATION COMPENSATION DEVICE OF A PROJECTION LENS (75) Inventors: Yasuyuki Unno, Hadano; Seiji Orii; Masami Yonekawa,
United States Patent (19) Unino et al. (54) PROJECTION EXPOSURE APPARATUS WITH AN ABERRATION COMPENSATION DEVICE OF A PROJECTION LENS (75) Inventors: Yasuyuki Unno, Hadano; Seiji Orii; Masami Yonekawa,
April 26, J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604
 April 26, 1932- J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet l 43 00009600 2/ 22 ' April 26, 1932. J'. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 46 l? wag Patented Apr. 26,
April 26, 1932- J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet l 43 00009600 2/ 22 ' April 26, 1932. J'. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 46 l? wag Patented Apr. 26,
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part II. OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part II. OPTICAL SYSTEMS 1 Introduction Optical systems can consist of a one element (a one lens or a mirror, a magnifying glass), two or three lenses (an eyepiece, theatrical
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part II. OPTICAL SYSTEMS 1 Introduction Optical systems can consist of a one element (a one lens or a mirror, a magnifying glass), two or three lenses (an eyepiece, theatrical
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
Optical Instruments. Chapter 25. Simple Magnifier. Clicker 1. The Size of a Magnified Image. Angular Magnification 4/12/2011
 Optical Instruments Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Optical Instruments Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
A Question. Simple Magnifier. Magnification by a Lens 11/29/2011. The last lecture
 The last lecture Exam: Final: Consult the website, especially room assignments. Makeup: Register with me today. Tea and Cookies: Tuesdays 5PM, NPB 2175 A Question Unpolarized light of intensity I goes
The last lecture Exam: Final: Consult the website, especially room assignments. Makeup: Register with me today. Tea and Cookies: Tuesdays 5PM, NPB 2175 A Question Unpolarized light of intensity I goes
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2
 USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
(19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS 22. 8a 1. United States Patent (19) Maru et al. 11 4,365,007 45) Dec. 21, 1982
 United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Schrader
 United States Patent (19) Schrader US005534997A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 54 RAMAN SPECTROMETER USING A REMOTE PROBE WITHENHANCED EFFICIENCY 75 Inventor: Bernhard Schrader, Essen-Heisingen,
United States Patent (19) Schrader US005534997A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 54 RAMAN SPECTROMETER USING A REMOTE PROBE WITHENHANCED EFFICIENCY 75 Inventor: Bernhard Schrader, Essen-Heisingen,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,167,752 B1. Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001
 USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace. Aig. / May 28, ,793,758. Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey. Filed March 28, 1956 MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING
 May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T (11) EP 2 618 130 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.07.13 Bulletin 13/30 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/ (06.01) G01N 21/77 (06.01) G01N 33/43 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T (11) EP 2 618 130 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.07.13 Bulletin 13/30 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/ (06.01) G01N 21/77 (06.01) G01N 33/43 (06.01) (21) Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,516,571 B2
 US007516571B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Scrogin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 2009 (54) INFRARED RANGE-FINDING AND 5,771,623 A 6/1998 Pernstich et al. COMPENSATING SCOPE FOR USE WITH
US007516571B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Scrogin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 2009 (54) INFRARED RANGE-FINDING AND 5,771,623 A 6/1998 Pernstich et al. COMPENSATING SCOPE FOR USE WITH
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,221,987 Laughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 1993
 H US0022 1987A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent umber:,221,987 Laughlin 4 Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 1993 4) FTIR MODULATOR 4,714,326 12/1987 Usui et al.... 39/222 4,738,00 4/1988 Gruppet al...... 39/199
H US0022 1987A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent umber:,221,987 Laughlin 4 Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 1993 4) FTIR MODULATOR 4,714,326 12/1987 Usui et al.... 39/222 4,738,00 4/1988 Gruppet al...... 39/199
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes
 Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In the early chapters of this book, you looked at the sky the way ancient astronomers did, with the unaided eye. In chapter 4, you got a glimpse through Galileo
Chapter 6 Light and Telescopes Guidepost In the early chapters of this book, you looked at the sky the way ancient astronomers did, with the unaided eye. In chapter 4, you got a glimpse through Galileo
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(12) United States Patent
 US007540229B2 (12) United States Patent Seo et al. (54) EXPLOSIVE REACTIVE ARMOR WITH MOMENTUMITRANSFER MECHANISM (75) Inventors: Yongseok Seo, Seongnam (KR): Jeong-Tae Kim, Daejeon (KR); Chang Choi, Daejeon
US007540229B2 (12) United States Patent Seo et al. (54) EXPLOSIVE REACTIVE ARMOR WITH MOMENTUMITRANSFER MECHANISM (75) Inventors: Yongseok Seo, Seongnam (KR): Jeong-Tae Kim, Daejeon (KR); Chang Choi, Daejeon
Astronomical Tools. Optics Telescope Design Optical Telescopes Radio Telescopes Infrared Telescopes X Ray Telescopes Gamma Ray Telescopes
 Astronomical Tools Optics Telescope Design Optical Telescopes Radio Telescopes Infrared Telescopes X Ray Telescopes Gamma Ray Telescopes Laws of Refraction and Reflection Law of Refraction n 1 sin θ 1
Astronomical Tools Optics Telescope Design Optical Telescopes Radio Telescopes Infrared Telescopes X Ray Telescopes Gamma Ray Telescopes Laws of Refraction and Reflection Law of Refraction n 1 sin θ 1
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
Optical Instruments. Optical Instruments 1. Physics 123, Fall 2012
 Optical Instruments 1 Physics 123, Fall 2012 Name Optical Instruments I. Magnifier The lens in the human eye adjusts its shape to change the focal length, so that objects at a variety of distances can
Optical Instruments 1 Physics 123, Fall 2012 Name Optical Instruments I. Magnifier The lens in the human eye adjusts its shape to change the focal length, so that objects at a variety of distances can
UNITED STATES PATENT NUMBER 3,626,605 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR GENERATING A SECONDARY GRAVITATIONAL FORCE FIELD
 UNITED STATES PATENT NUMBER 3,626,605 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR GENERATING A SECONDARY GRAVITATIONAL FORCE FIELD HENRY WILLIAM WALLACE DECEMBER 14, 1971 3 of the invention, are pointed out with particularity
UNITED STATES PATENT NUMBER 3,626,605 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR GENERATING A SECONDARY GRAVITATIONAL FORCE FIELD HENRY WILLIAM WALLACE DECEMBER 14, 1971 3 of the invention, are pointed out with particularity
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
Assignment 3 Due September 27, 2010
 Assignment 3 Due September 27, 2010 Text readings Stops section 5.3 Dispersing and Reflecting Prisms [sections 5.5.1 and 5.5.2] Optical systems section 5.7 Lens Aberrations [section 6.3] Be careful about
Assignment 3 Due September 27, 2010 Text readings Stops section 5.3 Dispersing and Reflecting Prisms [sections 5.5.1 and 5.5.2] Optical systems section 5.7 Lens Aberrations [section 6.3] Be careful about
UK Patent Application 9 >GB
 UK Patent Application 9 >GB 2 055 465 A (21) (22) (30) (31) (32) (33) (43) (51) (52) (56) (58) (71) (72) (74) Application No 8018366 Date of filing 4 Jun 1980 Priority data 79/20667 14Jun1979 United Kingdom
UK Patent Application 9 >GB 2 055 465 A (21) (22) (30) (31) (32) (33) (43) (51) (52) (56) (58) (71) (72) (74) Application No 8018366 Date of filing 4 Jun 1980 Priority data 79/20667 14Jun1979 United Kingdom
HENRY WILLIAM WALLACE UNITED STATES PATENTS NUMBER 3,626,605 AND NUMBER 3,626,606
 HENRY WILLIAM WALLACE UNITED STATES PATENTS NUMBER 3,626,605 AND NUMBER 3,626,606 UNITED STATES PATENT NUMBER 3,626,605 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR GENERATING A SECONDARY GRAVITATIONAL FORCE FIELD HENRY
HENRY WILLIAM WALLACE UNITED STATES PATENTS NUMBER 3,626,605 AND NUMBER 3,626,606 UNITED STATES PATENT NUMBER 3,626,605 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR GENERATING A SECONDARY GRAVITATIONAL FORCE FIELD HENRY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
Optical Telescopes. Telescopes. Refracting/Reflecting Telescopes. Physics 113 Goderya
 Telescopes Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 6 Learning Outcomes: Optical Telescopes Astronomers use telescopes to gather more light from astronomical objects. The larger the telescope, the more light it
Telescopes Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 6 Learning Outcomes: Optical Telescopes Astronomers use telescopes to gather more light from astronomical objects. The larger the telescope, the more light it
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
TEPZZ 95785_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
11.3 The Telescope. object. Figure 1 A Galilean telescope eye. reflecting telescope: telescope that uses a parabolic mirror to focus light
 (b) Most s are now made of two or more lenses. What kind of lenses are involved in Huygenian, Ramsden, Periplan, and Kellner designs? Which of those s is the best one to use? Why? (c) The Dutch naturalist
(b) Most s are now made of two or more lenses. What kind of lenses are involved in Huygenian, Ramsden, Periplan, and Kellner designs? Which of those s is the best one to use? Why? (c) The Dutch naturalist
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,765 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING. Filed Aug. 19, 1965 (,,,,, SR-33-R-N
 May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 US008561479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561479 B2 Hagedoorn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) CORIOLIS FLOW SENSOR 6,776,053 B2 * 8/2004 Schlosser et al.... T3/861,355
US008561479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561479 B2 Hagedoorn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) CORIOLIS FLOW SENSOR 6,776,053 B2 * 8/2004 Schlosser et al.... T3/861,355
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T990088-01- D 10/14/99 COS IFO Alignment Procedure
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T990088-01- D 10/14/99 COS IFO Alignment Procedure
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
TEPZZ 89955_A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
Laser Optics-II. ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh 1
 Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0011678A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0011678A1 Akinlade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR INJECTING A FLUID INTO
(19) United States US 2005.0011678A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0011678A1 Akinlade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR INJECTING A FLUID INTO
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01J 5/62 ( ) G01J 3/28 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
(19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
Telescopes: Portals of Discovery
 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How do light and matter interact? Emission Absorption Transmission Transparent objects transmit light Opaque objects block (absorb) light Reflection or Scattering Reflection
Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How do light and matter interact? Emission Absorption Transmission Transparent objects transmit light Opaque objects block (absorb) light Reflection or Scattering Reflection
ABOUT SPOTTINGSCOPES Background on Telescopes
 22 November 2010 ABOUT SPOTTINGSCOPES A spotting scope is a compact telescope designed primarily for terrestrial observing and is used in applications which require magnifications beyond the range of a
22 November 2010 ABOUT SPOTTINGSCOPES A spotting scope is a compact telescope designed primarily for terrestrial observing and is used in applications which require magnifications beyond the range of a
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,104,270 Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000
 USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000 54) LIFTER WITH ELECTROPERMANENT 4.956,625 9/1990 Cardone et al.... 335/290 MAGNETS PROVIDED WITH A SAFETY
USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000 54) LIFTER WITH ELECTROPERMANENT 4.956,625 9/1990 Cardone et al.... 335/290 MAGNETS PROVIDED WITH A SAFETY
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
1986 s Nobel Prize in Physics
 Revised version: 2017.12.19 1986 s Nobel Prize in Physics (Electron Microscope & STM) Huiwon Ahn Seoul National University Department of Physics & Astronomy, Korea Abstract The structure of matter or organisms
Revised version: 2017.12.19 1986 s Nobel Prize in Physics (Electron Microscope & STM) Huiwon Ahn Seoul National University Department of Physics & Astronomy, Korea Abstract The structure of matter or organisms
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kirson et al. Y 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4.885,977 Dec. 12, 1989 (54. STABILIZED LINE-OF-SIGHT AIMING SYSTEM FOR USE WITH FIRE CONTROL SYSTEMS 75 Inventors: Yoram
United States Patent (19) Kirson et al. Y 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4.885,977 Dec. 12, 1989 (54. STABILIZED LINE-OF-SIGHT AIMING SYSTEM FOR USE WITH FIRE CONTROL SYSTEMS 75 Inventors: Yoram
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki
United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
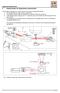 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F)
 B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
