IIIHIIIHIII. United States Patent (19) Chew et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, Patent Number: 5,417,389
|
|
|
- Wendy Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Chew et al. 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) METHOD OF, AND APPARATUS FOR, DE-CING AN AIRCRAFT BY NFRARED RADATION Inventors: Charles J. Chew, Ellicottville; Timothy P. Seel, Tonawanda, both of N.Y. Assignee: Radiant Energy Corporation, North York, Canada Appl. No.: 207,883 Filed: Mar. 7, 1994 Related U.S. Application Data (63) Continuation of Ser. No. 20,216, Feb. 19, 1993, aban doned. 51 int. Cl'... B64D 15/OO (52) U.S. C /134 R; 126/92 AC; 126/92 B 58 Field of Search /134 R, 134 C; 134/45, 123; 392/414; 126/92 AC, 92 B, 91 R (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,023,296 2/1962 Barber /414 3,194,960 7/1965 Tuttle /92 B 3,330,267 7/1967 Bauer /92 B 3,451,094 6/1969 Kywi ,378,755 4/1983 Magnusson et al... 34/23 4,682,578 7/1987 Schmidt /92 B 5,161,753 1 A1992 Vice et al /134 C IIIHIIIHIII USOO A 11 Patent Number: 5,417,389 (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 1995 Primary Examiner-William Grant Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Phillips, Lytle, Hitchcock, Blaine & Huber 57 ABSTRACT An improved apparatus (11) for emitting infrared radia tion of a desired wavelength includes a primary surface (35); a burner (24) for raising the temperature of the primary surface so as to cause the primary surface to emit infrared radiation of a first wavelength; a second ary surface (26) surrounding the primary surface in spaced relation thereto and arranged to be heated by infrared radiation emitted by the first surface and for emitting infrared radiation of a second wavelength toward the object; and an actuator (28) for selectively varying the spacing between the primary and secondary surfaces so that infrared radiation emitted by the sec ondary surface will be at a desired wavelength and will be focused; whereby the apparatus will emit infrared radiation of a desired wavelength toward the object. The improved apparatus may be used in a method of de-icing a portion of an aircraft, which includes the steps of: providing a structure (10) having an infrared heater (23); moving an aircraft relative to the structure to a position adjacent the heater; operating the heater so as to emit radiation toward the object; and controlling the wavelength of radiation emitted by the heater; thereby to melt snow and ice from the aircraft portion. 13 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets
2 U.S. Patent May 23, 1995 Sheet 1 of 3 5,417,389 Z ZZ 'ffig [ s
3 U.S. Patent May 23, 1995 Sheet 2 of 3 5,417,389
4 U.S. Patent May 23, 1995 Sheet 3 of 3 5,417,389
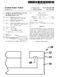
5 1. METHOD OF, AND APPARATUS FOR, DE-ICING AN AIRCRAFT BY INFRARED RADATION This is a continuation of copending application Ser. No. 08/020,216, filed on Feb. 19, 1993, now abandoned. TECHNICAL FIELD This invention relates generally to the field of meth ods of, and apparatae for, de-icing portions of an air craft on the ground, and, more particularly, to an im proved method and apparatus for de-icing an aircraft by means of a focusable, variable-wavelength infrared en ergy source. BACKGROUND ART It is sometimes necessary to de-ice certain portions of an aircraft prior to take-off. Existing technology in common use today involves the spraying of large quantities of chemicals onto the working surfaces (e.g., wings, rudder, ailerons, flaps, stabilizers, etc.) of the aircraft. These chemicals are normally applied just prior to the aircraft's departure from the boarding gate. Federal requirements dictate a maximum time interval between application of the de icing spray and take-off. This time interval is usually on the order of from about fifteen to about thirty minutes. Unfortunately, with the traffic jams common at some major airports, the departure interval is often extended beyond that recommended. If this occurs, the plane must sometimes be de-iced a second time before take off. The desire to maintain established schedules and to minimize costs makes this second step undesirable, even if needed. The presence of ice and snow on airfoil sur faces during take-off has been indicated as the probable cause of many crashes. The foregoing, when considered along with soon-to be-enforced stricter environmental regulations concern ing the handling, storage, use and collection of over sprayed de-icing chemicals, establishes a present need to find a better way to remove accumulations of ice and snow in preparation for take-off. Two types of de-icing chemicals are in use today. The United States typically uses Type I, which is a mixture of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol and water. This mixture is heated to about F., and then sprayed on the aircraft. European countries commonly use Type II. This is a blend of glycol and a thickening agent, which creates a thicker jelly-like substance. The Type It mixture does hold longer, but can affect take-off of small aircraft. Hence, it is not recommended for use on aircraft having rotation speeds of less than about 85 knots. It has been proposed that all U.S. airport de-icing equipment be modified to use European Type II chemi cals. However this has shortcomings. Upon information and belief, propylene glycol is considered safe to hu mans by the Food and Drug Administration, but is harmful to the environment. While not currently regu lated by OSHA, it has been reported to cause skin irrita tion, and is listed as a hazardous air pollutant in the Clean Air Act Amendments of Ethylene glycol is poisonous to humans, and is regulated by OSHA be cause of a risk of throat and respiratory tract irritation. The Water Quality Act of 1987 prohibits the discharge of polluted water into navigable waters and regulations have been promulgated to prevent airports from dump 5,417,389 5 O ing or discharging glycol-contaminated storm water run-off into rivers and sewer systems. Accordingly, there is believed to be a clear and pres ent need for an improved method of, and apparatus for, de-icing portions of an aircraft without the need of such de-icing chemicals. DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION This invention provides an improved method of, and apparatus for, de-icing portions of an aircraft without the need of such hazardous chemicals. In one aspect, the invention broadly provides an im proved method of deicing a portion of an aircraft, com prising the steps of: providing a structure having an infrared heater; moving an aircraft relative to said struc ture to a position adjacent said heater; operating said heater so as to emit infrared radiation toward said air craft portion; and controlling the wavelength of the radiation emitted by said heater; thereby to melt ice and snow from said aircraft portion. In another aspect, the invention provides an in proved apparatus for de-icing portions of an aircraft by a controllable radiant energy technique. The improved apparatus is arranged to emit infrared radiation of a desired wavelength toward an aircraft having a unde sired substance (e.g., ice, snow, water) thereon. The improved apparatus broadly comprises: a primary sur face (25); a heater or burner (24) for raising the tempera ture of the primary surface so as to cause the primary surface to emit infrared radiation of a first wavelength; a secondary surface (26) surrounding the primary sur face in spaced relation thereto and arranged to be heated by infrared radiation emitted by the first surface and for emitting infrared radiation of a second wave length toward the aircraft; and an actuator (28) for Selectively varying the spacing between the primary and secondary surfaces so that the wavelength of the infrared radiation emitted by the secondary surface will be at the wavelength determined by the design relation ship between the primary and secondary surfaces; whereby the apparatus will emit infrared radiation of a desired wavelength toward the aircraft. In the preferred embodiment, the wavelength of the radiation emitted toward the aircraft is the wavelength of maximum ab sorptivity of the substance-to-be-removed. Accordingly, the general object of the invention is to provide an improved method of de-icing portions of an aircraft prior to take-off. Another object is to provide improved apparatus for de-icing portions of an aircraft prior to take-off. Another object is to provide an improved method of, and apparatus for, de-icing portions of an aircraft by a radiant infrared technique, and by avoiding the use of potentially hazardous de-icing chemical in common use today. Still another object is to provide an improved method of, and apparatus for, heating a distant object by means of emitted infrared radiation. These and other objects will become apparent from the foregoing and ongoing written specification, the drawings, and the appended claims. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a flow chart of a preferred sequence of manipulative steps involved in practicing the improved method to de-ice an aircraft. FIG. 2 is a top plan view of a drive-through structure containing a plurality of infrared heaters, with the roof
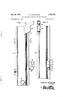
6 3 of the structure removed, and showing the array of heaters relative to two aircraft positions. FIG. 3 is the front elevational view of the drive through structure shown in FIG. 2. FIG. 4 is a fragmentary vertical sectional view of one of the heaters, showing the surrounding skirt as being in one position relative to the burner. FIG. 5 is a fragmentary vertical sectional view of one of the heaters, showing the surrounding skirt in another position relative to the burner. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT(S) At the outset, it should be clearly understood that like reference numerals are intended to identify the same structural elements, portions or surfaces consistently throughout the several drawing figures, as such ele ments, portions or surfaces may be further described or explained by the entire written specification of which this detailed description is an integral part. Unless oth erwise indicated, the drawings are intended to be read (e.g., arrangement of parts, mounting, etc.) together with the specification, and are to be considered a por tion of the entire written description of this invention. As used in the following description, the terms "hori zontal", "vertical, left, right", "up" and down", as well as adjectival and adverbial derivatives thereof (e.g., "horizontally", "rightwardly", "upwardly', etc.) simply refer to the orientation of the illustrated struc ture as the particular drawing figure faces the reader. Unless otherwise indicated, the terms "inwardly and "outwardly' refer to the orientation of a surface rela tive to its axis of elongation, or axis or rotation, as ap propriate. Turning now to the drawings, the present invention provides an improved method of, and apparatus for, heating a substance by means of emitted infrared radia tion. In one application, the method and apparatus are used to de-ice an aircraft. Referring now to FIGS. 1-3, an aircraft to be de-iced is driven through an open-ended structure, generally indicated at 10, having a plurality of overhead infrared heaters, severally indicated at 11 arranged in a rectan gular array. In FIG. 2, two aircraft positions are indi cated within the structure. The first is indicated at 12, and the second is indicated at 13. These two positions have been omitted from FIG. 3 in the interest of clarity. As best shown in FIG. 1, the aircraft first enters the drive-through de-icing structure 10, as indicated at block 14 in FIG. 1. Upon entry to that structure and/or when in the position of aircraft 12, as much ice, snow and/or water as can be removed are physically re moved. This is indicated in block 15 in FIG. 1. The means for physical removal may include an air curtain, or the like. After as much of the adherent substance as can be physically removed has been removed, the air craft then advances forwardly toward the second sta tion, indicated by aircraft position 13. This step is indi cated in block 16 of FIG. 1. Assuming that the type of aircraft is known, selected heaters are then operated to emit radiation. The particular heaters which may be operated may be determined either from the known type of the aircraft (i.e., having a known shape), or by proximity sensors (not shown) acting downwardly and operatively arranged to sense portions of the aircraft therebeneath. This latter step is indicated by block 18 in FIG. 1. In any event, only those heaters which arc aimed downwardly at portions of the aircraft are oper 5,417,389 O ated. Those heaters which are operated are selectively focused to emit radiation to maximize energy of the surface of the aircraft needed to melt ice or snow. This is indicated by blocks 19 and 20 in FIG. 1. The various heaters are operated so as to emit radiation toward the aircraft at a wavelength which coincides with the wavelength of the maximum absorptivity of the sub stance to be removed. In any event, after the adherent substances have been melted, the aircraft is then dried, as indicated in block 21 of FIG. I. The aircraft may be dried under the influence of heat with or without an accompanying air curtain. Thereafter, de-icing chemi cals are applied to the now-dry aircraft (as indicated at 22 in FIG. 1), and the aircraft then exits the de-icing structure (as indicated at 23 of FIG. 1), taxis to the runway, and is ready for take-off. FIG. 4 is a fragmentary vertical sectional view of one of the heaters shown in FIGS. 2 and 3. This heater apparatus, generally indicated at 11, broadly includes a burner 24 operatively arranged to heat a frusto-conical primary surface 25, a secondary surface 26 surrounding the primary surface in spaced relation thereto, and an actuator 28 operatively arranged to selectively vary the spacing between the primary and secondary surfaces. The heater or burner 24 is shown is including a control housing 29 having a downwardly-directed burner head 30 arranged concentrically within an elongated vertical tube 31. Thus, a flame emitted by burner 24 will travel down the tube and be discharged through the lower open end 32 thereof toward a dish-like layer of insula tion 33 arranged on the upper side of a wall 34. The heat of combustion will then heat primary surface 25, and will flow upwardly through the annular space between inner tube 31 and outer tube 35, and be vented through a lateral opening 36. The secondary surface 26 is shown as being frusto-conical in shape, and has a downwardly facing annular horizontal portion 38 at its upper end. The entire secondary surface 26,38 is insulated, as indi cated at 39. Actuator 28 has a body or housing 40 mounted on the control housing, and has a rod portion 41 connected to the insulated secondary surface. Actua tor 28 may be selectively operated to move rod 41 ei ther upwardly or downwardly, as desired. Such opera tion of the actuator effectively varies the spacing be tween the primary and secondary surfaces, and changes the output concentration and focal distance. In operation, a conventional gaseous fuel is supplied to the burner, and is ignited. The burner then issues a downwardly-directed flame against insulation 33. The flame then rolls reversely and rises upwardly to heat primary surface 25. The heat of combustion travels upwardly through the annular chamber between the inner and outer tubes 3135, and is then vented via lat eral opening 36. Thus, the heater raises the temperature of the primary surface 25, and causes it to emit infrared radiation. The temperature of the primary surface may be on the order of 2,000 F. The infrared radiation emit ted by the primary surface is directed toward the sec ondary surface and raises its temperature. The tempera ture of the secondary surface 26 is, therefore, less than that of the primary surface, and may typically be in the range of about 900-1,000 F. The secondary surface then emits infrared radiation of a desired wavelength downwardly toward the aircraft therebeneath. Thus, the primary surface radiates infrared energy to heat the secondary surface, which in turn emits radiation toward the object. The spacing between the primary and sec ondary surfaces determines the temperature of the sec
7 5 ondary surface, for a constant-temperature primary surface. One unique feature of the invention is that the actua tor 28 is selectively operated so as to vary the spacing between the primary and secondary surfaces so that the Secondary surface will emit infrared radiation of a de sired energy pattern. In the preferred embodiment, this desired wavelength is the wavelength of the maximum absorptivity of the material-to-be-removed (e.g., ice, Snow or water). Thus, the apparatus may be tuned to emit radiation at the desired wavelength by selectively varying the design between the primary and secondary surfaces. FIG. 4 depicts the depending cupshaped skirt having the secondary surface as being in one position relative to the burner, and FIG. 5 simply depicts such skirt as being in a lowered position relative to the body. This is simply to illustrate the difference in spacing between the primary and secondary surfaces. MODIFICATIONS The present invention contemplates that many changes and modifications may be made. While it is presently preferred to use the apparatus to selectively de-ice aircraft, the person skilled in this art will readily appreciate that the improved method and apparatus could, alternatively, be used to simply heat an object. Accordingly, this alternative use should not be ex cluded from the scope of the claims unless an express limitation to the effect appears therein. The improved method may include a greater or lesser number of steps than those shown in FIG. 1. Similarly, the structure of the apparatus may differ from that shown in FIGS. 4 and 5. For example, the primary surface 25 need not be frusto-conical, but could be con vex or arcuate, as desired. Similarly, the outer tube 35 could be tapered upwardly so as to provide a progres sive flow restriction, all with the concomitant advan tage of also heating outer tube 35. Similarly, the in verted cup-shaped skirt which forms the body of the secondary surface need not be of the particular form and shape shown. In other words, the secondary surface could be arcuate, parabolic, or some other concave surface, as desired. Therefore, while preferred forms of the improved method and apparatus have been shown and described, and several modifications thereof discussed, persons skilled in this art will readily appreciate the various additional changes and modifications may be made without departing from the spirit of the invention, as defined and differentiated by the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. A method of de-icing a portion of an object, com prising the steps of: providing a structure having a source of infrared radiation, said source including a first means for emitting infrared radiation of a first wavelength and a second means spaced from said first means and heated by the infrared radiation emitted by said first means for emitting infrared radiation of a sec ond wavelength; moving an object relative to said structure to a posi tion adjacent said source of infrared radiation; operating said source of infrared radiation so as to emit infrared radiation of said second wavelength toward the portion of said object to be de-iced; and controlling the second wavelength of the radiation emitted by said source of infrared radiation by adjusting the spacing between the first means and 5,417,389 S O the second means, thus controlling the emitted infrared radiation distribution so as to maximize the absorption of such radiation by any snow and ice to be melted from said object portion; thereby to provide radiant infrared energy at a high output and at a desired wavelength to melt the snow and ice from said object portion. 2. The method as set forth in claim 1, and further comprising the additional step of: physically removing accumulations or ice and snow from said object portion prior to the step of operating said source of infrared radiation. 3. The method as set forth in claim 1, and further comprising the additional step of drying said object portion after ice and snow have been melted therefrom. 4. The method as set forth in claim 3, and further comprising the additional step of applying an anti-icing chemical to said object portion after snow and ice have been melted therefron. 5. The method as set forth in claim 1, and further comprising the additional step of applying an anti-icing chemical to said object portion after snow and ice have been melted therefrom. 6. The method as set forth in claim 1, and further comprising the additional step of focusing such emitted radiation distribution said object portion. 7. The method as set forth in claim 1, wherein said source of infrared radiation further comprises: said first means comprising a primary surface; a heater for raising the temperature of said primary surface so as to cause said primary surface to emit said infrared radiation of said first wavelength; said second means comprising a secondary surface surrounding said primary surface in spaced relation thereto and arranged to be heated by said infrared radiation emitted by said primary surface for emit ting said infrared radiation at said second wave length toward said object; and an actuator for selectively varying the spacing be tween said primary and secondary surfaces so that said infrared radiation emitted by said secondary surface will be at said desired wavelength and will be focused. 8. A method of heating a portion of an object, con prising the steps of: providing a structure having an infrared heater, a first means for emitting infrared radiation of a first wavelength, and a second means spaced from said first means and heated by the infrared radiation emitted by said first means for emitting infrared radiation of a second wavelength; moving an object relative to said structure to a posi tion adjacent to said heater; operating said heater so as to emit infrared radiation of said second wavelength toward the portion of said object to be heated; and controlling the second wavelength of the radiation emitted by said heater by adjusting the spacing between the first means and the second means, thus controlling the emitted infrared radiation distribu tion so as to maximize the absorption of such radia tion by said object portion; thereby to heat said object portion. 9. Apparatus for emitting infrared radiation of a de sired wavelength toward an object, comprising: a primary surface;
8 5,417,389 7 a heater for raising the temperature of said primary Surface so as to cause said primary surface to emit infrared radiation of a first wavelength; a Secondary surface surrounding said primary surface in spaced relation thereto and arranged to be 5 heated by infrared radiation emitted by said pri mary surface and for emitting infrared radiation of a second wavelength toward said object; and an actuator for selectively varying the spacing be tween said primary and secondary surfaces so that 10 infrared radiation emitted by said secondary sur face will be at a desired wavelength and will be focused; whereby said apparatus will emit infrared radiation of a desired wavelength toward said object The apparatus as set forth in claim 9 wherein said primary surface is frusto-conical, and faces away from said object. 11. The apparatus as set forth in claim 10 wherein a portion of said secondary surface is frusto-conical, and faces toward said object. 12. The apparatus as set forth in claim 9 wherein said heater has an elongated tube, and wherein said second ary surface is slidably mounted on said tube. 13. The apparatus as set forth in claim 9 wherein said object is an aircraft having a substance thereon, and wherein the wavelength of infrared radiation emitted by said secondary surface is the wavelength of maxi mum absorptivity of said substance. k s
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace. Aig. / May 28, ,793,758. Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey. Filed March 28, 1956 MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING
 May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
- o. ( 12 ) United States Patent. ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2. ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, Wang
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB 3,187,583. ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION SPACE SIMULATOR A. IMAGE OF LIGHT SOURCE (C)
 June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION Filed Nov. 9, 196 4 SheetsSheet 1 RADIATION SOURCE (C) SPHERCA REFLECTOR EPICA REFLECTOR R 2 A. IMAGE OF LIGHT
June 8, 1965 JAMES E. WEBB ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NATIONAL AERONAUTCs AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION Filed Nov. 9, 196 4 SheetsSheet 1 RADIATION SOURCE (C) SPHERCA REFLECTOR EPICA REFLECTOR R 2 A. IMAGE OF LIGHT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
Ulllt?d States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,003,186. Chang et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 1991
![Ulllt?d States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,003,186. Chang et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 1991 Ulllt?d States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,003,186. Chang et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 1991](/thumbs/73/69581375.jpg) Ulllt?d States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,003,186 Chang et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 1991 [54] STRATOSPHERIC WELSBACH SEEDING Primary Examiner-Jack I. Berman FOR REDUCTION OF GLOBAL WARMING
Ulllt?d States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,003,186 Chang et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 1991 [54] STRATOSPHERIC WELSBACH SEEDING Primary Examiner-Jack I. Berman FOR REDUCTION OF GLOBAL WARMING
Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
United States Patent (19) Rex
 United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.:
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
100-N. (12) United States Patent N 2 Q US 7,234,334 B1. Jun. 26, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: SZZ
 USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1
 USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
III M
 III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
BY ye; v P. April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY 3,441,626. TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 INVENTOR. PRODUCT C. S.
 April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0087224 A1 Kim et al. US 20140087224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) ELECTRODE ASSEMBLY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2
 USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
AA. *alt24& DS. (12) United States Patent US 6,607,370 B2. Aug. 19, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Fukamachi et al.
 (12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Dorisio Deininger et al. 54 ELECTROCHEMICAL SENSOR FOR THE DETECTION OF HYDROGEN CYANIDE 75 Inventors: Debra J. Dorisio Deininger, Longmont, Colo.; Towner B. Scheffler, Butler,
United States Patent (19) Dorisio Deininger et al. 54 ELECTROCHEMICAL SENSOR FOR THE DETECTION OF HYDROGEN CYANIDE 75 Inventors: Debra J. Dorisio Deininger, Longmont, Colo.; Towner B. Scheffler, Butler,
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS 22. 8a 1. United States Patent (19) Maru et al. 11 4,365,007 45) Dec. 21, 1982
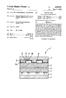 United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,261,710 B1
 USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
(19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
United States Patent (19) Eizenhoefer et al.
 United States Patent (19) Eizenhoefer et al. (54) PIEZOELECTRICSHOCKWAVE GENERATOR 75 Inventors: Harald Eizenhoefer, Johannesberg: Ernst Marlinghaus, Germering, both 73 Assignee: 21) Appl. No.: 779,113
United States Patent (19) Eizenhoefer et al. (54) PIEZOELECTRICSHOCKWAVE GENERATOR 75 Inventors: Harald Eizenhoefer, Johannesberg: Ernst Marlinghaus, Germering, both 73 Assignee: 21) Appl. No.: 779,113
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
2,479,673. Aug. 23, HTTO/P/VZY. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE. 2 Sheets~Sheet 1
 Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL MICROWAVE TRANSMISSION ' SYSTEM HAVING DIELECTRIC LENS 2 Sheets~Sheet 1 HTTO/P/VZY Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL
Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL MICROWAVE TRANSMISSION ' SYSTEM HAVING DIELECTRIC LENS 2 Sheets~Sheet 1 HTTO/P/VZY Aug. 23, 1949. Filed Aug. 20, 1945 H. B. DEVORE DIRECTIONAL
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
United States Patent (19) Baravaglio 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 1985 (54) BULLET TRAP FOR A SHOOTING STAND 76 Inventor: Marie E. Baravaglio, 5, rue des Lacs, 910 Grigny 2, France 21
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Jul.
 US 20060145019A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0145019 A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) TRIANGULAR SPACECRAFT Publication Classi?cation (51)
US 20060145019A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0145019 A1 St. Clair (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) TRIANGULAR SPACECRAFT Publication Classi?cation (51)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2
 USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
Anti-sway control system for cantilever cranes
 Wednesday, October 4, 2000 United States Patent: 5,526,946 Page: 1 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,526,946 Overton June 18, 1996 Anti-sway control system for cantilever cranes Abstract A process employing
Wednesday, October 4, 2000 United States Patent: 5,526,946 Page: 1 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,526,946 Overton June 18, 1996 Anti-sway control system for cantilever cranes Abstract A process employing
Method of modifying weather
 Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,277,278 B1
 USOO6277278B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,277,278 B1 Conrad et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 21, 2001 (54) CYCLONE SEPARATOR HAVING A 1897,144 2/1933 Prouty. WARIABLE LONGITUDINAL
USOO6277278B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,277,278 B1 Conrad et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 21, 2001 (54) CYCLONE SEPARATOR HAVING A 1897,144 2/1933 Prouty. WARIABLE LONGITUDINAL
Combustion knock detection and control through statistical characterization of knock levels
 Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Michigan Tech Patents Vice President for Research Office 8-19-2008 Combustion knock detection and control through statistical characterization
Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Michigan Tech Patents Vice President for Research Office 8-19-2008 Combustion knock detection and control through statistical characterization
United States Patent (19) Foosnaes et al.
 United States Patent (19) Foosnaes et al. USOO5606419A 11 Patent Number: 5,606,419 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 54 SPECTROSCOPIC MEASURING DEVICE HAVING FILTER CONSISTING OF INTERFERENCE FILTER, ONE
United States Patent (19) Foosnaes et al. USOO5606419A 11 Patent Number: 5,606,419 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 54 SPECTROSCOPIC MEASURING DEVICE HAVING FILTER CONSISTING OF INTERFERENCE FILTER, ONE
United States Patent (11) 3,630,782. electrical potential of primary batteries of the type immersible. Appl. No. 865,429
 United States Patent 72) 21 22 45) 54 52 51) Inventor Edwin K. Butler, deceased, late of St. Petersburg, Fa, by Adrina Neil Butler, beneficiary of the estate, 6762 7th St., South St. Petersburg, Fla. 33712
United States Patent 72) 21 22 45) 54 52 51) Inventor Edwin K. Butler, deceased, late of St. Petersburg, Fa, by Adrina Neil Butler, beneficiary of the estate, 6762 7th St., South St. Petersburg, Fla. 33712
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO6108491A Patent Number: Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2000 54) DUAL SURFACE REFLECTOR 5,556.275 9/1996 Sakata et al.. 5,595,241 1/1997 Jelinek. (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO6108491A Patent Number: Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2000 54) DUAL SURFACE REFLECTOR 5,556.275 9/1996 Sakata et al.. 5,595,241 1/1997 Jelinek. (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
TEPZZ 95785_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
No. 371,306. Patented 00t, ll, l887.
 (No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 1. H. CON ANT. ASTRONOMICAL CL00K. No. 371,306. Patented 00t, ll, l887. INVENTOR: ATTORNEYS, PETERs, Photo-Lithographer. Washinxton, C. * (No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 2. H. CONANT
(No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 1. H. CON ANT. ASTRONOMICAL CL00K. No. 371,306. Patented 00t, ll, l887. INVENTOR: ATTORNEYS, PETERs, Photo-Lithographer. Washinxton, C. * (No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 2. H. CONANT
