Computational Astrophysics
|
|
|
- Dorothy Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Alexander Knebe, Unversdad Autonoma de Madrd
2 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty the equatons full set of equatons collsonless matter (e.g. dark matter d x DM = v DM dt d v DM = φ dt Posson s equaton Δφ = 4πGρ tot collsonal matter (e.g. gas deal gas equatons ρ t + ρ v ( = 0 p = ( γ 1ρε ( ρ v t & + ρ v v & ( + ( p + 1 ' ' 2µ B2 " B B + * µ * = ρ ( φ ρε = ρe 1 2 ρv 2 ( ρe t,% +. ' ρe + p + 1 -& 2µ B2 ( * v 1 µ v B [ ] B / 1 0 = ρ v ( φ + ( Γ L Maxwell s equaton B t = v B (
3 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty the equatons full set of equatons collsonless matter (e.g. dark matter d x DM = v DM dt d v DM = φ and the force dt Posson s equaton Δφ = 4πGρ tot collsonal matter (e.g. gas deal gas equatons ρ t + ρ v ( = 0 p = ( γ 1ρε ( ρ v t & + ρ v v & ( + ( p + 1 ' ' 2µ B2 " B B + * µ * = ρ ( φ ρε = ρe 1 2 ρv 2 ( ρe t,% +. ' ρe + p + 1 -& 2µ B2 ( * v 1 µ v B [ ] B / 1 0 = ρ v ( φ + ( Γ L Maxwell s equaton B t = v B (
4 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Posson s Equaton Posson s equaton F ( x = m Φ( x ΔΦ( x = 4πGρ( x
5 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Posson s Equaton Posson s equaton F ( x = m Φ( x ΔΦ( x = 4πGρ( x partcle approach F ( x Gm = m j (x x j ( x 3 x j j grd approach ΔΦ( x, j,k = 4πGρ( x, j,k F ( x, j,k = m Φ( x, j,k ( x, j,k =poston of centre of grd cell (, j,k
6 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Posson s equaton F ( x = m Φ( x ΔΦ( x = 4πGρ( x weapon of choce: tree codes grd approach ΔΦ( x, j,k = 4πGρ( x, j,k F ( x, j,k = m Φ( x, j,k Posson s Equaton partcle approach F ( x Gm = m j (x x j ( x 3 x j j ( x, j,k =poston of centre of grd cell (, j,k
7 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Posson s Equaton Posson s equaton F ( x = m Φ( x ΔΦ( x = 4πGρ( x partcle approach F ( x Gm = m j (x x j ( x 3 x j j grd approach ΔΦ( x, j,k = 4πGρ( x, j,k F ( x, j,k = m Φ( x, j,k ( x, j,k =poston of centre of grd cell (, j,k weapon of choce: AMR codes
8 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty the partcle-mesh (PM method
9 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m
10 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m
11 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x N N
12 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x sounds lke a waste of tme and computer resources, but exceptonally fast n practce
13 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x
14 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m example: 1 partcle on 1 dmensonal grd M(g k = mw (d d = x g k ρ(g k = M(g k H partcle poston x grd pont g k H m x axs
15 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m example: 1 partcle on 1 dmensonal grd M(g k = mw (d ρ(g k = M(g k H d = x g k mass assgnment functon partcle poston x grd pont g k H m x axs
16 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m example: 1 partcle on 1 dmensonal grd herarchy of mass assgnment schemes: - Nearest-Grd-Pont NGP - Could-In-Cell CIC - Trangular-Shaped Cloud TSC - partcle poston x grd pont g k H m x axs
17 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m Nearest-Grd-Pont (NGP: mass assgnment functon: # W (d = $ 1 d H /2 % 0 otherwse H m x axs
18 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m Nearest-Grd-Pont (NGP: partcle shape: S(x = δ(x mass assgnment functon: # W (d = $ 1 d H /2 % 0 otherwse H m x axs
19 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m Cloud-In-Cell (CIC: mass assgnment functon: $ 1 d & H W (d = % d H & 0 '& otherwse H m x axs
20 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m Cloud-In-Cell (CIC: partcle shape: # S(x = $ 1 x H /2 % 0 otherwse mass assgnment functon: $ 1 d & H W (d = % d H & 0 '& otherwse H m x axs
21 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m Trangular-Shaped-Cloud (TSC: * 3 4 d 2 # &, % ( d H mass assgnment functon:, $ H ' 2, W (d = 1# 3 % 2 2 d 2 + & H, ( $ H ' 2 d 3H 2,, -, 0 otherwse H m x axs
22 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m Trangular-Shaped-Cloud (TSC: partcle shape: $ & S(x = 1 x % x H H '& 0 otherwse * 3 4 d 2 # &, % ( d H mass assgnment functon:, $ H ' 2, W (d = 1# 3 % 2 2 d 2 + & H, ( $ H ' 2 d 3H 2,, -, 0 otherwse H m x axs
23 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m N partcles on 3 dmensonal grd d = x g k,l,m M( g N k,l,m = m W ( d x W ( d y W ( d z =1 ρ( g k,l,m = M( g k,l,m H 3
24 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes x ρ( g k,l,m N partcles on 3 dmensonal grd d = x g k,l,m M( g N k,l,m = m W ( d x W ( d y W ( d z =1 for every grd pont we need to loop over all N partcles ρ( g k,l,m = M( g k,l,m H 3
25 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes - n practce x ρ( g k,l,m rather loop over all partcles and assgn them to the approprate grd ponts, because the mappng x g k s rather easy
26 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes - n practce x ρ( g k,l,m example for CIC assgnment n 2D: x contrbutes ts mass m to the 4 closest grd ponts : m
27 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes - n practce x ρ( g k,l,m example for CIC assgnment n 3D: x contrbutes ts mass m to the 8 closest grd ponts : g k,l,m +1 g k +1,l,m +1 g k,l,m g k +1,l,m g k,l +1,m +1 g k +1,l +1,m +1 g k,l +1,m g k +1,l +1,m
28 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes whch scheme to choose? NGP = stepwse force CIC = contnuous pecewse lnear force (1 grd pont (8 grd ponts TSC = contnuous force and frst dervatve (27 grd ponts
29 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes whch scheme to choose? NGP = too crude CIC = common choce ncreased smoothng of densty feld TSC = pretty smooth smoothng the densty feld wll lead to a bas n the forces but at the same tme decrease the varance bas = ( F( x F true ( x ε α var = F 2 ( x F( x 2 N β
30 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method densty assgnment schemes whch scheme to choose? NGP = too crude CIC = common choce TSC = pretty smooth smoothng the densty feld wll lead to a bas n the forces but at the same tme decrease the varance bas = ( F( x F true ( x ε α var = F 2 ( x F( x 2 N β (nterplay between N and ε: Nε 3 =const.
31 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x
32 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m relaxaton technque: FTT technque: applcable and usable for any dfferental equaton only applcable and usable for lnear dfferental equaton
33 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque obtan teratve solver by dscretzng dfferental equaton ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m
34 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque obtan teratve solver by dscretzng dfferental equaton ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m ΔΦ k,l,m = Φ k,l,m ' * ' Φ *, k,l,m, x, x, =, Φ k,l,m, y, y, Φ, k,l,m, ( z + ( z + ' *, ' = 1 x, Φ Φ * k + 1,l,m k 1,l,m 2 2,, Φ H y, Φ, k,l + 1,m k,l 1,m 2 2 Φ k,l,m + 1 Φ, k,l,m 1, ( ( z + = 1 ' Φ k + 1 Φ,l,m k 1,l,m H ( x x Φ k,l + 1 2,m y Φ k,l 1 2,m y + Φ k,l,m z Φ k,l,m 1 2 z = 1 ( Φ H 2 k +1,l,m 2Φ k,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m 2Φ k,l,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 2Φ k,l,m + Φ k,l,m 1 *, +
35 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque obtan teratve solver by dscretzng dfferental equaton ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m dscretzed Posson s equaton Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
36 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque obtan teratve solver by dscretzng dfferental equaton ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m teratve soluton: Φ k,l,m +1 Φ k,l,m dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
37 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque obtan teratve solver by dscretzng dfferental equaton k,l+1,m k-1,l,m k,l,m k+1,l,m k,l-1,m dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
38 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque obtan teratve solver by dscretzng dfferental equaton k-1,l,m k,l+1,m k,l,m k,l-1,m k+1,l,m applcable to grds of arbtrary geometry dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
39 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque how to sweep through the grd? k,l+1,m k-1,l,m k,l,m k+1,l,m k,l-1,m dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
40 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque how to sweep through the grd?? dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
41 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque how to sweep through the grd?? dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
42 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque Gauss-Sedel sweeps: k,l+1,m k-1,l,m k,l,m k+1,l,m k,l-1,m dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
43 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque Gauss-Sedel sweeps: loop over all black cells loop over all red cells one teraton of the potental Φ k,l,m +1 Φ k,l,m how many teratons are necessary? dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
44 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
45 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: ΔΦ k,l,m? ρ k,l,m & 0 dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
46 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: ΔΦ k,l,m? ρ k,l,m & 0 densty as gven by mass assgnment scheme densty as gven by currently best guess for Φ dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
47 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: ΔΦ k,l,m? ρ k,l,m & 0 resdual: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m = sutable norm dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
48 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: ΔΦ k,l,m? ρ k,l,m & 0 R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ = sutable norm tolerance error estmate dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
49 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ - truncaton error: error due to dscreteness of grd dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
50 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ - truncaton error: error due to dscreteness of grd estmaton "" " compare soluton on actual grd to soluton on coarser grd dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
51 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ = ε T k,l,m - truncaton error: [ ] ΔΦ k,l,m Τ k,l,m = P Δ( RΦ k,l,m ( RΦ k,l,m Δ RΦ k,l,m =Φ j,n,p 1 ( = ρ j,n, p ( [ ] = ρ k,l,m P Δ RΦ k,l,m restrcton to coarser grd prolongaton to fner grd dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
52 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ = ε T k,l,m - truncaton error: [ ] ΔΦ k,l,m Τ k,l,m = P Δ( RΦ k,l,m ( RΦ k,l,m =Φ j,n,p 1 Δ( RΦ k,l,m = ρ j,n, p [ ( ] = ρ k,l,m P Δ RΦ k,l,m? = ΔΦ k,l,m dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
53 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ = ε T k,l,m R εt dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
54 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque stoppng crteron: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m ετ = ε T k,l,m R faster convergence? εt dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
55 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque convergence: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m - slow convergence: R +1 R large-scale errors n Φ cannot be relaxed suffcently fast on the actual grd => use coarser grds to speed up convergence dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
56 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton relaxaton technque convergence: R = ΔΦ k,l,m ρ k,l,m - slow convergence: R +1 R mult-grd relaxaton technques => beyond the scope of ths lecture though dscretzed Posson s equaton +1 Φ k,l,m = 1 6 (Φ k +1,l,m + Φ k 1,l,m + Φ k,l +1,m + Φ k,l 1,m + Φ k,l,m +1 + Φ k,l,m 1 ρ k,l,m H 2
57 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ k,l,m = ρ k,l,m Green s functon method: - solve dfferental equaton by Fourer transformaton - applcable and usable for lnear dfferental equatons
58 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton fast fourer transform method Green s functon method ΔΦ = ρ Φ( x = G( x x $ ρ( x $ d 3 $ x ; G( x = 1 4π x
59 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton fast fourer transform method Green s functon method ΔΦ = ρ Φ( x = G( x x $ ρ( x $ d 3 $ x ; G( x = 1 4π x Φ = ρ G FFT " convoluton becomes multplcaton ˆ Φ = ˆ ρ ˆ G (wth G ˆ = 1 for Posson s equaton k 2
60 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton fast fourer transform method Green s functon method ΔΦ = ρ Φ( x = G( x x $ ρ( x $ d 3 $ x ; G( x = 1 4π x Φ = ρ G FFT " convoluton becomes multplcaton ˆ Φ = ˆ ρ ˆ G (wth G ˆ = 1 for Posson s equaton k 2 Φ FFT -1 (FFT demands a regular grd though
61 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton fast fourer transform method dscretzed Green s functon G ˆ ( k = 1 k 2 " G ˆ ( g k,l,m = # sn 2 % $ k x 2 1 & # ( + sn k & 2 y # k % ( + sn 2 z & % ( ' $ 2 ' $ 2 ' G ˆ ( g 0,0,0 = 0, k x = 2π k L, k y = 2π l L, k y = 2π m L
62 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton accuracy of ether relaxaton or FFT method to solve Posson s equaton?
63 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton
64 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton
65 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton the force s automatcally softened... (cf. tree-code lecture
66 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton the force s automatcally softened...but what f need to resolve smaller scales?
67 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton ntroducton of fner grds n hgh densty regons
68 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton AMR calculaton Yahag & Yosh (2001
69 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton AMR calculaton detals later Yahag & Yosh (2001
70 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton and what are these wggles?
71 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton and what are these wggles?
72 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton pure PM calculaton force ansotropy and what are these wggles?
73 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x
74 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method obtanng the forces F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m F x ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k +1,l,m Φ( g k 1,l,m 2H F y ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l +1,m Φ( g k,l 1,m F z ( g k,l,m = m Φ( 2H g k,l,m +1 Φ( g k,l,m 1 2H k-1,l,m k,l+1,m k,l,m k,l-1,m k+1,l,m H = (current grd spacng
75 Computatonal Astrophyscs Partcle-Mesh Method Solvng for Gravty numercally ntegrate Posson s equaton ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x
76 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method nterpolatng the forces F ( g k,l,m F ( r
77 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method nterpolatng the forces F ( g k,l,m F ( r use the nverse of the mass assgnment scheme to nsure momentum conservaton and mnmze force ansotropes F( r = k l m F( g k,l,m W ( r g k,l,m n practce the trple sum s only over 8 (CIC or 27 (TSC cells
78 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh Method nterpolatng the forces F ( g k,l,m F ( r use the nverse of the mass assgnment scheme to nsure momentum conservaton and mnmze force ansotropes F( r = k l m F( g k,l,m W ( r g k,l,m *check by calculatng the total (perodc force: N F tot = F( r = =... = N =1 =1 k l m N N =... =1 j=1 k,l,m k #, l #, m# F( g k,l,m W ( r g k,l,m m m j W ( r H 3 g k,l,m G( g k,l,m g k #, l #, m # W ( r j g # ant-symmetrc = 0 (because of nvarance under coordnate nverson k, l #, m # PM scheme: F x ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k+1,l,m Φ( g k 1,l,m 2H Φ( g k,l,m = G( g k,l,m g k #, l #, m # ρ( g # k# l# m# ρ( g k,l,m = M( g k,l,m H 3 N M( g k,l,m = m W ( r g k,l,m =1 k, l #, m #
79 Computatonal Astrophyscs Summary Solvng for Gravty Partcle-Mesh (PM method ΔΦ( g k,l,m = 4πGρ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m = m Φ( g k,l,m 1. calculate mass densty on grd 2. solve Posson s equaton on grd 3. dfferentate potental to get forces 4. nterpolate forces back to partcles x ρ( g k,l,m Φ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( g k,l,m F ( x anyone fances to wrte a PM code as the project?
80 Computatonal Astrophyscs Solvng for Gravty Alexander Knebe, Unversdad Autonoma de Madrd
CME 302: NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA FALL 2005/06 LECTURE 13
 CME 30: NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA FALL 005/06 LECTURE 13 GENE H GOLUB 1 Iteratve Methods Very large problems (naturally sparse, from applcatons): teratve methods Structured matrces (even sometmes dense,
CME 30: NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA FALL 005/06 LECTURE 13 GENE H GOLUB 1 Iteratve Methods Very large problems (naturally sparse, from applcatons): teratve methods Structured matrces (even sometmes dense,
Chapter 5. Solution of System of Linear Equations. Module No. 6. Solution of Inconsistent and Ill Conditioned Systems
 Numercal Analyss by Dr. Anta Pal Assstant Professor Department of Mathematcs Natonal Insttute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209 emal: anta.bue@gmal.com 1 . Chapter 5 Soluton of System of Lnear Equatons
Numercal Analyss by Dr. Anta Pal Assstant Professor Department of Mathematcs Natonal Insttute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209 emal: anta.bue@gmal.com 1 . Chapter 5 Soluton of System of Lnear Equatons
Lecture 21: Numerical methods for pricing American type derivatives
 Lecture 21: Numercal methods for prcng Amercan type dervatves Xaoguang Wang STAT 598W Aprl 10th, 2014 (STAT 598W) Lecture 21 1 / 26 Outlne 1 Fnte Dfference Method Explct Method Penalty Method (STAT 598W)
Lecture 21: Numercal methods for prcng Amercan type dervatves Xaoguang Wang STAT 598W Aprl 10th, 2014 (STAT 598W) Lecture 21 1 / 26 Outlne 1 Fnte Dfference Method Explct Method Penalty Method (STAT 598W)
STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 2018 LECTURE 16
 STAT 39: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 218 LECTURE 16 1 why teratve methods f we have a lnear system Ax = b where A s very, very large but s ether sparse or structured (eg, banded, Toepltz, banded plus
STAT 39: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 218 LECTURE 16 1 why teratve methods f we have a lnear system Ax = b where A s very, very large but s ether sparse or structured (eg, banded, Toepltz, banded plus
Polynomial Regression Models
 LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE XII Lecture - 6 Polynomal Regresson Models Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur Test of sgnfcance To test the sgnfcance
LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE XII Lecture - 6 Polynomal Regresson Models Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur Test of sgnfcance To test the sgnfcance
Relaxation Methods for Iterative Solution to Linear Systems of Equations
 Relaxaton Methods for Iteratve Soluton to Lnear Systems of Equatons Gerald Recktenwald Portland State Unversty Mechancal Engneerng Department gerry@pdx.edu Overvew Techncal topcs Basc Concepts Statonary
Relaxaton Methods for Iteratve Soluton to Lnear Systems of Equatons Gerald Recktenwald Portland State Unversty Mechancal Engneerng Department gerry@pdx.edu Overvew Techncal topcs Basc Concepts Statonary
6.3.4 Modified Euler s method of integration
 6.3.4 Modfed Euler s method of ntegraton Before dscussng the applcaton of Euler s method for solvng the swng equatons, let us frst revew the basc Euler s method of numercal ntegraton. Let the general from
6.3.4 Modfed Euler s method of ntegraton Before dscussng the applcaton of Euler s method for solvng the swng equatons, let us frst revew the basc Euler s method of numercal ntegraton. Let the general from
Lecture 12: Discrete Laplacian
 Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Georgia Tech PHYS 6124 Mathematical Methods of Physics I
 Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Lecture 13 APPROXIMATION OF SECOMD ORDER DERIVATIVES
 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS: FDM: Appromaton of Second Order Dervatves Lecture APPROXIMATION OF SECOMD ORDER DERIVATIVES. APPROXIMATION OF SECOND ORDER DERIVATIVES Second order dervatves appear n dffusve
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS: FDM: Appromaton of Second Order Dervatves Lecture APPROXIMATION OF SECOMD ORDER DERIVATIVES. APPROXIMATION OF SECOND ORDER DERIVATIVES Second order dervatves appear n dffusve
2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics Fall 2011 Lecture 12
 REVIEW Lecture 11: 2.29 Numercal Flud Mechancs Fall 2011 Lecture 12 End of (Lnear) Algebrac Systems Gradent Methods Krylov Subspace Methods Precondtonng of Ax=b FINITE DIFFERENCES Classfcaton of Partal
REVIEW Lecture 11: 2.29 Numercal Flud Mechancs Fall 2011 Lecture 12 End of (Lnear) Algebrac Systems Gradent Methods Krylov Subspace Methods Precondtonng of Ax=b FINITE DIFFERENCES Classfcaton of Partal
Integrals and Invariants of Euler-Lagrange Equations
 Lecture 16 Integrals and Invarants of Euler-Lagrange Equatons ME 256 at the Indan Insttute of Scence, Bengaluru Varatonal Methods and Structural Optmzaton G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechancal Engneerng,
Lecture 16 Integrals and Invarants of Euler-Lagrange Equatons ME 256 at the Indan Insttute of Scence, Bengaluru Varatonal Methods and Structural Optmzaton G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechancal Engneerng,
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructions
 THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
( ) [ ( k) ( k) ( x) ( ) ( ) ( ) [ ] ξ [ ] [ ] [ ] ( )( ) i ( ) ( )( ) 2! ( ) = ( ) 3 Interpolation. Polynomial Approximation.
![( ) [ ( k) ( k) ( x) ( ) ( ) ( ) [ ] ξ [ ] [ ] [ ] ( )( ) i ( ) ( )( ) 2! ( ) = ( ) 3 Interpolation. Polynomial Approximation. ( ) [ ( k) ( k) ( x) ( ) ( ) ( ) [ ] ξ [ ] [ ] [ ] ( )( ) i ( ) ( )( ) 2! ( ) = ( ) 3 Interpolation. Polynomial Approximation.](/thumbs/84/90601477.jpg) 3 Interpolaton {( y } Gven:,,,,,, [ ] Fnd: y for some Mn, Ma Polynomal Appromaton Theorem (Weerstrass Appromaton Theorem --- estence ε [ ab] f( P( , then there ests a polynomal
3 Interpolaton {( y } Gven:,,,,,, [ ] Fnd: y for some Mn, Ma Polynomal Appromaton Theorem (Weerstrass Appromaton Theorem --- estence ε [ ab] f( P( , then there ests a polynomal
10/23/2003 PHY Lecture 14R 1
 Announcements. Remember -- Tuesday, Oct. 8 th, 9:30 AM Second exam (coverng Chapters 9-4 of HRW) Brng the followng: a) equaton sheet b) Calculator c) Pencl d) Clear head e) Note: If you have kept up wth
Announcements. Remember -- Tuesday, Oct. 8 th, 9:30 AM Second exam (coverng Chapters 9-4 of HRW) Brng the followng: a) equaton sheet b) Calculator c) Pencl d) Clear head e) Note: If you have kept up wth
Multigrid Methods and Applications in CFD
 Multgrd Metods and Applcatons n CFD Mcael Wurst 0 May 009 Contents Introducton Typcal desgn of CFD solvers 3 Basc metods and ter propertes for solvng lnear systems of equatons 4 Geometrc Multgrd 3 5 Algebrac
Multgrd Metods and Applcatons n CFD Mcael Wurst 0 May 009 Contents Introducton Typcal desgn of CFD solvers 3 Basc metods and ter propertes for solvng lnear systems of equatons 4 Geometrc Multgrd 3 5 Algebrac
Some Comments on Accelerating Convergence of Iterative Sequences Using Direct Inversion of the Iterative Subspace (DIIS)
 Some Comments on Acceleratng Convergence of Iteratve Sequences Usng Drect Inverson of the Iteratve Subspace (DIIS) C. Davd Sherrll School of Chemstry and Bochemstry Georga Insttute of Technology May 1998
Some Comments on Acceleratng Convergence of Iteratve Sequences Usng Drect Inverson of the Iteratve Subspace (DIIS) C. Davd Sherrll School of Chemstry and Bochemstry Georga Insttute of Technology May 1998
MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING LEARNING. Gaussian Mixture Regression
 11 MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING LEARNING MACHINE LEARNING Gaussan Mture Regresson 22 MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING LEARNING Bref summary of last week s lecture 33 MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING
11 MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING LEARNING MACHINE LEARNING Gaussan Mture Regresson 22 MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING LEARNING Bref summary of last week s lecture 33 MACHINE APPLIED MACHINE LEARNING
2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics
 REVIEW Lecture 10: Sprng 2015 Lecture 11 Classfcaton of Partal Dfferental Equatons PDEs) and eamples wth fnte dfference dscretzatons Parabolc PDEs Ellptc PDEs Hyperbolc PDEs Error Types and Dscretzaton
REVIEW Lecture 10: Sprng 2015 Lecture 11 Classfcaton of Partal Dfferental Equatons PDEs) and eamples wth fnte dfference dscretzatons Parabolc PDEs Ellptc PDEs Hyperbolc PDEs Error Types and Dscretzaton
Lecture 2: Numerical Methods for Differentiations and Integrations
 Numercal Smulaton of Space Plasmas (I [AP-4036] Lecture 2 by Lng-Hsao Lyu March, 2018 Lecture 2: Numercal Methods for Dfferentatons and Integratons As we have dscussed n Lecture 1 that numercal smulaton
Numercal Smulaton of Space Plasmas (I [AP-4036] Lecture 2 by Lng-Hsao Lyu March, 2018 Lecture 2: Numercal Methods for Dfferentatons and Integratons As we have dscussed n Lecture 1 that numercal smulaton
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
A New Refinement of Jacobi Method for Solution of Linear System Equations AX=b
 Int J Contemp Math Scences, Vol 3, 28, no 17, 819-827 A New Refnement of Jacob Method for Soluton of Lnear System Equatons AX=b F Naem Dafchah Department of Mathematcs, Faculty of Scences Unversty of Gulan,
Int J Contemp Math Scences, Vol 3, 28, no 17, 819-827 A New Refnement of Jacob Method for Soluton of Lnear System Equatons AX=b F Naem Dafchah Department of Mathematcs, Faculty of Scences Unversty of Gulan,
Feb 14: Spatial analysis of data fields
 Feb 4: Spatal analyss of data felds Mappng rregularly sampled data onto a regular grd Many analyss technques for geophyscal data requre the data be located at regular ntervals n space and/or tme. hs s
Feb 4: Spatal analyss of data felds Mappng rregularly sampled data onto a regular grd Many analyss technques for geophyscal data requre the data be located at regular ntervals n space and/or tme. hs s
Chapter 7 Generalized and Weighted Least Squares Estimation. In this method, the deviation between the observed and expected values of
 Chapter 7 Generalzed and Weghted Least Squares Estmaton The usual lnear regresson model assumes that all the random error components are dentcally and ndependently dstrbuted wth constant varance. When
Chapter 7 Generalzed and Weghted Least Squares Estmaton The usual lnear regresson model assumes that all the random error components are dentcally and ndependently dstrbuted wth constant varance. When
Feature Selection: Part 1
 CSE 546: Machne Learnng Lecture 5 Feature Selecton: Part 1 Instructor: Sham Kakade 1 Regresson n the hgh dmensonal settng How do we learn when the number of features d s greater than the sample sze n?
CSE 546: Machne Learnng Lecture 5 Feature Selecton: Part 1 Instructor: Sham Kakade 1 Regresson n the hgh dmensonal settng How do we learn when the number of features d s greater than the sample sze n?
Electron-Impact Double Ionization of the H 2
 I R A P 6(), Dec. 5, pp. 9- Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule Internatonal Scence Press ISSN: 9-59 Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule. S. PINDZOLA AND J. COLGAN Department
I R A P 6(), Dec. 5, pp. 9- Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule Internatonal Scence Press ISSN: 9-59 Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule. S. PINDZOLA AND J. COLGAN Department
Turbulent Flow. Turbulent Flow
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xoll2kedog&feature=related http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=7kkftgx2any http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=vqhxihpvcvu 1. Caothc fluctuatons wth a wde range of frequences and
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xoll2kedog&feature=related http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=7kkftgx2any http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=vqhxihpvcvu 1. Caothc fluctuatons wth a wde range of frequences and
Chapter 3 Differentiation and Integration
 MEE07 Computer Modelng Technques n Engneerng Chapter Derentaton and Integraton Reerence: An Introducton to Numercal Computatons, nd edton, S. yakowtz and F. zdarovsky, Mawell/Macmllan, 990. Derentaton
MEE07 Computer Modelng Technques n Engneerng Chapter Derentaton and Integraton Reerence: An Introducton to Numercal Computatons, nd edton, S. yakowtz and F. zdarovsky, Mawell/Macmllan, 990. Derentaton
1 Matrix representations of canonical matrices
 1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
SOLVING NON-LINEAR SYSTEMS BY NEWTON s METHOD USING SPREADSHEET EXCEL Tay Kim Gaik Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
 SOLVING NON-LINEAR SYSTEMS BY NEWTON s METHOD USING SPREADSHEET EXCEL Tay Km Gak Unverst Tun Hussen Onn Malaysa Kek Se Long Unverst Tun Hussen Onn Malaysa Rosmla Abdul-Kahar
SOLVING NON-LINEAR SYSTEMS BY NEWTON s METHOD USING SPREADSHEET EXCEL Tay Km Gak Unverst Tun Hussen Onn Malaysa Kek Se Long Unverst Tun Hussen Onn Malaysa Rosmla Abdul-Kahar
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
4DVAR, according to the name, is a four-dimensional variational method.
 4D-Varatonal Data Assmlaton (4D-Var) 4DVAR, accordng to the name, s a four-dmensonal varatonal method. 4D-Var s actually a drect generalzaton of 3D-Var to handle observatons that are dstrbuted n tme. The
4D-Varatonal Data Assmlaton (4D-Var) 4DVAR, accordng to the name, s a four-dmensonal varatonal method. 4D-Var s actually a drect generalzaton of 3D-Var to handle observatons that are dstrbuted n tme. The
Chapter 4: Root Finding
 Chapter 4: Root Fndng Startng values Closed nterval methods (roots are search wthn an nterval o Bsecton Open methods (no nterval o Fxed Pont o Newton-Raphson o Secant Method Repeated roots Zeros of Hgher-Dmensonal
Chapter 4: Root Fndng Startng values Closed nterval methods (roots are search wthn an nterval o Bsecton Open methods (no nterval o Fxed Pont o Newton-Raphson o Secant Method Repeated roots Zeros of Hgher-Dmensonal
Chapter Newton s Method
 Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Quantum Mechanics I Problem set No.1
 Quantum Mechancs I Problem set No.1 Septembe0, 2017 1 The Least Acton Prncple The acton reads S = d t L(q, q) (1) accordng to the least (extremal) acton prncple, the varaton of acton s zero 0 = δs = t
Quantum Mechancs I Problem set No.1 Septembe0, 2017 1 The Least Acton Prncple The acton reads S = d t L(q, q) (1) accordng to the least (extremal) acton prncple, the varaton of acton s zero 0 = δs = t
Lossy Compression. Compromise accuracy of reconstruction for increased compression.
 Lossy Compresson Compromse accuracy of reconstructon for ncreased compresson. The reconstructon s usually vsbly ndstngushable from the orgnal mage. Typcally, one can get up to 0:1 compresson wth almost
Lossy Compresson Compromse accuracy of reconstructon for ncreased compresson. The reconstructon s usually vsbly ndstngushable from the orgnal mage. Typcally, one can get up to 0:1 compresson wth almost
1 GSW Iterative Techniques for y = Ax
 1 for y = A I m gong to cheat here. here are a lot of teratve technques that can be used to solve the general case of a set of smultaneous equatons (wrtten n the matr form as y = A), but ths chapter sn
1 for y = A I m gong to cheat here. here are a lot of teratve technques that can be used to solve the general case of a set of smultaneous equatons (wrtten n the matr form as y = A), but ths chapter sn
Classification as a Regression Problem
 Target varable y C C, C,, ; Classfcaton as a Regresson Problem { }, 3 L C K To treat classfcaton as a regresson problem we should transform the target y nto numercal values; The choce of numercal class
Target varable y C C, C,, ; Classfcaton as a Regresson Problem { }, 3 L C K To treat classfcaton as a regresson problem we should transform the target y nto numercal values; The choce of numercal class
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Hidden Markov Models & The Multivariate Gaussian (10/26/04)
 CS281A/Stat241A: Statstcal Learnng Theory Hdden Markov Models & The Multvarate Gaussan (10/26/04) Lecturer: Mchael I. Jordan Scrbes: Jonathan W. Hu 1 Hdden Markov Models As a bref revew, hdden Markov models
CS281A/Stat241A: Statstcal Learnng Theory Hdden Markov Models & The Multvarate Gaussan (10/26/04) Lecturer: Mchael I. Jordan Scrbes: Jonathan W. Hu 1 Hdden Markov Models As a bref revew, hdden Markov models
Chapter 9: Statistical Inference and the Relationship between Two Variables
 Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
MATH 5630: Discrete Time-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March 1, 2018
 MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
N-Body Simulation. Typical uncertainty: π = 4 Acircle/Asquare! 4 ncircle/n. πest π = O(n
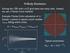 N-Body Smulaton Solvng the CBE wth a 6-D grd takes too many cells. Instead, we use a Monte-Carlo method. Example: Monte-Carlo calculaton of π. Scatter n ponts n square; count number ncrcle fallng wthn
N-Body Smulaton Solvng the CBE wth a 6-D grd takes too many cells. Instead, we use a Monte-Carlo method. Example: Monte-Carlo calculaton of π. Scatter n ponts n square; count number ncrcle fallng wthn
Statistical Inference. 2.3 Summary Statistics Measures of Center and Spread. parameters ( population characteristics )
 Ismor Fscher, 8//008 Stat 54 / -8.3 Summary Statstcs Measures of Center and Spread Dstrbuton of dscrete contnuous POPULATION Random Varable, numercal True center =??? True spread =???? parameters ( populaton
Ismor Fscher, 8//008 Stat 54 / -8.3 Summary Statstcs Measures of Center and Spread Dstrbuton of dscrete contnuous POPULATION Random Varable, numercal True center =??? True spread =???? parameters ( populaton
Nice plotting of proteins II
 Nce plottng of protens II Fnal remark regardng effcency: It s possble to wrte the Newton representaton n a way that can be computed effcently, usng smlar bracketng that we made for the frst representaton
Nce plottng of protens II Fnal remark regardng effcency: It s possble to wrte the Newton representaton n a way that can be computed effcently, usng smlar bracketng that we made for the frst representaton
A constant recursive convolution technique for frequency dependent scalar wave equation based FDTD algorithm
 J Comput Electron (213) 12:752 756 DOI 1.17/s1825-13-479-2 A constant recursve convoluton technque for frequency dependent scalar wave equaton bed FDTD algorthm M. Burak Özakın Serkan Aksoy Publshed onlne:
J Comput Electron (213) 12:752 756 DOI 1.17/s1825-13-479-2 A constant recursve convoluton technque for frequency dependent scalar wave equaton bed FDTD algorthm M. Burak Özakın Serkan Aksoy Publshed onlne:
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecture 7 Specal Relatvty (Chapter 7) What We Dd Last Tme Worked on relatvstc knematcs Essental tool for epermental physcs Basc technques are easy: Defne all 4 vectors Calculate c-o-m
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecture 7 Specal Relatvty (Chapter 7) What We Dd Last Tme Worked on relatvstc knematcs Essental tool for epermental physcs Basc technques are easy: Defne all 4 vectors Calculate c-o-m
5.04, Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II MIT Department of Chemistry Lecture 32: Vibrational Spectroscopy and the IR
 5.0, Prncples of Inorganc Chemstry II MIT Department of Chemstry Lecture 3: Vbratonal Spectroscopy and the IR Vbratonal spectroscopy s confned to the 00-5000 cm - spectral regon. The absorpton of a photon
5.0, Prncples of Inorganc Chemstry II MIT Department of Chemstry Lecture 3: Vbratonal Spectroscopy and the IR Vbratonal spectroscopy s confned to the 00-5000 cm - spectral regon. The absorpton of a photon
Integrals and Invariants of
 Lecture 16 Integrals and Invarants of Euler Lagrange Equatons NPTEL Course Varatonal Methods and Structural Optmzaton G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechancal Engneerng, Indan Insttute of Scence, Banagalore
Lecture 16 Integrals and Invarants of Euler Lagrange Equatons NPTEL Course Varatonal Methods and Structural Optmzaton G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechancal Engneerng, Indan Insttute of Scence, Banagalore
Module 1 : The equation of continuity. Lecture 1: Equation of Continuity
 1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
CHAPTER 14 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY
 CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
FTCS Solution to the Heat Equation
 FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton ME 448/548 Notes Gerald Recktenwald Portland State Unversty Department of Mechancal Engneerng gerry@pdx.edu ME 448/548: FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton Overvew 1. Use
FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton ME 448/548 Notes Gerald Recktenwald Portland State Unversty Department of Mechancal Engneerng gerry@pdx.edu ME 448/548: FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton Overvew 1. Use
LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS. MODULE IX Lecture Multicollinearity
 LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE IX Lecture - 31 Multcollnearty Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur 6. Rdge regresson The OLSE s the best lnear unbased
LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE IX Lecture - 31 Multcollnearty Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur 6. Rdge regresson The OLSE s the best lnear unbased
The EM Algorithm (Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977) The missing data or incomplete data setting: ODL(φ;Y ) = [Y;φ] = [Y X,φ][X φ] = X
![The EM Algorithm (Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977) The missing data or incomplete data setting: ODL(φ;Y ) = [Y;φ] = [Y X,φ][X φ] = X The EM Algorithm (Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977) The missing data or incomplete data setting: ODL(φ;Y ) = [Y;φ] = [Y X,φ][X φ] = X](/thumbs/94/122242296.jpg) The EM Algorthm (Dempster, Lard, Rubn 1977 The mssng data or ncomplete data settng: An Observed Data Lkelhood (ODL that s a mxture or ntegral of Complete Data Lkelhoods (CDL. (1a ODL(;Y = [Y;] = [Y,][
The EM Algorthm (Dempster, Lard, Rubn 1977 The mssng data or ncomplete data settng: An Observed Data Lkelhood (ODL that s a mxture or ntegral of Complete Data Lkelhoods (CDL. (1a ODL(;Y = [Y;] = [Y,][
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 151 Lecture 3 Lagrange s Equatons (Goldsten Chapter 1) Hamlton s Prncple (Chapter 2) What We Dd Last Tme! Dscussed mult-partcle systems! Internal and external forces! Laws of acton and
Mechancs Physcs 151 Lecture 3 Lagrange s Equatons (Goldsten Chapter 1) Hamlton s Prncple (Chapter 2) What We Dd Last Tme! Dscussed mult-partcle systems! Internal and external forces! Laws of acton and
Conservation of Angular Momentum = "Spin"
 Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
ME 501A Seminar in Engineering Analysis Page 1
 umercal Solutons of oundary-value Problems n Os ovember 7, 7 umercal Solutons of oundary- Value Problems n Os Larry aretto Mechancal ngneerng 5 Semnar n ngneerng nalyss ovember 7, 7 Outlne Revew stff equaton
umercal Solutons of oundary-value Problems n Os ovember 7, 7 umercal Solutons of oundary- Value Problems n Os Larry aretto Mechancal ngneerng 5 Semnar n ngneerng nalyss ovember 7, 7 Outlne Revew stff equaton
2 Finite difference basics
 Numersche Methoden 1, WS 11/12 B.J.P. Kaus 2 Fnte dfference bascs Consder the one- The bascs of the fnte dfference method are best understood wth an example. dmensonal transent heat conducton equaton T
Numersche Methoden 1, WS 11/12 B.J.P. Kaus 2 Fnte dfference bascs Consder the one- The bascs of the fnte dfference method are best understood wth an example. dmensonal transent heat conducton equaton T
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Army Ants Tunneling for Classical Simulations
 Electronc Supplementary Materal (ESI) for Chemcal Scence. Ths journal s The Royal Socety of Chemstry 2014 electronc supplementary nformaton (ESI) for Chemcal Scence Army Ants Tunnelng for Classcal Smulatons
Electronc Supplementary Materal (ESI) for Chemcal Scence. Ths journal s The Royal Socety of Chemstry 2014 electronc supplementary nformaton (ESI) for Chemcal Scence Army Ants Tunnelng for Classcal Smulatons
Report on Image warping
 Report on Image warpng Xuan Ne, Dec. 20, 2004 Ths document summarzed the algorthms of our mage warpng soluton for further study, and there s a detaled descrpton about the mplementaton of these algorthms.
Report on Image warpng Xuan Ne, Dec. 20, 2004 Ths document summarzed the algorthms of our mage warpng soluton for further study, and there s a detaled descrpton about the mplementaton of these algorthms.
Solution of the Navier-Stokes Equations
 Numercal Flud Mechancs Fall 2011 Lecture 25 REVIEW Lecture 24: Soluton of the Naver-Stokes Equatons Dscretzaton of the convectve and vscous terms Dscretzaton of the pressure term Conservaton prncples Momentum
Numercal Flud Mechancs Fall 2011 Lecture 25 REVIEW Lecture 24: Soluton of the Naver-Stokes Equatons Dscretzaton of the convectve and vscous terms Dscretzaton of the pressure term Conservaton prncples Momentum
n α j x j = 0 j=1 has a nontrivial solution. Here A is the n k matrix whose jth column is the vector for all t j=0
 MODULE 2 Topcs: Lnear ndependence, bass and dmenson We have seen that f n a set of vectors one vector s a lnear combnaton of the remanng vectors n the set then the span of the set s unchanged f that vector
MODULE 2 Topcs: Lnear ndependence, bass and dmenson We have seen that f n a set of vectors one vector s a lnear combnaton of the remanng vectors n the set then the span of the set s unchanged f that vector
NON-CENTRAL 7-POINT FORMULA IN THE METHOD OF LINES FOR PARABOLIC AND BURGERS' EQUATIONS
 IJRRAS 8 (3 September 011 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol8issue3/ijrras_8_3_08.pdf NON-CENTRAL 7-POINT FORMULA IN THE METHOD OF LINES FOR PARABOLIC AND BURGERS' EQUATIONS H.O. Bakodah Dept. of Mathematc
IJRRAS 8 (3 September 011 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol8issue3/ijrras_8_3_08.pdf NON-CENTRAL 7-POINT FORMULA IN THE METHOD OF LINES FOR PARABOLIC AND BURGERS' EQUATIONS H.O. Bakodah Dept. of Mathematc
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Application of the Adjoint Method for Vehicle Aerodynamic Optimization. Dr. Thomas Blacha, Audi AG
 Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc Optmzaton Dr. Thomas Blacha, Aud AG GoFun, Braunschweg 22.3.2017 2 AUDI AG, Dr. Thomas Blacha, Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc
Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc Optmzaton Dr. Thomas Blacha, Aud AG GoFun, Braunschweg 22.3.2017 2 AUDI AG, Dr. Thomas Blacha, Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc
Formal solvers of the RT equation
 Formal solvers of the RT equaton Formal RT solvers Runge- Kutta (reference solver) Pskunov N.: 979, Master Thess Long characterstcs (Feautrer scheme) Cannon C.J.: 970, ApJ 6, 55 Short characterstcs (Hermtan
Formal solvers of the RT equaton Formal RT solvers Runge- Kutta (reference solver) Pskunov N.: 979, Master Thess Long characterstcs (Feautrer scheme) Cannon C.J.: 970, ApJ 6, 55 Short characterstcs (Hermtan
Affine and Riemannian Connections
 Affne and Remannan Connectons Semnar Remannan Geometry Summer Term 2015 Prof Dr Anna Wenhard and Dr Gye-Seon Lee Jakob Ullmann Notaton: X(M) space of smooth vector felds on M D(M) space of smooth functons
Affne and Remannan Connectons Semnar Remannan Geometry Summer Term 2015 Prof Dr Anna Wenhard and Dr Gye-Seon Lee Jakob Ullmann Notaton: X(M) space of smooth vector felds on M D(M) space of smooth functons
Lectures - Week 4 Matrix norms, Conditioning, Vector Spaces, Linear Independence, Spanning sets and Basis, Null space and Range of a Matrix
 Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
High resolution entropy stable scheme for shallow water equations
 Internatonal Symposum on Computers & Informatcs (ISCI 05) Hgh resoluton entropy stable scheme for shallow water equatons Xaohan Cheng,a, Yufeng Ne,b, Department of Appled Mathematcs, Northwestern Polytechncal
Internatonal Symposum on Computers & Informatcs (ISCI 05) Hgh resoluton entropy stable scheme for shallow water equatons Xaohan Cheng,a, Yufeng Ne,b, Department of Appled Mathematcs, Northwestern Polytechncal
UPGRADE OF THE GSP GYROKINETIC CODE MID-YEAR PROGRESS REPORT
 12/6/211 1 UPGRADE OF THE GSP GYROKINETIC CODE MID-YEAR PROGRESS REPORT George Wlke gwlke@umd.edu December 6, 211 Supersor: Wllam Dorland, Dept. of Physcs bdorland@umd.edu Abstract: Smulatons of turbulent
12/6/211 1 UPGRADE OF THE GSP GYROKINETIC CODE MID-YEAR PROGRESS REPORT George Wlke gwlke@umd.edu December 6, 211 Supersor: Wllam Dorland, Dept. of Physcs bdorland@umd.edu Abstract: Smulatons of turbulent
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE
 CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
However, since P is a symmetric idempotent matrix, of P are either 0 or 1 [Eigen-values
 Fall 007 Soluton to Mdterm Examnaton STAT 7 Dr. Goel. [0 ponts] For the general lnear model = X + ε, wth uncorrelated errors havng mean zero and varance σ, suppose that the desgn matrx X s not necessarly
Fall 007 Soluton to Mdterm Examnaton STAT 7 Dr. Goel. [0 ponts] For the general lnear model = X + ε, wth uncorrelated errors havng mean zero and varance σ, suppose that the desgn matrx X s not necessarly
Using TranSIESTA (II): Integration contour and tbtrans
 Usng TranSIESTA (II): Integraton contour and tbtrans Frederco D. Novaes December 15, 2009 Outlne Usng TranSIESTA The ntegraton contour Electron densty from GF Why go complex? The non-equlbrum stuaton Usng
Usng TranSIESTA (II): Integraton contour and tbtrans Frederco D. Novaes December 15, 2009 Outlne Usng TranSIESTA The ntegraton contour Electron densty from GF Why go complex? The non-equlbrum stuaton Usng
Hongyi Miao, College of Science, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing ,China. (Received 20 June 2013, accepted 11 March 2014) I)ϕ (k)
 ISSN 1749-3889 (prnt), 1749-3897 (onlne) Internatonal Journal of Nonlnear Scence Vol.17(2014) No.2,pp.188-192 Modfed Block Jacob-Davdson Method for Solvng Large Sparse Egenproblems Hongy Mao, College of
ISSN 1749-3889 (prnt), 1749-3897 (onlne) Internatonal Journal of Nonlnear Scence Vol.17(2014) No.2,pp.188-192 Modfed Block Jacob-Davdson Method for Solvng Large Sparse Egenproblems Hongy Mao, College of
New Method for Solving Poisson Equation. on Irregular Domains
 Appled Mathematcal Scences Vol. 6 01 no. 8 369 380 New Method for Solvng Posson Equaton on Irregular Domans J. Izadan and N. Karamooz Department of Mathematcs Facult of Scences Mashhad BranchIslamc Azad
Appled Mathematcal Scences Vol. 6 01 no. 8 369 380 New Method for Solvng Posson Equaton on Irregular Domans J. Izadan and N. Karamooz Department of Mathematcs Facult of Scences Mashhad BranchIslamc Azad
STATISTICAL MECHANICS
 STATISTICAL MECHANICS Thermal Energy Recall that KE can always be separated nto 2 terms: KE system = 1 2 M 2 total v CM KE nternal Rgd-body rotaton and elastc / sound waves Use smplfyng assumptons KE of
STATISTICAL MECHANICS Thermal Energy Recall that KE can always be separated nto 2 terms: KE system = 1 2 M 2 total v CM KE nternal Rgd-body rotaton and elastc / sound waves Use smplfyng assumptons KE of
Lecture Notes on Linear Regression
 Lecture Notes on Lnear Regresson Feng L fl@sdueducn Shandong Unversty, Chna Lnear Regresson Problem In regresson problem, we am at predct a contnuous target value gven an nput feature vector We assume
Lecture Notes on Lnear Regresson Feng L fl@sdueducn Shandong Unversty, Chna Lnear Regresson Problem In regresson problem, we am at predct a contnuous target value gven an nput feature vector We assume
Inexact Newton Methods for Inverse Eigenvalue Problems
 Inexact Newton Methods for Inverse Egenvalue Problems Zheng-jan Ba Abstract In ths paper, we survey some of the latest development n usng nexact Newton-lke methods for solvng nverse egenvalue problems.
Inexact Newton Methods for Inverse Egenvalue Problems Zheng-jan Ba Abstract In ths paper, we survey some of the latest development n usng nexact Newton-lke methods for solvng nverse egenvalue problems.
Lab session: numerical simulations of sponateous polarization
 Lab sesson: numercal smulatons of sponateous polarzaton Emerc Boun & Vncent Calvez CNRS, ENS Lyon, France CIMPA, Hammamet, March 2012 Spontaneous cell polarzaton: the 1D case The Hawkns-Voturez model for
Lab sesson: numercal smulatons of sponateous polarzaton Emerc Boun & Vncent Calvez CNRS, ENS Lyon, France CIMPA, Hammamet, March 2012 Spontaneous cell polarzaton: the 1D case The Hawkns-Voturez model for
Solutions to Exercises in Astrophysical Gas Dynamics
 1 Solutons to Exercses n Astrophyscal Gas Dynamcs 1. (a). Snce u 1, v are vectors then, under an orthogonal transformaton, u = a j u j v = a k u k Therefore, u v = a j a k u j v k = δ jk u j v k = u j
1 Solutons to Exercses n Astrophyscal Gas Dynamcs 1. (a). Snce u 1, v are vectors then, under an orthogonal transformaton, u = a j u j v = a k u k Therefore, u v = a j a k u j v k = δ jk u j v k = u j
Grid Generation around a Cylinder by Complex Potential Functions
 Research Journal of Appled Scences, Engneerng and Technolog 4(): 53-535, 0 ISSN: 040-7467 Mawell Scentfc Organzaton, 0 Submtted: December 0, 0 Accepted: Januar, 0 Publshed: June 0, 0 Grd Generaton around
Research Journal of Appled Scences, Engneerng and Technolog 4(): 53-535, 0 ISSN: 040-7467 Mawell Scentfc Organzaton, 0 Submtted: December 0, 0 Accepted: Januar, 0 Publshed: June 0, 0 Grd Generaton around
Inner Product. Euclidean Space. Orthonormal Basis. Orthogonal
 Inner Product Defnton 1 () A Eucldean space s a fnte-dmensonal vector space over the reals R, wth an nner product,. Defnton 2 (Inner Product) An nner product, on a real vector space X s a symmetrc, blnear,
Inner Product Defnton 1 () A Eucldean space s a fnte-dmensonal vector space over the reals R, wth an nner product,. Defnton 2 (Inner Product) An nner product, on a real vector space X s a symmetrc, blnear,
12. The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Michael Fowler
 1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 2018 LECTURE 17. a ij x (k) b i. a ij x (k+1) (D + L)x (k+1) = b Ux (k)
 STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 08 LECTURE 7. sor method remnder: n coordnatewse form, Jacob method s = [ b a x (k) a and Gauss Sedel method s = [ b a = = remnder: n matrx form, Jacob method
STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 08 LECTURE 7. sor method remnder: n coordnatewse form, Jacob method s = [ b a x (k) a and Gauss Sedel method s = [ b a = = remnder: n matrx form, Jacob method
ECONOMICS 351*-A Mid-Term Exam -- Fall Term 2000 Page 1 of 13 pages. QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY AT KINGSTON Department of Economics
 ECOOMICS 35*-A Md-Term Exam -- Fall Term 000 Page of 3 pages QUEE'S UIVERSITY AT KIGSTO Department of Economcs ECOOMICS 35* - Secton A Introductory Econometrcs Fall Term 000 MID-TERM EAM ASWERS MG Abbott
ECOOMICS 35*-A Md-Term Exam -- Fall Term 000 Page of 3 pages QUEE'S UIVERSITY AT KIGSTO Department of Economcs ECOOMICS 35* - Secton A Introductory Econometrcs Fall Term 000 MID-TERM EAM ASWERS MG Abbott
Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Exerments-I MODULE III LECTURE - 2 EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN MODELS Dr. Shalabh Deartment of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanur 2 We consder the models
Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Exerments-I MODULE III LECTURE - 2 EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN MODELS Dr. Shalabh Deartment of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanur 2 We consder the models
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Errors for Linear Systems
 Errors for Lnear Systems When we solve a lnear system Ax b we often do not know A and b exactly, but have only approxmatons  and ˆb avalable. Then the best thng we can do s to solve ˆx ˆb exactly whch
Errors for Lnear Systems When we solve a lnear system Ax b we often do not know A and b exactly, but have only approxmatons  and ˆb avalable. Then the best thng we can do s to solve ˆx ˆb exactly whch
Physics 607 Exam 1. ( ) = 1, Γ( z +1) = zγ( z) x n e x2 dx = 1. e x2
 Physcs 607 Exam 1 Please be well-organzed, and show all sgnfcant steps clearly n all problems. You are graded on your wor, so please do not just wrte down answers wth no explanaton! Do all your wor on
Physcs 607 Exam 1 Please be well-organzed, and show all sgnfcant steps clearly n all problems. You are graded on your wor, so please do not just wrte down answers wth no explanaton! Do all your wor on
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 16 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 16 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 16 Sep 2013](/thumbs/71/66225386.jpg) Three-Dmensonal Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs Method for Smulatng Free Surface Flows Rzal Dw Prayogo a,b, Chrstan Fredy Naa a a Faculty of Mathematcs and Natural Scences, Insttut Teknolog Bandung, Jl.
Three-Dmensonal Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs Method for Smulatng Free Surface Flows Rzal Dw Prayogo a,b, Chrstan Fredy Naa a a Faculty of Mathematcs and Natural Scences, Insttut Teknolog Bandung, Jl.
EEL 6266 Power System Operation and Control. Chapter 3 Economic Dispatch Using Dynamic Programming
 EEL 6266 Power System Operaton and Control Chapter 3 Economc Dspatch Usng Dynamc Programmng Pecewse Lnear Cost Functons Common practce many utltes prefer to represent ther generator cost functons as sngle-
EEL 6266 Power System Operaton and Control Chapter 3 Economc Dspatch Usng Dynamc Programmng Pecewse Lnear Cost Functons Common practce many utltes prefer to represent ther generator cost functons as sngle-
Note 10. Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems
 Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introducton to Mechatroncs Note 0 Modelng and Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Unversty Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drve, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introducton to Mechatroncs Note 0 Modelng and Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Unversty Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drve, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
. The kinetic energy of this system is T = T i. m i. Now let s consider how the kinetic energy of the system changes in time. Assuming each.
 Chapter 2 Systems of Partcles 2. Work-Energy Theorem Consder a system of many partcles, wth postons r and veloctes ṙ. The knetc energy of ths system s T = T = 2 mṙ2. 2. Now let s consder how the knetc
Chapter 2 Systems of Partcles 2. Work-Energy Theorem Consder a system of many partcles, wth postons r and veloctes ṙ. The knetc energy of ths system s T = T = 2 mṙ2. 2. Now let s consder how the knetc
SIO 224. m(r) =(ρ(r),k s (r),µ(r))
 SIO 224 1. A bref look at resoluton analyss Here s some background for the Masters and Gubbns resoluton paper. Global Earth models are usually found teratvely by assumng a startng model and fndng small
SIO 224 1. A bref look at resoluton analyss Here s some background for the Masters and Gubbns resoluton paper. Global Earth models are usually found teratvely by assumng a startng model and fndng small
Computational Fluid Dynamics. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Simulations. Smoothing Kernels and Basis of SPH
 Computatonal Flud Dynamcs If you want to learn a bt more of the math behnd flud dynamcs, read my prevous post about the Naver- Stokes equatons and Newtonan fluds. The equatons derved n the post are the
Computatonal Flud Dynamcs If you want to learn a bt more of the math behnd flud dynamcs, read my prevous post about the Naver- Stokes equatons and Newtonan fluds. The equatons derved n the post are the
A linear imaging system with white additive Gaussian noise on the observed data is modeled as follows:
 Supplementary Note Mathematcal bacground A lnear magng system wth whte addtve Gaussan nose on the observed data s modeled as follows: X = R ϕ V + G, () where X R are the expermental, two-dmensonal proecton
Supplementary Note Mathematcal bacground A lnear magng system wth whte addtve Gaussan nose on the observed data s modeled as follows: X = R ϕ V + G, () where X R are the expermental, two-dmensonal proecton
Physics 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1
 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
