R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
|
|
|
- Bryan Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
2 Example 2 Multiple-Output Full-Bridge Buck Converter Q 1 D 1 Q 3 D 3 + T 1 : : n 2 D 5 i 2a I 5V 100 A + V g 160 V + i 1 v 1 D 6 i 2b 5 V D Q2 2 D Q4 4 Switching frequency 150 khz Transformer frequency 75 khz Turns ratio 110:5:15 : n 2 : n 3 : n 3 D 7 D 8 i 3a i 2b I 15V 15 A + 15 V Optimize transformer at D =
3 Other transformer design details Use Magnetics, Inc. ferrite P material. Loss parameters at 75 khz: K fe = 7.6 W/T cm 3 = 2.6 Use E-E core shape Assume fill factor of K u = 0.25 (reduced fill factor accounts for added insulation required in multiple-output off-line application) Allow transformer total power loss of P tot = 4 W Use copper wire, with = cm (approximately 0.5% of total output power) 26
4 Applied transformer waveforms D 3 i 1 D 4 T 1 : : n 2 + v 1 : n 2 : n 3 D 5 D 6 D 7 i 2a i 2b i 3a v 1 i 1 i 2a V g n 2 I 5V + n 3 I 15V Area λ 1 = V g DT s 0 n 2 I 5V + n 3 I 15V I 5V 0 0 V g 0.5I 5V 0 : n 3 D 8 i 2b i 3a I 15V 0.5I 15V 0 DT s T s T s +DT s 2T s 0 t 27
5 Applied primary volt-seconds v 1 V g Area λ 1 = V g DT s 0 0 V g λ 1 = DT s V g = (0.75) (6.67 µsec ) (160 V) = 800 V µsec 28
6 Applied primary rms current i 1 n 2 I 5V + n 3 I 15V 0 n 2 I 5V + n 3 I 15V I 1 = n 2 I 5V + n 3 I 15V D = 5.7 A 29
7 Applied rms current, secondary windings i 2a i 3a I 5V I 15V 0.5I 5V 0.5I 15V 0 DT s T s T s +DT s 2T s 0 0 t I 2 = 1 2 I 5V I 3 = 1 2 I 15V 1+D = 66.1 A 1+D = 9.9 A 30
8 I tot RMS currents, summed over all windings and referred to primary I tot = Σall 5 windings n j I j = 5.7 A = 14.4 A = I 1 +2 n 2 I 2 +2 n 3 I A A 31
9 Select core size K gfe ( )( ) 2 (14.4) 2 (7.6) 2/2.6 4 (0.25) (4) 4.6/ = From Appendix D A 32
10 Evaluate ac flux density B Eq. (15.20): B max = 10 8 ρλ I tot 2K u (MLT) W A A c 3 l m 1 βk fe 1 β +2 Plug in values: B = 10 8 ( )( ) 2 (14.4) 2 2(0.25) (8.5) (1.1)(1.27) 3 (7.7) 1 (2.6)(7.6) 1/4.6 =0.23 Tesla This is less than the saturation flux density of approximately 0.35 T 33
11 Evaluate turns Choose according to Eq. (15.21): = λ 1 2 BA c 10 4 = 10 4 ( ) 2(0.23)(1.27) = 13.7 turns Choose secondary turns according to desired turns ratios: n 2 = = 0.62 turns n 3 = = 1.87 turns Rounding the number of turns To obtain desired turns ratio of 110:5:15 we might round the actual turns to 22:1:3 Increased would lead to Less core loss More copper loss Increased total loss 34
12 Loss calculation with rounded turns With = 22, the flux density will be reduced to B = ( ) 2(22)(1.27) 104 = Tesla The resulting losses will be P fe = (7.6)(0.143) 2.6 (1.27)(7.7) = 0.47 W P cu = ( )( ) 2 (14.4) 2 4 (0.25) = 5.4 W P tot = P fe + P cu = 5.9 W (8.5) (1.1)(1.27) 2 1 (0.143) Which exceeds design goal of 4 W by 50%. So use next larger core size: EE50. 35
13 Calculations with EE50 Repeat previous calculations for EE50 core size. Results: B = 0.14 T, = 12, P tot = 2.3 W Again round to 22. Then B = 0.08 T, P cu = 3.89 W, P fe = 0.23 W, P tot = 4.12 W Which is close enough to 4 W. 36
14 Wire sizes for EE50 design Window allocations Wire gauges α 1 = I 1 I tot = = α 2 = n 2I 2 I tot = = α 3 = n 3I 3 I tot = = A w1 = α 1K u W A = (0.396)(0.25)(1.78) = cm (22) 2 AWG #19 A w2 = α 2K u W A = (0.209)(0.25)(1.78) = cm n 2 (1) 2 AWG #8 A w3 = α 3K u W A = (0.094)(0.25)(1.78) = cm n 3 (3) 2 AWG #16 Might actually use foil or Litz wire for secondary windings 37
15 Discussion: Transformer design Process is iterative because of round-off of physical number of turns and, to a lesser extent, other quantities Effect of proximity loss Not included in design process yet Requires additional iterations Can modify procedure as follows: After a design has been calculated, determine number of layers in each winding and then compute proximity loss Alter effective resistivity of wire to compensate: define eff = P cu /P dc where P cu is the total copper loss (including proximity effects) and P dc is the copper loss predicted by the dc resistance. Apply transformer design procedure using this effective wire resistivity, and compute proximity loss in the resulting design. Further iterations may be necessary if the specifications are not met. 38
16 Transformer design
17 Transformer design results Core: ETD 34, TSC 50ALL material
18 15.4 AC Inductor Design i + v L Window area W A Core mean length per turn (MLT) n turns Core Core area A c Air gap l g v Area λ Wire resistivity ρ Fill factor K u t 1 t 2 t i Design a single-winding inductor, having an air gap, accounting for core loss (note that the previous design procedure of this chapter did not employ an air gap, and inductance was not a specification) 39
19 Outline of key equations Obtain specified inductance: L = µ 0A c n 2 l g Relationship between applied volt-seconds and peak ac flux density: B = λ 2nA c Copper loss (using dc resistance): P cu = ρn2 (MLT) K u W A I 2 Total loss is minimized when B = ρλ2 I 2 2K u (MLT) W A A c 3 l m 1 βk fe Must select core that satisfies ρλ 2 I 2 2/β K fe K gfe 2K u P tot β +2/β 1 β +2 See Sectio5.4.2 for step-by-step design equations 40
15.1 Transformer Design: Basic Constraints. Chapter 15: Transformer design. Chapter 15 Transformer Design
 Chapter 5 Transformer Design Some more advanced design issues, not considered in previous chapter: : n Inclusion of core loss Selection of operating flux density to optimize total loss Multiple winding
Chapter 5 Transformer Design Some more advanced design issues, not considered in previous chapter: : n Inclusion of core loss Selection of operating flux density to optimize total loss Multiple winding
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure
Chapter 14: Inductor design
 Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure 14.3 Multiple-winding magnetics design using the K g method 14.4 Examples 14.5 Summary of key points
Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure 14.3 Multiple-winding magnetics design using the K g method 14.4 Examples 14.5 Summary of key points
In The Name of GOD. Switched Mode Power Supply
 In The Name of GOD Switched Mode Power Supply Switched Mode Power Supply Lecture 9 Inductor Design Φ Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Outline } Types of magnetic devices } Filter inductor } Ac inductor
In The Name of GOD Switched Mode Power Supply Switched Mode Power Supply Lecture 9 Inductor Design Φ Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Outline } Types of magnetic devices } Filter inductor } Ac inductor
Section 8: Magnetic Components
 Section 8: Magnetic omponents Inductors and transformers used in power electronic converters operate at quite high frequency. The operating frequency is in khz to MHz. Magnetic transformer steel which
Section 8: Magnetic omponents Inductors and transformers used in power electronic converters operate at quite high frequency. The operating frequency is in khz to MHz. Magnetic transformer steel which
Part III. Magnetics. Chapter 13: Basic Magnetics Theory. Chapter 13 Basic Magnetics Theory
 Part III. Magnetics 3 Basic Magnetics Theory Inductor Design 5 Transformer Design Chapter 3 Basic Magnetics Theory 3. Review of Basic Magnetics 3.. Basic relationships 3..2 Magnetic circuits 3.2 Transformer
Part III. Magnetics 3 Basic Magnetics Theory Inductor Design 5 Transformer Design Chapter 3 Basic Magnetics Theory 3. Review of Basic Magnetics 3.. Basic relationships 3..2 Magnetic circuits 3.2 Transformer
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Part III. Magnetics 13 Basic Magnetics Theory 14 Inductor Design 15 Transformer Design 1 Chapter
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder Part III. Magnetics 13 Basic Magnetics Theory 14 Inductor Design 15 Transformer Design 1 Chapter
Lecture 17 Push-Pull and Bridge DC-DC converters Push-Pull Converter (Buck Derived) Centre-tapped primary and secondary windings
 ecture 17 Push-Pull and Bridge DC-DC converters Push-Pull Converter (Buck Derived) Centre-tapped primary and secondary windings 1 2 D 1 i v 1 v 1s + v C o R v 2 v 2s d 1 2 T 1 T 2 D 2 Figure 17.1 v c (
ecture 17 Push-Pull and Bridge DC-DC converters Push-Pull Converter (Buck Derived) Centre-tapped primary and secondary windings 1 2 D 1 i v 1 v 1s + v C o R v 2 v 2s d 1 2 T 1 T 2 D 2 Figure 17.1 v c (
Switched Mode Power Conversion
 Inductors Devices for Efficient Power Conversion Switches Inductors Transformers Capacitors Inductors Inductors Store Energy Inductors Store Energy in a Magnetic Field In Power Converters Energy Storage
Inductors Devices for Efficient Power Conversion Switches Inductors Transformers Capacitors Inductors Inductors Store Energy Inductors Store Energy in a Magnetic Field In Power Converters Energy Storage
Analysis of Thermal Behavior of High Frequency Transformers Using Finite Element Method
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 010,, 67-63 doi:10.436/emaa.010.1108 ublished Online November 010 (http://www.scirp.org/ournal/emaa) Analysis of Thermal Behavior of High Frequency Transformers
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 010,, 67-63 doi:10.436/emaa.010.1108 ublished Online November 010 (http://www.scirp.org/ournal/emaa) Analysis of Thermal Behavior of High Frequency Transformers
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
Switched Mode Power Conversion Prof. L. Umanand Department of Electronics System Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Switched Mode Power Conversion Prof. L. Umanand Department of Electronics System Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 39 Magnetic Design Good day to all of you. Today, we shall
Switched Mode Power Conversion Prof. L. Umanand Department of Electronics System Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 39 Magnetic Design Good day to all of you. Today, we shall
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 . W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 2.4 Cuk converter example L 1 C 1 L 2 Cuk converter, with ideal switch i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk
. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 2.4 Cuk converter example L 1 C 1 L 2 Cuk converter, with ideal switch i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk
6.3. Transformer isolation
 6.3. Transformer isolation Objectives: Isolation of input and output ground connections, to meet safety requirements eduction of transformer size by incorporating high frequency isolation transformer inside
6.3. Transformer isolation Objectives: Isolation of input and output ground connections, to meet safety requirements eduction of transformer size by incorporating high frequency isolation transformer inside
Elements of Power Electronics PART I: Bases
 Elements of Power Electronics PART I: Bases Fabrice Frébel (fabrice.frebel@ulg.ac.be) September 21 st, 2017 Goal and expectations The goal of the course is to provide a toolbox that allows you to: understand
Elements of Power Electronics PART I: Bases Fabrice Frébel (fabrice.frebel@ulg.ac.be) September 21 st, 2017 Goal and expectations The goal of the course is to provide a toolbox that allows you to: understand
Design and analysis of the ferrite air-gapped cores for a resonant inductor
 ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 67(3), pp. 579 589 (2018) DOI 10.24425/123664 Design and analysis of the ferrite air-gapped cores for a resonant inductor JIANFEN ZHENG, CHUNFANG WANG, DONGWEI XIA
ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 67(3), pp. 579 589 (2018) DOI 10.24425/123664 Design and analysis of the ferrite air-gapped cores for a resonant inductor JIANFEN ZHENG, CHUNFANG WANG, DONGWEI XIA
Chapter 21. Derivations for the Design Equations
 Chapter 21 Derivations for the Design Equations The author would like to thank Richard Ozenbaugh of Linear Magnetics for his help with the derivations. Table of Contents 1. Output Power, P 0, Versus Apparent
Chapter 21 Derivations for the Design Equations The author would like to thank Richard Ozenbaugh of Linear Magnetics for his help with the derivations. Table of Contents 1. Output Power, P 0, Versus Apparent
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
CERN ACCELERATOR SCHOOL Power Converters. Passive components. Prof. Alfred Rufer
 CERN ACCELERATOR SCHOOL Power Converters Passive components Prof. Alfred Rufer Overview Part 1: (to be designed) Part 2: Capacitors (to be selected) Part 3: A new component: The Supercapacitor, component
CERN ACCELERATOR SCHOOL Power Converters Passive components Prof. Alfred Rufer Overview Part 1: (to be designed) Part 2: Capacitors (to be selected) Part 3: A new component: The Supercapacitor, component
Cross Regulation Mechanisms in Multiple-Output Forward and Flyback Converters
 Cross Regulation Mechanisms in Multiple-Output Forward and Flyback Converters Bob Erickson and Dragan Maksimovic Colorado Power Electronics Center (CoPEC) University of Colorado, Boulder 80309-0425 http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect
Cross Regulation Mechanisms in Multiple-Output Forward and Flyback Converters Bob Erickson and Dragan Maksimovic Colorado Power Electronics Center (CoPEC) University of Colorado, Boulder 80309-0425 http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect
Force and Displacement Measurement
 Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
TRANSFORMERS B O O K P G
 TRANSFORMERS B O O K P G. 4 4 4-449 REVIEW The RMS equivalent current is defined as the dc that will provide the same power in the resistor as the ac does on average P average = I 2 RMS R = 1 2 I 0 2 R=
TRANSFORMERS B O O K P G. 4 4 4-449 REVIEW The RMS equivalent current is defined as the dc that will provide the same power in the resistor as the ac does on average P average = I 2 RMS R = 1 2 I 0 2 R=
Book Page cgrahamphysics.com Transformers
 Book Page 444-449 Transformers Review The RMS equivalent current is defined as the dc that will provide the same power in the resistor as the ac does on average P average = I 2 RMS R = 1 2 I 0 2 R= V RMS
Book Page 444-449 Transformers Review The RMS equivalent current is defined as the dc that will provide the same power in the resistor as the ac does on average P average = I 2 RMS R = 1 2 I 0 2 R= V RMS
Reactor Characteristic Evaluation and Analysis Technologies of JFE Steel
 JFE TECHNICAL REPORT No. 21 (Mar. 2016) Reactor Characteristic Evaluation and Analysis Technologies of HIRATANI Tatsuhiko *1 NAMIKAWA Misao *2 NISHINA Yoshiaki *3 Abstract: Reactor characteristic evaluation
JFE TECHNICAL REPORT No. 21 (Mar. 2016) Reactor Characteristic Evaluation and Analysis Technologies of HIRATANI Tatsuhiko *1 NAMIKAWA Misao *2 NISHINA Yoshiaki *3 Abstract: Reactor characteristic evaluation
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency
 Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
Basic Electrical Technology Prof. Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Basic Electrical Technology Prof. Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 18 Transformer Basics Part - II Hello everybody, in the last session
Basic Electrical Technology Prof. Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 18 Transformer Basics Part - II Hello everybody, in the last session
Lecture 30: WED 04 NOV
 Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 30: WED 04 NOV Induction and Inductance II Fender Stratocaster Solenoid Pickup F a r a d a y ' s E x p e r i m e n t s I n a s e r i e s o f e x p e r i m e n t s,
Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 30: WED 04 NOV Induction and Inductance II Fender Stratocaster Solenoid Pickup F a r a d a y ' s E x p e r i m e n t s I n a s e r i e s o f e x p e r i m e n t s,
Lecture Set 1 Introduction to Magnetic Circuits
 Lecture Set 1 Introduction to Magnetic Circuits S.D. Sudhoff Spring 2017 1 Goals Review physical laws pertaining to analysis of magnetic systems Introduce concept of magnetic circuit as means to obtain
Lecture Set 1 Introduction to Magnetic Circuits S.D. Sudhoff Spring 2017 1 Goals Review physical laws pertaining to analysis of magnetic systems Introduce concept of magnetic circuit as means to obtain
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
Lecture 15: Inductor & Capacitor
 ECE 1270: Introduction to Electric Circuits 0 Lecture 15: Inductor & Capacitor Chapter 6 Inductance, Capacitance, and Mutual Inductance Sections 6.1-6.3 EE 1270: Introduction to Electric Circuits 1 Inductor
ECE 1270: Introduction to Electric Circuits 0 Lecture 15: Inductor & Capacitor Chapter 6 Inductance, Capacitance, and Mutual Inductance Sections 6.1-6.3 EE 1270: Introduction to Electric Circuits 1 Inductor
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Lecture 24. April 5 th, Magnetic Circuits & Inductance
 Lecture 24 April 5 th, 2005 Magnetic Circuits & Inductance Reading: Boylestad s Circuit Analysis, 3 rd Canadian Edition Chapter 11.1-11.5, Pages 331-338 Chapter 12.1-12.4, Pages 341-349 Chapter 12.7-12.9,
Lecture 24 April 5 th, 2005 Magnetic Circuits & Inductance Reading: Boylestad s Circuit Analysis, 3 rd Canadian Edition Chapter 11.1-11.5, Pages 331-338 Chapter 12.1-12.4, Pages 341-349 Chapter 12.7-12.9,
Thermal vs. Power Loss Efficiency Considerations for Powder Core Materials. Christopher Oliver Nien Teng Micrometals, Incorporated
 Thermal vs. Power Loss Efficiency Considerations for Powder Core Materials Christopher Oliver Nien Teng Micrometals, Incorporated Outline Powder Cores Description What properties change with temperature
Thermal vs. Power Loss Efficiency Considerations for Powder Core Materials Christopher Oliver Nien Teng Micrometals, Incorporated Outline Powder Cores Description What properties change with temperature
Measurements in Mechatronic design. Transducers
 Measurements in Mechatronic design Transducers Quantities Current Voltage Torque Force Magnetic flux Distance Temperature Measurement system Physical quanties Transducer Signal conditioning Measurement
Measurements in Mechatronic design Transducers Quantities Current Voltage Torque Force Magnetic flux Distance Temperature Measurement system Physical quanties Transducer Signal conditioning Measurement
Transformer Fundamentals
 Transformer Fundamentals 1 Introduction The physical basis of the transformer is mutual induction between two circuits linked by a common magnetic field. Transformer is required to pass electrical energy
Transformer Fundamentals 1 Introduction The physical basis of the transformer is mutual induction between two circuits linked by a common magnetic field. Transformer is required to pass electrical energy
Solution for Fq. A. up B. down C. east D. west E. south
 Solution for Fq A proton traveling due north enters a region that contains both a magnetic field and an electric field. The electric field lines point due west. It is observed that the proton continues
Solution for Fq A proton traveling due north enters a region that contains both a magnetic field and an electric field. The electric field lines point due west. It is observed that the proton continues
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Modellierung von Kern- und Wicklungsverlusten Jonas Mühlethaler, Johann W. Kolar
 Modellierung von Kern- und Wicklungsverlusten Jonas Mühlethaler, Johann W. Kolar Power Electronic Systems Laboratory, ETH Zurich Motivation Modeling Inductive Components Employing best state-of-the-art
Modellierung von Kern- und Wicklungsverlusten Jonas Mühlethaler, Johann W. Kolar Power Electronic Systems Laboratory, ETH Zurich Motivation Modeling Inductive Components Employing best state-of-the-art
Electric Circuits I. Inductors. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits I Inductors Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Inductors An inductor is a passive element designed to store energy in its magnetic field. They are used in power supplies, transformers, radios, TVs,
Electric Circuits I Inductors Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Inductors An inductor is a passive element designed to store energy in its magnetic field. They are used in power supplies, transformers, radios, TVs,
Power Handling Capability of Self-Resonant Structures for Wireless Power Transfer
 Power Handling Capability of Self-Resonant Structures for Wireless Power Transfer Phyo Aung Kyaw, Aaron L. F. Stein and Charles R. Sullivan Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth, Hanover, NH 03755,
Power Handling Capability of Self-Resonant Structures for Wireless Power Transfer Phyo Aung Kyaw, Aaron L. F. Stein and Charles R. Sullivan Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth, Hanover, NH 03755,
Circuit Analysis-II. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 5 Monday 23 rd April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
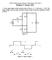 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
Suppose two uniform bars meet at an abrupt plane and there is a magnetic field induced by an extended core and coil structure off stage as in:
 Class Notes Week of 1/9 /3/017 ENGN1931F The magnetic structures that are central to the design of generators, transformers, motors, inductors, solenoids, etc. can be complex. We need a way to make approximate
Class Notes Week of 1/9 /3/017 ENGN1931F The magnetic structures that are central to the design of generators, transformers, motors, inductors, solenoids, etc. can be complex. We need a way to make approximate
[22.1 (2)(0.42) (3.38 / 2)] At/Wb
![[22.1 (2)(0.42) (3.38 / 2)] At/Wb [22.1 (2)(0.42) (3.38 / 2)] At/Wb](/thumbs/92/109471747.jpg) Transformers and Inductors for Power Electronics Theory, Design and Applications p. xiii: In Hurley bio add He received the IEEE Power Electronics Society Middlebrook Award for technical achievement in
Transformers and Inductors for Power Electronics Theory, Design and Applications p. xiii: In Hurley bio add He received the IEEE Power Electronics Society Middlebrook Award for technical achievement in
Part 4: Electromagnetism. 4.1: Induction. A. Faraday's Law. The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is
 1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
Capacitors. Charging a Capacitor. Charge and Capacitance. L05: Capacitors and Inductors
 L05: Capacitors and Inductors 50 Capacitors 51 Outline of the lecture: Capacitors and capacitance. Energy storage. Capacitance formula. Types of capacitors. Inductors and inductance. Inductance formula.
L05: Capacitors and Inductors 50 Capacitors 51 Outline of the lecture: Capacitors and capacitance. Energy storage. Capacitance formula. Types of capacitors. Inductors and inductance. Inductance formula.
Mutual Inductance: This is the magnetic flux coupling of 2 coils where the current in one coil causes a voltage to be induced in the other coil.
 agnetically Coupled Circuits utual Inductance: This is the magnetic flux coupling of coils where the current in one coil causes a voltage to be induced in the other coil. st I d like to emphasize that
agnetically Coupled Circuits utual Inductance: This is the magnetic flux coupling of coils where the current in one coil causes a voltage to be induced in the other coil. st I d like to emphasize that
magneticsp17 September 14, of 17
 EXPERIMENT Magnetics Faraday s Law in Coils with Permanent Magnet, DC and AC Excitation OBJECTIVE The knowledge and understanding of the behavior of magnetic materials is of prime importance for the design
EXPERIMENT Magnetics Faraday s Law in Coils with Permanent Magnet, DC and AC Excitation OBJECTIVE The knowledge and understanding of the behavior of magnetic materials is of prime importance for the design
Modelling Non-Ideal Inductors in SPICE
 Modelling Non-Ideal Inductors in SPICE Martin O'Hara Technical Manager, Newport Components, Milton Keynes November 1994 Abstract The non-ideal inductor exhibits both self resonance and non-linear current
Modelling Non-Ideal Inductors in SPICE Martin O'Hara Technical Manager, Newport Components, Milton Keynes November 1994 Abstract The non-ideal inductor exhibits both self resonance and non-linear current
Inductors. Hydraulic analogy Duality with capacitor Charging and discharging. Lecture 12: Inductors
 Lecture 12: nductors nductors Hydraulic analogy Duality with capacitor Charging and discharging Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://hilaroad.com/camp/projects/magnet.html 99 Lecture 12: nductors
Lecture 12: nductors nductors Hydraulic analogy Duality with capacitor Charging and discharging Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://hilaroad.com/camp/projects/magnet.html 99 Lecture 12: nductors
Physics 2B Spring 2010: Final Version A 1 COMMENTS AND REMINDERS:
 Physics 2B Spring 2010: Final Version A 1 COMMENTS AND REMINDERS: Closed book. No work needs to be shown for multiple-choice questions. 1. A charge of +4.0 C is placed at the origin. A charge of 3.0 C
Physics 2B Spring 2010: Final Version A 1 COMMENTS AND REMINDERS: Closed book. No work needs to be shown for multiple-choice questions. 1. A charge of +4.0 C is placed at the origin. A charge of 3.0 C
Scheme I SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER I
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER I Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hours Q.1) A) Attempt any FIVE of the following. a) Define active components. b) List different types of resistors. c) Describe method to test following passive
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER I Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hours Q.1) A) Attempt any FIVE of the following. a) Define active components. b) List different types of resistors. c) Describe method to test following passive
ELECTRONICS E # 1 FUNDAMENTALS 2/2/2011
 FE Review 1 ELECTRONICS E # 1 FUNDAMENTALS Electric Charge 2 In an electric circuit it there is a conservation of charge. The net electric charge is constant. There are positive and negative charges. Like
FE Review 1 ELECTRONICS E # 1 FUNDAMENTALS Electric Charge 2 In an electric circuit it there is a conservation of charge. The net electric charge is constant. There are positive and negative charges. Like
PHYS Fields and Waves
 PHYS 2421 - Fields and Waves Idea: how to deal with alternating currents Edison wanted direct current, Tesla alternating current, who won? Mathematically: Instantaneous current: Instantaneous voltage:
PHYS 2421 - Fields and Waves Idea: how to deal with alternating currents Edison wanted direct current, Tesla alternating current, who won? Mathematically: Instantaneous current: Instantaneous voltage:
Renewable Energy Systems
 Renewable Energy Systems 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd Chapter Outline Electrical Fundamentals 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd 2-1 ENERGY, CHARGE, AND VOLTAGE 2-2 ELECTRICAL CURRENT 2-3 RESISTANCE AND OHM'S LAW 2-4
Renewable Energy Systems 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd Chapter Outline Electrical Fundamentals 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd 2-1 ENERGY, CHARGE, AND VOLTAGE 2-2 ELECTRICAL CURRENT 2-3 RESISTANCE AND OHM'S LAW 2-4
Power Electronics Notes 30A Review of Magnetics
 Power Electronics Notes 30A Review of Magnetics Marc T. Thompson, Ph.D. Thompson Consulting, Inc. 9 Jacob Gates Road Harvard, MA 01451 Phone: (978) 456-7722 Fax: (240) 414-2655 Email: marctt@thompsonrd.com
Power Electronics Notes 30A Review of Magnetics Marc T. Thompson, Ph.D. Thompson Consulting, Inc. 9 Jacob Gates Road Harvard, MA 01451 Phone: (978) 456-7722 Fax: (240) 414-2655 Email: marctt@thompsonrd.com
Exam 2 Solutions. Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses.
 Exam 2 Solutions Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1 Part of a long, straight insulated wire carrying current i is bent into a circular
Exam 2 Solutions Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1 Part of a long, straight insulated wire carrying current i is bent into a circular
Electromagnetic Induction
 Faraday s Discovery Faraday found that there is a current in a coil of wire if and only if the magnetic field passing through the coil is changing. This is an informal statement of Faraday s law. Electromagnetic
Faraday s Discovery Faraday found that there is a current in a coil of wire if and only if the magnetic field passing through the coil is changing. This is an informal statement of Faraday s law. Electromagnetic
WLPN Series SMD Molded Power Choke Inductors
 WLPN303010 Series SMD Molded Power Choke Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 9 ASC_WLPN303010 Series_V3.0 Oct. 2016 Features 1. Close magnetic loop with
WLPN303010 Series SMD Molded Power Choke Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 9 ASC_WLPN303010 Series_V3.0 Oct. 2016 Features 1. Close magnetic loop with
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3. OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION 3 Understand the principles and properties of magnetism Magnetic field:
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION 3 Understand the principles and properties of magnetism Magnetic field:
Three Phase Circuits
 Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
ENGR 2405 Chapter 6. Capacitors And Inductors
 ENGR 2405 Chapter 6 Capacitors And Inductors Overview This chapter will introduce two new linear circuit elements: The capacitor The inductor Unlike resistors, these elements do not dissipate energy They
ENGR 2405 Chapter 6 Capacitors And Inductors Overview This chapter will introduce two new linear circuit elements: The capacitor The inductor Unlike resistors, these elements do not dissipate energy They
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 2
 PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three identical lightbulbs connected to a battery having a constant voltage across its terminals. What happens to the brightness
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three identical lightbulbs connected to a battery having a constant voltage across its terminals. What happens to the brightness
Electromagnetic Induction
 lectromagnetic Induction Induced MF We already know that moving charge (=current) causes magnetic field It also works the other way around: changing magnetic field (e.g. moving permanent magnet) causes
lectromagnetic Induction Induced MF We already know that moving charge (=current) causes magnetic field It also works the other way around: changing magnetic field (e.g. moving permanent magnet) causes
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Transformer. Transformer comprises two or more windings coupled by a common magnetic circuit (M.C.).
 . Transformers Transformer Transformer comprises two or more windings coupled by a common magnetic circuit (M.C.). f the primary side is connected to an AC voltage source v (t), an AC flux (t) will be
. Transformers Transformer Transformer comprises two or more windings coupled by a common magnetic circuit (M.C.). f the primary side is connected to an AC voltage source v (t), an AC flux (t) will be
Induction Heating: fundamentals
 LEP ELECTROMAGNETIC PROCESSING OF MATERIALS TECNOLGIE DEI PROCESSI ELETTROTERMICI Induction Heating: fundamentals Fabrizio Dughiero 2017-2018 Induction heating fundamentals May 28-30, 2014 1 Summary 1.
LEP ELECTROMAGNETIC PROCESSING OF MATERIALS TECNOLGIE DEI PROCESSI ELETTROTERMICI Induction Heating: fundamentals Fabrizio Dughiero 2017-2018 Induction heating fundamentals May 28-30, 2014 1 Summary 1.
Different Techniques for Calculating Apparent and Incremental Inductances using Finite Element Method
 Different Techniques for Calculating Apparent and Incremental Inductances using Finite Element Method Dr. Amer Mejbel Ali Electrical Engineering Department Al-Mustansiriyah University Baghdad, Iraq amerman67@yahoo.com
Different Techniques for Calculating Apparent and Incremental Inductances using Finite Element Method Dr. Amer Mejbel Ali Electrical Engineering Department Al-Mustansiriyah University Baghdad, Iraq amerman67@yahoo.com
Reading Assignments Please see the handouts for each lesson for the reading assignments.
 Preparation Assignments for Homework #5 Due at the start of class. These assignments will only be accepted from students attending class. Reading Assignments Please see the handouts for each lesson for
Preparation Assignments for Homework #5 Due at the start of class. These assignments will only be accepted from students attending class. Reading Assignments Please see the handouts for each lesson for
EE155/255 Green Electronics
 EE155/255 Green Electronics Electric Motors 10/19/16 Prof. William Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University This week is flipped Course Logistics Discussion on 10/17, Motors on 10/19, Isolated
EE155/255 Green Electronics Electric Motors 10/19/16 Prof. William Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University This week is flipped Course Logistics Discussion on 10/17, Motors on 10/19, Isolated
Wireless charging using a separate third winding for reactive power supply
 Wireless charging using a separate third winding for reactive power supply Master s thesis in Energy and Environment IAN ŠALKOIĆ Department of Energy and Environment Division of Electric Power Engineering
Wireless charging using a separate third winding for reactive power supply Master s thesis in Energy and Environment IAN ŠALKOIĆ Department of Energy and Environment Division of Electric Power Engineering
Pretest ELEA1831 Module 11 Units 1& 2 Inductance & Capacitance
 Pretest ELEA1831 Module 11 Units 1& 2 Inductance & Capacitance 1. What is Faraday s Law? Magnitude of voltage induced in a turn of wire is proportional to the rate of change of flux passing through that
Pretest ELEA1831 Module 11 Units 1& 2 Inductance & Capacitance 1. What is Faraday s Law? Magnitude of voltage induced in a turn of wire is proportional to the rate of change of flux passing through that
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
Iron-Silicon (Fe-Si ) Powder Cores
 Iron-Silicon (Fe-Si ) Powder Cores INTRODUCTION Arnold Magnetics, a world leader in magnetic alloy powder products such as MPP, High- Flux and Super-MSS, now offers a new series of powder cores using an
Iron-Silicon (Fe-Si ) Powder Cores INTRODUCTION Arnold Magnetics, a world leader in magnetic alloy powder products such as MPP, High- Flux and Super-MSS, now offers a new series of powder cores using an
Alternating Current Circuits
 Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Lecture 11 - AC Power
 - AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
- AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
Application Note. Paralleling of EconoPACK TM + Date: Page
 Date: 27.09.2004 Page 1 Paralleling of EconoPACK TM + 1. EconoPACK TM + Design 2. Paralleling of IGBT 3 and EmCon HE diodes 3. Methods of paralleling EconoPACK TM + 4. Dynamic and static current sharing
Date: 27.09.2004 Page 1 Paralleling of EconoPACK TM + 1. EconoPACK TM + Design 2. Paralleling of IGBT 3 and EmCon HE diodes 3. Methods of paralleling EconoPACK TM + 4. Dynamic and static current sharing
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 15
 8.0 (E&M) Lecture 5 Topics: More on Electromagnetic Inductance Mutual and self inductance Practical applications Last time Electromagnetic inductance Faraday s (and Lentz s) law: Φ Integral form: emf...
8.0 (E&M) Lecture 5 Topics: More on Electromagnetic Inductance Mutual and self inductance Practical applications Last time Electromagnetic inductance Faraday s (and Lentz s) law: Φ Integral form: emf...
Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter II Electromagnetic Induction Day 1 Induced EMF, Faraday s Law and Lenz s Law Sections 21-1 to 21-2 Electromotive Force Electromotive force (EMF ore) is a misnomer, as it is not really a force but
Chapter II Electromagnetic Induction Day 1 Induced EMF, Faraday s Law and Lenz s Law Sections 21-1 to 21-2 Electromotive Force Electromotive force (EMF ore) is a misnomer, as it is not really a force but
Lecture 4: RL Circuits. Inductive Kick. Diode Snubbers.
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 6 Lecture 4: RL Circuits. Inductive Kick. Diode Snubbers. Inductors are the third basic discrete coponent listed in Lecture 2. Uses for inductors in the NorCal 40A include
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 6 Lecture 4: RL Circuits. Inductive Kick. Diode Snubbers. Inductors are the third basic discrete coponent listed in Lecture 2. Uses for inductors in the NorCal 40A include
EE155/255 Green Electronics
 EE155/255 Green Electronics Electric Motors 10/16/17 Prof. William Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University Course Logistics Solar day is Monday 10/23 HW 3 is due today HW 4 out, due next
EE155/255 Green Electronics Electric Motors 10/16/17 Prof. William Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University Course Logistics Solar day is Monday 10/23 HW 3 is due today HW 4 out, due next
Inductance, RL Circuits, LC Circuits, RLC Circuits
 Inductance, R Circuits, C Circuits, RC Circuits Inductance What happens when we close the switch? The current flows What does the current look like as a function of time? Does it look like this? I t Inductance
Inductance, R Circuits, C Circuits, RC Circuits Inductance What happens when we close the switch? The current flows What does the current look like as a function of time? Does it look like this? I t Inductance
WLPN Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors
 WLPN404018 Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 11 ASC_WLPN404018 Series_V2.0 Oct. 2016 Features 1. Close magnetic loop with
WLPN404018 Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 11 ASC_WLPN404018 Series_V2.0 Oct. 2016 Features 1. Close magnetic loop with
Mutual Inductance. The field lines flow from a + charge to a - change
 Capacitors Mutual Inductance Since electrical charges do exist, electric field lines have a starting point and an ending point. For example, if you have a + and a - change, the field lines would look something
Capacitors Mutual Inductance Since electrical charges do exist, electric field lines have a starting point and an ending point. For example, if you have a + and a - change, the field lines would look something
WLPN Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors
 WLPN505020 Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 9 ASC_WLPN505020 Series_V0.0 Dec. 2016 1R0 Approval sheet Features 1. Close
WLPN505020 Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 9 ASC_WLPN505020 Series_V0.0 Dec. 2016 1R0 Approval sheet Features 1. Close
Physics 1c Practical, Spring 2015 Hw 3 Solutions
 Physics 1c Practical, Spring 2015 Hw 3 Solutions April 16, 2015 1 Serway 31.79 (5 points) By Lenz s Law, current will flow in each of the two sub-loops to oppose the change in flux. One can easily see
Physics 1c Practical, Spring 2015 Hw 3 Solutions April 16, 2015 1 Serway 31.79 (5 points) By Lenz s Law, current will flow in each of the two sub-loops to oppose the change in flux. One can easily see
WLPN Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors
 WLPN202012 Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 9 ASC_WLPN202012 Series_V2.0 Sep. 2014 Features 1. Close magnetic loop with
WLPN202012 Series Shielded SMD Power Inductors *Contents in this sheet are subject to change without prior notice. Page 1 of 9 ASC_WLPN202012 Series_V2.0 Sep. 2014 Features 1. Close magnetic loop with
Chapter 6: Efficiency and Heating. 9/18/2003 Electromechanical Dynamics 1
 Chapter 6: Efficiency and Heating 9/18/2003 Electromechanical Dynamics 1 Losses As a machine transforms energy from one form to another there is always a certain power loss the loss is expressed as heat,
Chapter 6: Efficiency and Heating 9/18/2003 Electromechanical Dynamics 1 Losses As a machine transforms energy from one form to another there is always a certain power loss the loss is expressed as heat,
Theoretical Analysis of AC Resistance of Coil Made by Copper Clad Aluminum Wires
 730 PIERS Proceedings, Stockholm, Sweden, Aug. 2 5, 203 Theoretical Analysis of AC Resistance of Coil Made by Copper Clad Aluminum Wires C. Kamidaki and N. Guan Power and Telecommunication Cable System
730 PIERS Proceedings, Stockholm, Sweden, Aug. 2 5, 203 Theoretical Analysis of AC Resistance of Coil Made by Copper Clad Aluminum Wires C. Kamidaki and N. Guan Power and Telecommunication Cable System
Development of axial flux HTS induction motors
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 35 (01 ) 4 13 International Meeting of Electrical Engineering Research ENIINVIE-01 Development of axial flux HTS induction motors A. González-Parada
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 35 (01 ) 4 13 International Meeting of Electrical Engineering Research ENIINVIE-01 Development of axial flux HTS induction motors A. González-Parada
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194
 MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
Non-Linear Saturable Kool Mu Core Model
 Non-Linear Saturable Kool Mu Core Model Scott Frankel, AEi Systems, LLC Iron Powder cores have been well suited for applications such as switching regulator inductors, in-line noise filters, and flyback
Non-Linear Saturable Kool Mu Core Model Scott Frankel, AEi Systems, LLC Iron Powder cores have been well suited for applications such as switching regulator inductors, in-line noise filters, and flyback
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies
 Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
Physics 2020 Exam 2 Constants and Formulae
 Physics 2020 Exam 2 Constants and Formulae Useful Constants k e = 8.99 10 9 N m 2 /C 2 c = 3.00 10 8 m/s ɛ = 8.85 10 12 C 2 /(N m 2 ) µ = 4π 10 7 T m/a e = 1.602 10 19 C h = 6.626 10 34 J s m p = 1.67
Physics 2020 Exam 2 Constants and Formulae Useful Constants k e = 8.99 10 9 N m 2 /C 2 c = 3.00 10 8 m/s ɛ = 8.85 10 12 C 2 /(N m 2 ) µ = 4π 10 7 T m/a e = 1.602 10 19 C h = 6.626 10 34 J s m p = 1.67
Chapter 1 Magnetic Circuits
 Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics Third Edition P. C. Sen Chapter 1 Magnetic Circuits Chapter 1: Main contents i-h relation, B-H relation Magnetic circuit and analysis Property of magnetic
Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics Third Edition P. C. Sen Chapter 1 Magnetic Circuits Chapter 1: Main contents i-h relation, B-H relation Magnetic circuit and analysis Property of magnetic
Magnetic Fields; Sources of Magnetic Field
 This test covers magnetic fields, magnetic forces on charged particles and current-carrying wires, the Hall effect, the Biot-Savart Law, Ampère s Law, and the magnetic fields of current-carrying loops
This test covers magnetic fields, magnetic forces on charged particles and current-carrying wires, the Hall effect, the Biot-Savart Law, Ampère s Law, and the magnetic fields of current-carrying loops
Some Important Electrical Units
 Some Important Electrical Units Quantity Unit Symbol Current Charge Voltage Resistance Power Ampere Coulomb Volt Ohm Watt A C V W W These derived units are based on fundamental units from the meterkilogram-second
Some Important Electrical Units Quantity Unit Symbol Current Charge Voltage Resistance Power Ampere Coulomb Volt Ohm Watt A C V W W These derived units are based on fundamental units from the meterkilogram-second
PHYS 241 EXAM #2 November 9, 2006
 1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1. "Electrical Eng Science"
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1 COURSE NAME: "Electrical Eng Science" CODE: GROUP: "[ADET 2]" DATE: December 2010 TIME: DURATION: 9:00 am "Two hours" INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1 COURSE NAME: "Electrical Eng Science" CODE: GROUP: "[ADET 2]" DATE: December 2010 TIME: DURATION: 9:00 am "Two hours" INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
