Angular Motion, Speed and Velocity
|
|
|
- Christopher Junior Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 163 Noe/Cue Here Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Underanding Goal: underand erm relaing o angular poiion, peed & velociy Language Objecive: Underand and correcly ue he erm angle and angular velociy. Accuraely decribe and apply he concep decribed in hi ecion uing appropriae academic language. Lab, Aciviie & Demonraion: Noe: Swing an objec on a ring. If an objec i roaing (raveling in a circle), hen i poiion a any given ime can be decribed uing polar coördinae by i diance from he cener of he circle (r) and i angle (θ ) relaive o ome reference angle (which we will call 0 ). arc lengh (): he lengh of an arc; he diance raveled around par of a circle. r Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
2 Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 164 Noe/Cue Here angular velociy (ω): he roaional velociy of an objec a i ravel around a circle, i.e., i change in angle per uni of ime. (For purpoe of comparion, he definiion of angular velociy i preened along wih i linear counerpar.) d x x xo v linear ω angular In general, phyici ue Greek leer for angular variable. The variable for angular velociy i he lower cae Greek leer omega (ω). Be careful o diinguih in your wriing beween he Greek leer ω and he Roman leer w. angenial velociy: he linear velociy of a poin on a rigid, roaing body. The erm angenial velociy i ued becaue he inananeou direcion of he velociy i angenial o he direcion of roaion. To find he angenial velociy of a poin on a roaing (rigid) body, he poin ravel an arc lengh of in ime. If angle θ i in radian, hen = rδθ. Thi mean: r vt rω and herefore vt rω Sample Problem: Q: Wha i he angular velociy ( rad ) in of a car engine ha i pinning a 400 rpm? A: 400 rpm mean 400 revoluion per minue. 400 rev 1min rad min 60 1rev 60 rev rev 51 o Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
3 Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 165 Noe/Cue Here Q: Find he oal diance raveled in 10 by a penny iing on a pinning dic wih a radiu of 0.5 m ha i roaing a a rae of 1 revoluion per. A: We are looking for he diance around he circle, which i he arc lengh. (Thi mean we need o work in radian.) r We know ha r = 0.5 m, bu we need o find ω. We know ha = 10, bu we need o find he angular velociy ω. rad 1 revoluion per i an angular velociy of ω. Now we can olve: ω ( )(10) 10 r (0.5)(10 ).5 m (.5)(3.14) 7.85m Exenion Ju a jerk i he rae of change of linear acceleraion, angular jerk i he rae of change of angular acceleraion. ζ α. (ζ i he Greek leer zea. Many college profeor canno draw i correcly and ju call i quiggle.) Angular jerk ha no been een on AP Phyic exam. Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
4 Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 166 Noe/Cue Here Homework Problem 1. Through wha angle mu he wheel hown a he righ urn in order o unwind 40 cm of ring? Anwer: rad. Find he average angular velociy of a ofball picher arm (in rad ) if, in hrowing he ball, her arm roae one-hird of a revoluion on 0.1. Anwer: 0.9 rad 3. A golfer wing a nine iron (radiu = 1.1 m) wih an average angular velociy of 5.0 rad. Find he angenial velociy of he club head. Anwer: 5.5 m Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
5 Add Imporan Angular Acceleraion Page: 167 Noe/Cue Here NGSS Sandard: N/A Angular Acceleraion MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Underanding Goal: Skill: wha angular acceleraion mean calculae angle, angular velociy and angular acceleraion for problem ha involve roaional moion. Language Objecive: Underand and correcly ue he erm angular acceleraion. Accuraely decribe and apply he concep decribed in hi ecion uing appropriae academic language. Lab, Aciviie & Demonraion: Noe: Swing an objec on a ring and hen change i angular velociy. If a roaing objec ar roaing faer or lower, hi mean i roaional velociy i changing. angular acceleraion (α): he change in angular velociy wih repec o ime. (Again, he definiion i preened wih he linear equaion for comparion.) v v a linear v o ω ω α angular A before, be careful o diinguih beween he lower cae Greek leer α and he lower cae Roman leer a. ω o Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
6 Add Imporan Angular Acceleraion Page: 168 Noe/Cue Here A wih linear acceleraion, if he objec ha angular velociy and hen accelerae, he poiion equaion look like hi: x x o vo linear 1 a θ θ o ωo angular 1 α angenial acceleraion: he linear acceleraion of a poin on a rigid, roaing body. The erm angenial acceleraion i ued becaue he inananeou direcion of he acceleraion i angenial o he direcion of roaion. The angenial acceleraion of a poin on a rigid, roaing body i: a rα Sample Problem: T Q: A bicycli i riding a an iniial (linear) velociy of 7.5 m, and accelerae o a velociy of 10.0 over a duraion of 5.0. If he wheel on he bicycle have a m radiu of m, wha i he angular acceleraion of he bicycle wheel? A: Fir we need o find he iniial and final angular velociie of he bike wheel. We can do hi from he angenial velociy, which equal he velociy of he bicycle. vo, T rωo 7.5 (0.343) ω ω o o 1.87 Then we can ue he equaion: rad rad vt rω 10.0 (0.343) ω ω ω ωo α α(5.0) α α rad Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
7 Add Imporan Angular Acceleraion Page: 169 Noe/Cue Here An alernaive mehod i o olve he equaion by finding he linear acceleraion fir: v vo a a(5).5 5a a m Then we can ue he relaionhip beween angenial acceleraion and angular acceleraion: at rα 0.5 (0.343) α a α 1.46 rad Homework Problem 1. A urnable roaing a 33⅓ RPM i hu off. I low down a a conan rae and coa o a op in 6. Wha i i angular acceleraion? rad Anwer: Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
8 Add Imporan Angular Acceleraion Page: 170 Noe/Cue Here. A urnable roaing wih an angular velociy of ω o i hu off. I low down a a conan rae and coa o a op in ime. Wha i i angular acceleraion, α? (You may ue your work from problem #1 above o guide you hrough he algebra.) Anwer: o 3. One of he demonraion we aw in cla wa winging a bucke of waer in a verical circle wihou pilling any of he waer. a. Explain why he waer ayed in he bucke. b. If he combined lengh of your arm and he bucke i 0.90 m, wha i he minimum angenial velociy ha he bucke mu have in order o no pill any waer? Anwer: 3.33 m Ue hi pace for ummary and/or addiional noe. AP Phyic 1: Algebra-Baed
Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity
 Add Iporan Linear Moion, Speed & Velociy Page: 136 Linear Moion, Speed & Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculu Fraework (2006): 1.1, 1.2 AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Underanding
Add Iporan Linear Moion, Speed & Velociy Page: 136 Linear Moion, Speed & Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculu Fraework (2006): 1.1, 1.2 AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Underanding
Physics 240: Worksheet 16 Name
 Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Discussion Session 2 Constant Acceleration/Relative Motion Week 03
 PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
13.1 Accelerating Objects
 13.1 Acceleraing Objec A you learned in Chaper 12, when you are ravelling a a conan peed in a raigh line, you have uniform moion. However, mo objec do no ravel a conan peed in a raigh line o hey do no
13.1 Acceleraing Objec A you learned in Chaper 12, when you are ravelling a a conan peed in a raigh line, you have uniform moion. However, mo objec do no ravel a conan peed in a raigh line o hey do no
and v y . The changes occur, respectively, because of the acceleration components a x and a y
 Week 3 Reciaion: Chaper3 : Problems: 1, 16, 9, 37, 41, 71. 1. A spacecraf is raveling wih a veloci of v0 = 5480 m/s along he + direcion. Two engines are urned on for a ime of 84 s. One engine gives he
Week 3 Reciaion: Chaper3 : Problems: 1, 16, 9, 37, 41, 71. 1. A spacecraf is raveling wih a veloci of v0 = 5480 m/s along he + direcion. Two engines are urned on for a ime of 84 s. One engine gives he
= + t ] can be used to calculate the angular
![= + t ] can be used to calculate the angular = + t ] can be used to calculate the angular](/thumbs/94/120776871.jpg) WEEK-7 Reciaion PHYS 3 Mar 8, 8 Ch. 8 FOC:, 4, 6,, 3 &5. () Using Equaion 8. (θ = Arc lengh / Raius) o calculae he angle (in raians) ha each objec subens a your eye shows ha θ Moon = 9. 3 ra, θ Pea = 7.
WEEK-7 Reciaion PHYS 3 Mar 8, 8 Ch. 8 FOC:, 4, 6,, 3 &5. () Using Equaion 8. (θ = Arc lengh / Raius) o calculae he angle (in raians) ha each objec subens a your eye shows ha θ Moon = 9. 3 ra, θ Pea = 7.
Roller-Coaster Coordinate System
 Winer 200 MECH 220: Mechanics 2 Roller-Coaser Coordinae Sysem Imagine you are riding on a roller-coaer in which he rack goes up and down, wiss and urns. Your velociy and acceleraion will change (quie abruply),
Winer 200 MECH 220: Mechanics 2 Roller-Coaser Coordinae Sysem Imagine you are riding on a roller-coaer in which he rack goes up and down, wiss and urns. Your velociy and acceleraion will change (quie abruply),
Motion In One Dimension. Graphing Constant Speed
 Moion In One Dimenion PLATO AND ARISTOTLE GALILEO GALILEI LEANING TOWER OF PISA Graphing Conan Speed Diance v. Time for Toy Car (0-5 ec.) be-fi line (from TI calculaor) d = 207.7 12.6 Diance (cm) 1000
Moion In One Dimenion PLATO AND ARISTOTLE GALILEO GALILEI LEANING TOWER OF PISA Graphing Conan Speed Diance v. Time for Toy Car (0-5 ec.) be-fi line (from TI calculaor) d = 207.7 12.6 Diance (cm) 1000
MEI Mechanics 1 General motion. Section 1: Using calculus
 Soluions o Exercise MEI Mechanics General moion Secion : Using calculus. s 4 v a 6 4 4 When =, v 4 a 6 4 6. (i) When = 0, s = -, so he iniial displacemen = - m. s v 4 When = 0, v = so he iniial velociy
Soluions o Exercise MEI Mechanics General moion Secion : Using calculus. s 4 v a 6 4 4 When =, v 4 a 6 4 6. (i) When = 0, s = -, so he iniial displacemen = - m. s v 4 When = 0, v = so he iniial velociy
2001 November 15 Exam III Physics 191
 1 November 15 Eam III Physics 191 Physical Consans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s 2 Circle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh 1 poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses:
1 November 15 Eam III Physics 191 Physical Consans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s 2 Circle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh 1 poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses:
TP B.2 Rolling resistance, spin resistance, and "ball turn"
 echnical proof TP B. olling reiance, pin reiance, and "ball urn" upporing: The Illuraed Principle of Pool and Billiard hp://billiard.coloae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore, PhD, PE ("Dr. Dae") echnical proof originally
echnical proof TP B. olling reiance, pin reiance, and "ball urn" upporing: The Illuraed Principle of Pool and Billiard hp://billiard.coloae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore, PhD, PE ("Dr. Dae") echnical proof originally
2002 November 14 Exam III Physics 191
 November 4 Exam III Physics 9 Physical onsans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s ircle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses: m = kg, m
November 4 Exam III Physics 9 Physical onsans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s ircle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses: m = kg, m
Chapter 1 Rotational dynamics 1.1 Angular acceleration
 Chaper Roaional dynamics. Angular acceleraion Learning objecives: Wha do we mean by angular acceleraion? How can we calculae he angular acceleraion of a roaing objec when i speeds up or slows down? How
Chaper Roaional dynamics. Angular acceleraion Learning objecives: Wha do we mean by angular acceleraion? How can we calculae he angular acceleraion of a roaing objec when i speeds up or slows down? How
2.1: What is physics? Ch02: Motion along a straight line. 2.2: Motion. 2.3: Position, Displacement, Distance
 Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
2. VECTORS. R Vectors are denoted by bold-face characters such as R, V, etc. The magnitude of a vector, such as R, is denoted as R, R, V
 ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration
 rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
AP Calculus BC Chapter 10 Part 1 AP Exam Problems
 AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
Equations of motion for constant acceleration
 Lecure 3 Chaper 2 Physics I 01.29.2014 Equaions of moion for consan acceleraion Course websie: hp://faculy.uml.edu/andriy_danylo/teaching/physicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo360.uml.edu/danylo2013/physics1spring.hml
Lecure 3 Chaper 2 Physics I 01.29.2014 Equaions of moion for consan acceleraion Course websie: hp://faculy.uml.edu/andriy_danylo/teaching/physicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo360.uml.edu/danylo2013/physics1spring.hml
Chapters 6 & 7: Trigonometric Functions of Angles and Real Numbers. Divide both Sides by 180
 Algebra Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers - Angle Measures Radians: - a uni (rad o measure he size of an angle. rad
Algebra Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers - Angle Measures Radians: - a uni (rad o measure he size of an angle. rad
3, so θ = arccos
 Mahemaics 210 Professor Alan H Sein Monday, Ocober 1, 2007 SOLUTIONS This problem se is worh 50 poins 1 Find he angle beween he vecors (2, 7, 3) and (5, 2, 4) Soluion: Le θ be he angle (2, 7, 3) (5, 2,
Mahemaics 210 Professor Alan H Sein Monday, Ocober 1, 2007 SOLUTIONS This problem se is worh 50 poins 1 Find he angle beween he vecors (2, 7, 3) and (5, 2, 4) Soluion: Le θ be he angle (2, 7, 3) (5, 2,
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
EF 151 Exam #2 - Spring, 2014 Page 1 of 6
 EF 5 Exam # - Spring, 04 Page of 6 Name: Secion: Inrucion: Pu your name and ecion on he exam. Do no open he e unil you are old o do o. Wrie your final anwer in he box proided If you finih wih le han 5
EF 5 Exam # - Spring, 04 Page of 6 Name: Secion: Inrucion: Pu your name and ecion on he exam. Do no open he e unil you are old o do o. Wrie your final anwer in he box proided If you finih wih le han 5
copper ring magnetic field
 IB PHYSICS: Magneic Fields, lecromagneic Inducion, Alernaing Curren 1. This quesion is abou elecromagneic inducion. In 1831 Michael Faraday demonsraed hree ways of inducing an elecric curren in a ring
IB PHYSICS: Magneic Fields, lecromagneic Inducion, Alernaing Curren 1. This quesion is abou elecromagneic inducion. In 1831 Michael Faraday demonsraed hree ways of inducing an elecric curren in a ring
Non-uniform circular motion *
 OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
Curvature. Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi pg. 1
 Dicipline Coure-I Semeer-I Paper: Calculu-I Leon: Leon Developer: Chaianya Kumar College/Deparmen: Deparmen of Mahemaic, Delhi College of r and Commerce, Univeriy of Delhi Iniue of Lifelong Learning, Univeriy
Dicipline Coure-I Semeer-I Paper: Calculu-I Leon: Leon Developer: Chaianya Kumar College/Deparmen: Deparmen of Mahemaic, Delhi College of r and Commerce, Univeriy of Delhi Iniue of Lifelong Learning, Univeriy
~v = x. ^x + ^y + ^x + ~a = vx. v = v 0 + at. ~v P=A = ~v P=B + ~v B=A. f k = k. W tot =KE. P av =W=t. W grav = mgy 1, mgy 2 = mgh =,U grav
 PHYSICS 5A FALL 2001 FINAL EXAM v = x a = v x = 1 2 a2 + v 0 + x 0 v 2 = v 2 0 +2a(x, x 0) a = v2 r ~v = x ~a = vx v = v 0 + a y z ^x + ^y + ^z ^x + vy x, x 0 = 1 2 (v 0 + v) ~v P=A = ~v P=B + ~v B=A ^y
PHYSICS 5A FALL 2001 FINAL EXAM v = x a = v x = 1 2 a2 + v 0 + x 0 v 2 = v 2 0 +2a(x, x 0) a = v2 r ~v = x ~a = vx v = v 0 + a y z ^x + ^y + ^z ^x + vy x, x 0 = 1 2 (v 0 + v) ~v P=A = ~v P=B + ~v B=A ^y
EF 151 Exam #1, Spring, 2009 Page 1 of 6
 EF 5 Exam #, Spring, 009 Page of 6 Name: Guideline: Aume 3 ignifican figure for all given number unle oherwie aed Show all of your work no work, no credi Wrie your final anwer in he box provided Include
EF 5 Exam #, Spring, 009 Page of 6 Name: Guideline: Aume 3 ignifican figure for all given number unle oherwie aed Show all of your work no work, no credi Wrie your final anwer in he box provided Include
Displacement ( x) x x x
 Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Parametrics and Vectors (BC Only)
 Paramerics and Vecors (BC Only) The following relaionships should be learned and memorized. The paricle s posiion vecor is r() x(), y(). The velociy vecor is v(),. The speed is he magniude of he velociy
Paramerics and Vecors (BC Only) The following relaionships should be learned and memorized. The paricle s posiion vecor is r() x(), y(). The velociy vecor is v(),. The speed is he magniude of he velociy
A man pushes a 500 kg block along the x axis by a constant force. Find the power required to maintain a speed of 5.00 m/s.
 Coordinaor: Dr. F. hiari Wednesday, July 16, 2014 Page: 1 Q1. The uniform solid block in Figure 1 has mass 0.172 kg and edge lenghs a = 3.5 cm, b = 8.4 cm, and c = 1.4 cm. Calculae is roaional ineria abou
Coordinaor: Dr. F. hiari Wednesday, July 16, 2014 Page: 1 Q1. The uniform solid block in Figure 1 has mass 0.172 kg and edge lenghs a = 3.5 cm, b = 8.4 cm, and c = 1.4 cm. Calculae is roaional ineria abou
Speed and Velocity. Overview. Velocity & Speed. Speed & Velocity. Instantaneous Velocity. Instantaneous and Average
 Overview Kinemaics: Descripion of Moion Posiion and displacemen velociy»insananeous acceleraion»insananeous Speed Velociy Speed and Velociy Speed & Velociy Velociy & Speed A physics eacher walks 4 meers
Overview Kinemaics: Descripion of Moion Posiion and displacemen velociy»insananeous acceleraion»insananeous Speed Velociy Speed and Velociy Speed & Velociy Velociy & Speed A physics eacher walks 4 meers
Physics 221 Fall 2008 Homework #2 Solutions Ch. 2 Due Tues, Sept 9, 2008
 Physics 221 Fall 28 Homework #2 Soluions Ch. 2 Due Tues, Sep 9, 28 2.1 A paricle moving along he x-axis moves direcly from posiion x =. m a ime =. s o posiion x = 1. m by ime = 1. s, and hen moves direcly
Physics 221 Fall 28 Homework #2 Soluions Ch. 2 Due Tues, Sep 9, 28 2.1 A paricle moving along he x-axis moves direcly from posiion x =. m a ime =. s o posiion x = 1. m by ime = 1. s, and hen moves direcly
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
y z P 3 P T P1 P 2. Werner Purgathofer. b a
 Einführung in Viual Compuing Einführung in Viual Compuing 86.822 in co T P 3 P co in T P P 2 co in Geomeric Tranformaion Geomeric Tranformaion W P h f Werner Purgahofer b a Tranformaion in he Rendering
Einführung in Viual Compuing Einführung in Viual Compuing 86.822 in co T P 3 P co in T P P 2 co in Geomeric Tranformaion Geomeric Tranformaion W P h f Werner Purgahofer b a Tranformaion in he Rendering
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #4
 PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
Giambattista, Ch 3 Problems: 9, 15, 21, 27, 35, 37, 42, 43, 47, 55, 63, 76
 Giambaisa, Ch 3 Problems: 9, 15, 21, 27, 35, 37, 42, 43, 47, 55, 63, 76 9. Sraeg Le be direced along he +x-axis and le be 60.0 CCW from Find he magniude of 6.0 B 60.0 4.0 A x 15. (a) Sraeg Since he angle
Giambaisa, Ch 3 Problems: 9, 15, 21, 27, 35, 37, 42, 43, 47, 55, 63, 76 9. Sraeg Le be direced along he +x-axis and le be 60.0 CCW from Find he magniude of 6.0 B 60.0 4.0 A x 15. (a) Sraeg Since he angle
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Test points. Provide the best answer to the following questions and problems. Watch your sig figs.
 Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Impulse. calculate the impulse given to an object calculate the change in momentum as the result of an impulse
 Add Important Impule Page: 386 Note/Cue Here NGSS Standard: N/A Impule MA Curriculum Framework (2006): 2.5 AP Phyic 1 Learning Objective: 3.D.2.1, 3.D.2.2, 3.D.2.3, 3.D.2.4, 4.B.2.1, 4.B.2.2 Knowledge/Undertanding
Add Important Impule Page: 386 Note/Cue Here NGSS Standard: N/A Impule MA Curriculum Framework (2006): 2.5 AP Phyic 1 Learning Objective: 3.D.2.1, 3.D.2.2, 3.D.2.3, 3.D.2.4, 4.B.2.1, 4.B.2.2 Knowledge/Undertanding
Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity
 Add Important Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity Page: 136 Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity NGSS Standard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objective: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Undertanding
Add Important Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity Page: 136 Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity NGSS Standard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objective: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Undertanding
Math 105 Second Midterm March 16, 2017
 Mah 105 Second Miderm March 16, 2017 UMID: Insrucor: Iniials: Secion: 1. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so. 2. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has 9 pages including his
Mah 105 Second Miderm March 16, 2017 UMID: Insrucor: Iniials: Secion: 1. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so. 2. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has 9 pages including his
!!"#"$%&#'()!"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./0)1-*23)
 "#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
"#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
x i v x t a dx dt t x
 Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
t A. 3. Which vector has the largest component in the y-direction, as defined by the axes to the right?
 Ke Name Insrucor Phsics 1210 Exam 1 Sepember 26, 2013 Please wrie direcl on he exam and aach oher shees of work if necessar. Calculaors are allowed. No noes or books ma be used. Muliple-choice problems
Ke Name Insrucor Phsics 1210 Exam 1 Sepember 26, 2013 Please wrie direcl on he exam and aach oher shees of work if necessar. Calculaors are allowed. No noes or books ma be used. Muliple-choice problems
Physics 20 Lesson 5 Graphical Analysis Acceleration
 Physics 2 Lesson 5 Graphical Analysis Acceleraion I. Insananeous Velociy From our previous work wih consan speed and consan velociy, we know ha he slope of a posiion-ime graph is equal o he velociy of
Physics 2 Lesson 5 Graphical Analysis Acceleraion I. Insananeous Velociy From our previous work wih consan speed and consan velociy, we know ha he slope of a posiion-ime graph is equal o he velociy of
Suggested Practice Problems (set #2) for the Physics Placement Test
 Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Rectilinear Kinematics
 Recilinear Kinemaic Coninuou Moion Sir Iaac Newon Leonard Euler Oeriew Kinemaic Coninuou Moion Erraic Moion Michael Schumacher. 7-ime Formula 1 World Champion Kinemaic The objecie of kinemaic i o characerize
Recilinear Kinemaic Coninuou Moion Sir Iaac Newon Leonard Euler Oeriew Kinemaic Coninuou Moion Erraic Moion Michael Schumacher. 7-ime Formula 1 World Champion Kinemaic The objecie of kinemaic i o characerize
Practicing Problem Solving and Graphing
 Pracicing Problem Solving and Graphing Tes 1: Jan 30, 7pm, Ming Hsieh G20 The Bes Ways To Pracice for Tes Bes If need more, ry suggesed problems from each new opic: Suden Response Examples A pas opic ha
Pracicing Problem Solving and Graphing Tes 1: Jan 30, 7pm, Ming Hsieh G20 The Bes Ways To Pracice for Tes Bes If need more, ry suggesed problems from each new opic: Suden Response Examples A pas opic ha
PHYS 100: Lecture 2. Motion at Constant Acceleration. Relative Motion: Reference Frames. x x = v t + a t. x = vdt. v = adt. x Tortoise.
 a PHYS 100: Lecure 2 Moion a Consan Acceleraion a 0 0 Area a 0 a 0 v ad v v0 a0 v 0 x vd 0 A(1/2)( v) Area v 0 v v-v 0 v 0 x x v + a 1 0 0 2 0 2 Relaive Moion: Reference Frames x d Achilles Toroise x Toroise
a PHYS 100: Lecure 2 Moion a Consan Acceleraion a 0 0 Area a 0 a 0 v ad v v0 a0 v 0 x vd 0 A(1/2)( v) Area v 0 v v-v 0 v 0 x x v + a 1 0 0 2 0 2 Relaive Moion: Reference Frames x d Achilles Toroise x Toroise
4.5 Constant Acceleration
 4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
Kinematics Vocabulary. Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion. Position. Coordinate System in One Dimension. Kinema means movement 8.
 Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
d = ½(v o + v f) t distance = ½ (initial velocity + final velocity) time
 BULLSEYE Lab Name: ANSWER KEY Dae: Pre-AP Physics Lab Projecile Moion Weigh = 1 DIRECTIONS: Follow he insrucions below, build he ramp, ake your measuremens, and use your measuremens o make he calculaions
BULLSEYE Lab Name: ANSWER KEY Dae: Pre-AP Physics Lab Projecile Moion Weigh = 1 DIRECTIONS: Follow he insrucions below, build he ramp, ake your measuremens, and use your measuremens o make he calculaions
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Kinematics. Position. Lectures 3 and 4 Motion in One Dimension. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Week 1 Lecture 2 Problems 2, 5. What if something oscillates with no obvious spring? What is ω? (problem set problem)
 Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
2. What is the displacement of the bug between t = 0.00 s and t = 20.0 s? A) cm B) 39.9 cm C) cm D) 16.1 cm E) +16.
 1. For which one of he following siuaions will he pah lengh equal he magniude of he displacemen? A) A jogger is running around a circular pah. B) A ball is rolling down an inclined plane. C) A rain ravels
1. For which one of he following siuaions will he pah lengh equal he magniude of he displacemen? A) A jogger is running around a circular pah. B) A ball is rolling down an inclined plane. C) A rain ravels
One-Dimensional Kinematics
 One-Dimensional Kinemaics One dimensional kinemaics refers o moion along a sraigh line. Een hough we lie in a 3-dimension world, moion can ofen be absraced o a single dimension. We can also describe moion
One-Dimensional Kinemaics One dimensional kinemaics refers o moion along a sraigh line. Een hough we lie in a 3-dimension world, moion can ofen be absraced o a single dimension. We can also describe moion
1. The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object from t = 0 to t = T. a
 Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
5.2 GRAPHICAL VELOCITY ANALYSIS Polygon Method
 ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
AP CALCULUS AB 2003 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion A blood vessel is 6 millimeers (mm) long Disance wih circular cross secions of varying diameer. x (mm) 6 8 4 6 Diameer The able above gives he measuremens of he B(x)
SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion A blood vessel is 6 millimeers (mm) long Disance wih circular cross secions of varying diameer. x (mm) 6 8 4 6 Diameer The able above gives he measuremens of he B(x)
Motion along a Straight Line
 chaper 2 Moion along a Sraigh Line verage speed and average velociy (Secion 2.2) 1. Velociy versus speed Cone in he ebook: fer Eample 2. Insananeous velociy and insananeous acceleraion (Secions 2.3, 2.4)
chaper 2 Moion along a Sraigh Line verage speed and average velociy (Secion 2.2) 1. Velociy versus speed Cone in he ebook: fer Eample 2. Insananeous velociy and insananeous acceleraion (Secions 2.3, 2.4)
Best test practice: Take the past test on the class website
 Bes es pracice: Take he pas es on he class websie hp://communiy.wvu.edu/~miholcomb/phys11.hml I have posed he key o he WebAssign pracice es. Newon Previous Tes is Online. Forma will be idenical. You migh
Bes es pracice: Take he pas es on he class websie hp://communiy.wvu.edu/~miholcomb/phys11.hml I have posed he key o he WebAssign pracice es. Newon Previous Tes is Online. Forma will be idenical. You migh
Physics 4A FINAL EXAM Chapters 1-16 Fall 1998
 Name: Posing Code Solve he following problems in he space provided Use he back of he page if needed Each problem is worh 10 poins You mus show our work in a logical fashion saring wih he correcl applied
Name: Posing Code Solve he following problems in he space provided Use he back of he page if needed Each problem is worh 10 poins You mus show our work in a logical fashion saring wih he correcl applied
EQUATIONS REVIEW I Lesson Notes. Example 1. Example 2. Equations Review. 5 2 x = 1 6. Simple Equations
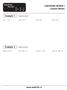 Equaions Review x + 3 = 6 EQUATIONS REVIEW I Example Simple Equaions a) a - 7 = b) m - 9 = -7 c) 6r = 4 d) 7 = -9x Example Simple Equaions a) 6p + = 4 b) 4 = 3k + 6 c) 9 + k = + 3k d) 8-3n = -8n + 3 EQUATIONS
Equaions Review x + 3 = 6 EQUATIONS REVIEW I Example Simple Equaions a) a - 7 = b) m - 9 = -7 c) 6r = 4 d) 7 = -9x Example Simple Equaions a) 6p + = 4 b) 4 = 3k + 6 c) 9 + k = + 3k d) 8-3n = -8n + 3 EQUATIONS
Randomized Perfect Bipartite Matching
 Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
How to Solve System Dynamic s Problems
 How o Solve Sye Dynaic Proble A ye dynaic proble involve wo or ore bodie (objec) under he influence of everal exernal force. The objec ay uliaely re, ove wih conan velociy, conan acceleraion or oe cobinaion
How o Solve Sye Dynaic Proble A ye dynaic proble involve wo or ore bodie (objec) under he influence of everal exernal force. The objec ay uliaely re, ove wih conan velociy, conan acceleraion or oe cobinaion
x(m) t(sec ) Homework #2. Ph 231 Introductory Physics, Sp-03 Page 1 of 4
 Homework #2. Ph 231 Inroducory Physics, Sp-03 Page 1 of 4 2-1A. A person walks 2 miles Eas (E) in 40 minues and hen back 1 mile Wes (W) in 20 minues. Wha are her average speed and average velociy (in ha
Homework #2. Ph 231 Inroducory Physics, Sp-03 Page 1 of 4 2-1A. A person walks 2 miles Eas (E) in 40 minues and hen back 1 mile Wes (W) in 20 minues. Wha are her average speed and average velociy (in ha
Farr High School NATIONAL 5 PHYSICS. Unit 3 Dynamics and Space. Exam Questions
 Farr High School NATIONAL 5 PHYSICS Uni Dynamics and Space Exam Quesions VELOCITY AND DISPLACEMENT D B D 4 E 5 B 6 E 7 E 8 C VELOCITY TIME GRAPHS (a) I is acceleraing Speeding up (NOT going down he flume
Farr High School NATIONAL 5 PHYSICS Uni Dynamics and Space Exam Quesions VELOCITY AND DISPLACEMENT D B D 4 E 5 B 6 E 7 E 8 C VELOCITY TIME GRAPHS (a) I is acceleraing Speeding up (NOT going down he flume
WELCOME TO 1103 PERIOD 3. Homework Exercise #2 is due at the beginning of class. Please put it on the stool in the front of the classroom.
 WELCOME TO 1103 PERIOD 3 Homework Exercise #2 is due a he beginning of class. Please pu i on he sool in he fron of he classroom. Ring of Truh: Change 1) Give examples of some energy ransformaions in he
WELCOME TO 1103 PERIOD 3 Homework Exercise #2 is due a he beginning of class. Please pu i on he sool in he fron of he classroom. Ring of Truh: Change 1) Give examples of some energy ransformaions in he
Physics Notes - Ch. 2 Motion in One Dimension
 Physics Noes - Ch. Moion in One Dimension I. The naure o physical quaniies: scalars and ecors A. Scalar quaniy ha describes only magniude (how much), NOT including direcion; e. mass, emperaure, ime, olume,
Physics Noes - Ch. Moion in One Dimension I. The naure o physical quaniies: scalars and ecors A. Scalar quaniy ha describes only magniude (how much), NOT including direcion; e. mass, emperaure, ime, olume,
Conceptual Physics Review (Chapters 2 & 3)
 Concepual Physics Review (Chapers 2 & 3) Soluions Sample Calculaions 1. My friend and I decide o race down a sraigh srech of road. We boh ge in our cars and sar from res. I hold he seering wheel seady,
Concepual Physics Review (Chapers 2 & 3) Soluions Sample Calculaions 1. My friend and I decide o race down a sraigh srech of road. We boh ge in our cars and sar from res. I hold he seering wheel seady,
Guest Lecturer Friday! Symbolic reasoning. Symbolic reasoning. Practice Problem day A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 8 E. 16 Q25. Will Armentrout.
 Pracice Problem day Gues Lecurer Friday! Will Armenrou. He d welcome your feedback! Anonymously: wrie somehing and pu i in my mailbox a 111 Whie Hall. Email me: sarah.spolaor@mail.wvu.edu Symbolic reasoning
Pracice Problem day Gues Lecurer Friday! Will Armenrou. He d welcome your feedback! Anonymously: wrie somehing and pu i in my mailbox a 111 Whie Hall. Email me: sarah.spolaor@mail.wvu.edu Symbolic reasoning
Today: Graphing. Note: I hope this joke will be funnier (or at least make you roll your eyes and say ugh ) after class. v (miles per hour ) Time
 +v Today: Graphing v (miles per hour ) 9 8 7 6 5 4 - - Time Noe: I hope his joke will be funnier (or a leas make you roll your eyes and say ugh ) afer class. Do yourself a favor! Prof Sarah s fail-safe
+v Today: Graphing v (miles per hour ) 9 8 7 6 5 4 - - Time Noe: I hope his joke will be funnier (or a leas make you roll your eyes and say ugh ) afer class. Do yourself a favor! Prof Sarah s fail-safe
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
AP Calculus BC - Parametric equations and vectors Chapter 9- AP Exam Problems solutions
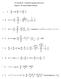 AP Calculus BC - Parameric equaions and vecors Chaper 9- AP Exam Problems soluions. A 5 and 5. B A, 4 + 8. C A, 4 + 4 8 ; he poin a is (,). y + ( x ) x + 4 4. e + e D A, slope.5 6 e e e 5. A d hus d d
AP Calculus BC - Parameric equaions and vecors Chaper 9- AP Exam Problems soluions. A 5 and 5. B A, 4 + 8. C A, 4 + 4 8 ; he poin a is (,). y + ( x ) x + 4 4. e + e D A, slope.5 6 e e e 5. A d hus d d
Lab #2: Kinematics in 1-Dimension
 Reading Assignmen: Chaper 2, Secions 2-1 hrough 2-8 Lab #2: Kinemaics in 1-Dimension Inroducion: The sudy of moion is broken ino wo main areas of sudy kinemaics and dynamics. Kinemaics is he descripion
Reading Assignmen: Chaper 2, Secions 2-1 hrough 2-8 Lab #2: Kinemaics in 1-Dimension Inroducion: The sudy of moion is broken ino wo main areas of sudy kinemaics and dynamics. Kinemaics is he descripion
Physics 1502: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda
 Physics 152: Lecure 2 Today s Agenda Announcemens: Chap.27 & 28 Homework 6: Friday nducion Faraday's Law ds N S v S N v 1 A Loop Moving Through a Magneic Field ε() =? F() =? Φ() =? Schemaic Diagram of
Physics 152: Lecure 2 Today s Agenda Announcemens: Chap.27 & 28 Homework 6: Friday nducion Faraday's Law ds N S v S N v 1 A Loop Moving Through a Magneic Field ε() =? F() =? Φ() =? Schemaic Diagram of
Welcome Back to Physics 215!
 Welcome Back o Physics 215! (General Physics I) Thurs. Jan 19 h, 2017 Lecure01-2 1 Las ime: Syllabus Unis and dimensional analysis Today: Displacemen, velociy, acceleraion graphs Nex ime: More acceleraion
Welcome Back o Physics 215! (General Physics I) Thurs. Jan 19 h, 2017 Lecure01-2 1 Las ime: Syllabus Unis and dimensional analysis Today: Displacemen, velociy, acceleraion graphs Nex ime: More acceleraion
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 02 Motion, Forces, and Newton s Laws Textbook Sections
 PHYSICS 220 Lecure 02 Moion, Forces, and Newon s Laws Texbook Secions 2.2-2.4 Lecure 2 Purdue Universiy, Physics 220 1 Overview Las Lecure Unis Scienific Noaion Significan Figures Moion Displacemen: Δx
PHYSICS 220 Lecure 02 Moion, Forces, and Newon s Laws Texbook Secions 2.2-2.4 Lecure 2 Purdue Universiy, Physics 220 1 Overview Las Lecure Unis Scienific Noaion Significan Figures Moion Displacemen: Δx
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion I
 Chaper 15 Oscillaory Moion I Level : AP Physics Insrucor : Kim Inroducion A very special kind of moion occurs when he force acing on a body is proporional o he displacemen of he body from some equilibrium
Chaper 15 Oscillaory Moion I Level : AP Physics Insrucor : Kim Inroducion A very special kind of moion occurs when he force acing on a body is proporional o he displacemen of he body from some equilibrium
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup Sample Midterm. Useful Equations. x f. x i v x. a x. x i. v xi v xf. 2a x f x i. y f. a r.
 Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup Sample Miderm Useful Equaions A y Asin A A x A y an A y A x A = A x i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A x B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z A x B =
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup Sample Miderm Useful Equaions A y Asin A A x A y an A y A x A = A x i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A x B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z A x B =
Q2.1 This is the x t graph of the motion of a particle. Of the four points P, Q, R, and S, the velocity v x is greatest (most positive) at
 Q2.1 This is he x graph of he moion of a paricle. Of he four poins P, Q, R, and S, he velociy is greaes (mos posiive) a A. poin P. B. poin Q. C. poin R. D. poin S. E. no enough informaion in he graph o
Q2.1 This is he x graph of he moion of a paricle. Of he four poins P, Q, R, and S, he velociy is greaes (mos posiive) a A. poin P. B. poin Q. C. poin R. D. poin S. E. no enough informaion in he graph o
v x + v 0 x v y + a y + v 0 y + 2a y + v y Today: Projectile motion Soccer problem Firefighter example
 Thurs Sep 10 Assign 2 Friday SI Sessions: Moron 227 Mon 8:10-9:10 PM Tues 8:10-9:10 PM Thur 7:05-8:05 PM Read Read Draw/Image lay ou coordinae sysem Wha know? Don' know? Wan o know? Physical Processes?
Thurs Sep 10 Assign 2 Friday SI Sessions: Moron 227 Mon 8:10-9:10 PM Tues 8:10-9:10 PM Thur 7:05-8:05 PM Read Read Draw/Image lay ou coordinae sysem Wha know? Don' know? Wan o know? Physical Processes?
This is an example to show you how SMath can calculate the movement of kinematic mechanisms.
 Dec :5:6 - Kinemaics model of Simple Arm.sm This file is provided for educaional purposes as guidance for he use of he sofware ool. I is no guaraeed o be free from errors or ommissions. The mehods and
Dec :5:6 - Kinemaics model of Simple Arm.sm This file is provided for educaional purposes as guidance for he use of he sofware ool. I is no guaraeed o be free from errors or ommissions. The mehods and
AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 2016 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 1. 1 : estimate = = 120 liters/hr
 AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 16 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion 1 (hours) R ( ) (liers / hour) 1 3 6 8 134 119 95 74 7 Waer is pumped ino a ank a a rae modeled by W( ) = e liers per hour for 8, where is measured
AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 16 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion 1 (hours) R ( ) (liers / hour) 1 3 6 8 134 119 95 74 7 Waer is pumped ino a ank a a rae modeled by W( ) = e liers per hour for 8, where is measured
University Physics with Modern Physics 14th Edition Young TEST BANK
 Universi Phsics wih Modern Phsics 14h Ediion Young SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formaing errors) a: hps://esbankreal.com/download/universi-phsics-modern-phsics- 14h-ediion-oung-soluions-manual-/
Universi Phsics wih Modern Phsics 14h Ediion Young SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formaing errors) a: hps://esbankreal.com/download/universi-phsics-modern-phsics- 14h-ediion-oung-soluions-manual-/
Solution: b All the terms must have the dimension of acceleration. We see that, indeed, each term has the units of acceleration
 PHYS 54 Tes Pracice Soluions Spring 8 Q: [4] Knowing ha in he ne epression a is acceleraion, v is speed, is posiion and is ime, from a dimensional v poin of view, he equaion a is a) incorrec b) correc
PHYS 54 Tes Pracice Soluions Spring 8 Q: [4] Knowing ha in he ne epression a is acceleraion, v is speed, is posiion and is ime, from a dimensional v poin of view, he equaion a is a) incorrec b) correc
Applications of the Basic Equations Chapter 3. Paul A. Ullrich
 Applicaions of he Basic Equaions Chaper 3 Paul A. Ullrich paullrich@ucdavis.edu Par 1: Naural Coordinaes Naural Coordinaes Quesion: Why do we need anoher coordinae sysem? Our goal is o simplify he equaions
Applicaions of he Basic Equaions Chaper 3 Paul A. Ullrich paullrich@ucdavis.edu Par 1: Naural Coordinaes Naural Coordinaes Quesion: Why do we need anoher coordinae sysem? Our goal is o simplify he equaions
Course II. Lesson 7 Applications to Physics. 7A Velocity and Acceleration of a Particle
 Course II Lesson 7 Applicaions o Physics 7A Velociy and Acceleraion of a Paricle Moion in a Sraigh Line : Velociy O Aerage elociy Moion in he -ais + Δ + Δ 0 0 Δ Δ Insananeous elociy d d Δ Δ Δ 0 lim [ m/s
Course II Lesson 7 Applicaions o Physics 7A Velociy and Acceleraion of a Paricle Moion in a Sraigh Line : Velociy O Aerage elociy Moion in he -ais + Δ + Δ 0 0 Δ Δ Insananeous elociy d d Δ Δ Δ 0 lim [ m/s
Physics 218 Exam 1 with Solutions Spring 2011, Sections ,526,528
 Physics 18 Exam 1 wih Soluions Sprin 11, Secions 513-515,56,58 Fill ou he informaion below bu do no open he exam unil insruced o do so Name Sinaure Suden ID E- mail Secion # Rules of he exam: 1. You have
Physics 18 Exam 1 wih Soluions Sprin 11, Secions 513-515,56,58 Fill ou he informaion below bu do no open he exam unil insruced o do so Name Sinaure Suden ID E- mail Secion # Rules of he exam: 1. You have
Kinematics of Wheeled Robots
 1 Kinemaics of Wheeled Robos hps://www.ouube.com/wach?=gis41ujlbu 2 Wheeled Mobile Robos robo can hae one or more wheels ha can proide seering direcional conrol power eer a force agains he ground an ideal
1 Kinemaics of Wheeled Robos hps://www.ouube.com/wach?=gis41ujlbu 2 Wheeled Mobile Robos robo can hae one or more wheels ha can proide seering direcional conrol power eer a force agains he ground an ideal
AP CALCULUS BC 2016 SCORING GUIDELINES
 6 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion A ime, he posiion of a paricle moving in he xy-plane is given by he parameric funcions ( x ( ), y ( )), where = + sin ( ). The graph of y, consising of hree line segmens, is
6 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion A ime, he posiion of a paricle moving in he xy-plane is given by he parameric funcions ( x ( ), y ( )), where = + sin ( ). The graph of y, consising of hree line segmens, is
When analyzing an object s motion there are two factors to consider when attempting to bring it to rest. 1. The object s mass 2. The object s velocity
 SPH4U Momenum LoRuo Momenum i an exenion of Newon nd law. When analyzing an ojec moion here are wo facor o conider when aeming o ring i o re.. The ojec ma. The ojec velociy The greaer an ojec ma, he more
SPH4U Momenum LoRuo Momenum i an exenion of Newon nd law. When analyzing an ojec moion here are wo facor o conider when aeming o ring i o re.. The ojec ma. The ojec velociy The greaer an ojec ma, he more
Physics 218 Exam 1. with Solutions Fall 2010, Sections Part 1 (15) Part 2 (20) Part 3 (20) Part 4 (20) Bonus (5)
 Physics 18 Exam 1 wih Soluions Fall 1, Secions 51-54 Fill ou he informaion below bu o no open he exam unil insruce o o so! Name Signaure Suen ID E-mail Secion # ules of he exam: 1. You have he full class
Physics 18 Exam 1 wih Soluions Fall 1, Secions 51-54 Fill ou he informaion below bu o no open he exam unil insruce o o so! Name Signaure Suen ID E-mail Secion # ules of he exam: 1. You have he full class
The Contradiction within Equations of Motion with Constant Acceleration
 The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
Today: Falling. v, a
 Today: Falling. v, a Did you ge my es email? If no, make sure i s no in your junk box, and add sbs0016@mix.wvu.edu o your address book! Also please email me o le me know. I will be emailing ou pracice
Today: Falling. v, a Did you ge my es email? If no, make sure i s no in your junk box, and add sbs0016@mix.wvu.edu o your address book! Also please email me o le me know. I will be emailing ou pracice
3.6 Derivatives as Rates of Change
 3.6 Derivaives as Raes of Change Problem 1 John is walking along a sraigh pah. His posiion a he ime >0 is given by s = f(). He sars a =0from his house (f(0) = 0) and he graph of f is given below. (a) Describe
3.6 Derivaives as Raes of Change Problem 1 John is walking along a sraigh pah. His posiion a he ime >0 is given by s = f(). He sars a =0from his house (f(0) = 0) and he graph of f is given below. (a) Describe
From Particles to Rigid Bodies
 Rigid Body Dynamics From Paricles o Rigid Bodies Paricles No roaions Linear velociy v only Rigid bodies Body roaions Linear velociy v Angular velociy ω Rigid Bodies Rigid bodies have boh a posiion and
Rigid Body Dynamics From Paricles o Rigid Bodies Paricles No roaions Linear velociy v only Rigid bodies Body roaions Linear velociy v Angular velociy ω Rigid Bodies Rigid bodies have boh a posiion and
PSAT/NMSQT PRACTICE ANSWER SHEET SECTION 3 EXAMPLES OF INCOMPLETE MARKS COMPLETE MARK B C D B C D B C D B C D B C D 13 A B C D B C D 11 A B C D B C D
 PSTNMSQT PRCTICE NSWER SHEET COMPLETE MRK EXMPLES OF INCOMPLETE MRKS I i recommended a you ue a No pencil I i very imporan a you fill in e enire circle darkly and compleely If you cange your repone, erae
PSTNMSQT PRCTICE NSWER SHEET COMPLETE MRK EXMPLES OF INCOMPLETE MRKS I i recommended a you ue a No pencil I i very imporan a you fill in e enire circle darkly and compleely If you cange your repone, erae
