Generalized Lorentz Transformation Allowing the Relative Velocity of Inertial Reference Systems Greater Than the Light Velocity
|
|
|
- Baldwin Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Generlzed Lorentz Trnsformton Allowng the Relte Veloty of Inertl Referene Systems Greter Thn the Lght Veloty Yu-Kun Zheng Memer of the Chnese Soety of Grtton nd Reltst Astrophyss Astrt: Ths pper dsusses theoretlly the posslty of onstrutng spe-tme oordnte trnsformton onnetng two nertl referene systems whh possesses relte mong eloty greter thn tht of lght Our nlyss shows tht the orgn of lght eloty s lmt eloty n the Spel Theory of Reltty s the postulte of onstny of the eloty of lght Hene we me new postulte tht lght eloty depends on the stte of moton of the lght soure Bsed upon t we dere new system of trnsformton equtons Ths new spetme trnsformton ontns onstnt whh theoretlly s undetermned due to the ndonment of the postulte of onstny of the eloty of lght We propose method of eperment usng the optl Doppler Effet to determne ths onstnt The uthor epets tht ths onstnt wll e numer smller thn ut ery lose to In ths se the new trnsformton llows the relte eloty of the nertl referene systems to e equl to or greter thn the lght eloty nd thus the trnsformton oeromes the lmtton of the Spel Theory of Reltty It lso predts new lmt eloty of the relte elotes of ll nertl referene systems The new spe-tme oordnte trnsformton nludes the Lorentz trnsformton nd the Gllen trnsformton s ts two lmt ses Key words: lght soure; lmt eloty; superlumnl; trnsformton group; optl Doppler effet; new lmt eloty; l mong ody; ultmte lmt eloty Introduton The prnple of reltty nd the prnple of onstny of the eloty of lght (CVL) re two ornerstones of the Spel Theory of Reltty (STR) Bsed upon ths foundton Ensten dered the Lorentz trnsformton nd founded the STR [] But the STR ontns lmtton tht t nnot del wth the prolem of moton t eloty equl to or greter thn tht of lght The Lorentz trnsformton ontns the lght eloty s lmt eloty suh tht no eloty of moton of nertl system of referene n eeed tht eloty On the other hnd n reent yers mny superlumnl phenomen he een osered usng people to st the douts on the theoretl ss of the STR The mn prolem here s tht whether the postulte of CVL etly reflets the nture of the lght propgton The purpose of the present pper s to onstrut new spe-tme oordntes trnsformton lnng nertl systems whh llows the relte mong eloty of the nertl systems greter thn the lght eloty n order to re the lght-speed rrer n the Lorentz
2 trnsformton We strt our wor from nestgtng the CVL Our nlyss (n Seton Ⅰ) shows tht the eloty of lght s lmt eloty tully s smply result of the postulte of CVL Therefore for solng the prolem tht the spe-tme oordntes trnsformton lnng two nertl systems possle possessng relte eloty greter thn we must ndon the postulte of CVL Hene we me new postulte tht lght eloty my depend on the moton stte of the lght soure to reple the postulte of CVL Usng ths new postulte together wth some other hypotheses of the STR we dere new spe-tme oordntes trnsformton Ths new trnsformton s generlzton of the Lorentz trnsformton Andonng the postulte of CVL uses the new trnsformton to ontn onstnt whh nnot e determned theoretlly We propose n epermentl method usng the optl Doppler Effet to determne ths onstnt We epet ths onstnt to e numer smller thn ut ery lose to In tht se the otned trnsformton would llow the relte eloty of nertl systems equl to or greter thn tht of lght ⅠThe Lmt Veloty nd the Postulte of Constny of the Veloty of Lght S Let S nd e two nertl systems of referene where s mong wth onstnt eloty relte to S Assume tht there s lght soure L fed n S P s pont fed n S nd L wll go through P when t moes wth S Now suppose tht t the moment when L ondes wth P t emts sgnl n the dreton of moton of S If the lght sgnl trels n S wth the eloty then y the postulte of CVL ths lght sgnl trels on S s lso wth the eloty Therefore the eloty of the lght sgnl relte to the pont P s On the other hnd the mong eloty of the lght soure L relte to P s nd the lght sgnl emtted n the dreton of moton of the soure lwys trels n the front of the lght soure Hene udged from the pont P of system S the lght sgnl lwys trels fster thn the lght soure Tht mens tht s relte eloty of n nert system of referene no mtter how gret t s the nequlty < should lwys hold nmely the lght eloty under the postulte of CVL s n upper lmt of the relte elotes of moton of ll nertl systems of referene The oe nlyss shows tht the lght eloty s lmt eloty s ust orollry of the postulte of CVL Therefore for onstrutng new spe-tme oordnte trnsformton lnng two nertl systems of referene llowng the relte eloty greter thn we should he to ndon the postulte of CVL nd ntrodue new postulte to reple t We propose the followng postultes for derng the new trnsformton: <> All systems of nert re equlent <> Spe-tme oordntes trnsformton lnng nertl systems slner trnsformton <> Lght eloty depends on the moton stte of lght soure <4> Lght eloty s the onstnt only n the referene system relte to whh the soure of lght s t rest (ths s the defnton of n the sequel) Note: The postulte <> s tully the result of theorem nd the deduton of ts lner trnsformtons generlly needs the ondton of CVL [] Thus t seems tht there s n nter-ontrdton etween the postultes <> nd <> But the tul stuton n e unle so We fnd tht the lner trnsformtons n e dedued wthout the ondton of CVL ut only from the nture of nertl system (See Append) S
3 ⅡThe Derton of the Trnsformton of Spe-tme Coordntes wth Lmt Veloty Greter Thn Let S ( t y z) nd S ( t y z ) e two nertl oordnte systems We ssume tht the three oordnte es n nd re prllel to eh other orrespondngly nd tht S s mong relte to S wth eloty n the dreton of the poste -s Let us moreoer ssume tht the orgn O of S ondes wth the orgn O of S t the tme t = t= Then ordng to the postulte <> nd y the onsderton sed on the postulte <> the spe-tme oordntes trnsformton from S to S possess the followng smplest lner epressons: t = p + qt () = m + nt () y = y () z = z (4) where p q m nd n re onstnts to e determned Applyng the relte moton eloty of the two systems the trnsformton equtons () nd () n e hnged mmedtely nto the followng form: t m( r + t) = m( t) p = ( ) m S r = (5) (6) Thus the oeffents to e determned re redued nto two nmely m nd r Frst we determne m Assume tht there s lght soure fed on the orgn O of S nd t the moment t = t = ths lght soure emts lght sgnl L n the poste dreton of the y -s s shown n F: S Suppose tht the sgnl rehes t pont P on y -s wth y = h t tme t = t Let the orrespondng spe nd tme oordntes of P on system S e = y = h nd t = t Then we he from (5) nd (6) t = m( r + t ) (7) = m( t ) (8) Elmntng from these two epressons ges t = m( r + ) t (9)
4 Note tht the proess of the lght sgnl propgtng from O to s udged from the oordnte system S proess of lght sgnl P t propgtng on the lne onnetng O nd nd s the neessry tme of ths proess mesured n oordnte system S Net we onsder proess symmetr to tht n F s shown n F: P Assume tht there s lght soure fed on the orgn O of S nd t tme t = t emts lght sgnl L n the poste dreton of y - s Suppose tht the sgnl rehes t pont P on y -s wth y = h t tme t = t Let the orrespondng spe nd tme oordnte of P on the oordnte system S e t = t Note tht here the y oordntes of the ponts P nd P possess the sme lue h (ths mens tully tht t the moment t = t = the two ponts P nd P " onde wth one nother) Then we he from (5) t = mt () Here smlr s n F the lne onnetng O nd P s the propgtng proess of the lght sgnl L udged n the oordnte system S nd the tme t s the neessry tme of ths proess mesured n oordnte system S Now sne the pont P n oordnte system S s well s the pont P n oordnte system S possess the sme lue h of the y oordntes nd y the hypothess <4> oth the lght sgnls sme eloty we he L nd L possess the t = t = h () Ths ges t = t () On the other hnd euse the proesses of propgton of the two lght sgnls L nd L n ther orgnl oordnte systems S nd S re the sme y the postulte <> ther orrespondng proesses n the mong oordnte systems S nd S respetely (shown y the olque lnes n F nd F) should e the sme too Hene we he t = t () 4
5 Susttutng () nd () nto () ges t = mt (4) Susttutng (4) nto (9) ges t ( ) = m r + t (5) Elmntng t from (5) we get the followng equton out m : = m ( r + ) (6) Solng for m from (6) we otn m + r Thus we he found the lue of m whh s epressed y r nd The trnsformton whh we re now seeng for possesses the followng form: t = m( r + t) (8) = m( t) (9) m + r Now we he to determne the oeffent r In the Lorentz trnsformton ths oeffent s determned s r = / usng the postulte of CVL Here sne we he ndoned ths postulte of ourse r nnot e determned dretly In the followng we nlyze the struture of the oeffent r For ths purpose we requre the tegory of trnsformtons whh we re seeng for to form group of trnsformtons Let us onsder thrd nertl oordntes system S" ( t" " y" z") whh s mong long the poste dreton of -s wth unform eloty relte to the oordnte system S Smlr to the trnsformton from S to S n (8)-() the trnsformton from S to S" should he the followng form of trnsformton equtons: t " = m ( r + t ) () " = m ( t ) () m + r () Susttutng (8)-(9) nto ()-() fter smplfton we get the reltons etween t " " nd t s the follows: t " = m" ( r" + q" t) (4) " = m" ( " t) (5) where m" = mm ( r ) (6) + " = r (7) r+ r r" = r (8) q" = r r (9) By the nture of group of trnsformtons the two trnsformtons omned together should e lso trnsformton nmely the equtons (4)-(5) should represent spe-tme oordntes trnsformton from S to S" Therefore y omprng (4)-(5) wth (8)-(9) nd ()-() we fnd tht the quntty q" n (4) defned n (9) should stsfy r q " = r = () Ths leds to r r = () The equlty () shows tht the two rtos r / nd r / must e ommon onstnt ndependent of oth nd denotng ths onstnt y w we he: 5
6 r r = = () Hene we get the reltons etween r nd s well s r nd : r = w r = w () Now we susttute r nd r epressed y w n () nto ll the relted epressons dsussed oe Thus susttutng the r of () nto (8)-() ges the trnsformton from S to S s t = m( t + w) (4) = m( t) (5) m = (6) w + w Susttutng the r of () nto ()-() ges the trnsformton from S to S" s t " = m ( t + w ) (7) " = m ( t ) (8) m = (9) + w r of () nto (7)-(8) ges = (4) Further susttutng the r nd + " r" w w + = w ( ) = w" (4) Susttutng (6) (9) nd the r of () nto (6) nd usng (4)-(4) fter smplfton we otn m" = (4) + w" Fnlly susttutng the q " of () nd the r " of (4) nto (4) ges t " = m" ( t + w" ) (4) Referrng to (4) (5) nd (4) now we he the followng equtons onnetng the spe-tme oordntes ( t ) ) nd ( t" ") : t " = m" ( t + w" ) (44) " = m" ( " t) (45) m" (46) + w" Comprng (44)-(46) wth (4)-(6) nd (7)-(9) we see tht the equtons (44)-(46) (together wth y " = y nd z " = z ) omned wth the trnsformtons (4)-(6) nd (7)-(9) re relly spe-tme oordntes trnsformton from system S to system S " where system S" moes unformly long the poste dreton of -s of system S wth the eloty " defned n (4) Ths shows tht the lue q" thus determned n () s resonle; t mes the tegory of the trnsformtons whh we re seeng for group of trnsformton Now let us turn to the smpler oeffent to e determned the onstnt w (ndependent of ) In the followng we wll me use of the mn postulte n ths pper nmely the postulte <> tht lght eloty depends on the moton stte of lght soure to get the struture of the onstnt w Assume tht there s lght soure fed on some pont of - s of the oordnte system S nd t some moment t emts lght sgnl towrd the poste dreton of -s The propgton of ths sgnl n the oordnte systems S nd S s desred y the equtons = ( t ) nd = (t) respetely The spe-tme oordntes nd t re onneted wth nd t y the trnsformtons (4)-(6) Aordng to the postulte 6
7 <4> the eloty of ths lght sgnl on the oordnte system S s Hene we he d dt = (47) On the other hnd y the postulte <> the eloty of ths lght sgnl on the oordnte system S s no longer the onstnt ut some other qunttes dfferent from we denote t y * Therefore we he d dt = * (48) Dfferenttng (4)-(5) nd usng (47) nd (48) we get * = + w* (49) The oe equlty ontns two unnown qunttes w nd * we wll use the nture of w eng rrelent of to determne w nd * Solng w from (49) we he * w = * (5) Note tht w nd re ndependent of whle * depends on Dfferenttng the oe equlty wth respet to we otn dfferentl equton for * : d* ( * ) * d = ( + ) (5) Ths equton possesses two solutons (eept the trl soluton * = ): * = (5) nd ( + = ) (5) * + The soluton (5) orresponds ust to the se of the Ensten postulte we should dopt the soluton of (5) other thn t tht s the soluton (5) where s n ntegrton onstnt Susttutng (5) nto (5) ges w = (54) Thus we he otned the detled epressons for * nd w showng n (5) nd (54) respetely oth these two qunttes ontn the onstnt The epresson for * n (5) lso ontns ths shows the nfluene of the moton of lght soure on the eloty of lght The epresson for w n (54) should e ts fnl form As for the ntegrton onstnt lter we wll propose method of eperment of the optl Doppler Effet to determne t Susttutng (54) nto (4)-(6) we rre t the fnl form of the spe-tme trnsformton of two nertl systems whh we were seeng for: t t = (55) = (56) t y = y (57) z = z (58) Note In solng the funton * from the dfferentl equton (5) we he seleted the ntegrton onstnt s spel epresson of the onstnt to ensure tht the oeffent of the quntty under the squre root of the equtons (55)-(56) eng negte numer otherwse the orrespondng trnsformton wll e n ordnry orthogonl trnsformton of the t -plne or Gllen trnsformton these re not the se we onsder here Note In determnng the onstnt spel dreton the dreton of w of (54) we he seleted -s s the dreton for emttng 7
8 the lght sgnl Atully we ould selet ny dreton to e the dreton of emsson the result for w s the sme s tht of (54) only mng n pproprte seleton of the ntegrton onstnt From (55)-(58) we see tht our trnsformton s dfferent formlly from the Lorentz trnsformton y onstnt When = t eomes the Lorentz trnsformton; when = t eomes the Gllen trnsformton Therefore (55)-(58) nludes the Lorentz trnsformton nd Gllen trnsformton s ts two spel ses Now the prolem s whether the otned spe-tme trnsformton (55)-(58) n stsfy our orgnl purpose nmely whether t n permt the eloty of moton of system S relte to system S to e equl to or greter thn the lght eloty Ths depends mnly on the lue of the onstnt If the lue of stsfes the nequlty < < (59) nd let = (6) then when stsfes (59) we wll he > (6) nmely s eloty greter thn On the other hnd the trnsformton (55)-(58) shows tht the eloty of the nertl system S should stsfy < < (6) ths mens tht s lmt eloty n (55)-(58) Consequently under the ondton (59) the permtted rnge of hs een etended gong eyond the lmtton of the lght eloty nd (55)-(58) s spe-tme oordntes trnsformton whh permts the relted nertl systems to he superlumnl relte eloty Thus under the ondton (59) the trnsformton (55)-(58) stsfes the purpose stted n the egnnng of ths pper Smultneously we n otn new lmt eloty for ll elotes of moton of the nertl systems ⅢThe Trnsformton of Veloty For the determnton of the onstnt t s neessry to now the trnsformton of eloty under the spe-tme oordntes trnsformton (55)-(58) (ⅰ)Trnsformton of eloty of prtle Let prtle moe n the oordnte system S wth the eloty d dy dz ( u u u ) = ( ) dt dt dt (6) nd n the oordnte system S wth the eloty d dy dz ( u u u ) = ( ) dt dt dt (64) We wnt to fnd the relton etween these two elotes From the trnsformton (55)-(58) we he the nerse trnsformton s t t + = + t (66) = (65) y = y (67) z = z (68) Dfferenttng (65)-(68) nd pplyng (6) nd (64) we he 8
9 u u u + u u = (69) + u u + = (7) u u + = (7) These re the eloty trnsformton formuls whh trnsform the eloty of prtle mong n the oordnte system S nto ts eloty n the oordnte system S If the prtle moes long the -s then we he u = nd u = By (69)-(7) we he u u + = (7) + u nd u = u = Let u = u + (7) + u u u = u + (74) + u u Susttutng (69)-(7) nto (7) nd usng (74) we get u u ( )( ) ( ) / u = + (75) (ⅱ)Trnsformton of lght eloty We he otned erler n (5) n epresson of eloty * of lght emtted y mong soure The soure s mong wth eloty long the -s of oordnte system S nd * s mesured n S Atully ths s ust the se of the generl formul of eloty trnsformton (7) wth u = nd u = * Our postulte <> uses the lght eloty now s no longer n spel poston s tht t s n the STR nd ts trnsformton s ust s the generl eloty trnsformton (69)-(7) only we te (64) s the eloty of lght emtted y soure fed on the oordnte system S Thus for lght whose soue s fed n S f we denote the omponents of ts eloty n S y ( ) (76) nd denote the orrespondng omponents of eloty of ths lght n S y ( * * *) (77) then we he y (69)-(7) + * = (78) + + * = (79) * + Besdes we he = (8) = + (8) + ( *) + ( *) ( ) * = + (8) * then y susttutng (78)-(8) nto (8) nd usng (8) we get 9
10 ( )( ) ( ) / * = + (8) Ths s the generlzton of the epresson of lght eloty * n (5) for f we susttute y n (8) then (8) wll turn to (5) Ⅳ Determnng the Constnt y mens of eperment of the optl Doppler effet We now dsuss how to determne the onstnt epermentlly y usng the Doppler effet Let λ e the welength of lght we emtted y the lght soure n ts rest frme λ e the welength of the Doppler lue shft when the lght soure moes towrd the oserer nd λ r e the welength of the Doppler red shft when the lght soure moes wy from the oserer We shll fnd formul whh epresses the lue of n terms of λ λ nd λ r We ontnue to use the nertl oordnte systems S nd S defned n the egnnng of seton Ⅱ Assume tht there s lght soure Q fed t some pont on the -s of the referene system S (F) So Q s mong reltely to S n the poste dreton of the -s wth the eloty Let M e n oserton ϕ nstrument tht s used for detetng the Doppler effet of the reeed lght we fed t some pont on the y -plne of the referene system S Assume tht the lght we emtted y Q s y plne we when t rehes M Let ϕ e the ngle etween the propgton dreton of the we nd the -s n S Then y (55)-(57) we otn the generl epresson for the Doppler effet s follows: * + osϕ λ = λ (84) where * s the solute lue of the lght eloty defned n (8) wth = os λ s the welength of the lght we reeed y M ϕ
11 To otn the epresson for the onstnt let us onsder some spel ses of the Doppler Effet Let M e loted on some pont on - s of the oordnte system S Then M wll reee lght wes orrespondng to When M s loted n the poston suh tht Q ϕ = nd ϕ = π M wll reee the lght we emtted y Q = λ of the moes towrd t then n the dreton ϕ nd peree the lue shft welength lght we By (84) we he + λ = λ (85) When M s loted n the poston suh tht moes wy from t then M wll reee the lght we emtted y Q n the dreton ϕ = π nd peree the red shft welength λ r By (84) we he λ = λ (86) r Further we ssume tht n the oe two eperments the lght soures possess the sme mong eloty (t s no neessry to now the lue of ths wll redue the dffulty of the eperments) then we n elmnte the quntty from (85) nd (86) By ths mens we get the followng formul of : ( λr λ ) λ = (87) ( λr + λ ) λ 4λλr The epresson (87) s the formul for epressng the lue of n terms of λ λ nd λ r Therefore f we n perform the Doppler effet eperments stsfyng the oe mentoned ondtons nd suessfully otn mesurements of these welengths then the lue of wll e determned Mesurements of ths sort do not pper n the lterture We hope tht physst of eperment nd stronomer ould rrnge suh eperments or osertons of stronomy n order to ge udgement for the onstnt Suh eperments would e qute sgnfnt for f we n determne tht the onstnt s smller thn then the lmtton of the STR hs een suessfully oerome wth suh lue of the oordnte trnsformton (55)-(58) res the lght-speed rrer s dsussed t the end of Seton Ⅱ On the ontrry f s determned to e etly equl to then Enstens postulte tht lght eloty s ndependent of the stte of moton of the lght soure s erfed (It seems tht the onstnt nnot e greter thn sne ths shows tht the lmt eloty n (6) for ll moton of the nertl referene systems s een smller thn ) The followng re some onse results from (87): = λ λ = λr = λ = λ λr = Gllen trnsformton (88) Lorentz trnsformton (89) We ntpte tht stsfes the nequlty (59) orrespondngly we he < < λ r > λ > λλr Trnsformton (55)-(58) (9) Sne the onstnt n (55)-(56) hrterzes the deton of the new trnsformton (55)-(58) from the Lorentz trnsformton nd the ltter hs een erfed to ery hgh degree of ury y numerous eperments the lue of must e lose to It s mportnt howeer to determne how lose Note: Reently the Europen Centre for Nuler Reserh delred tht they hd deteted the neutrnos trel n speed of m/se Ths speed s greter thn the lght speed (= m/se) Ths Q
12 nformton supports the ntpton mde from the result of ths pper e there my est new lmt speed n the nture If we te ths neutrno s speed s the new lmt speed defned n (59)-(6) then the onstnt whh we hope to determne here my e dedued s = Ths lue tlles well wth our ntpton n degree of mgntude: lue smller thn ut ery lose to Ⅴ Deton of * from under < < We now estmte the deton of * the lght eloty ffeted y the moton of lght soure from Let Δ = * (9) pplyng (5) we he ( ) + ( ) Δ = + (9) + ges Mng n epnson n terms of ( ) ( ) ( ) Δ + ( ) + = + + (9) Mng further epnson n terms of / ( < < ) nd tng ppromton to the seond order of / we otn Δ ( )( ) (94) Ths s n estmte for the deton Δ wth n ury up to the seond nd / order of oth the smll qunttes ( ) Ⅵ Superlumnl moton of lght soure S Assume tht the oordnte system wth eloty stsfyng < S moes relte to oordnte system < (95) where stsfes (59) nd lght soure s fed on the orgn of S tht s the lght soure s mong relte to S wth eloty greter thn Let us onsder the lght sgnl emtted y the lght soure towrd the negte dreton of -s Aordng to the hypothess <4> the eloty of ths lght sgnl n S s On the other hnd the eloty of ths lght sgnl n S ordng to (5) s ( + ) ( ) * = = (96) + Beuse of nd stsfy (59) nd (95) respetely the quntty * n (96) s poste numer Thus udged n oordnte system S ths lght sgnl s trellng wy from the orgn O Ths mens tht f lght soure s mong wy from the oserer wth eloty fster thn tht of lght then the lght sgnl emtted towrd the oserer neer rehes the oserer A ody mong wy t superlumnl eloty nnot e seen Smlrly to the onept of l hole n the Generl Theory of Reltty we ould ll suh mong ody l mong ody Ⅶ Some Other Propertes of the Trnsformton (55)-(58) ()The lmt eloty = s nrnt y the trnsformton of eloty (7)
13 (ⅱ)Let P ( t y z) nd P ( t + dt + d y + dy z + dz) e two neghorng ponts n the spe-tme oordntes system S The quntty ds defned y the equton ds = ( ) dt d dy dz (97) s nrnt y the trnsformton (55)-(58) ( ⅲ )The Mwell eletrodynms equtons re not ornt under the trnsformton (55)-(58) Ths shows tht our result onflts wth the etnt theory of physs Howeer f eperment n proe tht the onstnt s not equl to nmely the lght eloty s dependent on the moton stte of lght soure then Mwell s equtons should he to e resed ⅧThe Ultmte Lmt Veloty As we n see the Lorentz trnsformton nd our trnsformton (55)- (58) show tht the spe-tme oordntes trnsformtons etween the nertl systems lwys ontn eloty s lmt eloty of ll the relte elotes of nertl system The orgn of ths result s the equlene of nertl systems whh leds to tht n the determnton of the oeffents of the trnsformton the ommon ftor possessed y ll the oeffents of the trnsformton should stsfy seond degree equton s shown n (6) The Spel Theory of Reltty sserts tht the lmt eloty s the lght eloty whle our trnsformton (55)- (58) shows tht the lmt eloty s the quntty defned n (6) whh s lrger thn nd wll supplnt the poston of Now nturl queston s whether ths new lmt eloty (f t ests nd s greter thn ) s n ultmte lmt eloty The lmt elotes nd relted here re generted usng lght we s tool for trnsmttng messges We n epet tht f there s n oet possessng eloty greter thn tht of lght n e used s tool for trnsmttng messges then t s possle to generte new lmt eloty s we he done here nd the new lmt eloty wll e een greter thn APPENDIX Proe of the Lnerty of the Trnsformton Lnng Two Inertl Frms y Usng Sngly the Mehnl Property of the Inertl Systems Let S nd S e two systems of nert mong relte to eh other Aordng to the property of nertl systems the property of moton to e unform nd retlner must e presered n gong from one nertl system to nother In the lterture [] wth ths sngle property of nertl systems (nmely no neessry of the ondton CVL) there hs eer proed tht the oordnte trnsformton lnng two systems of nert s trnsformton of lner frtons ll wth the sme denomntor Let us denote ths trnsformton s αβ β β = α = (A) + β β = β where the rles α nd β ( α β = ) re the orrespondng spetme oordntes of spe pont n the system S nd S respetely We
14 set = t ( lso = t ) nd suppose tht the oth orgns of S nd S ust onde t = nd = Another property of two nertl systems mong relte to eh other s tht ll the ponts of ny one of the two systems moe relte to the other system wth the sme eloty s tht of the system relte to whh these ponts re t rest We wll use ths property to proe tht the denomntor n (A) must e onstnt nmely ll the lues of β ( β = ) must e zero Let the eloty of S mong relte to S e ( ) (A) Let P ( ) ( = ) e n rtrry fed pont of S nd P( ) e the orrespondng mong pont n S then we he d = ( = ) (A) d d = ( = ) (A4) Dfferenttng the logrthm of oth sdes of (A) nd usng (A) - (A4) ges + = = = β = β β + + β = β β ( = ) (A5) After smplfton we he + + ( ) + = = + + = = = = = (A6) Now we ssume tht the seleted fed pont n S to e the orgn P() nd onsder ts moton n S t = the orrespondng pont of P() wll e the orgn P() of S t ths moment Under ths ondton equton (A6) ges + = (A7) = nd now (A6) eomes ( ) + = = = = (A8) Further we ssume tht the seleted fed pont n S to e pont other thn the orgn P () ut t wll pss the orgn P() of S durng ts moton Oously when ths pont ondes wth P() the tme n S wll e n ths stuton(a8)ges ( ) = = (A9) From (A7) nd (A9) we get 4
15 + = (A) = We then onsder the eloty of n rtrry pont P( α ) fed n S mong relte to S Let the eloty of S mong relte to S e ) (A) ( nd the orrespondng mong pont of P ) n S e P ( ) Then we he d d = ( = ) (A) nd d = ( = ) (A) Dfferenttng (A) nd pplyng (A) nd (A) ges + β β β β d β = β = = = d + β β β β β = β = ( = ) (A4) After smplfton we he ( α ( ) [ ( ) ( ) ] = ( = ) = P( α α (A5) Beuse the pont ) n e seleted rtrrly we n otn the followng two equltes from (A5) = ( = ) (A6) nd ( ) = (for ll spe ponts ( ) = ) (A7) Equlty (A7) mples the followng two possltes: = (A8) or ( ) = (for ll spe ponts ( ) = If (A8) holds then fter susttutng t nto (A) we get = ) (A9) = (A) Due to the eloty omponent n e ny lue the epresson (A) should led to = ( = ) (A) The results of (A8) nd (A) show tht (A) must e lner trnsformton = ( α = ) (A) α β = αβ β The equlty (A9) nnot e ld Sne f we pply t nd (A6) to (A) we wll otn the followng trnsformton equtons 5
16 + β = = = ( = ) (A) + β β + + β = = = β β (A4) Ths trnsformton trnsforms ll the ponts of S nto strght lne n S : = ( = ) (A5) Nmely the trnsformton (A) - (A4) s degenerte trnsformton tht s oously unresonle Therefore (A) s the only possle result ACKNOWLEDGMENT The uthor thns Dr M Mrshll for hs refully redng nd resng ths pper nd for hs lule suggestons The uthor lso thns Prof L Lu Prof SL Co Prof J Luo Dr HS Lu nd Prof MC Chu for helpful dsussons The uthor wshes espelly to thn Mr L Tsu for hs deeply onerned t ths wor REFERENCES [] HA Lorentz A Ensten H Mnows nd H Weyl The Prnple of Reltty (Doer Pultons In 9) 5-65 [] V Fo The Theory of Spe Tme nd Grtton Append A Pergmon Press London 959 6
VECTORS VECTORS VECTORS VECTORS. 2. Vector Representation. 1. Definition. 3. Types of Vectors. 5. Vector Operations I. 4. Equal and Opposite Vectors
 1. Defnton A vetor s n entt tht m represent phsl quntt tht hs mgntude nd dreton s opposed to slr tht ls dreton.. Vetor Representton A vetor n e represented grphll n rrow. The length of the rrow s the mgntude
1. Defnton A vetor s n entt tht m represent phsl quntt tht hs mgntude nd dreton s opposed to slr tht ls dreton.. Vetor Representton A vetor n e represented grphll n rrow. The length of the rrow s the mgntude
Abhilasha Classes Class- XII Date: SOLUTION (Chap - 9,10,12) MM 50 Mob no
 hlsh Clsses Clss- XII Dte: 0- - SOLUTION Chp - 9,0, MM 50 Mo no-996 If nd re poston vets of nd B respetvel, fnd the poston vet of pont C n B produed suh tht C B vet r C B = where = hs length nd dreton
hlsh Clsses Clss- XII Dte: 0- - SOLUTION Chp - 9,0, MM 50 Mo no-996 If nd re poston vets of nd B respetvel, fnd the poston vet of pont C n B produed suh tht C B vet r C B = where = hs length nd dreton
" = #N d$ B. Electromagnetic Induction. v ) $ d v % l. Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law of Induction
 Eletromgnet Induton nd Frdy s w Eletromgnet Induton Mhel Frdy (1791-1867) dsoered tht hngng mgnet feld ould produe n eletr urrent n ondutor pled n the mgnet feld. uh urrent s lled n ndued urrent. The phenomenon
Eletromgnet Induton nd Frdy s w Eletromgnet Induton Mhel Frdy (1791-1867) dsoered tht hngng mgnet feld ould produe n eletr urrent n ondutor pled n the mgnet feld. uh urrent s lled n ndued urrent. The phenomenon
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Principle Component Analysis
 Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Concept of Activity. Concept of Activity. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants [ C] [ D] [ A] [ B]
![Concept of Activity. Concept of Activity. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants [ C] [ D] [ A] [ B] Concept of Activity. Concept of Activity. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants [ C] [ D] [ A] [ B]](/thumbs/80/81967334.jpg) Conept of Atvty Equlbrum onstnt s thermodynm property of n equlbrum system. For heml reton t equlbrum; Conept of Atvty Thermodynm Equlbrum Constnts A + bb = C + dd d [C] [D] [A] [B] b Conentrton equlbrum
Conept of Atvty Equlbrum onstnt s thermodynm property of n equlbrum system. For heml reton t equlbrum; Conept of Atvty Thermodynm Equlbrum Constnts A + bb = C + dd d [C] [D] [A] [B] b Conentrton equlbrum
Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 5: Solid Elements
 Modue : Eement Propertes eture 5: Sod Eements There re two s fmes of three-dmenson eements smr to two-dmenson se. Etenson of trngur eements w produe tetrhedrons n three dmensons. Smr retngur preeppeds
Modue : Eement Propertes eture 5: Sod Eements There re two s fmes of three-dmenson eements smr to two-dmenson se. Etenson of trngur eements w produe tetrhedrons n three dmensons. Smr retngur preeppeds
Lecture 7 Circuits Ch. 27
 Leture 7 Cruts Ch. 7 Crtoon -Krhhoff's Lws Tops Dret Current Cruts Krhhoff's Two ules Anlyss of Cruts Exmples Ammeter nd voltmeter C ruts Demos Three uls n rut Power loss n trnsmsson lnes esstvty of penl
Leture 7 Cruts Ch. 7 Crtoon -Krhhoff's Lws Tops Dret Current Cruts Krhhoff's Two ules Anlyss of Cruts Exmples Ammeter nd voltmeter C ruts Demos Three uls n rut Power loss n trnsmsson lnes esstvty of penl
Multiple view geometry
 EECS 442 Computer vson Multple vew geometry Perspectve Structure from Moton - Perspectve structure from moton prolem - mgutes - lgerc methods - Fctorzton methods - Bundle djustment - Self-clrton Redng:
EECS 442 Computer vson Multple vew geometry Perspectve Structure from Moton - Perspectve structure from moton prolem - mgutes - lgerc methods - Fctorzton methods - Bundle djustment - Self-clrton Redng:
INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX NUMBERS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX NUMBERS The numers -4, -3, -, -1, 0, 1,, 3, 4 represent the negtve nd postve rel numers termed ntegers. As one frst lerns n mddle school they cn e thought of s unt dstnce spced
INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX NUMBERS The numers -4, -3, -, -1, 0, 1,, 3, 4 represent the negtve nd postve rel numers termed ntegers. As one frst lerns n mddle school they cn e thought of s unt dstnce spced
2.12 Pull Back, Push Forward and Lie Time Derivatives
 Secton 2.2 2.2 Pull Bck Push Forwrd nd e me Dertes hs secton s n the mn concerned wth the follown ssue: n oserer ttched to fxed sy Crtesn coordnte system wll see mterl moe nd deform oer tme nd wll osere
Secton 2.2 2.2 Pull Bck Push Forwrd nd e me Dertes hs secton s n the mn concerned wth the follown ssue: n oserer ttched to fxed sy Crtesn coordnte system wll see mterl moe nd deform oer tme nd wll osere
ME 501A Seminar in Engineering Analysis Page 1
 More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os ovemer 9, 7 More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os Lrr retto Menl ngneerng 5 Semnr n ngneerng nlss ovemer 9, 7 Outlne Revew oundr-vlue prolems Soot
More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os ovemer 9, 7 More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os Lrr retto Menl ngneerng 5 Semnr n ngneerng nlss ovemer 9, 7 Outlne Revew oundr-vlue prolems Soot
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT. PART IA (First Year) Paper 4 : Mathematical Methods
 Engneerng Prt I 009-0, Pper 4, Mthemtl Methods, Fst Course, J.B.Young CMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT PRT I (Frst Yer) 009-00 Pper 4 : Mthemtl Methods Leture ourse : Fst Mths Course, Letures
Engneerng Prt I 009-0, Pper 4, Mthemtl Methods, Fst Course, J.B.Young CMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT PRT I (Frst Yer) 009-00 Pper 4 : Mthemtl Methods Leture ourse : Fst Mths Course, Letures
COMPLEX NUMBER & QUADRATIC EQUATION
 MCQ COMPLEX NUMBER & QUADRATIC EQUATION Syllus : Comple numers s ordered prs of rels, Representton of comple numers n the form + nd ther representton n plne, Argnd dgrm, lger of comple numers, modulus
MCQ COMPLEX NUMBER & QUADRATIC EQUATION Syllus : Comple numers s ordered prs of rels, Representton of comple numers n the form + nd ther representton n plne, Argnd dgrm, lger of comple numers, modulus
REGULARIZATION IN QUANTUM GAUGE THEORY OF GRAVITATION WITH DE SITTER INNER SYMMETRY
 THEORETICAL PHYSICS REGULARIZATION IN QUANTUM GAUGE THEORY OF GRAVITATION WITH DE SITTER INNER SYMMETRY V. CHIRIÞOIU 1, G. ZET 1 Poltehn Unversty Tmºor, Tehnl Physs Deprtment, Romn E-ml: vorel.hrtou@et.upt.ro
THEORETICAL PHYSICS REGULARIZATION IN QUANTUM GAUGE THEORY OF GRAVITATION WITH DE SITTER INNER SYMMETRY V. CHIRIÞOIU 1, G. ZET 1 Poltehn Unversty Tmºor, Tehnl Physs Deprtment, Romn E-ml: vorel.hrtou@et.upt.ro
7.2 Volume. A cross section is the shape we get when cutting straight through an object.
 7. Volume Let s revew the volume of smple sold, cylnder frst. Cylnder s volume=se re heght. As llustrted n Fgure (). Fgure ( nd (c) re specl cylnders. Fgure () s rght crculr cylnder. Fgure (c) s ox. A
7. Volume Let s revew the volume of smple sold, cylnder frst. Cylnder s volume=se re heght. As llustrted n Fgure (). Fgure ( nd (c) re specl cylnders. Fgure () s rght crculr cylnder. Fgure (c) s ox. A
MATHEMATICS II PUC VECTOR ALGEBRA QUESTIONS & ANSWER
 MATHEMATICS II PUC VECTOR ALGEBRA QUESTIONS & ANSWER I One M Queston Fnd the unt veto n the deton of Let ˆ ˆ 9 Let & If Ae the vetos & equl? But vetos e not equl sne the oespondng omponents e dstnt e detons
MATHEMATICS II PUC VECTOR ALGEBRA QUESTIONS & ANSWER I One M Queston Fnd the unt veto n the deton of Let ˆ ˆ 9 Let & If Ae the vetos & equl? But vetos e not equl sne the oespondng omponents e dstnt e detons
Lecture 6: Coding theory
 Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Homework Math 180: Introduction to GR Temple-Winter (3) Summarize the article:
 Homework Math 80: Introduton to GR Temple-Wnter 208 (3) Summarze the artle: https://www.udas.edu/news/dongwthout-dark-energy/ (4) Assume only the transformaton laws for etors. Let X P = a = a α y = Y α
Homework Math 80: Introduton to GR Temple-Wnter 208 (3) Summarze the artle: https://www.udas.edu/news/dongwthout-dark-energy/ (4) Assume only the transformaton laws for etors. Let X P = a = a α y = Y α
CENTROID (AĞIRLIK MERKEZİ )
 CENTOD (ĞLK MEKEZİ ) centrod s geometrcl concept rsng from prllel forces. Tus, onl prllel forces possess centrod. Centrod s tougt of s te pont were te wole wegt of pscl od or sstem of prtcles s lumped.
CENTOD (ĞLK MEKEZİ ) centrod s geometrcl concept rsng from prllel forces. Tus, onl prllel forces possess centrod. Centrod s tougt of s te pont were te wole wegt of pscl od or sstem of prtcles s lumped.
4. Eccentric axial loading, cross-section core
 . Eccentrc xl lodng, cross-secton core Introducton We re strtng to consder more generl cse when the xl force nd bxl bendng ct smultneousl n the cross-secton of the br. B vrtue of Snt-Vennt s prncple we
. Eccentrc xl lodng, cross-secton core Introducton We re strtng to consder more generl cse when the xl force nd bxl bendng ct smultneousl n the cross-secton of the br. B vrtue of Snt-Vennt s prncple we
ragsdale (zdr82) HW6 ditmire (58335) 1 the direction of the current in the figure. Using the lower circuit in the figure, we get
 rgsdle (zdr8) HW6 dtmre (58335) Ths prnt-out should hve 5 questons Multple-choce questons my contnue on the next column or pge fnd ll choces efore nswerng 00 (prt of ) 00 ponts The currents re flowng n
rgsdle (zdr8) HW6 dtmre (58335) Ths prnt-out should hve 5 questons Multple-choce questons my contnue on the next column or pge fnd ll choces efore nswerng 00 (prt of ) 00 ponts The currents re flowng n
New Exact Solutions for Static Axially Symmetric Einstein Vacuum Equations
 The Arn Revew o Physs : 8 New Et Solutons or Stt Ally Symmetr Ensten Vuum Equtons Ahmd T. Al Froo Rhmn * nd Syeedul Islm Kng Adul A nversty Fulty o Sene Deprtment o Mthemts Jeddh Sud Ar nd Mthemts Deprtment
The Arn Revew o Physs : 8 New Et Solutons or Stt Ally Symmetr Ensten Vuum Equtons Ahmd T. Al Froo Rhmn * nd Syeedul Islm Kng Adul A nversty Fulty o Sene Deprtment o Mthemts Jeddh Sud Ar nd Mthemts Deprtment
New Algorithms: Linear, Nonlinear, and Integer Programming
 New Algorthms: ner, Nonlner, nd Integer Progrmmng Dhnnjy P. ehendle Sr Prshurmhu College, Tl Rod, Pune-400, Ind dhnnjy.p.mehendle@gml.om Astrt In ths pper we propose new lgorthm for lner progrmmng. Ths
New Algorthms: ner, Nonlner, nd Integer Progrmmng Dhnnjy P. ehendle Sr Prshurmhu College, Tl Rod, Pune-400, Ind dhnnjy.p.mehendle@gml.om Astrt In ths pper we propose new lgorthm for lner progrmmng. Ths
Trigonometry. Trigonometry. Solutions. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 223, 224, 245.
 Trgonometry Trgonometry Solutons Currulum Redy CMMG:, 4, 4 www.mthlets.om Trgonometry Solutons Bss Pge questons. Identfy f the followng trngles re rght ngled or not. Trngles,, d, e re rght ngled ndted
Trgonometry Trgonometry Solutons Currulum Redy CMMG:, 4, 4 www.mthlets.om Trgonometry Solutons Bss Pge questons. Identfy f the followng trngles re rght ngled or not. Trngles,, d, e re rght ngled ndted
Rank One Update And the Google Matrix by Al Bernstein Signal Science, LLC
 Introducton Rnk One Updte And the Google Mtrx y Al Bernsten Sgnl Scence, LLC www.sgnlscence.net here re two dfferent wys to perform mtrx multplctons. he frst uses dot product formulton nd the second uses
Introducton Rnk One Updte And the Google Mtrx y Al Bernsten Sgnl Scence, LLC www.sgnlscence.net here re two dfferent wys to perform mtrx multplctons. he frst uses dot product formulton nd the second uses
Learning Enhancement Team
 Lernng Enhnement Tem Worsheet: The Cross Produt These re the model nswers for the worsheet tht hs questons on the ross produt etween vetors. The Cross Produt study gude. z x y. Loong t mge, you n see tht
Lernng Enhnement Tem Worsheet: The Cross Produt These re the model nswers for the worsheet tht hs questons on the ross produt etween vetors. The Cross Produt study gude. z x y. Loong t mge, you n see tht
Two Coefficients of the Dyson Product
 Two Coeffcents of the Dyson Product rxv:07.460v mth.co 7 Nov 007 Lun Lv, Guoce Xn, nd Yue Zhou 3,,3 Center for Combntorcs, LPMC TJKLC Nnk Unversty, Tnjn 30007, P.R. Chn lvlun@cfc.nnk.edu.cn gn@nnk.edu.cn
Two Coeffcents of the Dyson Product rxv:07.460v mth.co 7 Nov 007 Lun Lv, Guoce Xn, nd Yue Zhou 3,,3 Center for Combntorcs, LPMC TJKLC Nnk Unversty, Tnjn 30007, P.R. Chn lvlun@cfc.nnk.edu.cn gn@nnk.edu.cn
The Schur-Cohn Algorithm
 Modelng, Estmton nd Otml Flterng n Sgnl Processng Mohmed Njm Coyrght 8, ISTE Ltd. Aendx F The Schur-Cohn Algorthm In ths endx, our m s to resent the Schur-Cohn lgorthm [] whch s often used s crteron for
Modelng, Estmton nd Otml Flterng n Sgnl Processng Mohmed Njm Coyrght 8, ISTE Ltd. Aendx F The Schur-Cohn Algorthm In ths endx, our m s to resent the Schur-Cohn lgorthm [] whch s often used s crteron for
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Bath. Mathematics ME Problem sheet 11 Least Squares Fitting of data
 Deprtment of Mechncl Engneerng, Unversty of Bth Mthemtcs ME10305 Prolem sheet 11 Lest Squres Fttng of dt NOTE: If you re gettng just lttle t concerned y the length of these questons, then do hve look t
Deprtment of Mechncl Engneerng, Unversty of Bth Mthemtcs ME10305 Prolem sheet 11 Lest Squres Fttng of dt NOTE: If you re gettng just lttle t concerned y the length of these questons, then do hve look t
Proof that if Voting is Perfect in One Dimension, then the First. Eigenvector Extracted from the Double-Centered Transformed
 Proof tht f Votng s Perfect n One Dmenson, then the Frst Egenvector Extrcted from the Doule-Centered Trnsformed Agreement Score Mtrx hs the Sme Rn Orderng s the True Dt Keth T Poole Unversty of Houston
Proof tht f Votng s Perfect n One Dmenson, then the Frst Egenvector Extrcted from the Doule-Centered Trnsformed Agreement Score Mtrx hs the Sme Rn Orderng s the True Dt Keth T Poole Unversty of Houston
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday 17 October 2012 Geometry II: Side Lengths
 Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
CHENG Chun Chor Litwin The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
Section 1.3 Triangles
 Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Probability. b a b. a b 32.
 Proility If n event n hppen in '' wys nd fil in '' wys, nd eh of these wys is eqully likely, then proility or the hne, or its hppening is, nd tht of its filing is eg, If in lottery there re prizes nd lnks,
Proility If n event n hppen in '' wys nd fil in '' wys, nd eh of these wys is eqully likely, then proility or the hne, or its hppening is, nd tht of its filing is eg, If in lottery there re prizes nd lnks,
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
Quiz: Experimental Physics Lab-I
 Mxmum Mrks: 18 Totl tme llowed: 35 mn Quz: Expermentl Physcs Lb-I Nme: Roll no: Attempt ll questons. 1. In n experment, bll of mss 100 g s dropped from heght of 65 cm nto the snd contner, the mpct s clled
Mxmum Mrks: 18 Totl tme llowed: 35 mn Quz: Expermentl Physcs Lb-I Nme: Roll no: Attempt ll questons. 1. In n experment, bll of mss 100 g s dropped from heght of 65 cm nto the snd contner, the mpct s clled
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sc. Technol., () (), pp. 44-49 Interntonl Journl of Pure nd Appled Scences nd Technolog ISSN 9-67 Avlle onlne t www.jopst.n Reserch Pper Numercl Soluton for Non-Lner Fredholm Integrl
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sc. Technol., () (), pp. 44-49 Interntonl Journl of Pure nd Appled Scences nd Technolog ISSN 9-67 Avlle onlne t www.jopst.n Reserch Pper Numercl Soluton for Non-Lner Fredholm Integrl
Global alignment. Genome Rearrangements Finding preserved genes. Lecture 18
 Computt onl Biology Leture 18 Genome Rerrngements Finding preserved genes We hve seen before how to rerrnge genome to obtin nother one bsed on: Reversls Knowledge of preserved bloks (or genes) Now we re
Computt onl Biology Leture 18 Genome Rerrngements Finding preserved genes We hve seen before how to rerrnge genome to obtin nother one bsed on: Reversls Knowledge of preserved bloks (or genes) Now we re
x=0 x=0 Positive Negative Positions Positions x=0 Positive Negative Positions Positions
 Knemtc Quntte Lner Moton Phyc 101 Eyre Tme Intnt t Fundmentl Tme Interl Defned Poton x Fundmentl Dplcement Defned Aerge Velocty g Defned Aerge Accelerton g Defned Knemtc Quntte Scler: Mgntude Tme Intnt,
Knemtc Quntte Lner Moton Phyc 101 Eyre Tme Intnt t Fundmentl Tme Interl Defned Poton x Fundmentl Dplcement Defned Aerge Velocty g Defned Aerge Accelerton g Defned Knemtc Quntte Scler: Mgntude Tme Intnt,
CISE 301: Numerical Methods Lecture 5, Topic 4 Least Squares, Curve Fitting
 CISE 3: umercl Methods Lecture 5 Topc 4 Lest Squres Curve Fttng Dr. Amr Khouh Term Red Chpter 7 of the tetoo c Khouh CISE3_Topc4_Lest Squre Motvton Gven set of epermentl dt 3 5. 5.9 6.3 The reltonshp etween
CISE 3: umercl Methods Lecture 5 Topc 4 Lest Squres Curve Fttng Dr. Amr Khouh Term Red Chpter 7 of the tetoo c Khouh CISE3_Topc4_Lest Squre Motvton Gven set of epermentl dt 3 5. 5.9 6.3 The reltonshp etween
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
Definition of Tracking
 Trckng Defnton of Trckng Trckng: Generte some conclusons bout the moton of the scene, objects, or the cmer, gven sequence of mges. Knowng ths moton, predct where thngs re gong to project n the net mge,
Trckng Defnton of Trckng Trckng: Generte some conclusons bout the moton of the scene, objects, or the cmer, gven sequence of mges. Knowng ths moton, predct where thngs re gong to project n the net mge,
DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMERICAL METHODS (COS 233-8) Solutions to Assignment 3. x f(x)
 DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMEICAL METHODS (COS -8) Solutons to Assgnment Queston Consder the followng dt: 5 f() 8 7 5 () Set up dfference tble through fourth dfferences. (b) Wht s the mnmum degree tht n nterpoltng
DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMEICAL METHODS (COS -8) Solutons to Assgnment Queston Consder the followng dt: 5 f() 8 7 5 () Set up dfference tble through fourth dfferences. (b) Wht s the mnmum degree tht n nterpoltng
Introduction to Olympiad Inequalities
 Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Effects of polarization on the reflected wave
 Lecture Notes. L Ros PPLIED OPTICS Effects of polrzton on the reflected wve Ref: The Feynmn Lectures on Physcs, Vol-I, Secton 33-6 Plne of ncdence Z Plne of nterfce Fg. 1 Y Y r 1 Glss r 1 Glss Fg. Reflecton
Lecture Notes. L Ros PPLIED OPTICS Effects of polrzton on the reflected wve Ref: The Feynmn Lectures on Physcs, Vol-I, Secton 33-6 Plne of ncdence Z Plne of nterfce Fg. 1 Y Y r 1 Glss r 1 Glss Fg. Reflecton
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
Lecture 36. Finite Element Methods
 CE 60: Numercl Methods Lecture 36 Fnte Element Methods Course Coordntor: Dr. Suresh A. Krth, Assocte Professor, Deprtment of Cvl Engneerng, IIT Guwht. In the lst clss, we dscussed on the ppromte methods
CE 60: Numercl Methods Lecture 36 Fnte Element Methods Course Coordntor: Dr. Suresh A. Krth, Assocte Professor, Deprtment of Cvl Engneerng, IIT Guwht. In the lst clss, we dscussed on the ppromte methods
STRENGTH FIELDS AND LAGRANGIANS ON GOsc (2) M
 NLELE ŞTIINŢIICE LE UNIERSITĂŢII L.I.CUZ IŞI Toul XLII, s.i, Mtetă, 2001, f.2. STRENGTH IELDS ND LGRNGINS ON GOs 2 M BY DRIN SNDOICI strt. In ths pper we stud the strength felds of the seond order on the
NLELE ŞTIINŢIICE LE UNIERSITĂŢII L.I.CUZ IŞI Toul XLII, s.i, Mtetă, 2001, f.2. STRENGTH IELDS ND LGRNGINS ON GOs 2 M BY DRIN SNDOICI strt. In ths pper we stud the strength felds of the seond order on the
Chapter Gauss Quadrature Rule of Integration
 Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vectors and Vector Calculus
 ESI 34 tmospherc Dnmcs I Lesson 1 Vectors nd Vector lculus Reference: Schum s Outlne Seres: Mthemtcl Hndbook of Formuls nd Tbles Suggested Redng: Mrtn Secton 1 OORDINTE SYSTEMS n orthonorml coordnte sstem
ESI 34 tmospherc Dnmcs I Lesson 1 Vectors nd Vector lculus Reference: Schum s Outlne Seres: Mthemtcl Hndbook of Formuls nd Tbles Suggested Redng: Mrtn Secton 1 OORDINTE SYSTEMS n orthonorml coordnte sstem
Chapter Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear Equation
 Chpter.4 Newton-Rphson Method of Solvng Nonlner Equton After redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method formul,. develop the lgorthm of the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chpter.4 Newton-Rphson Method of Solvng Nonlner Equton After redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method formul,. develop the lgorthm of the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
A Lower Bound for the Length of a Partial Transversal in a Latin Square, Revised Version
 A Lower Bound for the Length of Prtil Trnsversl in Ltin Squre, Revised Version Pooy Htmi nd Peter W. Shor Deprtment of Mthemtil Sienes, Shrif University of Tehnology, P.O.Bo 11365-9415, Tehrn, Irn Deprtment
A Lower Bound for the Length of Prtil Trnsversl in Ltin Squre, Revised Version Pooy Htmi nd Peter W. Shor Deprtment of Mthemtil Sienes, Shrif University of Tehnology, P.O.Bo 11365-9415, Tehrn, Irn Deprtment
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
Appendix C Partial discharges. 1. Relationship Between Measured and Actual Discharge Quantities
 Appendi Prtil dishrges. Reltionship Between Mesured nd Atul Dishrge Quntities A dishrging smple my e simply represented y the euilent iruit in Figure. The pplied lternting oltge V is inresed until the
Appendi Prtil dishrges. Reltionship Between Mesured nd Atul Dishrge Quntities A dishrging smple my e simply represented y the euilent iruit in Figure. The pplied lternting oltge V is inresed until the
8 THREE PHASE A.C. CIRCUITS
 8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
6 Roots of Equations: Open Methods
 HK Km Slghtly modfed 3//9, /8/6 Frstly wrtten t Mrch 5 6 Roots of Equtons: Open Methods Smple Fed-Pont Iterton Newton-Rphson Secnt Methods MATLAB Functon: fzero Polynomls Cse Study: Ppe Frcton Brcketng
HK Km Slghtly modfed 3//9, /8/6 Frstly wrtten t Mrch 5 6 Roots of Equtons: Open Methods Smple Fed-Pont Iterton Newton-Rphson Secnt Methods MATLAB Functon: fzero Polynomls Cse Study: Ppe Frcton Brcketng
VECTORS AND TENSORS IV.1.1. INTRODUCTION
 Chpter IV Vector nd Tensor Anlyss IV. Vectors nd Tensors Septemer 5, 08 05 IV. VECTORS AND TENSORS IV... INTRODUCTION In mthemtcs nd mechncs, we he to operte wth qunttes whch requre dfferent mthemtcl ojects
Chpter IV Vector nd Tensor Anlyss IV. Vectors nd Tensors Septemer 5, 08 05 IV. VECTORS AND TENSORS IV... INTRODUCTION In mthemtcs nd mechncs, we he to operte wth qunttes whch requre dfferent mthemtcl ojects
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
A Study on the Properties of Rational Triangles
 Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
= x x 2 = 25 2
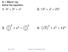 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
2 a Mythili Publishers, Karaikkudi
 Wnglsh Tuton Centre Puduvl + Mths Q & A Mthl Pulshers Krud. 8000 PROVE BY FACTOR METHOD OF DETERMINANTS. ). ). ). ). ) 6. ) ) ) ). ) ) 8. ) 9 ) 9. 8 0. 0 Solve ) PROPERTIES OF DETERMINANTS. 0 / / /. 0.
Wnglsh Tuton Centre Puduvl + Mths Q & A Mthl Pulshers Krud. 8000 PROVE BY FACTOR METHOD OF DETERMINANTS. ). ). ). ). ) 6. ) ) ) ). ) ) 8. ) 9 ) 9. 8 0. 0 Solve ) PROPERTIES OF DETERMINANTS. 0 / / /. 0.
e a = 12.4 i a = 13.5i h a = xi + yj 3 a Let r a = 25cos(20) i + 25sin(20) j b = 15cos(55) i + 15sin(55) j
 Vetors MC Qld-3 49 Chapter 3 Vetors Exerse 3A Revew of vetors a d e f e a x + y omponent: x a os(θ 6 os(80 + 39 6 os(9.4 omponent: y a sn(θ 6 sn(9 0. a.4 0. f a x + y omponent: x a os(θ 5 os( 5 3.6 omponent:
Vetors MC Qld-3 49 Chapter 3 Vetors Exerse 3A Revew of vetors a d e f e a x + y omponent: x a os(θ 6 os(80 + 39 6 os(9.4 omponent: y a sn(θ 6 sn(9 0. a.4 0. f a x + y omponent: x a os(θ 5 os( 5 3.6 omponent:
Al-Zangana Iraqi Journal of Science, 2016, Vol. 57, No.2A, pp:
 Results n Projetve Geometry PG( r,), r, Emd Bkr Al-Zngn* Deprtment of Mthemts, College of Sene, Al-Mustnsryh Unversty, Bghdd, Ir Abstrt In projetve plne over fnte feld F, on s the unue omplete ( ) r nd
Results n Projetve Geometry PG( r,), r, Emd Bkr Al-Zngn* Deprtment of Mthemts, College of Sene, Al-Mustnsryh Unversty, Bghdd, Ir Abstrt In projetve plne over fnte feld F, on s the unue omplete ( ) r nd
Fall 2012 Analysis of Experimental Measurements B. Eisenstein/rev. S. Errede. with respect to λ. 1. χ λ χ λ ( ) λ, and thus:
 More on χ nd errors : uppose tht we re fttng for sngle -prmeter, mnmzng: If we epnd The vlue χ ( ( ( ; ( wth respect to. χ n Tlor seres n the vcnt of ts mnmum vlue χ ( mn χ χ χ χ + + + mn mnmzes χ, nd
More on χ nd errors : uppose tht we re fttng for sngle -prmeter, mnmzng: If we epnd The vlue χ ( ( ( ; ( wth respect to. χ n Tlor seres n the vcnt of ts mnmum vlue χ ( mn χ χ χ χ + + + mn mnmzes χ, nd
GEOMETRY OF THE CIRCLE TANGENTS & SECANTS
 Geometry Of The ircle Tngents & Secnts GEOMETRY OF THE IRLE TNGENTS & SENTS www.mthletics.com.u Tngents TNGENTS nd N Secnts SENTS Tngents nd secnts re lines tht strt outside circle. Tngent touches the
Geometry Of The ircle Tngents & Secnts GEOMETRY OF THE IRLE TNGENTS & SENTS www.mthletics.com.u Tngents TNGENTS nd N Secnts SENTS Tngents nd secnts re lines tht strt outside circle. Tngent touches the
April 8, 2017 Math 9. Geometry. Solving vector problems. Problem. Prove that if vectors and satisfy, then.
 pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field
 Charged Partle n a Magnet Feld Mhael Fowler 1/16/08 Introduton Classall, the fore on a harged partle n eletr and magnet felds s gven b the Lorentz fore law: v B F = q E+ Ths velot-dependent fore s qute
Charged Partle n a Magnet Feld Mhael Fowler 1/16/08 Introduton Classall, the fore on a harged partle n eletr and magnet felds s gven b the Lorentz fore law: v B F = q E+ Ths velot-dependent fore s qute
MAT 403 NOTES 4. f + f =
 MAT 403 NOTES 4 1. Fundmentl Theorem o Clulus We will proo more generl version o the FTC thn the textook. But just like the textook, we strt with the ollowing proposition. Let R[, ] e the set o Riemnn
MAT 403 NOTES 4 1. Fundmentl Theorem o Clulus We will proo more generl version o the FTC thn the textook. But just like the textook, we strt with the ollowing proposition. Let R[, ] e the set o Riemnn
PHYSICS 212 MIDTERM II 19 February 2003
 PHYSICS 1 MIDERM II 19 Feruary 003 Exam s losed ook, losed notes. Use only your formula sheet. Wrte all work and answers n exam ooklets. he aks of pages wll not e graded unless you so request on the front
PHYSICS 1 MIDERM II 19 Feruary 003 Exam s losed ook, losed notes. Use only your formula sheet. Wrte all work and answers n exam ooklets. he aks of pages wll not e graded unless you so request on the front
Introduction to Numerical Integration Part II
 Introducton to umercl Integrton Prt II CS 75/Mth 75 Brn T. Smth, UM, CS Dept. Sprng, 998 4/9/998 qud_ Intro to Gussn Qudrture s eore, the generl tretment chnges the ntegrton prolem to ndng the ntegrl w
Introducton to umercl Integrton Prt II CS 75/Mth 75 Brn T. Smth, UM, CS Dept. Sprng, 998 4/9/998 qud_ Intro to Gussn Qudrture s eore, the generl tretment chnges the ntegrton prolem to ndng the ntegrl w
Shuai Dong. Using Math and Science to improve your game
 Computtonl phscs Shu Dong Usng Mth nd Sene to mprove our gme Appromton of funtons Lner nterpolton Lgrnge nterpolton Newton nterpolton Lner sstem method Lest-squres ppromton Mllkn eperment Wht s nterpolton?
Computtonl phscs Shu Dong Usng Mth nd Sene to mprove our gme Appromton of funtons Lner nterpolton Lgrnge nterpolton Newton nterpolton Lner sstem method Lest-squres ppromton Mllkn eperment Wht s nterpolton?
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
CS 491G Combinatorial Optimization Lecture Notes
 CS 491G Comintoril Optimiztion Leture Notes Dvi Owen July 30, August 1 1 Mthings Figure 1: two possile mthings in simple grph. Definition 1 Given grph G = V, E, mthing is olletion of eges M suh tht e i,
CS 491G Comintoril Optimiztion Leture Notes Dvi Owen July 30, August 1 1 Mthings Figure 1: two possile mthings in simple grph. Definition 1 Given grph G = V, E, mthing is olletion of eges M suh tht e i,
Exercise sheet 6: Solutions
 Eerise sheet 6: Solutions Cvet emptor: These re merel etended hints, rther thn omplete solutions. 1. If grph G hs hromti numer k > 1, prove tht its verte set n e prtitioned into two nonempt sets V 1 nd
Eerise sheet 6: Solutions Cvet emptor: These re merel etended hints, rther thn omplete solutions. 1. If grph G hs hromti numer k > 1, prove tht its verte set n e prtitioned into two nonempt sets V 1 nd
Chapter Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear Equation
 Chpter 0.04 Newton-Rphson Method o Solvng Nonlner Equton Ater redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method ormul,. develop the lgorthm o the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chpter 0.04 Newton-Rphson Method o Solvng Nonlner Equton Ater redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method ormul,. develop the lgorthm o the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Name: SID: Discussion Session:
 Nme: SID: Dscusson Sesson: hemcl Engneerng hermodynmcs -- Fll 008 uesdy, Octoer, 008 Merm I - 70 mnutes 00 onts otl losed Book nd Notes (5 ponts). onsder n del gs wth constnt het cpctes. Indcte whether
Nme: SID: Dscusson Sesson: hemcl Engneerng hermodynmcs -- Fll 008 uesdy, Octoer, 008 Merm I - 70 mnutes 00 onts otl losed Book nd Notes (5 ponts). onsder n del gs wth constnt het cpctes. Indcte whether
2.4 Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation
 .4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
.4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
Reflection Property of a Hyperbola
 Refletion Propert of Hperol Prefe The purpose of this pper is to prove nltill nd to illustrte geometrill the propert of hperol wherein r whih emntes outside the onvit of the hperol, tht is, etween the
Refletion Propert of Hperol Prefe The purpose of this pper is to prove nltill nd to illustrte geometrill the propert of hperol wherein r whih emntes outside the onvit of the hperol, tht is, etween the
LESSON 11: TRIANGLE FORMULAE
 . THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
. THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
A New Method of Construction of Robust Second Order Rotatable Designs Using Balanced Incomplete Block Designs
 Open Journal of Statsts 9-7 http://d.do.org/.6/os..5 Publshed Onlne January (http://www.srp.org/ournal/os) A ew Method of Construton of Robust Seond Order Rotatable Desgns Usng Balaned Inomplete Blok Desgns
Open Journal of Statsts 9-7 http://d.do.org/.6/os..5 Publshed Onlne January (http://www.srp.org/ournal/os) A ew Method of Construton of Robust Seond Order Rotatable Desgns Usng Balaned Inomplete Blok Desgns
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, November 14, 2018 Finite Automata II. Nickolas Rollick a b b. a b 4
 Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Kinematics Quantities. Linear Motion. Coordinate System. Kinematics Quantities. Velocity. Position. Don t Forget Units!
 Knemtc Quntte Lner Phyc 11 Eyre Tme Intnt t Fundmentl Tme Interl t Dened Poton Fundmentl Dplcement Dened Aerge g Dened Aerge Accelerton g Dened Knemtc Quntte Scler: Mgntude Tme Intnt, Tme Interl nd Speed
Knemtc Quntte Lner Phyc 11 Eyre Tme Intnt t Fundmentl Tme Interl t Dened Poton Fundmentl Dplcement Dened Aerge g Dened Aerge Accelerton g Dened Knemtc Quntte Scler: Mgntude Tme Intnt, Tme Interl nd Speed
Chapter 5 Supplemental Text Material R S T. ij i j ij ijk
 Chpter 5 Supplementl Text Mterl 5-. Expected Men Squres n the Two-fctor Fctorl Consder the two-fctor fxed effects model y = µ + τ + β + ( τβ) + ε k R S T =,,, =,,, k =,,, n gven s Equton (5-) n the textook.
Chpter 5 Supplementl Text Mterl 5-. Expected Men Squres n the Two-fctor Fctorl Consder the two-fctor fxed effects model y = µ + τ + β + ( τβ) + ε k R S T =,,, =,,, k =,,, n gven s Equton (5-) n the textook.
Remember: Project Proposals are due April 11.
 Bonformtcs ecture Notes Announcements Remember: Project Proposls re due Aprl. Clss 22 Aprl 4, 2002 A. Hdden Mrov Models. Defntons Emple - Consder the emple we tled bout n clss lst tme wth the cons. However,
Bonformtcs ecture Notes Announcements Remember: Project Proposls re due Aprl. Clss 22 Aprl 4, 2002 A. Hdden Mrov Models. Defntons Emple - Consder the emple we tled bout n clss lst tme wth the cons. However,
Ellipses. The second type of conic is called an ellipse.
 Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Technische Universität München Winter term 2009/10 I7 Prof. J. Esparza / J. Křetínský / M. Luttenberger 11. Februar Solution
 Tehnishe Universität Münhen Winter term 29/ I7 Prof. J. Esprz / J. Křetínský / M. Luttenerger. Ferur 2 Solution Automt nd Forml Lnguges Homework 2 Due 5..29. Exerise 2. Let A e the following finite utomton:
Tehnishe Universität Münhen Winter term 29/ I7 Prof. J. Esprz / J. Křetínský / M. Luttenerger. Ferur 2 Solution Automt nd Forml Lnguges Homework 2 Due 5..29. Exerise 2. Let A e the following finite utomton:
Tutorial Worksheet. 1. Find all solutions to the linear system by following the given steps. x + 2y + 3z = 2 2x + 3y + z = 4.
 Mth 5 Tutoril Week 1 - Jnury 1 1 Nme Setion Tutoril Worksheet 1. Find ll solutions to the liner system by following the given steps x + y + z = x + y + z = 4. y + z = Step 1. Write down the rgumented mtrix
Mth 5 Tutoril Week 1 - Jnury 1 1 Nme Setion Tutoril Worksheet 1. Find ll solutions to the liner system by following the given steps x + y + z = x + y + z = 4. y + z = Step 1. Write down the rgumented mtrix
GENERALIZED OPERATIONAL RELATIONS AND PROPERTIES OF FRACTIONAL HANKEL TRANSFORM
 S. Res. Chem. Commu.: (3 8-88 ISSN 77-669 GENERLIZED OPERTIONL RELTIONS ND PROPERTIES OF FRCTIONL NKEL TRNSFORM R. D. TYWDE *. S. GUDDE d V. N. MLLE b Pro. Rm Meghe Isttute o Teholog & Reserh Bder MRVTI
S. Res. Chem. Commu.: (3 8-88 ISSN 77-669 GENERLIZED OPERTIONL RELTIONS ND PROPERTIES OF FRCTIONL NKEL TRNSFORM R. D. TYWDE *. S. GUDDE d V. N. MLLE b Pro. Rm Meghe Isttute o Teholog & Reserh Bder MRVTI
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unfom Ccul Moton Unfom ccul Moton An object mong t constnt sped n ccle The ntude of the eloct emns constnt The decton of the eloct chnges contnuousl!!!! Snce cceleton s te of chnge of eloct:!! Δ Δt The
Unfom Ccul Moton Unfom ccul Moton An object mong t constnt sped n ccle The ntude of the eloct emns constnt The decton of the eloct chnges contnuousl!!!! Snce cceleton s te of chnge of eloct:!! Δ Δt The
(a) A partition P of [a, b] is a finite subset of [a, b] containing a and b. If Q is another partition and P Q, then Q is a refinement of P.
![(a) A partition P of [a, b] is a finite subset of [a, b] containing a and b. If Q is another partition and P Q, then Q is a refinement of P. (a) A partition P of [a, b] is a finite subset of [a, b] containing a and b. If Q is another partition and P Q, then Q is a refinement of P.](/thumbs/72/66745617.jpg) Chpter 7: The Riemnn Integrl When the derivtive is introdued, it is not hrd to see tht the it of the differene quotient should be equl to the slope of the tngent line, or when the horizontl xis is time
Chpter 7: The Riemnn Integrl When the derivtive is introdued, it is not hrd to see tht the it of the differene quotient should be equl to the slope of the tngent line, or when the horizontl xis is time
6 Random Errors in Chemical Analysis
 6 Rndom Error n Cheml Anl 6A The ture of Rndom Error 6A- Rndom Error Soure? Fg. 6- Three-dmenonl plot howng olute error n Kjeldhl ntrogen determnton for four dfferent nlt. Anlt Pree Aurte 4 Tle 6- Pole
6 Rndom Error n Cheml Anl 6A The ture of Rndom Error 6A- Rndom Error Soure? Fg. 6- Three-dmenonl plot howng olute error n Kjeldhl ntrogen determnton for four dfferent nlt. Anlt Pree Aurte 4 Tle 6- Pole
CS 573 Automata Theory and Formal Languages
 Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Math 497C Sep 17, Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU
 Mth 497C Sep 17, 004 1 Curves nd Surfces Fll 004, PSU Lecture Notes 3 1.8 The generl defnton of curvture; Fox-Mlnor s Theorem Let α: [, b] R n be curve nd P = {t 0,...,t n } be prtton of [, b], then the
Mth 497C Sep 17, 004 1 Curves nd Surfces Fll 004, PSU Lecture Notes 3 1.8 The generl defnton of curvture; Fox-Mlnor s Theorem Let α: [, b] R n be curve nd P = {t 0,...,t n } be prtton of [, b], then the
System Validation (IN4387) November 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00
 System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
