DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION BİLGE BOZKURT
|
|
|
- Shanon Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B. BOZKURT METU 6 DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION BİLGE BOZKURT JANUARY 6
2 DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES OF MIDDLE EAST TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY BY BİLGE BOZKURT IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS JANUARY 6
3 Appoval of he Gaduae School of Naual and Applied Sciences Pof. D. Canan Özgen Dieco I ceify ha his hesis saisfies all he equieens as a hesis fo he degee of Mase of Science. Pof. D. Sinan Biliken Head of Depaen This is o ceify ha we have ead his hesis and ha in ou opinion i is fully adequae, in scope and qualiy, as a hesis fo he degee of Mase of Science. Pof. D. Sinan Biliken Supeviso Exaining Coiee Mebes Pof. D. Aif Dei (Kocaeli Unv, PHYS Pof. D. Sinan Biliken (METU, PHYS Assis. Pof. D. İsail Rafaov (METU, PHYS Assoc. Pof. D. Akif Esendei (METU, PHYS Assoc. Pof. D. Seha Çakõ (METU, PHYS
4 I heeby declae ha all infoaion in his docuen has been obained and pesened in accodance wih acadeic ules and ehical conduc. I also declae ha, as equied by hese ules and conduc, I have fully cied and efeenced all aeial and esuls ha ae no oiginal o his wok. Nae, Las nae: Bilge Bozku Signaue : iii
5 ABSTRACT DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION Bozku, Bilge M. S., Depaen of Physics Supeviso: Pof. D. Sinan Biliken Januay 6, 7 pages The ai of his wok is o analyically ea he dynaic ion behavio duing he evoluion of he ion aix sheah, consideing he indusial applicaion plasa souce ion iplanaion fo boh plana and cylindical ages, and hen o develop a code ha siulaes his dynaic ion behavio nueically. If he sepaaion beween he elecodes in a dischage ube is sall, upon he applicaion of a lage poenial beween he elecodes, an ion aix sheah is foed, which fills he whole ine-elecode space. Afe a sho ie, he ion aix sheah sas oving owads he cahode and disappeas hee. Two egions ae foed as he aix sheah evolves. The poenial pofiles of hese wo egions ae deived and he ion flux on he cahode is esiaed. Then, by using he finie-diffeences ehod, he poble is siulaed nueically. I has been seen ha he esuls of boh analyical calculaions and nueical siulaions ae in a good ageeen. Keywods: Ion iplanaion, Plasa Souce Ion Iplanaion, Plasa Iesion Ion Iplanaion, Dynaic Ion Behavio, Modeling iv
6 ÖZ PLAZMA KAYNAKLI İYON EKİMİNDE DİNAMİK İYON HAREKETİ Bozku, Bilge Yüksek Lisans, Fizik Bölüü Tez Yöneicisi: Pof. D. Sinan Biliken Ocak 6, 7 sayfa Bu çalõşanõn aacõ, plaza kaynaklõ iyon ekii ile düzlesel ve silindiik hedefle için endüsiyel uygulaa düşünüleek iyon-ais plakalaõnõn evii esnasõndaki dinaik iyon haekeini analiik olaak çalõşak ve sona bu dinaik iyon haekeini sayõsal olaak siüle eden bi kod gelişieki. Eğe bi deşa üpünde elekola aasõ esafe az ise, elekola aasõna yüksek bi poansiyel uygulandõğõnda, ü elekola aasõ esafeyi dolduan bi iyonais plakasõ oluşu. Kõsa bi süe sona iyon-ais plakasõ kaoda doğu haeke eeye başla ve oada kaybolu. Mais plakasõnõn evii esnasõnda iki bölge oluşu. Bu iki bölgenin poansiyel pofili üeiliş ve kaoaki iyon akõsõ hesap edilişi. Sona, sonlu fakla eodu kullanõlaak poble sayõsal olaak siüle edilişi. Analiik hesaplaalaõn sonuçlaõ ile sayõsal siülasyonlaõn uyulu olduğu gözlelenişi. Anaha Keliele: İyon Ekii, Plaza Kaynaklõ İyon Ekii, Dinaik İyon Haekei, Sayõsal Çözülee, Modellee v
7 FOR PROF. DR. ORDAL DEMOKAN vi
8 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like o expess y deepes gaiude o dea Pof. D. Odal Deokan fo suggesing his eseach and his guidance, advice, suppo and insigh in his sudy unil his soowful deise. I would like o expess y gaiude o y supeviso Pof. D. Sinan Biliken fo his guidance, suggesions, coens, conibuion and suppo. I would also like o expess y gaeful hanks o Assis. Pof. D. İsail Rafaov and Pof. D. Ayşe Kaasu fo hei guidance, conibuions and suggesions. I would like o hank y faily and y fiancé fo hei oal suppo and encouageen. I would also like o hank İnanç Kanõk and Yasein Filiz fo hei invaluable discussions, suggesions, coens and suppo. vii
9 TABLE OF CONTENTS PLAGIARISM...iii ABSTRACT...iv ÖZ...v DEDICATION...vi ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS...vii TABLE OF CONTENTS...viii LIST OF FIGURES...xii CHAPTER. INTRODUCTION.... Plasa Pocessing.. Plasa Souce Ion Iplanaion...3 Basic Plasa Sheah Physics.. viii
10 .3. Phase..3. Phase Phase The Obecives and Conen of he Thesis 8. THEORY AND CALCULATIONS.. 9. Plana Configuaion. 9.. The Model The Deeinaion of Poenials..3 The Deeinaion of Ion Velociy and Flux 7.. Gaphical Repesenaion.. 9. Cylindical Configuaion..... The Model The Deeinaion of Poenials The Deeinaion of Ion Velociy and Flux 35 ix
11 3. SIMULATION The Basics of Siulaion Nueical Analysis The Finie-Diffeences Mehod Plana Configuaion The Model Equaions Bounday and Iniial Condiions Nueical Pocedue Poisson s Equaion Coninuiy Equaion Moenu Balance Equaion Nueical Resuls Cylindical Configuaion The Model 6 x
12 3.3.. Equaions Bounday and Iniial Condiions Nueical Pocedue Poisson s Equaion Coninuiy Equaion Moenu Balance Equaion Nueical Resuls. 6. CONCLUSIONS.. 67 REFERENCES 7 xi
13 LIST OF FIGURES FIGURES Figue. Block diaga of a ypical PSII syse Figue. When a lage negaive sep poenial o a ain of high volage negaive pulses,, is applied o he cahode, elecons ae quickly epelled fo he cahode on he ie scale of elecon plasa fequency 5 Figue.3 An ion-aix sheah is lef behind 5 Figue. Afe a ie scale of he ion plasa fequency, ions sa esponding and he ion aix sheah sas o expand.. 6 Figue.5 The seady sae poenial pofile 7 Figue. When he applied poenial,, is lage (~ kv and he elecode sepaaion is sall (~ -, he aix can fill he enie ineelecode space ( / ω pe < < / ω pi, whee ω pe and ω pi ae elecon and ion plasa fequencies, especively 9 Figue. Afe a sho ie, he aix sas oving owads he cahode. The noaion s( epesens he ie-dependen locaion of he sheah edge... Figue.3 The aix disappeas as all ions ae iplaned. Figue. Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie = ax xii
14 Figue.5 Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie =. ax Figue.6 Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie = 3 ax Figue.7 Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie = ax.. Figue.8 Ion flux as a funcion of a x = L Figue.9 When he applied poenial, elecode sepaaion is sall (~ -, is lage (~ kv and he, he aix can fill he enie ineelecode space ( / ω pe < < / ω pi, whee ω pe and ω pi ae elecon and ion plasa fequencies, especively 3 Figue. Afe a sho ie, he aix sas oving owads he cahode. s( is he ie-dependen locaion of he sheah edge 3 Figue. The aix disappeas as all ions ae iplaned Figue. The gaph of i π Ef ( i ln x whee a Figue.3 The gaph of i π Ef ( i / x = /. 37 = ln( wih aken as = 38 Figue. A copaison of he gaphs of equaion (..6 and (..67 fo = ax = and 39 Figue.5 The gaph of ( Figue.6 The egions whee he oos of coespond. 3 xiii
15 Figue.7 The ion velociy as a funcion of a he insans = ax, = ax, 3 = ax and = ax obained as a esul of nueic calculaions Figue.8: The ion flux as a funcion of a he age suface obained as a esul of nueic calculaions 5 Figue 3. Copuaional doain 5 Figue 3. Ion densiy and ion velociy as a funcion of = ax, = ax, x a he insans 3 = ax and = ax 57 Figue 3.3 Ion velociy vesus posiion gaphs ploed using analyical esuls 59 Figue 3. The analyically calculaed ion velociy as a funcion of posiion and ie 59 Figue 3.5 Copuaional doain 6 Figue 3.6 Ion densiy and ion velociy as a funcion of a he insans = ax, = ax, 3 = ax and = ax 65 Figue 3.7 Ion velociy as a funcion of a fou paicula insans = ax, = ax, 3 = ax and = ax 66 xiv
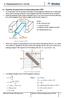
16 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION.. Plasa Pocessing Plasa pocessing is a plasa-based aeial pocessing echnology, he ai of which is o odify he popeies of he sufaces of aeials such as eals, plasics and ceaics by vaious pocesses like deposiion, iplanaion, and eching ec [] [3]. The pincipal coponen of plasa pocessing is he plasa ediu, in which he aeial o be pocessed is iesed. To ainain he desied plasa ediu, geneally DC and adio fequency (RF dischages ae used. RF dischages ae used fo a boad ange of pocesses such as deposiion, eching and eaen while DC dischages ae pefeed in ion iplanaion pocesses as DC dischages involve lage poenials []. The applicaions of plasa pocessing include: he anufacuing of inegaed cicuis; he deconainaion of wase aeials and sufaces; plasa souce ion iplanaion and he eching of silicon wafes fo seiconduco fabicaion [, ]... Plasa Souce Ion Iplanaion Plasa souce ion iplanaion (PSII, which was invened by Conad in 987 [3], has becoe well-known as one of he well-esablished plasa-based anufacuing echnique, fequenly used in he suface odificaion of aeials fo indusial applicaions [5] [8].
17 PSII is a oo epeaue suface enhanceen echnique ha uses a plasa ediu suounding a age and high-negaive-volage, high-cuen pulses o acceleae ions ino a age suface fo all diecions. PSII odifies he age suface in beneficial ways, aking i hade, ipoving wea popeies, educing he coefficien of ficion, enhancing is esisance o coosion and daaically ipoving he wea-life of anufacuing ools in acual indusial applicaions. The block diaga of a ypical PSII syse is given in figue. [9] []. Figue.: Block diaga of a ypical PSII syse. PSII depas adically fo convenional ion iplanaion echnology in he following aspecs [7,, ]:
18 . In PSII, ages ae placed diecly ino a plasa ediu and ions ae acceleaed ono he age hough a plasa sheah ha suounds he age. Hence, PSII is a non-line-of-sigh echnique which eans a pah fo a single ion souce o he suface of he age is no equied. This enables PSII o ea he enie age suface siulaneously wihou he need of he ie-consuing oaion of he age and o ea uliple age sufaces siulaneously wihou he need fo in-vacuu anipulaion of he age assebly.. In PSII, he ions ae acceleaed noal o he suface of he age so hee is no eained dose poble. Even wih age oaion, he convenional ion iplanaion echnique equies age asking in ode o iniize he gazing incidence, which poduces excessive spueing, and heefoe liis he eained dose. 3. PSII is no liied by ion opics chaaceisics o by he Child-Langui space chage liied flow popeies of convenional ion iplanaion echniques. Due o his fac, he aveage ion flux o he age suface can be oe han an ode of agniude lage han using convenional echniques a low enegies, which significanly educes he equied eaen ie fo lage, coplex age asseblies and enables PSII o iplan ions efficienly o concenaions and dephs equied fo suface odificaion.. PSII is a siple and low-cos echnique because a he ion acceleao sage, he age oaion appaaus is eliinaed in PSII. 5. Since he age oaion sage does no exis in PSII, lage and heavy ages can also be eaed by PSII. The age oaion in convenional ion iplanaion echnique adds coplexiy o he pocess and educes he size of he age. 6. PSII is a oo epeaue pocess. The oaion poble in he convenional ion iplanaion echnique is aggavaed by he need fo adequae hea sinks a he ages o lii he epeaue ise duing iplanaion. 7. I has high dose aes, ininsic chage neualizaion capabiliy, and adapabiliy o ohe suface odificaion pocesses. 3
19 .3. Basic Plasa Sheah Physics In he PSII echnique, he aeial, whose suface is o be odified, acs as he cahode in a gounded vacuu chabe, in which a flow of he gas equied fo iplanaion is ainained. The gas inside he vacuu chabe is ionized by one of he vaious dischage ehods [5, 6, 7, ]..3.. Phase When a lage negaive sep poenial o a ain of high volage negaive pulses, a ie, ha has a agniude beween kv and kv is applied o he cahode =, he elecons ae quickly epelled fo he cahode on he ie scale of elecon plasa fequency ( as shown in figue. [5] [7]. On /ω pe his ie scale, as elecons ecede, he ions oion is negligible so ha he epelled elecons leave behind an elecon-fee egion, naely he ion aix sheah []. The ion aix sheah consiss of unifoly disibued, saionay ions, confoally apping he cahode suface, which is shown in figue.3 [5] [7]. An ion aix sheah is a egion beween a quasi-neual plasa and a negaive elecode o which a lage negaive sep poenial,, is applied [].
20 Figue.: When a lage negaive sep poenial o a ain of high volage negaive pulses,, is applied o he cahode, elecons ae quickly epelled fo he cahode on he ie scale of elecon plasa fequency. Figue.3: An ion-aix sheah is lef behind. 5
21 .3.. Phase Afe a ie scale of he ion plasa fequency ( / ω pi, he ions sa esponding o he sheah elecic field and sa o acceleae owads he cahode [5] [7], which is usually he age in PSII. The deceasing ion densiy in he sheah egion causes a decease in he elecon densiy [] and consequenly he sheah sas expanding a appoxiaely he ion acousic velociy owads he Child Langui lii, uncoveing ions which ae hen acceleaed owads he cahode by he field in he sheah [5] [7], which is shown in figue.. Figue.: Afe a ie scale of he ion plasa fequency, ions sa esponding and he ion aix sheah sas o expand. These ions evenually bobad he age cahode pependiculaly and unifoly, wih sufficien enegies o poduce iplanaion. The expeienal and nueical 6
22 [] [5] invesigaions show ha he ion-aix phase plays a vial ole in deeining he consequen ion flux o he age suface [5, 6, ] Phase 3 Afe he sheah edge eaches he Child-Langui lii, i sops expanding and launches an ion-acousic wave ino he plasa, which poduces ion aeficaion as i popagaes. This aeficaion ceaes a quasi-neual pesheah egion beween he plasa and he sheah, which acceleaes ions up o Boh s speed befoe eneing he sheah. The poenial pofile in his sae is given in figue.5. Figue.5: The seady sae poenial pofile. Sheah volages ae ofen vey lage copaed o he elecon epeaue,. The poenial in ion aix sheahs is highly negaive wih espec o he / T plasa-sheah edge; hence n ~ n e e whee n is he elecon densiy and e s e T e n s is he densiy of elecons a he sheah edge, which eans ha hee ae only ions in he aix sheah. Theefoe, fo a high-volage sheah, he cuen a he cahode is alos all ion cuen [6]. 7
23 .. The Obecives and Conen of he Thesis Theoeical invesigaions of ion-aix sheahs fo plana, cylindical, and spheical ages have been successfully caied ou by Conad [], whee he plana and cylindical ages wee assued o have infinie aeas and lenghs, especively, educing he analysis o one-diensional cases [5]. Sheidan [7] and Zeng [8] have applied he sae foulaion o sudy he ion-aix sheahs in cylindical boes, wih and wihou axial elecodes, especively. Deokan [7] and Filiz [] pesened he fis analyic eaens of ion-aix sheahs in wo diensions, by consideing fis a ecangula and hen a sei-cylindical goove of infinie lenghs in an infinie, plana age. Finally, Deokan [5] epesened he poble of ion aix sheahs inside cylindical boes wih sall adii and longiudinal gooves analyically, which eaed he poble oe ealisically o pooe he applicaion of plasa souce ion iplanaion echniques o a boad ange of poducs, especially hose concening defense indusies. Howeve, fo he ages consideed in his wok, iplanaion on he side walls of he gooves is elaively poo, since he ions ae acceleaed pedoinanly in he adial diecion befoe eneing he gooves [5]. In his pape Deokan suggesed axiizing he aio of he ion velociy coponens inside he gooves by using a new echnique, inceasing he aio n n (whee is iniial ion densiy and is he age poenial and leing he ine-elecode space appoxiaely equal he age adius ies he age poenial. In his hesis, a new analyical echnique o sudy he evoluion of ion aix sheahs will be exained fo plana and cylindical configuaions, a copue poga will be developed o siulae he sheah evoluion nueically and a basis fo fuue sudies on he poble of cylindical boes wih sall adii and gooves will be esablished. 8
24 CHAPTER THEORY AND CALCULATIONS.. PLANAR CONFIGURATION... The Model The poble, subec o ou wok is illusaed in figues.,. and.3, consideing he iniial phase and he poceeding evoluion. Figue.: When he applied poenial,, is lage (~ kv and he elecode sepaaion is sall (~ -, he aix can fill he enie ine-elecode space ( / ω pe < / ω < pi, whee pe ω and ω pi ae elecon and ion plasa fequencies, especively. 9
25 Figue.: Afe a sho ie, he aix sas oving owads he cahode. The noaion s( epesens he ie-dependen locaion of he sheah edge. Figue.3: The aix disappeas as all ions ae iplaned. The odel pesened hee is a one-diensional odel, wih a plana anode of infinie aea placed a is placed a x = L x = and a plana cahode whee he age o be iplaned. The age consideed is also a plana plae ha has an infinie
26 - aea. The agniude of L is ~. The negaive poenial applied o he cahode is ~ kv, wheeas he anode is kep a zeo poenial. Poenial fo < x < s( is labeled as > and he poenial fo s ( < x < L is labeled as <. The following assupions have been ade: The ion densiy n, he poenials < and >, and he ion velociy have a fo, which is a zeoh ode e ha does no ake ino accoun he conibuions fo he ion densiy plus a fis ode e due o he conibuions fo he ion densiy; Since he conibuion of n is aleady a fis ode e, any flucuaion in his e is a second ode e, and can be negleced in Poisson s Equaion; 3 Howeve, boh < and > will be ie dependen due o s(. u i Theefoe, ( ( < = < < ( ( > = > > ( n n = i, (.., (.. = n, (..3 u u u =. (.. ( i ( i... The Deeinaion of Poenials To deeine he poenials in boh egions < x < s( and s ( < x < L, he Poisson s equaions in hese egions have o be solved and he bounday condiions have o be iposed.
27 ( > ( < Since he zeoh ode poenials, and, neglec he effec of n, which is a fis ode e, hey ae equal, ( x = < ( ( > ( x, and he fis ode poenials ( > and ( < will depend on ie. ( > ( < The Poisson s Equaions fo and ae ( > x ( < x =, (..5 =. (..6 ( > ( < The bounday condiions o be iposed fo and ae ( x =, ( =, (..7 > ( ( x = L, ( L = ( =. (..8 > < L ( > ( < Then, he soluions fo and ae found as ( x = L ( ( ( x = < x >. (..9 ( > ( < The Poisson s equaions fo and ae ( > x ( < x =, (.. en = ε ( en = ε. (..
28 ( > ( < The bounday condiions o be iposed fo and ae ( x =, (, =, (.. > x = s(, ( x,, (..3 ( ( > ( x, = s( < s( x = s(, ( ( > < x s( = x s(, (.. ( x = L, ( L, = (..5 < ( > ( < Then, he soluions fo and ae found as ( en > ( x, = ( L s( x, (..6 ε L en x ε en [( s( L ] x ( s( ( < (, =. (..7 x en ε L ε Theefoe, he poenials in he egions < x < s( and s ( < x < L, i.e. and <, ae found as > en > ( x, = x ( L s( x, (..8 L ε L L en x ε en [( s( L ] x ( s( < (, =. (..9 x x en ε L ε These poenials do no depend on ie explicily. To find he explici ie dependence of he poenials, he explici fo of s( us be deeined. 3
29 To do his, he equaion of oion a x = s( is used, which is d s d > = e. (.. x x= s( Subsiuing > gives d s d e = L enl ε s(. (.. L ( ( To be consisen, s ( is also assued o have a fo s ( = s ( s (. d s d d s = d ( d s d ( e = L enl s ε ( s L ( ( L ( (.. To find he zeoh and fis ode es in his diffeenial equaion, le us exaine he poenial of oion is <. Since ( ( < ( x = ( x = x, he zeoh ode equaion L > s d e = (..3 L ( d which gives ds d ( ( e = ui =. (.. L
30 Reaanging is es, equaion (..7 becoes en x ( x, = L ε ( s( ( s( ( < x L x. (..6 The es in backes have a axiu value of ( s( ( s( L x = L L x ax. Then, ( < is on he ode of enxl ε, which gives ( < enl ( < ε en L. So, ε is a fis ode e. Then, he zeoh ode equaion of oion is given by equaion (..3 and he fis ode equaion of oion is given by d s d ( e = L ( enl s ( ε L (..6 Theefoe, fo he diffeenial equaions (..3 and (..6, s ( ( and s ( ( ae found as given in equaions (..7 and (..8. s s ( ( e ( L = (..7 e A e ( A e ( A ( L L L = ( whee A enl = ε, which is a fis ode e. 5
31 To copae hese es, axiu ie,, involved in his pocess us be esiaed. Then, ax ax ax ( ( ( L e L s gives / ax e L. (..9 So, he es in, in equaion (..8, coespond o, /3, /5, especively. Then, he fis wo es can be consideed of equal ode and is found as given ( ( s s( 6 ( L A e A L e s =. (..3 Neglecing he second ode es, which coe fo he squae of A, he explici fos of he poenials > and < ae given by ( ( 3 8 (, ( x A L n e x A L n e x A L n e x L en x L x ε ε ε ε = >, (..3 ( ( ( ( 8 ( 8 (, ( A L n e x A L n e A L n e x A L n e x L en x en x L x ε ε ε ε ε ε = <. (..3 6
32 ..3. The Deeinaion of Ion Velociy and Flux To exaine he ion behavio, he ion velociy and he flux us be deeined. To do his, he equaion of oion is consideed. dui d ui ui e ui = x x = <. (..33 u i ( x, Subsiuing equaions (.. and (..3, i.e. and ( x,, he zeoh and fis ode equaions of he ion velociy can be found as given by equaions (..3 and (..35. < u ui ui x e L ( ( i ( ui = ( u ( i ui x ( u ( i ui x ( 5 3 e no e ( n A = x 5 ε ε L e ( n ( A 3 3 8ε L 6 e nol ε (..3 (..35 Since he igh hand side of equaion (..3 is a consan, his diffeenial equaion can be wien as ( u i ( x, = ( du i d, i has a soluion in he fo e =, and iposing he iniial condiion L ( e u i ( L =. (..36 Subsiuing his soluion, equaion (..36, ino equaion (..35, he diffeenial equaion becoes 7
33 L n e L A n e L A n e x n e x u L e u o o i i ( ( 8 ( ( ( ε ε ε ε =. (..37 The soluion of a quasi-linea equaion of fis ode ha has a geneal fo of,, (, (, (, (, ( x u R x u x Q x x u x P = is found by he ehod of chaaceisics, ha is by siulaneously solving he equaions R du Q d P dx = =. Applying his ehod o ou diffeenial equaion, equaion (..37, and iposing he iniial condiion,, he soluion is found o be, ( ( = x u i L n e L A n e L A n e L e n e x n e x u o o o i ( 5 8 ( ( 7 ( 3, ( ε ε ε ε ε =. (..38 Using he esiaed value of axiu ie,, involved in his pocess, which is given by equaion (..9, he es of ae copaed wih he e of and he coefficiens of and ae found o be negligible. Then, he fis ode ion velociy becoes ax, ( ax ( x u i ( ax ( u i 5 7 L n e L e n e x n e x u o o o i 3 ( 3, ( ε ε ε =. (..39 8
34 Cobining equaions (..36 and (..39, he ion velociy has he fo e ui ( x, = L e n L o e no e no e x ε ε ε L 3 3. (.. Theefoe, he ion flux has he fo Γ( x, = n u ( x, en = L i e ( n L e ( no ε ε e ( no x ε e L 3 3. (..... Gaphical Repesenaion The ion velociy is given by equaion (... A a paicula ie, his ion velociy has a fo u ( x = Cx D whee C and D ae consans. In figues., i.5,.6, and.7, his alos linea dependence is shown gaphically a = ax, 3 = ax, and = ax, especively. = ax, In he calculaions, he ions ae assued o be ianiu ions and he ion ass is aken o be kg. Also in he calculaions, he agniude of he disance beween he elecodes, L, is aken o be ~ -, he negaive poenial applied o he cahode,, is aken o be ~ kv, poenial applied o he anode is aken o be. kv, he iniial ion velociy is aken o be. /s and he iniial ion densiy, n, is aken o be ~ 5 / 3. 9
35 Figue.: Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie = ax. Figue.5: Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie = ax.
36 Figue.6: Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie =. 3 ax Figue.7: Ion velociy as a funcion of x a ie = ax.
37 Also, he ion flux is given by equaion (... Figue.8 shows he ion flux as a funcion of ie a x = L. Figue.8: Ion flux as a funcion of a x = L... CYLINDRICAL CONFIGURATION... The Model The poble subec o ou wok is illusaed in figues.9,. and., consideing he iniial phase and he poceeding evoluion.
38 Figue.9: When he applied poenial,, is lage (~ kv and he elecode sepaaion is sall (~ -, he aix can fill he enie ine-elecode space ( / ω pe < / ω < pi, whee pe ω and ω pi ae elecon and ion plasa fequencies, especively. Figue.: Afe a sho ie, he aix sas oving owads he cahode. s( is he ie-dependen locaion of he sheah edge. 3
39 Figue.: The aix disappeas as all ions ae iplaned. The odel pesened hee is a one-diensional odel, wih a cylindical anode of infinie lengh and adius. The age consideed is he inenal suface of an infiniely long cylinde whose inne adius is. The anode is axially placed inside he age. The agniude of is ~ -, is ~ 3 -, he negaive poenial applied o he age,, is ~ kv, wheeas he anode is kep a zeo poenial. Poenial fo < < s( is labeled as > and he poenial fo s ( < < < is labeled as. The following assupions have been ade: The ion densiy n, he poenials < and >, and he ion velociy have a fo, which is a zeoh ode e ha does no ake ino accoun he conibuions fo he ion densiy plus a fis ode e due o he conibuions fo he ion densiy; u i
40 Since he conibuion of n is aleady a fis ode e, any flucuaion in his e is a second ode e, and can be negleced in Poisson s Equaion; 3 Howeve, boh < and > will be ie dependen due o s(. Theefoe, equaions (.., (.., (..3 and (.. ae also assued o be ue fo he cylindical case.... The Deeinaion of Poenials To deeine he poenials in boh egions < < s( and s ( < <, he Poisson s Equaions in hese egions have o be solved and he bounday condiions have o be iposed. ( ( ( ( Since and neglec he effec of n, which is fis ode, ( = ( > < ( > ( < and he fis ode poenials and will depend on ie. > < ( > ( < The Poisson s equaions fo and ae > = ( ( ( > > < ( =, (.. =. (.. ( > ( < The bounday condiions o be iposed fo and ae ( =, ( =, (..3 > ( ( =, ( = ( =. (.. > < 5
41 ( > ( < Then, he soluions fo and ae found as ( ( = ( ln ( ( ( < > =. (..5 ln ( > ( < The Poisson s equaions fo and ae ( > =, (..6 ( < en en = = ε ε. (..7 ( > ( < The bounday condiions o be iposed fo and ae ( =, =, (..8 > (, = s(, (,, (..9 ( ( > (, = s( < s( = s(, ( ( > < s( = s(, (.. ( =, =. (.. < (, ( > ( < Then, he soluions fo and ae found as ( > ln = ln ( ( en ε ( [ s s ln( s ] ( ( ( en ln en < = s s ln ε ln ε [, (.. ( s ]. (..3 6
42 Theefoe, he poenials in he egions < < s( and s ( < <, i.e. > and <, ae found as > < ( ( ( ( [ s s ( s ] ln ln en = ln ln ln ε = ln ln ln( ln( ( ( en ε en ε ( [ s s ln( s ], (... (..5 These poenials do no depend on ie explicily. To find he explici ie dependence of he poenials, he explici fo of s( us be deeined. To do his, he equaion of oion a = s( is used, which is d s d > = e. (..6 = s( Subsiuing > gives d s d e en = [ s s ln( s ]. (..7 ln( s ε ( ( To be consisen, s ( is also assued o have a fo s ( = s ( s (. Then, d s d ( ( d s d s = d d e en = ln( s ε [ s s ln( s ]. (..8 7
43 In s(, he fis ode e is uch salle han he zeoh ode e. Then, and s can be expanded as given by equaions (..9 and (... s = s s s = s s s = s ( ( ( ( ( ( s s ( (, (..9 = ( ( ( ( ( s ( = ( s s ( s s. (.. s s Then, he equaion of oion a = s( becoes d s d ( d s d ( = e ln ( s ( s ε s s s ( ( ( ( ( s en ( s s ( s ( ( ( s ln ( s s ( ( (.. ( en ( s Noe ha en = ε ε ax, which is a fis ode e. Then, oiing he second ode es in equaion (.. equaion (.. is obained. d s d ( d s d ( = ln e s s ( ( ( s en ( s ( ( ε s ( ln s ( (.. 8
44 Since ae fis ode es, he diffeenial equaion of s s ( ( s ( ( and is ( en s en = ε ε ax d s d ( e ln =. (..3 ( ( s The diffeenial equaion of s ( ( is d s d ( s s ( ( s s ( e en = ( ( ln ( ( ( s ln ε s. (.. Theefoe, fo he diffeenial equaions (..3, o find s ( ( le ds d ( = p, hen d s d ( d ( p e = = (..5 ( ( ds ln( s which can be sepaaed as d ( p e ln ( = (..6 ( ( s ds Hence, inegaing boh sides equaion (..7 is obained. ( ds e ( p = = s C d ln ln(. (..7 9
45 The iniial condiions o be iposed fo ( s and ds ( ae d ( ds =, ( = = = d p (..8 = ( =, s ( = =. (..9 Then, he following esuls ae found. C e ln ln = (..3 ( ds d ( e ( ( s = ln ln( / (..3 To siplify he equaion, he following definiions ae ade / e 7 =.696 ln( = s a (..3 ( ( s x =. (..33 Then, he diffeenial equaion (..3 akes he fo ( x d d [ ln( x ] / = a (..3 which is given in equaion (..35 in inegal fo. = x dx' a x [ ln '] / (..35 3
46 To find he soluion of his inegal, assupion / / [ ln x' ] [ x' ].5[ x' ] fo x 3, (..36 is ade wih a axiu eo of %. Then, he inegal equaion becoes x a =.5[ x' ] dx' / fo x 3. (..37 [ x' ] [ ] / u = x' Defining, du =, he soluion is found as [ x' ] dx' / u a = u.3 (..38 which can be wien as u 6.6u 3.3a =. (..39 Noe ha [] u ax. and [ u ] ax (. = 3. 8 which is vey sall copaed o [ 6.6u] ax 37.. So i can be ignoed. Then, a u. (.. 3
47 To ge a bee esul u is defined as u = u ( (.. δ whee a u (.. δ <<. (..3 Subsiuing hese values ino equaion (..39 and using he fac ha a a a u ax and << 6.6 []. ax ( a, δ is found as 3 δ << ( Then, u is found as 3 ( a u = u( δ = ( a ( ( / u = x Since, x is found as ( a ( 3 5 a x = ( a = ( a (
48 a 5 << 3.3 Again using he fac ha (, x a (. (..7 ( Reebe ha ( s ( s ( x =. Theefoe s is found as [ ( ] ( a (..8 whee a is defined by he equaion (..3. ( ( To find s, s is subsiued ino equaion (... d s d ( = e e n ε ln( [ ( a ] [ ( ] a ( ln( [ ( a ] s ( ln [ ] ( ln ( a (..9 To siplify his equaion, he change of vaiables = ( a ω is ade. d s dω ( s ( [ ω ] 3 en = ε [ ω ] ( [ ω ] ln ln[ ω ] (..5 This equaion can be solved using vaiaion of paaees bu his is no necessay. Dividing expessions fo and by gives fis ode es on he lef hand side. ( > ( < ( 33
49 ( < ( en ε ( > ( ( ln ln ( ( ens = ε ln = ln ( ( [ ( s ln( s ] ens ε [ ( s ln( s ] (..5 Since ( ( s en en = ε ε ax is a fis ode e, fo he es on he igh ( hand side no o be second ode es, only ( s is needed as ε ( ( ( s s en will be of second ode. Also fo his eason, he appoxiaion of ( s given by equaion (..8 can be ade. Then, he explici fos of he poenials > and < ae given by > < ln = ln ln ln = ( ( ( ( ln ln en ε ( ( ln ln en ( ( en ( a [ ( ] ( ε a ( a [ ( ] ( ε a ( ln a ln [ ] [ ] a ln (..5 (..53 3
50 ..3. The Deeinaion of Ion Velociy and Flux To exaine he ion behavio, he ion velociy and he flux us be deeined. To do his, he equaion of oion is consideed. e u u u d du i i i i = = <. (..5 Subsiuing <, equaion (..5 akes he fo ( ( [ ] ( ( [ ] n e a en e u u u d du a a i i i i ln ln ε ε = = (..55 Using he assupion given by equaion (.., wo diffeenial equaions fo he zeoh ode ion velociy and fo he fis ode ion velociy ae obained. ( e u u u i i i ln ( ( ( = (..56 ( [ ] ( ( ( [ ] n e a n e u u u u u a a i i i i i ( ( ( ( ( ln ln ε ε = (..57 Equaion (..56 is a quasi-linea paial diffeenial equaion and can be solved by he ehod of chaaceisics, i.e. by solving he odinay diffeenial equaions given by equaion (
51 d ( d dui = = (..58 ( u e i ln( The diffeenial equaion d u ( dui = (..59 e ln( ( i has a soluion in he fo / [ ln( / ( u i = a ] (..6 whee denoes he iniial posiion a =, which can be any poin in he ineval, and a is given by equaion (..3. Using ( u i given by equaion (..6, he diffeenial equaion d d = ( (..6 ui can be wien in inegal fo as d = a / d( / [ ln( / ] /. (..6 Wih he siplificaion, he inegal in equaion (..6 becoes x = / 36
52 a = x dx' ln x'. (..63 The soluion of equaion (..63 is found o be a i π Ef ( i ln x =. (..6 Figue. shows he gaph of i π Ef ( i ln x gaph of he soluion given by equaion (..6. and figue.3 shows he Figue.: The gaph of i π Ef ( i ln x x = / whee. 37
53 a Figue.3: The gaph of i π Ef ( i / = wih aken as ln( =. The soluion given by (..6 canno be used in his fo since i is iaginay. When i π Ef ( i / ln( is wien in he infinie seies fo, equaion (..65, i is obseved ha he soluion is eal. ( i ln( / n= [ ln( / ] n i π Ef = (..65 n!(n Using he fac ha can ake values in he ineval / 3 /, ln( / can ake values in he ineval ln( /. 8. The axiu value of ln( / is used o copae he fis five es ( n in he infinie seies 38
54 given by equaion (..65. These five es coespond o,.37,.,.3 and.7, especively. Then, he fis hee es ( n =,, can be consideed of equal odes and he ohe es can be excluded. Howeve, i is no possible o solve equaion (..65 analyically afe his appoxiaion unless he hid e is also excluded. Then, equaion (..65 can be wien in he fo given by equaion (..66 whee only he fis wo es in he expansion ae aken wih an eo of 9 %. The soluion of equaion (..6 is given by (..67. ( i ln( / = ln( / [ ln( / ] 3 i π Ef ( a [ ln( / ] 3 ln( / 3 =. (..67 When he gaphs of equaion (..6 and (..67 ae ploed fo =, he diffeence in soluions can be seen in figue.. = ax and Figue.: A copaison of he gaphs of equaion (..6 and (..67 fo = ax and =. 39
55 Equaion (..67 is solved fo ( by using he aheaical packe poga Maheaica and hus hee oos ae obained. The only eal oo is given in equaion (..68. ( = e f ( (..68 whee f ( = / 3 / 3 (..69 When equaion (..68 is aken as he soluion fo ( and his soluion is subsiued ino he equaion (..6, equaion (..7 is obained. ( u i = a [ f (] / (..7 I can be easily seen ha his soluion ehod has lead o a soluion fo he zeoh ode ion velociy wih he fo u ( i = u ( i (. Howeve, siulaions have shown ha he zeoh ode ion velociy has he fo ( u i (,. Since solving ( (, (, equaion (..67 fo, which ay lead o a soluion of he fo, is no analyically possible, i can be concluded ha expessing of he iaginay eo funcion in infinie seies fo will no give an accepable soluion. u i
56 To find an accepable soluion fo he zeoh ode ion velociy, he fac ha equaion (..63 has he sae fo wih equaion (..35 is aken ino accoun. Then, doing siila calculaions, ( / is found as a ( =, ( 3 (..7 whee a is given by equaion (..3. Equaion (..7 can be wien in quadaic fo as a = (..7 This quadaic equaion has wo oos in he following fo (, ± a = (..73 ( To find he oo ha is valid, he gaph of, which is shown in figue.5, is ploed and exained. Noe ha he gaph in figue.5 acually belongs o a. ( =
57 Figue.5: The gaph of. ( Fo he gaph i is easily seen ha boh oos of ae valid soluions. The negaive oo coesponds o he egion and he posiive oo coesponds o he egion. In ou odel = and he egions whee oos coespond ae shown in figue.6.
58 Figue.6: The egions whee he oos of coespond. Subsiuing he oos of ino equaion (..6 and using he appoxiaion given by equaion (..36, ( u i is found a = a a z [ z ].3[ z ] z ( u i (..7 a z, [ ] [ ] z.3 z z, whee = a and a is defined by he equaion (..3. Howeve, equaion z (..7, which is obained analyically unde he appoxiaion (..36, needs o be sudied fuhe because i does no fully saisfy equaion (
59 Solving equaion (..56 and (..57 by using nueic ehods, he ion velociy, u = u u i ( i ( i, was obained as shown in figue.7. In he nueical calculaions, he ions ae assued o be ianiu ions and he ion ass is aken o be kg, he adius of anode,, is aken o be ~ -, he inne adius of cahode,, is aken o be ~3 -, he agniude of he disance beween he elecodes, L, is aken o be ~ -, he negaive poenial applied o he cahode,, is aken o be ~ kv, poenial applied o he anode is aken o be. kv, he iniial ion velociy is aken o be. /s and he iniial ion densiy, n, is aken o be ~ 5 / 3. Figue.7: The ion velociy as a funcion of a he insans = ax, 3 = ax and = ax obained as a esul of nueic calculaions. = ax, Then, he ion flux on he suface of he age as a funcion of ie is found nueically. Figue.8 shows he gaph of he ion flux obained as a esul of hese nueic calculaions.
60 Figue.8: The ion flux as a funcion of a he age suface obained as a esul of nueic calculaions. 5
61 CHAPTER 3 SIMULATION 3.. THE BASICS OF SIMULATION 3... Nueical Analysis Many pobles in aheaics do no have a soluion in closed fo. In hese siuaions, an appoxiae soluion using asypoic analysis o a nueical soluion is sough. The nueical analysis is he sudy of algoihs fo he pobles of coninuous aheaics using basic aiheical opeaions [9]. In nueical analysis, he algoihs ha can solve a poble exacly ae called diec ehods; he algoihs ha solve he poble by successive appoxiaions ae called ieaive ehods. The pocess of eplacing a coninuous poble wih a discee poble whose soluion is appoxiaely equal o ha of he coninuous poble is called disceizaion. Nueical analysis is concened wih copuing he soluion of boh odinay diffeenial equaions and paial diffeenial equaions in is applicaion aeas, which include copuaional physics, copuaional fluid dynaics, weahe foecasing, cliae odels, he analysis and design of olecules (copuaional cheisy and econoy. Paial diffeenial equaions ae solved by fis disceizing he equaion. Thee coon ehods of disceizaion of paial diffeenial equaions ae he finie eleen ehod, he finie volue ehod and he finie-diffeences ehod. 6
62 3... The Finie-Diffeences Mehod The finie-diffeences ehod is a nueical ehod fo solving paial and odinay diffeenial equaions, which ais o eplace he coninuous deivaives wih diffeence equaions ha involve only he discee values of he unknown funcion elaed o he posiion in he doain of he poble []. The finie-diffeences ehod disceizes he doain of he poble ino a egula gid (esh defined by a ceain nube of nodes which ae sepaaed in he diecion of coodinaes by a ceain spaial and ie ineval. Fo a poble solved wih he explici finie-diffeences ehod o convege o he exac soluion, he ie sep us be salle han a ceain axial value []. Fo exaple, he sable explici diffeencing schees fo solving he advecion equaion ae subec o he Couan-Fiedichs-Levy (CFL condiion, which deeines he axiu allowable ie sep []. The CFL condiion, which gives he condiion of he convegence of a diffeence appoxiaion in es of he concep of doain dependence, saes ha fo a convegen algoih, he doain of dependence of he paial diffeenial equaion us lie wihin he doain of dependence of he nueical algoih. This, in un iplies a condiion on he ie sep, given by equaion (3.. [3]. The CFL condiion on he ie sep: δ x δ (3.. v whee v is a phase speed o an advecion velociy and v >. On he ohe hand, fo a poble solved wih he iplici finie-diffeences ehod, hee is no sabiliy equieen on he ie sep; he value of he ie sep is dicaed by accuacy only. 7
63 When he finie-diffeences ehod is applied ove he esh, he unknown funcion is appoxiaed a each one of he nodes, giving a diffeence equaion ha elaes he value of he funcion a a paicula node wih is value a he neighboing nodes []. This pocedue is epeaed a each node coposing he gid esuling in a syse of diffeence equaions which ay be nueically solved eihe wih ieaive appoxiae ehods o wih diec decoposiion ehods. The disceizaion of one-diensional paial diffeenial equaions usually leads o sandad hee-poin pobles (also known as idiagonal equaion syses [5 6] which ay be wien as. (3.. = = = =.,,..,,, n n n n n d b U a U n d U c b U a U d cu bu In hee-poin pobles, he equaion nube involves only he es wih nubes, and so ha he aix of he syse has non-zeo eleens only on he diagonal and in he posiions iediaely o he lef and igh of he diagonal as shown in equaion (3..3 [6]. (3..3 = n n n n n d d d U U U b a c b a c b a c b To solve hee-poin pobles, idiagonal aix algoihs such as he Thoas algoih ae used. The Thoas algoih, which is a diec ehod, equies he known coefficiens, and o saisfy he condiions given by equaions (3.. and (3..5, a b c 8
64 which ensue ha he aix fo of he hee-poin poble is diagonally doinan [6]. a >, b >, > (3.. c b > a c (3..5 The Thoas algoih solves he hee-poin poble by educing he syse of equaions o uppe iangula fo, by eliinaing he e U in each equaion uning he ino a new fo given by equaion (3..6 [6]. U = e U f, =,,..., n (3..6 e whee and saisfy he ecuence elaions given by equaions (3..7 and f (3..8 and have iniial values given by equaion (3..9 [6]. c e =, =,,..., n (3..7 b a e d a f f =, =,,..., n (3..8 b a e c e = and b d f =. (3..9 b Afe finding he coefficiens by using he ecuence elaions given by equaions (3..7 and (3..8, he values of U ae easily calculaed using equaion (3..6. Fo sabiliy, he condiion each e < in equaion (3..6 us hold, which is aleady guaaneed by he equaions (3.. and (
65 3.. PLANAR CONFIGURATION 3... The Model The odel pesened in he plana pa of ou poble is a one-diensional odel, wih a plana anode of infinie aea placed a x = and a plana cahode a x = L whee he age o be iplaned is placed. The age consideed is also a plana plae ha has an infinie aea. The agniude of is ~ -, and he negaive poenial applied o he cahode,, is ~ kv, wheeas he anode is kep a zeo poenial, he ion velociy is iniially zeo and he iniial ion densiy, n, has a value of ~ 5 / 3. L 3... Equaions The equaions ha have o be solved o siulae he plana pa of ou poble ae given by equaions (3.. (3..3. Poisson s Equaion: x = en ε. (3.. Coninuiy Equaion: n ( un =. (3.. Moenu Balance Equaion: u u u x = e i E. (3..3 5
66 In equaions (3.. (3..3, is he poenial, e is he elecic chage of an ion, u is he ion velociy, n is he ion densiy, ε is he elecic peiiviy of fee space, E is he elecic field beween he elecodes. i is he ass of an ion, and 3... Bounday and Iniial Condiions The bounday condiions o be iposed ae given by equaions (3.. (3..7. x =, (, =, (3.. x = L, ( L, =, (3..5 x =, u (, =, (3..6 x =, n (, = n. (3..7 The iniial condiions o be iposed ae given by equaions (3..8 and (3..9. =, ( x, = u, (3..8 { [ ] } n 3 =, x, = acan 5 ( x π n. (3..9 π ( 3... Nueical Pocedue x = x = L Equaions (3.. (3..3, which ae subec o he bounday and iniial condiions given by equaions (3.. (3..9, have been solved nueically using a finie-diffeences echnique. The copuaional doain is esiaed o be beween and, which is illusaed by figue 3.. 5
67 Figue 3.: Copuaional doain A unifo veex-ceneed gid x x, x = L N, =,,.., N = (3.. is used whee is he spaial index. The ie level is given by =, >, =,,.. (3.. = whee subscip denoes he ie level wih a sep size. Densiy n and elecic poenial ae evaluaed a he nodes of he gids, while he ion velociy u and he elecic field E ae a he cenes of he copuaional cells. 5
68 3... Poisson s Equaion To obain a finie-diffeences appoxiaion of Poisson s equaion (3.., which has he bounday condiions given by equaions (3.. and (3..5, a sandad second ode discee schee of he fo given by equaion (3.. is used. ( x, x O ( x. (3.. ( x As a esul, Poisson s equaion uns o he sandad hee-poin poble given by equaion (3..3. en = ( x ε (3..3 Equaion (3..3 is solved by he Thoas algoih, using bounday condiions descibed in equaions (3.. and (3..5 in discee fo, which is given by equaions (3.. and (3..5. = (3.. N = ( Coninuiy Equaion x x x To obain a finie-diffeences epesenaion of equaion (3.., i is fis inegaed ove he cell volue / /. As a esul, we have dn d ( un = ( un / / x (
69 whee u is he ion velociy and n is ion densiy. A choice of n ±/ a he cenes of he copuaional cells deeines he concee disceizaion ehod fo he convecive es of equaion (3... We used he hid-ode upwind-biased schee [7], which has he fo ( un [ u ( n 5n n u ( n n n ] / = / / 5 6 (3..7 whee u ( u, and ( u / = ax, / u. (3..8 / = ax, / Fo he nueical ie inegaion, he exapolaed second ode backwad diffeeniaion foula (BDF is used [8]: 3 n n n = (, F n n,. (3..9 Hee, F conains he disceized convecive es. Noe, ha spaial indices in equaion (3..9 have been dopped. Since wo-sep ehod needs n and n as saing values, he explici Eule ehod given by equaion (3.. is used on he fis sep. n = n F(, n (3.. Because of he explici ie inegaion, we ae esiced by he sandad CFL condiion fo sabiliy. 5
70 Moenu Balance Equaion Le us conside he oenu equaion, which is given by equaion (3..3. This equaion can be ewien in he fo of u u x = e i E. (3.. To have a consevaive diffeence schee fo (3..3, i is consuced by he inego-inepolaed ehod; inegaing equaion (3..3 ove he copuaional cell x x x equaion (3.. is obained. x e ( u u dx ( u u d = x i x x Edxd (3.. Diffeen appoxiaions of he inegals in equaion (3.. lead o diffeen diffeence schees. One of he is a schee iplici in ie and of he following fo: u u ( u ( u x = f (3..3 wih e f = E(, x. (3.. i I is obvious ha equaion (3..3 epesens a quadaic algebaic equaion wih espec o u. Using he ion velociy known fo he pevious ie level u 55
71 ( =,,..., N, a nueical pocedue can be oganized by a successive calcula- ion of saing fo he lef bounday ( x = u u = (3..5 o he igh by he equaion u x x x = u ( u xf (3..6 = =,,3,... whee,3,..., N, Nueical Resuls Nueical pocedue is oganized as follows. On evey new h ie sep, fis, Poisson s equaion is solved, using he known ion densiy in is souce e; hence, elecic field in he new ie sep is deeined. Then, he oenu balance equaion is solved, using he known elecic field, n E, and he ion velociy in he new ie sep is deeined. Finally, he coninuiy equaion is solved, using he known ion velociy and heefoe he ion densiy in he new ie sep, n, is deeined. The nueical convegence is checked by pefoing seveal calculaions using efineen of he space gid and diffeen ie sepping paaees. The nube of gid nodes used in he calculaions was. In he siulaion, he ions ae assued o be ianiu ions and he ion ass is aken o be kg, he agniude of he disance beween he elecodes, L, is aken o be ~. -, he negaive poenial applied o he cahode,, is aken o be ~. kv, poenial applied o he anode is aken o 56
72 be. kv, he iniial ion velociy is aken o be. /s and he iniial ion densiy, n, is aken o be ~. 5 / 3 The daa obained fo he siulaion is used o plo he ion densiy vesus posiion gaph and ion velociy vesus posiion gaph a a paicula ie. Figue 3. shows hese gaphs a he insans = ax, = ax, 3 = ax and = ax. Figue 3.: Ion densiy and ion velociy as a funcion of x a he insans = ax, = ax, 3 = ax and = ax. I can be easily seen fo figue 3. ha he ions a a paicula posiion x ove wih alos he sae velociy as hey ae acceleaed owads he age. The oion of he aix sheah and he posiion of he sheah edge can be seen fo he densiy vesus posiion gaph in figue 3.. The iplanaion of ions ends, i.e. he ion aix sheah disappeas, a a ie ax, which is found as s in he analyical calculaions and s in he siulaion. The final ion velociy a x = L and = ax is obained as.8 5 /s fo he siulaion daa. The analyically calculaed final ion velociy, which 57
73 is.78 5 /s, is appoxiaely equal o he siulaion esul wih an eo of.7 %. I is also obseved fo figue 3. ha he ion velociy inside he ion aix a a paicula insan is alos linea. Howeve, he ion velociy vesus posiion gaphs ploed by using he analyical daa, figue 3.3, and he nueical daa, figue 3., indicae diffeen elaions beween he ion velociy and posiion. The gaphs of he analyical daa indicae a linea elaionship beween ion velociy and posiion wheeas he gaphs of he nueical daa indicae a cuvilinea elaionship beween ion velociy and posiion. This lineaizaion of analyically calculaed ion velociy is due o he appoxiaions ade in he analyical calculaions. This causes he analyically calculaed ion velociy o incease oe slowly han he siulaed velociy in he ie ineval siulaed values in he ie ineval 3 ax < <. ax 3 < < ax and o cach he The gaph in figue 3. gives he analyically calculaed ion velociy as a funcion of posiion and ie. Alhough he analyically calculaed ion velociy is slighly diffeen fo he siulaed ion velociy egading he dependence on posiion, i can be concluded ha hee is a good ageeen beween he analyical and he nueical soluions. 58
74 Figue 3.3: Ion velociy vesus posiion gaphs ploed using analyical esuls. Figue 3.: The analyically calculaed ion velociy as a funcion of posiion and ie. 59
75 3.3. CYLINDRICAL CONFIGURATION The Model The odel pesened hee is a one-diensional odel, wih a cylindical anode of infinie lengh and adius and a cylindical cahode whee he age o be iplaned is placed. The age consideed is he inenal suface of an infiniely long cylinde whose inne adius is. The anode is axially placed inside he age. The agniude of is ~ -, is ~ 3 -, he negaive poenial applied o he cahode,, is ~ kv, wheeas he anode is kep a zeo poenial. The ion velociy is iniially zeo and he iniial ion densiy, n, has a value of ~ 5 / Equaions The equaions ha have o be solved o siulae he cylindical pa of ou poble ae given by equaions (3.3. ( Poisson s Equaion: = en ε. (3.3. Coninuiy Equaion: n ( un =. (3.3. Moenu Balance Equaion: u u u = e i E. (
76 In equaions (3.3. (3.3.3, is he poenial, e is he elecic chage of an ion, u is he ion velociy, n is he ion densiy, ε is he elecic peiiviy of fee space, E is he elecic field beween he elecodes. i is he ass of an ion, and Bounday and Iniial Condiions The bounday condiions o be iposed ae given by equaions (3.3. ( =, (, =, (3.3. =, (, =, (3.3.5 =, u (, =, (3.3.6, =, n ( = n. (3.3.7 The iniial condiions o be iposed ae given by equaions (3.3.8 and ( =, u (, =, (3.3.8 n 3 π =, (, = { acan[ 5 ( ] } n. (3.3.9 π Nueical Pocedue Equaions (3.3. (3.3.3, which ae subec o he bounday and iniial condiions given by equaions (3.3. (3.3.9, have been solved nueically using a finie-diffeences echnique. The copuaional doain is esiaed o be beween he adius of anode,, and he inne adius of cahode,, whee he disance beween he elecodes is figue 3.5. = L. The copuaional doain is given by 6
77 Figue 3.5: Copuaional doain A unifo veex-ceneed gid, = L N, =,.., N = (3.3. is used whee is he spaial index. The ie level is given by equaion (3... Densiy n and elecic poenial ae evaluaed a he nodes of he gids, while he ion velociy u and he elecic field E ae a he cenes of he copuaional cells Poisson s Equaion To obain a finie-diffeences appoxiaion of Poisson s equaion (3.3., which has he bounday condiions given by equaions (3.3. and (3.3.5, he inegoinepolaed ehod is used; inegaing equaion (3.3. ove he copuaional cell equaion (3.3. is obained. 6
78 (, / / ( O (3.3. ( As a esul, his poble uns o he sandad hee-poin poble of he fo (3.. which is again solved by he Thoas algoih using he foulaion given by equaions (3..3 ( Coninuiy Equaion To obain a finie-diffeences epesenaion of equaion (3.3., i is inegaed i ove he cell volue / / and equaion (3.3. is obained. dn d = / ( un / / ( un / (3.3. The hid-ode upwind-biased schee [7], which has a fo given by equaions (3..7 and (3..8, and he exapolaed second ode BDF [8] given by equaion (3.3.3 ae used. 3 n n n = F(,n n,, (3.3.3 Since he wo-sep ehod equies n and n as saing values, he explici Eule ehod, given by equaion (3.., is used again on he fis sep wih he sandad CFL condiion fo sabiliy Moenu Balance Equaion Equaion (3.3.3 can be ewien in he fo given by equaion (3... The inego-inepolaed ehod ove he copuaional cell and he 63
79 u schee iplici in ie given by equaions (3..3 and (3.. ae again used in he nueical copuaion of oenu balance equaion by a successive cal- culaion of saing fo he lef bounday ( = o he igh by he equaion ( Nueical Resuls The nueical pocedue is oganized in he sae fo as he nueical pocedue given in secion In he siulaion, he ions ae assued o be ianiu ions and he ion ass is aken o be kg, he adius of he anode,, is aken o be ~. -, he inne adius of he cahode,, is aken o be ~3. -, he - agniude of he disance beween he elecodes, L, is aken o be ~., he negaive poenial applied o he cahode,, is aken o be ~. kv, poenial applied o he anode is aken o be. kv, he iniial ion velociy is 5 aken o be. /s and he iniial ion densiy, n, is aken o be ~. / 3. The daa obained fo he siulaion is used o plo he ion densiy vesus posiion gaph and ion velociy vesus posiion gaph a a paicula ie. Figue 3.6 shows hese gaphs a he insans = ax, = ax, 3 = ax and = ax. 6
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
Stress Analysis of Infinite Plate with Elliptical Hole
 Sess Analysis of Infinie Plae ih Ellipical Hole Mohansing R Padeshi*, D. P. K. Shaa* * ( P.G.Suden, Depaen of Mechanical Engg, NRI s Insiue of Infoaion Science & Technology, Bhopal, India) * ( Head of,
Sess Analysis of Infinie Plae ih Ellipical Hole Mohansing R Padeshi*, D. P. K. Shaa* * ( P.G.Suden, Depaen of Mechanical Engg, NRI s Insiue of Infoaion Science & Technology, Bhopal, India) * ( Head of,
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
On Control Problem Described by Infinite System of First-Order Differential Equations
 Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Physics 207 Lecture 13
 Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Introduction to Numerical Analysis. In this lesson you will be taken through a pair of techniques that will be used to solve the equations of.
 Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Sharif University of Technology - CEDRA By: Professor Ali Meghdari
 Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
An Automatic Door Sensor Using Image Processing
 An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Monochromatic Wave over One and Two Bars
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Chapter 5. Canopy Spectral Invariants
 Chape 5 Canopy Specal Invaians. Inoducion.... Physical Pinciples of Specal Invaians... 3. RT Theoy of Specal Invaians... 5 4. Scaling Popeies of Specal Invaians... 6 Poble Ses... 39 Refeences... 4. Inoducion
Chape 5 Canopy Specal Invaians. Inoducion.... Physical Pinciples of Specal Invaians... 3. RT Theoy of Specal Invaians... 5 4. Scaling Popeies of Specal Invaians... 6 Poble Ses... 39 Refeences... 4. Inoducion
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Pressure Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Stress Analysis
 Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Design Considerations for Achieving ZVS in a Half Bridge Inverter that Drives a Piezoelectric Transformer with No Series Inductor
 Design onsideaions fo Achievg ZS a Half Bidge Invee ha Dives a iezoelecic Tansfoe wih No Seies Induco Svelana Bonse and Sa Ben-Yaaov* owe Eleconics aboaoy Depaen of Elecical and opue Engeeg Ben-Guion Univesiy
Design onsideaions fo Achievg ZS a Half Bidge Invee ha Dives a iezoelecic Tansfoe wih No Seies Induco Svelana Bonse and Sa Ben-Yaaov* owe Eleconics aboaoy Depaen of Elecical and opue Engeeg Ben-Guion Univesiy
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
An Open cycle and Closed cycle Gas Turbine Engines. Methods to improve the performance of simple gas turbine plants
 An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
Two-Pion Exchange Currents in Photodisintegration of the Deuteron
 Two-Pion Exchange Cuens in Phoodisinegaion of he Deueon Dagaa Rozędzik and Jacek Goak Jagieonian Univesiy Kaków MENU00 3 May 00 Wiiasbug Conen Chia Effecive Fied Theoy ChEFT Eecoagneic cuen oeaos wihin
Two-Pion Exchange Cuens in Phoodisinegaion of he Deueon Dagaa Rozędzik and Jacek Goak Jagieonian Univesiy Kaków MENU00 3 May 00 Wiiasbug Conen Chia Effecive Fied Theoy ChEFT Eecoagneic cuen oeaos wihin
Chapter Finite Difference Method for Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
Fundamental Vehicle Loads & Their Estimation
 Fundaenal Vehicle Loads & Thei Esiaion The silified loads can only be alied in he eliinay design sage when he absence of es o siulaion daa They should always be qualified and udaed as oe infoaion becoes
Fundaenal Vehicle Loads & Thei Esiaion The silified loads can only be alied in he eliinay design sage when he absence of es o siulaion daa They should always be qualified and udaed as oe infoaion becoes
Chapter 9 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Chaper 9 Sinusoidal Seady Sae Analysis 9.-9. The Sinusoidal Source and Response 9.3 The Phasor 9.4 pedances of Passive Eleens 9.5-9.9 Circui Analysis Techniques in he Frequency Doain 9.0-9. The Transforer
Chaper 9 Sinusoidal Seady Sae Analysis 9.-9. The Sinusoidal Source and Response 9.3 The Phasor 9.4 pedances of Passive Eleens 9.5-9.9 Circui Analysis Techniques in he Frequency Doain 9.0-9. The Transforer
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
FARADAY'S LAW. dates : No. of lectures allocated. Actual No. of lectures 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09
 FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
Trajectory estimation based on extended state observer with Fal-filter
 The Aeonauical Jounal Augus 05 Volue 9 No 8 07 Tajecoy esiaion based on exended sae obseve wih Fal-file C- in chunlin@dagon.nchu.edu.w S- Hsieh and Y-P in Depaen of Elecical Engineeing Naional Chung Hsing
The Aeonauical Jounal Augus 05 Volue 9 No 8 07 Tajecoy esiaion based on exended sae obseve wih Fal-file C- in chunlin@dagon.nchu.edu.w S- Hsieh and Y-P in Depaen of Elecical Engineeing Naional Chung Hsing
FINITE DIFFERENCE APPROACH TO WAVE GUIDE MODES COMPUTATION
 FINITE DIFFERENCE ROCH TO WVE GUIDE MODES COMUTTION Ing.lessando Fani Elecomagneic Gou Deamen of Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Univesiy of Cagliai iazza d mi, 93 Cagliai, Ialy SUMMRY Inoducion Finie
FINITE DIFFERENCE ROCH TO WVE GUIDE MODES COMUTTION Ing.lessando Fani Elecomagneic Gou Deamen of Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Univesiy of Cagliai iazza d mi, 93 Cagliai, Ialy SUMMRY Inoducion Finie
156 There are 9 books stacked on a shelf. The thickness of each book is either 1 inch or 2
 156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
AB for hydrogen in steel is What is the molar flux of the hydrogen through the steel? Δx Wall. s kmole
 ignen 6 Soluion - Hydogen ga i oed a high peue in a ecangula conaine (--hick wall). Hydogen concenaion a he inide wall i kole / and eenially negligible on he ouide wall. The B fo hydogen in eel i.6 / ec
ignen 6 Soluion - Hydogen ga i oed a high peue in a ecangula conaine (--hick wall). Hydogen concenaion a he inide wall i kole / and eenially negligible on he ouide wall. The B fo hydogen in eel i.6 / ec
Ch23. Introduction to Analytical Separations
 Ch3. Inoducion o Analyical Sepaaions 3. Medical Issue : Measuing Silicones Leaking fo Beas Iplans High olecula ass poly(diehylsiloane), PDMS, [(CH 3 ) SiO] n : Used as GC saionay phase, gels in beas iplans
Ch3. Inoducion o Analyical Sepaaions 3. Medical Issue : Measuing Silicones Leaking fo Beas Iplans High olecula ass poly(diehylsiloane), PDMS, [(CH 3 ) SiO] n : Used as GC saionay phase, gels in beas iplans
TIME DELAY BASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OBSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM
 TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
 Chape 7 7 Roaional Moion and he Law of Gaiy PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 7.1 (a) Eah oaes adians (360 ) on is axis in 1 day. Thus, ad 1 day 5 7.7 10 ad s 4 1 day 8.64 10 s Because of is oaion abou is axis, Eah bulges
Chape 7 7 Roaional Moion and he Law of Gaiy PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 7.1 (a) Eah oaes adians (360 ) on is axis in 1 day. Thus, ad 1 day 5 7.7 10 ad s 4 1 day 8.64 10 s Because of is oaion abou is axis, Eah bulges
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
FARADAY'S LAW dt
 FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
Variance and Covariance Processes
 Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL METHOD FOR THE COMPUTATION OF THE BODIES MOTION IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL METHOD FOR THE COMPUTATION OF THE BODIES MOTION IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD GEORGE-MARIAN VASILESCU, MIHAI MARICARU, BOGDAN DUMITRU VĂRĂTICEANU, MARIUS AUREL COSTEA Key wods: Eddy cuen
AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL METHOD FOR THE COMPUTATION OF THE BODIES MOTION IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD GEORGE-MARIAN VASILESCU, MIHAI MARICARU, BOGDAN DUMITRU VĂRĂTICEANU, MARIUS AUREL COSTEA Key wods: Eddy cuen
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Method for simulation of the fractional order chaotic systems
 Aca Monanisica Slovaca Ročník (26), číslo 4, 273-277 Mehod fo siulaion of he facional ode chaoic syses Ivo Peáš Absac This pape deals wih he ehod of siulaion of facional ode chaoic syses. We pesen a bief
Aca Monanisica Slovaca Ročník (26), číslo 4, 273-277 Mehod fo siulaion of he facional ode chaoic syses Ivo Peáš Absac This pape deals wih he ehod of siulaion of facional ode chaoic syses. We pesen a bief
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Extremal problems for t-partite and t-colorable hypergraphs
 Exemal poblems fo -paie and -coloable hypegaphs Dhuv Mubayi John Talbo June, 007 Absac Fix ineges and an -unifom hypegaph F. We pove ha he maximum numbe of edges in a -paie -unifom hypegaph on n veices
Exemal poblems fo -paie and -coloable hypegaphs Dhuv Mubayi John Talbo June, 007 Absac Fix ineges and an -unifom hypegaph F. We pove ha he maximum numbe of edges in a -paie -unifom hypegaph on n veices
A Mathematical study of Two Species Amensalism Model With a Cover for the first Species by Homotopy Analysis Method
 Available online a www.pelagiaeseachlibay.co Advances in Applied Science Reseach,, 3 (3):8-86 A Maheaical sudy of Two Species Aensalis Model Wih a Cove fo he fis Species by Hooopy Analysis Mehod B. Sia
Available online a www.pelagiaeseachlibay.co Advances in Applied Science Reseach,, 3 (3):8-86 A Maheaical sudy of Two Species Aensalis Model Wih a Cove fo he fis Species by Hooopy Analysis Mehod B. Sia
Homework 2 Solutions
 Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
2.7. Some common engineering functions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Some common engineering funcions 2.7 Inroducion This secion provides a caalogue of some common funcions ofen used in Science and Engineering. These include polynomials, raional funcions, he modulus funcion
Some common engineering funcions 2.7 Inroducion This secion provides a caalogue of some common funcions ofen used in Science and Engineering. These include polynomials, raional funcions, he modulus funcion
Physics 2001/2051 Moments of Inertia Experiment 1
 Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Final Spring 2007
 .615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
.615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
Lecture 23 Damped Motion
 Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
On The Estimation of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complete Block Designs
 Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Lecure 22 Ordinary Differenial Equaions Course Coordinaor: Dr. Suresh A. Karha, Associae Professor, Deparmen of Civil Engineering, IIT Guwahai. In naure, mos of he phenomena ha can be mahemaically described
Lecure 22 Ordinary Differenial Equaions Course Coordinaor: Dr. Suresh A. Karha, Associae Professor, Deparmen of Civil Engineering, IIT Guwahai. In naure, mos of he phenomena ha can be mahemaically described
An Analytical Study of Strong Non Planer Shock. Waves in Magnetogasdynamics
 Adv Theo Appl Mech Vol no 6 9-97 An Analyical Sdy of Song Non Plane Shock Waves in Magneogasdynaics L P Singh Depaen of Applied Maheaics Insie of Technology Banaas Hind Univesiy Vaanasi-5 India Akal Hsain
Adv Theo Appl Mech Vol no 6 9-97 An Analyical Sdy of Song Non Plane Shock Waves in Magneogasdynaics L P Singh Depaen of Applied Maheaics Insie of Technology Banaas Hind Univesiy Vaanasi-5 India Akal Hsain
The k-filtering Applied to Wave Electric and Magnetic Field Measurements from Cluster
 The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 8: State Variable Feedback Control Systems
 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 8: Sae Variable Feedback Conrol Syses INTRODUCTION Sae variable descripions for dynaical syses describe he evoluion of he sae vecor, as a funcion of he sae and he inpu. There
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 8: Sae Variable Feedback Conrol Syses INTRODUCTION Sae variable descripions for dynaical syses describe he evoluion of he sae vecor, as a funcion of he sae and he inpu. There
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
THE FINITE HAUSDORFF AND FRACTAL DIMENSIONS OF THE GLOBAL ATTRACTOR FOR A CLASS KIRCHHOFF-TYPE EQUATIONS
 European Journal of Maheaics and Copuer Science Vol 4 No 7 ISSN 59-995 HE FINIE HAUSDORFF AND FRACAL DIMENSIONS OF HE GLOBAL ARACOR FOR A CLASS KIRCHHOFF-YPE EQUAIONS Guoguang Lin & Xiangshuang Xia Deparen
European Journal of Maheaics and Copuer Science Vol 4 No 7 ISSN 59-995 HE FINIE HAUSDORFF AND FRACAL DIMENSIONS OF HE GLOBAL ARACOR FOR A CLASS KIRCHHOFF-YPE EQUAIONS Guoguang Lin & Xiangshuang Xia Deparen
Eigenvalue problems of rotor system with uncertain parameters
 Jounal of Mechanical Science and echnology 6 () () ~ www.singelink.co/conen/738-494x DOI.7/s6--8-5 Eigenvalue obles of oo syse wih unceain aaees Bao-Guo Liu * Insiue of Mechaonic Engineeing, Henan Univesiy
Jounal of Mechanical Science and echnology 6 () () ~ www.singelink.co/conen/738-494x DOI.7/s6--8-5 Eigenvalue obles of oo syse wih unceain aaees Bao-Guo Liu * Insiue of Mechaonic Engineeing, Henan Univesiy
ME 304 FLUID MECHANICS II
 ME 304 LUID MECHNICS II Pof. D. Haşme Tükoğlu Çankaya Uniesiy aculy of Engineeing Mechanical Engineeing Depamen Sping, 07 y du dy y n du k dy y du k dy n du du dy dy ME304 The undamenal Laws Epeience hae
ME 304 LUID MECHNICS II Pof. D. Haşme Tükoğlu Çankaya Uniesiy aculy of Engineeing Mechanical Engineeing Depamen Sping, 07 y du dy y n du k dy y du k dy n du du dy dy ME304 The undamenal Laws Epeience hae
EN221 - Fall HW # 7 Solutions
 EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
15. Vector Valued Functions
 1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
NPA Storrs Conference University of Connecticut. Copyright Francis V. Fernandes 2008
 NPA 009 Sos Confeence Univesiy of Connecicu Copyigh Fancis V. Fenandes 008 Unificaion of Gaviy wih Eleco-Magneic Phenoena: GEM Gaviy, g, is Volage, V Fancis V. Fenandes 13 Behany B, Kodaikanal, Tail Nadu,
NPA 009 Sos Confeence Univesiy of Connecicu Copyigh Fancis V. Fenandes 008 Unificaion of Gaviy wih Eleco-Magneic Phenoena: GEM Gaviy, g, is Volage, V Fancis V. Fenandes 13 Behany B, Kodaikanal, Tail Nadu,
AN EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 AN EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS M. KAMESWAR RAO AND K.P. RAVINDRAN Depamen of Mechanical Engineeing, Calicu Regional Engineeing College, Keala-67 6, INDIA. Absac:- We eploe
AN EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS M. KAMESWAR RAO AND K.P. RAVINDRAN Depamen of Mechanical Engineeing, Calicu Regional Engineeing College, Keala-67 6, INDIA. Absac:- We eploe
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Adsorption and Desorption Kinetics for Diffusion Controlled Systems with a Strongly Concentration Dependent Diffusivity
 The Open-Access Jounal fo the Basic Pinciples of Diffusion Theoy, Expeient and Application Adsoption and Desoption Kinetics fo Diffusion Contolled Systes with a Stongly Concentation Dependent Diffusivity
The Open-Access Jounal fo the Basic Pinciples of Diffusion Theoy, Expeient and Application Adsoption and Desoption Kinetics fo Diffusion Contolled Systes with a Stongly Concentation Dependent Diffusivity
Robust Output Command Tracking for Linear Systems with Nonlinear Uncertain Structure with Application to Flight Control
 Poceedings of he 44h IEEE Confeence on Decision and Conol and he Euopean Conol Confeence 5 Seville Spain Decebe -5 5 hb5.6 Robus Oupu Coand acking fo Linea Syses wih Nonlinea Unceain Sucue wih Applicaion
Poceedings of he 44h IEEE Confeence on Decision and Conol and he Euopean Conol Confeence 5 Seville Spain Decebe -5 5 hb5.6 Robus Oupu Coand acking fo Linea Syses wih Nonlinea Unceain Sucue wih Applicaion
Gauge invariance and the vacuum state. Dan Solomon Rauland-Borg Corporation 3450 W. Oakton Skokie, IL Please send all correspondence to:
 Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae 1 Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae by Dan Solomon Rauland-Bog Copoaion 345 W. Oakon Skokie, IL 676 Please send all coespondence o: Dan Solomon 164 Bummel Evanson, IL
Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae 1 Gauge invaiance and he vacuum sae by Dan Solomon Rauland-Bog Copoaion 345 W. Oakon Skokie, IL 676 Please send all coespondence o: Dan Solomon 164 Bummel Evanson, IL
[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u
![[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u [ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u](/thumbs/89/100187624.jpg) Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
EFFECT OF PERMISSIBLE DELAY ON TWO-WAREHOUSE INVENTORY MODEL FOR DETERIORATING ITEMS WITH SHORTAGES
 Volume, ssue 3, Mach 03 SSN 39-4847 EFFEC OF PERMSSBLE DELAY ON WO-WAREHOUSE NVENORY MODEL FOR DEERORANG EMS WH SHORAGES D. Ajay Singh Yadav, Ms. Anupam Swami Assisan Pofesso, Depamen of Mahemaics, SRM
Volume, ssue 3, Mach 03 SSN 39-4847 EFFEC OF PERMSSBLE DELAY ON WO-WAREHOUSE NVENORY MODEL FOR DEERORANG EMS WH SHORAGES D. Ajay Singh Yadav, Ms. Anupam Swami Assisan Pofesso, Depamen of Mahemaics, SRM
Measures the linear dependence or the correlation between r t and r t-p. (summarizes serial dependence)
 . Definiions Saionay Time Seies- A ime seies is saionay if he popeies of he pocess such as he mean and vaiance ae consan houghou ime. i. If he auocoelaion dies ou quickly he seies should be consideed saionay
. Definiions Saionay Time Seies- A ime seies is saionay if he popeies of he pocess such as he mean and vaiance ae consan houghou ime. i. If he auocoelaion dies ou quickly he seies should be consideed saionay
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Probabilistic Models
 CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
Design Guideline for Buried Hume Pipe Subject to Coupling Forces
 Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
Wave Mechanics. January 16, 2017
 Wave Mechanics January 6, 7 The ie-dependen Schrödinger equaion We have seen how he ie-dependen Schrodinger equaion, Ψ + Ψ i Ψ follows as a non-relaivisic version of he Klein-Gordon equaion. In wave echanics,
Wave Mechanics January 6, 7 The ie-dependen Schrödinger equaion We have seen how he ie-dependen Schrodinger equaion, Ψ + Ψ i Ψ follows as a non-relaivisic version of he Klein-Gordon equaion. In wave echanics,
Research on the Algorithm of Evaluating and Analyzing Stationary Operational Availability Based on Mission Requirement
 Reseach on he Algoihm of Evaluaing and Analyzing Saionay Opeaional Availabiliy Based on ission Requiemen Wang Naichao, Jia Zhiyu, Wang Yan, ao Yilan, Depamen of Sysem Engineeing of Engineeing Technology,
Reseach on he Algoihm of Evaluaing and Analyzing Saionay Opeaional Availabiliy Based on ission Requiemen Wang Naichao, Jia Zhiyu, Wang Yan, ao Yilan, Depamen of Sysem Engineeing of Engineeing Technology,
Heat Conduction Problem in a Thick Circular Plate and its Thermal Stresses due to Ramp Type Heating
 ISSN(Online): 319-8753 ISSN (Pin): 347-671 Inenaional Jounal of Innovaive Reseac in Science, Engineeing and Tecnology (An ISO 397: 7 Ceified Oganiaion) Vol 4, Issue 1, Decembe 15 Hea Concion Poblem in
ISSN(Online): 319-8753 ISSN (Pin): 347-671 Inenaional Jounal of Innovaive Reseac in Science, Engineeing and Tecnology (An ISO 397: 7 Ceified Oganiaion) Vol 4, Issue 1, Decembe 15 Hea Concion Poblem in
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
Module 4: Time Response of discrete time systems Lecture Note 2
 Module 4: Time Response of discree ime sysems Lecure Noe 2 1 Prooype second order sysem The sudy of a second order sysem is imporan because many higher order sysem can be approimaed by a second order model
Module 4: Time Response of discree ime sysems Lecure Noe 2 1 Prooype second order sysem The sudy of a second order sysem is imporan because many higher order sysem can be approimaed by a second order model
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
