Relative and Circular Motion
|
|
|
- Augustine Bryant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1
2 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2
3 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you o hose of you who did! Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 3
4 Lecue Thoughs Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 4
5 Wha is he speed of Mike elaie o he saion? A. -1 m/s B. 30 m/s C. 29 m/s D. 31 m/s 70% 30% 0% 0% Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 5
6 Relaie Moion in 1 dimension Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 6
7 Relaie Posiion and Refeence Fames Posiion of Mike in he gound fame is he eco sum of he posiion eco of Mike in he ain efeence fame and he posiion eco of he ain in he gound efeence fame. Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 7
8 Relaie Moion and Refeence Fames Diffeeniae he posiion ecos o obain he elociy ecos Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 8
9 Relaie Moion and Refeence Fames Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 9
10 Relaie Moion and Refeence Fames Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 10
11 Pelecue 3 Quesions 1 again A. B. C. D. -12m 0% 0% 0% 0% Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 11
12 CheckPoin A gil sands on a moing sidewalk ha moes o he igh a 2 m/s elaie o he gound. A dog uns owad he gil in he opposie diecion along he sidewalk a a speed of 8 m/s elaie o he sidewalk. Wha is he speed of he dog elaie o he gound? dogbel 8 m/s belgound 2 m/s A) 6 m/s B) 8 m/s C) 10 m/s Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 12
13 Wha is he speed of he dog elaie o he gound? dogbel 8 m/s belgound 2 m/s A) 6 m/s B) 8 m/s C) 10 m/s x dog gound dog bel bel gound ( 8 m/s) (2 m/s) 6 m/s Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 13
14 CheckPoin A gil sands on a moing sidewalk ha moes o he igh a 2 m/s elaie o he gound. A dog uns owad he gil in he opposie diecion along he sidewalk a a speed of 8 m/s elaie o he sidewalk. Wha is he speed of he dog elaie o he gil? dogbel 8 m/s belgound 2 m/s A) 6 m/s B) 8 m/s C) 10 m/s 42% of you go his igh le s do his again Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 14
15 Wha is he speed of he dog elaie o he gil? A. B. C. dogbel 8 m/s 0% 0% 0% belgound 2 m/s A) 6 m/s B) 8 m/s C) 10 m/s A) Because he gil is acually moing and he wo ecos ae opposie so ogehe hey make 6 m/s B) Because he gil is no moing elaie o he bel and he dog is going 8 m/s elaie o he bel he dog is also moing 8 m/s elaie o he gil.. C) The dog and gil ae unning owads each ohe so when you add he wo elociies ogehe i would be 82. Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 15
16 Wha is he speed of he dog elaie o he gil? dogbel 8 m/s belgound 2 m/s A) 6 m/s B) 8 m/s C) 10 m/s B) Because he gil is no moing elaie o he bel and he dog is going 8 m/s elaie o he bel he dog is also moing 8 m/s elaie o he gil. Using he elociy fomula: dog gil dog bel bel gil 8 m/s 0 m/s 8 m/s Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 16
17 Relaie Moion in 2 Dimensions Speed elaie o shoe Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 17
18 Relaie Moion in 2 Dimensions Diecion w.. shoeline Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 18
19 Relaie Moion in 2 Dimensions Caea!!!! The simple addiion of elociies as shown only woks fo speeds much less han he speed of ligh need special elaiiy a ~c. Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 19
20 Moing Sidewalk Quesion A man sas o walk along he doed line pained on a moing sidewalk owad a fie hydan ha is diecly acoss fom him. The widh of he walkway is 4 m and i is moing a 2 m/s elaie o he fie-hydan. If his walking speed is 1 m/s how fa away will he be fom he hydan when he eaches he ohe side? A. B. C. D. A) 2 m B) 4 m C) 6 m D) 8 m 90% 0% 10% 0% Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 20
21 If he sidewalk wasn moing: Time o ge acoss: disance / speed 4m / 1m/s 4 s man sidewalk Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 21
22 Jus he sidewalk: sidewalk hydan Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 22
23 D D (speed of sidewalk) (ime o ge acoss) (2 m/s) (4 s) 8 m Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 23
24 Combinaion of moions: Veco soluion man hydan man sidewalk man hydan sidewalk hydan man sidewalk 1ˆ i 0 ˆj 0ˆ i 2 ˆj 1ˆ i 2 ˆj sidewalk hydan man hydan man hydan man hydan man hydan ( 4 ) 2 coss coss ˆj ( ) 4ˆ i 0 ˆj 0 ( ) ( coss coss man hydan 0 ) 4ˆ i 0 ˆj iˆ 0ˆ i coss yj ˆ y 8m man hydan 0 4s man hydan man hydan ( 1ˆ i 2 ˆj ) coss coss 0ˆ i yj ˆ Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 24
25 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 25
26 Swim Race A. B. C. Thee swimmes can swim equally fas elaie o he wae. They hae a ace o see who can swim acoss a ie in he leas ime. Relaie o he wae Beh swims pependicula o he flow Ann swims upseam a 30 degees and Caly swims downseam a 30 degees. Who ges acoss he ie fis? A) Ann B) Beh C) Caly Ann Beh Caly 60% y x 20% 20% 0% Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 26
27 Look a jus wae & swimmes Time o ge acoss D / V y D A B 30 o 30 o C y x V ybeh V o V yann V o cos(30 o ) V ycaly V o cos(30 o ) Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 27
28 Clicke Quesion Thee swimmes can swim equally fas elaie o he wae. They hae a ace o see who can swim acoss a ie in he leas ime. Relaie o he wae Beh swims pependicula o he flow Ann swims upseam a 30 degees and Caly swims downseam a 30 degees. Who ges acoss he ie second? A) Ann B) Caly C) Boh same Ann Caly y x Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 28
29 Acceleaing (Non-Ineial) Fames of Refeence Acceleaing Fame of Refeence Confusing due o he fac ha he acceleaion can esul in wha appeas o be a push o pull. Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 29
30 Acceleaed Fames of Refeence Acceleaing Fame of Refeence Acceleomee can deec change in elociy Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 30
31 Ineial Fames of Refeence Ineial Fames of Refeence Non-acceleaing fames of efeence in a sae of consan ecilinea moion wih espec o one anohe. An acceleomee moing wih any of hem would deec zeo acceleaion. Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 31
32 CheckPoin A gil wils a ock on he end of a sing aound in a hoizonal cicle aboe he head as shown fom aboe in he diagam. If he sing beaks a he insan shown which of he aows bes epesens he esuling pah of he ock? A B C D Afe he sing beaks he ock will hae no foce acing on i so i canno acceleae. Theefoe i will mainain is elociy a he ime of he beak in he sing which is dieced angen o he cicle. Top iew looking down Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 32
33 Suey Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 33
34 Roaing Refeence Fames Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 34
35 Roaing Refeence Fames Speed is consan. Diecion Changing Acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 35
36 Roaing Refeence Fames Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 36
37 Roaing Refeence Fames Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 37
38 Roaing Refeence Fames Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 38
39 Cenipeal Acceleaion Consan speed in cicula pah Acceleaion dieced owad cene of cicle Wha is he magniude of acceleaion? Popoional o: 1. Speed 1. ime ae of change of angle o angula elociy Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 39
40 Cenipeal Acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 40
41 Cenipeal Acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 41
42 Cenipeal Acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 42
43 ωr ω is he ae a which he angle θ changes: ω dθ d θ Once aound: x / 2πR / T ω θ / 2π / Τ Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 43
44 ωr Anohe way o see i: dθ R dr dθ dθ R d Rω Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 44
45 Cenipeal Acceleaion-Example Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 45
46 Cenipeal Acceleaion due o Eah s oaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 46
47 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 47
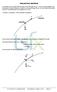
48 Rie Rescue N Dock Fame boa dock boa ie θ E ie dock Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 48
49 Rie Rescue-Dock Fame j i j i j i j i dock dock dock dock dock ie dock ie boa ie ie 0.6 ˆ 2.5ˆ ) ( ˆ (0) (3.1)ˆ ˆ ) (24.8*sin )ˆ (24.8* cos 0 ˆ 0ˆ 0 0 θ θ N E dock î ĵ boa Dock Fame dock 0-2.5i0.6j ) ( mee dock ( ) ( ) j i j i j i j i j i j i mee boa mee mee boa boa dock boa boa boa mee mee dock dock mee dock ie boa boa ie boa 0 ˆ 0ˆ ) ( ˆ ) 24.8*sin ( )ˆ 24.8*cos ( 0.6 ˆ 2.5ˆ ) ( ) ( ˆ (0) (3.1)ˆ 0.6 ˆ 2.5ˆ ) ( ˆ ) 24.8*sin ( )ˆ 24.8*cos ( ) ( θ θ θ θ Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 49
50 Rie Rescue-Dock Fame -2.5i0.6j ( ) dock 0 dock mee Dock Fame *cosθ *sinθ mee mee 0 cosθ 0 sinθ mee mee N ĵ î dock E boa mee mee 2 1 mee ( 2.5) ( 0.6) h Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 50
51 mee dock dock h ( dock mee dock0 d d ( ( dock mee mee ( Rie Rescue-Dock Fame ) mee -2.5i0.6j ( ) ) 2.5ˆ i 0.6 ˆj ) dock ( ) ) dock 0 ((3.1)ˆ i (0) ˆj ) mee mee iˆ 0.6 ˆj 2 ( ) ( 0.6) mee 2 2 ( ) ( 0.6) 2.26km cosθ sinθ θ deg mee mee dock mee mee d ( ˆ i boa ie N ĵ Dock Fame dock mee î dock E (5.786) ˆj ) boa Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 51
52 Rie Rescue- fame Child Fame boa dock N θ ĵ î E ie boa ie dock dock boa dock dock ie (24.8* cosθ )ˆ i (24.8*sinθ ) ˆj i ˆ ie dock (3.1)ˆ (0) j dock ( 3.1)ˆ i (0) ˆ j ( ) boa ie ( 24.8* cosθ )ˆ i ( 24.8*sinθ ) ( ) 0 dock 2.5ˆ i 0.6 ˆj 0ˆ i 0 ˆj 0 dock 0 dock 2.5i-0.6j ˆj ( dock mee ) Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 52
53 Rie Rescue- fame ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) h j i j i j i j i j i mee mee mee mee mee mee mee mee boa mee mee boa ie boa dock boa boa boa mee mee dock dock mee dock sin *sin cos *cos ˆ 0ˆ ) ( ˆ ) (24.8*sin )ˆ (24.8*cos 0.6 ˆ 2.5ˆ ) ( ) ( ˆ (0) 3.1)ˆ ( 0.6 ˆ 2.5ˆ ) ( θ θ θ θ θ θ N E dock î ĵ boa Child Fame dock 0 2.5i-0.6j ) ( mee dock θ Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 53
54 dock mee dock d h ( ( dock mee mee ) ) ( mee dock 0 ( ) ) Rie Rescue dock mee iˆ 0.6 ˆj 2.5ˆ i 0.6 ˆj 2 ( ) ( 0.6) mee mee 2 ( 3.1)ˆ i (0) ˆj ) mee d 2 2 ( ) ( 0.6) 2.26km cosθ sinθ θ deg mee mee Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 54
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
2-d Motion: Constant Acceleration
 -d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
-d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
Kinematics in two dimensions
 Lecure 5 Phsics I 9.18.13 Kinemaics in wo dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teaching/phsicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo36.uml.edu/danlo13/phsics1fall.hml 95.141, Fall 13, Lecure 5
Lecure 5 Phsics I 9.18.13 Kinemaics in wo dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teaching/phsicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo36.uml.edu/danlo13/phsics1fall.hml 95.141, Fall 13, Lecure 5
 Page 1 o 13 1. The brighes sar in he nigh sky is α Canis Majoris, also known as Sirius. I lies 8.8 ligh-years away. Express his disance in meers. ( ligh-year is he disance coered by ligh in one year. Ligh
Page 1 o 13 1. The brighes sar in he nigh sky is α Canis Majoris, also known as Sirius. I lies 8.8 ligh-years away. Express his disance in meers. ( ligh-year is he disance coered by ligh in one year. Ligh
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
2. v = 3 4 c. 3. v = 4c. 5. v = 2 3 c. 6. v = 9. v = 4 3 c
 Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
1. The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object from t = 0 to t = T. a
 Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
 Chape 7 7 Roaional Moion and he Law of Gaiy PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 7.1 (a) Eah oaes adians (360 ) on is axis in 1 day. Thus, ad 1 day 5 7.7 10 ad s 4 1 day 8.64 10 s Because of is oaion abou is axis, Eah bulges
Chape 7 7 Roaional Moion and he Law of Gaiy PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 7.1 (a) Eah oaes adians (360 ) on is axis in 1 day. Thus, ad 1 day 5 7.7 10 ad s 4 1 day 8.64 10 s Because of is oaion abou is axis, Eah bulges
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
P h y s i c s F a c t s h e e t
 P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) , PART A PHYSICS
 Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Ch04: Motion in two and three dimensions (2D and 3D)
 Ch4: Motion in two and thee dimensions (D and 3D) Displacement, elocity and acceleation ectos Pojectile motion Cicula motion Relatie motion 4.: Position and displacement Position of an object in D o 3D
Ch4: Motion in two and thee dimensions (D and 3D) Displacement, elocity and acceleation ectos Pojectile motion Cicula motion Relatie motion 4.: Position and displacement Position of an object in D o 3D
Physics 201, Lecture 6
 Physics 201, Lectue 6 Today s Topics q Unifom Cicula Motion (Section 4.4, 4.5) n Cicula Motion n Centipetal Acceleation n Tangential and Centipetal Acceleation q Relatie Motion and Refeence Fame (Sec.
Physics 201, Lectue 6 Today s Topics q Unifom Cicula Motion (Section 4.4, 4.5) n Cicula Motion n Centipetal Acceleation n Tangential and Centipetal Acceleation q Relatie Motion and Refeence Fame (Sec.
Motion on a Curve and Curvature
 Moion on Cue nd Cuue his uni is bsed on Secions 9. & 9.3, Chpe 9. All ssigned edings nd execises e fom he exbook Objecies: Mke cein h you cn define, nd use in conex, he ems, conceps nd fomuls lised below:
Moion on Cue nd Cuue his uni is bsed on Secions 9. & 9.3, Chpe 9. All ssigned edings nd execises e fom he exbook Objecies: Mke cein h you cn define, nd use in conex, he ems, conceps nd fomuls lised below:
Physics 207 Lecture 13
 Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Control Volume Derivation
 School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
5-1. We apply Newton s second law (specifically, Eq. 5-2). F = ma = ma sin 20.0 = 1.0 kg 2.00 m/s sin 20.0 = 0.684N. ( ) ( )
 5-1. We apply Newon s second law (specfcally, Eq. 5-). (a) We fnd he componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma cos 0.0 = 1.00kg.00m/s cos 0.0 = 1.88N. (b) The y componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma
5-1. We apply Newon s second law (specfcally, Eq. 5-). (a) We fnd he componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma cos 0.0 = 1.00kg.00m/s cos 0.0 = 1.88N. (b) The y componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma
Ch.4 Motion in 2D. Ch.4 Motion in 2D
 Moion in plne, such s in he sceen, is clled 2-dimensionl (2D) moion. 1. Posiion, displcemen nd eloci ecos If he picle s posiion is ( 1, 1 ) 1, nd ( 2, 2 ) 2, he posiions ecos e 1 = 1 1 2 = 2 2 Aege eloci
Moion in plne, such s in he sceen, is clled 2-dimensionl (2D) moion. 1. Posiion, displcemen nd eloci ecos If he picle s posiion is ( 1, 1 ) 1, nd ( 2, 2 ) 2, he posiions ecos e 1 = 1 1 2 = 2 2 Aege eloci
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
2002 November 14 Exam III Physics 191
 November 4 Exam III Physics 9 Physical onsans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s ircle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses: m = kg, m
November 4 Exam III Physics 9 Physical onsans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s ircle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses: m = kg, m
Kinematics in two Dimensions
 Lecure 5 Chaper 4 Phsics I Kinemaics in wo Dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teachin/phsicsi PHYS.141 Lecure 5 Danlo Deparmen of Phsics and Applied Phsics Toda we are oin o discuss:
Lecure 5 Chaper 4 Phsics I Kinemaics in wo Dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teachin/phsicsi PHYS.141 Lecure 5 Danlo Deparmen of Phsics and Applied Phsics Toda we are oin o discuss:
Physics 101: Lecture 03 Kinematics Today s lecture will cover Textbook Sections (and some Ch. 4)
 Physics 101: Lecure 03 Kinemaics Today s lecure will coer Texbook Secions 3.1-3.3 (and some Ch. 4) Physics 101: Lecure 3, Pg 1 A Refresher: Deermine he force exered by he hand o suspend he 45 kg mass as
Physics 101: Lecure 03 Kinemaics Today s lecure will coer Texbook Secions 3.1-3.3 (and some Ch. 4) Physics 101: Lecure 3, Pg 1 A Refresher: Deermine he force exered by he hand o suspend he 45 kg mass as
Kinematics Vocabulary. Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion. Position. Coordinate System in One Dimension. Kinema means movement 8.
 Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Test points. Provide the best answer to the following questions and problems. Watch your sig figs.
 Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
x i v x t a dx dt t x
 Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
Chapter 12: Velocity, acceleration, and forces
 To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
Reinforcement learning
 Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
ME 141. Engineering Mechanics
 ME 141 Engineeing Mechnics Lecue 13: Kinemics of igid bodies hmd Shhedi Shkil Lecue, ep. of Mechnicl Engg, UET E-mil: sshkil@me.bue.c.bd, shkil6791@gmil.com Websie: eche.bue.c.bd/sshkil Couesy: Veco Mechnics
ME 141 Engineeing Mechnics Lecue 13: Kinemics of igid bodies hmd Shhedi Shkil Lecue, ep. of Mechnicl Engg, UET E-mil: sshkil@me.bue.c.bd, shkil6791@gmil.com Websie: eche.bue.c.bd/sshkil Couesy: Veco Mechnics
NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION
 Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
Course II. Lesson 7 Applications to Physics. 7A Velocity and Acceleration of a Particle
 Course II Lesson 7 Applicaions o Physics 7A Velociy and Acceleraion of a Paricle Moion in a Sraigh Line : Velociy O Aerage elociy Moion in he -ais + Δ + Δ 0 0 Δ Δ Insananeous elociy d d Δ Δ Δ 0 lim [ m/s
Course II Lesson 7 Applicaions o Physics 7A Velociy and Acceleraion of a Paricle Moion in a Sraigh Line : Velociy O Aerage elociy Moion in he -ais + Δ + Δ 0 0 Δ Δ Insananeous elociy d d Δ Δ Δ 0 lim [ m/s
Department of Chemical Engineering University of Tennessee Prof. David Keffer. Course Lecture Notes SIXTEEN
 D. Keffe - ChE 40: Hea Tansfe and Fluid Flow Deamen of Chemical Enee Uniesi of Tennessee Pof. Daid Keffe Couse Lecue Noes SIXTEEN SECTION.6 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS OF CONTINUITY SECTION.7 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS
D. Keffe - ChE 40: Hea Tansfe and Fluid Flow Deamen of Chemical Enee Uniesi of Tennessee Pof. Daid Keffe Couse Lecue Noes SIXTEEN SECTION.6 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS OF CONTINUITY SECTION.7 DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
scalar TIME TIME INTERVAL [second s] t t T t i or t 1 s > 0 +x s < 0 t f or t 2 t = t f t i = t 2 t 1 acceleration a = constant v u at
![scalar TIME TIME INTERVAL [second s] t t T t i or t 1 s > 0 +x s < 0 t f or t 2 t = t f t i = t 2 t 1 acceleration a = constant v u at scalar TIME TIME INTERVAL [second s] t t T t i or t 1 s > 0 +x s < 0 t f or t 2 t = t f t i = t 2 t 1 acceleration a = constant v u at](/thumbs/86/93672801.jpg) POSITION / LENGTH /DISTANCE / DISPLACEMENT [ee ] L d d D h H R a x x y s s x s y W N S E disance aelled d sx scos sy ssin S displaceen S agniude s / diecion N of E wok = change in KE aeage speed aeage
POSITION / LENGTH /DISTANCE / DISPLACEMENT [ee ] L d d D h H R a x x y s s x s y W N S E disance aelled d sx scos sy ssin S displaceen S agniude s / diecion N of E wok = change in KE aeage speed aeage
Physics NYB problem set 5 solution
 Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 9
 PHYSICS 149: Lecure 9 Chaper 3 3.2 Velociy and Acceleraion 3.3 Newon s Second Law of Moion 3.4 Applying Newon s Second Law 3.5 Relaive Velociy Lecure 9 Purdue Universiy, Physics 149 1 Velociy (m/s) The
PHYSICS 149: Lecure 9 Chaper 3 3.2 Velociy and Acceleraion 3.3 Newon s Second Law of Moion 3.4 Applying Newon s Second Law 3.5 Relaive Velociy Lecure 9 Purdue Universiy, Physics 149 1 Velociy (m/s) The
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
AP Physics Gravity Wrapup
 AP Phyic Gaiy Wapup You ge hee equaion o wok wih, and only hee. Eeyhing ele you hae o deelop fo hee hee equaion (alo hae o ue oe ohe one). Hee hey ae: F a G c G = Newon law of gaiy. 1 = Cenipeal acceleaion
AP Phyic Gaiy Wapup You ge hee equaion o wok wih, and only hee. Eeyhing ele you hae o deelop fo hee hee equaion (alo hae o ue oe ohe one). Hee hey ae: F a G c G = Newon law of gaiy. 1 = Cenipeal acceleaion
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
Suggested Practice Problems (set #2) for the Physics Placement Test
 Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
EN221 - Fall HW # 7 Solutions
 EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
Physics 201 Lecture 18
 Phsics 0 ectue 8 ectue 8 Goals: Define and anale toque ntoduce the coss poduct Relate otational dnamics to toque Discuss wok and wok eneg theoem with espect to otational motion Specif olling motion (cente
Phsics 0 ectue 8 ectue 8 Goals: Define and anale toque ntoduce the coss poduct Relate otational dnamics to toque Discuss wok and wok eneg theoem with espect to otational motion Specif olling motion (cente
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Physics 201, Lecture 5
 Phsics 1 Lecue 5 Tod s Topics n Moion in D (Chp 4.1-4.3): n D Kinemicl Quniies (sec. 4.1) n D Kinemics wih Consn Acceleion (sec. 4.) n D Pojecile (Sec 4.3) n Epeced fom Peiew: n Displcemen eloci cceleion
Phsics 1 Lecue 5 Tod s Topics n Moion in D (Chp 4.1-4.3): n D Kinemicl Quniies (sec. 4.1) n D Kinemics wih Consn Acceleion (sec. 4.) n D Pojecile (Sec 4.3) n Epeced fom Peiew: n Displcemen eloci cceleion
Topic 1: Linear motion and forces
 TOPIC 1 Topic 1: Linear moion and forces 1.1 Moion under consan acceleraion Science undersanding 1. Linear moion wih consan elociy is described in erms of relaionships beween measureable scalar and ecor
TOPIC 1 Topic 1: Linear moion and forces 1.1 Moion under consan acceleraion Science undersanding 1. Linear moion wih consan elociy is described in erms of relaionships beween measureable scalar and ecor
The study of the motion of a body along a general curve. û N the unit vector normal to the curve. Clearly, these unit vectors change with time, uˆ
 Secion. Curilinear Moion he sudy of he moion of a body along a general cure. We define û he uni ecor a he body, angenial o he cure û he uni ecor normal o he cure Clearly, hese uni ecors change wih ime,
Secion. Curilinear Moion he sudy of he moion of a body along a general cure. We define û he uni ecor a he body, angenial o he cure û he uni ecor normal o he cure Clearly, hese uni ecors change wih ime,
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Theme Music: MGMT Electric Feel* Cartoon: Bob Thaves Frank & Ernest
 Octobe7, 013 Physics 131 Pof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: MGMT Electic Feel* Catoon: Bob Thaves Fank & Enest 1 Foothold ideas: Chage A hidden popety of matte Matte is made up of two kinds of electical matte
Octobe7, 013 Physics 131 Pof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: MGMT Electic Feel* Catoon: Bob Thaves Fank & Enest 1 Foothold ideas: Chage A hidden popety of matte Matte is made up of two kinds of electical matte
Displacement ( x) x x x
 Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
( ) ( ) Review of Force. Review of Force. r = =... Example 1. What is the dot product for F r. Solution: Example 2 ( )
 : PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
: PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
Velocity is a relative quantity
 Veloci is a relaie quani Disenangling Coordinaes PHY2053, Fall 2013, Lecure 6 Newon s Laws 2 PHY2053, Fall 2013, Lecure 6 Newon s Laws 3 R. Field 9/6/2012 Uniersi of Florida PHY 2053 Page 8 Reference Frames
Veloci is a relaie quani Disenangling Coordinaes PHY2053, Fall 2013, Lecure 6 Newon s Laws 2 PHY2053, Fall 2013, Lecure 6 Newon s Laws 3 R. Field 9/6/2012 Uniersi of Florida PHY 2053 Page 8 Reference Frames
LAB # 2 - Equilibrium (static)
 AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba
![( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba ( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba](/thumbs/83/87856399.jpg) THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
PROJECTILE MOTION. At any given point in the motion, the velocity vector is always a tangent to the path.
 PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
Science Advertisement Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis 2/3/2007 Physics 253
 Science Adeisemen Inegoenmenl Pnel on Clime Chnge: The Phsicl Science Bsis hp://www.ipcc.ch/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 hp://www.fonews.com/pojecs/pdf/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 3 Sus: Uni, Chpe 3 Vecos
Science Adeisemen Inegoenmenl Pnel on Clime Chnge: The Phsicl Science Bsis hp://www.ipcc.ch/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 hp://www.fonews.com/pojecs/pdf/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 3 Sus: Uni, Chpe 3 Vecos
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
CHAPTER 5 NONINERTIAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 5 NONINERTIAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS 5. (a The non-ineia oseve eieves ha he is in equiiium and ha he ne foce acin on him is zeo. The scae exes an upwad foce, N, whose vaue is equa o he scae eadin ---
CHAPTER 5 NONINERTIAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS 5. (a The non-ineia oseve eieves ha he is in equiiium and ha he ne foce acin on him is zeo. The scae exes an upwad foce, N, whose vaue is equa o he scae eadin ---
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup Sample Midterm. Useful Equations. x f. x i v x. a x. x i. v xi v xf. 2a x f x i. y f. a r.
 Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup Sample Miderm Useful Equaions A y Asin A A x A y an A y A x A = A x i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A x B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z A x B =
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup Sample Miderm Useful Equaions A y Asin A A x A y an A y A x A = A x i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A x B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z A x B =
Review Equations. Announcements 9/8/09. Table Tennis
 Announcemens 9/8/09 1. Course homepage ia: phsics.bu.edu Class web pages Phsics 105 (Colon J). (Class-wide email sen) Iclicker problem from las ime scores didn ge recorded. Clicker quizzes from lecures
Announcemens 9/8/09 1. Course homepage ia: phsics.bu.edu Class web pages Phsics 105 (Colon J). (Class-wide email sen) Iclicker problem from las ime scores didn ge recorded. Clicker quizzes from lecures
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1-3
 A.P. Physics B Uni 1 Tes Reiew Physics Basics, Moemen, and Vecors Chapers 1-3 * In sudying for your es, make sure o sudy his reiew shee along wih your quizzes and homework assignmens. Muliple Choice Reiew:
A.P. Physics B Uni 1 Tes Reiew Physics Basics, Moemen, and Vecors Chapers 1-3 * In sudying for your es, make sure o sudy his reiew shee along wih your quizzes and homework assignmens. Muliple Choice Reiew:
e.g: If A = i 2 j + k then find A. A = Ax 2 + Ay 2 + Az 2 = ( 2) = 6
 MOTION IN A PLANE 1. Scala Quantities Physical quantities that have only magnitude and no diection ae called scala quantities o scalas. e.g. Mass, time, speed etc. 2. Vecto Quantities Physical quantities
MOTION IN A PLANE 1. Scala Quantities Physical quantities that have only magnitude and no diection ae called scala quantities o scalas. e.g. Mass, time, speed etc. 2. Vecto Quantities Physical quantities
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
MOMENTUM CONSERVATION LAW
 1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
In this chapter the model of free motion under gravity is extended to objects projected at an angle. When you have completed it, you should
 Cambridge Universiy Press 978--36-60033-7 Cambridge Inernaional AS and A Level Mahemaics: Mechanics Coursebook Excerp More Informaion Chaper The moion of projeciles In his chaper he model of free moion
Cambridge Universiy Press 978--36-60033-7 Cambridge Inernaional AS and A Level Mahemaics: Mechanics Coursebook Excerp More Informaion Chaper The moion of projeciles In his chaper he model of free moion
INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY
 INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY I claim ha ha if acceleraion is consan, hen he elociy is a linear funcion of ime and he posiion a quadraic funcion of ime. We wan o inesigae hose claims, and a he same ime, work
INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY I claim ha ha if acceleraion is consan, hen he elociy is a linear funcion of ime and he posiion a quadraic funcion of ime. We wan o inesigae hose claims, and a he same ime, work
Rotational Motion: Statics and Dynamics
 Physics 07 Lectue 17 Goals: Lectue 17 Chapte 1 Define cente of mass Analyze olling motion Intoduce and analyze toque Undestand the equilibium dynamics of an extended object in esponse to foces Employ consevation
Physics 07 Lectue 17 Goals: Lectue 17 Chapte 1 Define cente of mass Analyze olling motion Intoduce and analyze toque Undestand the equilibium dynamics of an extended object in esponse to foces Employ consevation
4.5 Constant Acceleration
 4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
KEPLER S LAWS AND PLANETARY ORBITS
 KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
Brock University Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agostino. Solutions for Tutorial 3: Chapter 2, Motion in One Dimension
 Brock Uniersiy Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agosino Soluions for Tuorial 3: Chaper 2, Moion in One Dimension The goals of his uorial are: undersand posiion-ime graphs, elociy-ime graphs, and heir
Brock Uniersiy Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agosino Soluions for Tuorial 3: Chaper 2, Moion in One Dimension The goals of his uorial are: undersand posiion-ime graphs, elociy-ime graphs, and heir
Non-uniform circular motion *
 OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
total distance cov ered time int erval v = average speed (m/s)
 Physics Suy Noes Lesson 4 Linear Moion 1 Change an Moion a. A propery common o eeryhing in he unierse is change. b. Change is so imporan ha he funamenal concep of ime woul be meaningless wihou i. c. Since
Physics Suy Noes Lesson 4 Linear Moion 1 Change an Moion a. A propery common o eeryhing in he unierse is change. b. Change is so imporan ha he funamenal concep of ime woul be meaningless wihou i. c. Since
Physics 2001/2051 Moments of Inertia Experiment 1
 Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
1. Kinematics I: Position and Velocity
 1. Kinemaics I: Posiion and Velociy Inroducion The purpose of his eperimen is o undersand and describe moion. We describe he moion of an objec by specifying is posiion, velociy, and acceleraion. In his
1. Kinemaics I: Posiion and Velociy Inroducion The purpose of his eperimen is o undersand and describe moion. We describe he moion of an objec by specifying is posiion, velociy, and acceleraion. In his
Q.1 Define work and its unit?
 CHP # 6 ORK AND ENERGY Q.1 Define work and is uni? A. ORK I can be define as when we applied a force on a body and he body covers a disance in he direcion of force, hen we say ha work is done. I is a scalar
CHP # 6 ORK AND ENERGY Q.1 Define work and is uni? A. ORK I can be define as when we applied a force on a body and he body covers a disance in he direcion of force, hen we say ha work is done. I is a scalar
One-Dimensional Kinematics
 One-Dimensional Kinemaics One dimensional kinemaics refers o moion along a sraigh line. Een hough we lie in a 3-dimension world, moion can ofen be absraced o a single dimension. We can also describe moion
One-Dimensional Kinemaics One dimensional kinemaics refers o moion along a sraigh line. Een hough we lie in a 3-dimension world, moion can ofen be absraced o a single dimension. We can also describe moion
Module 3: The Damped Oscillator-II Lecture 3: The Damped Oscillator-II
 Module 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II Lecure 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II 3. Over-damped Oscillaions. This refers o he siuaion where β > ω (3.) The wo roos are and α = β + α 2 = β β 2 ω 2 = (3.2) β 2 ω 2 = 2
Module 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II Lecure 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II 3. Over-damped Oscillaions. This refers o he siuaion where β > ω (3.) The wo roos are and α = β + α 2 = β β 2 ω 2 = (3.2) β 2 ω 2 = 2
() t. () t r () t or v. ( t) () () ( ) = ( ) or ( ) () () () t or dv () () Section 10.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
 Secion 1.4 Moion in Spce: Velociy nd Acceleion We e going o dive lile deepe ino somehing we ve ledy inoduced, nmely () nd (). Discuss wih you neighbo he elionships beween posiion, velociy nd cceleion you
Secion 1.4 Moion in Spce: Velociy nd Acceleion We e going o dive lile deepe ino somehing we ve ledy inoduced, nmely () nd (). Discuss wih you neighbo he elionships beween posiion, velociy nd cceleion you
UCSD Phys 4A Intro Mechanics Winter 2016 Ch 5 Solutions
 UCSD Phs 4 Into Mechanics Winte 016 Ch 5 Solutions 0. Since the uppe bloc has a highe coefficient of iction, that bloc will dag behind the lowe bloc. Thus thee will be tension in the cod, and the blocs
UCSD Phs 4 Into Mechanics Winte 016 Ch 5 Solutions 0. Since the uppe bloc has a highe coefficient of iction, that bloc will dag behind the lowe bloc. Thus thee will be tension in the cod, and the blocs
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension
 Physics for Scieniss and Engineers Chaper Kinemaics in One Dimension Spring, 8 Ho Jung Paik Kinemaics Describes moion while ignoring he agens (forces) ha caused he moion For now, will consider moion in
Physics for Scieniss and Engineers Chaper Kinemaics in One Dimension Spring, 8 Ho Jung Paik Kinemaics Describes moion while ignoring he agens (forces) ha caused he moion For now, will consider moion in
Cartesian Coordinate System and Vectors
 Catesian Coodinate System and Vectos Coodinate System Coodinate system: used to descibe the position of a point in space and consists of 1. An oigin as the efeence point 2. A set of coodinate axes with
Catesian Coodinate System and Vectos Coodinate System Coodinate system: used to descibe the position of a point in space and consists of 1. An oigin as the efeence point 2. A set of coodinate axes with
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
4. Two and Three Dimensional Motion
 4. Two and Thee Dimensional Motion 1 Descibe motion using position, displacement, elocity, and acceleation ectos Position ecto: ecto fom oigin to location of the object. = x i ˆ + y ˆ j + z k ˆ Displacement:
4. Two and Thee Dimensional Motion 1 Descibe motion using position, displacement, elocity, and acceleation ectos Position ecto: ecto fom oigin to location of the object. = x i ˆ + y ˆ j + z k ˆ Displacement:
6.4 Period and Frequency for Uniform Circular Motion
 6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
q r 1 4πε Review: Two ways to find V at any point in space: Integrate E dl: Sum or Integrate over charges: q 1 r 1 q 2 r 2 r 3 q 3
 Review: Lectue : Consevation of negy and Potential Gadient Two ways to find V at any point in space: Integate dl: Sum o Integate ove chages: q q 3 P V = i 4πε q i i dq q 3 P V = 4πε dq ample of integating
Review: Lectue : Consevation of negy and Potential Gadient Two ways to find V at any point in space: Integate dl: Sum o Integate ove chages: q q 3 P V = i 4πε q i i dq q 3 P V = 4πε dq ample of integating
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
a. Show that these lines intersect by finding the point of intersection. b. Find an equation for the plane containing these lines.
 Mah A Final Eam Problems for onsideraion. Show all work for credi. Be sure o show wha you know. Given poins A(,,, B(,,, (,, 4 and (,,, find he volume of he parallelepiped wih adjacen edges AB, A, and A.
Mah A Final Eam Problems for onsideraion. Show all work for credi. Be sure o show wha you know. Given poins A(,,, B(,,, (,, 4 and (,,, find he volume of he parallelepiped wih adjacen edges AB, A, and A.
