Thoughts on Maser Case
|
|
|
- Archibald Abel Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 School of Statistics University of Minnesota March 5, 2007
2 Maser case SiO masers orbiting variable star. Could be radiatively pumped or shockwave pumped. If radiatively pumped, all fluxes should go up and down together. If shock pumped, fluxes may peak at different times. Velocity centroid should be correlated with flux if shock pumped.
3 Client questions Base question: radiation or shock pumping? Specific question: should I look at lagged cross correlation plots? I gave you guys some specific questions.
4 What further information would you like to have about the set up? I d like to know about the velocity centroid. I guess that velocity is the orbital velocity of the maser around the star, but it could be the velocity of the maser relative to earth. (Both based on Dopler shift of the radio frequency?) Velocity centroid is some kind of mean velocity.
5 Set up continued Kepler s third law implies that orbital velocity decreases with distance to the star, so VC may be an inverse measure of distance. Presumably greater flux at lesser distance, so greater flux at greater velocity. But I d expect this for both radiative and shock pumped masers, so what am I missing? This is all guess work, so I may be completely wrong about what the velocity centroid is.
6 What further information would you like to have about the data? How often do we observe multiple masers on the same night? How smooth is the temporal pattern? Does the temporal pattern look sinusoidal? Is the periodic pattern stable? How much noise is there? Do we have similar amounts of data for all masers? Do we have flux data for the star?
7 Lagged cross-correlation Two sequences of data x 1, x 2,..., x n and y 1, y 2,..., y n. We can correlate x i and y i ; this is a cross-correlation. We can correlate x i and y i k ; this is a lag-k cross-correlation. For example, if we have hourly temperatures at two stations, we could correlate x i and y i 24. If they are two time zones apart, might want to correlate x i and y i 22.
8 Lagged cross-correlation, continued By changing the lag k, find the shift k m with highest correlation. If k m = 0, the sequences are in phase. Otherwise, out of phase by lag amount. So lagged cross-correlation gets at what she wants.
9 But... We need concurrent data for lagged cross-correlation. Equal spacing is even better. We have neither. So, either we abandon the approach, or we have to impute to equal-spaced concurrent data. Imputing should give a decent answer if temporal patterns are smooth and regular. There may be problems if relative lag changes over time, because the statistic is for all the data.
10 What do we tell her? If data are reasonably smooth, regular, and dense, peak of lagged cross-correlation after imputation should work OK. However, don t make confidence/reliability statements about the correlations. Otherwise, need to work with statistician.
11 OK, now with data Always begin with graphics!
12 Three with most data
13 Magnitude of star Data from the AAVSO International data base,
14 What do we see? Four masers, two with lots of data, one with very little. Some drift in flux. Seem to go up and down together at first, perhaps not later. Period should be 1 (length of period of star), but seems longer at the end. At least at first, masers peak after the star. Star is fairly regular, but a bit less bright near the end.
15 Sinuosids Let t be time in solar phase cycles, and let y t = µ t + A t cos(2π(t φ t )) A t is amplitude and φ t is phase (here, in cycles). Equivalent to y t = µ t + A t cos(2πφ t ) cos(2πt) + sin(2πφ t ) sin(2πt) or y t = µ t + w 0t cos(2πt) + w 1t sin(2πt) where A t = w 2 0t + w 2 1t φ t = atan(w 0t, w 1t )/(2π)
16 Local Sinusoidal Regression For general data, A t and φ t will change over time, but they may change smoothly. 1 Take a window of data, say one nominal cycle. 2 Regress y t on cos(2πt), sin(2πt), and t. 3 Convert coefficients to amplitude and phase. 4 Shift window over (can overlap current window) and repeat. This gives a series of amplitude and phase. Note: I added a trend term in the regression (for drift in flux) and require at least 10 data points in the window to do the fit.
17 Phase tells us... If masers are radiatively pumped, they should all have phase zero (ie, in lock step with the star). If masers all have the same non-zero phase, they could be shock pumped and the same distance from the star If phase increases, period of maser is lengthening (vice versa for decreases). Increasing phase could be due to period of star changing (does not seem to be happening here, but does for some variable stars). Increasing phase might suggest that maser has eccentric elliptical orbit and is moving away from the star (and the shock waves).
18 The envelope please
19 Mixed results 1 All masers have the same phase up to cumulative phase 3. 2 This phase is about 1/3 to 1/5 of a cycle behind the star, decreasing over the first two cycles. 3 After 3, first maser continues slight phase decrease but is fairly stable. 4 After 3, the other two masers increase phase (lengthen period). 5 This seems to argue that all three are shock pumped.
20 Constant term
21 Slope term
22 Constant and slope and star By size, largest peaks in star brightness are at 1, 3, 2, and 4 (much smaller). Constant terms follow this pattern: higher mean when star is brighter. At 1, we must have a general decrease to have a lower peak at 2; at 2 we must have a general increase to have a higher peak at three; etc. Slope terms follow this pattern.
23 Amplitude term Difficult to generalize here:
24 Velocity centroid
25 Who knows? Overall negative correlation between velocity and flux. Maser with smallest flux has highest velocities, and masers with greastest flux have smallest velocities. No correlation between flux and velocity for masers 1 and 3. Positive correlation between flux and velocity for maser 2. I don t know what to say about this.
26 Summary Masers seem to be shock pumped. Behavior changes after cumulative phase 3. Velocity centroid is still a mystery.
THE SUN, THE MOON AND OUR SOLAR SYSTEM TEACHER NOTES TO SHARE WITH STUDENTS
 THE SUN, THE MOON AND OUR SOLAR SYSTEM TEACHER NOTES TO SHARE WITH STUDENTS The Sun is the biggest feature in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar
THE SUN, THE MOON AND OUR SOLAR SYSTEM TEACHER NOTES TO SHARE WITH STUDENTS The Sun is the biggest feature in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Name: Here are those topics:
 Name: Spring Break Project rowittscience@gmail.com The wonders of our Earth extend beyond the confines of the rocky sediments that hold the story of our past. Scientists, with their continued determination
Name: Spring Break Project rowittscience@gmail.com The wonders of our Earth extend beyond the confines of the rocky sediments that hold the story of our past. Scientists, with their continued determination
Every Galaxy has a massive black hole. Review 20 Nov
 Every Galaxy has a massive black hole. Review 20 Nov Homework 9 is due at the end of class. Pick up answers. Answers will also be on angel. Black holes in the centers of galaxies Wed: Milky Way has a black
Every Galaxy has a massive black hole. Review 20 Nov Homework 9 is due at the end of class. Pick up answers. Answers will also be on angel. Black holes in the centers of galaxies Wed: Milky Way has a black
The Revolution of the Moons of Jupiter
 The Revolution of the Moons of Jupiter Overview: During this lab session you will make use of a CLEA (Contemporary Laboratory Experiences in Astronomy) computer program generously developed and supplied
The Revolution of the Moons of Jupiter Overview: During this lab session you will make use of a CLEA (Contemporary Laboratory Experiences in Astronomy) computer program generously developed and supplied
Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe. Galactic rotation curves
 Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe Galactic rotation curves Orbital speed as a function of distance from the center: rotation_of_spiral_galaxy.htm Use Kepler s Third Law to get
Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe Galactic rotation curves Orbital speed as a function of distance from the center: rotation_of_spiral_galaxy.htm Use Kepler s Third Law to get
How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy?
 Ch 14: Mysteries of the Milky Way How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy? The Structure of the Galaxy We know that our galaxy has
Ch 14: Mysteries of the Milky Way How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy? The Structure of the Galaxy We know that our galaxy has
Extrasolar planets. Lecture 23, 4/22/14
 Extrasolar planets Lecture 23, 4/22/14 Extrasolar planets Extrasolar planets: planets around other stars Also called exoplanets 1783 exoplanets discovered as of 4/21/14 Orbitting 1105 different stars Number
Extrasolar planets Lecture 23, 4/22/14 Extrasolar planets Extrasolar planets: planets around other stars Also called exoplanets 1783 exoplanets discovered as of 4/21/14 Orbitting 1105 different stars Number
[04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17)
![[04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17) [04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17)](/thumbs/79/80259995.jpg) 1 [04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17) Upcoming Items Homework #2 due next lecture. Read Ch. 3.3 and do the self-study quizzes for next lecture, and skim 2.4, 3.1, 3.2, & 3.4. https://pbs.twimg.com/media/dh69il_u0aenivq.jpg:large
1 [04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17) Upcoming Items Homework #2 due next lecture. Read Ch. 3.3 and do the self-study quizzes for next lecture, and skim 2.4, 3.1, 3.2, & 3.4. https://pbs.twimg.com/media/dh69il_u0aenivq.jpg:large
The Milky Way Galaxy
 1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
Seasons Motions of the Sun
 ASTR1010 Lecture 6 31 Jan 13 Today How the Sky Works: Phases, Eclipses, Precession, Planets Announcements: Exam 1 Review sheets available up front Old-Fashioned Homework 1 emailed, due ON PAPER Tues SkyGazer
ASTR1010 Lecture 6 31 Jan 13 Today How the Sky Works: Phases, Eclipses, Precession, Planets Announcements: Exam 1 Review sheets available up front Old-Fashioned Homework 1 emailed, due ON PAPER Tues SkyGazer
Planet Detection. AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System
 Review AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM III this THURSDAY 04/8 covering LECT. 17 through We ve talked about the Terrestrial Planets and the Jovian Planets - What about planets around other
Review AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM III this THURSDAY 04/8 covering LECT. 17 through We ve talked about the Terrestrial Planets and the Jovian Planets - What about planets around other
Quasars, Pulsars, Gamma- Ray Bursts! Oh, my! Collapsars, magnetars, X- ray pulsars, γ-ray pulsars, millisecond radio pulsars...
 Quasars, Pulsars, Gamma- Ray Bursts! Oh, my! Collapsars, magnetars, X- ray pulsars, γ-ray pulsars, millisecond radio pulsars... Giacconi et al. (1962) Rocket carried 3 Geiger counters to 225km - one counter
Quasars, Pulsars, Gamma- Ray Bursts! Oh, my! Collapsars, magnetars, X- ray pulsars, γ-ray pulsars, millisecond radio pulsars... Giacconi et al. (1962) Rocket carried 3 Geiger counters to 225km - one counter
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us.
 Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Galaxy Classification
 Galaxies Galaxies are collections of billons of stars; our home galaxy, the Milky Way, is a typical example. Stars, gas, and interstellar dust orbit the center of the galaxy due to the gravitational attraction
Galaxies Galaxies are collections of billons of stars; our home galaxy, the Milky Way, is a typical example. Stars, gas, and interstellar dust orbit the center of the galaxy due to the gravitational attraction
Properties of Stars. 1.1 Brightnesses of Stars
 Properties of Stars 1.1 Brightnesses of Stars I m sure you have noticed that some stars are very bright, others less bright, and some are quite dim. There is a true brightness of a star and an apparent
Properties of Stars 1.1 Brightnesses of Stars I m sure you have noticed that some stars are very bright, others less bright, and some are quite dim. There is a true brightness of a star and an apparent
Name. F = ma P 2 = a 3 (M + m) P 2 = a 3. maxt = 2900 K m
 Spring 2019 Astronomy - Test 1 Test form D Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form D on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Spring 2019 Astronomy - Test 1 Test form D Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form D on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
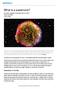 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry. Exoplanets
 Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
When to Do the Gridding?
 Part 6: Objective Analysis Optimum Interpolation Composite Analysis When to Do the Gridding? The methods described are applicable to any problem where the data you are given do not fill the domain of interest
Part 6: Objective Analysis Optimum Interpolation Composite Analysis When to Do the Gridding? The methods described are applicable to any problem where the data you are given do not fill the domain of interest
Solar Observation Class Project
 Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
What does the Sun tell us about circular polarization on stars? Stephen White
 What does the Sun tell us about circular polarization on stars? Stephen White The Radio Sun at 4.6 GHz Combination of: optically thick upper chromosphere, optically thick coronal gyroresonance where B>500
What does the Sun tell us about circular polarization on stars? Stephen White The Radio Sun at 4.6 GHz Combination of: optically thick upper chromosphere, optically thick coronal gyroresonance where B>500
ATMS 321: Natural Climate Variability Chapter 11
 ATMS 321: Natural Climate Variability Chapter 11 Solar Variability: Total solar irradiance variability is relatively small about a tenth of a percent. Ultraviolet variability is larger, and so could affect
ATMS 321: Natural Climate Variability Chapter 11 Solar Variability: Total solar irradiance variability is relatively small about a tenth of a percent. Ultraviolet variability is larger, and so could affect
ORF 245 Fundamentals of Statistics Practice Final Exam
 Princeton University Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering ORF 245 Fundamentals of Statistics Practice Final Exam January??, 2016 1:00 4:00 pm Closed book. No computers. Calculators
Princeton University Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering ORF 245 Fundamentals of Statistics Practice Final Exam January??, 2016 1:00 4:00 pm Closed book. No computers. Calculators
The Dark Side of the Universe: Dark matter in the galaxy and Cosmos
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Public Talks Astrophysics 1-18-2011 The Dark Side of the Universe: Dark matter in the galaxy and Cosmos Shane L. Larson Utah State University Follow this and additional
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Public Talks Astrophysics 1-18-2011 The Dark Side of the Universe: Dark matter in the galaxy and Cosmos Shane L. Larson Utah State University Follow this and additional
Nibiru Is Not Here Yet
 Nibiru Is Not Here Yet The title says it all. Do not be fooled, any photos of the sun that show a bright object near to the sun is either a lens artifact caused by internal reflection of light in the camera
Nibiru Is Not Here Yet The title says it all. Do not be fooled, any photos of the sun that show a bright object near to the sun is either a lens artifact caused by internal reflection of light in the camera
Next quiz: Monday, October 24
 No homework for Wednesday Read Chapter 8! Next quiz: Monday, October 24 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Types of Spectra: Pictorial Some light sources are comprised of all colors (white light). Other light
No homework for Wednesday Read Chapter 8! Next quiz: Monday, October 24 1 Chapter 7 Atoms and Starlight Types of Spectra: Pictorial Some light sources are comprised of all colors (white light). Other light
Introduction to the Sun
 Lecture 15 Introduction to the Sun Jiong Qiu, MSU Physics Department Open Q: what physics do we learn about the Sun? 1. Energy - nuclear energy - magnetic energy 2. Radiation - continuum and line emissions;
Lecture 15 Introduction to the Sun Jiong Qiu, MSU Physics Department Open Q: what physics do we learn about the Sun? 1. Energy - nuclear energy - magnetic energy 2. Radiation - continuum and line emissions;
What is a Satellite? A satellite is an object that orbits another object. Ex. Radio satellite, moons, planets
 Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
ASTR 200 : Lecture 13 Doppler Effect and binary motion
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 13 Doppler Effect and binary motion 1 Announcements Reminder: Midterm is Oct 22, in class, 50 minutes long. More information provided next week. HW 1 solutions now posted on the course
ASTR 200 : Lecture 13 Doppler Effect and binary motion 1 Announcements Reminder: Midterm is Oct 22, in class, 50 minutes long. More information provided next week. HW 1 solutions now posted on the course
10/16/ Detecting Planets Around Other Stars. Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds
 10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
Unit 5 Gravitation. Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion
 Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
University of Maryland Department of Physics. Spring 2009 Final Exam 20. May (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No
 University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I
 Astrophysics Study of Light Study of Atoms Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I 1 Atomic Physics elements: substances which cannot be broken down into simpler substances atom : smallest unit of an element
Astrophysics Study of Light Study of Atoms Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I 1 Atomic Physics elements: substances which cannot be broken down into simpler substances atom : smallest unit of an element
Regression I - the least squares line
 Regression I - the least squares line The difference between correlation and regression. Correlation describes the relationship between two variables, where neither variable is independent or used to predict.
Regression I - the least squares line The difference between correlation and regression. Correlation describes the relationship between two variables, where neither variable is independent or used to predict.
Lecture 25: The Outer Planets
 Lecture 25: The Outer Planets Neptune Uranus Pluto/Charon Uranus and three moons Neptune and two moons 1 The Outer Planets Uranus Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, who realized that this extended
Lecture 25: The Outer Planets Neptune Uranus Pluto/Charon Uranus and three moons Neptune and two moons 1 The Outer Planets Uranus Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, who realized that this extended
The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets!
 The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets! Kepler Spacecraft Can we believe this result? What techniques and data were used to derive this important result? 1 How to
The Kepler Mission: 20% of all Stars in the Milky Way Have Earth like Planets! Kepler Spacecraft Can we believe this result? What techniques and data were used to derive this important result? 1 How to
Final key scientist in this story: Galileo Galilei
 Announcements Astronomy 101: 9/30/2008 Exam study materials are posted on the course web page, and a practice exam is available in OWL. Homework 2 is now available on the OWL Due 10/01/08 before midnight
Announcements Astronomy 101: 9/30/2008 Exam study materials are posted on the course web page, and a practice exam is available in OWL. Homework 2 is now available on the OWL Due 10/01/08 before midnight
Recall: The Importance of Light
 Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations. Earth-Sun Distance. Eccentricity 2/2/2010. ATS351 Lecture 3
 Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations ATS351 Lecture 3 Earth-Sun Distance Change in distance has only a minimal effect on seasonal temperature. Note that during the N. hemisphere winter, we are CLOSER to
Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations ATS351 Lecture 3 Earth-Sun Distance Change in distance has only a minimal effect on seasonal temperature. Note that during the N. hemisphere winter, we are CLOSER to
Binary sources of gravitational waves
 Binary sources of gravitational waves For our final two lectures we will explore binary systems in general and the Advanced LIGO detections in particular. Binaries obviously have a large and varying quadrupole
Binary sources of gravitational waves For our final two lectures we will explore binary systems in general and the Advanced LIGO detections in particular. Binaries obviously have a large and varying quadrupole
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
The Double Pulsar:! A Decade of Discovery! (and what you can do over the next decade with FAST!)
 The Double Pulsar:! A Decade of Discovery! (and what you can do over the next decade with FAST!) Maura McLaughlin West Virginia University 20 May 2014 : Double neutron star systems" The pulsar catalog
The Double Pulsar:! A Decade of Discovery! (and what you can do over the next decade with FAST!) Maura McLaughlin West Virginia University 20 May 2014 : Double neutron star systems" The pulsar catalog
Masers around evolved stars from kinematics to physics
 Masers around evolved stars from kinematics to physics Anita Richards UK ARC, JBCA, Manchester with thanks to Al-Muntafki, Bains, Bartkiewicz, Diamond, Elitzur, Etoka, Gray, Humphreys, Murakawa, Rosa-Gonzalez,
Masers around evolved stars from kinematics to physics Anita Richards UK ARC, JBCA, Manchester with thanks to Al-Muntafki, Bains, Bartkiewicz, Diamond, Elitzur, Etoka, Gray, Humphreys, Murakawa, Rosa-Gonzalez,
The Challenge of AZ Cas-Part 1. John Menke Barnesville, MD Abstract
 The Challenge of AZ Cas-Part 1 John Menke Barnesville, MD 20838 john@menkescientific.com www.menkescientific.com Abstract This is an interim report on observations of the spectrum of AZCas taken during
The Challenge of AZ Cas-Part 1 John Menke Barnesville, MD 20838 john@menkescientific.com www.menkescientific.com Abstract This is an interim report on observations of the spectrum of AZCas taken during
An introduction to closure phases
 An introduction to closure phases Michelson Summer Workshop Frontiers of Interferometry: Stars, disks, terrestrial planets Pasadena, USA, July 24 th -28 th 2006 C.A.Haniff Astrophysics Group, Department
An introduction to closure phases Michelson Summer Workshop Frontiers of Interferometry: Stars, disks, terrestrial planets Pasadena, USA, July 24 th -28 th 2006 C.A.Haniff Astrophysics Group, Department
PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #5 (Page 1/4) NAME: KEY
 PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #5 (Page 1/) NAME: KEY Due Date: start of class /12/2007 5 pts extra credit if turned in before 9:00AM (early!) (To get the extra credit, the assignment must
PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #5 (Page 1/) NAME: KEY Due Date: start of class /12/2007 5 pts extra credit if turned in before 9:00AM (early!) (To get the extra credit, the assignment must
Class 16. Prof J. Kenney October 31, Relativity
 Class 16 Prof J. Kenney October 31, 2016 Relativity Length contraction (moving sticks are shorter) A measuring stick at rest has a length Lo. When it is propelled at velocity v, it has a shorter length
Class 16 Prof J. Kenney October 31, 2016 Relativity Length contraction (moving sticks are shorter) A measuring stick at rest has a length Lo. When it is propelled at velocity v, it has a shorter length
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
7/9. What happens to a star depends almost completely on the mass of the star. Mass Categories: Low-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses and less
 7/9 What happens to a star depends almost completely on the mass of the star. Mass Categories: Low-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses and less Medium-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses up to between 2 and 3 solar masses.
7/9 What happens to a star depends almost completely on the mass of the star. Mass Categories: Low-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses and less Medium-Mass Stars 0.2 solar masses up to between 2 and 3 solar masses.
Name. Satellite Motion Lab
 Name Satellite Motion Lab Purpose To experiment with satellite motion using an interactive simulation in order to gain an understanding of Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion and Newton s Law of Universal
Name Satellite Motion Lab Purpose To experiment with satellite motion using an interactive simulation in order to gain an understanding of Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion and Newton s Law of Universal
Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars
 Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars Finding Black Holes "Yesterday upon the stair I met a man who wasn't there. He wasn't there again today. I wish that man would go away." Hughes Mearns (1875-1965)
Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars Finding Black Holes "Yesterday upon the stair I met a man who wasn't there. He wasn't there again today. I wish that man would go away." Hughes Mearns (1875-1965)
Space! Science Year 5/6B Autumn 2. Earth and Space. Session 2. Resource Pack
 Science Year 5/6B Autumn 2 Earth and Space Space! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you
Science Year 5/6B Autumn 2 Earth and Space Space! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you
Analysis of the 500 mb height fields and waves: testing Rossby wave theory
 Analysis of the 500 mb height fields and waves: testing Rossby wave theory Jeffrey D. Duda, Suzanne Morris, Michelle Werness, and Benjamin H. McNeill Department of Geologic and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa
Analysis of the 500 mb height fields and waves: testing Rossby wave theory Jeffrey D. Duda, Suzanne Morris, Michelle Werness, and Benjamin H. McNeill Department of Geologic and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa
Alien Skies. Todd Timberlake
 Alien Skies Todd Timberlake Have you ever wanted to send your students to another planet? What would they see while looking up at the skies from their new home? Would they be able to interpret what they
Alien Skies Todd Timberlake Have you ever wanted to send your students to another planet? What would they see while looking up at the skies from their new home? Would they be able to interpret what they
The Physics of Light, part 2. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Chapter 7 SAMPLE OBSERVATION by Gene Hanson, experienced AAVSO member/observer and mentor
 Chapter 7 SAMPLE OBSERVATION by Gene Hanson, experienced AAVSO member/observer and mentor In this chapter, we will review the step-by-step instructions that were presented in Chapter 2 (page 9) by making
Chapter 7 SAMPLE OBSERVATION by Gene Hanson, experienced AAVSO member/observer and mentor In this chapter, we will review the step-by-step instructions that were presented in Chapter 2 (page 9) by making
Time Variability of Molecular Line Emission in IRC+10216
 Time Variability of Molecular Line Emission in IRC+10216 David Teyssier, ESA-ESAC, Spain J. Cernicharo, G. Quintana-Lacaci, M. Agúndez, M. Barlow, E. de Beck, F. Daniel, L. Decin, P. GarciaLario, M. Groenewegen,
Time Variability of Molecular Line Emission in IRC+10216 David Teyssier, ESA-ESAC, Spain J. Cernicharo, G. Quintana-Lacaci, M. Agúndez, M. Barlow, E. de Beck, F. Daniel, L. Decin, P. GarciaLario, M. Groenewegen,
60 C From Bicycle to Space. Dionysis Konstantinou Corina Toma. Space Travel
 60 C From Bicycle to Space Dionysis Konstantinou Corina Toma C Space Travel From Bicycle Length to Space of the CDay61 introduction Imagine travelling from one planet to another Why is it that we have
60 C From Bicycle to Space Dionysis Konstantinou Corina Toma C Space Travel From Bicycle Length to Space of the CDay61 introduction Imagine travelling from one planet to another Why is it that we have
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8
 The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
Relativity. Class 16 Prof J. Kenney June 18, boss
 Relativity Class 16 Prof J. Kenney June 18, 2018 boss Length contraction (moving sticks are shorter) A measuring stick at rest has a length Lo. When it is propelled at velocity v, it has a shorter length
Relativity Class 16 Prof J. Kenney June 18, 2018 boss Length contraction (moving sticks are shorter) A measuring stick at rest has a length Lo. When it is propelled at velocity v, it has a shorter length
Mercury Data (Table 11-1) 11a. Sun-Scorched Mercury. Mercury Data: Numbers
 11a. Sun-Scorched Mercury Earth-based observations of Mercury Mercury s rotation & year Mariner 10 s images of Mercury Mercury s interior Mercury Data (Table 11-1) Mercury Data: Numbers Diameter: 4,878.km
11a. Sun-Scorched Mercury Earth-based observations of Mercury Mercury s rotation & year Mariner 10 s images of Mercury Mercury s interior Mercury Data (Table 11-1) Mercury Data: Numbers Diameter: 4,878.km
Cosmology. What is Cosmology?
 Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Eclipsing binary stars
 SEMINAR - 4. LETNIK Eclipsing binary stars Author: Daša Rozmus Mentor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Ljubljana, November 2010 Abstract Observations indicate that the majority of stars have a companion, thus that stars
SEMINAR - 4. LETNIK Eclipsing binary stars Author: Daša Rozmus Mentor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Ljubljana, November 2010 Abstract Observations indicate that the majority of stars have a companion, thus that stars
2. Can observe radio waves from the nucleus see a strong radio source there Sagittarius A* or Sgr A*.
 7/7 The Nucleus of the MW its center 1. Can t see the nucleus in visible light too much stuff in the way. 2. Can observe radio waves from the nucleus see a strong radio source there Sagittarius A* or Sgr
7/7 The Nucleus of the MW its center 1. Can t see the nucleus in visible light too much stuff in the way. 2. Can observe radio waves from the nucleus see a strong radio source there Sagittarius A* or Sgr
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology
 AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E S 8-9 Part B, Lectures 8-9 23 March, 2017 C O N T E N T S In this lecture, we will look at factors that cause an orbit to change over time orbital
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E S 8-9 Part B, Lectures 8-9 23 March, 2017 C O N T E N T S In this lecture, we will look at factors that cause an orbit to change over time orbital
Point Spread Functions. Aperture Photometry. Obs Tech Obs Tech 26 Sep 2017
 Point Spread Functions & Aperture Photometry Obs Tech Obs Tech 26 Sep 2017 Point Spread Functions (PSFs) Stars are far away (typically d >> 3x10 15 km) Stars are relatively small (D ~ 10 6 km) Angular
Point Spread Functions & Aperture Photometry Obs Tech Obs Tech 26 Sep 2017 Point Spread Functions (PSFs) Stars are far away (typically d >> 3x10 15 km) Stars are relatively small (D ~ 10 6 km) Angular
A MULTI-TRANSITION SEARCH FOR CLASS I METHANOL MASERS
 A MULTI-TRANSITION SEARCH FOR CLASS I METHANOL MASERS Cara Denise Battersby MIT Haystack Observatory REU Summer 2004 Mentors: Preethi Pratap and Phil Shute ABSTRACT Class I methanol masers have been detected
A MULTI-TRANSITION SEARCH FOR CLASS I METHANOL MASERS Cara Denise Battersby MIT Haystack Observatory REU Summer 2004 Mentors: Preethi Pratap and Phil Shute ABSTRACT Class I methanol masers have been detected
The sun then falls below the horizon, and it is nighttime for our little person:
 Venus Update! Problem 6 on Homework 1 in Physics 2A last September asked you to find the distance from Earth to Venus at that time. I gave you the angle between the sun and Venus at that time; you drew
Venus Update! Problem 6 on Homework 1 in Physics 2A last September asked you to find the distance from Earth to Venus at that time. I gave you the angle between the sun and Venus at that time; you drew
Copernican revolution Review
 opernican revolution Review Score: 1. How long does it take a planet to orbit the sun exactly once? Sidereal period Synodic period One rotation One day 2. Which of Kepler's laws is illustrated in the diagram?
opernican revolution Review Score: 1. How long does it take a planet to orbit the sun exactly once? Sidereal period Synodic period One rotation One day 2. Which of Kepler's laws is illustrated in the diagram?
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
> = + - < > = + - < > = + - < > + - < > = + - < > = + - < > = + - < > = By Marjorie Sheridan
 + - < = By Marjorie Sheridan + - < = + - < = Copyright 2013 All rights reserved by Marjorie Sheridan No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, graphic, electronic,
+ - < = By Marjorie Sheridan + - < = + - < = Copyright 2013 All rights reserved by Marjorie Sheridan No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, graphic, electronic,
Unit 16: Astronomy and space science. Learning aim A Understand the fundamental aspects of the solar system
 Unit 16: Astronomy and space science Learning aim A Understand the fundamental aspects of the solar system Contents page Note: anywhere you see a capital D means you MUST draw a diagram. Radiative zone
Unit 16: Astronomy and space science Learning aim A Understand the fundamental aspects of the solar system Contents page Note: anywhere you see a capital D means you MUST draw a diagram. Radiative zone
Abstract: Here, I use the basic principles of the McMahon field theory to explain the strong force and the weak force, as described for atoms.
 Copyright Version: 2 nd March, 2015, updated 10 th April, 2015 Page: 1 of 8 The Strong and weak forces- explained via McMahon field theory Abstract: Here, I use the basic principles of the McMahon field
Copyright Version: 2 nd March, 2015, updated 10 th April, 2015 Page: 1 of 8 The Strong and weak forces- explained via McMahon field theory Abstract: Here, I use the basic principles of the McMahon field
What is the evidence that Big Bang really occurred
 What is the evidence that Big Bang really occurred Hubble expansion of galaxies Microwave Background Abundance of light elements but perhaps most fundamentally... Darkness of the night sky!! The very darkness
What is the evidence that Big Bang really occurred Hubble expansion of galaxies Microwave Background Abundance of light elements but perhaps most fundamentally... Darkness of the night sky!! The very darkness
The Milky Way & Galaxies
 The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
Web sites and Worksheets
 Introduction Web sites and Worksheets Sandra Woodward Oakhill College Castle Hill (swoodward@oakhill.nsw.edu.au) Astronomy is a practical subject by nature. Unfortunately for teachers, many of the practical
Introduction Web sites and Worksheets Sandra Woodward Oakhill College Castle Hill (swoodward@oakhill.nsw.edu.au) Astronomy is a practical subject by nature. Unfortunately for teachers, many of the practical
Time Series and Forecasting
 Time Series and Forecasting Introduction to Forecasting n What is forecasting? n Primary Function is to Predict the Future using (time series related or other) data we have in hand n Why are we interested?
Time Series and Forecasting Introduction to Forecasting n What is forecasting? n Primary Function is to Predict the Future using (time series related or other) data we have in hand n Why are we interested?
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
Period Analysis on a Spreadsheet
 Aliases in Depth An alias for a period is another period where the data seemingly fits as well, or nearly so, as the correct period. The most common encounter with aliasing is when you observe a target
Aliases in Depth An alias for a period is another period where the data seemingly fits as well, or nearly so, as the correct period. The most common encounter with aliasing is when you observe a target
SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES
 HANDS-ON UNIVERSE DISCUSSION SHEET SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES In the spring of 1994 several high school students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various images had
HANDS-ON UNIVERSE DISCUSSION SHEET SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES In the spring of 1994 several high school students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various images had
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations You ve found planets in your data (or not)...... now what?! Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Why Astrostats? This week: a sample of
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Planet Populations You ve found planets in your data (or not)...... now what?! Angie Wolfgang NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Penn State Why Astrostats? This week: a sample of
Problem Set I Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy
 Problem Set I Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy Problem 1.1 The ideal terrestrial locations from which one can observe all the stars over the course of a year lie along the Earth s equator, which,
Problem Set I Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy Problem 1.1 The ideal terrestrial locations from which one can observe all the stars over the course of a year lie along the Earth s equator, which,
Astronomy 421. Lecture 8: Binary stars
 Astronomy 421 Lecture 8: Binary stars 1 Key concepts: Binary types How to use binaries to determine stellar parameters The mass-luminosity relation 2 Binary stars So far, we ve looked at the basic physics
Astronomy 421 Lecture 8: Binary stars 1 Key concepts: Binary types How to use binaries to determine stellar parameters The mass-luminosity relation 2 Binary stars So far, we ve looked at the basic physics
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Light carries energy. Lecture 5 Understand Light. Is light. Light as a Particle. ANSWER: Both.
 Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Determining the magnitudes and spectral types of the components of the binary Mira X Ophiuchi
 Determining the magnitudes and spectral types of the components of the binary Mira X Ophiuchi David Boyd Variable Star Section, British Astronomical Association, [davidboyd@orion.me.uk] Abstract Several
Determining the magnitudes and spectral types of the components of the binary Mira X Ophiuchi David Boyd Variable Star Section, British Astronomical Association, [davidboyd@orion.me.uk] Abstract Several
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes
 Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Exam# 1 Review Gator 1 Keep the first page of the exam. Scores will be published using the exam number Chapter 0 Charting the Heavens
 Exam# 1 Review Exam is Wednesday October 11 h at 10:40AM, room FLG 280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 (HB) with eraser. We provide the scantrons No use of calculator or any electronic device during
Exam# 1 Review Exam is Wednesday October 11 h at 10:40AM, room FLG 280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 (HB) with eraser. We provide the scantrons No use of calculator or any electronic device during
AP Statistics. Chapter 6 Scatterplots, Association, and Correlation
 AP Statistics Chapter 6 Scatterplots, Association, and Correlation Objectives: Scatterplots Association Outliers Response Variable Explanatory Variable Correlation Correlation Coefficient Lurking Variables
AP Statistics Chapter 6 Scatterplots, Association, and Correlation Objectives: Scatterplots Association Outliers Response Variable Explanatory Variable Correlation Correlation Coefficient Lurking Variables
Galileo Educator Network
 Galileo Educator Network D1.3 Moons of Jupiter (1 hour and 45 minutes + 15 minute Break) 1. Observing Jupiter s Moons (15 minutes) Explain how Galileo used the telescope to learn more about objects in
Galileo Educator Network D1.3 Moons of Jupiter (1 hour and 45 minutes + 15 minute Break) 1. Observing Jupiter s Moons (15 minutes) Explain how Galileo used the telescope to learn more about objects in
Nonlinear Equations. Not guaranteed to have any real solutions, but generally do for astrophysical problems.
 Nonlinear Equations Often (most of the time??) the relevant system of equations is not linear in the unknowns. Then, cannot decompose as Ax = b. Oh well. Instead write as: (1) f(x) = 0 function of one
Nonlinear Equations Often (most of the time??) the relevant system of equations is not linear in the unknowns. Then, cannot decompose as Ax = b. Oh well. Instead write as: (1) f(x) = 0 function of one
Physics Lab #5: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon
 Physics 10293 Lab #5: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon Introduction Today, we are going to use the Starry Night software to learn about motion of the stars, sun and moon on the celestial sphere.
Physics 10293 Lab #5: Starry Night Observations of the Sun and Moon Introduction Today, we are going to use the Starry Night software to learn about motion of the stars, sun and moon on the celestial sphere.
It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick, and our solar system is located 26,000 ly away from the center of the galaxy.
 The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
Figure 1: three bodies orbiting each other
 PHAS2443 Practical Mathematics II Orbiting Bodies: The Dance of the Stars Introduction When one thinks of planetary motion a similar image of our solar system comes up where one massive body is being orbited
PHAS2443 Practical Mathematics II Orbiting Bodies: The Dance of the Stars Introduction When one thinks of planetary motion a similar image of our solar system comes up where one massive body is being orbited
Elizabeth Lovegrove. Los Alamos National Laboratory
 Elizabeth Lovegrove Los Alamos National Laboratory 06.08.2017 OUTLINE VLE SNe & Shock Breakout Theory CASTRO Simulations Prospects for Observations Conclusions & Future Work 06.08.2017 2 IN CASE YOU HAVE
Elizabeth Lovegrove Los Alamos National Laboratory 06.08.2017 OUTLINE VLE SNe & Shock Breakout Theory CASTRO Simulations Prospects for Observations Conclusions & Future Work 06.08.2017 2 IN CASE YOU HAVE
Today in Astronomy 328: binary stars
 Today in Astronomy 38: binary stars Binary-star systems. Direct measurements of stellar mass and radius in eclipsing binary-star systems. At right: two young binary star systems in the Taurus star-forming
Today in Astronomy 38: binary stars Binary-star systems. Direct measurements of stellar mass and radius in eclipsing binary-star systems. At right: two young binary star systems in the Taurus star-forming
Milky Way Structure. Nucleus Disk Halo Sun is about 30,000 LY from center
 Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way spiral galaxy - flattened disk 150,000 LY in diameter with about 400 billion stars we sit in a gas/dust arm - active star formation - absorbs visible light study using IR/radio/gamma
Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way spiral galaxy - flattened disk 150,000 LY in diameter with about 400 billion stars we sit in a gas/dust arm - active star formation - absorbs visible light study using IR/radio/gamma
ASTR Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
UCSD SIO221c: (Gille) 1
 UCSD SIO221c: (Gille) 1 Edge effects in spectra: detrending, windowing and pre-whitening One of the big challenges in computing spectra is to figure out how to deal with edge effects. Edge effects matter
UCSD SIO221c: (Gille) 1 Edge effects in spectra: detrending, windowing and pre-whitening One of the big challenges in computing spectra is to figure out how to deal with edge effects. Edge effects matter
