Point Spread Functions. Aperture Photometry. Obs Tech Obs Tech 26 Sep 2017
|
|
|
- Mervin Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Point Spread Functions & Aperture Photometry Obs Tech Obs Tech 26 Sep 2017
2 Point Spread Functions (PSFs) Stars are far away (typically d >> 3x10 15 km) Stars are relatively small (D ~ 10 6 km) Angular spread D/d = 3x10-10 rad < 60 microarcsec This is very close to "point-like" Atmospheric turbulence blurs this to ~1 arcsec The shape of the blur is the "point spread function" p p p (how the light from a point is spread out)
3 What do PSFs look like? Surface plot of bright star in skysubtracted version of pstds.0001 Axi-symmetric, centrally peaked Basically 2-D Gaussian
4 PSF: Real vs. Gaussian Real Star 2-D Gaussian Difference
5 Implications Atmospheric turbulence produces Gaussian profiles (Central Limit Theorem) If turbulence dominates (typically true), we can understand PSFs Light from stars spread all over the place 1 radius 67% insideid 2 radius 95% inside 3 radius 99.8% inside
6 Why ydo brighter big stars appear larger than fainter stars? Hint1: The turbulence is the same PSF is the same Hint2: We don't see starlight everywhere. A Question:
7 Stellar Photometry We want the starlight, the whole starlight, and nothing but the starlight We went to great efforts to get rid of nonstarlight effects But the whole starlight Gaussian PSF means light spread all over the sky (with exponentially decaying amplitude) What do we do?
8 Gaussian-Selected Aperture Photometry If we select a fiducial radius in terms of the Gaussian, we know what fraction of the total signal is inside that radius So... we measure the Gaussian shape using a bright star in the image (gauss2dfit.pro) We then measure the total number of ADU inside id some radius r As long as r is constant in (not necessarily in pixels), we can compare fluxes between images
9
10
11 How many?(cont.) So, the best number depends on the star But, we MUST choose 1 value for consistency Note that even for bright stars, ~2-3 gives near maximum Signal/Noise Also, must deal with other real-world effects (e.g. crowding/overlap)
12 One last thing IR sky varies fast (remember?) So: Image 0001 has 2.7 ADU/pixel residual sky background 0002 has -1.0 ADU/pix 0003 has has has has -0.3 etc.
13 Aperture Photometry (finally) Use bright star to get (why bright?) using gauss2dfit Pick fiducial num_sigma Find star center (not usually integer pixels) Get total flux inside num_sigma radius, and num_pixels Get average sky flux per pixel from annulus Subtract num_pixels*sky_ave from total flux Done! (Sort of...)
14 Practical points Getting ggaussian fits Getting star centers (gaussian fit or centroid?) Centroid: i c = ( i j i*im(i,j))/(σ i Σ j im(i,j)) j c = (Σ i Σ j j*im(i,j))/(σ i Σ j im(i,j)) Choosing annular regions for background
15 PSF-Fitting Fitting Photometry Obs Tech 24 Sep 2013
16 WhydoPSF-fitting? Star light not uniformly distributed inside aperture 2-D Gaussian (duh) Sky noise is uniformly distributed So, points far from center of aperature have much lower signal-to-noise noise ratio why give them equal weight? PSF-fitting (Gaussian fitting) gives lower weight to pixels expected to have lower SNR
17 PSF-Fitting Fitting Theory Amplitude = F pix /e -(r2/2* 2) Optimal weighting 1/ 2 2 A = 2 pix (e r2/2* 2 ) 2 For star flux dominated (bright star), this simplifies to simple aperture photometry For sky noise dominated (faint star), this simplifies to Gaussian weighting So, aperture photometry often OK PSF-fitting i photometry sometimes better...
18 PSF-Fitting Fitting Application Need to develop model for PSF usually NOT a simple Gaussian in real life PSF often changes across field of view as well Very hard to do by hand Typically rely on DAOPhot or similar code
19 Photometric Calibration: How bright IS it?
20 A Photometric Summary: We've subtracted sky background, electronic offsets, dark current We've corrected small-scale gain & QE variations iti We've corrected bad pixels and cosmic rays We've measured the (correct) number of ADU/s from a star Now, we need to convert this number of ADU to a physical flux standard star calibration
21 Photometric units Flux is energy per unit area per unit time ergs cm -2 s -1 W m -2 ADU/s (relative units) Absolute calibration is tough (sky and optical transmission, detector QE calibration, etc.) Vega ( Lyra) is THE standard star best absolute calibration (~10%) All other standard stars calibrated RELATIVE to Vega, using the magnitude system
22 Stellar Magnitudes Thus, stellar magnitudes are excellent relative brightness measurements, but mediocre absolute measurements Given two stars with fluxes (ADU or other units) we calculate the magnitudes m 2 -m 1 = -2.5 log(f 1 /F 2 ) mag g = 2.5 factor of 10 mag = 1.0 factor of 2.5 Larger mag fainter star (and vice versa)
23 Standard Star Calibration Measure ADU/s from target (F targ ) Measure ADU/s from standard star (F std ) Standard star has known magnitude (m std ) relative to Vega Magnitude of target is: m targ = -2.5*log(F targ /F std ) + m std
24 It's not quite that easy... This calibrates out the optical transmission, overall gain & QE, and rough atmospheric transmission Optical system, gain, QE generally constant Atmosphere roughly constant on good nights, but transmission depends on airmass (sec z) [explain airmass] Need atmospheric correction mag(z) = mag 0 + *sec(z)
25 Some common calibration mistakes Always compare ADU/s; same band; same telescope/instrument Always compare same aperture size (in ) Use normalized flatfield (or same flatfield image) Use same filter band Use band-dependent depe de atmospheric correction (varies night to night)
26 Extended Object Photometry Obs Tech Obs Tech 26 Sep 2017
27 Observing Extended Objects For point sources, we combine dithered images to get sky frames For this to work, most of the pixels in the image must be "sky-only" (no starlight); thus, median will pick the sky value For large extended targets (comparable to the field of view), this won't be the case So, the "standard" dither approach we have used will not work
28 Extended Targets - Solutions Sol'n 1: Dither around on target; move completely off-target and repeat dither; median-combine off-target frames for sky background; subtract this from individual ontarget frames; [why dither target?] Sol'n 2: Suck it up [meaning: do lots of ontarget dithering and median-combine; this will smooth out the pseudo-sky frame; this frame will have some residual target flux in each pixel; if this is small OK (?)]
29 Galaxy Photometry Stars are intrinsically "point-like" if you know the PSF shape (2-D Gaussian), measure some portion of it and extrapolate to total flux (e.g. 2 Galaxies are not point-like; in addition to the PSF, they have their own distribution of light F(x,y) Galaxy light comes from stars, clouds, etc. lumpy But, ~10 11 stars, etc. averages to smooth
30 Surface brightness Measure brightness per unit area as a function of position = "surface brightness" Typically units are magnitudes per square arcsecond Why use this? Because integrated brightness difficult/impossible to measure (vs. stars) More below...
31 "Iso" = same "phote" = light "Isophote" = same light Contours of equal light levels (units of mag per sq. arcsec) Useful for defining light profiles of galaxies - F sb (R) Isophotes
32 Types of Galaxies ë Elliptical Galaxy Spiral Galaxy ë R = sqrt(r 1 *r 2 ) R = radius ë Includes inclination Inclination elliptical
33 Galaxy Profiles "de Vaucouleurs law" F sb (R) ] exp(-r 1/4 ) Applies to elliptical galaxies; (Why?) Spiral galaxies have two components: bulge follows de Vaucouleurs law; disk follows F sb (R) ] exp(-r); (Why?) These are NOT caused by statistical averages of atmospheric turbulence, they are intrinsic to the galaxies Thus, they are typical approximations, NOT exact/correct; sometimes dead wrong
34 Isophotal Exceptions Foreground stars (can subtract using PSF model) dl) Nebulae in the galaxy ("valid" light) Dust lanes in the galaxy (ditto) Azimuthal asymmetry (e.g. Spiral galaxies) Irregular galaxies Isophote twists in otherwise "normal" galaxies
35 Misfit Galaxies - I
36 Misfit Galaxies - II
37 Misfit Galaxies - III Isophote twists in a spiral lbulge
38 So, now what? Given their limitations, isophote analysis is still useful Galaxy "effective radius" radius which encloses 50% of the total light Problem: How do you know light distribution shape (necessary for knowing "total light")? Answer: Assume de Vaucouleurs and/or exponential profiles But... are these correct? Probably not...
39 Other isophotal parameters Radius at the xx th mag isophote E.g. radius at V= 25 mag/sq. arcsec isophote This is an easily-definable quantity observationally Problem: To what physical quantity does this correspond? How does that complicate things?
40 Summary Very extended objects require different data- taking approaches Important concept for analysis are surface brightness and isophotes Surface brightness profiles have descriptive "laws" (which are broken more often than not) Isophote analysis can help quantify things, but is far from perfect This is all FAR more complicated than stars...
This week at Astro Lecture 06, Sep 13, Pick up PE#6. Please turn in HW#2. HW#3 is posted
 This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
Photometric Techniques II Data analysis, errors, completeness
 Photometric Techniques II Data analysis, errors, completeness Sergio Ortolani Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita di Padova, Italy. The fitting technique assumes the linearity of the intensity values
Photometric Techniques II Data analysis, errors, completeness Sergio Ortolani Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita di Padova, Italy. The fitting technique assumes the linearity of the intensity values
ASTRO 310: Galac/c & Extragalac/c Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney. Class 17 Mar 30, 2016 Starlight Distribu/ons in Disk Galaxies
 ASTRO 310: Galac/c & Extragalac/c Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 17 Mar 30, 2016 Starlight Distribu/ons in Disk Galaxies reminder no class next Monday, April 3!! 3 Color op/cal image of spiral galaxy
ASTRO 310: Galac/c & Extragalac/c Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 17 Mar 30, 2016 Starlight Distribu/ons in Disk Galaxies reminder no class next Monday, April 3!! 3 Color op/cal image of spiral galaxy
Basics of Photometry
 Basics of Photometry Photometry: Basic Questions How do you identify objects in your image? How do you measure the flux from an object? What are the potential challenges? Does it matter what type of object
Basics of Photometry Photometry: Basic Questions How do you identify objects in your image? How do you measure the flux from an object? What are the potential challenges? Does it matter what type of object
Data Processing in DES
 Data Processing in DES Brian Yanny Oct 28, 2016 http://data.darkenergysurvey.org/fnalmisc/talk/detrend.p Basic Signal-to-Noise calculation in astronomy: Assuming a perfect atmosphere (fixed PSF of p arcsec
Data Processing in DES Brian Yanny Oct 28, 2016 http://data.darkenergysurvey.org/fnalmisc/talk/detrend.p Basic Signal-to-Noise calculation in astronomy: Assuming a perfect atmosphere (fixed PSF of p arcsec
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe
 Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
Astronomy IRAF Tutorial for Exercise II Quick-look Photometry with Imexamine
 Astronomy 480 - IRAF Tutorial for Exercise II Quick-look Photometry with Imexamine Learning Objectives Files Used Define apparent and absolute magnitude. Explain how the magnitude scale is defined. Summarize
Astronomy 480 - IRAF Tutorial for Exercise II Quick-look Photometry with Imexamine Learning Objectives Files Used Define apparent and absolute magnitude. Explain how the magnitude scale is defined. Summarize
Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope
 Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope S.N. Kemp (skemp@ll.iac.es) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La
Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope S.N. Kemp (skemp@ll.iac.es) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La
Galaxies Astro 430/530 Prof. Jeff Kenney. CLASS 2 Jan 19, 2018 QuanDtaDve Morphology, Surface Brightness Profiles & Disks
 Galaxies Astro 430/530 Prof. Jeff Kenney CLASS 2 Jan 19, 2018 QuanDtaDve Morphology, Surface Brightness Profiles & Disks 1 2 Color opdcal image of spiral galaxy Isophotes contours of equal surface brightness
Galaxies Astro 430/530 Prof. Jeff Kenney CLASS 2 Jan 19, 2018 QuanDtaDve Morphology, Surface Brightness Profiles & Disks 1 2 Color opdcal image of spiral galaxy Isophotes contours of equal surface brightness
Ay Fall 2012 Imaging and Photometry Part I
 Ay 122 - Fall 2012 Imaging and Photometry Part I (Many slides today c/o Mike Bolte, UCSC) Imaging and Photometry Now essentially always done with imaging arrays (e.g., CCDs); it used to be with single-channel
Ay 122 - Fall 2012 Imaging and Photometry Part I (Many slides today c/o Mike Bolte, UCSC) Imaging and Photometry Now essentially always done with imaging arrays (e.g., CCDs); it used to be with single-channel
Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology. Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology
 Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology Galaxy structure contains clues about galaxy formation and evolution Point
Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology Galaxy structure contains clues about galaxy formation and evolution Point
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
IN REPORT: Plate Scale and FOV of CCD for Each Telescope using Albireo Stars
 USE ASTROIMAGEJ NOT AIP4WIN To download ALL the public data from Canvas, go to Files, then click the 3 dots next to the Public Data Folder and click Download. It will download all the files at once. 6.1
USE ASTROIMAGEJ NOT AIP4WIN To download ALL the public data from Canvas, go to Files, then click the 3 dots next to the Public Data Folder and click Download. It will download all the files at once. 6.1
AS750 Observational Astronomy
 Lecture 9 0) Poisson! (quantum limitation) 1) Diffraction limit 2) Detection (aperture) limit a)simple case b)more realistic case 3) Atmosphere 2) Aperture limit (More realistic case) Aperture has m pixels
Lecture 9 0) Poisson! (quantum limitation) 1) Diffraction limit 2) Detection (aperture) limit a)simple case b)more realistic case 3) Atmosphere 2) Aperture limit (More realistic case) Aperture has m pixels
Galaxy formation and evolution. Astro 850
 Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project
 AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
1 General Considerations: Point Source Sensitivity, Surface Brightness Sensitivity, and Photometry
 MUSTANG Sensitivities and MUSTANG-1.5 and - Sensitivity Projections Brian S. Mason (NRAO) - 6sep1 This technical note explains the current MUSTANG sensitivity and how it is calculated. The MUSTANG-1.5
MUSTANG Sensitivities and MUSTANG-1.5 and - Sensitivity Projections Brian S. Mason (NRAO) - 6sep1 This technical note explains the current MUSTANG sensitivity and how it is calculated. The MUSTANG-1.5
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
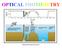 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment
 GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
PHYSICS Observing Guide
 PHYSICS 123-253 Observing Guide v1.4 November 2013 TEAMWORK Working in pairs or groups is quite common in science labs, and this lab is no exception. Teamwork can be quite effective; it's often possible
PHYSICS 123-253 Observing Guide v1.4 November 2013 TEAMWORK Working in pairs or groups is quite common in science labs, and this lab is no exception. Teamwork can be quite effective; it's often possible
STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES
 STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES 2., classification, surface photometry Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen the Netherlands February 2010, classification, surface photometry
STRUCTURE OF GALAXIES 2., classification, surface photometry Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen the Netherlands February 2010, classification, surface photometry
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared
 Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider
 Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider Copenhagen University Observatory Edited November 10, 2005 Figure 1: First light image for the Hanle autoguider, obtained on September 17, 2005. A 5 second exposure
Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider Copenhagen University Observatory Edited November 10, 2005 Figure 1: First light image for the Hanle autoguider, obtained on September 17, 2005. A 5 second exposure
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation
 NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
optical / IR: photon counting flux density or magnitude corresponds to number of electrons per second (mean rate)
 optical / IR: photon counting flux density or magnitude corresponds to number of electrons per second (mean rate) N electrons/sec = ɛ F λ λa hc/λ 0 efficiency factor flux density x bandpass x collecting
optical / IR: photon counting flux density or magnitude corresponds to number of electrons per second (mean rate) N electrons/sec = ɛ F λ λa hc/λ 0 efficiency factor flux density x bandpass x collecting
A Random Walk Through Astrometry
 A Random Walk Through Astrometry Astrometry: The Second Oldest Profession George H. Kaplan Astronomical Applications Department Astrometry Department U.S. Naval Observatory Random Topics to be Covered
A Random Walk Through Astrometry Astrometry: The Second Oldest Profession George H. Kaplan Astronomical Applications Department Astrometry Department U.S. Naval Observatory Random Topics to be Covered
Shape Measurement: An introduction to KSB
 Shape Measurement: An introduction to KSB Catherine Heymans Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, UK DUEL Weak Lensing School September 2009 at the end of the week you ll be able to... Use
Shape Measurement: An introduction to KSB Catherine Heymans Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, UK DUEL Weak Lensing School September 2009 at the end of the week you ll be able to... Use
Photometric Products. Robert Lupton, Princeton University LSST Pipeline/Calibration Scientist PST/SAC PST/SAC,
 Photometric Products Robert Lupton, Princeton University LSST Pipeline/Calibration Scientist PST/SAC 2018-02-27 PST/SAC, 2018-02-27 LSST2017 Tucson, AZ August 14-18, 2017 1 Outline Photometry Point Sources
Photometric Products Robert Lupton, Princeton University LSST Pipeline/Calibration Scientist PST/SAC 2018-02-27 PST/SAC, 2018-02-27 LSST2017 Tucson, AZ August 14-18, 2017 1 Outline Photometry Point Sources
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect
 Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Images acquired with the Wide Field Channel (WFC) of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) are
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Images acquired with the Wide Field Channel (WFC) of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) are
Galaxies. Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations
 Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Astronomical image reduction using the Tractor
 the Tractor DECaLS Fin Astronomical image reduction using the Tractor Dustin Lang McWilliams Postdoc Fellow Carnegie Mellon University visiting University of Waterloo UW / 2015-03-31 1 Astronomical image
the Tractor DECaLS Fin Astronomical image reduction using the Tractor Dustin Lang McWilliams Postdoc Fellow Carnegie Mellon University visiting University of Waterloo UW / 2015-03-31 1 Astronomical image
EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION
 ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
September 2008 LGS Science Observing Plan 9/18/08 v1.1, A. Bouchez
 1. General Procedures September 2008 LGS Science Observing Plan 9/18/08 v1.1, A. Bouchez We should attempt to complete highest priority observing programs first, before proceeding to lower priority programs.
1. General Procedures September 2008 LGS Science Observing Plan 9/18/08 v1.1, A. Bouchez We should attempt to complete highest priority observing programs first, before proceeding to lower priority programs.
On the calibration of WFCAM data from 2MASS
 On the calibration of WFCAM data from 2MASS Authors: Simon Hodgkin, Mike Irwin Draft: September 28 th 2006 Modifications: ID: VDF-TRE-IOA-00011-0000* 1 Introduction The requirement on VDFS is to photometrically
On the calibration of WFCAM data from 2MASS Authors: Simon Hodgkin, Mike Irwin Draft: September 28 th 2006 Modifications: ID: VDF-TRE-IOA-00011-0000* 1 Introduction The requirement on VDFS is to photometrically
You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3
 You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3 Calibration and data reduction Useful references, besides Lessons 1 and 2: The AST 142 Projects manual: http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~dmw/ast142/projects/project.pdf
You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3 Calibration and data reduction Useful references, besides Lessons 1 and 2: The AST 142 Projects manual: http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~dmw/ast142/projects/project.pdf
SKINAKAS OBSERVATORY. Astronomy Projects for University Students PROJECT GALAXIES
 PROJECT 7 GALAXIES Objective: The topics covered in the previous lessons target celestial objects located in our neighbourhood, i.e. objects which are within our own Galaxy. However, the Universe extends
PROJECT 7 GALAXIES Objective: The topics covered in the previous lessons target celestial objects located in our neighbourhood, i.e. objects which are within our own Galaxy. However, the Universe extends
U B V R AND HST MID-UV AND NEAR-IR SURFACE PHOTOMETRY AND RADIAL COLOR GRADIENTS OF LATE-TYPE, IRREGULAR, AND PECULIAR GALAXIES.
 Draft version June, 5 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6//4 U B V R AND HST MID-UV AND NEAR-IR SURFACE PHOTOMETRY AND RADIAL COLOR GRADIENTS OF LATE-TYPE, IRREGULAR, AND PECULIAR GALAXIES.
Draft version June, 5 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6//4 U B V R AND HST MID-UV AND NEAR-IR SURFACE PHOTOMETRY AND RADIAL COLOR GRADIENTS OF LATE-TYPE, IRREGULAR, AND PECULIAR GALAXIES.
The Impact of x-cte in the WFC3/UVIS detector on Astrometry
 Instrument Science Report WFC3 2014-02 The Impact of x-cte in the WFC3/UVIS detector on Astrometry Jay Anderson April 4, 2014 ABSTRACT Recent observations of the center of globular cluster Omega Centauri
Instrument Science Report WFC3 2014-02 The Impact of x-cte in the WFC3/UVIS detector on Astrometry Jay Anderson April 4, 2014 ABSTRACT Recent observations of the center of globular cluster Omega Centauri
Galaxy photometry. The surface brightness of a galaxy I(x) is the amount of light on the sky at a particular point x on the image.
 Galaxy photometry The surface brightness of a galaxy I(x) is the amount of light on the sky at a particular point x on the image. A small patch of side D in a galaxy located at a distance d, will subtend
Galaxy photometry The surface brightness of a galaxy I(x) is the amount of light on the sky at a particular point x on the image. A small patch of side D in a galaxy located at a distance d, will subtend
An Example of Telescope Resolution
 An Example of Telescope Resolution J. Kielkopf September 23, 2012 1 Principles Light leaves a distant source with the properties of a spherical wave. That is, the phase of the wave is constant on the surface
An Example of Telescope Resolution J. Kielkopf September 23, 2012 1 Principles Light leaves a distant source with the properties of a spherical wave. That is, the phase of the wave is constant on the surface
The luminosity function of cluster galaxies
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS DECEMBER I 1999, PAGE 155 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 140, 155 170 (1999) The luminosity function of cluster galaxies II. Data reduction procedures applied
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS DECEMBER I 1999, PAGE 155 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 140, 155 170 (1999) The luminosity function of cluster galaxies II. Data reduction procedures applied
Corotation Resonance of Non-barred Spiral Galaxies
 Corotation Resonance of Non-barred Spiral Galaxies A Research work By Arjun Karki Kark with Prof. Marc Seigar (Research advisor) Outline Motivation / Objective Introduction - Density wave theory - Corotation
Corotation Resonance of Non-barred Spiral Galaxies A Research work By Arjun Karki Kark with Prof. Marc Seigar (Research advisor) Outline Motivation / Objective Introduction - Density wave theory - Corotation
More on Galaxy Classifcation
 More on Galaxy Classifcation Trends within the Hubble Sequence E0 --> S0 --> Sb Decreasing bulge to disk ratio Decreasing stellar age Increasing gas content Increasing star formation rate Problems Constructed
More on Galaxy Classifcation Trends within the Hubble Sequence E0 --> S0 --> Sb Decreasing bulge to disk ratio Decreasing stellar age Increasing gas content Increasing star formation rate Problems Constructed
Keck Adaptive Optics Note 1069
 Keck Adaptive Optics Note 1069 Tip-Tilt Sensing with Keck I Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics: Sensor Selection and Performance Predictions DRAFT to be updated as more performance data becomes available
Keck Adaptive Optics Note 1069 Tip-Tilt Sensing with Keck I Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics: Sensor Selection and Performance Predictions DRAFT to be updated as more performance data becomes available
The HII Regions of Sextans A
 Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 6: 765-769, 1994 July The HII Regions of Sextans A Paul Hodge 1 Astronomy Department, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195 Electronic
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 6: 765-769, 1994 July The HII Regions of Sextans A Paul Hodge 1 Astronomy Department, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195 Electronic
Journal Club Presentation on The BIMA Survey of Nearby Galaxies. I. The Radial Distribution of CO Emission in Spiral Galaxies by Regan et al.
 Journal Club Presentation on The BIMA Survey of Nearby Galaxies. I. The Radial Distribution of CO Emission in Spiral Galaxies by Regan et al. ApJ, 561:218-237, 2001 Nov 1 1 Fun With Acronyms BIMA Berkely
Journal Club Presentation on The BIMA Survey of Nearby Galaxies. I. The Radial Distribution of CO Emission in Spiral Galaxies by Regan et al. ApJ, 561:218-237, 2001 Nov 1 1 Fun With Acronyms BIMA Berkely
Imaging with Micado at the E-ELT. WORKSHOP: Imaging at the E-ELT
 Imaging with Micado at the E-ELT Renato Falomo INAF Observatory of Padova, Italy WORKSHOP: Imaging at the E-ELT 29 May 2009, Garching Resolved stellar population in Virgo (high SB) Detailed View of high
Imaging with Micado at the E-ELT Renato Falomo INAF Observatory of Padova, Italy WORKSHOP: Imaging at the E-ELT 29 May 2009, Garching Resolved stellar population in Virgo (high SB) Detailed View of high
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies
 Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Observed Properties of Stars ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Observed Properties of Stars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Extrinsic Properties Location Motion kinematics Extrinsic Properties Location Use spherical coordinate system centered on Solar System Two angles (θ,φ) Right
Observed Properties of Stars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Extrinsic Properties Location Motion kinematics Extrinsic Properties Location Use spherical coordinate system centered on Solar System Two angles (θ,φ) Right
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Lab 4: Differential Photometry of an Extrasolar Planetary Transit
 Lab 4: Differential Photometry of an Extrasolar Planetary Transit Neil Lender 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Sean Lockwood 3 December 3, 2007 Abstract An upward change in brightness of 3.97 ± 0.29 millimags in
Lab 4: Differential Photometry of an Extrasolar Planetary Transit Neil Lender 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Sean Lockwood 3 December 3, 2007 Abstract An upward change in brightness of 3.97 ± 0.29 millimags in
STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF IN HERCULES VOID
 STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF 1600+18 IN HERCULES VOID G.Petrov [1], A.Y.Kniazev [2], and J.W. Fried [2] 1 Institute of Astronomy, Bulgarian Academy
STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF 1600+18 IN HERCULES VOID G.Petrov [1], A.Y.Kniazev [2], and J.W. Fried [2] 1 Institute of Astronomy, Bulgarian Academy
Corotation Resonance of Nonbarred Spiral Galaxies. A Research work By Arjun Karki with Prof. Marc Seigar (Research advisor)
 Corotation Resonance of Nonbarred Spiral Galaxies A Research work By Arjun Karki with Prof. Marc Seigar (Research advisor) Outline Motivation / Objective Introduction - Density Wave Theory - Corotation
Corotation Resonance of Nonbarred Spiral Galaxies A Research work By Arjun Karki with Prof. Marc Seigar (Research advisor) Outline Motivation / Objective Introduction - Density Wave Theory - Corotation
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System
 Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey
 First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
Binning (how to do HW#3, problem #3)
 Binning (how to do HW#3, problem #3) Say you have a dataset of noisy (x,y) values. You want to make a binned plot of the median value of y, in bins of x. You also want to esamate the sum of all the y values
Binning (how to do HW#3, problem #3) Say you have a dataset of noisy (x,y) values. You want to make a binned plot of the median value of y, in bins of x. You also want to esamate the sum of all the y values
Optics of the Atmosphere and Seeing
 Optics of the Atmosphere and Seeing Cristobal Petrovich Department of Astrophysical Sciences Princeton University 03/23/2011 Outline Review general concepts: Airmass Atmospheric refraction Atmospheric
Optics of the Atmosphere and Seeing Cristobal Petrovich Department of Astrophysical Sciences Princeton University 03/23/2011 Outline Review general concepts: Airmass Atmospheric refraction Atmospheric
Structure and stellar content of dwarf galaxies
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JANUARY II 2000, PAGE 211 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 141, 211 220 (2000) Structure and stellar content of dwarf galaxies IV. B and R photometry of dwarf galaxies
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JANUARY II 2000, PAGE 211 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 141, 211 220 (2000) Structure and stellar content of dwarf galaxies IV. B and R photometry of dwarf galaxies
Inclination-Dependent Extinction Effects in Disk Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey aa aa. A Senior Honors Thesis
 1 Inclination-Dependent Extinction Effects in Disk Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey aa aa aa aa A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation with Distinction
1 Inclination-Dependent Extinction Effects in Disk Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey aa aa aa aa A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation with Distinction
Deep Surveys or How We Learn About the Early Universe When We Can t Measure All that Would Be Nice!
 Deep Surveys or How We Learn About the Early Universe When We Can t Measure All that Would Be Nice! Presented at the AAS Seminar on Infrared Astronomy, AAS Meeting, Jan 7, 2003, Seattle Marcia Rieke mrieke@as.
Deep Surveys or How We Learn About the Early Universe When We Can t Measure All that Would Be Nice! Presented at the AAS Seminar on Infrared Astronomy, AAS Meeting, Jan 7, 2003, Seattle Marcia Rieke mrieke@as.
astro-ph/ May 94
 Invited talk at 4th DAEC meeting \Unveiling Large-Scale Structure behind the Milky-Way", ed. C. Balkowski & R. Kraan-Korteweg (San Fransisco: A.S.P.), in press. How well should the DENIS Survey probe through
Invited talk at 4th DAEC meeting \Unveiling Large-Scale Structure behind the Milky-Way", ed. C. Balkowski & R. Kraan-Korteweg (San Fransisco: A.S.P.), in press. How well should the DENIS Survey probe through
A down-to-earth guide to high-resolution solar observations. Kevin Reardon National Solar Observatory
 A down-to-earth guide to high-resolution solar observations Kevin Reardon kreardon@nso.edu National Solar Observatory Seeing Adaptive Optics Image Reconstruction Atmospheric Effects Spectral Lines Calibration
A down-to-earth guide to high-resolution solar observations Kevin Reardon kreardon@nso.edu National Solar Observatory Seeing Adaptive Optics Image Reconstruction Atmospheric Effects Spectral Lines Calibration
Extra Gal 9: Photometry & Dynamics
 Extra Gal 9: Photometry & Dynamics Two books, among many others, that can be used by the studenys for extensive references and details are: Binney and Merrifield: Galactic Astronomy Binney and Tremaine
Extra Gal 9: Photometry & Dynamics Two books, among many others, that can be used by the studenys for extensive references and details are: Binney and Merrifield: Galactic Astronomy Binney and Tremaine
Deep fields around bright stars ( Galaxies around Stars )
 Deep fields around bright stars ( Galaxies around Stars ) Scientific context: the morphological evolution of faint field galaxies Near-IR observations ground-based observations with AO: PUEO/CFHT deep
Deep fields around bright stars ( Galaxies around Stars ) Scientific context: the morphological evolution of faint field galaxies Near-IR observations ground-based observations with AO: PUEO/CFHT deep
Performance of the NICMOS ETC Against Archived Data
 Performance of the NICMOS ETC Against Archived Data M. Sosey June 19, 2001 ABSTRACT A robust test of the newest version of the NICMOS Exposure Time Calculator (ETC) was conducted in order to assess its
Performance of the NICMOS ETC Against Archived Data M. Sosey June 19, 2001 ABSTRACT A robust test of the newest version of the NICMOS Exposure Time Calculator (ETC) was conducted in order to assess its
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 2. September 13, 2018 Coordinates, Telescopes and Observing
 Lecture 2 September 13, 2018 Coordinates, Telescopes and Observing News Lab time assignments are on class webpage. Lab 2 Handed out today and is due September 27. Observing commences starting tomorrow.
Lecture 2 September 13, 2018 Coordinates, Telescopes and Observing News Lab time assignments are on class webpage. Lab 2 Handed out today and is due September 27. Observing commences starting tomorrow.
1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions
 26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars
 Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars What do we know about individual stars?! Determination of stellar luminosity from measured flux and distance Magnitudes! Determination of stellar surface temperature
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars What do we know about individual stars?! Determination of stellar luminosity from measured flux and distance Magnitudes! Determination of stellar surface temperature
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SEPTEMBER 1996, PAGE 557 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 118, (1996)
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SEPTEMBER 1996, PAGE 557 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 118, 557-573 (1996) Near-infrared and optical broadband surface photometry of 86 face-on disk dominated
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SEPTEMBER 1996, PAGE 557 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 118, 557-573 (1996) Near-infrared and optical broadband surface photometry of 86 face-on disk dominated
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2013W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 GALAXIES Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2013W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 GALAXIES Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the
Lecture 8. October 25, 2017 Lab 5
 Lecture 8 October 25, 2017 Lab 5 News Lab 2 & 3 Handed back next week (I hope). Lab 4 Due today Lab 5 (Transiting Exoplanets) Handed out and observing will start Friday. Due November 8 (or later) Stellar
Lecture 8 October 25, 2017 Lab 5 News Lab 2 & 3 Handed back next week (I hope). Lab 4 Due today Lab 5 (Transiting Exoplanets) Handed out and observing will start Friday. Due November 8 (or later) Stellar
Comet Measurement Techniques. Karen Meech Institute for Astronomy Session 27 1/18/05
 Comet Measurement Techniques Karen Meech Institute for Astronomy Session 27 1/18/05 Image copyright, R. Wainscoat, IfA Image courtesy K. Meech Techniques Summary Imaging & Detectors Photometry Deep Imaging
Comet Measurement Techniques Karen Meech Institute for Astronomy Session 27 1/18/05 Image copyright, R. Wainscoat, IfA Image courtesy K. Meech Techniques Summary Imaging & Detectors Photometry Deep Imaging
SKINAKAS OBSERVATORY. Astronomy Projects for University Students PROJECT SUPERNOVA REMNANTS
 PROJECT 10 SUPERNOVA REMNANTS Objective: The purpose of this exercise is also twofold. The first one is to gain further experience with the analysis of narrow band images (as in the case of planetary nebulae)
PROJECT 10 SUPERNOVA REMNANTS Objective: The purpose of this exercise is also twofold. The first one is to gain further experience with the analysis of narrow band images (as in the case of planetary nebulae)
Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) A Science Use Case for GMT and TMT Origin of Elliptical Galaxies! Elliptical Galaxies Form Through Mergers!
Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) A Science Use Case for GMT and TMT Origin of Elliptical Galaxies! Elliptical Galaxies Form Through Mergers!
GALACTIC DYNAMICS AND INTERSTELLAR MATTER
 GALACTIC DYNAMICS AND INTERSTELLAR MATTER Isaac Shlosman Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Kentucky at Lexington, USA and Theoretical Astrophysics Osaka University, Japan The goal: Explain
GALACTIC DYNAMICS AND INTERSTELLAR MATTER Isaac Shlosman Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Kentucky at Lexington, USA and Theoretical Astrophysics Osaka University, Japan The goal: Explain
Chapter 5: Telescopes
 Chapter 5: Telescopes You don t have to know different types of reflecting and refracting telescopes. Why build bigger and bigger telescopes? There are a few reasons. The first is: Light-gathering power:
Chapter 5: Telescopes You don t have to know different types of reflecting and refracting telescopes. Why build bigger and bigger telescopes? There are a few reasons. The first is: Light-gathering power:
VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1992) 13, 293 305 VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT P. N. Bhat & K. P. Singh Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay 400 005 T. P. Prabhu Indian Institute
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1992) 13, 293 305 VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT P. N. Bhat & K. P. Singh Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay 400 005 T. P. Prabhu Indian Institute
Open Cluster Research Project
 Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO?
 Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Galaxy Luminosity Function. Galaxy Luminosity Function. Schechter Function. Schechter Function by environment. Schechter (1976) found that
 Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
High Time Resolution Photometry of V458 Vul
 High Time Resolution Photometry of V458 Vul Samia Bouzid 2010 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisor: Dr. Peter Garnavich High Time-Resolution Photometry of Nova V458 Vul
High Time Resolution Photometry of V458 Vul Samia Bouzid 2010 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisor: Dr. Peter Garnavich High Time-Resolution Photometry of Nova V458 Vul
Exponential Profile Fitting on the Unusual SAB(s)bc galaxy M106 Alex K Chen Astronomy Department, University of Washington
 Exponential Profile Fitting on the Unusual SAB(s)bc galaxy M106 Alex K Chen Astronomy Department, University of Washington Abstract M106 is a late type spiral galaxy with an inclination of 64 degrees.
Exponential Profile Fitting on the Unusual SAB(s)bc galaxy M106 Alex K Chen Astronomy Department, University of Washington Abstract M106 is a late type spiral galaxy with an inclination of 64 degrees.
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Hipparchus 1) Classified stars by brightness,
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Hipparchus 1) Classified stars by brightness,
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
Cosmic Optical Background: The View from Pioneer 10/11. Cosmic Optical Background the View from Pioneer 10/11
 Cosmic Optical Background: The View from Pioneer 10/11 Cosmic Optical Background the View from Pioneer 10/11 Matsuoka et al. 2011, ApJ, 736, 119 Yoshiki Matsuoka (Nagoya University) Nobuyuki Ienaka, Kimiaki
Cosmic Optical Background: The View from Pioneer 10/11 Cosmic Optical Background the View from Pioneer 10/11 Matsuoka et al. 2011, ApJ, 736, 119 Yoshiki Matsuoka (Nagoya University) Nobuyuki Ienaka, Kimiaki
DIFFUSE OPTICAL LIGHT IN GALAXY CLUSTERS. II. CORRELATIONS WITH CLUSTER PROPERTIES
 The Astronomical Journal, 134:466Y493, 2007 August # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DIFFUSE OPTICAL LIGHT IN GALAXY CLUSTERS. II. CORRELATIONS WITH CLUSTER
The Astronomical Journal, 134:466Y493, 2007 August # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DIFFUSE OPTICAL LIGHT IN GALAXY CLUSTERS. II. CORRELATIONS WITH CLUSTER
b a = 1 n 10. Surface brightness profile of most elliptical galaxies can be fit well by the R 1/4 (or de Vaucouleurs) law, (1 ɛ) 2 a 2 = 1.
 7 Elliptical Galaxies Basic properties of elliptical galaxies Formation of elliptical galaxies 7.1 Photometric Properties Isophotes of elliptical galaxies are usually fitted by ellipses: Major axis a;
7 Elliptical Galaxies Basic properties of elliptical galaxies Formation of elliptical galaxies 7.1 Photometric Properties Isophotes of elliptical galaxies are usually fitted by ellipses: Major axis a;
Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale
 Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Lecture 12: Distances to stars. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 12: Distances to stars Astronomy 111 Why are distances important? Distances are necessary for estimating: Total energy released by an object (Luminosity) Masses of objects from orbital motions
Lecture 12: Distances to stars Astronomy 111 Why are distances important? Distances are necessary for estimating: Total energy released by an object (Luminosity) Masses of objects from orbital motions
Observer Anomaly(?): Recent Jitter and PSF Variations
 Instrument Science Report TEL 2005-01 Observer Anomaly(?): Recent Jitter and PSF Variations R. L. Gilliland gillil@stsci.edu February 2005 Abstract An anomaly in the HST Pointing Control System (PCS) has
Instrument Science Report TEL 2005-01 Observer Anomaly(?): Recent Jitter and PSF Variations R. L. Gilliland gillil@stsci.edu February 2005 Abstract An anomaly in the HST Pointing Control System (PCS) has
Homework 6, due October 27: Problems in Measuring the Universe:
 Homework 6, due October 27: Problems in Measuring the Universe: 4.2. You want to observe a star at -10 degrees declination through no more than two air masses from a telescope at 20 degrees north latitude.
Homework 6, due October 27: Problems in Measuring the Universe: 4.2. You want to observe a star at -10 degrees declination through no more than two air masses from a telescope at 20 degrees north latitude.
3 Effects of the earth s atmosphere
 Astr 535 Class Notes Fall 2017 29 3 Effects of the earth s atmosphere The earth s atmosphere has several different effects: it emits light, it absorbs light, it shifts the apparent direction of incoming
Astr 535 Class Notes Fall 2017 29 3 Effects of the earth s atmosphere The earth s atmosphere has several different effects: it emits light, it absorbs light, it shifts the apparent direction of incoming
An Introduction to. Adaptive Optics. Presented by. Julian C. Christou Gemini Observatory
 An Introduction to Adaptive Optics Presented by Julian C. Christou Gemini Observatory Gemini North in action Turbulence An AO Outline Atmospheric turbulence distorts plane wave from distant object. How
An Introduction to Adaptive Optics Presented by Julian C. Christou Gemini Observatory Gemini North in action Turbulence An AO Outline Atmospheric turbulence distorts plane wave from distant object. How
