SOIL MECHANICS
|
|
|
- Kerry Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4.330 SOIL MECHANICS BERNOULLI S EQUATION Were: u w g Z = Total Head u = Pressure = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Graity w = Unit Weigt of Water Slide of 37
2 4.330 SOIL MECHANICS BERNOULLI S EQUATION IN SOIL u w g Z 0 0 (i.e. elocity of water in soil is negligible). Terefore: u Z w Slide of 37
3 A B CHANGE IN HEAD FROM POINTS A & B (H) A B A B Figure 5.. Das FGE (005). Were: u A w i Z A u L B w Z can be expressed in non-dimensional form i = Hydraulic Gradient L = Lengt of Flow between Points A & B B Slide 3 of 37
4 VELOCITY () VS. HYDRAULIC GRADIENT (i) General relationsip sown in Figure 5. Tree Zones:. Laminar Flow (I). Transition Flow (II) 3. Turbulent Flow (III) For most soils, flow is laminar. Terefore: i Figure 5.. Das FGE (005). Slide 4 of 37
5 DARCY S LAW (856) Were: = Discarge Velocity (i.e. quantity of water in unit time troug unit cross-sectional area at rigt angles to te direction of flow) = (i.e. coefficient of permeability) i = Hydraulic Gradient * Based on obserations of flow of water troug clean sands Slide 5 of 37
6 HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY () w K Were: = Viscosity of Water K = Absolute Permeability (units of L ) Typical Values of per Soil Type Soil Type (cm/sec) (ft/min) Clean Grael Coarse Sand Fine Sand Silty Clay Clay < < after Table 5.. Das FGE (005) Slide 6 of 37
7 DISCHARGE AND SEEPAGE VELOCITIES q A A s Were: q = Flow Rate (quantity of water/unit time) A = Total Cross-sectional Area A = Area of Voids s = Seepage Velocity Figure 5.3. Das FGE (005). Slide 7 of 37
8 Slide 8 of SOIL MECHANICS n e e V V V V V V V A L A A A A A A A A q s s s s s s s s s ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( Figure 5.3. Das FGE (005). DISCHARGE AND SEEPAGE VELOCITIES
9 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: FIND i AND q GIVEN: ft REQUIRED: Find Hydraulic Gradient (i) and Flow Rate (q) 5 ft CL (Imperious Layer) 5 ft SM ( = ft/min) CL (Imperious Layer) 75 ft Slide 9 of 37
10 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: FIND i AND q GIVEN: SOLUTION: Hydraulic Gradient (i): 5 ft 5 ft ft CL (Imperious Layer) i L i ft 75 ft cos SM ( = ft/min) CL (Imperious Layer) 75 ft Rate of Flow per Time (q): q q q ia ft (0.067)(5 ft)(cos min ft / min/ ft )( ft) Slide 0 of 37
11 HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY: LABORATORY TESTING Constant Head (ASTM D434) Falling Head (no ASTM) Figure 5.4. Das FGE (005). Figure 5.5. Das FGE (005). Slide of 37
12 HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY: LABORATORY TESTING Constant Head (ASTM D434) Q At A( i) t Figure 5.4. Das FGE (005). Were: Q = Quantity of water collected oer time t t = Duration of water collection Q A QL At t L Slide of 37
13 4.330 SOIL MECHANICS HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY: LABORATORY TESTING Falling Head (No ASTM) d q A a L dt Were: A = Cross-sectional area of Soil a = Cross-sectional area of Standpipe Integrate from limits 0 to t t al A dt Figure 5.5. Das FGE (005). after rearranging aboe equation log e al A d after integration or.303 al At Integrate from limits to Log 0 Slide 3 of 37
14 HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY: EMPIRICAL RELATIONSHIPS Uniform Sands - Hazen Formula (Hazen, 930): ( cm / sec) cd 0 Were: c = Constant between to.5 D 0 = Effectie Size (in mm) Sands Kozeny-Carman (Loudon 95 and Perloff and Baron 976): C e Were: C = Constant (to be determined) e = Void Ratio 3 e Sands Casagrande (Unpublised):.4e 0.85 Were: e = Void Ratio 0.85 e = 0.85 Normally Consolidated Clays (Samarasinge, Huang, and Drneic, 98): C n e e Were: C = Constant to be determined experimentally n = Constant to be determined experimentally e = Void Ratio Slide 4 of 37
15 4.330 SOIL MECHANICS HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY: EMPIRICAL RELATIONSHIPS EXAMPLE NORMALLY CONSOLIDATED CLAYS GIVEN: Normally consolidated clay wit e and measurements from D Consolidation Test. Void Ratio (e) (cm/sec). 0.6 x x 0-7 REQUIRED: Find for same clay wit a oid ratio of.4. SOLUTION: Using (Samarasinge, Huang, and Drneic, 98) Equation: C C n e e n e e Substituting nown quantities 0.6cm / sec.5cm / sec..5 Example 5.6 Das PGE (005). n.5. Slide 5 of 37
16 e SOIL MECHANICS HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY: EMPIRICAL RELATIONSHIPS EXAMPLE NORMALLY CONSOLIDATED CLAYS 0.6cm / sec.5cm / sec 0.6x0 C 7 C n e e cm / sec 0.58x cm / sec (0.58x0 7cm / sec).4..5 n.5. n 4.5.x0 7 cm / sec Example 5.6 Das PGE (005). Slide 6 of 37
17 STRATIFIED SOILS: EQUIVALENT HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY HORIZONTAL DIRECTION Considering cross-section of Unit Lengt. Total flow troug cross-section can be written as: q q H H H... n H n Were: = Aerage Discarge Velocity = Discarge Velocity in Layer Figure 5.7. Das FGE (005). Slide 7 of 37
18 STRATIFIED SOILS: EQUIVALENT HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY HORIZONTAL DIRECTION Substituting =i into q equation and using H to denote Horizontal Direction H ( eq) H i eq i ; i ;...; H n n i n Noting tat i eq =i =i = =i n H ( H... H ( eq) H H Hn n Were: H(eq) = Equialent in Horizontal Direction H H ) Figure 5.7. Das FGE (005). Slide 8 of 37
19 STRATIFIED SOILS: EQUIVALENT HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY VERTICAL DIRECTION Total Head Loss = = Sum Head Loss in Eac Layer... V ( eq) H and V... Using Darcy s Law (=i) into equation and using V to denote Vertical Direction n n i... Vn Were: V(eq) = Equialent in Vertical Direction i n Figure 5.8. Das FGE (005). Slide 9 of 37
20 4.330 SOIL MECHANICS FIELD PERMEABILITY TESTING BY PUMPING WELLS UNCONFINED PERMEABLE LAYER UNDERLAIN BY IMPERMEABLE LAYER Figure 5.9. Das FGE (005). Field Measurements Taen: q, r, r,, q = Groundwater Flow into Well q also is rate of discarge from pumping Equation: r q d r dr r field can be re-written as dr r q Soling Equation: d r.303q log0 r ( ) Slide 0 of 37
21 FIELD PERMEABILITY TESTING BY PUMPING WELLS WELL PENETRATING CONFINED AQUIFER q = Groundwater Flow into Well q also is rate of discarge from pumping Equation: r q dr r r d rh dr can be re-written as H q d Figure 5.0. Das FGE (005). Field Measurements Taen: q, r, r,, Soling Equation: field q log0.77h ( r r ) Slide of 37
22 SOIL PERMEABILITY AND DRAINAGE SOIL MECHANICS after Casagrande and Fadum (940) and Terzagi et al. (996). Slide of 37
23 SOIL PERMEABILITY AND DRAINAGE COEFFICIENT OF PERMEABILITY CM/S (LOG SCALE) Drainage property Good drainage Poor drainage Practically imperious Application in eart dams and dies Perious sections of dams and dies Imperious sections of eart dams and dies Type of soil Clean grael Clean sands, Clean sand and grael mixtures Very fine sands, organic and inorganic silts, mixtures of sand, silt, and clay glacial till, stratified clay deposits, etc. Imperious soils e.g., omogeneous clays below zone of weatering Imperious soils wic are modified by te effect of egetation and weatering; fissured, weatered clays; fractured OC clays Direct determination of coefficient of permeability Direct testing of soil in its original position (e.g., well points). If properly conducted, reliable; considerable experience required. Constant Head Permeameter; little experience required. (Note: Considerable experience also required in tis range.) Constant ead test in triaxial cell; reliable w it experience and no leas. Reliable; Little experience required Falling Head Per meameter; Range of unstable permeability;* muc experience necessary to correct interpretation Fairly reliable; considerable experience necessary (do in triaxial cell) Indirect determination of coefficient of permeability Computat ion: From te grain size distribution (e.g., Hazen s formula). Only applicable to clean, coesionless sands and graels Horizontal Capillarity Test: Very little experience necessary; especially useful for rapid testing of a large number of samples in te field w itout laboratory facilities. Computations: from consolidation tests; expensie laboratory equipment and considerable experience required *Due to migration of fines, cannels, and air in oids. From FHWA IF Ealuation of Soil and Roc Properties. Slide 3 of 37
24 LAPLACE'S EQUATION OF CONTINUITY y z x Steady-State Flow around an imperious Seet Pile Wall Consider water flow at Point A: x = Discarge Velocity in x Direction Figure 5.. Das FGE (005). z = Discarge Velocity in z Direction Y Direction Out Of Plane Slide 4 of 37
25 LAPLACE'S EQUATION OF CONTINUITY Consider water flow at Point A (Soil Bloc at Pt A sown left) Rate of water flow into soil bloc in x direction: x dzdy Figure 5.. Das FGE (005). Rate of water flow into soil bloc in z direction: z dxdy Rate of water flow out of soil bloc in x,z directions: x z x x z z dxdzdy dz dxdy Slide 5 of 37
26 LAPLACE'S EQUATION OF CONTINUITY Consider water flow at Point A (Soil Bloc at Pt A sown left) Total Inflow = Total Outflow Figure 5.. Das FGE (005). x x x z dxdzdy z dz dxdy z dzdy dxdy 0 x x x z or z 0 z Slide 6 of 37
27 Slide 7 of SOIL MECHANICS 0 z x z i x i z x z z z z x x x x Consider water flow at Point A (Soil Bloc at Pt A sown left) Figure 5.. Das FGE (005). Using Darcy s Law (=i) LAPLACE'S EQUATION OF CONTINUITY
28 FLOW NETS: DEFINITION OF TERMS Flow Net: Grapical Construction used to calculate groundwater flow troug soil. Comprised of Flow Lines and Equipotential Lines. Flow Line: A line along wic a water particle moes troug a permeable soil medium. Flow Cannel: Strip between any two adjacent Flow Lines. Equipotential Lines: A line along wic te potential ead at all points is equal. NOTE: Flow Lines and Equipotential Lines must meet at rigt angles! Slide 8 of 37
29 FLOW NETS FLOW AROUND SHEET PILE WALL Figure 5.a. Das FGE (005). Slide 9 of 37
30 FLOW NETS FLOW AROUND SHEET PILE WALL Figure 5.b. Das FGE (005). Slide 30 of 37
31 FLOW NETS: BOUNDARY CONDITIONS. Te upstream and downstream surfaces of te permeable layer (i.e. lines ab and de in Figure b Das FGE (005)) are equipotential lines.. Because ab and de are equipotential lines, all te flow lines intersect tem at rigt angles. 3. Te boundary of te impreious layer (i.e. line fg in Figure b Das FGE (005)) is a flow line, as is te surface of te imperious seet pile (i.e. line acd in Figure b Das FGE (005)). 4. Te equipontential lines intersect acd and fg (Figure b Das FGE (005)) at rigt angles. Slide 3 of 37
32 FLOW NETS FLOW UNDER AN IMPERMEABLE DAM Figure 5.3. Das FGE (005). Slide 3 of 37
33 q q q SOIL MECHANICS FLOW NETS: DEFINITION OF TERMS Rate of Seepage Troug Flow Cannel (per unit lengt): Using Darcy s Law (q=a=ia) q n q l 3 l 3 4 l l Potential Drop H N d l 3 l 3... Figure 5.4. Das FGE (005). Were: H = Head Difference N d = Number of Potential Drops Slide 33 of 37
34 Terefore, flow troug one cannel is: q q N H N d If Number of Flow Cannels = N f, ten te total flow for all cannels per unit lengt is: HN d f SOIL MECHANICS FLOW NETS FLOW AROUND SHEET PILE WALL EXAMPLE Figure 5.b. Das FGE (005). Slide 34 of 37
35 GIVEN: Flow Net in Figure 5.7. N f = 3 N d = 6 x = z =5x0-3 cm/sec DETERMINE: a. How ig water will rise in piezometers at points a, b, c, and d. b. Rate of seepage troug flow cannel II. c. Total rate of seepage SOIL MECHANICS FLOW NETS FLOW AROUND SHEET PILE WALL EXAMPLE Figure 5.7. Das FGE (005). Slide 35 of 37
36 SOLUTION: Potential Drop = (5m.67m) 6 H N d 0.56m At Pt a: Water in standpipe = (5m x0.56m) = 4.44m At Pt b: Water in standpipe = (5m x0.56m) = 3.88m At Pts c and d: Water in standpipe = (5m 5x0.56m) =.0m SOIL MECHANICS FLOW NETS FLOW AROUND SHEET PILE WALL EXAMPLE Figure 5.7. Das FGE (005). Slide 36 of 37
37 FLOW NETS FLOW AROUND SHEET PILE WALL EXAMPLE SOLUTION: q = 5x0-3 cm/sec = 5x0-5 m/sec H N d q = (5x0-5 m/sec)(0.56m) q =.8x0-5 m 3 /sec/m q HN N d f qn q = (.8x0-5 m 3 /sec/m) * 3 q = 8.4x0-5 m3/sec/m f Figure 5.7. Das FGE (005). Slide 37 of 37
ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS
 BERNOULLI S EQUATION h Where: u w g Z h = Total Head u = Pressure = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Graity w = Unit Weight of Water h 14.531 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS BERNOULLI S EQUATION IN SOIL u w g
BERNOULLI S EQUATION h Where: u w g Z h = Total Head u = Pressure = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Graity w = Unit Weight of Water h 14.531 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS BERNOULLI S EQUATION IN SOIL u w g
GEOTECHNICAL LABORATORY
 14.333 GEOTECHNICAL LABORATORY BERNOULLI S EQUATION h u w v 2 2g Z h = Total Head u = Pressure v = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Gravity w = Unit Weight of Water Slide 1 of 14 h 14.333 GEOTECHNICAL
14.333 GEOTECHNICAL LABORATORY BERNOULLI S EQUATION h u w v 2 2g Z h = Total Head u = Pressure v = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Gravity w = Unit Weight of Water Slide 1 of 14 h 14.333 GEOTECHNICAL
Chapter 7 Permeability and Seepage
 Permeability and Seepage - N. Sivakugan (2005) 1 7.1 INTRODUCTION Chapter 7 Permeability and Seepage Permeability, as the name implies (ability to permeate), is a measure of how easily a fluid can flow
Permeability and Seepage - N. Sivakugan (2005) 1 7.1 INTRODUCTION Chapter 7 Permeability and Seepage Permeability, as the name implies (ability to permeate), is a measure of how easily a fluid can flow
Outline. Seepage Analysis. Soil Mechanics. Laplace Equation of Continuity
 Soil Mecanics Seepage nalysis Ci-Ping Lin National Ciao Tung Uni. cplin@mail.nctu.edu.tw Outline Laplace Equation of Continuity 1-D D Eample (-D) Computations using in nisotropic Soil Seepage troug an
Soil Mecanics Seepage nalysis Ci-Ping Lin National Ciao Tung Uni. cplin@mail.nctu.edu.tw Outline Laplace Equation of Continuity 1-D D Eample (-D) Computations using in nisotropic Soil Seepage troug an
(Refer Slide Time: 02:10)
 Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 24 Flow of water through soils-v Welcome to lecture five of flow of water through
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 24 Flow of water through soils-v Welcome to lecture five of flow of water through
*** ***! " " ) * % )!( & ' % # $. 0 1 %./ +, - 7 : %8% 9 ) 7 / ( * 7 : %8% 9 < ;14. " > /' ;-,=. / ١
 ١ ******!" #$ % & '!( ) % * ") +,-./ % 01. 3 ( 4 56 7/4 ) 8%9 % : 7 ;14 < 8%9 % : *7./ = ;-, >/'." Soil Permeability & Seepage ٢ Soil Permeability- Definition ٣ What is Permeability? Permeability is the
١ ******!" #$ % & '!( ) % * ") +,-./ % 01. 3 ( 4 56 7/4 ) 8%9 % : 7 ;14 < 8%9 % : *7./ = ;-, >/'." Soil Permeability & Seepage ٢ Soil Permeability- Definition ٣ What is Permeability? Permeability is the
All soils in natural are permeable materials, water being free to flow through the interconnected pores between the solid particles.
 8.1 Introduction Among construction materials, soil is very unique. Because of a relatively large space of void in its constituent, water can flow through soil. The water flow (seepage) characteristics
8.1 Introduction Among construction materials, soil is very unique. Because of a relatively large space of void in its constituent, water can flow through soil. The water flow (seepage) characteristics
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad. Chapter (7)
 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Water in Soil Sections in Craig
 Water in Soil Sections 2.1-2.6 in Craig Outlines Introduction Darcy s Law Volume of water flowing per unit time Measuring K in laboratory Seepage Theory Flow Net Introduction All soils are permeable materials,
Water in Soil Sections 2.1-2.6 in Craig Outlines Introduction Darcy s Law Volume of water flowing per unit time Measuring K in laboratory Seepage Theory Flow Net Introduction All soils are permeable materials,
5. TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILS 5.1 INTRODUCTION
 5. TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER TROUG SOILS 5.1 INTRODUCTION In many instances the flo of ater through soils is neither one-dimensional nor uniform over the area perpendicular to flo. It is often necessary
5. TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER TROUG SOILS 5.1 INTRODUCTION In many instances the flo of ater through soils is neither one-dimensional nor uniform over the area perpendicular to flo. It is often necessary
Geo-E2010 Advanced Soil Mechanics L Wojciech Sołowski. 26 February 2017
 Geo-E2010 Advanced Soil Mechanics L Wojciech Sołowski 26 February 2017 Permeability, consolidation and seepage Department of Civil Engineering Advanced Soil Mechanics W. Sołowski 2 To learn 1. What is
Geo-E2010 Advanced Soil Mechanics L Wojciech Sołowski 26 February 2017 Permeability, consolidation and seepage Department of Civil Engineering Advanced Soil Mechanics W. Sołowski 2 To learn 1. What is
- To determine the coefficient of permeability (or coefficient of hydraulic
 39 2.6 Permeability Tests 2.6.1 General - To determine te coefficient of permeability (or coefficient of ydraulic conductivity) k. - General metod for determining k directly. 1) Constant-ead metod (for
39 2.6 Permeability Tests 2.6.1 General - To determine te coefficient of permeability (or coefficient of ydraulic conductivity) k. - General metod for determining k directly. 1) Constant-ead metod (for
b) EFFECTIVE STRESS (c) SEEPAGE
 b) EFFECTIVE STRESS B1. A fine sand layer of 5 m thickness lies on a 5 m clay deposit. The water table is at the ground surface. Below the clay is a rock formation. Piezometers installed in the rock show
b) EFFECTIVE STRESS B1. A fine sand layer of 5 m thickness lies on a 5 m clay deposit. The water table is at the ground surface. Below the clay is a rock formation. Piezometers installed in the rock show
Seepage Analysis through Earth Dam Based on Finite Difference Method
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (11)111-1, 1 1, TetRoad Publication ISSN -44 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Researc www.tetroad.com Seepage Analysis troug Eart Dam Based on Finite Difference Metod
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (11)111-1, 1 1, TetRoad Publication ISSN -44 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Researc www.tetroad.com Seepage Analysis troug Eart Dam Based on Finite Difference Metod
Permeability in Soils
 Permeability in Soils Contents: Darcy s law- assumption and validity, coefficient of permeability and its determination (laboratory and field), factors affecting permeability, permeability of stratified
Permeability in Soils Contents: Darcy s law- assumption and validity, coefficient of permeability and its determination (laboratory and field), factors affecting permeability, permeability of stratified
Darcy s law in 3-D. K * xx K * yy K * zz
 PART 7 Equations of flow Darcy s law in 3-D Specific discarge (vector) is calculated by multiplying te ydraulic conductivity (second-order tensor) by te ydraulic gradient (vector). We obtain a general
PART 7 Equations of flow Darcy s law in 3-D Specific discarge (vector) is calculated by multiplying te ydraulic conductivity (second-order tensor) by te ydraulic gradient (vector). We obtain a general
Module 2 Lecture 9 Permeability and Seepage -5 Topics
 Module 2 Lecture 9 Permeability and Seepage -5 Topics 1.2.7 Numerical Analysis of Seepage 1.2.8 Seepage Force per Unit Volume of Soil Mass 1.2.9 Safety of Hydraulic Structures against Piping 1.2.10 Calculation
Module 2 Lecture 9 Permeability and Seepage -5 Topics 1.2.7 Numerical Analysis of Seepage 1.2.8 Seepage Force per Unit Volume of Soil Mass 1.2.9 Safety of Hydraulic Structures against Piping 1.2.10 Calculation
FUNDAMENTALS OF CONSOLIDATION
 FUNDAMENTALS OF CONSOLIDATION σ (Vertical Stress Increase) SAND CLAY CONSOLIDATION: Volume change in saturated soils caused by the expulsion of pore water from loading. Saturated Soils: σ causes u to increase
FUNDAMENTALS OF CONSOLIDATION σ (Vertical Stress Increase) SAND CLAY CONSOLIDATION: Volume change in saturated soils caused by the expulsion of pore water from loading. Saturated Soils: σ causes u to increase
Soil Mechanics I 3 Water in Soils. 1. Capillarity, swelling 2. Seepage 3. Measurement of hydraulic conductivity 4. Effective stress in the ground
 Soil Mechanics I 3 Water in Soils 1. Capillarity, swelling 2. Seepage 3. Measurement of hydraulic conductivity 4. Effective stress in the ground 1 Influence of Water - Basics WATER IN SOIL - affects soil
Soil Mechanics I 3 Water in Soils 1. Capillarity, swelling 2. Seepage 3. Measurement of hydraulic conductivity 4. Effective stress in the ground 1 Influence of Water - Basics WATER IN SOIL - affects soil
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING II (Subject Code: 06CV64) UNIT 4: FLOW NETS 4.1 Introduction
 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING II (Subject Code: 06CV64) UNIT 4: FLOW NETS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter the topics that are covered include principles of seepage analysis, graphical solutions for seepage
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING II (Subject Code: 06CV64) UNIT 4: FLOW NETS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter the topics that are covered include principles of seepage analysis, graphical solutions for seepage
Time Rate of Consolidation Settlement
 Time Rate of Consolidation Settlement We know how to evaluate total settlement of primary consolidation S c which will take place in a certain clay layer. However this settlement usually takes place over
Time Rate of Consolidation Settlement We know how to evaluate total settlement of primary consolidation S c which will take place in a certain clay layer. However this settlement usually takes place over
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow
 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Carles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow Simulation: Te prediction of quantities of interest (dependent variables) based upon an equation
1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Carles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow Simulation: Te prediction of quantities of interest (dependent variables) based upon an equation
Geotechnical Properties of Soil
 Geotechnical Properties of Soil 1 Soil Texture Particle size, shape and size distribution Coarse-textured (Gravel, Sand) Fine-textured (Silt, Clay) Visibility by the naked eye (0.05 mm is the approximate
Geotechnical Properties of Soil 1 Soil Texture Particle size, shape and size distribution Coarse-textured (Gravel, Sand) Fine-textured (Silt, Clay) Visibility by the naked eye (0.05 mm is the approximate
16 Rainfall on a Slope
 Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
5.1 We will begin this section with the definition of a rational expression. We
 Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Soil Mechanics Permeability of Soils and Seepage page 1 CHAPITRE 9. PERMEABILITY OF SOILS AND SEEPAGE...1
 Soil Mechanics Permeability of Soils and Seepage page 1 Contents of this chapter : CHAPITRE 9. PERMEABILITY OF SOILS AND SEEPAGE...1 9.1 INTRODUCTION...1 9.2 DARCY S LAW...1 9.2.1 DEFINITION OF HEAD...1
Soil Mechanics Permeability of Soils and Seepage page 1 Contents of this chapter : CHAPITRE 9. PERMEABILITY OF SOILS AND SEEPAGE...1 9.1 INTRODUCTION...1 9.2 DARCY S LAW...1 9.2.1 DEFINITION OF HEAD...1
Principles of Foundation Engineering 8th Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL
 Principles of Foundation Engineering 8th Edition SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-foundation-engineering- 8th-edition-das-solutions-manual/
Principles of Foundation Engineering 8th Edition SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-foundation-engineering- 8th-edition-das-solutions-manual/
11/22/2010. Groundwater in Unconsolidated Deposits. Alluvial (fluvial) deposits. - consist of gravel, sand, silt and clay
 Groundwater in Unconsolidated Deposits Alluvial (fluvial) deposits - consist of gravel, sand, silt and clay - laid down by physical processes in rivers and flood plains - major sources for water supplies
Groundwater in Unconsolidated Deposits Alluvial (fluvial) deposits - consist of gravel, sand, silt and clay - laid down by physical processes in rivers and flood plains - major sources for water supplies
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUBJECT CODE : CE6405 YEAR : II SUBJECT NAME : SOIL MECHANICS SEM : IV QUESTION BANK (As per Anna University 2013 regulation) UNIT 1- SOIL
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUBJECT CODE : CE6405 YEAR : II SUBJECT NAME : SOIL MECHANICS SEM : IV QUESTION BANK (As per Anna University 2013 regulation) UNIT 1- SOIL
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 13 Permeability and Seepage -2 Conditions favourable for the formation quick sand Quick sand is not a type of sand but a flow condition occurring within a cohesion-less soil when its effective stress is
13 Permeability and Seepage -2 Conditions favourable for the formation quick sand Quick sand is not a type of sand but a flow condition occurring within a cohesion-less soil when its effective stress is
Interpretation of Flow Parameters from In-Situ Tests (P.W. Mayne, November 2001)
 Interpretation of Flow Parameters from In-Situ Tests (P.W. Mayne, November 2001) FLOW PROPERTIES Soils exhibit flow properties that control hydraulic conductivity (k), rates of consolidation, construction
Interpretation of Flow Parameters from In-Situ Tests (P.W. Mayne, November 2001) FLOW PROPERTIES Soils exhibit flow properties that control hydraulic conductivity (k), rates of consolidation, construction
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 2251 / SOIL MECHANICS SEMESTER: IV UNIT 1- INTRODUCTION PART - A (2 marks) 1. Distinguish between Residual and Transported soil. (AUC May/June 2012)
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 2251 / SOIL MECHANICS SEMESTER: IV UNIT 1- INTRODUCTION PART - A (2 marks) 1. Distinguish between Residual and Transported soil. (AUC May/June 2012)
YOUR HW MUST BE STAPLED YOU MUST USE A PENCIL (no pens)
 Spring 2008 CIVE 462 HOMEWORK #1 1. Print out the syllabus. Read it. Write the grade percentages in the first page of your notes. 2. Go back to your 301 notes, internet, etc. and find the engineering definition
Spring 2008 CIVE 462 HOMEWORK #1 1. Print out the syllabus. Read it. Write the grade percentages in the first page of your notes. 2. Go back to your 301 notes, internet, etc. and find the engineering definition
Darcy's Law. Laboratory 2 HWR 531/431
 Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
FUNDAMENTALS SOIL MECHANICS. Isao Ishibashi Hemanta Hazarika. >C\ CRC Press J Taylor & Francis Group. Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
 SOIL MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALS Isao Ishibashi Hemanta Hazarika >C\ CRC Press J Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
SOIL MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALS Isao Ishibashi Hemanta Hazarika >C\ CRC Press J Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
Course Scheme -UCE501: SOIL MECHANICS L T P Cr
 Course Scheme -UCE501: SOIL MECHANICS L T P Cr 3 1 2 4.5 Course Objective: To expose the students about the various index and engineering properties of soil. Introduction: Soil formation, various soil
Course Scheme -UCE501: SOIL MECHANICS L T P Cr 3 1 2 4.5 Course Objective: To expose the students about the various index and engineering properties of soil. Introduction: Soil formation, various soil
PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
 PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING Fourth Edition BRAJA M. DAS California State University, Sacramento I(T)P Boston Albany Bonn Cincinnati London Madrid Melbourne Mexico City New York Paris San Francisco
PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING Fourth Edition BRAJA M. DAS California State University, Sacramento I(T)P Boston Albany Bonn Cincinnati London Madrid Melbourne Mexico City New York Paris San Francisco
1.5 Permeability Tests
 1-17 1.5 Permeability Tests 1.5.1 General - To determine the coefficient of permeability(or coefficient of hydraulic conductivity) k - General method for determining k directly. 1) Constant-head method
1-17 1.5 Permeability Tests 1.5.1 General - To determine the coefficient of permeability(or coefficient of hydraulic conductivity) k - General method for determining k directly. 1) Constant-head method
Distribution of pore water pressure in an earthen dam considering unsaturated-saturated seepage analysis
 E3S Web of Conferences 9, 194 (16) DOI: 1.11/ e3sconf/169194 E-UNSAT 16 Distribution of pore water in an earthen dam considering unsaturated-saturated seepage analysis 1a Kumar Venkatesh, Siva Ram Karumanchi
E3S Web of Conferences 9, 194 (16) DOI: 1.11/ e3sconf/169194 E-UNSAT 16 Distribution of pore water in an earthen dam considering unsaturated-saturated seepage analysis 1a Kumar Venkatesh, Siva Ram Karumanchi
Civil Engineering Department College of Engineering
 Civil Engineering Department College of Engineering Course: Soil Mechanics (CE 359) Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Owusu-Nimo FREQUENCY CE 260 Results (2013) 30 25 23 25 26 27 21 20 18 15 14 15 Civil Geological
Civil Engineering Department College of Engineering Course: Soil Mechanics (CE 359) Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Owusu-Nimo FREQUENCY CE 260 Results (2013) 30 25 23 25 26 27 21 20 18 15 14 15 Civil Geological
Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering 1.1 Geotechnical Engineering 1.2 The Unique Nature of Soil and Rock Materials
 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering 1.1 Geotechnical Engineering 1.2 The Unique Nature of Soil and Rock Materials 1.3 Scope of This Book 1.4 Historical Development of Geotechnical
Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering 1.1 Geotechnical Engineering 1.2 The Unique Nature of Soil and Rock Materials 1.3 Scope of This Book 1.4 Historical Development of Geotechnical
ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS FINAL EXAM (TAKE HOME):DUE THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 6PM.
 14.531 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS FINAL EXAM (TAKE HOME):DUE THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2013 @ 6PM. Problem #1. Field load tests on strip footings yielded the test data provided below in Figure 1 and Table 1
14.531 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS FINAL EXAM (TAKE HOME):DUE THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2013 @ 6PM. Problem #1. Field load tests on strip footings yielded the test data provided below in Figure 1 and Table 1
Chapter 2. 53% v. 2.2 a. From Eqs. (2.11) and (2.12), it can be seen that, 2.67
 Chapter 2 2.1 d. (87.5)(9.81) (1000)(0.05) 3 17.17 kn/m c. d 1 w 17.17 1 0.15 3 14.93 kn/m G a. Eq. (2.12): s w (2.68)(9.81). 14.93 ; e 0.76 1 e 1 e e 0.76 b. Eq. (2.6): n 0.43 1 e 1 0.76 Vw wgs (0.15)(2.68)
Chapter 2 2.1 d. (87.5)(9.81) (1000)(0.05) 3 17.17 kn/m c. d 1 w 17.17 1 0.15 3 14.93 kn/m G a. Eq. (2.12): s w (2.68)(9.81). 14.93 ; e 0.76 1 e 1 e e 0.76 b. Eq. (2.6): n 0.43 1 e 1 0.76 Vw wgs (0.15)(2.68)
Tikrit University. College of Engineering Civil engineering Department CONSOILDATION. Soil Mechanics. 3 rd Class Lecture notes Up Copyrights 2016
 Tikrit University CONSOILDATION College of Engineering Civil engineering Department Soil Mechanics 3 rd Class Lecture notes Up Copyrights 2016 Stresses at a point in a soil mass are divided into two main
Tikrit University CONSOILDATION College of Engineering Civil engineering Department Soil Mechanics 3 rd Class Lecture notes Up Copyrights 2016 Stresses at a point in a soil mass are divided into two main
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 5.2. Permeability III (Das, Ch. 6) Summary Soil Index Properties (Das, Ch. 2-6)
 CE 40 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 5. Permeability III (Das, Ch. 6) Summary Soil Index Properties (Das, Ch. -6) Outline of this Lecture 1. Getting the in situ hydraulic conductivity 1.1 pumping
CE 40 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 5. Permeability III (Das, Ch. 6) Summary Soil Index Properties (Das, Ch. -6) Outline of this Lecture 1. Getting the in situ hydraulic conductivity 1.1 pumping
A PHYSICAL MODEL STUDY OF SCOURING EFFECTS ON UPSTREAM/DOWNSTREAM OF THE BRIDGE
 A PHYSICA MODE STUDY OF SCOURING EFFECTS ON UPSTREAM/DOWNSTREAM OF THE BRIDGE JIHN-SUNG AI Hydrotec Researc Institute, National Taiwan University Taipei, 1617, Taiwan HO-CHENG IEN National Center for Hig-Performance
A PHYSICA MODE STUDY OF SCOURING EFFECTS ON UPSTREAM/DOWNSTREAM OF THE BRIDGE JIHN-SUNG AI Hydrotec Researc Institute, National Taiwan University Taipei, 1617, Taiwan HO-CHENG IEN National Center for Hig-Performance
Review of the Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow
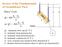 Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
3. Gradually-Varied Flow
 5/6/18 3. Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow vs Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow /g EGL (energy grade line) iction slope Geometric slope S Normal flow: Downslope component of weigt balances bed friction
5/6/18 3. Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow vs Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow /g EGL (energy grade line) iction slope Geometric slope S Normal flow: Downslope component of weigt balances bed friction
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq
 qwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwerty uiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasd fgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzx cbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmq Projectile Motion Quick concepts regarding Projectile Motion wertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyui
qwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwerty uiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasd fgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzx cbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmq Projectile Motion Quick concepts regarding Projectile Motion wertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyui
Shear Strength of Soils
 Shear Strength of Soils STRESSES IN A SOIL ELEMENT t s v Analyze Effective Stresses (s ) Load carried by Soil t Where: s H t t s H s = t f = s v = s H = t = s v Stresses in a Soil Element after Figure
Shear Strength of Soils STRESSES IN A SOIL ELEMENT t s v Analyze Effective Stresses (s ) Load carried by Soil t Where: s H t t s H s = t f = s v = s H = t = s v Stresses in a Soil Element after Figure
GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE
 GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE Prof. J. N. Mandal Department of civil engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Tel.022-25767328 email: cejnm@civil.iitb.ac.in Module - 4
GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE Prof. J. N. Mandal Department of civil engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Tel.022-25767328 email: cejnm@civil.iitb.ac.in Module - 4
Permeability and fluid transport
 Permeability and fluid transport Thermal transport: Fluid transport: q = " k # $p with specific discharge (filter velocity) q [m s 1 ] pressure gradient p [N m 3 ] dynamic viscosity η [N s m 2 ] (intrinsic)
Permeability and fluid transport Thermal transport: Fluid transport: q = " k # $p with specific discharge (filter velocity) q [m s 1 ] pressure gradient p [N m 3 ] dynamic viscosity η [N s m 2 ] (intrinsic)
Part 2: Introduction to Open-Channel Flow SPRING 2005
 Part : Introduction to Open-Cannel Flow SPRING 005. Te Froude number. Total ead and specific energy 3. Hydraulic jump. Te Froude Number Te main caracteristics of flows in open cannels are tat: tere is
Part : Introduction to Open-Cannel Flow SPRING 005. Te Froude number. Total ead and specific energy 3. Hydraulic jump. Te Froude Number Te main caracteristics of flows in open cannels are tat: tere is
Earth dam steady state seepage analysis
 Engineering manual No. 32 Updated 3/2018 Earth dam steady state seepage analysis Program: FEM Water Flow File: Demo_manual_32.gmk Introduction This example illustrates an application of the GEO5 FEM module
Engineering manual No. 32 Updated 3/2018 Earth dam steady state seepage analysis Program: FEM Water Flow File: Demo_manual_32.gmk Introduction This example illustrates an application of the GEO5 FEM module
The process of consolidation and settlement
 Consolidation Based on part of the GeotechniCAL reference package by Prof. John Atkinson, City University, London The process of consolidation and settlement One-dimensional consolidation theory The oedometer
Consolidation Based on part of the GeotechniCAL reference package by Prof. John Atkinson, City University, London The process of consolidation and settlement One-dimensional consolidation theory The oedometer
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
Chapter 3 Permeability
 3.2 Darcy s Law In 1856, Darcy investigated the flow of water through sand filters for water purification. His experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 3.11. By empirical observation Figure 3.11 Schematic
3.2 Darcy s Law In 1856, Darcy investigated the flow of water through sand filters for water purification. His experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 3.11. By empirical observation Figure 3.11 Schematic
COMPUTATION OF ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE OF COHESIVE BACKFILL ON RETAINING WALL CONSIDERING SEISMIC FORCE
 COMPUTATION OF ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE OF COHESIVE BACKFILL ON RETAINING WALL CONSIDERING SEISMIC FORCE Feng Zen Wang Na. Scool of Ciil Engineering and Arcitecture Beijing Jiaotong Uniersity Beijing 00044
COMPUTATION OF ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE OF COHESIVE BACKFILL ON RETAINING WALL CONSIDERING SEISMIC FORCE Feng Zen Wang Na. Scool of Ciil Engineering and Arcitecture Beijing Jiaotong Uniersity Beijing 00044
HEADLOSS ESTIMATION. Mekanika Fluida 1 HST
 HEADLOSS ESTIMATION Mekanika Fluida HST Friction Factor : Major losses Laminar low Hagen-Poiseuille Turbulent (Smoot, Transition, Roug) Colebrook Formula Moody diagram Swamee-Jain 3 Laminar Flow Friction
HEADLOSS ESTIMATION Mekanika Fluida HST Friction Factor : Major losses Laminar low Hagen-Poiseuille Turbulent (Smoot, Transition, Roug) Colebrook Formula Moody diagram Swamee-Jain 3 Laminar Flow Friction
Permeability of Sandy Soil CIVE 2341 Section 2 Soil Mechanics Laboratory Experiment #5, Laboratory #6 SPRING 2015 Group #3
 Permeability of Sandy Soil CIVE 2341 Section 2 Soil Mechanics Laboratory Experiment #5, Laboratory #6 SPRING 2015 Group #3 Abstract: The purpose of this experiment was to determine the coefficient of permeability
Permeability of Sandy Soil CIVE 2341 Section 2 Soil Mechanics Laboratory Experiment #5, Laboratory #6 SPRING 2015 Group #3 Abstract: The purpose of this experiment was to determine the coefficient of permeability
CIV E Geotechnical Engineering I Hydraulic Conductivity Tests (Permeability Tests)
 Purpose Determine the hydraulic conductivity (coefficient of permeability) of sand using the constant-head and falling-head permeameters. Required reading Das 006 Sections 6.1 to 6.6 (pages 156 to 177).
Purpose Determine the hydraulic conductivity (coefficient of permeability) of sand using the constant-head and falling-head permeameters. Required reading Das 006 Sections 6.1 to 6.6 (pages 156 to 177).
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses.
 8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
Used to estimate energy loss due to friction in pipe. D = internal diameter of pipe (feet) L = length of pipe (feet) Penn State-Harrisburg
 Module b: Flow in Pipes Darcy-Weisbac Robert Pitt University o Alabama and Sirley Clark Penn State-Harrisburg Darcy-Weisbac can be written or low (substitute V Q/A, were A (π/4)d in te above equation):
Module b: Flow in Pipes Darcy-Weisbac Robert Pitt University o Alabama and Sirley Clark Penn State-Harrisburg Darcy-Weisbac can be written or low (substitute V Q/A, were A (π/4)d in te above equation):
NOTES ON OPEN CHANNEL FLOW
 NOTES ON OPEN CANNEL FLOW Prof. Marco Pilotti Facoltà di Ingegneria, Università degli Studi di Brescia Profili di moto permanente in un canale e in una serie di due canali - Boudine, 86 OPEN CANNEL FLOW:
NOTES ON OPEN CANNEL FLOW Prof. Marco Pilotti Facoltà di Ingegneria, Università degli Studi di Brescia Profili di moto permanente in un canale e in una serie di due canali - Boudine, 86 OPEN CANNEL FLOW:
Problem Solving. Problem Solving Process
 Problem Solving One of te primary tasks for engineers is often solving problems. It is wat tey are, or sould be, good at. Solving engineering problems requires more tan just learning new terms, ideas and
Problem Solving One of te primary tasks for engineers is often solving problems. It is wat tey are, or sould be, good at. Solving engineering problems requires more tan just learning new terms, ideas and
PHY121 Physics for the Life Sciences I
 PHY Physics for the Life Sciences I Lecture 0. Fluid flow: kinematics describing the motion. Fluid flow: dynamics causes and effects, Bernoulli s Equation 3. Viscosity and Poiseuille s Law for narrow tubes
PHY Physics for the Life Sciences I Lecture 0. Fluid flow: kinematics describing the motion. Fluid flow: dynamics causes and effects, Bernoulli s Equation 3. Viscosity and Poiseuille s Law for narrow tubes
Boreholes. Implementation. Boring. Boreholes may be excavated by one of these methods: 1. Auger Boring 2. Wash Boring 3.
 Implementation Boreholes 1. Auger Boring 2. Wash Boring 3. Rotary Drilling Boring Boreholes may be excavated by one of these methods: 4. Percussion Drilling The right choice of method depends on: Ground
Implementation Boreholes 1. Auger Boring 2. Wash Boring 3. Rotary Drilling Boring Boreholes may be excavated by one of these methods: 4. Percussion Drilling The right choice of method depends on: Ground
6. Non-uniform bending
 . Non-uniform bending Introduction Definition A non-uniform bending is te case were te cross-section is not only bent but also seared. It is known from te statics tat in suc a case, te bending moment in
. Non-uniform bending Introduction Definition A non-uniform bending is te case were te cross-section is not only bent but also seared. It is known from te statics tat in suc a case, te bending moment in
Bedrock Dewatering for Construction of Marmet and Soo Lock Projects
 Bedrock Dewatering for Construction of Marmet and Soo Lock Projects Michael Nield Engineering Geologist Dam Safety Production Center, Huntington, WV August 2012 US Army Corps of Engineers BEDROCK DEWATERING
Bedrock Dewatering for Construction of Marmet and Soo Lock Projects Michael Nield Engineering Geologist Dam Safety Production Center, Huntington, WV August 2012 US Army Corps of Engineers BEDROCK DEWATERING
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets
 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets Equation of Continuity Our equations of hydrogeology are a combination of o Conservation of mass o Some empirical
1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets Equation of Continuity Our equations of hydrogeology are a combination of o Conservation of mass o Some empirical
Mechanical Energy. Kinetic Energy. Gravitational Potential Energy
 Mechanical Energy Kinetic Energy E k = 1 2 mv2 where E k is energy (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) v is velocity (m/s) Gravitational Potential Energy E g = W = mgz where w is work (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) m is mass (kg) z is elevation
Mechanical Energy Kinetic Energy E k = 1 2 mv2 where E k is energy (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) v is velocity (m/s) Gravitational Potential Energy E g = W = mgz where w is work (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) m is mass (kg) z is elevation
INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF FLUID. U p F FLUID IS A SUBSTANCE THAT CAN NOT SUPPORT SHEAR FORCES OF ANY MAGNITUDE WITHOUT CONTINUOUS DEFORMATION
 INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF FLUID plate solid F at t = 0 t > 0 = F/A plate U p F fluid t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 FLUID IS A SUBSTANCE THAT CAN NOT SUPPORT SHEAR FORCES OF ANY MAGNITUDE WITHOUT CONTINUOUS DEFORMATION
INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF FLUID plate solid F at t = 0 t > 0 = F/A plate U p F fluid t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 FLUID IS A SUBSTANCE THAT CAN NOT SUPPORT SHEAR FORCES OF ANY MAGNITUDE WITHOUT CONTINUOUS DEFORMATION
Parshall Flume Discharge Relation under Free Flow Condition
 Journal omepage: ttp://www.journalijar.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH RESEARCH ARTICLE Parsall Flume Discarge Relation under Free Flow Condition 1 Jalam Sing, 2 S.K.Mittal, and 3 H.L.Tiwari
Journal omepage: ttp://www.journalijar.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH RESEARCH ARTICLE Parsall Flume Discarge Relation under Free Flow Condition 1 Jalam Sing, 2 S.K.Mittal, and 3 H.L.Tiwari
EFFECTIVE STRESS CONCEPT NO SEEPAGE
 4.53 DVNED SOIL MENIS EFFETIVE STRESS ONEPT NO SEEPGE Total Stress ( at Point ( sat Satrated Soil olmn (Figre 6.. Das FGE (005 Revised /03 from Water from Soil Were: = Unit Weigt of Water sat = Satrated
4.53 DVNED SOIL MENIS EFFETIVE STRESS ONEPT NO SEEPGE Total Stress ( at Point ( sat Satrated Soil olmn (Figre 6.. Das FGE (005 Revised /03 from Water from Soil Were: = Unit Weigt of Water sat = Satrated
" = ˆ i # #x + ˆ j # #y + ˆ k # #z. "t = D #2 h
 del operator " = ˆ i # #x + ˆ j # #y + ˆ k # #z Hydrology Gradient: "h = ˆ i #h #x + ˆ j #h #y + k ˆ #h #z q = - K"h Darcy s Law Divergence: " q = #q 1 #x + #q 2 #y + #q 3 #z Laplacian: " 2 h = #2 h #x
del operator " = ˆ i # #x + ˆ j # #y + ˆ k # #z Hydrology Gradient: "h = ˆ i #h #x + ˆ j #h #y + k ˆ #h #z q = - K"h Darcy s Law Divergence: " q = #q 1 #x + #q 2 #y + #q 3 #z Laplacian: " 2 h = #2 h #x
APPENDIX G APPENDIX G SEDIMENT CONTAINMENT SYSTEM DESIGN RATIONALE
 APPENDIX G SEDIMENT CONTAINMENT SYSTEM DESIGN RATIONALE March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 G-2 FIGURES Page # Figure G.1 Estimated Runoff from Precipitation Over Different
APPENDIX G SEDIMENT CONTAINMENT SYSTEM DESIGN RATIONALE March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 G-2 FIGURES Page # Figure G.1 Estimated Runoff from Precipitation Over Different
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
MATH CALCULUS I 2.1: Derivatives and Rates of Change
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 2.1: Derivatives and Rates of Cange Professor Donald L. Wite Department of Matematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. Wite (Kent State University) 1 / 1 Introduction Our main
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 2.1: Derivatives and Rates of Cange Professor Donald L. Wite Department of Matematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. Wite (Kent State University) 1 / 1 Introduction Our main
Cone Penetration Test (CPT) Interpretation
 Cone Penetration Test (CPT) Interpretation Gregg uses a proprietary CPT interpretation and plotting software. The software takes the CPT data and performs basic interpretation in terms of soil behavior
Cone Penetration Test (CPT) Interpretation Gregg uses a proprietary CPT interpretation and plotting software. The software takes the CPT data and performs basic interpretation in terms of soil behavior
Soils, Hydrogeology, and Aquifer Properties. Philip B. Bedient 2006 Rice University
 Soils, Hydrogeology, and Aquifer Properties Philip B. Bedient 2006 Rice University Charbeneau, 2000. Basin Hydrologic Cycle Global Water Supply Distribution 3% of earth s water is fresh - 97% oceans 1%
Soils, Hydrogeology, and Aquifer Properties Philip B. Bedient 2006 Rice University Charbeneau, 2000. Basin Hydrologic Cycle Global Water Supply Distribution 3% of earth s water is fresh - 97% oceans 1%
Influence of Surrounding Soil Conditions and Joint Sealing on Seepage Resistance of a Sheet Pile Wall, Three Dimensional Numerical Analyses
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of Surrounding Soil Conditions and Joint Sealing on Seepage Resistance of a Sheet Pile Wall, Three Dimensional Numerical
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of Surrounding Soil Conditions and Joint Sealing on Seepage Resistance of a Sheet Pile Wall, Three Dimensional Numerical
Third Year. Soil Mechanics Lectures. Students
 Soil Mechanics Lectures 2014-2015 Third Year Students Includes: Soil Formation, Basic Phase Relationship, soil classification, compaction, Consistency of soil, one dimensional fluid flow, two dimensional
Soil Mechanics Lectures 2014-2015 Third Year Students Includes: Soil Formation, Basic Phase Relationship, soil classification, compaction, Consistency of soil, one dimensional fluid flow, two dimensional
Principal Symbols. f. Skin friction G Shear modulus. Cu Coefficient of uniformity Cc Coefficient of curvature
 Principal Symbols A, a Area A Air content A, A Pore pre.ssure coefficients a' Modified shear strength parameter (effective stress) a Dial gauge reading in oedometer test B Width of footing B, B Pore pressure
Principal Symbols A, a Area A Air content A, A Pore pre.ssure coefficients a' Modified shear strength parameter (effective stress) a Dial gauge reading in oedometer test B Width of footing B, B Pore pressure
Cyclic Triaxial Behavior of an Unsaturated Silty Soil Subjected to Suction Changes
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 215 Christchurch, New Zealand Cyclic Triaxial Behavior of an Unsaturated Silty Soil Subjected to Suction Changes T. Nishimura
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 215 Christchurch, New Zealand Cyclic Triaxial Behavior of an Unsaturated Silty Soil Subjected to Suction Changes T. Nishimura
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns. Local Flow System. Intermediate Flow System
 1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns c Local Flow System 10,000 feet Intermediate Flow System Regional Flow System 20,000 feet Hydrologic section
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns c Local Flow System 10,000 feet Intermediate Flow System Regional Flow System 20,000 feet Hydrologic section
10. GEOTECHNICAL EXPLORATION PROGRAM
 Geotechnical site investigations should be conducted in multiple phases to obtain data for use during the planning and design of the tunnel system. Geotechnical investigations typically are performed in
Geotechnical site investigations should be conducted in multiple phases to obtain data for use during the planning and design of the tunnel system. Geotechnical investigations typically are performed in
' International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement. 2 Groundwater Investigations. N.A. de Ridder'? 2.1 Introduction. 2.
 2 Groundwater Investigations N.A. de Ridder'? 2.1 Introduction Successful drainage depends largely on a proper diagnosis of the causes of the excess water. For this diagnosis, one must consider: climate,
2 Groundwater Investigations N.A. de Ridder'? 2.1 Introduction Successful drainage depends largely on a proper diagnosis of the causes of the excess water. For this diagnosis, one must consider: climate,
Excerpt from "Calculus" 2013 AoPS Inc.
 Excerpt from "Calculus" 03 AoPS Inc. Te term related rates refers to two quantities tat are dependent on eac oter and tat are canging over time. We can use te dependent relationsip between te quantities
Excerpt from "Calculus" 03 AoPS Inc. Te term related rates refers to two quantities tat are dependent on eac oter and tat are canging over time. We can use te dependent relationsip between te quantities
Continuity and Differentiability Worksheet
 Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Homework 1. Problem 1 Browse the 331 website to answer: When you should use data symbols on a graph. (Hint check out lab reports...
 Homework 1 Problem 1 Browse te 331 website to answer: Wen you sould use data symbols on a grap. (Hint ceck out lab reports...) Solution 1 Use data symbols to sow data points unless tere is so muc data
Homework 1 Problem 1 Browse te 331 website to answer: Wen you sould use data symbols on a grap. (Hint ceck out lab reports...) Solution 1 Use data symbols to sow data points unless tere is so muc data
Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 12.
 Capter 6. Fluid Mecanics Notes: Most of te material in tis capter is taken from Young and Freedman, Cap. 12. 6.1 Fluid Statics Fluids, i.e., substances tat can flow, are te subjects of tis capter. But
Capter 6. Fluid Mecanics Notes: Most of te material in tis capter is taken from Young and Freedman, Cap. 12. 6.1 Fluid Statics Fluids, i.e., substances tat can flow, are te subjects of tis capter. But
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 31 Module 7: Lecture - 6 on Geotechnical Physical Modelling Scaling laws in centrifuge modelling Force, work, and energy Consider the definition of potential energy PE normally expressed as energy lost
31 Module 7: Lecture - 6 on Geotechnical Physical Modelling Scaling laws in centrifuge modelling Force, work, and energy Consider the definition of potential energy PE normally expressed as energy lost
A. V T = 1 B. Ms = 1 C. Vs = 1 D. Vv = 1
 Geology and Soil Mechanics 55401 /1A (2002-2003) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Soil mechanics is the application of hydraulics, geology and mechanics to problems relating
Geology and Soil Mechanics 55401 /1A (2002-2003) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Soil mechanics is the application of hydraulics, geology and mechanics to problems relating
Introduction to Soil Mechanics
 Introduction to Soil Mechanics Sela Sode and Colin Jones WILEY Blackwell Contents Preface Dedication and Acknowledgments List of Symbols Soil Structure 1.1 Volume relationships 1.1.1 Voids ratio (e) 1.1.2
Introduction to Soil Mechanics Sela Sode and Colin Jones WILEY Blackwell Contents Preface Dedication and Acknowledgments List of Symbols Soil Structure 1.1 Volume relationships 1.1.1 Voids ratio (e) 1.1.2
Chapter 5 Control Volume Approach and Continuity Equation
 Chapter 5 Control Volume Approach and Continuity Equation Lagrangian and Eulerian Approach To evaluate the pressure and velocities at arbitrary locations in a flow field. The flow into a sudden contraction,
Chapter 5 Control Volume Approach and Continuity Equation Lagrangian and Eulerian Approach To evaluate the pressure and velocities at arbitrary locations in a flow field. The flow into a sudden contraction,
A = h w (1) Error Analysis Physics 141
 Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Lateral Earth Pressure
 1 of 11 6/2/2012 4:28 AM Lateral Earth Pressure The magnitude of lateral earth pressure depends on: 1. Shear strength characteristics of soil 2. Lateral strain condition 3. Pore water pressure 4. State
1 of 11 6/2/2012 4:28 AM Lateral Earth Pressure The magnitude of lateral earth pressure depends on: 1. Shear strength characteristics of soil 2. Lateral strain condition 3. Pore water pressure 4. State
APPENDIX C. Borehole Data
 APPENDIX C Borehole Data MAJOR DIVISIONS SOIL CLASSIFICATION CHART SYMBOLS GRAPH LETTER TYPICAL DESCRIPTIONS ADDITIONAL MATERIAL
APPENDIX C Borehole Data MAJOR DIVISIONS SOIL CLASSIFICATION CHART SYMBOLS GRAPH LETTER TYPICAL DESCRIPTIONS ADDITIONAL MATERIAL
Hydraulic properties of porous media
 PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
Evaluation of Flow Transmissibility of Rockfill Structures
 Evaluation of Flow Transmissibility of Rockfill Structures Toshihiro MORII 1 and Takahiko TATEISHI 2 Abstract To predict the hydraulic conditions during and after the construction of such structures as
Evaluation of Flow Transmissibility of Rockfill Structures Toshihiro MORII 1 and Takahiko TATEISHI 2 Abstract To predict the hydraulic conditions during and after the construction of such structures as
