1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow
|
|
|
- Phebe Fields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Carles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow Simulation: Te prediction of quantities of interest (dependent variables) based upon an equation or series of equations tat describe system beavior under a set of assumed simplifications. Groundwater Flow Simulation Predict ydraulic eads (1D, D, 3D) For particular conditions confined, unconfined, isotropic, anisotropic, omogeneous, eterogeneous, infinite, finite, steady, transient. Varying levels of complexity: Analystic solutions Teim, Teis, etc. Advantages: exact, simple, ceap, can provide sufficient insigt Analog simulation Pysical models scale models of aquifers Numerical Simulation Numerical Simulation Given a PDE and appropriate ICs and BCs Discretize te system Approximate te PDE corresponding to te discretization Solve te approximated PDE on a computer Commonly finite differences or finite elements for GW flow Advantages: can andle complex geometries, ICs, and C conditions; can be used for nonlinear systems. Beware of te term Model and ow it is used A model sould be used as simple as possible, but not simpler Matematical model a PDE Numerical model a particular tecnique is applied Computer or simulation model a code Finite Differences A numerical metod tat approximates te governing PDE by replacing te derivatives in te equation wit teir respective difference representations. Procedure involves: Grid (or Mes) and Equation Grid a representation of te pysical domain tat enables one to account for te boundaries and internal features 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page 1 of 7
2 Equation Difference Approximation of Derivatives S + x y T t D flow equation Approximating te Time Derivative: Backward Difference: i, j i, j,n i, j,n 1 t t t n t n ead n-1 t time t n-1 t n End of were, time step n te current time step index t time step i,j x and y coordinate indices Approximating te Space Derivatives: Consider a D discretization, if we assume tat te grid spacing in te x-direction and y-direction are te same, our discretized grid for an internal node will be: i,j+1 i-1,j i,j i+1,j i-1/ i+1/ i,j-1 y y x x 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page of 7
3 In te x-direction: Approximate derivative at location i,j : x Approximate te second spatial derivative at i,j as follows: i + 1/, j i 1/, j x x x x x We can approximate te first spatial derivative at i-1/,j and i+1/,j as follows: i 1/, j i, j i 1, j i + 1 /, j i + 1, j i, j x and x Substitute te above equations to obtain: i, x j + i, i i 1, j j, j i 1, j or i x +, j i 1, j i, j i + 1, j In te y-direction: i, y i, 1 i, + i, + 1 y j j j j Combining Flow Equation Terms: i, j i, j S i, j + x y T t η t For te backwards difference time derivative (note: all left and side values of are for time n-1) i 1, j i, j +i+ 1, j i, j 1 i, j + i, j +1 S i, j, n i, j, n 1 + y T t Linear diff. eq n. Tis eq n is not explicit for at any particular time If x and y are equal tis is te finite difference groundwater flow equation 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page 3 of 7
4 i 1, j + i + 1, j + i, j 1 + i, j i, j S i, j, n i, j, n 1 x T t Wat does te finite-difference equation indicate for steady state conditions? S S i, j, n i, j, n 1 0 t t j i + 1, j i, j 1 i, j + 1 i, j x i, 0 i 1, j + i + 1, j + i, j 1 + i, j i, j j i + 1, j i, j 1 i, j + 1 i, j 4 i, i,j+1 i-1,j i,j i+1,j i,j-1 Flow Value of ead at node is te average of te surrounding nodes (for SS isotropic omogeneous case) Consider te 1D steady-state flow equation wit a sink is: d H T w ' 0 or dx d H w ' dx T x H 1 3 H9 Node , Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page 4 of 7
5 Te nodal finite difference equation is: i, j 1 i, j + i, j +1 w ' T Or ( x ) w ' i, j 1 i, j + i, j +1 T Node 1: 1H () Node : Node 3: Node 3 as a forcing term due to te pumping of te well. Tis translates into an initial rigtand side of te equation: x w ' ( 0. 1) 1 ( ) Given 0.1, 1 T H (9) Te system of finite-difference equations consists of 3 equations and 3 unknowns Unknowns Or in coeffiecient matrix form Knowns FD Coeff. Unknown RHS containing Matrix Heads boundary conditions and known pumping 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page 5 of 7
6 Or in matrix notation it can be written as A b A is te matrix of difference coefficients H is te vector of unknown eads b is te RHS vector of known quantities A computational linear solve yields te vector : Transient Simulation Using Finite Differences Procedure: Marc Troug Time Start wit initial conditions (tese are known) Solve for eads at end of first time step t; tis give te spatial distribution of ead (a map) after a small time increment. Given known eads at end of first time step solve for eads at te end of te second time step. Wit known value at te end of time step solve for next time step tis is called marcing troug time A n b* were b* b + n-1 Te rigt-and side always contains knowns. Te matrix A is te matrix of finite difference coefficients reflecting te system parameters and discretization. So if you can solve spatial equations for one time step. Ten you can solve it for as many time steps as you like. Te time step must be small wen canges in eads are rapid suc as, wen you start to pump a well, t must be seconds or minutes. It can be increased as canges in ead become smaller. FD Simulation Models: codes tat solve te above system of linear algebraic equations fairly robust. 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page 6 of 7
7 Time Stepping S i, n, n i 1 i + i + 1 x n? n-1? T t n Someting else? Explicit i 1 Crank- Nicolson Implicit ead n-1 t T t s x ( i 1 i + i + 1 ) i, n, n i 1 t n-1 t n Explicit: i,n c i-1,n-1 + (1-C) i,n-1 + c i+1,n-1 T t Were: c s x Easy to calculate no linear algebra, but unstable if time-steps are too large. Implicit: c i-1,n - (1+C) i,n + c i+1,n - i,n-1 Results in system of linear equations tat must be solved simultaneously. Stable, but issues of accuracy. c Crank Nicolson: i 1, n (1+ c ) i, n + c i + 1, n ( c 1) i 1, n c ( i 1, n 1 + i, Not muc more numerical expense tan fully implicit, but more accurate Boundary Conditions: 1 n 1 ) Constant Head Don t write equation for constant ead node. Use value of constant ead in equations for neigboring nodes. Flux Boundary replace first derivative term wit constant i 1, j i, j i, j i + 1, j i, j x x x x i, j i +, x 1 j Q T 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Lecture Packet 9 Prof. Carles Harvey Page 7 of 7
Darcy s law in 3-D. K * xx K * yy K * zz
 PART 7 Equations of flow Darcy s law in 3-D Specific discarge (vector) is calculated by multiplying te ydraulic conductivity (second-order tensor) by te ydraulic gradient (vector). We obtain a general
PART 7 Equations of flow Darcy s law in 3-D Specific discarge (vector) is calculated by multiplying te ydraulic conductivity (second-order tensor) by te ydraulic gradient (vector). We obtain a general
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION. James T. Smith San Francisco State University. In calculus classes, you compute derivatives algebraically: for example,
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION James T Smit San Francisco State University In calculus classes, you compute derivatives algebraically: for example, f( x) = x + x f ( x) = x x Tis tecnique requires your knowing
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION James T Smit San Francisco State University In calculus classes, you compute derivatives algebraically: for example, f( x) = x + x f ( x) = x x Tis tecnique requires your knowing
Practice Problem Solutions: Exam 1
 Practice Problem Solutions: Exam 1 1. (a) Algebraic Solution: Te largest term in te numerator is 3x 2, wile te largest term in te denominator is 5x 2 3x 2 + 5. Tus lim x 5x 2 2x 3x 2 x 5x 2 = 3 5 Numerical
Practice Problem Solutions: Exam 1 1. (a) Algebraic Solution: Te largest term in te numerator is 3x 2, wile te largest term in te denominator is 5x 2 3x 2 + 5. Tus lim x 5x 2 2x 3x 2 x 5x 2 = 3 5 Numerical
How to Find the Derivative of a Function: Calculus 1
 Introduction How to Find te Derivative of a Function: Calculus 1 Calculus is not an easy matematics course Te fact tat you ave enrolled in suc a difficult subject indicates tat you are interested in te
Introduction How to Find te Derivative of a Function: Calculus 1 Calculus is not an easy matematics course Te fact tat you ave enrolled in suc a difficult subject indicates tat you are interested in te
Preface. Here are a couple of warnings to my students who may be here to get a copy of what happened on a day that you missed.
 Preface Here are my online notes for my course tat I teac ere at Lamar University. Despite te fact tat tese are my class notes, tey sould be accessible to anyone wanting to learn or needing a refreser
Preface Here are my online notes for my course tat I teac ere at Lamar University. Despite te fact tat tese are my class notes, tey sould be accessible to anyone wanting to learn or needing a refreser
lecture 26: Richardson extrapolation
 43 lecture 26: Ricardson extrapolation 35 Ricardson extrapolation, Romberg integration Trougout numerical analysis, one encounters procedures tat apply some simple approximation (eg, linear interpolation)
43 lecture 26: Ricardson extrapolation 35 Ricardson extrapolation, Romberg integration Trougout numerical analysis, one encounters procedures tat apply some simple approximation (eg, linear interpolation)
Notes on wavefunctions II: momentum wavefunctions
 Notes on wavefunctions II: momentum wavefunctions and uncertainty Te state of a particle at any time is described by a wavefunction ψ(x). Tese wavefunction must cange wit time, since we know tat particles
Notes on wavefunctions II: momentum wavefunctions and uncertainty Te state of a particle at any time is described by a wavefunction ψ(x). Tese wavefunction must cange wit time, since we know tat particles
Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria
 Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria Date: September 27, 20 Assignment Due Date: October 4, 20 Goal: In tis lab you will furter explore te concept of a derivative using R. You will use your knowledge
Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria Date: September 27, 20 Assignment Due Date: October 4, 20 Goal: In tis lab you will furter explore te concept of a derivative using R. You will use your knowledge
REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY. Witout using SN, find te derivative of eac of te following (you do not need to simplify your answers): a. f x 3x 3 5x x 6 f x 3 3x 5 x 0 b. g x 4 x x x notice te trick ere! x x g
REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY. Witout using SN, find te derivative of eac of te following (you do not need to simplify your answers): a. f x 3x 3 5x x 6 f x 3 3x 5 x 0 b. g x 4 x x x notice te trick ere! x x g
Finite Difference Methods Assignments
 Finite Difference Metods Assignments Anders Söberg and Aay Saxena, Micael Tuné, and Maria Westermarck Revised: Jarmo Rantakokko June 6, 1999 Teknisk databeandling Assignment 1: A one-dimensional eat equation
Finite Difference Metods Assignments Anders Söberg and Aay Saxena, Micael Tuné, and Maria Westermarck Revised: Jarmo Rantakokko June 6, 1999 Teknisk databeandling Assignment 1: A one-dimensional eat equation
AMS 147 Computational Methods and Applications Lecture 09 Copyright by Hongyun Wang, UCSC. Exact value. Effect of round-off error.
 Lecture 09 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Te total error in numerical differentiation fl( f ( x + fl( f ( x E T ( = f ( x Numerical result from a computer Exact value = e + f x+ Discretization error
Lecture 09 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Te total error in numerical differentiation fl( f ( x + fl( f ( x E T ( = f ( x Numerical result from a computer Exact value = e + f x+ Discretization error
Review of the Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow
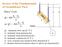 Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Lesson 6: The Derivative
 Lesson 6: Te Derivative Def. A difference quotient for a function as te form f(x + ) f(x) (x + ) x f(x + x) f(x) (x + x) x f(a + ) f(a) (a + ) a Notice tat a difference quotient always as te form of cange
Lesson 6: Te Derivative Def. A difference quotient for a function as te form f(x + ) f(x) (x + ) x f(x + x) f(x) (x + x) x f(a + ) f(a) (a + ) a Notice tat a difference quotient always as te form of cange
Section 3: The Derivative Definition of the Derivative
 Capter 2 Te Derivative Business Calculus 85 Section 3: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Returning to te tangent slope problem from te first section, let's look at te problem of finding te slope
Capter 2 Te Derivative Business Calculus 85 Section 3: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Returning to te tangent slope problem from te first section, let's look at te problem of finding te slope
Chapter 5 FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD (FDM)
 MEE7 Computer Modeling Tecniques in Engineering Capter 5 FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD (FDM) 5. Introduction to FDM Te finite difference tecniques are based upon approximations wic permit replacing differential
MEE7 Computer Modeling Tecniques in Engineering Capter 5 FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD (FDM) 5. Introduction to FDM Te finite difference tecniques are based upon approximations wic permit replacing differential
Simulation and verification of a plate heat exchanger with a built-in tap water accumulator
 Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
ETNA Kent State University
 Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 34, pp. 14-19, 2008. Copyrigt 2008,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA A NOTE ON NUMERICALLY CONSISTENT INITIAL VALUES FOR HIGH INDEX DIFFERENTIAL-ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS
Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 34, pp. 14-19, 2008. Copyrigt 2008,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA A NOTE ON NUMERICALLY CONSISTENT INITIAL VALUES FOR HIGH INDEX DIFFERENTIAL-ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS
Lecture 21. Numerical differentiation. f ( x+h) f ( x) h h
 Lecture Numerical differentiation Introduction We can analytically calculate te derivative of any elementary function, so tere migt seem to be no motivation for calculating derivatives numerically. However
Lecture Numerical differentiation Introduction We can analytically calculate te derivative of any elementary function, so tere migt seem to be no motivation for calculating derivatives numerically. However
INTRODUCTION TO CALCULUS LIMITS
 Calculus can be divided into two ke areas: INTRODUCTION TO CALCULUS Differential Calculus dealing wit its, rates of cange, tangents and normals to curves, curve sketcing, and applications to maima and
Calculus can be divided into two ke areas: INTRODUCTION TO CALCULUS Differential Calculus dealing wit its, rates of cange, tangents and normals to curves, curve sketcing, and applications to maima and
Differential Equations
 Pysics-based simulation xi Differential Equations xi+1 xi xi+1 xi + x x Pysics-based simulation xi Wat is a differential equation? Differential equations describe te relation between an unknown function
Pysics-based simulation xi Differential Equations xi+1 xi xi+1 xi + x x Pysics-based simulation xi Wat is a differential equation? Differential equations describe te relation between an unknown function
Math 312 Lecture Notes Modeling
 Mat 3 Lecture Notes Modeling Warren Weckesser Department of Matematics Colgate University 5 7 January 006 Classifying Matematical Models An Example We consider te following scenario. During a storm, a
Mat 3 Lecture Notes Modeling Warren Weckesser Department of Matematics Colgate University 5 7 January 006 Classifying Matematical Models An Example We consider te following scenario. During a storm, a
Continuity and Differentiability Worksheet
 Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION
 LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION LAURA EVANS.. Introduction Not all differential equations can be explicitly solved for y. Tis can be problematic if we need to know te value of y
LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION LAURA EVANS.. Introduction Not all differential equations can be explicitly solved for y. Tis can be problematic if we need to know te value of y
Consider a function f we ll specify which assumptions we need to make about it in a minute. Let us reformulate the integral. 1 f(x) dx.
 Capter 2 Integrals as sums and derivatives as differences We now switc to te simplest metods for integrating or differentiating a function from its function samples. A careful study of Taylor expansions
Capter 2 Integrals as sums and derivatives as differences We now switc to te simplest metods for integrating or differentiating a function from its function samples. A careful study of Taylor expansions
Numerical Differentiation
 Numerical Differentiation Finite Difference Formulas for te first derivative (Using Taylor Expansion tecnique) (section 8.3.) Suppose tat f() = g() is a function of te variable, and tat as 0 te function
Numerical Differentiation Finite Difference Formulas for te first derivative (Using Taylor Expansion tecnique) (section 8.3.) Suppose tat f() = g() is a function of te variable, and tat as 0 te function
MVT and Rolle s Theorem
 AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
2.3 Product and Quotient Rules
 .3. PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 75.3 Product and Quotient Rules.3.1 Product rule Suppose tat f and g are two di erentiable functions. Ten ( g (x)) 0 = f 0 (x) g (x) + g 0 (x) See.3.5 on page 77 for a proof.
.3. PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 75.3 Product and Quotient Rules.3.1 Product rule Suppose tat f and g are two di erentiable functions. Ten ( g (x)) 0 = f 0 (x) g (x) + g 0 (x) See.3.5 on page 77 for a proof.
CHAPTER 2 MODELING OF THREE-TANK SYSTEM
 7 CHAPTER MODELING OF THREE-TANK SYSTEM. INTRODUCTION Te interacting tree-tank system is a typical example of a nonlinear MIMO system. Heiming and Lunze (999) ave regarded treetank system as a bencmark
7 CHAPTER MODELING OF THREE-TANK SYSTEM. INTRODUCTION Te interacting tree-tank system is a typical example of a nonlinear MIMO system. Heiming and Lunze (999) ave regarded treetank system as a bencmark
Integral Calculus, dealing with areas and volumes, and approximate areas under and between curves.
 Calculus can be divided into two ke areas: Differential Calculus dealing wit its, rates of cange, tangents and normals to curves, curve sketcing, and applications to maima and minima problems Integral
Calculus can be divided into two ke areas: Differential Calculus dealing wit its, rates of cange, tangents and normals to curves, curve sketcing, and applications to maima and minima problems Integral
Chapter 8. Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations. Module No. 2. Predictor-Corrector Methods
 Numerical Analysis by Dr. Anita Pal Assistant Professor Department of Matematics National Institute of Tecnology Durgapur Durgapur-7109 email: anita.buie@gmail.com 1 . Capter 8 Numerical Solution of Ordinary
Numerical Analysis by Dr. Anita Pal Assistant Professor Department of Matematics National Institute of Tecnology Durgapur Durgapur-7109 email: anita.buie@gmail.com 1 . Capter 8 Numerical Solution of Ordinary
Comment on Experimental observations of saltwater up-coning
 1 Comment on Experimental observations of saltwater up-coning H. Zang 1,, D.A. Barry 2 and G.C. Hocking 3 1 Griffit Scool of Engineering, Griffit University, Gold Coast Campus, QLD 4222, Australia. Tel.:
1 Comment on Experimental observations of saltwater up-coning H. Zang 1,, D.A. Barry 2 and G.C. Hocking 3 1 Griffit Scool of Engineering, Griffit University, Gold Coast Campus, QLD 4222, Australia. Tel.:
1 Limits and Continuity
 1 Limits and Continuity 1.0 Tangent Lines, Velocities, Growt In tion 0.2, we estimated te slope of a line tangent to te grap of a function at a point. At te end of tion 0.3, we constructed a new function
1 Limits and Continuity 1.0 Tangent Lines, Velocities, Growt In tion 0.2, we estimated te slope of a line tangent to te grap of a function at a point. At te end of tion 0.3, we constructed a new function
Click here to see an animation of the derivative
 Differentiation Massoud Malek Derivative Te concept of derivative is at te core of Calculus; It is a very powerful tool for understanding te beavior of matematical functions. It allows us to optimize functions,
Differentiation Massoud Malek Derivative Te concept of derivative is at te core of Calculus; It is a very powerful tool for understanding te beavior of matematical functions. It allows us to optimize functions,
A = h w (1) Error Analysis Physics 141
 Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Differential Calculus (The basics) Prepared by Mr. C. Hull
 Differential Calculus Te basics) A : Limits In tis work on limits, we will deal only wit functions i.e. tose relationsips in wic an input variable ) defines a unique output variable y). Wen we work wit
Differential Calculus Te basics) A : Limits In tis work on limits, we will deal only wit functions i.e. tose relationsips in wic an input variable ) defines a unique output variable y). Wen we work wit
Numerical Analysis MTH603. dy dt = = (0) , y n+1. We obtain yn. Therefore. and. Copyright Virtual University of Pakistan 1
 Numerical Analysis MTH60 PREDICTOR CORRECTOR METHOD Te metods presented so far are called single-step metods, were we ave seen tat te computation of y at t n+ tat is y n+ requires te knowledge of y n only.
Numerical Analysis MTH60 PREDICTOR CORRECTOR METHOD Te metods presented so far are called single-step metods, were we ave seen tat te computation of y at t n+ tat is y n+ requires te knowledge of y n only.
3.4 Algebraic Limits. Ex 1) lim. Ex 2)
 Calculus Maimus.4 Algebraic Limits At tis point, you sould be very comfortable finding its bot grapically and numerically wit te elp of your graping calculator. Now it s time to practice finding its witout
Calculus Maimus.4 Algebraic Limits At tis point, you sould be very comfortable finding its bot grapically and numerically wit te elp of your graping calculator. Now it s time to practice finding its witout
Taylor Series and the Mean Value Theorem of Derivatives
 1 - Taylor Series and te Mean Value Teorem o Derivatives Te numerical solution o engineering and scientiic problems described by matematical models oten requires solving dierential equations. Dierential
1 - Taylor Series and te Mean Value Teorem o Derivatives Te numerical solution o engineering and scientiic problems described by matematical models oten requires solving dierential equations. Dierential
FINITE ELEMENT STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS
 FINITE ELEMENT STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS Murray Fredlund, P.D., P.Eng., SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, SK ABSTRACT Numerical models can be valuable tools in te prediction of seepage. Te results can often
FINITE ELEMENT STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS Murray Fredlund, P.D., P.Eng., SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, SK ABSTRACT Numerical models can be valuable tools in te prediction of seepage. Te results can often
Dedicated to the 70th birthday of Professor Lin Qun
 Journal of Computational Matematics, Vol.4, No.3, 6, 4 44. ACCELERATION METHODS OF NONLINEAR ITERATION FOR NONLINEAR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS Guang-wei Yuan Xu-deng Hang Laboratory of Computational Pysics,
Journal of Computational Matematics, Vol.4, No.3, 6, 4 44. ACCELERATION METHODS OF NONLINEAR ITERATION FOR NONLINEAR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS Guang-wei Yuan Xu-deng Hang Laboratory of Computational Pysics,
These errors are made from replacing an infinite process by finite one.
 Introduction :- Tis course examines problems tat can be solved by metods of approximation, tecniques we call numerical metods. We begin by considering some of te matematical and computational topics tat
Introduction :- Tis course examines problems tat can be solved by metods of approximation, tecniques we call numerical metods. We begin by considering some of te matematical and computational topics tat
MATH745 Fall MATH745 Fall
 MATH745 Fall 5 MATH745 Fall 5 INTRODUCTION WELCOME TO MATH 745 TOPICS IN NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Instructor: Dr Bartosz Protas Department of Matematics & Statistics Email: bprotas@mcmasterca Office HH 36, Ext
MATH745 Fall 5 MATH745 Fall 5 INTRODUCTION WELCOME TO MATH 745 TOPICS IN NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Instructor: Dr Bartosz Protas Department of Matematics & Statistics Email: bprotas@mcmasterca Office HH 36, Ext
Definition of the Derivative
 Te Limit Definition of te Derivative Tis Handout will: Define te limit grapically and algebraically Discuss, in detail, specific features of te definition of te derivative Provide a general strategy of
Te Limit Definition of te Derivative Tis Handout will: Define te limit grapically and algebraically Discuss, in detail, specific features of te definition of te derivative Provide a general strategy of
Average Rate of Change
 Te Derivative Tis can be tougt of as an attempt to draw a parallel (pysically and metaporically) between a line and a curve, applying te concept of slope to someting tat isn't actually straigt. Te slope
Te Derivative Tis can be tougt of as an attempt to draw a parallel (pysically and metaporically) between a line and a curve, applying te concept of slope to someting tat isn't actually straigt. Te slope
Problem Solving. Problem Solving Process
 Problem Solving One of te primary tasks for engineers is often solving problems. It is wat tey are, or sould be, good at. Solving engineering problems requires more tan just learning new terms, ideas and
Problem Solving One of te primary tasks for engineers is often solving problems. It is wat tey are, or sould be, good at. Solving engineering problems requires more tan just learning new terms, ideas and
Quaternion Dynamics, Part 1 Functions, Derivatives, and Integrals. Gary D. Simpson. rev 01 Aug 08, 2016.
 Quaternion Dynamics, Part 1 Functions, Derivatives, and Integrals Gary D. Simpson gsim1887@aol.com rev 1 Aug 8, 216 Summary Definitions are presented for "quaternion functions" of a quaternion. Polynomial
Quaternion Dynamics, Part 1 Functions, Derivatives, and Integrals Gary D. Simpson gsim1887@aol.com rev 1 Aug 8, 216 Summary Definitions are presented for "quaternion functions" of a quaternion. Polynomial
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES CONDITIONS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF A LIMIT
 LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Te limit of a function is defined as te value of y tat te curve approaces, as x approaces a particular value. Te limit of f (x) as x approaces a is written as f (x) approaces, as
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Te limit of a function is defined as te value of y tat te curve approaces, as x approaces a particular value. Te limit of f (x) as x approaces a is written as f (x) approaces, as
Seepage Analysis through Earth Dam Based on Finite Difference Method
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (11)111-1, 1 1, TetRoad Publication ISSN -44 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Researc www.tetroad.com Seepage Analysis troug Eart Dam Based on Finite Difference Metod
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (11)111-1, 1 1, TetRoad Publication ISSN -44 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Researc www.tetroad.com Seepage Analysis troug Eart Dam Based on Finite Difference Metod
Pre-Calculus Review Preemptive Strike
 Pre-Calculus Review Preemptive Strike Attaced are some notes and one assignment wit tree parts. Tese are due on te day tat we start te pre-calculus review. I strongly suggest reading troug te notes torougly
Pre-Calculus Review Preemptive Strike Attaced are some notes and one assignment wit tree parts. Tese are due on te day tat we start te pre-calculus review. I strongly suggest reading troug te notes torougly
Lecture XVII. Abstract We introduce the concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation with the gradient operator.
 Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Order of Accuracy. ũ h u Ch p, (1)
 Order of Accuracy 1 Terminology We consider a numerical approximation of an exact value u. Te approximation depends on a small parameter, wic can be for instance te grid size or time step in a numerical
Order of Accuracy 1 Terminology We consider a numerical approximation of an exact value u. Te approximation depends on a small parameter, wic can be for instance te grid size or time step in a numerical
Parameter Fitted Scheme for Singularly Perturbed Delay Differential Equations
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2013. 11, 4: 361-373 Parameter Fitted Sceme for Singularly Perturbed Delay Differential Equations Awoke Andargiea* and Y. N. Reddyb a b Department
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2013. 11, 4: 361-373 Parameter Fitted Sceme for Singularly Perturbed Delay Differential Equations Awoke Andargiea* and Y. N. Reddyb a b Department
Time (hours) Morphine sulfate (mg)
 Mat Xa Fall 2002 Review Notes Limits and Definition of Derivative Important Information: 1 According to te most recent information from te Registrar, te Xa final exam will be eld from 9:15 am to 12:15
Mat Xa Fall 2002 Review Notes Limits and Definition of Derivative Important Information: 1 According to te most recent information from te Registrar, te Xa final exam will be eld from 9:15 am to 12:15
THE IDEA OF DIFFERENTIABILITY FOR FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES Math 225
 THE IDEA OF DIFFERENTIABILITY FOR FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES Mat 225 As we ave seen, te definition of derivative for a Mat 111 function g : R R and for acurveγ : R E n are te same, except for interpretation:
THE IDEA OF DIFFERENTIABILITY FOR FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES Mat 225 As we ave seen, te definition of derivative for a Mat 111 function g : R R and for acurveγ : R E n are te same, except for interpretation:
Key Concepts. Important Techniques. 1. Average rate of change slope of a secant line. You will need two points ( a, the formula: to find value
 AB Calculus Unit Review Key Concepts Average and Instantaneous Speed Definition of Limit Properties of Limits One-sided and Two-sided Limits Sandwic Teorem Limits as x ± End Beaviour Models Continuity
AB Calculus Unit Review Key Concepts Average and Instantaneous Speed Definition of Limit Properties of Limits One-sided and Two-sided Limits Sandwic Teorem Limits as x ± End Beaviour Models Continuity
SECTION 3.2: DERIVATIVE FUNCTIONS and DIFFERENTIABILITY
 (Section 3.2: Derivative Functions and Differentiability) 3.2.1 SECTION 3.2: DERIVATIVE FUNCTIONS and DIFFERENTIABILITY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Know, understand, and apply te Limit Definition of te Derivative
(Section 3.2: Derivative Functions and Differentiability) 3.2.1 SECTION 3.2: DERIVATIVE FUNCTIONS and DIFFERENTIABILITY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Know, understand, and apply te Limit Definition of te Derivative
CS522 - Partial Di erential Equations
 CS5 - Partial Di erential Equations Tibor Jánosi April 5, 5 Numerical Di erentiation In principle, di erentiation is a simple operation. Indeed, given a function speci ed as a closed-form formula, its
CS5 - Partial Di erential Equations Tibor Jánosi April 5, 5 Numerical Di erentiation In principle, di erentiation is a simple operation. Indeed, given a function speci ed as a closed-form formula, its
A h u h = f h. 4.1 The CoarseGrid SystemandtheResidual Equation
 Capter Grid Transfer Remark. Contents of tis capter. Consider a grid wit grid size and te corresponding linear system of equations A u = f. Te summary given in Section 3. leads to te idea tat tere migt
Capter Grid Transfer Remark. Contents of tis capter. Consider a grid wit grid size and te corresponding linear system of equations A u = f. Te summary given in Section 3. leads to te idea tat tere migt
LECTURE 14 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION. Find
 LECTURE 14 NUMERCAL NTEGRATON Find b a fxdx or b a vx ux fx ydy dx Often integration is required. However te form of fx may be suc tat analytical integration would be very difficult or impossible. Use
LECTURE 14 NUMERCAL NTEGRATON Find b a fxdx or b a vx ux fx ydy dx Often integration is required. However te form of fx may be suc tat analytical integration would be very difficult or impossible. Use
New Streamfunction Approach for Magnetohydrodynamics
 New Streamfunction Approac for Magnetoydrodynamics Kab Seo Kang Brooaven National Laboratory, Computational Science Center, Building 63, Room, Upton NY 973, USA. sang@bnl.gov Summary. We apply te finite
New Streamfunction Approac for Magnetoydrodynamics Kab Seo Kang Brooaven National Laboratory, Computational Science Center, Building 63, Room, Upton NY 973, USA. sang@bnl.gov Summary. We apply te finite
Continuity. Example 1
 Continuity MATH 1003 Calculus and Linear Algebra (Lecture 13.5) Maoseng Xiong Department of Matematics, HKUST A function f : (a, b) R is continuous at a point c (a, b) if 1. x c f (x) exists, 2. f (c)
Continuity MATH 1003 Calculus and Linear Algebra (Lecture 13.5) Maoseng Xiong Department of Matematics, HKUST A function f : (a, b) R is continuous at a point c (a, b) if 1. x c f (x) exists, 2. f (c)
Mass Lumping for Constant Density Acoustics
 Lumping 1 Mass Lumping for Constant Density Acoustics William W. Symes ABSTRACT Mass lumping provides an avenue for efficient time-stepping of time-dependent problems wit conforming finite element spatial
Lumping 1 Mass Lumping for Constant Density Acoustics William W. Symes ABSTRACT Mass lumping provides an avenue for efficient time-stepping of time-dependent problems wit conforming finite element spatial
The total error in numerical differentiation
 AMS 147 Computational Metods and Applications Lecture 08 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Loss of accuracy due to numerical cancellation A B 3, 3 ~10 16 In calculating te difference between A and
AMS 147 Computational Metods and Applications Lecture 08 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Loss of accuracy due to numerical cancellation A B 3, 3 ~10 16 In calculating te difference between A and
Introduction to Multigrid Method
 Introduction to Multigrid Metod Presented by: Bogojeska Jasmina /08/005 JASS, 005, St. Petersburg 1 Te ultimate upsot of MLAT Te amount of computational work sould be proportional to te amount of real
Introduction to Multigrid Metod Presented by: Bogojeska Jasmina /08/005 JASS, 005, St. Petersburg 1 Te ultimate upsot of MLAT Te amount of computational work sould be proportional to te amount of real
Section 2: The Derivative Definition of the Derivative
 Capter 2 Te Derivative Applied Calculus 80 Section 2: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Suppose we drop a tomato from te top of a 00 foot building and time its fall. Time (sec) Heigt (ft) 0.0 00
Capter 2 Te Derivative Applied Calculus 80 Section 2: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Suppose we drop a tomato from te top of a 00 foot building and time its fall. Time (sec) Heigt (ft) 0.0 00
, meant to remind us of the definition of f (x) as the limit of difference quotients: = lim
 Mat 132 Differentiation Formulas Stewart 2.3 So far, we ave seen ow various real-world problems rate of cange and geometric problems tangent lines lead to derivatives. In tis section, we will see ow to
Mat 132 Differentiation Formulas Stewart 2.3 So far, we ave seen ow various real-world problems rate of cange and geometric problems tangent lines lead to derivatives. In tis section, we will see ow to
The derivative function
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter : Definition of derivative Section Te derivative function Wat you need to know already: f is at a point on its grap and ow to compute it. Wat te derivative
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter : Definition of derivative Section Te derivative function Wat you need to know already: f is at a point on its grap and ow to compute it. Wat te derivative
Section 2.7 Derivatives and Rates of Change Part II Section 2.8 The Derivative as a Function. at the point a, to be. = at time t = a is
 Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Introduction to Derivatives
 Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
2.11 That s So Derivative
 2.11 Tat s So Derivative Introduction to Differential Calculus Just as one defines instantaneous velocity in terms of average velocity, we now define te instantaneous rate of cange of a function at a point
2.11 Tat s So Derivative Introduction to Differential Calculus Just as one defines instantaneous velocity in terms of average velocity, we now define te instantaneous rate of cange of a function at a point
4.2 - Richardson Extrapolation
 . - Ricardson Extrapolation. Small-O Notation: Recall tat te big-o notation used to define te rate of convergence in Section.: Definition Let x n n converge to a number x. Suppose tat n n is a sequence
. - Ricardson Extrapolation. Small-O Notation: Recall tat te big-o notation used to define te rate of convergence in Section.: Definition Let x n n converge to a number x. Suppose tat n n is a sequence
Quantum Numbers and Rules
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42614 1 Quantum Numbers and Rules OpenStax College Tis work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under te Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene quantum number.
OpenStax-CNX module: m42614 1 Quantum Numbers and Rules OpenStax College Tis work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under te Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene quantum number.
Brief Review of Vector Calculus
 Darc s Law in 3D Toda Vector Calculus Darc s Law in 3D q " A scalar as onl a magnitude A vector is caracteried b bot direction and magnitude. e.g, g, q, v,"," Vectors are represented b : boldface in boos,
Darc s Law in 3D Toda Vector Calculus Darc s Law in 3D q " A scalar as onl a magnitude A vector is caracteried b bot direction and magnitude. e.g, g, q, v,"," Vectors are represented b : boldface in boos,
Material for Difference Quotient
 Material for Difference Quotient Prepared by Stepanie Quintal, graduate student and Marvin Stick, professor Dept. of Matematical Sciences, UMass Lowell Summer 05 Preface Te following difference quotient
Material for Difference Quotient Prepared by Stepanie Quintal, graduate student and Marvin Stick, professor Dept. of Matematical Sciences, UMass Lowell Summer 05 Preface Te following difference quotient
Mathematics 5 Worksheet 11 Geometry, Tangency, and the Derivative
 Matematics 5 Workseet 11 Geometry, Tangency, and te Derivative Problem 1. Find te equation of a line wit slope m tat intersects te point (3, 9). Solution. Te equation for a line passing troug a point (x
Matematics 5 Workseet 11 Geometry, Tangency, and te Derivative Problem 1. Find te equation of a line wit slope m tat intersects te point (3, 9). Solution. Te equation for a line passing troug a point (x
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. Section 1.5 = = = 4. Check Point Exercises The slope of the line y = 3x+ 1 is 3.
 Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Physically Based Modeling: Principles and Practice Implicit Methods for Differential Equations
 Pysically Based Modeling: Principles and Practice Implicit Metods for Differential Equations David Baraff Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Please note: Tis document is 997 by David Baraff
Pysically Based Modeling: Principles and Practice Implicit Metods for Differential Equations David Baraff Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Please note: Tis document is 997 by David Baraff
3.4 Worksheet: Proof of the Chain Rule NAME
 Mat 1170 3.4 Workseet: Proof of te Cain Rule NAME Te Cain Rule So far we are able to differentiate all types of functions. For example: polynomials, rational, root, and trigonometric functions. We are
Mat 1170 3.4 Workseet: Proof of te Cain Rule NAME Te Cain Rule So far we are able to differentiate all types of functions. For example: polynomials, rational, root, and trigonometric functions. We are
5 Ordinary Differential Equations: Finite Difference Methods for Boundary Problems
 5 Ordinary Differential Equations: Finite Difference Metods for Boundary Problems Read sections 10.1, 10.2, 10.4 Review questions 10.1 10.4, 10.8 10.9, 10.13 5.1 Introduction In te previous capters we
5 Ordinary Differential Equations: Finite Difference Metods for Boundary Problems Read sections 10.1, 10.2, 10.4 Review questions 10.1 10.4, 10.8 10.9, 10.13 5.1 Introduction In te previous capters we
A MONTE CARLO ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECTS OF COVARIANCE ON PROPAGATED UNCERTAINTIES
 A MONTE CARLO ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECTS OF COVARIANCE ON PROPAGATED UNCERTAINTIES Ronald Ainswort Hart Scientific, American Fork UT, USA ABSTRACT Reports of calibration typically provide total combined uncertainties
A MONTE CARLO ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECTS OF COVARIANCE ON PROPAGATED UNCERTAINTIES Ronald Ainswort Hart Scientific, American Fork UT, USA ABSTRACT Reports of calibration typically provide total combined uncertainties
1 Calculus. 1.1 Gradients and the Derivative. Q f(x+h) f(x)
 Calculus. Gradients and te Derivative Q f(x+) δy P T δx R f(x) 0 x x+ Let P (x, f(x)) and Q(x+, f(x+)) denote two points on te curve of te function y = f(x) and let R denote te point of intersection of
Calculus. Gradients and te Derivative Q f(x+) δy P T δx R f(x) 0 x x+ Let P (x, f(x)) and Q(x+, f(x+)) denote two points on te curve of te function y = f(x) and let R denote te point of intersection of
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL IFFERENTIATION FIRST ERIVATIVES Te simplest difference formulas are based on using a straigt line to interpolate te given data; tey use two data pints to estimate te derivative. We assume tat
NUMERICAL IFFERENTIATION FIRST ERIVATIVES Te simplest difference formulas are based on using a straigt line to interpolate te given data; tey use two data pints to estimate te derivative. We assume tat
Bob Brown Math 251 Calculus 1 Chapter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 CCBC Dundalk
 Bob Brown Mat 251 Calculus 1 Capter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 Te Tangent Line Problem Te idea of a tangent line first arises in geometry in te context of a circle. But before we jump into a discussion of
Bob Brown Mat 251 Calculus 1 Capter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 Te Tangent Line Problem Te idea of a tangent line first arises in geometry in te context of a circle. But before we jump into a discussion of
. Compute the following limits.
 Today: Tangent Lines and te Derivative at a Point Warmup:. Let f(x) =x. Compute te following limits. f( + ) f() (a) lim f( +) f( ) (b) lim. Let g(x) = x. Compute te following limits. g(3 + ) g(3) (a) lim
Today: Tangent Lines and te Derivative at a Point Warmup:. Let f(x) =x. Compute te following limits. f( + ) f() (a) lim f( +) f( ) (b) lim. Let g(x) = x. Compute te following limits. g(3 + ) g(3) (a) lim
1. Which one of the following expressions is not equal to all the others? 1 C. 1 D. 25x. 2. Simplify this expression as much as possible.
 004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
Differential equations. Differential equations
 Differential equations A differential equation (DE) describes ow a quantity canges (as a function of time, position, ) d - A ball dropped from a building: t gt () dt d S qx - Uniformly loaded beam: wx
Differential equations A differential equation (DE) describes ow a quantity canges (as a function of time, position, ) d - A ball dropped from a building: t gt () dt d S qx - Uniformly loaded beam: wx
Solution for the Homework 4
 Solution for te Homework 4 Problem 6.5: In tis section we computed te single-particle translational partition function, tr, by summing over all definite-energy wavefunctions. An alternative approac, owever,
Solution for te Homework 4 Problem 6.5: In tis section we computed te single-particle translational partition function, tr, by summing over all definite-energy wavefunctions. An alternative approac, owever,
(4.2) -Richardson Extrapolation
 (.) -Ricardson Extrapolation. Small-O Notation: Recall tat te big-o notation used to define te rate of convergence in Section.: Suppose tat lim G 0 and lim F L. Te function F is said to converge to L as
(.) -Ricardson Extrapolation. Small-O Notation: Recall tat te big-o notation used to define te rate of convergence in Section.: Suppose tat lim G 0 and lim F L. Te function F is said to converge to L as
Derivatives. By: OpenStaxCollege
 By: OpenStaxCollege Te average teen in te United States opens a refrigerator door an estimated 25 times per day. Supposedly, tis average is up from 10 years ago wen te average teenager opened a refrigerator
By: OpenStaxCollege Te average teen in te United States opens a refrigerator door an estimated 25 times per day. Supposedly, tis average is up from 10 years ago wen te average teenager opened a refrigerator
MAT244 - Ordinary Di erential Equations - Summer 2016 Assignment 2 Due: July 20, 2016
 MAT244 - Ordinary Di erential Equations - Summer 206 Assignment 2 Due: July 20, 206 Full Name: Student #: Last First Indicate wic Tutorial Section you attend by filling in te appropriate circle: Tut 0
MAT244 - Ordinary Di erential Equations - Summer 206 Assignment 2 Due: July 20, 206 Full Name: Student #: Last First Indicate wic Tutorial Section you attend by filling in te appropriate circle: Tut 0
Entropy and the numerical integration of conservation laws
 Pysics Procedia Pysics Procedia 00 2011) 1 28 Entropy and te numerical integration of conservation laws Gabriella Puppo Dipartimento di Matematica, Politecnico di Torino Italy) Matteo Semplice Dipartimento
Pysics Procedia Pysics Procedia 00 2011) 1 28 Entropy and te numerical integration of conservation laws Gabriella Puppo Dipartimento di Matematica, Politecnico di Torino Italy) Matteo Semplice Dipartimento
The Electron in a Potential
 Te Electron in a Potential Edwin F. Taylor July, 2000 1. Stopwatc rotation for an electron in a potential For a poton we found tat te and of te quantum stopwatc rotates wit frequency f given by te equation:
Te Electron in a Potential Edwin F. Taylor July, 2000 1. Stopwatc rotation for an electron in a potential For a poton we found tat te and of te quantum stopwatc rotates wit frequency f given by te equation:
A method of Lagrange Galerkin of second order in time. Une méthode de Lagrange Galerkin d ordre deux en temps
 A metod of Lagrange Galerkin of second order in time Une métode de Lagrange Galerkin d ordre deux en temps Jocelyn Étienne a a DAMTP, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, Great-Britain.
A metod of Lagrange Galerkin of second order in time Une métode de Lagrange Galerkin d ordre deux en temps Jocelyn Étienne a a DAMTP, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, Great-Britain.
Polynomial Functions. Linear Functions. Precalculus: Linear and Quadratic Functions
 Concepts: definition of polynomial functions, linear functions tree representations), transformation of y = x to get y = mx + b, quadratic functions axis of symmetry, vertex, x-intercepts), transformations
Concepts: definition of polynomial functions, linear functions tree representations), transformation of y = x to get y = mx + b, quadratic functions axis of symmetry, vertex, x-intercepts), transformations
Derivatives of Exponentials
 mat 0 more on derivatives: day 0 Derivatives of Eponentials Recall tat DEFINITION... An eponential function as te form f () =a, were te base is a real number a > 0. Te domain of an eponential function
mat 0 more on derivatives: day 0 Derivatives of Eponentials Recall tat DEFINITION... An eponential function as te form f () =a, were te base is a real number a > 0. Te domain of an eponential function
Exam in Fluid Mechanics SG2214
 Exam in Fluid Mecanics G2214 Final exam for te course G2214 23/10 2008 Examiner: Anders Dalkild Te point value of eac question is given in parentesis and you need more tan 20 points to pass te course including
Exam in Fluid Mecanics G2214 Final exam for te course G2214 23/10 2008 Examiner: Anders Dalkild Te point value of eac question is given in parentesis and you need more tan 20 points to pass te course including
1watt=1W=1kg m 2 /s 3
 Appendix A Matematics Appendix A.1 Units To measure a pysical quantity, you need a standard. Eac pysical quantity as certain units. A unit is just a standard we use to compare, e.g. a ruler. In tis laboratory
Appendix A Matematics Appendix A.1 Units To measure a pysical quantity, you need a standard. Eac pysical quantity as certain units. A unit is just a standard we use to compare, e.g. a ruler. In tis laboratory
INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS
 Capter 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PREVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips
Capter 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PREVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips
Chapter 2 Ising Model for Ferromagnetism
 Capter Ising Model for Ferromagnetism Abstract Tis capter presents te Ising model for ferromagnetism, wic is a standard simple model of a pase transition. Using te approximation of mean-field teory, te
Capter Ising Model for Ferromagnetism Abstract Tis capter presents te Ising model for ferromagnetism, wic is a standard simple model of a pase transition. Using te approximation of mean-field teory, te
ERROR BOUNDS FOR THE METHODS OF GLIMM, GODUNOV AND LEVEQUE BRADLEY J. LUCIER*
 EO BOUNDS FO THE METHODS OF GLIMM, GODUNOV AND LEVEQUE BADLEY J. LUCIE* Abstract. Te expected error in L ) attimet for Glimm s sceme wen applied to a scalar conservation law is bounded by + 2 ) ) /2 T
EO BOUNDS FO THE METHODS OF GLIMM, GODUNOV AND LEVEQUE BADLEY J. LUCIE* Abstract. Te expected error in L ) attimet for Glimm s sceme wen applied to a scalar conservation law is bounded by + 2 ) ) /2 T
