2010 National Science Olympiad Fossil Test Final Qs & A s
|
|
|
- Shana Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2010 National Science Olympiad Fossil Test Final Qs & A s Note: Fossil pictures are unavailable (consider using the internet for samples) Station 1 Specimens A and B. DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET (rolled trilobite and metasequoia) 1. What is A (common name of Class)? (Trilobita) 2. Why would this fossil form occur (self protection) 3. For B, what is a common name for the feature that is fossilized? (pinecone or cone) 4. What is the genus name of B? (Metasequoia) 5. Which specimen is older, A or B? ( A)
2 Station 2 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET Identify fossils A., B., C., D., and E. to their common name Phylum or subphylum and Class 6. A = (crinoid, Phylum Echinodermata, Class Crinoidea, range Ord Recent 7. B =(Jellyfish, Phylum Cnidaria, subphylum/class Scyphozoa, age range PC to Recent) 8. C= (shrimp, Phylum Arthropoda, Subphylum Crustacea, range Lower Jurrasic Recent 9. D= (horn coral, Phylum Cnidaria, Class Anthozoa, Order Rugosa, range Ord Permian 10. E = (trilobite, Phylum Arthropoda, Class Trilobita, age range Cambrian Permian 11. Based on time of first appearance in the fossil record, place fossils in order of oldest to youngest as best you can. (B, jellyfish, E trilobite, A/D crinoid & horn coral, C shrimp. 12. What are age ranges of oldest and youngest? (B jellyfish PC to Recent, C shrimp L Jurassic Recent)
3 Station 3 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS; USE ANSWER PAGE Two fossils, A., and B. 13. Identify A to its Kingdom and Genus and age range (K Plantae, Genus Calamites; 14. Identify B to its Kingdom and Genus (kingdom Plantae, Genus Ginkgo) 15. Which is older, A or B? (A, Calamites) 16. Are there living counterparts to A today? If so, list/describe their living counterparts. (Yes, modern horsetails; but calamites is extinct) 17. Are there living counterparts to B today? If so, list/describe living counterparts (ginkgos live unchanged to this day) 18. How is A preserved? (internal mold or cast) 19. How is B preserved? (Impression in a concretion)
4 Station 4 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! 20. What is specimen A? A)it is a vertebrae or backbone B) it is a coral C) it is a cephalopod D) is a Bryozoan (answer= C) 21. Describe and name the distinguishing feature did you base your decision on (for Specimen A) =(bands or lines encircling specimen; septa, simple) 22. What is the environment A lived in? (Answer = B) A)terrestrial B) Marine C) terrestrial OR marine D) none of the above 23. What is specimen B? A) root i. bone C)bark D)none of the above (Answer A, root) 24. How did A move around OR did it move around? (Answer: it floated or swam jet propulsion squirting water through body) 25. Was A: (answer D none of above) 26. What Genus is B from? (Lepidodendron, stigmara or root)
5 Station 5 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! 27. What is Phylum, Genus, range of A? (Phylum Brachiopoda, Genus Platystrophia, Ord Sil) 28. What Phylum, Genus, range of B? (Phylum Brachiopoda, Genus Mucrospirifer, range Dev) 29. What Phylum, Genus, range of C? (Phylum Mollusca, Genus Gryphaea, extinct, bivalve, Jur Cret range ) 30. Choose the correct answer. Are they? A. articulate (answer A) 31. How can you distinguish the phyla represented? (answer: Brachiopods have upper and lower valves, bivalve mollusks have left and right arrangement)
6 Station 6 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! 32. What Phylum and Class is A? or is it a trace fossil? (Phylum Mollusca, Class Gastropoda) 33. What Phylum and Class is B? (Phylum Mollusca, Class Gastropoda) 34. What does the Genus name of B mean? (little tower or little turret) 35. What is the test in these fossils symmetrical around or associated with? (C,symmetrical about an axis ) 36. How did B feed? (A, filter feeder, living in sediment) 37. Would you expect to see this from sediments of the Devonian Era? (No, range is Cretaceous Recent)
7 Station 7 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! 38. What is this fossil commonly known as? Fish 39. How is it preserved? (film, or mineralized film or impression film) 40. What is the age range of these creatures? (answer D, Ordovician to present 41. What are the earliest of this group commonly known as? (jawless fish) 42. What was the geological period when these creatures were dominant? (Devonian, the age of fishes)
8 Station 8 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! Specimens A, B and C. 43. What Phylum is represented, and what is its range (Echinodermata, Cambrian Recent) 44. What is common about specimen B s and C s appearance?(5 fold symmetry, or radial symmetry) 45. What Class is A? (Crinoidea) 46. What Class is B?, and is it extant? (Blastoid, no) 47. What Class is C, and what is its common name? (Echinoid, sea urchin) 48. How is C preserved? (internal mold)
9 Station 9 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! Three specimens, A, B, C. 49. What Phyla or Phylum is represented by specimens (are they from the same or from two different Phyla?) (Cnidaria, coral) 50. What is genus and the common name of A? (Halysites, chain coral) 51. What is genus of B? (Favosites) 52. What is genus of C, and a common name for it? (hexagonaria, Petosky stone) 53. Describe the setting you would find these specimens in? (marine, reef) 54. Which is the youngest, in terms of their first appearance in the geologic record? When was that? (Hexagonaria, first appeared in Devonian)
10 Station 10 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET 55. What Phylum is represented by the samples?bryozoa) 56. Identify Genus of A (Archimedes) 57. Identify fossil labeled B (Rhombopora) 58. What growth form is represented by B? (branching) 59. How did it get energy/food? (filter feeding) 60. What is an individual, connected organism known as? (zooid)
11 Station 11 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! 61. What is specimen A? (bone) 62. how is A preserved? (replacement) 63. Was A solitary or colonial? (solitary) 64. Was the creature mobile or sessile? (mobile) 65. What is specimen B? (coral) 66. How is B preserved? (replacement) 67. Is B mobile or sessile? (SESSILE) 68. Which is older, A or B? (B)
12 Station 12 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET use your answer sheet! 69. What is this specimen? Give the general or common name. (FISH) 70. List 2 or more features you observed that lead you to choose your answer in 73? (EYE SOCKETS, JAW, TEETH) 71. What is the age range of this Class? (FIRST FISH WAS ORDOVICIAN)
13 Station 13. DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE, USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET Two specimens, A and B. 72. What Phylum and Class does specimen A come from? (Phylum Chordata, Class Condrichthyes) 73. What is the function of fossil A? (a shell crushing tooth, not meat biting) How does this fossil grow? (from the gums of cartilagenous fish) 75. What Phylum and Class does specimen B come from? (Phylum Mollusca, Class Bivalvia) 76. How are both A and B preserved? (as concretions with replacement of original parts)
14 Station 14 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE; USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET 77. One specimen, name 4 different Phyla represented (Mollusca, Crinoidea, Bryozoa, Brachiopoda) 78. What is the oldest geologic period that may be represented by this slab, and why? (Ordovician, because Crinoids and Bryozoans are not known in the fossil record until then). 79. What kind of rock is this? (fossiliferous limestone or fossiliferous dolomite) 80. Are the general life forms represented by these phyla extinct or extant, and what does this mean? (extant, meaning existing today)
15 STATION 15 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET Specimens, A, B, and C. Two are models from fossils, one is a naturallyoccurring fossil. 81. What is the Class and Genus and range of A? (Class Aves, Genus Archaeopteryx, late Jurassic) 82. What is the Class, Order and general name of B? (Class Reptilia, a Pterosaur, pterodactylus) 83. What is the genus represented by C, and what general group is this from? (Lepidodendron, a Lycopod or scale tree) 84. What is similar about these three specimens? (all are fossils, prehistoric, extinct) 85. What are three marked differences between the specimens? (A is Archaeopteryx, a bird with feathers, B is a winged Reptile, Pterosaur, no feathers; C is a plant, club moss, scale tree) 86. Which one displays a most remarkable new evolutionary step? And what is that step? (A, Archaeopteryx, feathers)
16 Station 16 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE, USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET Two specimens, A and B 87. Identify A to Kingdom. (Animalia) BONE 88. Identify B to Kingdom. (Plantae) PETRIFIED WOOD 89. How is B preserved? Define the preservation term. (petrification, where original matter is replaced with minerals) 90. Specimen A is from an age range of about 100 My to about 65 My. What sort of host is this most likely to be a fossil from? (dinosaur or reptile) 91. Would fossil A be extant? Why or why not? (No, post Cretaceous extinction event)
17 Station 17 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE, USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET Three specimens, A, B, and C 92. What is the general term for this kind of fossil? Contrast it with other kinds of fossils. (TRACE FOSSIL, NOT A LIFE FORM BUT EVIDENCE LIFE WAS THERE) 93. What is the mode of preservation of A? (A, cast or mold) 94. Which type of ichnofossil is A? (trace of trail) 95. Which type of ichnofossil is B? (Domicle or burrow) 96. Which type of ichnofossil is C? (Coprolite, fossil poop, dung)
18 Station 18 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE, USE YOUR ANSWER SHEET Specimen Y 97. What general type of fossil is Y? (stromatolite) 98. How does Y form? (algae and sediment layers, as sediment is deposited and sticks to algal gel, the algae grows up to stay in sunlight) 99. What is the age range of Y? (Precambrian to present) 100. How is it preserved? (silicification, petrification) 101. Where might you see this forming today? (Australia coast)
19 Station 19 These are two views a creature that is significant in the fossil record for several primary reasons. List two of the most significant reasons Reason 1: SURVIVED END OF PERMIAN EXTINCTION EVENT 103. Reason 2: WAS ONLY LARGE LAND ANIMAL TO SURVIVE & BECAME MOST POPULOUS LAND ANIMAL IMMEDIATELY AFTER EXTINCTION EVENT 104. What is the creature s Genus? GENUS LYSTOSAURUS a synapsid (subclass) 105. How can you tell the fossil s Class? (can tell it is a reptile, it walks with 4 feet on ground, not upright or leaning 106. Can tell it is Reptilia (Class) because it walks on 4 feet, not upright, not.
20 Station 20 (Tiebreaker, answer only counts if you are tied after 1 19.) C A B D 107. This chart shows major extinction events in geological time.the chart starts in the deep past on the lower left corner. The generalized extremity of the event in numbers of genus lost to extinction is denoted by increasing amounts on the left ( y ) axis. Time in millions of years ago is on the bottom ( x ) axis. Name the events noted at A, B, C and D by the common names for the event, their approximate time of occurrence A =Ordovican Silurian MYA 109. B = Late Devonian MYA near Devonian carboniferous transition 110. C = C Permian Triassic, the Great Dying, 251 MYA (=end of many species, especially end of many mammal like reptiles; mammals took 30 MY to rise again 111. D = Cretaceous Tertiary (K T) 65 MYA (end of dinosaurs, followed by rise of mammals and birds)
21 C A B D This chart shows major extinction events in geological time. The chart starts in the deep past on the lower left corner. The generalized extremity of the event in numbers of genus lost to extinction is denoted by increasing amounts on the left ( y ) axis. Time in millions of years ago is on the bottom ( x ) axis. Label the events noted at A. B, C and D by the common names for the event, their approximate time of occurrence. A = B = C = D = What was a significant change in life on earth following D? What was a significant change in life on earth following C?
Wisconsin Science Olympiad 2015 West Regional Fossils. Team Name:
 Wisconsin Science Olympiad 2015 West Regional Fossils Team Name: Team Members: There are 12 stations and you will have approximately 3-4 minutes at each one. Each page of the test corresponds to one of
Wisconsin Science Olympiad 2015 West Regional Fossils Team Name: Team Members: There are 12 stations and you will have approximately 3-4 minutes at each one. Each page of the test corresponds to one of
STATION 4. STATION refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version. Can you name this fossil? Class
 STATION 1 Can you name this fossil? Phylum Class STATION 2 --- refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version Identify the Phylum of each specimen Genus When did he live? Cambrian,
STATION 1 Can you name this fossil? Phylum Class STATION 2 --- refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version Identify the Phylum of each specimen Genus When did he live? Cambrian,
Activity Two: The Classic Fossil Lab - Simple Format
 Activity Two: The Classic Fossil Lab - Simple Format Materials: Lab Handout, One Baggy for each group with the following items: trilobite, brachiopod, pelecypod, horn coral, blastoid, shark s tooth, gastropod,
Activity Two: The Classic Fossil Lab - Simple Format Materials: Lab Handout, One Baggy for each group with the following items: trilobite, brachiopod, pelecypod, horn coral, blastoid, shark s tooth, gastropod,
Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups
 Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups The objective of this lab is to classify all of the fossils from your site to phylum (or to plant group)
Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups The objective of this lab is to classify all of the fossils from your site to phylum (or to plant group)
Station Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus
 Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Directed Reading. Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era EVOLUTION. beginning of life is called. to. PRECAMBRIAN TIME.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Geologic Time. What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.
 Geologic Time There are 2 kinds: What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.) Relative Age The age compared to the ages of other
Geologic Time There are 2 kinds: What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.) Relative Age The age compared to the ages of other
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Radiolaria and the Rock Record
 1 Radiolaria and the Rock Record Radiolarians are important constituents of chert at certain times in geologic history. Their tests accumulate on the seafloor today to form radiolarian ooze, particularly
1 Radiolaria and the Rock Record Radiolarians are important constituents of chert at certain times in geologic history. Their tests accumulate on the seafloor today to form radiolarian ooze, particularly
Marine Invertebrates in the Paleozoic Seas
 Marine Invertebrates in the Paleozoic Seas The fossils of shell-bearing invertebrates that inhabited shallow seas are common in Paleozoic rocks. Archaeocyathids, sponges, corals, bryozoans, trilobites,
Marine Invertebrates in the Paleozoic Seas The fossils of shell-bearing invertebrates that inhabited shallow seas are common in Paleozoic rocks. Archaeocyathids, sponges, corals, bryozoans, trilobites,
TIME LINE OF LIFE. Strip for Clock of Eras representing the circumference. 1. Review the eras represented on the Clock of Eras:
 TIME LINE OF LIFE Material Time Line of Life Working Time Line of Life Clock of Eras Strip for Clock of Eras representing the circumference Elastic strip for Clock of Eras Presentation 1: Overview 1. Review
TIME LINE OF LIFE Material Time Line of Life Working Time Line of Life Clock of Eras Strip for Clock of Eras representing the circumference Elastic strip for Clock of Eras Presentation 1: Overview 1. Review
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Beaming in your answers
 Bio 112 Handout for Evolution 8 This handout contains: Today s iclicker Questions Handouts for today s lecture iclicker Question #5A - before lecture Consider the hypothetical creatures on the last page
Bio 112 Handout for Evolution 8 This handout contains: Today s iclicker Questions Handouts for today s lecture iclicker Question #5A - before lecture Consider the hypothetical creatures on the last page
Fossils. Ch. 29 and 30 Overview
 Ch. 29 and 30 Overview What you need to know: Chapter 29: Fossils, Relative Time, Absolute Time Chapter 30: Geologic Time Fossils Study of fossils called paleontology Original remains rare usually dead
Ch. 29 and 30 Overview What you need to know: Chapter 29: Fossils, Relative Time, Absolute Time Chapter 30: Geologic Time Fossils Study of fossils called paleontology Original remains rare usually dead
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 WS #3 GEOLOGIC TIME & THE FOSSIL RECORD
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 WS #3 GEOLOGIC TIME & THE FOSSIL RECORD NAME Multiple Choice 1. Fossils are most commonly found in A. sedimentary rocks. B. metamorphic rocks. C. igneous rocks. D. all kinds of rocks.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 WS #3 GEOLOGIC TIME & THE FOSSIL RECORD NAME Multiple Choice 1. Fossils are most commonly found in A. sedimentary rocks. B. metamorphic rocks. C. igneous rocks. D. all kinds of rocks.
11/5/2015. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. The Geologic Time Scale
 GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
2009 Colorado Science Olympiad Fossils Test Station 1:
 2009 Colorado Science Olympiad Fossils Test Station 1: 1. Identify the genus for these specimens (diameters range from 2.5 to 5 mm). 2. In which Kingdom do these organisms belong? 3. What famous structures
2009 Colorado Science Olympiad Fossils Test Station 1: 1. Identify the genus for these specimens (diameters range from 2.5 to 5 mm). 2. In which Kingdom do these organisms belong? 3. What famous structures
Fossils: evidence of past life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Skeletal grains. Pores. Matrix <20 m) Cement. Non-skeletal grains. 1 cm
 Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix
Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck)
 The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11
 Correlation of rock layers Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Correlation of rock layers Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Earth Science 105. Geologic Time Chapter 11. Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Correlation of rock layers Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Correlation of rock layers Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Shield was above sea-level during the Cambrian and provided the sediment for the basins.
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
Answers to Section G: Time and the Fossil Record (Relative Dating)
 Answers to Section G: Time and the Fossil Record (Relative Dating) Use the following sketch of a geological cross section to answer questions 1 to 3. 1. The most important principle used to determine the
Answers to Section G: Time and the Fossil Record (Relative Dating) Use the following sketch of a geological cross section to answer questions 1 to 3. 1. The most important principle used to determine the
Lab 9: Fossils, paleontology and the complete reconstruction
 Geology 103 Name: Lab 9: Fossils, paleontology and the complete reconstruction Objective: To classify fossil organisms and to demonstrate how fossil assemblages are constructed. Finally, to determine the
Geology 103 Name: Lab 9: Fossils, paleontology and the complete reconstruction Objective: To classify fossil organisms and to demonstrate how fossil assemblages are constructed. Finally, to determine the
Remains or traces of prehistoric life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Who s On First? A Relative Dating Activity
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: Who s On First? A Relative Dating Activity Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very old, approximately four and one-half billion years old. Scientific measurements such
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: Who s On First? A Relative Dating Activity Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very old, approximately four and one-half billion years old. Scientific measurements such
Team members (First and Last Names): Fossil lab
 Team members (First and Last Names): Period: Group #: Fossil lab Background: Fossils are traces of organisms that lived in the past. When fossils are found, they are carefully excavated and then analyzed.
Team members (First and Last Names): Period: Group #: Fossil lab Background: Fossils are traces of organisms that lived in the past. When fossils are found, they are carefully excavated and then analyzed.
Fossils Fossil Identification and Analysis Lab Walk Through Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson
 Fossils Fossil Identification and Analysis Lab Walk Through Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson I've provided more specific guidance for this lab than for the previous ones, including giving
Fossils Fossil Identification and Analysis Lab Walk Through Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson I've provided more specific guidance for this lab than for the previous ones, including giving
Team Name/School Total Points / 230 Team Member 2
 Team Name/School Total Points / 230 Team Member 1 Team Member 2 Score % Science Olympiad - National Tournament: Fossils Exam 21 May, 2016 University of Wisconsin-Stout There are 12 stations for this exam
Team Name/School Total Points / 230 Team Member 1 Team Member 2 Score % Science Olympiad - National Tournament: Fossils Exam 21 May, 2016 University of Wisconsin-Stout There are 12 stations for this exam
Chapter 12. Life of the Paleozoic
 Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
CRETACEOUS ALBERTA SCIENCE HALL. 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in
 Worksheet Level 3 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site, how many individuals were there, and what was their age range?
Worksheet Level 3 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site, how many individuals were there, and what was their age range?
Geologic History. A. Basic Geologic Principles The relative age of rock formations relies on the following basic geologic principles:
 Geologic History I. Relative Age Dating of Rocks Relative age of rocks does not rely on an exact date of a rock, but relates its age relative to other rock formations or layers. A. Basic Geologic Principles
Geologic History I. Relative Age Dating of Rocks Relative age of rocks does not rely on an exact date of a rock, but relates its age relative to other rock formations or layers. A. Basic Geologic Principles
THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE
 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE FOSSILS Paleontology is the study of life that existed in prehistoric times A fossil is any evidence of earlier life preserved in rock. Shells Bones Petrified trees
THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE FOSSILS Paleontology is the study of life that existed in prehistoric times A fossil is any evidence of earlier life preserved in rock. Shells Bones Petrified trees
Name: Hour: Date: Materials: two sets of sequence cards in random order (set A: nonsense syllables; set B: sketches of fossils), pencil, paper
 INTRODUCTION Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very old, approximately four and one-half billion years old. Scientific measurements such as radiometric dating use the natural radioactivity
INTRODUCTION Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very old, approximately four and one-half billion years old. Scientific measurements such as radiometric dating use the natural radioactivity
Module 9: Earth's History Topic 3 Content: A Tour of Geologic Time Notes
 The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
STATION # 1 (4 Carnegie models)
 STATION # 1 (4 Carnegie models) 1. Genus? Iguanodon 2. Genus? velociraptor 3. Genus? allosaurus 4. Genus? plateosaurus 5. Of the four samples, which Genus first appeared in the Geologic record? Plateosaurs
STATION # 1 (4 Carnegie models) 1. Genus? Iguanodon 2. Genus? velociraptor 3. Genus? allosaurus 4. Genus? plateosaurus 5. Of the four samples, which Genus first appeared in the Geologic record? Plateosaurs
Earth s s Geologic History
 The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
GY 112L: Earth History Lab
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 11 Paleozoic Part 2 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 (Lab 8 exercises) 1) Sponges & Stromatoporoids 2)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 11 Paleozoic Part 2 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 (Lab 8 exercises) 1) Sponges & Stromatoporoids 2)
Illustrations of Selected Ordovician fossils
 Illustrations of Selected Ordovician fossils Appendix 1 Brachiopods Cephalopods Brachiopods (brack'-i-oh-pods) are a group of marine animals with two shells. They all have an upper and lower shell. The
Illustrations of Selected Ordovician fossils Appendix 1 Brachiopods Cephalopods Brachiopods (brack'-i-oh-pods) are a group of marine animals with two shells. They all have an upper and lower shell. The
Fossils Biology 2 Thursday, January 31, 2013
 Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale
 Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced 451/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit P.M. THURSDAY, 10 January 2008 (1 hour) Examiner Question
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced 451/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit P.M. THURSDAY, 10 January 2008 (1 hour) Examiner Question
Unit 5: Earth s History Practice Problems
 Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
Fossils, Geologic Time, Absolute & Relative Dating, and Natural Resources. Chapters 5 & 6
 Fossils, Geologic Time, Absolute & Relative Dating, and Natural Resources Chapters 5 & 6 How Do Fossils Form? Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks like sandstone, limestone, and shale In Virginia, most
Fossils, Geologic Time, Absolute & Relative Dating, and Natural Resources Chapters 5 & 6 How Do Fossils Form? Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks like sandstone, limestone, and shale In Virginia, most
Common Fossils in Pennsylvania
 Common Fossils in Pennsylvania Dinosaurs? Not common in Pennsylvania Only found in Southeastern Part of the state Dinosaurs wondered near the lakes and swamps and are preserved there dating from the Triassic
Common Fossils in Pennsylvania Dinosaurs? Not common in Pennsylvania Only found in Southeastern Part of the state Dinosaurs wondered near the lakes and swamps and are preserved there dating from the Triassic
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION. 444 million years ago
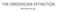 THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
Monday 3 June 2013 Morning
 Monday 3 June 2013 Morning A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *F713200613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
Monday 3 June 2013 Morning A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *F713200613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
Final Revision G8 Biology ( ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past
 FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY
 Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY Use Figure 2 to answer the following two questions. 10. Interpreting Graphics Which is older the sandstone layer or Dike A? Explain your answer. Conglomerate Sandstone
Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY Use Figure 2 to answer the following two questions. 10. Interpreting Graphics Which is older the sandstone layer or Dike A? Explain your answer. Conglomerate Sandstone
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Geologic Time. Mr. Skirbst
 Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon
 Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *1242977619* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *1242977619* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time. Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic
 Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time Soft bodied fauna Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic Modern fauna Cambrian fauna Paleozoic
Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time Soft bodied fauna Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic Modern fauna Cambrian fauna Paleozoic
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP
 L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
Geology 1023 Lab #6, Winter Introduction to fossils and fossilisation
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #6, Winter 2014 Introduction to fossils and fossilisation What is a fossil? A fossil is any evidence of ancient life preserved in sediments or rocks. Why are fossils important?
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #6, Winter 2014 Introduction to fossils and fossilisation What is a fossil? A fossil is any evidence of ancient life preserved in sediments or rocks. Why are fossils important?
GY 112 Lecture Notes Cambrian Explosion
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Cambrian Explosion Lecture Goals: A) Phanerozoic time frame (Paleozoic Era) B) Why a Cambrian explosion C) Introducing our ancestors Textbook
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Cambrian Explosion Lecture Goals: A) Phanerozoic time frame (Paleozoic Era) B) Why a Cambrian explosion C) Introducing our ancestors Textbook
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
The Fossil Record. CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163
 The Fossil Record CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163 Objectives 1. Describe how most fossils form. 2. Explain how scientists can determine a fossil s age. 3. Identify some unanswered
The Fossil Record CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163 Objectives 1. Describe how most fossils form. 2. Explain how scientists can determine a fossil s age. 3. Identify some unanswered
WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY
 WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY MARSHA BARBER and DIANA SCHEIDLE BARTOS INTRODUCTION PALEONTOLOGY, AND in particular the study of dinosaurs, is an exciting topic to people of all ages. Although
WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY MARSHA BARBER and DIANA SCHEIDLE BARTOS INTRODUCTION PALEONTOLOGY, AND in particular the study of dinosaurs, is an exciting topic to people of all ages. Although
The Origin of Life. Lab Exercise 18. Contents. Introduction. Objectives
 Lab Exercise The Origin of Life Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Geologic Time 2 Activity.2 Time Periods 2 Resutls Section 6 Introduction The history of the earth is recorded in the rocks
Lab Exercise The Origin of Life Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Geologic Time 2 Activity.2 Time Periods 2 Resutls Section 6 Introduction The history of the earth is recorded in the rocks
Who s on First?
 Who s on First? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fosrec/barbar.html Focus on Inquiry The students will focus on inquiry by identifying patterns in fossils and explaining their understanding of how rock layers
Who s on First? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fosrec/barbar.html Focus on Inquiry The students will focus on inquiry by identifying patterns in fossils and explaining their understanding of how rock layers
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Tales of the Past. Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education
 Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
 The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
1 Looking at Fossils. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Geologic Time Test Study Guide
 Geologic Time Test Study Guide Chapter 12 Section 1 The Earth s Story and Those Who First Listened 1. What is the difference between uniformitarianism and catastrophism? Uniformitarianism: the same geologic
Geologic Time Test Study Guide Chapter 12 Section 1 The Earth s Story and Those Who First Listened 1. What is the difference between uniformitarianism and catastrophism? Uniformitarianism: the same geologic
Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time. What is geologic time?
 Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time What is geologic time? The division of Earth s history into time units back to 4.6 b.y.a. Usually based on the life-forms that lived during certain periods May be based
Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time What is geologic time? The division of Earth s history into time units back to 4.6 b.y.a. Usually based on the life-forms that lived during certain periods May be based
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY. Relative & Absolute age, fossils and geologic time
 HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Relative & Absolute age, fossils and geologic time Historical Geology A. Measuring Time 1. Relative Time (Relative Age) Measurement of time using comparison. No numbers used; uses words
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Relative & Absolute age, fossils and geologic time Historical Geology A. Measuring Time 1. Relative Time (Relative Age) Measurement of time using comparison. No numbers used; uses words
Name. Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008
 Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008 1. Use the following list of fossil taxa to answer parts a through g below. (2 pts each) 2 Aegyptopithecus Australopithecus africanus Diacronis
Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008 1. Use the following list of fossil taxa to answer parts a through g below. (2 pts each) 2 Aegyptopithecus Australopithecus africanus Diacronis
History of Life on Earth
 Lesson 4 The History of Life on Earth ESSENTIAL QUESTION How has life on Earth changed over time? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the evolution of life on Earth over time, using
Lesson 4 The History of Life on Earth ESSENTIAL QUESTION How has life on Earth changed over time? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the evolution of life on Earth over time, using
Topic 7: Historical Geology
 Topic 7: Historical Geology (ES. 8 b, 9 a-e, 10 a-d, 12 a, b, e) ES.8 The student will investigate and understand geologic processes including plate tectonics. Key concepts include: b) processes (faulting,
Topic 7: Historical Geology (ES. 8 b, 9 a-e, 10 a-d, 12 a, b, e) ES.8 The student will investigate and understand geologic processes including plate tectonics. Key concepts include: b) processes (faulting,
Earth Science. Name Block. Unit 3 Review Worksheet. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Geologic time. 8 th Grade
 + Geologic time 8 th Grade + Trilobites n Trilobites are small, hard-shelled animals that lived in ancient seas. Trilobites are considered to be index fossils. n Index fossils lived over vast regions of
+ Geologic time 8 th Grade + Trilobites n Trilobites are small, hard-shelled animals that lived in ancient seas. Trilobites are considered to be index fossils. n Index fossils lived over vast regions of
Ecology and Paleoecology. A brief review
 Ecology and Paleoecology A brief review Definitions Fossil assemblages Collection of fossils of organisms Lived in the same environment At the same time In the same rock record Diversity The measure of
Ecology and Paleoecology A brief review Definitions Fossil assemblages Collection of fossils of organisms Lived in the same environment At the same time In the same rock record Diversity The measure of
Name Class Date. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 5 2 Looking at Fossils SECTION The Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils
CHAPTER 5 2 Looking at Fossils SECTION The Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils
STATION A. 2. For its size, a mammoth had relatively small ears and tails. Explain why.
 STATION A 1. Mammoths are often depicted as having been Arctic-dwelling creatures whose habitats were dominated by ice and snow during much of the year. What can be determined about a mammoth s lifestyle
STATION A 1. Mammoths are often depicted as having been Arctic-dwelling creatures whose habitats were dominated by ice and snow during much of the year. What can be determined about a mammoth s lifestyle
GY 112L: Earth History Lab
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 9: Paleozoic Part 3 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 3 (Week 9 exercises) 1) Brachiopods 2) Molluscs 3) Alabama
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 9: Paleozoic Part 3 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 3 (Week 9 exercises) 1) Brachiopods 2) Molluscs 3) Alabama
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 Date Class _ A Trip Through Geologic Time Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Late in the Paleozoic Era, the supercontinent Pangaea formed.
Date Class _ A Trip Through Geologic Time Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Late in the Paleozoic Era, the supercontinent Pangaea formed.
Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past
 Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Fossils, Environments, and Geologic Time
 Fossils, Environments, and Geologic Time By Rachel Dolbier, W.M. Keck Earth Science and Mineral Engineering Museum & D.D. LaPointe, Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology In this activity, we will evaluate
Fossils, Environments, and Geologic Time By Rachel Dolbier, W.M. Keck Earth Science and Mineral Engineering Museum & D.D. LaPointe, Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology In this activity, we will evaluate
Geologic Time. Early Earth History
 chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
Cycles in the Phanerozoic
 Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
There are actually 5 processes
 There are actually 5 processes )WEATHERING hen rocks are roken down nto sediment y Physical and hemical orces 2) ERODE - when sediment is CARRIED to a new location 3) DEPOSIT - when sediment is DROPPED
There are actually 5 processes )WEATHERING hen rocks are roken down nto sediment y Physical and hemical orces 2) ERODE - when sediment is CARRIED to a new location 3) DEPOSIT - when sediment is DROPPED
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
12.1 The Fossil Record. KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form.
 KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form. Fossils can form in several ways. Premineralization occurs when minerals carried by water are deposited around
KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form. Fossils can form in several ways. Premineralization occurs when minerals carried by water are deposited around
