6. SURVEY MAPS OF THE ISLE OF ARRAN MAP 1: DRUMADOON POINT TO AIRD NAN RON
|
|
|
- Malcolm Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
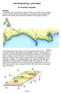
1 6. SURVEY MAPS OF THE ISLE OF ARRAN MAP 1: DRUMADOON POINT TO AIRD NAN RON Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Both Permian sandstone and Triassic mudstones are represented in this coastal section. Tertiary basalt dykes also outcrop along the inter-tidal zone. An area of marine sand is present towards Drumadoon Point. The dune area is bounded by impressive sequences of raised marine platforms that occur as far as Kilpatrick Point. Freshwater alluvium is present at the outfall of the River Black Water. The beach morphology at Kilpatrick Point becomes very irregular with wide exposed abrasion platforms. South of this area a series of sea caves within the former shoreline are present and these features demonstrate how the area has been effected by isostatic uplift. Towards Aird nan Ron the shoreline is mainly boulders backed by a high raised marine shoreline. Erosion Class: Coastal erosion was noted from Drumadoon Point to Blackwater Foot. The sandy beach along this length of coast has been protected by gabion sea defence works at the border between the beach and the hinterland. At Blackwater Foot sea defence works have been established along the foreshore and around the small harbour. Two boulder dump breakwaters have been built down to the MLWMST area in an attempt to protect the navigable river channel leading into the harbour. Built Heritage & Archaeology: The majority of the archaeology within this area is dated to between the 18 th and 20 th centuries. There is one prehistoric site comprising a cist, discovered at Broombrae in 1924, though there is no other information available for them. There is one site dated to the medieval period, that of a bloomery mound. Most of the other sites are of buildings which are either still standing today or successive buildings have been built on the same location. These sites concentrate around Blackwaterfoot. Most sites are set back from the shoreline and therefore are not in imminent danger of erosion from tidal action. 107
2 ARRAN MAP 1: HINTERLAND GEOLOGY AND COASTAL GEOMORPHOLOGY ID Name of section NGR Length Typical deposit type on the foreshore Height of cliff Hinterland geomorphology Description 1 DRUMADOON POINT NR to NR km Mainly rock platform. Low edge (<10m) Dune sand. Rocky headland superimposed by marine derived sand. 2 DRUMADOON STRAND NR to NR km Mainly sand. Low edge (<10m) Dune sand. Marine derived dunes sand forming links environment within the hinterland. Fossil raised terrace backs onto rocky point at Drumadoon Point where exposed rock platform is present. Minor Tertiary 3 BLACK WATER FOOT NR to NR EILEAN MOR NR to NR BROWN HEAD NR to NR intrusion offshore. 0.2km Mainly shingle. Low edge (<10m) Marine deposits. Freshwater alluvium present at outfall of Black Water - beach dominated by shingle and sand. 1.2km Marine deposits over rock. Low edge (<10m) Marine deposits. Low cliff with sea caves present. Shoreline dominated by low marine terrace and backed by steep cliffs. Exposed rock platforms at LWM. 2.9 km Mainly rock. Low edge (<10m) Exposed rock some superficial thin soil mantle. Low former marine terrace backed by fragments of post-glacial higher marine shoreline. Bedrock dominated shoreline with boulder beds and exposed abrasion platforms. Hint at possible degraded saltmarsh presence at base of cliff. Pasture land to cliff edge. 108
3 ARRAN MAP 1 -HINTERLAND GEOLOGY AND FORESHORE GEOMORPHOLOGY Drumadoon Point to Aird nan Ron km LEGEND Scale 1:25,000 K I N T Y R E ISLE OF ARRAN Brodick LARGS ARDROSSAN TROON AYR CAMPBELTOWN Crown Copyright. All rights reserved [Historic Scotland] [ ][2005] 109
4 ARRAN MAP 1: EROSION ID Name of coastal section NGR Length of coastal section Type of erosion present Description 1 Drumadoon Point to Blackwaterfoot NR to NR km Definitely eroding Sandy beach along this length of coast with gambions evident on border between the beach and hinterland. 2 Blackwaterfoot to Aird nan Ron NR to NR km Eroding and accreting Pebble beaches with sea defences particularly along the road and around the small harbour at the mouth of the Black Water. 110
5 ARRAN MAP 1 - EROSION CLASS Drumadoon Point to Aird nan Ron 1 2 SEE MAP km LEGEND Scale 1:25,000 K I N T Y R E ISLE OF ARRAN Brodick LARGS ARDROSSAN TROON AYR CAMPBELTOWN Crown Copyright. All rights reserved [Historic Scotland] [ ][2005] 111
6 ARRAN MAP 1: BUILT HERITAGE AND ARCHAEOLOGY Sites on the Coast Edge and Foreshore ID Name NMRS Source WoSAS Pin NGR Status Type Condition Date Recommendation 1 Annie: Drumadoon Point NR82NE 8001 NMRS NR Shipwreck Unknown 1877 Nil 2 Drumadoon Point Field walking NR Anchor Fair 18th-20th C Monitor 7 Blackwaterfoot OS 1st ed NR Footbridge Unknown Unknown Nil 8 Mary: Blackwaterfoot NR82NE 8003 NMRS NR Shipwreck Unknown 1897 Nil 9 Blackwaterfoot NR82NE 16 NMRS NR Village Good Unknown Nil 15 Kilpatrick Point OS 1st ed NR Preaching Cave Good Unknown Nil 16 Brown Head Field walking NR Stones Good Unknown Survey Sites in the Hinterland ID Name NMRS Source WoSAS Pin NGR Status Type Condition Date Recommendation 3 Blackwaterfoot, Club House NR82NE 18 NMRS NR Club House Good 18th-20th C Nil 4 Blackwaterfoot OS 1st ed NR Building Good 18th-20th C Nil 5 Blackwaterfoot OS 1st ed NR Building; Enclosure Unknown Unknown Nil 6 Blackwaterfoot OS 2nd ed NR Milestone Good 18th-20th C Nil 10 Blackwaterfoot OS 1st ed NR Building Good 18th-20th C Nil 11 Blackwaterfoot OS 1st ed NR Well Unknown Unknown Nil 12 Broombrae NR92NW 7 NMRS NR Cist Unknown Prehistoric Nil 13 Kilpatrick Moor NR92NW 14 NMRS NR Findspot Unknown Unknown Nil 14 Kilpatrick NR92NW 15 NMRS NR Bloomery Unknown 11th-15th C Nil 17 Leacach Bhreac OS 2nd ed NR Milestone Good 18th-20th C Nil 18 Leacach Bhreac NR92SW 1 NMRS NR Cairn Good Unknown Nil 19 Leacach Bhreac OS 1st ed NR Enclosures Good Unknown Survey 112
7 ARRAN MAP 1 - BUILT HERITAGE AND ARCHAEOLOGY Drumadoon Point to Aird nan Ron km Scale 1:25,000 LARGS LEGEND Protected Ancient Monument, or area of designated wreck Listed Historic Building Other known Ancient Monuments, or Undesignated wreck K I N T Y R E ISLE OF ARRAN Brodick ARDROSSAN TROON AYR CAMPBELTOWN Crown Copyright. All rights reserved [Historic Scotland] [ ][2005] 113
MAP 6: PORT LEACACH TO WHITING BAY
 MAP 6: PORT LEACACH TO WHITING BAY Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: A large mass of olivine basalt dominates the Dippen Head area. The hinterland is dominated by a raised marine shoreline.
MAP 6: PORT LEACACH TO WHITING BAY Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: A large mass of olivine basalt dominates the Dippen Head area. The hinterland is dominated by a raised marine shoreline.
MAP 14: VALLAY ISLAND. Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology:
 MAP 14: VALLAY ISLAND Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: The Vallay strand and island are a conspicuous landscape element within this area. The island is largely sand-covered and consists of
MAP 14: VALLAY ISLAND Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: The Vallay strand and island are a conspicuous landscape element within this area. The island is largely sand-covered and consists of
MAP 4: HORNAIS TO SGIOBANAIS. Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology:
 MAP 4: HORNAIS TO SGIOBANAIS Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Lewisian Gneiss is the basement geology which outcrops at or near the surface. This area is highly irregular with machair soils
MAP 4: HORNAIS TO SGIOBANAIS Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Lewisian Gneiss is the basement geology which outcrops at or near the surface. This area is highly irregular with machair soils
Built Heritage & Archaeology Crown copyright. All rights reserved. Historic Scotland Licence No [2007] a
![Built Heritage & Archaeology Crown copyright. All rights reserved. Historic Scotland Licence No [2007] a Built Heritage & Archaeology Crown copyright. All rights reserved. Historic Scotland Licence No [2007] a](/thumbs/92/110316004.jpg) : Tràigh an Tobair Fhuair to Meall Lamalum This map section stretches along s west coast from Tràigh an Tobair Fhuair to Meall Lamalum. The entire coastline comprises a rock platform, with the exception
: Tràigh an Tobair Fhuair to Meall Lamalum This map section stretches along s west coast from Tràigh an Tobair Fhuair to Meall Lamalum. The entire coastline comprises a rock platform, with the exception
5. SURVEY MAPS OF NORTH UIST MAP 1: BERNERAY CAUSEWAY TO ROGH. Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology:
 5. SURVEY MAPS OF NORTH UIST MAP 1: BERNERAY CAUSEWAY TO ROGH Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: The island of Bernerary measures 5km long and 3km wide. The southern portion of the island is
5. SURVEY MAPS OF NORTH UIST MAP 1: BERNERAY CAUSEWAY TO ROGH Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: The island of Bernerary measures 5km long and 3km wide. The southern portion of the island is
Map 12: Ayrshire Coast: Doonfoot Beach to Dunure Map Content Descriptions
 Map 12: Ayrshire Coast: Doonfoot Beach to Dunure Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of twenty three sites were located in the area covered by Map 12. Of these seventeen
Map 12: Ayrshire Coast: Doonfoot Beach to Dunure Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of twenty three sites were located in the area covered by Map 12. Of these seventeen
Map 9: Ayrshire Coast: Stevenston Pier to Barassie Map Content Descriptions
 Map 9: Ayrshire Coast: Stevenston Pier to Barassie Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 9. Of these five were previously
Map 9: Ayrshire Coast: Stevenston Pier to Barassie Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 9. Of these five were previously
Map Introduction: South Uist Map 1
 96 Map Introduction: Map This map section covers part of the south coast of, including the head of the causeway which links the island to Eriskay. It extends from South Glen Dale to Taobh a'caolas. There
96 Map Introduction: Map This map section covers part of the south coast of, including the head of the causeway which links the island to Eriskay. It extends from South Glen Dale to Taobh a'caolas. There
BUTE MAP 6: GARROCH HEAD to STRAVANNAN BAY
 BUTE MAP 6: GARROCH HEAD to STRAVANNAN BAY Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Old Red Sandstone and lavas form the principal base deposits and are overlain by marine deposits towards Port Dornoch.
BUTE MAP 6: GARROCH HEAD to STRAVANNAN BAY Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Old Red Sandstone and lavas form the principal base deposits and are overlain by marine deposits towards Port Dornoch.
Map 2: Cowal Peninsula: Lazaretto Point to Dunoon Harbour North Map Content Descriptions
 Map 2: Cowal Peninsula: Lazaretto Point to Dunoon Harbour North Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 2. Of these
Map 2: Cowal Peninsula: Lazaretto Point to Dunoon Harbour North Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 2. Of these
Map 10: Ayrshire Coast: Barassie to Prestwick North Map Content Descriptions
 Map 10: Ayrshire Coast: Barassie to Prestwick North Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 10. Of these nine were
Map 10: Ayrshire Coast: Barassie to Prestwick North Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 10. Of these nine were
Map 7: Barns Ness to Thorntonloch
 92 Map 7: Barns Ness to Thorntonloch From the low-lying headland of Barns Ness, this section extends along an undulating coast edge to Chapel Point and Skateraw and from there, around the armoured headland
92 Map 7: Barns Ness to Thorntonloch From the low-lying headland of Barns Ness, this section extends along an undulating coast edge to Chapel Point and Skateraw and from there, around the armoured headland
Map Introduction: South Uist Map 6
 6 Map Introduction: Map 6 This map section covers part of the west coast of. It extends from Cill Donnain to Ardvule and onwards to Ormacleit. There is no modern settlement within the coastal zone but
6 Map Introduction: Map 6 This map section covers part of the west coast of. It extends from Cill Donnain to Ardvule and onwards to Ormacleit. There is no modern settlement within the coastal zone but
BUTE MAP 2: ARDMALEISH POINT to ARDBEG
 BUTE MAP 2: ARDMALEISH POINT to ARDBEG Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Dalradian schists continue to dominate this coastal region. The Kames Bay area is dominated by Dunoon Phylites which
BUTE MAP 2: ARDMALEISH POINT to ARDBEG Hinterland Geology and Coastal Geomorphology: Dalradian schists continue to dominate this coastal region. The Kames Bay area is dominated by Dunoon Phylites which
Map 4: Cowal Peninsula: Cluniter to Ardyne Point Map Content Descriptions
 Map 4: Cowal Peninsula: Cluniter to Ardyne Point Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of twenty four sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 4. Of these six were previously
Map 4: Cowal Peninsula: Cluniter to Ardyne Point Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of twenty four sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 4. Of these six were previously
Map 10: Siccar Point to Telegraph Hill
 116 Map 10: Siccar Point to Telegraph Hill From Siccar Point to Telegraph Hill the coast edge is continuously high and rugged, with coastal cliff reaching to over 100m in height. There are beaches below
116 Map 10: Siccar Point to Telegraph Hill From Siccar Point to Telegraph Hill the coast edge is continuously high and rugged, with coastal cliff reaching to over 100m in height. There are beaches below
Map 1: North Berwick to Canty Bay
 42 Map 1: North Berwick to Canty Bay This map section begins within the town of North Berwick and extends as far as the hamlet of Canty Bay. Within North Berwick, much of the hinterland is developed, with
42 Map 1: North Berwick to Canty Bay This map section begins within the town of North Berwick and extends as far as the hamlet of Canty Bay. Within North Berwick, much of the hinterland is developed, with
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
COASTAL ZONE ASSESSMENT SURVEY
 COASTAL ZONE ASSESSMENT SURVEY KINTYRE & isle OF ARRAN Commissioned by The SCAPE Trust on behalf of Historic Scotland S CA P E Scottish Coastal Archaeology and the Problem of Erosion ARCHAEOLOGY LTD January
COASTAL ZONE ASSESSMENT SURVEY KINTYRE & isle OF ARRAN Commissioned by The SCAPE Trust on behalf of Historic Scotland S CA P E Scottish Coastal Archaeology and the Problem of Erosion ARCHAEOLOGY LTD January
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2. Implications for Coastal Engineering
 SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
2.0 Introduction. 3.0 Aims and Objectives. 2.1 Background. 2.2 Survey Area. 2.3 Survey Conditions
 1.0 Executive Summary A rapid coastal zone assessment survey was conducted by Glasgow University Archaeological Research Division (GUARD) along three areas of the Firth of Clyde coastline. The sections
1.0 Executive Summary A rapid coastal zone assessment survey was conducted by Glasgow University Archaeological Research Division (GUARD) along three areas of the Firth of Clyde coastline. The sections
Phillip Island Nature Parks Coastal Process Study 8 October 2014
 Phillip Island Nature Parks Coastal Process Study 8 October 2014 Project Overview Coastal Geology Basaltic and fragmented lavas, granite at Pyramid Rock and Cape Woolamai Weathered basalt (>10m thick)
Phillip Island Nature Parks Coastal Process Study 8 October 2014 Project Overview Coastal Geology Basaltic and fragmented lavas, granite at Pyramid Rock and Cape Woolamai Weathered basalt (>10m thick)
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis
 Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Appletree Bay, Scilly Isles
 Appletree Bay, Scilly Isles Record ID 662 NMR Amongst shoreline boulders on the south side of the bay. Seven small peat beds visible as two main fragmentary groups (part of old land surface). Pitted and
Appletree Bay, Scilly Isles Record ID 662 NMR Amongst shoreline boulders on the south side of the bay. Seven small peat beds visible as two main fragmentary groups (part of old land surface). Pitted and
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10
 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
Black Point & Bihler Point
 Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
15.0 Appendices Appendix 1: List of Map Sources (arranged in chronological order)
 15.0 Appendices 15.1 Appendix 1: List of Map Sources (arranged in chronological order) Nicolas de Nicolay 1583 Vraye & exacte description Hydrographique des costes martimes d Ecosse & des Isles Orchades
15.0 Appendices 15.1 Appendix 1: List of Map Sources (arranged in chronological order) Nicolas de Nicolay 1583 Vraye & exacte description Hydrographique des costes martimes d Ecosse & des Isles Orchades
Seaton to Seaton Hole SUMMARY OF PREFERRED PLAN RECOMMENDATIONS AND JUSTIFICATION
 Location reference: Policy Unit reference: Plan: Seaton to Seaton Hole 6a29 and 6a30 SUMMARY OF PREFERRED PLAN RECOMMENDATIONS AND JUSTIFICATION The large number of properties and assets at risk in the
Location reference: Policy Unit reference: Plan: Seaton to Seaton Hole 6a29 and 6a30 SUMMARY OF PREFERRED PLAN RECOMMENDATIONS AND JUSTIFICATION The large number of properties and assets at risk in the
Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1
 Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1 Magdy Torab* 2 * Prof. of Geomorphology, Department of Geography, Damanhour University, Egypt 3 E-mail: magdytorab@hotmail.com.
Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1 Magdy Torab* 2 * Prof. of Geomorphology, Department of Geography, Damanhour University, Egypt 3 E-mail: magdytorab@hotmail.com.
Coastal Erosion Landforms on the Gower Peninsula
 Geo Factsheet www.curriculum-press.co.uk Number 356 Coastal Erosion Landforms on the Gower Peninsula The Gower The rocky southern coast of the Gower Peninsula in South Wales is home to long stretches of
Geo Factsheet www.curriculum-press.co.uk Number 356 Coastal Erosion Landforms on the Gower Peninsula The Gower The rocky southern coast of the Gower Peninsula in South Wales is home to long stretches of
Australian Coastal Councils Conference
 Australian Coastal Councils Conference 11 March 2015 Estimating Future Coastal Inundation and Erosion Hazards Dr Andrew McCowan Dr Christine Lauchlan-Arrowsmith Warwick Bishop Background Victorian Future
Australian Coastal Councils Conference 11 March 2015 Estimating Future Coastal Inundation and Erosion Hazards Dr Andrew McCowan Dr Christine Lauchlan-Arrowsmith Warwick Bishop Background Victorian Future
Holderness Erosion and Evolution of the Spurn Peninsula
 Holderness Erosion and Evolution of the Spurn Peninsula Prof. Ken Pye and Dr. Simon Blott Kenneth Pye Associates Ltd. Outline of the Presentation Overview of historical erosion trends Effects of coast
Holderness Erosion and Evolution of the Spurn Peninsula Prof. Ken Pye and Dr. Simon Blott Kenneth Pye Associates Ltd. Outline of the Presentation Overview of historical erosion trends Effects of coast
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Coasts Key Word Glossary
 Coasts Key Word Glossary Abrasion Also known as corrosion. It is the wearing away of the cliff by sand, fragments of rock and boulders that are being hurled at the cliff by the waves. It causes grinding
Coasts Key Word Glossary Abrasion Also known as corrosion. It is the wearing away of the cliff by sand, fragments of rock and boulders that are being hurled at the cliff by the waves. It causes grinding
1 Shoreline Landforms 2. 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2. 3 Wavecutting 3. 4 Planview 4. 5 Marine Terraces 5. 6 California 7. 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8
 Shorelines November 9, 2008 Contents 1 Shoreline Landforms 2 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2 3 Wavecutting 3 4 Planview 4 5 Marine Terraces 5 6 California 7 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8 8 Active Processes 9 9 Emergence
Shorelines November 9, 2008 Contents 1 Shoreline Landforms 2 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2 3 Wavecutting 3 4 Planview 4 5 Marine Terraces 5 6 California 7 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8 8 Active Processes 9 9 Emergence
The River Otter: A Field Guide to the. Palaeolithic Landscape Picture of Otter Valley taken by Laura Basell (PRoSWeB)
 The River Otter: A Field Guide to the Palaeolithic Landscape Picture of Otter Valley taken by Laura Basell (PRoSWeB) Produced by The Palaeolithic Rivers of South-West Britain Project and the National Ice
The River Otter: A Field Guide to the Palaeolithic Landscape Picture of Otter Valley taken by Laura Basell (PRoSWeB) Produced by The Palaeolithic Rivers of South-West Britain Project and the National Ice
Coastal Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms, and Human Interaction
 Coastal Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms, and Human Interaction Coastal processes, patterns and associated landforms Coastal processes and the impact of recreational pressures, coastal defence
Coastal Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms, and Human Interaction Coastal processes, patterns and associated landforms Coastal processes and the impact of recreational pressures, coastal defence
Appendix A16.11 Intertidal Archaeological Survey Undertaken as Part of the Environmental Impact Assessment
 Environmental Impact Assessment Report: Volume 3 Part B of 6 Appendix A16.11 Intertidal Archaeological Survey Undertaken as Part of the Environmental Impact Assessment 32102902/EIAR/3B GREATER DUBLIN DRAINAGE
Environmental Impact Assessment Report: Volume 3 Part B of 6 Appendix A16.11 Intertidal Archaeological Survey Undertaken as Part of the Environmental Impact Assessment 32102902/EIAR/3B GREATER DUBLIN DRAINAGE
What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using
 7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
The Systems Approach. Alun Williams, ABPmer
 The Systems Approach Alun Williams, ABPmer Overview What is A Systems Approach? Behavioural / Qualitative Modelling? System Definition / Mapping (Behavioural Statements Objective) What is a Systems Approach?
The Systems Approach Alun Williams, ABPmer Overview What is A Systems Approach? Behavioural / Qualitative Modelling? System Definition / Mapping (Behavioural Statements Objective) What is a Systems Approach?
Figure 45. Plan of Pukaroro drawn from aerial photograph. K. Jones, drawn by C. Edkins, DOC.
 Figure 45. Plan of Pukaroro drawn from aerial photograph. K. Jones, drawn by C. Edkins, DOC. 101 length, and there are cross-rows forming semi-enclosures. House floors are also present at the southern
Figure 45. Plan of Pukaroro drawn from aerial photograph. K. Jones, drawn by C. Edkins, DOC. 101 length, and there are cross-rows forming semi-enclosures. House floors are also present at the southern
Scenarios for the NI coast in the 21 st Century
 Scenarios for the NI coast in the 21 st Century Prof Julian Orford Geography, Archaeology & Palaeoecology Queen s University, Belfast Challenging perspective Living by the coast is good for your health!
Scenarios for the NI coast in the 21 st Century Prof Julian Orford Geography, Archaeology & Palaeoecology Queen s University, Belfast Challenging perspective Living by the coast is good for your health!
1. Which type of climate has the greatest amount of rock weathering caused by frost action? A) a wet climate in which temperatures remain below
 1. Which type of climate has the greatest amount of rock weathering caused by frost action? A) a wet climate in which temperatures remain below freezing B) a wet climate in which temperatures alternate
1. Which type of climate has the greatest amount of rock weathering caused by frost action? A) a wet climate in which temperatures remain below freezing B) a wet climate in which temperatures alternate
PiXL Independence: Geography Answer Booklet KS4. AQA Style, UK Physical Landscapes. Contents: Answers
 PiXL Independence: Geography Answer Booklet KS4 AQA Style, UK Physical Landscapes Contents: Answers 1 I. Multiple Choice Questions 1 Where in the UK would you describe as having large areas of uplands?
PiXL Independence: Geography Answer Booklet KS4 AQA Style, UK Physical Landscapes Contents: Answers 1 I. Multiple Choice Questions 1 Where in the UK would you describe as having large areas of uplands?
Isle of Arran DRUMADOON AND THE TORMORE DYKES
 Geological Society of Glasgow Excursion Itineraries Isle of Arran DRUMADOON AND THE TORMORE DYKES Version 1.0 J.G. MacDonald Geological Society of Glasgow Registered Scottish Charity No. SC007013 Cover
Geological Society of Glasgow Excursion Itineraries Isle of Arran DRUMADOON AND THE TORMORE DYKES Version 1.0 J.G. MacDonald Geological Society of Glasgow Registered Scottish Charity No. SC007013 Cover
1. The coastal system. Constructive and destructive waves, Tides Sediment sources and cells.
 Features of the Coastal System INPUTS PROCESSES OUTPUTS Sediment 95% = 5% = 5% = 1. The coastal system Constructive and destructive waves, Tides Sediment sources and cells. The Coastal System Identify
Features of the Coastal System INPUTS PROCESSES OUTPUTS Sediment 95% = 5% = 5% = 1. The coastal system Constructive and destructive waves, Tides Sediment sources and cells. The Coastal System Identify
Excavations at Clocken Syke Farm, Dairy Lane,Dacre By Nidderdale Iron-age Archaeology community group 2015 and 2016
 Excavations at Clocken Syke Farm, Dairy Lane,Dacre By Nidderdale Iron-age Archaeology community group 2015 and 2016 1 Introduction The Nidderdale Iron-Age group and its forerunners have been investigating
Excavations at Clocken Syke Farm, Dairy Lane,Dacre By Nidderdale Iron-age Archaeology community group 2015 and 2016 1 Introduction The Nidderdale Iron-Age group and its forerunners have been investigating
Pratice Surface Processes Test
 1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
WEST COAST OF JURA. Introduction. Description. J.D. Hansom. OS Grid Reference: NR NR442724
 WEST COAST OF JURA J.D. Hansom OS Grid Reference: NR659985 NR442724 Introduction The west coast of Jura (see Figure 6.2 for general location) contains a remarkable assemblage of emerged coastal landforms
WEST COAST OF JURA J.D. Hansom OS Grid Reference: NR659985 NR442724 Introduction The west coast of Jura (see Figure 6.2 for general location) contains a remarkable assemblage of emerged coastal landforms
Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
3 3 Sannox to Lochranza
 3 3 Sannox to Lochranza Distance 9. 8 miles 15. 7 km Terrain rocky sections with easy scrambling; path muddy in places, especially after rain; stepped path makes boulder field passable at all states of
3 3 Sannox to Lochranza Distance 9. 8 miles 15. 7 km Terrain rocky sections with easy scrambling; path muddy in places, especially after rain; stepped path makes boulder field passable at all states of
Aim and objectives Components of vulnerability National Coastal Vulnerability Assessment 2
 ASSESSING THE UTILITY OF GEOMORPHIC SENSITIVITY MAPPING ON THE ILLAWARRA COAST Pamela Abuodha, Christina Baker, Chris Sharples, Darren Skene and Colin Woodroffe Geoquest Research Centre, University of
ASSESSING THE UTILITY OF GEOMORPHIC SENSITIVITY MAPPING ON THE ILLAWARRA COAST Pamela Abuodha, Christina Baker, Chris Sharples, Darren Skene and Colin Woodroffe Geoquest Research Centre, University of
Erosion along the Holderness Coast
 PT-2013: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. John s, NL, Canada March, 2013 Paper Code. (PT-2013 - Carson)
PT-2013: Coastal and Ocean Engineering ENGI.8751 Undergraduate Student Forum Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University, St. John s, NL, Canada March, 2013 Paper Code. (PT-2013 - Carson)
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
Amble Bay, Northumberland
 Amble Bay, Northumberland Record ID 390 Shennan, I., Horton, B., Innes, J., Gehrels, R., Lloyd, McArthur, J. and Rutherford, M. Embayment between rocky headlands SE of Amble. Thin well-humified surface
Amble Bay, Northumberland Record ID 390 Shennan, I., Horton, B., Innes, J., Gehrels, R., Lloyd, McArthur, J. and Rutherford, M. Embayment between rocky headlands SE of Amble. Thin well-humified surface
Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to
 Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to foleyd@plu.edu Figure list 1. Trailer photograph 2. Location map
Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to foleyd@plu.edu Figure list 1. Trailer photograph 2. Location map
Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property.
 Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
LAB 6: TRINIDAD BEACH FIELD TRIP
 OBJECTIVES: LAB 6: TRINIDAD BEACH FIELD TRIP 1) to develop your powers of observation, especially of geological phenomena; 2) to identify the rocks exposed at Trinidad Beach; 3) to reconstruct some of
OBJECTIVES: LAB 6: TRINIDAD BEACH FIELD TRIP 1) to develop your powers of observation, especially of geological phenomena; 2) to identify the rocks exposed at Trinidad Beach; 3) to reconstruct some of
Oceanography Field Trip One Key
 Oceanography Field Trip One Key If you are using this key as a make-up guide, you should get a COLOR version of this field trip guide by going to http://www.mpcfaculty.net/alfred_hochstaedter/oceanography.htm
Oceanography Field Trip One Key If you are using this key as a make-up guide, you should get a COLOR version of this field trip guide by going to http://www.mpcfaculty.net/alfred_hochstaedter/oceanography.htm
Abrasion: The physical weathering of rocks by particles rubbing against each other.
 FOSS Earth History Course Glossary (10-4-04) Abrasion: The physical weathering of rocks by particles rubbing against each other. Absolute age: The exact age of an object (such as a rock or artifact); found
FOSS Earth History Course Glossary (10-4-04) Abrasion: The physical weathering of rocks by particles rubbing against each other. Absolute age: The exact age of an object (such as a rock or artifact); found
EROSION HAZARD OF MINNESOTA'S LAKE SUPERIOR SHORELINE. Carol A. Johnston Principal Investigator
 EROSION HAZARD OF MINNESOTA'S LAKE SUPERIOR SHORELINE Carol A. Johnston Principal Investigator Maps prepared by: James Salés, John Bonde, Tim Aunan, and Richard Raby Minnesota Sea Grant Research Bulletin
EROSION HAZARD OF MINNESOTA'S LAKE SUPERIOR SHORELINE Carol A. Johnston Principal Investigator Maps prepared by: James Salés, John Bonde, Tim Aunan, and Richard Raby Minnesota Sea Grant Research Bulletin
Edexcel 2 Landscape systems, processes and change
 Edexcel 2 Landscape systems, processes and change Area of the Spec Field Site Research areas Primary data collection Secondary data access Statistical analysis High and low Identifying of different Local
Edexcel 2 Landscape systems, processes and change Area of the Spec Field Site Research areas Primary data collection Secondary data access Statistical analysis High and low Identifying of different Local
Coastal Systems and Landscapes
 AQA Geography A-level Coastal Systems and Landscapes PMT Education Written by Jeevan Singh Coastal Systems and Landscapes Features of Coastal Zones Coastal zones develop from interactions between the winds,
AQA Geography A-level Coastal Systems and Landscapes PMT Education Written by Jeevan Singh Coastal Systems and Landscapes Features of Coastal Zones Coastal zones develop from interactions between the winds,
How does erosion happen?
 How does erosion happen? By National Geographic, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.03.17 Word Count 682 Level 830L These rock formations, in Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah, are called hoodoos. Although
How does erosion happen? By National Geographic, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.03.17 Word Count 682 Level 830L These rock formations, in Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah, are called hoodoos. Although
Erosion and Deposition
 CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Erosion and Deposition Landforms Shaped by Water and Wind Key Concepts What are the stages of stream development? How do water erosion and deposition change Earth s surface? How do wind
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Erosion and Deposition Landforms Shaped by Water and Wind Key Concepts What are the stages of stream development? How do water erosion and deposition change Earth s surface? How do wind
core mantle crust the center of the Earth the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock
 core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
Scotland s centre of expertise for waters. Dynamic Coast - National Coastal Change Assessment: Defence Asset Database
 Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Dynamic Coast - National Coastal Change Assessment: Defence Asset Database Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Published by CREW Scotland s Centre of Expertise
Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Dynamic Coast - National Coastal Change Assessment: Defence Asset Database Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Published by CREW Scotland s Centre of Expertise
L.O: SLOWING STREAMS DEPOSIT (SORT) SEDIMENT HORIZONTALLY BY SIZE.
 L.O: SLOWING STREAMS DEPOSIT (SORT) SEDIMENT HORIZONTALLY BY SIZE. 1. Base your answer to the following question on the profile shown below, which shows the pattern of horizontal sorting produced at a
L.O: SLOWING STREAMS DEPOSIT (SORT) SEDIMENT HORIZONTALLY BY SIZE. 1. Base your answer to the following question on the profile shown below, which shows the pattern of horizontal sorting produced at a
NAME: GEL 109 Final Winter 2010
 GEL 109 Final Winter 2010 1. The following stratigraphic sections represents a single event followed by the slow accumulation of background sedimentation of shale. Describe the flows that produced the
GEL 109 Final Winter 2010 1. The following stratigraphic sections represents a single event followed by the slow accumulation of background sedimentation of shale. Describe the flows that produced the
Active Coastal Processes in the Lubec Embayment
 The Lubec Embayment Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 1998 Active Coastal Processes in the Lubec Embayment 44 49 50.51 N, 66 59 34.16 W Text by Joseph T. Kelley, Department of Agriculture, Conservation
The Lubec Embayment Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 1998 Active Coastal Processes in the Lubec Embayment 44 49 50.51 N, 66 59 34.16 W Text by Joseph T. Kelley, Department of Agriculture, Conservation
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms
 Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
COASTLINES MARINE EROSION PROCESSES. Read the course booklet.
 MARINE EROSION Read the course booklet. PROCESSES. You will need to know and be able to explain the four methods of coastal erosion and two of weathering The next few slides illustrate these processes.
MARINE EROSION Read the course booklet. PROCESSES. You will need to know and be able to explain the four methods of coastal erosion and two of weathering The next few slides illustrate these processes.
Coastal Management on the Isle of Wight
 Coastal Management on the Isle of Wight Setting the scene The Isle of Wight has 65 miles of spectacular coastline, 28 miles of which are designated Heritage Coast. This varied coastline is one of the Island
Coastal Management on the Isle of Wight Setting the scene The Isle of Wight has 65 miles of spectacular coastline, 28 miles of which are designated Heritage Coast. This varied coastline is one of the Island
3.1 GEOLOGY AND SOILS Introduction Definition of Resource
 3.1 GEOLOGY AND SOILS 3.1.1 Introduction 3.1.1.1 Definition of Resource The geologic resources of an area consist of all soil and bedrock materials. This includes sediments and rock outcroppings in the
3.1 GEOLOGY AND SOILS 3.1.1 Introduction 3.1.1.1 Definition of Resource The geologic resources of an area consist of all soil and bedrock materials. This includes sediments and rock outcroppings in the
Excursion guide NW Skåne, NGEA 01, 2018 PART 3. ASSIGNMENTS
 Excursion guide NW Skåne, NGEA 01, 2018 PART 3. ASSIGNMENTS by Associate Prof. Jonas Åkerman 1 Cover photo; The NW exposed coastline at Josefinelust with coarse beach boulders (Sw. malar ), gneiss is the
Excursion guide NW Skåne, NGEA 01, 2018 PART 3. ASSIGNMENTS by Associate Prof. Jonas Åkerman 1 Cover photo; The NW exposed coastline at Josefinelust with coarse beach boulders (Sw. malar ), gneiss is the
Depositional Environment
 Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Changes to Land 5.7B. landforms: features on the surface of Earth such as mountains, hills, dunes, oceans and rivers
 All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
THE SCIENCE OF MAPS. ATL Skill: Critical thinking - Use models and simulations to explore complex systems and issues
 THE SCIENCE OF MAPS 8.9C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering ATL Skill: Critical thinking
THE SCIENCE OF MAPS 8.9C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering ATL Skill: Critical thinking
Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon
 Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon Scenic shoreline vista of Bolinas Lagoon and ridges, from Letter Parcel, March 2016 Peter Baye, Coastal Ecologist
Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon Scenic shoreline vista of Bolinas Lagoon and ridges, from Letter Parcel, March 2016 Peter Baye, Coastal Ecologist
Think about the landforms where you live. How do you think they have changed over time? How do you think they will change in the future?
 reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore cliff BLU FF For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore cliff BLU FF For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Read Across America. Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano
 Read Across America Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano Constructive & Destructive Processes Earth s surface is always changing. Blowing wind and flowing water causes
Read Across America Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano Constructive & Destructive Processes Earth s surface is always changing. Blowing wind and flowing water causes
Geology of Havering-atte-Bower
 Geology of Havering-atte-Bower The geology of Havering village consists of deposits of clays, gravels and sands variously classed as bedrock and superficial deposits. Clays and sands seem rather dull but
Geology of Havering-atte-Bower The geology of Havering village consists of deposits of clays, gravels and sands variously classed as bedrock and superficial deposits. Clays and sands seem rather dull but
Flooding in Dolgellau
 Flooding in Dolgellau Graham Hall MMath, PhD University of Wales, Bangor Background Flooding has historically been a cause for concern in Dolgellau. Following a serious flood in December 1964 when shops
Flooding in Dolgellau Graham Hall MMath, PhD University of Wales, Bangor Background Flooding has historically been a cause for concern in Dolgellau. Following a serious flood in December 1964 when shops
Lyme Regis. Environmental Improvements Phase 2. Securing the future of Lyme Regis
 Lyme Regis Environmental Improvements Phase 2 Securing the future of Lyme Regis Wave attack on Marine Parade The spectacular scenery around Lyme Regis is a result of erosion by the sea and landsliding
Lyme Regis Environmental Improvements Phase 2 Securing the future of Lyme Regis Wave attack on Marine Parade The spectacular scenery around Lyme Regis is a result of erosion by the sea and landsliding
THE ARFORDIR COASTAL HERITAGE SITE RECORDING FORM
 THE ARFORDIR COASTAL HERITAGE SITE RECORDING FORM Information to assist with filling in the form Why do we need to use the form? Archaeology is not only about finding things, but about telling others about
THE ARFORDIR COASTAL HERITAGE SITE RECORDING FORM Information to assist with filling in the form Why do we need to use the form? Archaeology is not only about finding things, but about telling others about
Topic: Coastal Systems Geomorphological & coastal processes
 Topic: Coastal Systems 3.1.3.2 Geomorphological & coastal processes What you need to know How weathering and mass movement affects the coastline How erosion, transportation and deposition affect the coastline
Topic: Coastal Systems 3.1.3.2 Geomorphological & coastal processes What you need to know How weathering and mass movement affects the coastline How erosion, transportation and deposition affect the coastline
depression above scarp scarp
 1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Guided Notes
 1. Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition 2. Outline Section 1: Weathering Section 2: Erosion Section 3: Deposition Section 4: Case Study Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Guided Notes 3. Section 1: Weathering
1. Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition 2. Outline Section 1: Weathering Section 2: Erosion Section 3: Deposition Section 4: Case Study Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Guided Notes 3. Section 1: Weathering
LAB - Rock Classification
 NAME: LAB - Rock Classification Date: Introduction: A rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of minerals, mineral-like solids, glass, or organic particles. The properties that can be observed in a rock
NAME: LAB - Rock Classification Date: Introduction: A rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of minerals, mineral-like solids, glass, or organic particles. The properties that can be observed in a rock
Waves approach the beach at an angle similar to the prevailing wind.
 COASTAL EROSION, FLOODING AND DEFENCE Coastlines are one of the most varied landforms. Erosion, deposition and transport are finely balanced and all affect the geology. If any of these factors are disturbed
COASTAL EROSION, FLOODING AND DEFENCE Coastlines are one of the most varied landforms. Erosion, deposition and transport are finely balanced and all affect the geology. If any of these factors are disturbed
Controlling Processes That Change Land
 1 Name Date Controlling Processes That Change Land People try to control some of the processes that change land. To do this, people apply technology- the use of science to solve problems in everyday life.
1 Name Date Controlling Processes That Change Land People try to control some of the processes that change land. To do this, people apply technology- the use of science to solve problems in everyday life.
