New Madrid Earthquakes
|
|
|
- Judith Hicks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seismic Hazard Maps A presentation by Dr. Chris Cramer, U.S. Geological Survey, Memphis, TN at University of Memphis, TN November 22, New Madrid Earthquakes 1
2 1886 Charleston Earthquake 2
3 3
4 4
5 Overview Seismic Hazard Maps What are seismic hazard maps? What goes into making seismic hazard maps? How are uncertainties handled? What about site amplification from soils? Seismic Hazard Maps Summary There have been devastating earthquakes in the past in the central U.S. And there will be devastating earthquakes in the future. Because of large population centers with vulnerable infrastructure, there is a strong need to prepare for these rare, devastating events. 5
6 What are Seismic Hazard Maps? Mainly they are earthquake shaking maps that indicate ground motions expected from earthquakes. Basically there are two classes: Scenario (Deterministic) Probabilistic 6
7 What Question Does Each Type Address? Scenario (Deterministic): What ground motions can I expect from a specific earthquake scenario? Probabilistic: What is the likelihood (probability) of ground motions from future earthquakes in a region? Note that both are based on ground-motion probability distributions. National Seismic Hazard Maps Developed from the Best Earth Science Information Represent Current Understanding of Seismic Ground Motion Hazard Incorporates Uncertainty in our Knowledge Show Average (Expected) Ground Motion for given Level of Risk, NOT the Worst Case They are NOT Engineering Design Maps! 7
8 Basic Earthquake Hazard Lets keep it simple! Larger earthquakes cause more damage! Earthquake hazard increases with earthquake magnitude and occurrence rate. Earthquake shaking decreases more slowly with distance in the central and eastern U.S. than in the western U.S. For the same magnitude, eastern U.S. earthquakes have larger high-frequency ground motions than western U.S. earthquakes. 8
9 The Largest Earthquakes Dominate The largest earthquakes are more damaging over a larger area. Generally in the eastern U.S., the rate of smaller earthquakes can underestimate the rate of larger earthquakes. M7.6,
10 Frankel, Armenia Earthquake: Devastation from a rare M6.9 earthquake in an area known to have such events. 10
11 CEUS Seismic Hazard Conclusions There is a significant earthquake hazard in the central U.S. and it should not be ignored! There is a strong need for cost-effective engineering mitigation to reduce future losses from major earthquakes. The Details! 11
12 What Information Is Needed? Earthquake Sources Earthquake Recurrence Rates Earthquake Ground Motions as a Function of Distance and Magnitude (Attenuation Relations) Steps in Deterministic Seismic Hazard Analysis 12
13 Steps in Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis Acceleration Types of Source Models Fault Models (Line Sources) Area Models Distributed Line Sources Distributed Point Sources (Eqk( Eqk.. Hypocenters) Zoneless Model (Smoothed Seismicity Model) Zone Models 13
14 14
15 Frankel, 1995 Reiter,
16 Models used for the Central and Eastern U.S. in the 1996 National Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps Earthquake Recurrence Distributions Gutenberg-Richter (Power Law) Characteristic (Individual Fault) 16
17 And how often earthquakes of each size occur Guttenberg-Richter Distribution And how often earthquakes of each size occur Characteristic Distribution 17
18 Determining Recurrence Rates Geodesy Observed Strain Across Faults (Plate Boundaries) Record of several years to decades Historical Earthquake Activity Record of several hundred years or less in most of U.S., with decreasing completeness of record back in time. Paleoseismicity (Geology) Record of perhaps 20,000 years Average no of years between events New Madrid Magnitude vs. Frequency 1 historical to modern seismicity Big Jump! 1,000 10,000 3 extrapolated Earthquake Magnitude 7 8 Cramer,
19 PALEOSEISMOLOGY Interpreting the location, timing, and magnitude of prehistoric earthquakes 19
20 PALEOSEISMOLOGY Unlike in California, we don t t have surface faults to study. In the New Madrid seismic zone, our most powerful tool has been ancient liquefaction deposits, which we can date with carbon-14 and Native American artifacts 20
21 What remains today (Blytheville, Arkansas) sand blow Sand Blows in Southeastern Missouri 1 km Each white spot is a sand blow from or earlier earthquakes 21
22 We can use sand blows to date old earthquakes if: they bury old plant remains of archeological artifacts we can date the sand blows are themselves buried by materials we can date We then know the earthquakes occurred between the two time periods 22
23 An example of a sand blow in a drainage ditch, southeast Missouri 23
24 After digging dozens of trenches through sand blows 24
25 And examining hundreds of miles of river banks... And plotting them on maps 25
26 We now know: New Madrid Magnitude vs. Frequency Average no of years between events Large earthquakes in 1450 and 900 A.D. The average time between the large earthquakes is about 500 years The prehistoric earthquakes were approximately the same size as the earthquakes Each may actually represent sequences of large earthquakes, as in historical to modern seismicity Geology (2003 maps) 1, maps 10,000 3 extrapolated Earthquake Magnitude 7 8 Cramer,
27 Estimating Ground Motions 27
28 ENA Ground Motion Attenuation Relations Cramer and Kumar,
29 Cramer and Kumar, 2003 Putting It All Together: Hazard Curves 29
30 What is a Hazard Curve? Acc Single Earthquake Ground Motion Hazard = Rate times Pe(M,d) where Pe(M,d) is the probability of exceeding a given ground motion level as a function of magnitude and distance. 30
31 How is a Hazard Curve Formed? Accele ration Frankel,
32 All Modeled Earthquakes Total Hazard Curve = Sum( Rate i *Pe(M,d) i ) Note that you always sum probabilities and never ground motions! Poisson vs. Time Dependent 32
33 Types of Seismic Hazard Maps Poisson or Time Independent Earthquakes occur randomly in time Time Dependent (characteristic model) The occurrence of earthquakes is dependent on the time since the last one
34 M > 7: New Madrid Probabilities Time Independent» 10% in 50 years Time Dependent» 7% for the next 50 years See USGS Fact Sheet FS Earthquake Hazard in the Heart of the Homeland M ~ 7: Charleston Probabilities Time Independent» 10% in 50 years Time Dependent» 2% for the next 50 years 34
35 Including Uncertainties Types of Uncertainty Random (Aleatory) Uncertainty Generally not reducible with more knowledge Model or Knowledge (Epistemic) Uncertainty Can be reduced with improved understanding Generally handled differently in calculations! 35
36 Cramer and Kumar,
37 Handling Epistemic Uncertainty Logic or Decision Trees 37
38 38
39 39
40 Urban earthquake hazard mapping in the Central U.S. St. Louis Memphis Evansville What is an urban earthquake hazard map? Show expected levels of shaking/ amplification or likelihood of ground failure (liquefaction, landslides) The scale is useful locally, but not site specific Includes the effects of the local geology 40
41 Memphis vs National Maps NEHRP D and 1 km thick vs B/C boundary Ground Motions relative to national maps PGA is similar 0.2 s Sa for Memphis maps are 0-30% lower 1.0 s Sa for Memphis maps are 100% higher What determines the shaking that affects a structure? SITE SOURCE PATH 41
42 The urban hazard maps include the site effects SITE SOURCE PATH Basic Methodology Use three dimensional geology (well data) Generate site amplification distributions (median and ln sd) at each grid point Modify hard-rock ground motion attenuation relations with site amplification distribution prior to hazard calculation at each grid point. Calculate hazard using national map PSHA model for CEUS. 42
43 Shear Wave Velocity Profile Locations Shear Wave Velocity Profile & Well Log Locations 43
44 Gomberg et al Sedimentary Layers & Shear Wave Velocity Profiles at 2 Sites 44
45 Site Amplification Approach Monte Carlo Randomization Input time series (record) Soil profile (Vs and depth-to-top) Dynamic Soil Properties (EPRI, 1993) Method Randomly select soil profile and time series. For 3 periods (PGA, 0.2 s, 1.0 s), scale to 10 ground motion levels ( g). Calculate soil column response (1D) for each period and ground motion level. Develop amplification distribution from 100 iterations. Typical Examples Compare to NEHRP 1997 site factors Three ground motions PGA 0.2 s Sa 1.0 s Sa 45
46 46
47 Comparison of National and Memphis Seismic Hazard Maps Periods: PGA 0.2 s Sa 1.0 s Sa 47
48 At PGA (peak ground acceleration), two maps are very similar National Map Memphis Map Increasing hazard Effects of the thick sediment pile beneath Memphis: High frequencies-likely to affect shorter structures (0.2 sec SA) National Map Memphis Map Increasing hazard 48
49 Effects of the thick sediment pile beneath Memphis: Low frequencies-likely to affect tall and long structures (1.0 sec SA) National Map Memphis Map Increasing hazard Sources of Uncertainty Input Time Series Soil Profile Dynamic Soil Properties Choice of Soil Response Code Dynamic Pore Pressure Changes (future) 49
50 Input Rock Seismograms Used M~7 to M8 records from seven earthquakes and one NMSZ synthetics database: 1989 M6.9 Loma Prieta - G M7.1 Cape Mendocino - CPM 1992 M7.3 Landers - JOS 1995 M6.9 Kobe - KJM 1999 M7.4 Kocaeli - GBZ, IZT 1999 M7.6 Chi Chi - TCU 1999 M7.1 Duzce Atkinson and Beresnev, M7.5, M8.0 Gomberg et al
51 Vs Uncertainty (m/s) Alluvium Loess Lafayette Sand & Gravel Upper Clairborne Clay Memphis Sand Flower Island Clay Fort Pillow Sand Old Breastworks Clay Cretaceous Sediments Paleozoic Limestones Dynamic Soil Properties No measurements for Mississippi embayment EPRI (1993) modulus and damping curves with their ln sd of
52 Soil Response Program Uncertainty Unmodeled Pore Pressure Uncertainty 52
53 Summary of Uncertainties (ln sd) Type\ Sensitivity PGA 0.2 s 1.0 s Overall Input Time Series Soil Profile (Vs) Dyn. Properties Top Layer Lithology < 0.02 < 0.08 < 0.03 Soil Response Code median ranges + 50 % Pore Pressure significant but not modeled yet 53
54 National vs. Local Maps Alameda County National vs. Local Maps Urban hazard maps may be probabilistic or deterministic Alameda County (i.e., use a scenario). 54
55 Who might use them? 1998: Three Urban Earthquake Hazard Maps Planned Seattle, Washington Three trial urban areas: Oakland, California Seattle, Washington Oakland, California Memphis, Tennessee Memphis, Tennessee 55
56 Why Memphis? Typical of the central and eastern U.S. few seismically engineered buildings and infrastructure dense urban population near major seismogenic faults Sits on a very thick pile of Mississippi River sediments Closest major urban area to the New Madrid seismic zone A sound scientific foundation had already been established in the region Advisory Board Chosen from users, others with experience outside the region, universities, consultants, government, including: Utilities, Insurance, Emergency Management, City and County Government, Red Cross, Utilities 56
57 Map Area Memphis maps are consistent with USGS National Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps 57
58 Differs from the National map in the addition of local soil conditions Products include Online database of all available subsurface information Surficial geological maps of all quads Probabilistic ground motion maps (2% chance of exceedance in 50 y; PGA, 0.2 sec, 1.0 sec) Scenario ground motion maps (repeat of New Madrid; M 6.0 near Memphis) Liquefaction hazard maps All products will be available digitally 58
59 Online database of all available subsurface information: COMPLETE Surficial geological maps: Completed and online Memphis Northwest Broughton and Van Arsdale,
60 Ground motion maps All ground motion calculations complete (probabilistic and scenario) Map layout being finalized User guides in preparation Liquefaction Hazard Maps: Winter/04 Use engineering data (CPT and SPT) to characterize geologic units Factor of safety calculated as a function of depth Liquefaction potential index used measure of liquefaction susceptibility for given level of shaking and earthquake magnitude Work by Glenn J. Rix and Salome Romero-Hudock, Georgia Institute of Technology. 60
61 Liquefaction Hazard Maps: Winter/04 Byproducts of the Process Brought many groups together (engineers, emergency planners, earth scientists, utilities) Research and dozens of publications on Central U.S. earthquake recurrence, magnitudes, and hazard Central U.S. tectonics New logic tree for hazard analysis Improved understanding of uncertainties Non-linear soil response Spawned a desire for maps by other communities 61
62 St. Louis Evansville Memphis St. Louis and Evansville Apply lessons learned to other central U.S. urban areas and increase local ownership in the mapping process St. Louis and Evansville each ready to move forward on hazard maps At Little Rock 5-Year Planning Meeting, decided to go forward on both in spite of limited funding 62
63 St. Louis Area Map Largest metropolitan area in the region Hazard from New Madrid seismic zone and local sources Geology more complex than Memphis More local leadership and participation by Missouri and Illinois Surveys Surficial Geology completed on Illinois side Working group formed Contacts: Phyllis Steckel and Buddy Schweig 63
64 29 quadrangles, if possible Products will be similar to Memphis, with addition of landslide hazards Three meetings in the past year State surveys funded to create and populate databases Others applying for funding Evansville, Indiana Small urban area with an extremely proactive business and government community Hazard from Wabash Valley seismic zone, News Madrid seismic zone, and other local sources (recent M4.5 earthquake with light damage) Much geological and geotechnical data already collected (mapping in progress by KGS, IGS, USGS) Local leadership and participation by Indiana, Kentucy, and Illinois Surveys Working group formed Contacts: Dave Williams (KGS), Joan Gomberg (USGS), Christine Martin (Southwest Indiana Disaster Resistant Community Corp) 64
65 Ill Indiana Kentucky 7 quadrangles planned Products will be similar to Memphis Four meetings and field trip in the past year CUSEC State Geologists funded to create shear wave velocity database USGS Geologic Mapping Program donating time for 2 people to help with mapping 65
66 Some things we have learned Involvement of local users and researchers at earliest stages is critical if the results of the map are going to be accepted Be flexible Each city has different circumstances The pace of work is subject to the availability of funding and people We have successfully used these hazard map products to drive central U.S. earthquake research in a more directed way than ever before Special Zones 66
Probabilistic Seismic-Hazard Assessment Including Site Effects for Evansville, Indiana, and the Surrounding Region
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 101, No. 3, pp. 1039 1054, June 2011, doi: 10.1785/0120090322 Probabilistic Seismic-Hazard Assessment Including Site Effects for Evansville, Indiana,
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 101, No. 3, pp. 1039 1054, June 2011, doi: 10.1785/0120090322 Probabilistic Seismic-Hazard Assessment Including Site Effects for Evansville, Indiana,
Integration of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis with Nonlinear Site Effects and Application to the Mississippi Embayment
 Integration of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis with Nonlinear Site Effects and Application to the Mississippi Embayment Duhee Park and Youssef M.A. Hashash ABSTRACT An integrated probabilistic seismic
Integration of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis with Nonlinear Site Effects and Application to the Mississippi Embayment Duhee Park and Youssef M.A. Hashash ABSTRACT An integrated probabilistic seismic
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone
 General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code
 Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS. Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
Overview of Seismic PHSA Approaches with Emphasis on the Management of Uncertainties
 H4.SMR/1645-29 "2nd Workshop on Earthquake Engineering for Nuclear Facilities: Uncertainties in Seismic Hazard" 14-25 February 2005 Overview of Seismic PHSA Approaches with Emphasis on the Management of
H4.SMR/1645-29 "2nd Workshop on Earthquake Engineering for Nuclear Facilities: Uncertainties in Seismic Hazard" 14-25 February 2005 Overview of Seismic PHSA Approaches with Emphasis on the Management of
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
SURFACE GEOLOGY AND LIQUEFACTION SUSCEPTIBILITY IN THE INNER RIO GRANDE VALLEY NEAR ALBUQUERQUE, NEW MEXICO
 SURFACE GEOLOGY AND LIQUEFACTION SUSCEPTIBILITY IN THE INNER RIO GRANDE VALLEY NEAR ALBUQUERQUE, NEW MEXICO Keith I. Kelson, Christopher S. Hitchcock, and Carolyn E. Randolph William Lettis & Associates,
SURFACE GEOLOGY AND LIQUEFACTION SUSCEPTIBILITY IN THE INNER RIO GRANDE VALLEY NEAR ALBUQUERQUE, NEW MEXICO Keith I. Kelson, Christopher S. Hitchcock, and Carolyn E. Randolph William Lettis & Associates,
Final Report Non-Linear Seismic Site Response of Deep Deposits in West Tennessee
 Final Report Non-Linear Seismic Site Response of Deep Deposits in West Tennessee Prepared for Tennessee Department of Transportation Principal Investigators: Youssef Hashash Assistant Professor University
Final Report Non-Linear Seismic Site Response of Deep Deposits in West Tennessee Prepared for Tennessee Department of Transportation Principal Investigators: Youssef Hashash Assistant Professor University
I. Locations of Earthquakes. Announcements. Earthquakes Ch. 5. video Northridge, California earthquake, lecture on Chapter 5 Earthquakes!
 51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
Unique Site Conditions and Response Analysis Challenges in the Central and Eastern U.S.
 Unique Site Conditions and Response Analysis Challenges in the Central and Eastern U.S. James R. Martin, C. Guney Olgun, & Morgan Eddy Civil and Environmental Engineering World Institute for Disaster Risk
Unique Site Conditions and Response Analysis Challenges in the Central and Eastern U.S. James R. Martin, C. Guney Olgun, & Morgan Eddy Civil and Environmental Engineering World Institute for Disaster Risk
Interpretive Map Series 24
 Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries Interpretive Map Series 24 Geologic Hazards, Earthquake and Landslide Hazard Maps, and Future Earthquake Damage Estimates for Six Counties in the Mid/Southern
Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries Interpretive Map Series 24 Geologic Hazards, Earthquake and Landslide Hazard Maps, and Future Earthquake Damage Estimates for Six Counties in the Mid/Southern
Arthur Frankel, William Stephenson, David Carver, Jack Odum, Robert Williams, and Susan Rhea U.S. Geological Survey
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps for Seattle: 3D Sedimentary Basin Effects, Nonlinear Site Response, and Uncertainties from Random Velocity Variations Arthur Frankel, William Stephenson, David Carver,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps for Seattle: 3D Sedimentary Basin Effects, Nonlinear Site Response, and Uncertainties from Random Velocity Variations Arthur Frankel, William Stephenson, David Carver,
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS WITH NONLINEAR SITE EFFECTS IN THE MISSISSIPPI EMBAYMENT
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 549 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS WITH NONLINEAR SITE EFFECTS IN THE MISSISSIPPI EMBAYMENT Duhee
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 549 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS WITH NONLINEAR SITE EFFECTS IN THE MISSISSIPPI EMBAYMENT Duhee
New USGS Maps Identify Potential Ground- Shaking Hazards in 2017
 New USGS Maps Identify Potential Ground- Shaking Hazards in 2017 New USGS Maps Identify Potential Ground-Shaking Hazards in 2017 The central U.S. faces continued hazards from human-induced earthquakes
New USGS Maps Identify Potential Ground- Shaking Hazards in 2017 New USGS Maps Identify Potential Ground-Shaking Hazards in 2017 The central U.S. faces continued hazards from human-induced earthquakes
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY
 32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures
 Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
5. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Seismic Source Characterization in Siting New Nuclear Power Plants in the Central and Eastern United States
 Seismic Source Characterization in Siting New Nuclear Power Plants in the Central and Eastern United States ABSTRACT : Yong Li 1 and Nilesh Chokshi 2 1 Senior Geophysicist, 2 Deputy Director of DSER Nuclear
Seismic Source Characterization in Siting New Nuclear Power Plants in the Central and Eastern United States ABSTRACT : Yong Li 1 and Nilesh Chokshi 2 1 Senior Geophysicist, 2 Deputy Director of DSER Nuclear
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon
 Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard.
 Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Preliminary Earthquake Risk Management Strategy Plan of Eskisehir, Turkey by using GIS
 Preliminary Earthquake Risk Management Strategy Plan of Eskisehir, Turkey by using GIS Metin Altan, Ferah Özturk and Can Ayday Space and Satellite Sciences Research Institute Anadolu University, TURKEY
Preliminary Earthquake Risk Management Strategy Plan of Eskisehir, Turkey by using GIS Metin Altan, Ferah Özturk and Can Ayday Space and Satellite Sciences Research Institute Anadolu University, TURKEY
What will a Magnitude 6.0 to 6.8 Earthquake do to the St. Louis Metro Area?
 What will a Magnitude 6.0 to 6.8 Earthquake do to the St. Louis Metro Area? J. David Rogers Natural Hazards Mitigation Center University of Missouri-Rolla USGS Mid-Continent Geographic Science Center Missouri
What will a Magnitude 6.0 to 6.8 Earthquake do to the St. Louis Metro Area? J. David Rogers Natural Hazards Mitigation Center University of Missouri-Rolla USGS Mid-Continent Geographic Science Center Missouri
New Madrid and Central U.S. Region Earthquake Hazard
 New Madrid and Central U.S. Region Earthquake Hazard Rob Williams U.S. Geological Survey, Golden, CO March 16, 2017 Reelfoot Lake, TN U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey 1811-12 New
New Madrid and Central U.S. Region Earthquake Hazard Rob Williams U.S. Geological Survey, Golden, CO March 16, 2017 Reelfoot Lake, TN U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey 1811-12 New
Paleoseismic Investigations for Determining the Design Ground Motions for Nuclear Power Plants
 Paleoseismic Investigations for Determining the Design Ground Motions for Nuclear Power Plants Russell A. Green Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Purdue Geotechnical Society Workshop May
Paleoseismic Investigations for Determining the Design Ground Motions for Nuclear Power Plants Russell A. Green Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Purdue Geotechnical Society Workshop May
Identification of Lateral Spread Features in the Western New Madrid Seismic Zone J. David Rogers and Briget C. Doyle
 Identification of Lateral Spread Features in the Western New Madrid Seismic Zone J. David Rogers and Briget C. Doyle Department of Geological Engineering University of Missouri-Rolla rogersda@umr.edu doyle@hope.edu
Identification of Lateral Spread Features in the Western New Madrid Seismic Zone J. David Rogers and Briget C. Doyle Department of Geological Engineering University of Missouri-Rolla rogersda@umr.edu doyle@hope.edu
Estimation of Non-linear Seismic Site Effects for Deep Deposits of the Mississippi Embayment
 Estimation of Non-linear Seismic Site Effects for Deep Deposits of the Mississippi Embayment Duhee Park, Ph.D. Post Doctoral Researcher Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Illinois
Estimation of Non-linear Seismic Site Effects for Deep Deposits of the Mississippi Embayment Duhee Park, Ph.D. Post Doctoral Researcher Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Illinois
Scholars' Mine. Deniz Karadeniz. Fall 2007
 Scholars' Mine Doctoral Dissertations Student Theses and Dissertations Fall 2007 Pilot program to assess seismic hazards of the Granite City, Monks Mound, and Columbia Bottom quadrangles, St. Louis Metropolitan
Scholars' Mine Doctoral Dissertations Student Theses and Dissertations Fall 2007 Pilot program to assess seismic hazards of the Granite City, Monks Mound, and Columbia Bottom quadrangles, St. Louis Metropolitan
Seismic Hazard Assessment of Switzerland, Falko Bethmann October 1 st, 2008
 Seismic Hazard Assessment of Switzerland, 2004 Falko Bethmann October 1 st, 2008 Outline Definition of earthquake sources Definition of seismic recurrence characteristics for each source Ground motion
Seismic Hazard Assessment of Switzerland, 2004 Falko Bethmann October 1 st, 2008 Outline Definition of earthquake sources Definition of seismic recurrence characteristics for each source Ground motion
Final Technical Report COLLECTION, COMPILATION AND ANALYSIS OF GEOLOGIC AND GEOTECHNICAL DATA FOR MAP PRODUCTION
 Final Technical Report COLLECTION, COMPILATION AND ANALYSIS OF GEOLOGIC AND GEOTECHNICAL DATA FOR MAP PRODUCTION External Grant Award Number 99-HQ-GR-0086 Robert A. Bauer, Coordinator CUSEC State Geologists,
Final Technical Report COLLECTION, COMPILATION AND ANALYSIS OF GEOLOGIC AND GEOTECHNICAL DATA FOR MAP PRODUCTION External Grant Award Number 99-HQ-GR-0086 Robert A. Bauer, Coordinator CUSEC State Geologists,
SEISMIC CODE ISSUES IN CENTRAL UNITED STATES
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1843 SEISMIC CODE ISSUES IN CENTRAL UNITED STATES SHAHRAM PEZESHK 1 SUMMARY The Applied Technology Council
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1843 SEISMIC CODE ISSUES IN CENTRAL UNITED STATES SHAHRAM PEZESHK 1 SUMMARY The Applied Technology Council
THE RESPONSE SPECTRUM
 (NBCC 25) Gail M. The Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Vancouver Section THE RESPONSE SPECTRUM Seismic Hazard Analysis to obtain Uniform Hazard Response Spectrum (NBCC 25) Gail M. Department of
(NBCC 25) Gail M. The Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Vancouver Section THE RESPONSE SPECTRUM Seismic Hazard Analysis to obtain Uniform Hazard Response Spectrum (NBCC 25) Gail M. Department of
GENERATION OF NEAR-FIELD ROCK MOTIONS WITH A COMPOSITE SOURCE MODEL WITHIN THE NEW MADRID SEISMIC ZONE
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 244 GENERATION OF NEAR-FIELD ROCK MOTIONS WITH A COMPOSITE SOURCE MODEL WITHIN THE NEW MADRID SEISMIC ZONE
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 244 GENERATION OF NEAR-FIELD ROCK MOTIONS WITH A COMPOSITE SOURCE MODEL WITHIN THE NEW MADRID SEISMIC ZONE
2 Approaches To Developing Design Ground Motions
 2 Approaches To Developing Design Ground Motions There are two basic approaches to developing design ground motions that are commonly used in practice: deterministic and probabilistic. While both approaches
2 Approaches To Developing Design Ground Motions There are two basic approaches to developing design ground motions that are commonly used in practice: deterministic and probabilistic. While both approaches
Occurrence of negative epsilon in seismic hazard analysis deaggregation, and its impact on target spectra computation
 Occurrence of negative epsilon in seismic hazard analysis deaggregation, and its impact on target spectra computation Lynne S. Burks 1 and Jack W. Baker Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Occurrence of negative epsilon in seismic hazard analysis deaggregation, and its impact on target spectra computation Lynne S. Burks 1 and Jack W. Baker Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM OBSERVED STRONG-MOTION RECORDS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
Development of Seismic Ground Motions at Four Bridge Sites in the State of Illinois. By Shahram Pezeshk, Ph.D., P.E.
 Development of Seismic Ground Motions at Four Bridge Sites in the State of Illinois By Shahram Pezeshk, Ph.D., P.E. Email: spezeshk@memphis.edu April 2004 i TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Methodology
Development of Seismic Ground Motions at Four Bridge Sites in the State of Illinois By Shahram Pezeshk, Ph.D., P.E. Email: spezeshk@memphis.edu April 2004 i TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Methodology
Liquefaction Potential Mapping in Memphis and Shelby County, Tennessee
 Liquefaction Potential Mapping in Memphis and Shelby County, Tennessee Glenn J. Rix 1 and Salome Romero-Hudock 1 The Earthquake Hazards Program of the U.S. Geological Survey is developing seismic hazard
Liquefaction Potential Mapping in Memphis and Shelby County, Tennessee Glenn J. Rix 1 and Salome Romero-Hudock 1 The Earthquake Hazards Program of the U.S. Geological Survey is developing seismic hazard
St. Louis Area Earthquake Hazards Mapping Project December 2008 June 2009 Progress Report
 St. Louis Area Earthquake Hazards Mapping Project December 2008 June 2009 Progress Report By R.A. Williams, R.A. Bauer, O.S. Boyd, J. Chung, C.H. Cramer, D.A. Gaunt, D. Hoffman, G.L. Hempen, N.S. McCallister,
St. Louis Area Earthquake Hazards Mapping Project December 2008 June 2009 Progress Report By R.A. Williams, R.A. Bauer, O.S. Boyd, J. Chung, C.H. Cramer, D.A. Gaunt, D. Hoffman, G.L. Hempen, N.S. McCallister,
Micro Seismic Hazard Analysis
 Micro Seismic Hazard Analysis Mark van der Meijde INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Overview Site effects Soft ground effect Topographic effect Liquefaction Methods
Micro Seismic Hazard Analysis Mark van der Meijde INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Overview Site effects Soft ground effect Topographic effect Liquefaction Methods
A technical note on seismic microzonation in the central United States
 A technical note on seismic microzonation in the central United States Zhenming Wang Kentucky Geological Survey, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky 40506, USA. e-mail: zmwang@uky.edu Microzonation
A technical note on seismic microzonation in the central United States Zhenming Wang Kentucky Geological Survey, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky 40506, USA. e-mail: zmwang@uky.edu Microzonation
Borah Peak Earthquake HAZUS Scenario Project Executive Summary Idaho Bureau of Homeland Security Idaho Geological Survey Western States Seismic
 Borah Peak Earthquake HAZUS Scenario Project Executive Summary Idaho Bureau of Homeland Security Idaho Geological Survey Western States Seismic Policy Council 12/30/2008 The HAZUS-MH analysis of the Borah
Borah Peak Earthquake HAZUS Scenario Project Executive Summary Idaho Bureau of Homeland Security Idaho Geological Survey Western States Seismic Policy Council 12/30/2008 The HAZUS-MH analysis of the Borah
The Seattle-area geologic mapping project and the geologic framework of Seattle
 The Seattle-area geologic mapping project and the geologic framework of Seattle Troost, K.G., D.B. Booth, S.A. Shimel, and M.A. O Neal, Univ. of Washington, Seattle 98195 Introduction The Puget Lowland
The Seattle-area geologic mapping project and the geologic framework of Seattle Troost, K.G., D.B. Booth, S.A. Shimel, and M.A. O Neal, Univ. of Washington, Seattle 98195 Introduction The Puget Lowland
PROBABILISTIC LIQUEFACTION HAZARD ANALYSIS IN JAPAN
 SECED 2015 Conference: Earthquake Risk and Engineering towards a Resilient World 9-10 July 2015, Cambridge UK PROBABILISTIC LIQUEFACTION HAZARD ANALYSIS IN JAPAN Tetsushi KURITA 1 and Sei ichiro FUKUSHIMA
SECED 2015 Conference: Earthquake Risk and Engineering towards a Resilient World 9-10 July 2015, Cambridge UK PROBABILISTIC LIQUEFACTION HAZARD ANALYSIS IN JAPAN Tetsushi KURITA 1 and Sei ichiro FUKUSHIMA
Amplification of Seismic Motion at Deep Soil Sites
 20th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 20) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 2009 SMiRT 20-Division 5, Paper 1740 Amplification of Seismic Motion at Deep Soil Sites
20th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 20) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 2009 SMiRT 20-Division 5, Paper 1740 Amplification of Seismic Motion at Deep Soil Sites
Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants.
 Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants. Development of seismotectonic models Ramon Secanell Kuala Lumpur, 26-30 August 2013 Overview of Presentation
Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants. Development of seismotectonic models Ramon Secanell Kuala Lumpur, 26-30 August 2013 Overview of Presentation
ACCOUNTING FOR SITE EFFECTS IN PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS: OVERVIEW OF THE SCEC PHASE III REPORT
 ACCOUNTING FOR SITE EFFECTS IN PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS: OVERVIEW OF THE SCEC PHASE III REPORT Edward H FIELD 1 And SCEC PHASE III WORKING GROUP 2 SUMMARY Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis
ACCOUNTING FOR SITE EFFECTS IN PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS: OVERVIEW OF THE SCEC PHASE III REPORT Edward H FIELD 1 And SCEC PHASE III WORKING GROUP 2 SUMMARY Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis
Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis for International Sites, Challenges and Guidelines
 Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis for International Sites, Challenges and Guidelines ABSTRACT Dr. Antonio Fernandez Ares Paul C. Rizzo Associates, Inc. 500 Penn Center Boulevard, Suite
Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis for International Sites, Challenges and Guidelines ABSTRACT Dr. Antonio Fernandez Ares Paul C. Rizzo Associates, Inc. 500 Penn Center Boulevard, Suite
Pilot Seismic Hazard Assessment of the Granite City, Monks Mound, and Columbia Bottom Quadrangles, St. Louis Metropolitan Area
 Pilot Seismic Hazard Assessment of the Granite City, Monks Mound, and Columbia Bottom Quadrangles, St. Louis Metropolitan Area Research Proposal Submitted by Deniz Karadeniz Ph.D. Candidate in Geological
Pilot Seismic Hazard Assessment of the Granite City, Monks Mound, and Columbia Bottom Quadrangles, St. Louis Metropolitan Area Research Proposal Submitted by Deniz Karadeniz Ph.D. Candidate in Geological
SEISMIC THREAT POSED BY THE NEW MADRID SEISMIC ZONE for Earthquakes Mean Business Seminar AT&T Data Center St. Louis, MO Friday February 3, 2006
 BRIEF OVERVIEW OF SEISMIC THREAT POSED BY THE NEW MADRID SEISMIC ZONE for Earthquakes Mean Business Seminar AT&T Data Center St. Louis, MO Friday February 3, 2006 J. David Rogers, Ph.D., P.E., R.G. Karl
BRIEF OVERVIEW OF SEISMIC THREAT POSED BY THE NEW MADRID SEISMIC ZONE for Earthquakes Mean Business Seminar AT&T Data Center St. Louis, MO Friday February 3, 2006 J. David Rogers, Ph.D., P.E., R.G. Karl
(Seismological Research Letters, July/August 2005, Vol.76 (4): )
 (Seismological Research Letters, July/August 2005, Vol.76 (4):466-471) Comment on How Can Seismic Hazard around the New Madrid Seismic Zone Be Similar to that in California? by Arthur Frankel Zhenming
(Seismological Research Letters, July/August 2005, Vol.76 (4):466-471) Comment on How Can Seismic Hazard around the New Madrid Seismic Zone Be Similar to that in California? by Arthur Frankel Zhenming
Earthquake Hazards in Henderson
 Earthquake Hazards in Henderson Craig M. depolo Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Nevada Hazard Mitigation Planning Committee November 15, 2012 Earthquake Truths The consequences of bad earthquakes to
Earthquake Hazards in Henderson Craig M. depolo Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Nevada Hazard Mitigation Planning Committee November 15, 2012 Earthquake Truths The consequences of bad earthquakes to
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 This topic addresses deterministic and probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, ground
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 This topic addresses deterministic and probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, ground
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard. Earthquake Environment
 Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code
 Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code John Adams Earthquakes Canada Geological Survey of Canada Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2004 CSCE Workshop
Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code John Adams Earthquakes Canada Geological Survey of Canada Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2004 CSCE Workshop
Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk
 Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Interpretation of Ground Shaking from Paleoliquefaction Features
 Grant Award 01HQGR0030 Dr. Timothy D. Stark Stark Consultants, Inc. Interpretation of Ground Shaking from Paleoliquefaction Features NEHRP Element: II (Memphis Metropolitan Area) Research supported by
Grant Award 01HQGR0030 Dr. Timothy D. Stark Stark Consultants, Inc. Interpretation of Ground Shaking from Paleoliquefaction Features NEHRP Element: II (Memphis Metropolitan Area) Research supported by
GEOL 380: Earthquake Hazards in the Puget Sound Region (in class and assignment) Due in class Wednesday, Nov 109th
 GEOL 380: Earthquake Hazards in the Puget Sound Region (in class and assignment) Due in class Wednesday, Nov 109th The purpose of this exercise/assignment is for you to gain practice and experience in
GEOL 380: Earthquake Hazards in the Puget Sound Region (in class and assignment) Due in class Wednesday, Nov 109th The purpose of this exercise/assignment is for you to gain practice and experience in
A METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RISK. Agency for the Environmental Protection, ITALY (
 A METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RISK Roberto W. Romeo 1, Randall W. Jibson 2 & Antonio Pugliese 3 1 University of Urbino, ITALY (e-mail: rwromeo@uniurb.it) 2 U.S. Geological Survey
A METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RISK Roberto W. Romeo 1, Randall W. Jibson 2 & Antonio Pugliese 3 1 University of Urbino, ITALY (e-mail: rwromeo@uniurb.it) 2 U.S. Geological Survey
Location Option Details. 1. Florida
 1. Florida Florida has the smallest number of earthquaes in the United States. Florida is the U.S. location where hurricanes are most frequent. Of the six deadliest hurricanes to hit the continental U.S.,
1. Florida Florida has the smallest number of earthquaes in the United States. Florida is the U.S. location where hurricanes are most frequent. Of the six deadliest hurricanes to hit the continental U.S.,
SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS
 SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS Seismotectonics Fault mechanics Ground motion considerations for design Deterministic and probabilistic analysis Estimation of ground motions Scaling of ground
SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS Seismotectonics Fault mechanics Ground motion considerations for design Deterministic and probabilistic analysis Estimation of ground motions Scaling of ground
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design
 Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS E. GEOLOGY AND SOILS
 IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS E. GEOLOGY AND SOILS The following section is a summary of the geotechnical report conducted for the Proposed Project. The Geotechnical Engineering Investigation (the
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS E. GEOLOGY AND SOILS The following section is a summary of the geotechnical report conducted for the Proposed Project. The Geotechnical Engineering Investigation (the
Impact : Changes to Existing Topography (Less than Significant)
 4.2 Land Resources 4.2.1 Alternative A Proposed Action Impact 4.2.1-1: Changes to Existing Topography (Less than Significant) Development of the project site would involve grading and other earthwork as
4.2 Land Resources 4.2.1 Alternative A Proposed Action Impact 4.2.1-1: Changes to Existing Topography (Less than Significant) Development of the project site would involve grading and other earthwork as
A Technical Note on Seismic Microzonation in the Central United States. Zhenming Wang
 A Technical Note on Seismic Microzonation in the Central United States Zhenming Wang Kentucky Geological Survey University of Kentucky Lexington, Kentucky 40506 USA Email: zmwang@uky.edu Phone: 1-859-257-5500
A Technical Note on Seismic Microzonation in the Central United States Zhenming Wang Kentucky Geological Survey University of Kentucky Lexington, Kentucky 40506 USA Email: zmwang@uky.edu Phone: 1-859-257-5500
Seismic Geotechnical Hazard Zonation Of Geological Factors
 1 st Workshop of M.E.E.T.I.N.G Project Seismic Geotechnical Hazard Zonation Of Geological Factors Maja Oštri, dipl.ing.geol Dubrovnik, March 3rd-4th 2008 SUBJECT OF THE INVESTIGATION? Geological Factors
1 st Workshop of M.E.E.T.I.N.G Project Seismic Geotechnical Hazard Zonation Of Geological Factors Maja Oštri, dipl.ing.geol Dubrovnik, March 3rd-4th 2008 SUBJECT OF THE INVESTIGATION? Geological Factors
By Chris Mikes and David Fleck Digital Terrain Analysis GEOG 593. Overview
 Earthquake and Infrastructure Damage Analysis in Multnomah and Clackamas Counties: The Application of LiDAR In The Development of an Emergency Response Plan By Chris Mikes and David Fleck Digital Terrain
Earthquake and Infrastructure Damage Analysis in Multnomah and Clackamas Counties: The Application of LiDAR In The Development of an Emergency Response Plan By Chris Mikes and David Fleck Digital Terrain
Model Uncertainties of the 2002 Update of California Seismic Hazard Maps
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 95, No. 6, pp. 24 257, December 25, doi: 1.1785/12517 Model Uncertainties of the 22 Update of California Seismic Hazard Maps by Tianqing Cao, Mark
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 95, No. 6, pp. 24 257, December 25, doi: 1.1785/12517 Model Uncertainties of the 22 Update of California Seismic Hazard Maps by Tianqing Cao, Mark
Geotechnical Aspects of the Seismic Update to the ODOT Bridge Design Manual. Stuart Edwards, P.E Geotechnical Consultant Workshop
 Geotechnical Aspects of the Seismic Update to the ODOT Bridge Design Manual Stuart Edwards, P.E. 2017 Geotechnical Consultant Workshop Changes Role of Geotechnical Engineer Background Methodology Worked
Geotechnical Aspects of the Seismic Update to the ODOT Bridge Design Manual Stuart Edwards, P.E. 2017 Geotechnical Consultant Workshop Changes Role of Geotechnical Engineer Background Methodology Worked
Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan
 Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Graduate Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, Taiwan Seismology Forum 27: Natural Hazards and Surface
Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Graduate Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, Taiwan Seismology Forum 27: Natural Hazards and Surface
Seismic Site Classification and Soil Amplification Assessment of Chiang Rai City, Northern Thailand
 Seismic Site Classification and Soil Amplification Assessment of Chiang Rai City, Northern Thailand Ratchadaporn Jintaprasat and Thanop Thitimakorn 1 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn
Seismic Site Classification and Soil Amplification Assessment of Chiang Rai City, Northern Thailand Ratchadaporn Jintaprasat and Thanop Thitimakorn 1 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn
Assessment and Mitigation of Ground Motion Hazards from Induced Seismicity. Gail M. Atkinson
 Assessment and Mitigation of Ground Motion Hazards from Induced Seismicity Gail M. Atkinson (with acknowledgement to many collaborators, especially Ghofrani and Assatourians) NSERC/TransAlta/Nanometrics
Assessment and Mitigation of Ground Motion Hazards from Induced Seismicity Gail M. Atkinson (with acknowledgement to many collaborators, especially Ghofrani and Assatourians) NSERC/TransAlta/Nanometrics
Improved Liquefaction Hazard Evaluation through PLHA. Steven L. Kramer University of Washington
 Improved Liquefaction Hazard Evaluation through PLHA Steven L. Kramer University of Washington il Liquefaction hree primary questions to answer: Is the soil susceptible to liquefaction? If so, is the anticipated
Improved Liquefaction Hazard Evaluation through PLHA Steven L. Kramer University of Washington il Liquefaction hree primary questions to answer: Is the soil susceptible to liquefaction? If so, is the anticipated
Seismic-Hazard Map of Southeast Missouri and Likely Magnitude of the February 1812 New Madrid Earthquake
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 105, No. 4, pp., August 2015, doi: 10.1785/0120140307 Seismic-Hazard Map of Southeast Missouri and Likely Magnitude of the February 1812 New Madrid
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 105, No. 4, pp., August 2015, doi: 10.1785/0120140307 Seismic-Hazard Map of Southeast Missouri and Likely Magnitude of the February 1812 New Madrid
The New Madrid seismic zone and its influence on seismic hazard. Robin K. McGuire Reinsurance Association of America Meeting February 14, 2018.
 The New Madrid seismic zone and its influence on seismic hazard Robin K. McGuire Reinsurance Association of America Meeting February 14, 2018. USGS PGA hazard map, 500-year return period, B-C site, 2014
The New Madrid seismic zone and its influence on seismic hazard Robin K. McGuire Reinsurance Association of America Meeting February 14, 2018. USGS PGA hazard map, 500-year return period, B-C site, 2014
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S
 I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2015 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2015)
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2015 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2015)
PROJECT SITE. Ione St. VICINITY MAP. Sutter. Creek. Jackson. Newman Ridge Quarry Project Amador County, California. Scale in Miles. Old. Rd.
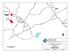 124 Old Hwy. Ione Michigan Bar Irish Hill Ione Sutter Creek Ridge PROJECT SITE Dutschke Mile Dr. 124 Sutter Loch Lane Res. Old Five Stockton Castle Oaks Golf Club Marlette Ione St. 124 Charles Howard Park
124 Old Hwy. Ione Michigan Bar Irish Hill Ione Sutter Creek Ridge PROJECT SITE Dutschke Mile Dr. 124 Sutter Loch Lane Res. Old Five Stockton Castle Oaks Golf Club Marlette Ione St. 124 Charles Howard Park
Important Concepts. Earthquake hazards can be categorized as:
 Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Module 7 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS (Lectures 33 to 36)
 Lecture 34 Topics Module 7 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS (Lectures 33 to 36) 7.3 DETERMINISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS 7.4 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS 7.4.1 Earthquake Source Characterization 7.4.2
Lecture 34 Topics Module 7 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS (Lectures 33 to 36) 7.3 DETERMINISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS 7.4 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS 7.4.1 Earthquake Source Characterization 7.4.2
KTC-07-07/SPR F (Revised on March 27, 2012) SEISMIC-HAZARD MAPS AND TIME HISTORIES FOR THE COMMONWEALTH OF KENTUCKY
 KTC-7-7/SPR246-2-6F (Revised on March 27, 22) SEISMIC-HAZARD MAPS AND TIME HISTORIES FOR THE COMMONWEALTH OF KENTUCKY Research Report KTC-7-7/SPR246-2-6F SEISMIC-HAZARD MAPS AND TIME HISTORIES FOR THE
KTC-7-7/SPR246-2-6F (Revised on March 27, 22) SEISMIC-HAZARD MAPS AND TIME HISTORIES FOR THE COMMONWEALTH OF KENTUCKY Research Report KTC-7-7/SPR246-2-6F SEISMIC-HAZARD MAPS AND TIME HISTORIES FOR THE
2.0 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Model
 1.0 Introduction The study involves probabilistic seismic hazard mapping for South Carolina. A hazard model is developed which defines the sources for potential earthquakes and earthquake recurrence relations.
1.0 Introduction The study involves probabilistic seismic hazard mapping for South Carolina. A hazard model is developed which defines the sources for potential earthquakes and earthquake recurrence relations.
Evaluating the Seismic Coefficient for Slope Stability Analyses
 Evaluating the Seismic Coefficient for Slope Stability Analyses by Edward Kavazanjian, Jr., Ph.D., P.E.,D.GE., NAE Ira A. Fulton Professor of Geotechnical Engineering School of Sustainable Engineering
Evaluating the Seismic Coefficient for Slope Stability Analyses by Edward Kavazanjian, Jr., Ph.D., P.E.,D.GE., NAE Ira A. Fulton Professor of Geotechnical Engineering School of Sustainable Engineering
Forecasting Hazard from Induced Earthquakes. Ryan Schultz
 Forecasting Hazard from Induced Earthquakes Ryan Schultz Overview 1) Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA). Ground Motions Parameters Earthquake Catalogues & Recurrence Relations GMPEs Hazard Calculation
Forecasting Hazard from Induced Earthquakes Ryan Schultz Overview 1) Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA). Ground Motions Parameters Earthquake Catalogues & Recurrence Relations GMPEs Hazard Calculation
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. GEOLOGY AND SOILS
 IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. GEOLOGY AND SOILS The following section is a summary of the geotechnical report conducted for the proposed project. The Report of Geotechnical Investigation Proposed
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. GEOLOGY AND SOILS The following section is a summary of the geotechnical report conducted for the proposed project. The Report of Geotechnical Investigation Proposed
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S
 I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2013 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2013)
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2013 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2013)
Earthquake Hazards in Douglas County
 Earthquake Hazards in Douglas County Craig M. depolo Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Nevada Hazard Mitigation Planning Committee August 9, 2012 Earthquake Truths The consequences of bad earthquakes
Earthquake Hazards in Douglas County Craig M. depolo Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Nevada Hazard Mitigation Planning Committee August 9, 2012 Earthquake Truths The consequences of bad earthquakes
Nonlinear shear stress reduction factor (r d ) for Christchurch Central Business District
 Dismuke, J.N. (2013) Proc. 19 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium. Ed. CY Chin, Queenstown Nonlinear shear stress reduction factor (r d ) for Christchurch Central Business District J N Dismuke Golder Associates,
Dismuke, J.N. (2013) Proc. 19 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium. Ed. CY Chin, Queenstown Nonlinear shear stress reduction factor (r d ) for Christchurch Central Business District J N Dismuke Golder Associates,
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
Comparison of CPT Based Liquefaction Potential and Shear Wave Velocity Maps by Using 3-Dimensional GIS
 Comparison of CPT Based Liquefaction Potential and Shear Wave Velocity Maps by Using 3-Dimensional GIS Muammer Tün, Uğur Avdan, Metin Altan, Can Ayday Anadolu University, Satellite and Space Sciences Research
Comparison of CPT Based Liquefaction Potential and Shear Wave Velocity Maps by Using 3-Dimensional GIS Muammer Tün, Uğur Avdan, Metin Altan, Can Ayday Anadolu University, Satellite and Space Sciences Research
CHARACTERIZING SPATIAL CROSS-CORRELATION BETWEEN GROUND- MOTION SPECTRAL ACCELERATIONS AT MULTIPLE PERIODS. Nirmal Jayaram 1 and Jack W.
 Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering Compte Rendu de la 9ième Conférence Nationale Américaine et 10ième Conférence Canadienne de Génie Parasismique
Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering Compte Rendu de la 9ième Conférence Nationale Américaine et 10ième Conférence Canadienne de Génie Parasismique
Japan Seismic Hazard Information Station
 Japan Seismic Hazard Information Station (J-SHIS) Hiroyuki Fujiwara National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED) Background of the Project Headquarters for Earthquake Research
Japan Seismic Hazard Information Station (J-SHIS) Hiroyuki Fujiwara National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED) Background of the Project Headquarters for Earthquake Research
Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Analysis. Hong Kie Thio AECOM, Los Angeles
 Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Analysis Hong Kie Thio AECOM, Los Angeles May 18, 2015 Overview Introduction Types of hazard analysis Similarities and differences to seismic hazard Methodology Elements o
Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Analysis Hong Kie Thio AECOM, Los Angeles May 18, 2015 Overview Introduction Types of hazard analysis Similarities and differences to seismic hazard Methodology Elements o
Seth J. Wittke Wyoming State Geological Survey
 Seth J. Wittke Wyoming State Geological Survey Project initiation Data manipulation Scenarios Creating the IMS Lessons learned County-wide block level probabilistic models created in 2004 for state mitigation
Seth J. Wittke Wyoming State Geological Survey Project initiation Data manipulation Scenarios Creating the IMS Lessons learned County-wide block level probabilistic models created in 2004 for state mitigation
Crustal Plate Boundaries Convection Drives the Plates
 SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS Seismic Activity > M5 Since 1980 Seismotectonics Fault mechanics Ground motion considerations for design Ring of Fire Mid-Atlantic Ridge Alpide Belt Deterministic
SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS Seismic Activity > M5 Since 1980 Seismotectonics Fault mechanics Ground motion considerations for design Ring of Fire Mid-Atlantic Ridge Alpide Belt Deterministic
Cascadia megathrust earthquakes: reducing risk through science, engineering, and planning
 Cascadia megathrust earthquakes: reducing risk through science, engineering, and planning NSF Hazards SEES EAR-1331412 Urban Science and Engineering Workshop 21 July 2014 Everything to do with M9 Cascadia
Cascadia megathrust earthquakes: reducing risk through science, engineering, and planning NSF Hazards SEES EAR-1331412 Urban Science and Engineering Workshop 21 July 2014 Everything to do with M9 Cascadia
Synthetic Near-Field Rock Motions in the New Madrid Seismic Zone
 Synthetic Near-Field Rock Motions in the New Madrid Seismic Zone Genda Chen*, Ph.D., P.E., and Mostafa El-Engebawy Engebawy,, Ph.D. *Associate Professor of Civil Engineering Department of Civil, Architecture
Synthetic Near-Field Rock Motions in the New Madrid Seismic Zone Genda Chen*, Ph.D., P.E., and Mostafa El-Engebawy Engebawy,, Ph.D. *Associate Professor of Civil Engineering Department of Civil, Architecture
#13 Earthquake Prediction
 #13 Earthquake Prediction Obvious importance Earthquake Prediction Save lives, reduce damage Earthquake Prediction - Types Long-range prediction - involves EQ probability over long time period (years to
#13 Earthquake Prediction Obvious importance Earthquake Prediction Save lives, reduce damage Earthquake Prediction - Types Long-range prediction - involves EQ probability over long time period (years to
Ground Motion Studies for Critical Sites in North-West Bangladesh
 Science & Technology Conference 2011 Vienna, June 8-10, 2011 Ground Motion Studies for Critical Sites in North-West Bangladesh Dr. Tahmeed M. Al Hussaini Professor of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University
Science & Technology Conference 2011 Vienna, June 8-10, 2011 Ground Motion Studies for Critical Sites in North-West Bangladesh Dr. Tahmeed M. Al Hussaini Professor of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University
