1 INTRODUCTION AND MAJOR FINDINGS... 1
|
|
|
- Marshall Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater Conservation District Administrator Date: 8/2/2016 Re: 1 INTRODUCTION AND MAJOR FINDINGS Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. (Pioneer) and Applied Geomorphology (AGI) were contracted as a project team to evaluate a reach of the West Fork Stillwater River (West Fork) located in the southwest quarter of Section 26, Township 04 South, Range 15 East, Principal Montana Meridian, (project site) that was identified as potentially prone to an avulsion (rapid relocation of the main river channel). The main concern with an avulsion occurring within this reach is the potential for flooding and geomorphic instability downstream through the community of Nye, Montana. The purpose of this document is to summarize existing site conditions and potential treatment alternatives at the project site. The information provided in this document was also presented at a stakeholder meeting in Fishtail, Montana on April 19, Conclusions developed by the project team resulting from the assessment are as follows: 1. The identified avulsion risk is associated with the recent enlargement of a side channel that has the potential to feed a much older floodplain channel that extends from the project site southeast through Nye to its confluence with the Stillwater River. The side channel enlarged and migrated towards the older floodplain channel during the 2011 flood. Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION AND MAJOR FINDINGS SITE CONDITIONS AND RISK OF AVULSION Potential Avulsion Mechanisms at Site Continued Enlargement and Migration of South Channel Erosion and Enlargement of Historic Channel by Floodwaters Backwatering in the Historic Channel by Beaver Dams ALTERNATIVES TO REDUCE EROSION RISK Alternative 1: No Action Alternative 2: Adaptive Management Alternative 3: Flow Deflectors and Bank Reconstruction on Main Thread Alternative 4: Install Grade Control and Riprap in South Channel Alternative 5: Install Floodplain Berm and Introduce Additional Floodplain Roughness COST BREAKDOWN FOR PROJECT ALTERNATIVES REFERENCES Although the risk of avulsion at the site has increased with the recent side channel enlargement, the overall risk of a wholesale avulsion at the site remains low. 3. Several natural features are in place to dissuade erosion at the site including channel topography, floodplain topography, and floodplain roughness. 4. If landowners are interested, further measures could be implemented to additionally reduce the long-term risk of erosion at the site. 5. Although the risk of a rapid, catastrophic avulsion into the historic floodplain channel at the project site is low, the channel will convey any water received through Nye and thus should be recognized as a potential flood hazard. 6. There are other locations down the valley that may pose some avulsion risk into the historic channel. Figure 1 shows the location of the project site, which is about 2.7 miles upstream of the mouth of the West Fork near Nye. As the West Fork flows southeastward towards Nye, it flows across a coarse glacial outwash/alluvial fan that has 2310 BROADWATER AVE., STE. 1 BILLINGS, MT PH: FX: TECHNICAL.COM HEADQUARTERS: PO BOX 3445 BUTTE, MT A N A C O N D A B I L L I N G S B O Z E M A N H E L E N A M I S S O U L A L A S V E G A S, NV K E L L O G G, ID
2 both active and inactive channel threads. Many of these channels probably reflect historic glacial conditions rather than modern hydrology and sediment loads. That said, there are distinct channels that are continuous and well-vegetated, with the potential to convey flow and/or sediment down the valley. The issue at the project site is whether a historical channel that originates near the mouth of Horseman Creek has the potential to capture the main thread of the West Fork. Figure 1. West Fork avulsion project location map showing major features. 2 SITE CONDITIONS AND RISK OF AVULSION The project site was identified as having a risk of avulsion in the Upper Stillwater Watershed Assessment (Kellogg, 2014). The assessment noted that the bendway migration that occurred on a side channel of the West Fork during high water in 2011 increased the risk of the West Fork being captured by a historic channel that could cause erosion and flood damages in Nye. Figure 2 shows several features at the project site that relate to the potential avulsion issue. The North Channel is the main thread of the West Fork. It is a steep, boulder bed channel that carries coarse glacially derived bedload material. The South Channel refers to the side channel that has enlarged with recent flooding (notably 2011). The South Channel is blocked at its entrance by a woody debris jam, which currently limits flow into the South Channel (see Figure 3). Just downstream of the debris jam, however, the South Channel shows evidence of floodinduced enlargement, downcutting, and migration (see Figure 4), including high eroding banks, a distinct headcut, and variable bank heights due to headcut migration. One concern is that the failure of the debris jam at the entrance of the South Channel may cause it to enlarge further and potentially become a more prominent secondary channel or even the main thread of the West Fork. This would in turn increase the frequency and duration of overbank flows into the area where the historic channel flows towards Nye. Increased flow into the South Channel could also drive its migration down valley into the historic channel area. Assessment Page 2 of 13
3 Figure 2. Project site overview (avulsion path of concern in yellow). Figure 3. Debris jam at the entrance of the South Channel (main thread of the West Fork flows to the left). Assessment Page 3 of 13
4 Figure 4. View down the South Channel showing unarmored bendway (avulsion point of concern is at the pickup). 2.1 Potential Avulsion Mechanisms at Site Alluvial fan systems should always be evaluated in terms of avulsion potential when there are investments made along historic distributary channels. These alluvial fan features are notoriously dynamic and susceptible to dramatic change during floods. At the project site, there are several potential scenarios that could drive an avulsion at the site, although site conditions do not indicate that an avulsion is imminent without some sort of large scale flood event. Regardless, it is important to understand the dominant mechanisms presented on site when considering risk and potential alternatives to mitigate that risk. The overall mechanism for an avulsion at the site is the whole or partial capture of the West Fork by the historic outwash fan channel. There are potential conditions/events that would contribute factors to that mechanism, and they are described below Continued Enlargement and Migration of South Channel The relocation of the majority of the West Fork flow into the South Channel would increase the risk of subsequent avulsion into the historic channel. Typical drivers for this could include debris or ice blockages on the main channel, or perching of the main channel above the South Channel, making the current flow split unstable. A major blockage of the main West Fork channel ( North Channel shown on Figure 2) may be the most likely scenario for wholesale flow relocation into the South Channel. This would require a blockage to form in the North Channel somewhere near the entrance of the South Channel, which is currently blocked by a debris jam of its own. Thus, a major relocation of flow would require blockage of the main North Channel and simultaneous breaching of the existing debris jam at the entrance of the South Channel (see Figure 3). With regard to topographic perching, a survey of the project site indicates that the secondary South Channel is currently perched above the main North Channel (see Figure 5), which greatly reduces the potential for the South Channel to capture the main thread flow of the West Fork. Assessment Page 4 of 13
5 Figure 5. Surveyed profile of the main North Channel (green) and secondary South Channel (red) showing perching of the South Channel. The bed of the South Channel is covered in coarse boulders that probably accumulated as an armor layer during the flood-induced erosion of In the event that the channel receives more flow, this coarse boulder material will help resist continued channel enlargement under most flow conditions. In the event of an extreme event, however, the boulders should be considered mobile (see Figure 6). Figure 6. View upstream of South Channel showing boulder bed material Erosion and Enlargement of Historic Channel by Floodwaters If flood flows were to extend across the floodplain surface and reach the head of the historic channel, there is a possibility that those overbank flows would concentrate in historic channel and enlarge it, which could create upstream migrating headcuts that would increase the risk of wholesale avulsion. The primary mechanisms for this scenario would include floodwater access to the floodplain channel and erosion of that feature. Figure 7 shows that the Historic Assessment Page 5 of 13
6 Channel Area is out of the 100-floodplain and separated from the South Channel by a Natural Floodplain Berm which is probably a glacial moraine remnant from the mouth of Horseman Creek (see Figure 8). Figure 7. Stillwater County FIRM map of the project site showing the historical channel area outside the 100 Year floodplain and separated by a natural floodplain berm. Figure 8. View down valley (east) showing coarse floodplain berm separating secondary South Channel (behind photographer) and potential avulsion site in distance. Assessment Page 6 of 13
7 2.1.3 Backwatering in the Historic Channel by Beaver Dams Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Another means of increasing flows over the floodplain and into the historic channel is backwatering in the South Channel by beaver damming. At the time of our field investigation there was a large beaver dam remnant that had clearly backwatered much of the South Channel. Numerous beavers have been trapped out of this area and as a result backwatering is minimal (see Figure 9). Figure 9. View upstream on lower end of South Channel showing the historic beaver dam impoundment. In the event the historic channel area is accessed by floodwater, it would take high energy flows to erode the existing material due to its coarseness. In general, one major characteristic of this site is coarse floodplain material, which adds natural resilience to avulsion (see Figure 10). Assessment Page 7 of 13
8 Figure 10. Floodplain roughness near potential avulsion site. 3 ALTERNATIVES TO REDUCE EROSION RISK Although all of the characteristics of the project site indicate that the likelihood of the West Fork avulsing into the historic channel is low, it is important to recognize that one component of risk assessment is considering the consequences of an event. Even if the likelihood of occurrence is low, it may be appropriate to implement measures to further avoid the event (in this case channel avulsion) if the consequences are high. Since the community of Nye is located on the historic channel and prone to major damages in the event of an avulsion, consideration of mitigation measures is appropriate. In the event that the measures presented below are further considered for implementation, it is strongly recommend that the channels below the project site that connect the West Fork to the historic channel be similarly evaluated for avulsion risk. This evaluation would identify and prioritize sites posing the greatest demonstrable risk downstream. 3.1 Alternative 1: No Action Under the No Action alternative, there would be no attempts to modify current conditions and the channel configurations would be left in place. This alternative would also require the acknowledgement that even without an avulsion, flooding could occur downstream along the historic channel during high water events. There are no costs associated with Alternative Alternative 2: Adaptive Management The concept of Adaptive Management allows stakeholders to respond to changing conditions in a measured, strategic, and cost-effective manner. This is appropriate in systems where catastrophic change or a continued degradation of site conditions is not anticipated. At this site, adaptive management may be appropriate due to the current system resilience to the mechanisms of avulsions. This would include monitoring and managing debris jams, beaver dams, bank erosion, and floodplain erosion, and continually maintaining system resilience. Assessment Page 8 of 13
9 Costs have not been developed for Alternative 2; however this approach would require expenditures for monitoring, design, and implementation as necessary. 3.3 Alternative 3: Flow Deflectors and Bank Reconstruction on Main Thread As described previously, there is currently a large debris jam blocking the entrance of the South Channel (see Figure 11). Just upstream of this debris jam, the right bank of the main North Channel has experienced some accelerated erosion due to the flanking of bank armor, which has made the entrance of the secondary South Channel more accessible to typical river flows. Alternative 3 would consist of reconstructing the right bank and installing flow deflectors to reduce access to the South Channel feature. The complete blockage of the secondary South Channel is not recommended due to its contribution to fish habitat and geomorphic complexity on the West Fork. The estimated cost for Alternative 3 is approximately $118,000. Figure 11. View downstream towards debris jam located at the secondary South Channel entrance (center of photo) showing right bank erosion and flanked large boulder riprap remnants in the Main Channel. 3.4 Alternative 4: Install Grade Control and Riprap in South Channel As enlargement of the secondary South Channel is a major concern with regard to increased avulsion potential, preventing additional enlargement and channel migration in the South Channel may be appropriate. Alternative 4 consists of installing a grade control structure in the bed of the South Channel and placing riprap along the eroding bend at the potential point of avulsion (see Figure 12). Schematic cross-sections for the grade control structure and riprap are shown on Figure 13 and Figure 14, respectively. The estimated cost for Alternative 4 is approximately $70,000. Assessment Page 9 of 13
10 Figure 12. Proposed locations for a grade control structure and riprap, Alternative 4. Figure 13. Schematic cross section of the proposed South Channel grade control structure. Assessment Page 10 of 13
11 Figure 14. Schematic cross section of the proposed South Channel riprap. 3.5 Alternative 5: Install Floodplain Berm and Introduce Additional Floodplain Roughness To reduce overbank flows into the historic channel and prevent floodplain erosion, Alternative 5 consists of installing a floodplain berm and incorporating floodplain roughness elements (see Figure 15). The proposed floodplain berm would be approximately 200 feet long and would be integrated with large woody debris to further dissuade floodplain erosion. Assessment Page 11 of 13
12 Figure 15. Proposed locations for a floodplain berm and roughness elements. The estimated cost for Alternative 5 is approximately $83, COST BREAKDOWN FOR PROJECT ALTERNATIVES The table below shows a cost breakdown for the alternatives described above. Assessment Page 12 of 13
13 5 REFERENCES Kellogg, W., Upper Stillwater River Assessment. Stream & Watershed Counsulting, Helena, Montana. March Page 65. Assessment Page 13 of 13
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes
 Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage
 Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
The last three sections of the main body of this report consist of:
 Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report No.2
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
Case Study 2: Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords
 Case Study : Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords Location Crossing Description Washington. Okanagan National Forest. Methow Valley Ranger District. Chewuch river basin, East Chewuch Road. The Twenty-mile Creek
Case Study : Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords Location Crossing Description Washington. Okanagan National Forest. Methow Valley Ranger District. Chewuch river basin, East Chewuch Road. The Twenty-mile Creek
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration
 Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN
 ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
Dan Miller + Kelly Burnett, Kelly Christiansen, Sharon Clarke, Lee Benda. GOAL Predict Channel Characteristics in Space and Time
 Broad-Scale Models Dan Miller + Kelly Burnett, Kelly Christiansen, Sharon Clarke, Lee Benda GOAL Predict Channel Characteristics in Space and Time Assess Potential for Fish Use and Productivity Assess
Broad-Scale Models Dan Miller + Kelly Burnett, Kelly Christiansen, Sharon Clarke, Lee Benda GOAL Predict Channel Characteristics in Space and Time Assess Potential for Fish Use and Productivity Assess
Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road
 Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Fluvial Geomorphology Assessment of Northern Connecticut River Tributaries
 Fluvial Geomorphology Assessment of Northern Connecticut River Tributaries Final Report Upper Ammonoosuc River in Stark, NH Prepared for Connecticut River Joint Commissions Charlestown, New Hampshire Prepared
Fluvial Geomorphology Assessment of Northern Connecticut River Tributaries Final Report Upper Ammonoosuc River in Stark, NH Prepared for Connecticut River Joint Commissions Charlestown, New Hampshire Prepared
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods
 Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash
 Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley).
Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley).
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
Application of GIS Technology in Reach- Scale Channel Migration Zone Mapping: Yellowstone River, Montana
 Application of GIS Technology in Reach- Scale Channel Migration Zone Mapping: Yellowstone River, Montana Karin Boyd Applied Geomorphology, Inc. Bozeman, MT Tony Thatcher DTM Consulting, Inc Bozeman, MT
Application of GIS Technology in Reach- Scale Channel Migration Zone Mapping: Yellowstone River, Montana Karin Boyd Applied Geomorphology, Inc. Bozeman, MT Tony Thatcher DTM Consulting, Inc Bozeman, MT
GENERAL SUMMARY BIG WOOD RIVER GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT BLAINE COUNTY, IDAHO
 GENERAL SUMMARY BIG WOOD RIVER GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT BLAINE COUNTY, IDAHO Prepared For Trout Unlimited 300 North Main Street, Hailey, Idaho, 83333 Prepared By P. O. Box 8578, 140 E. Broadway, Suite 23,
GENERAL SUMMARY BIG WOOD RIVER GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT BLAINE COUNTY, IDAHO Prepared For Trout Unlimited 300 North Main Street, Hailey, Idaho, 83333 Prepared By P. O. Box 8578, 140 E. Broadway, Suite 23,
6.11 Naas River Management Unit
 6.11 Naas River Management Unit 6.11.1 Site 41 Issue: Bed and bank erosion Location: E 0685848 N 6058358 Waterway: Naas River Management Unit: Naas River Facing downstream from Bobeyan Rd bridge Facing
6.11 Naas River Management Unit 6.11.1 Site 41 Issue: Bed and bank erosion Location: E 0685848 N 6058358 Waterway: Naas River Management Unit: Naas River Facing downstream from Bobeyan Rd bridge Facing
Geomorphic Importance of Winter Peak Flows and Annual Snowmelt Hydrographs in a Sierra Nevada Boulder-Bedrock River
 Geomorphic Importance of Winter Peak Flows and Annual Snowmelt Hydrographs in a Sierra Nevada Boulder-Bedrock River Scott McBain and Bill Trush McBain & Trush, Inc. Clavey River and Cherry Creek vicinity
Geomorphic Importance of Winter Peak Flows and Annual Snowmelt Hydrographs in a Sierra Nevada Boulder-Bedrock River Scott McBain and Bill Trush McBain & Trush, Inc. Clavey River and Cherry Creek vicinity
CR AAO Bridge. Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design. Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District
 CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
4.1 Review the Road Context. 4.2 Review Resource Values. 4.3 Evaluate Watershed Risk Factors. 4.4 Conduct the Initial Site Reconnaissance
 4Initial Watershed and Reach Review 4.1 Review the Road Context 4.2 Review Resource Values 4.3 Evaluate Watershed Risk Factors 4.4 Conduct the Initial Site Reconnaissance 4.5 Assess Site Suitability 4.6
4Initial Watershed and Reach Review 4.1 Review the Road Context 4.2 Review Resource Values 4.3 Evaluate Watershed Risk Factors 4.4 Conduct the Initial Site Reconnaissance 4.5 Assess Site Suitability 4.6
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution % in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b.
 ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms
 Scott Jackson University of Massachusetts Amherst Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms Dams Sub-standard Culverts Excessive Velocities Inlet Drop
Scott Jackson University of Massachusetts Amherst Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms Dams Sub-standard Culverts Excessive Velocities Inlet Drop
Perspectives on river restoration science, geomorphic processes, and channel stability
 Perspectives on river restoration science, geomorphic processes, and channel stability Stream Restoration Forum: Science and Regulatory Connections Andrew C. Wilcox Department of Geosciences University
Perspectives on river restoration science, geomorphic processes, and channel stability Stream Restoration Forum: Science and Regulatory Connections Andrew C. Wilcox Department of Geosciences University
Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta
 Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to
Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to
NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA
 QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007
 Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007 Appendix Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Methods 3 Results 3 Discussion 5 Conclusion 11 1 Abstract Half Moon Lake appears to be an
Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007 Appendix Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Methods 3 Results 3 Discussion 5 Conclusion 11 1 Abstract Half Moon Lake appears to be an
APPENDIX E. GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2013
 APPENDIX E GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2 Introduction Keystone Restoration Ecology (KRE) conducted geomorphological monitoring in
APPENDIX E GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2 Introduction Keystone Restoration Ecology (KRE) conducted geomorphological monitoring in
Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River
 Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River US Army Corps Of Engineers St. Louis District Fayette County Soil and Water Conservation District Team Partners : Carlyle Lake Ecosystem Partnership Vicinity
Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River US Army Corps Of Engineers St. Louis District Fayette County Soil and Water Conservation District Team Partners : Carlyle Lake Ecosystem Partnership Vicinity
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments
 GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
Streams. Stream Water Flow
 CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
PolyMet NorthMet Project
 RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop
 Presentation to the Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop by Michael Rodgers River Engineer US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Louis District August 17, 2007 Engineering
Presentation to the Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop by Michael Rodgers River Engineer US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Louis District August 17, 2007 Engineering
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle. Runoff Transpiration
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
GLG362/GLG598 Geomorphology K. Whipple October, 2009 I. Characteristics of Alluvial Channels
 I. Characteristics of Alluvial Channels Self-formed morphology set by entrainment, transport, and deposition They move unconsolidated sedimentary materials present in the valley fill flood plain/bank flow
I. Characteristics of Alluvial Channels Self-formed morphology set by entrainment, transport, and deposition They move unconsolidated sedimentary materials present in the valley fill flood plain/bank flow
Technical Memorandum. To: From: Copies: Date: 10/19/2017. Subject: Project No.: Greg Laird, Courtney Moore. Kevin Pilgrim and Travis Stroth
 Technical Memorandum To: From: Greg Laird, Courtney Moore Kevin Pilgrim and Travis Stroth 5777 Central Avenue Suite 228 Boulder, CO 80301 www.otak.com Copies: [Electronic submittal] Date: 10/19/2017 Subject:
Technical Memorandum To: From: Greg Laird, Courtney Moore Kevin Pilgrim and Travis Stroth 5777 Central Avenue Suite 228 Boulder, CO 80301 www.otak.com Copies: [Electronic submittal] Date: 10/19/2017 Subject:
Summary of Hydraulic and Sediment-transport. Analysis of Residual Sediment: Alternatives for the San Clemente Dam Removal/Retrofit Project,
 Appendix N SUMMARY OF HYDRAULIC AND SEDIMENT-TRANSPORT ANALYSIS OF RESIDUAL SEDIMENT: ALTERNATIVES FOR THE SAN CLEMENTE DAM REMOVAL/RETROFIT PROJECT, CALIFORNIA the San Clemente Dam Removal/Retrofit Project,
Appendix N SUMMARY OF HYDRAULIC AND SEDIMENT-TRANSPORT ANALYSIS OF RESIDUAL SEDIMENT: ALTERNATIVES FOR THE SAN CLEMENTE DAM REMOVAL/RETROFIT PROJECT, CALIFORNIA the San Clemente Dam Removal/Retrofit Project,
CASE STUDIES. Introduction
 Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points
 Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points Traci Sylte, P.E. Hydrology/Fluvial Geomorphology Lolo National Forest Is It True? Are Road Crossings a Dam with
Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points Traci Sylte, P.E. Hydrology/Fluvial Geomorphology Lolo National Forest Is It True? Are Road Crossings a Dam with
Do you think sediment transport is a concern?
 STREAM RESTORATION FRAMEWORK AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT BASICS Pete Klingeman 1 What is Your Restoration Project Like? k? Do you think sediment transport is a concern? East Fork Lewis River, WA Tidal creek,
STREAM RESTORATION FRAMEWORK AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT BASICS Pete Klingeman 1 What is Your Restoration Project Like? k? Do you think sediment transport is a concern? East Fork Lewis River, WA Tidal creek,
Fluvial Driven Alluvial Fans
 Fluvial Driven Alluvial Fans Restoration Project Evaluations - Examples from the Russian and Napa River Watersheds Mia Docto Masters Thesis UC Berkeley 1. Basic Fan Description 2. Fluvial Driven Fan Characteristics
Fluvial Driven Alluvial Fans Restoration Project Evaluations - Examples from the Russian and Napa River Watersheds Mia Docto Masters Thesis UC Berkeley 1. Basic Fan Description 2. Fluvial Driven Fan Characteristics
Lower South Fork McKenzie River Floodplain Enhancement Project
 Lower South Fork McKenzie River Floodplain Enhancement Project McKenzie River Ranger District Willamette National Forest Project Location The project is located in the South Fork McKenzie River Watershed,
Lower South Fork McKenzie River Floodplain Enhancement Project McKenzie River Ranger District Willamette National Forest Project Location The project is located in the South Fork McKenzie River Watershed,
Updated Fluvial Geomorphology Modeling Approach
 (FERC No. 14241) Updated Fluvial Geomorphology Modeling Approach Technical Memorandum Prepared for Prepared by Tetra Tech Original Submitted June 30, 2013 Updated May 2014 Page intentionally left blank
(FERC No. 14241) Updated Fluvial Geomorphology Modeling Approach Technical Memorandum Prepared for Prepared by Tetra Tech Original Submitted June 30, 2013 Updated May 2014 Page intentionally left blank
Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018
 Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018 EXISTING CONDITION The proposed Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project
Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018 EXISTING CONDITION The proposed Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Working with Natural Stream Systems
 Working with Natural Stream Systems Graydon Dutcher Delaware County Soil & Water Conservation District Stream Corridor Management Program Tropical Storm Sandy October 29,2012 What is a Watershed?
Working with Natural Stream Systems Graydon Dutcher Delaware County Soil & Water Conservation District Stream Corridor Management Program Tropical Storm Sandy October 29,2012 What is a Watershed?
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget
 Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Best Management Practices for Coldwater Fisheries Enhancement and Restoration
 Best Management Practices for Coldwater Fisheries Enhancement and Restoration MACC Annual Environmental Conference 2017 March 3, 2017 Tim Dexter, MassDOT Highway Division 1 Leading the Nation in Transportation
Best Management Practices for Coldwater Fisheries Enhancement and Restoration MACC Annual Environmental Conference 2017 March 3, 2017 Tim Dexter, MassDOT Highway Division 1 Leading the Nation in Transportation
Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam
 Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam Following the removal of Marmot Dam in 2007, the fate of the reservoir sediments has been monitored through a series of surveys and sediment transport measurements.
Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam Following the removal of Marmot Dam in 2007, the fate of the reservoir sediments has been monitored through a series of surveys and sediment transport measurements.
Dolores River Watershed Study
 CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology
 Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Evaluation of Geomorphic Effects of Removal of Marmot and Little Sandy Dams and Potential Impacts on Anadromous Salmonids
 PRELIMINARY FINAL Evaluation of Geomorphic Effects of Removal of Marmot and Little Sandy Dams and Potential Impacts on Anadromous Salmonids Prepared for: Portland General Electric 121 SW Salmon Street
PRELIMINARY FINAL Evaluation of Geomorphic Effects of Removal of Marmot and Little Sandy Dams and Potential Impacts on Anadromous Salmonids Prepared for: Portland General Electric 121 SW Salmon Street
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS
 EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS
 LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS BRUCE M. PHILLIPS 1 ABSTRACT The dynamic nature of alluvial fans in arid environments offers numerous floodplain management challenges primarily due to
LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS BRUCE M. PHILLIPS 1 ABSTRACT The dynamic nature of alluvial fans in arid environments offers numerous floodplain management challenges primarily due to
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin?
 How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Swift Creek Sediment Management Action Plan (SCSMAP)
 Swift Creek Sediment Management Action Plan (SCSMAP) PHASE 2 PROJECT PLAN PROPOSAL Whatcom County Public Works Department 322 N. Commercial Street, Suite 210 Bellingham, WA 98225 (360) 676-6692 June 2013
Swift Creek Sediment Management Action Plan (SCSMAP) PHASE 2 PROJECT PLAN PROPOSAL Whatcom County Public Works Department 322 N. Commercial Street, Suite 210 Bellingham, WA 98225 (360) 676-6692 June 2013
Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding
 Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Flooding in Pakistan 2010-1600 killed/20000 affected The hydrologic cycle is powered by the Sun The cycle includes evaporation, precipitation, infiltration,
Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Flooding in Pakistan 2010-1600 killed/20000 affected The hydrologic cycle is powered by the Sun The cycle includes evaporation, precipitation, infiltration,
Phase 2 Stream Geomorphic Assessment of Walloomsac River and Roaring Branch, Bennington County, Vermont FINAL REPORT. March 2007
 Phase 2 Stream Geomorphic Assessment of and Roaring Branch, Bennington County, Vermont FINAL REPORT March 2007 Prepared for: Town of Bennington, Vermont and Bennington County Conservation District Prepared
Phase 2 Stream Geomorphic Assessment of and Roaring Branch, Bennington County, Vermont FINAL REPORT March 2007 Prepared for: Town of Bennington, Vermont and Bennington County Conservation District Prepared
New Approaches to Restoring NH s Rivers Natural Channel Design and Dam Removal
 NHACC Annual Meeting 2012 New Approaches to Restoring NH s Rivers Natural Channel Design and Dam Removal Peter J. Walker CROOKED STREAMS are a menace to life and crops in the areas bordering on their banks.
NHACC Annual Meeting 2012 New Approaches to Restoring NH s Rivers Natural Channel Design and Dam Removal Peter J. Walker CROOKED STREAMS are a menace to life and crops in the areas bordering on their banks.
River floodplain regime and stratigraphy. Drs. Nanette C. Kingma.
 River floodplain regime and stratigraphy. Drs. Nanette C. Kingma. Formation of floodplain. Formation of floodplains: lateral channel migration in channel deposition suspended-load fall out during higher
River floodplain regime and stratigraphy. Drs. Nanette C. Kingma. Formation of floodplain. Formation of floodplains: lateral channel migration in channel deposition suspended-load fall out during higher
Technical Memorandum No
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
60 PERCENT DESIGN REPORT HABITAT RESTORATION OF THE CHELAN RIVER REACH 4 AND TAILRACE
 60 PERCENT DESIGN REPORT HABITAT RESTORATION OF THE CHELAN RIVER REACH 4 AND TAILRACE Prepared for Public Utility District Number 1 of Chelan County 327 North Wenatchee Avenue Wenatchee, Washington 98801
60 PERCENT DESIGN REPORT HABITAT RESTORATION OF THE CHELAN RIVER REACH 4 AND TAILRACE Prepared for Public Utility District Number 1 of Chelan County 327 North Wenatchee Avenue Wenatchee, Washington 98801
Fish Passage at Road Crossings
 Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Final Exam. Running Water Erosion and Deposition. Willamette Discharge. Running Water
 Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal
 Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal August 4, 2011 Jennifer Bountry, M.S., P.E. Tim Randle, M.S., P.E., D.WRE. Blair Greimann, Ph.D., P.E. Sedimentation and
Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal August 4, 2011 Jennifer Bountry, M.S., P.E. Tim Randle, M.S., P.E., D.WRE. Blair Greimann, Ph.D., P.E. Sedimentation and
Annotated Bibliography of River Avulsions Pat Dryer Geography 364 5/14/2007
 Annotated Bibliography of River Avulsions Pat Dryer Geography 364 5/14/2007 1 Table of Contents Introduction 2 Annotations I. River avulsions and their deposits 2 II. Channel avulsion on alluvial fans
Annotated Bibliography of River Avulsions Pat Dryer Geography 364 5/14/2007 1 Table of Contents Introduction 2 Annotations I. River avulsions and their deposits 2 II. Channel avulsion on alluvial fans
DISCUSSION PURPOSES ONLY C A L I F O R N I A S T A T E L A N D S C O M M I S S I O N
 C A L I F O R N I A S T A T E L A N D S C O M M I S S I O N SAN JOAQUIN RIVER REACH 2B OVERVIEW OF THE CALIFORNIA STATE LANDS COMMISSION ADMINISTRATIVE MAPS PRESENTATION Water Boundary Principles Best
C A L I F O R N I A S T A T E L A N D S C O M M I S S I O N SAN JOAQUIN RIVER REACH 2B OVERVIEW OF THE CALIFORNIA STATE LANDS COMMISSION ADMINISTRATIVE MAPS PRESENTATION Water Boundary Principles Best
Diagnostic Geomorphic Methods for Understanding Future Behavior of Lake Superior Streams What Have We Learned in Two Decades?
 Diagnostic Geomorphic Methods for Understanding Future Behavior of Lake Superior Streams What Have We Learned in Two Decades? Faith Fitzpatrick USGS WI Water Science Center, Middleton, WI fafitzpa@usgs.gov
Diagnostic Geomorphic Methods for Understanding Future Behavior of Lake Superior Streams What Have We Learned in Two Decades? Faith Fitzpatrick USGS WI Water Science Center, Middleton, WI fafitzpa@usgs.gov
Island Design. UMRS EMP Regional Workshop. Presentation for the
 Island Design Presentation for the UMRS EMP Regional Workshop by Jon Hendrickson Hydraulic Engineer Regional Technical Specialist, Water Quality and Habitat Restoration August 17 19, 2005 Project Delivery
Island Design Presentation for the UMRS EMP Regional Workshop by Jon Hendrickson Hydraulic Engineer Regional Technical Specialist, Water Quality and Habitat Restoration August 17 19, 2005 Project Delivery
SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET
 SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET INTRODUCTION A sediment budget has been constructed for the for the time period 1952-2000. The purpose of the sediment budget is to determine the relative importance of different
SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET INTRODUCTION A sediment budget has been constructed for the for the time period 1952-2000. The purpose of the sediment budget is to determine the relative importance of different
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012
 GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
Summary. Streams and Drainage Systems
 Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
DAM REMOVAL ENGINEERING ISSUES & OPTIONS
 DAM REMOVAL ENGINEERING ISSUES & OPTIONS Presented by: James G. Mac Broom, P.E. Milone & Mac Broom, Inc. October 2011 CLEAR GOALS and OBJECTIVES Fish Passage Habitat Defragmentation Water Quality Dam Failure
DAM REMOVAL ENGINEERING ISSUES & OPTIONS Presented by: James G. Mac Broom, P.E. Milone & Mac Broom, Inc. October 2011 CLEAR GOALS and OBJECTIVES Fish Passage Habitat Defragmentation Water Quality Dam Failure
3.12 Geology and Topography Affected Environment
 3 Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3.12 Geology and Topography 3.12.1 Affected Environment 3.12.1.1 Earthquakes Sterling Highway MP 45 60 Project Draft SEIS The Kenai Peninsula is predisposed
3 Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3.12 Geology and Topography 3.12.1 Affected Environment 3.12.1.1 Earthquakes Sterling Highway MP 45 60 Project Draft SEIS The Kenai Peninsula is predisposed
Watershed Assessment of River Stability and Sediment Supply: Advancing the Science of Watershed Analysis
 Watershed Assessment of River Stability and Sediment Supply: Advancing the Science of Watershed Analysis 2009 MWEA Annual Conference Rob Myllyoja, CET rmyllyoja@hrc-engr.com Watershed Assessment of River
Watershed Assessment of River Stability and Sediment Supply: Advancing the Science of Watershed Analysis 2009 MWEA Annual Conference Rob Myllyoja, CET rmyllyoja@hrc-engr.com Watershed Assessment of River
FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE ENTIAT RIVER, WA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR STREAM RESTORATION
 FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE ENTIAT RIVER, WA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR STREAM RESTORATION Godaire, Jeanne E., Bureau of Reclamation, P.O. Box 25007, Denver, CO 80225, 303-445- 3164, jgodaire@usbr.gov; Russell,
FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE ENTIAT RIVER, WA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR STREAM RESTORATION Godaire, Jeanne E., Bureau of Reclamation, P.O. Box 25007, Denver, CO 80225, 303-445- 3164, jgodaire@usbr.gov; Russell,
APPENDIX A REACH DECRIPTIONS. Quantico Creek Watershed Assessment April 2011
 APPENDIX A REACH DECRIPTIONS Basin 615, South Fork of Quantico Creek - Project Reach Descriptions Reach Name: 615-A Coordinates (NAD 83, Virginia State Plane North): 11796510.57, 6893938.95 to 11801555.79,
APPENDIX A REACH DECRIPTIONS Basin 615, South Fork of Quantico Creek - Project Reach Descriptions Reach Name: 615-A Coordinates (NAD 83, Virginia State Plane North): 11796510.57, 6893938.95 to 11801555.79,
Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010
 Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010 Contents Glenorchy s hazardscape Environment setting Flood hazard Earthquakes and seismic hazards Hazards Mass movement Summary Glossary Introduction
Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010 Contents Glenorchy s hazardscape Environment setting Flood hazard Earthquakes and seismic hazards Hazards Mass movement Summary Glossary Introduction
Massachusetts Rivers & Roads Training
 Massachusetts Rivers & Roads Training Using Fluvial Geomorphology (FGM) to Reduce Conflicts Between Transportation Assets and Rivers Roy Schiff, Jessica Louisos, and Jim MacBroom, Milone & MacBroom Tim
Massachusetts Rivers & Roads Training Using Fluvial Geomorphology (FGM) to Reduce Conflicts Between Transportation Assets and Rivers Roy Schiff, Jessica Louisos, and Jim MacBroom, Milone & MacBroom Tim
Whatcom County Flood Control Zone District. Canyon Creek Alluvial Fan Risk Assessment
 Whatcom County Flood Control Zone District Canyon Creek Alluvial Fan Risk Assessment Final Report September 2003 Whatcom County Flood Control Zone District Canyon Creek Alluvial Fan Risk Assessment Final
Whatcom County Flood Control Zone District Canyon Creek Alluvial Fan Risk Assessment Final Report September 2003 Whatcom County Flood Control Zone District Canyon Creek Alluvial Fan Risk Assessment Final
Landscape Development
 Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Site and Reach Assessment, Glacier Creek side SR542. Site and Reach Assessment Side Channel, Glacier Creek at SR542
 Site and Reach Assessment, Glacier Creek side channel @ SR542 Site and Reach Assessment Side Channel, Glacier Creek at SR542 Garrett Jackson, Hydrologist WSDOT Environmental Services Hydrology Program
Site and Reach Assessment, Glacier Creek side channel @ SR542 Site and Reach Assessment Side Channel, Glacier Creek at SR542 Garrett Jackson, Hydrologist WSDOT Environmental Services Hydrology Program
Restoration Goals TFG Meeting. Agenda
 San Joaquin River Restoration Program Restoration Goals TFG Meeting Reach 2B Update April 28, 2010 Agenda 1. Introductions 2. Program Restoration Goal Context 3. Program Update a) Interim Flows b) EIS/EIR
San Joaquin River Restoration Program Restoration Goals TFG Meeting Reach 2B Update April 28, 2010 Agenda 1. Introductions 2. Program Restoration Goal Context 3. Program Update a) Interim Flows b) EIS/EIR
SCOPE OF PRESENTATION STREAM DYNAMICS, CHANNEL RESTORATION PLANS, & SEDIMENT TRANSPORT ANALYSES IN RELATION TO RESTORATION PLANS
 DESIGN METHODS B: SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES FOR STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN PETER KLINGEMAN OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPT., CORVALLIS 2 ND ANNUAL NORTHWEST STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN SYMPOSIUM
DESIGN METHODS B: SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES FOR STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN PETER KLINGEMAN OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPT., CORVALLIS 2 ND ANNUAL NORTHWEST STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN SYMPOSIUM
Elwha River response to dam removals through four years and a big flood:
 Elwha River response to dam removals through four years and a big flood: Lessons learned, channel response, and sediment effects from the world s largest engineered dam removal Andy Ritchie NPS Elwha Restoration
Elwha River response to dam removals through four years and a big flood: Lessons learned, channel response, and sediment effects from the world s largest engineered dam removal Andy Ritchie NPS Elwha Restoration
4. FLOOD HISTORY AND IDENTIFICATION OF FLOOD HAZARDS
 4. FLOOD HISTORY AND IDENTIFICATION OF FLOOD HAZARDS River channels shift naturally, and can have dramatic impacts on houses and structures built close to the river when flood events occur (photo). Historically,
4. FLOOD HISTORY AND IDENTIFICATION OF FLOOD HAZARDS River channels shift naturally, and can have dramatic impacts on houses and structures built close to the river when flood events occur (photo). Historically,
Technical Memorandum No Sediment Model
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines
 Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines FACT SHEET I: GEOMORPHOLOGICAL HAZARDS CONFINED AND UNCONFINED WATERCOURSES Channel migration and erosion can create substantial risk to inappropriately located infrastructure
Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines FACT SHEET I: GEOMORPHOLOGICAL HAZARDS CONFINED AND UNCONFINED WATERCOURSES Channel migration and erosion can create substantial risk to inappropriately located infrastructure
NATURE OF RIVERS B-1. Channel Function... ALLUVIAL FEATURES. ... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed. ...dissipate energy.
 1 2 Function... Sevier River... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed....dissipate energy. 3 ALLUVIAL FEATURES 4 CHANNEL DIMENSION The purpose of a stream is to carry water and sediment
1 2 Function... Sevier River... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed....dissipate energy. 3 ALLUVIAL FEATURES 4 CHANNEL DIMENSION The purpose of a stream is to carry water and sediment
Kootenai River Habitat Restoration Program Update
 Kootenai River Habitat Restoration Program Update Kootenai Tribe of Idaho Kootenai Valley Resource Initiative November 19, 2012 Bonners Ferry, Idaho Changes to Kootenai Basin Beaver trapping Floodplain
Kootenai River Habitat Restoration Program Update Kootenai Tribe of Idaho Kootenai Valley Resource Initiative November 19, 2012 Bonners Ferry, Idaho Changes to Kootenai Basin Beaver trapping Floodplain
Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road
 Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September 2013 Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September
Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September 2013 Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
Section 5. Low-Gradient Streams. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 4 Surface Processes Section 5 Low-Gradient Streams What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Use models and real-time streamflow data to understand the characteristics of lowgradient
Chapter 4 Surface Processes Section 5 Low-Gradient Streams What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Use models and real-time streamflow data to understand the characteristics of lowgradient
Susitna-Watana Hydroelectric Project (FERC No ) Geomorphology Study Study Plan Section Study Implementation Report.
 (FERC No. 14241) Geomorphology Study Study Plan Section 6.5 2014-2015 Study Implementation Report Prepared for Prepared by Tetra Tech Watershed GeoDynamics October 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
(FERC No. 14241) Geomorphology Study Study Plan Section 6.5 2014-2015 Study Implementation Report Prepared for Prepared by Tetra Tech Watershed GeoDynamics October 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
IMPACTS OF SECONDARY FLOOD EMBANKMENTS ON THE WAIMAKARIRI FLOODPLAIN, NEW ZEALAND
 IMPACTS OF SECONDARY FLOOD EMBANKMENTS ON THE WAIMAKARIRI FLOODPLAIN, NEW ZEALAND Terry van Kalken (1), Tony Oliver (2), Ian Heslop (2), Tony Boyle (2) (1) DHI Water & Environment, e-centre, Oaklands Road,
IMPACTS OF SECONDARY FLOOD EMBANKMENTS ON THE WAIMAKARIRI FLOODPLAIN, NEW ZEALAND Terry van Kalken (1), Tony Oliver (2), Ian Heslop (2), Tony Boyle (2) (1) DHI Water & Environment, e-centre, Oaklands Road,
Identifying, Understanding and Addressing Flood-Related Hazards
 Identifying, Understanding and Addressing Flood-Related Hazards Julie Moore, P.E. July 9, 2012 Agenda Traditional approach to river management Understanding flood-related hazards Common flood and flood
Identifying, Understanding and Addressing Flood-Related Hazards Julie Moore, P.E. July 9, 2012 Agenda Traditional approach to river management Understanding flood-related hazards Common flood and flood
River Response. Sediment Water Wood. Confinement. Bank material. Channel morphology. Valley slope. Riparian vegetation.
 River Response River Response Sediment Water Wood Confinement Valley slope Channel morphology Bank material Flow obstructions Riparian vegetation climate catchment vegetation hydrological regime channel
River Response River Response Sediment Water Wood Confinement Valley slope Channel morphology Bank material Flow obstructions Riparian vegetation climate catchment vegetation hydrological regime channel
The subject paper is being submitted for approval for publication in the annual volume entitled Geological Survey Research.
 Water Resources Division 345 Middlefield Road Menlo Park, California January 12, 1965 Memorandum To: Mr. Frank E. Clark, Chief, General Hydrology Branch Thru: Area Hydrologist PCA From: Valmore C. LaMarche
Water Resources Division 345 Middlefield Road Menlo Park, California January 12, 1965 Memorandum To: Mr. Frank E. Clark, Chief, General Hydrology Branch Thru: Area Hydrologist PCA From: Valmore C. LaMarche
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
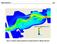 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
