KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST. YEAR 88 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas.
|
|
|
- Lorin Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 88 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas.
2 Topic Name BIOLOGY the human skeleton Analysing the skeleton the role of skeletal joints Content The structure and functions of the human skeleton, to include support, protection, movement and making blood cells The structure and functions of the human skeleton, to include support, protection, movement and making blood cells Biomechanics the interaction between skeleton and muscles, including the measurement of force exerted by different muscles Revision Tally (How many times have you completed a revision activity connected to this?) Other Comments muscle strength Biomechanics the interaction between skeleton and muscles, including the measurement of force exerted by different muscles Analysing muscle strength Examining interacting muscles Biomechanics the interaction between skeleton and muscles, including the measurement of force exerted by different muscles The function of muscles and examples of antagonistic muscles problems with the skeletal system The structure and functions of the human skeleton, to include support, protection, movement and making blood cells Biomechanics the interaction between skeleton and muscles, including the measurement of force exerted by different muscles
3 how our muscles get energy respiration Analysing adaptations for respiration Examining links between respiration and body systems respiration in sport anaerobic respiration fermentation Comparing aerobic and Aerobic and anaerobic respiration in living organisms, including the breakdown of organic molecules to enable all the other chemical processes necessary for life The word equation for aerobic respiration Aerobic and anaerobic respiration in living organisms, including the breakdown of organic molecules to enable all the other chemical processes necessary for life The word equation for aerobic respiration Aerobic and anaerobic respiration in living organisms, including the breakdown of organic molecules to enable all the other chemical processes necessary for life Aerobic and anaerobic respiration in living organisms, including the breakdown of organic molecules to enable all the other chemical processes necessary for life Aerobic and anaerobic respiration in living organisms, including the breakdown of organic molecules to enable all the other chemical processes necessary for life The process of anaerobic respiration in humans and micro-organisms, including fermentation, and the word equation for anaerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration in humans and micro-organisms, including fermentation, and the word equation for anaerobic respiration The differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in terms of the reactants, the products formed and the implications for the organism
4 anaerobic respiration the importance of plants how plants make food Looking at leaves the role of stomata photosynthesis the movement of water and minerals in plants the importance of minerals to plants chemosynthesis food webs The dependence of almost all life on Earth on the ability of photosynthetic organisms, such as plants and algae, to use sunlight in photosynthesis to build organic molecules that are an essential energy store, and to maintain levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere The reactants in, and products of, photosynthesis, and a word summary for photosynthesis Plants making carbohydrates in their leaves by photosynthesis The adaptations of leaves for photosynthesis The adaptations of leaves for photosynthesis The role of leaf stomata in gas exchange in plants The reactants in, and products of, photosynthesis, and a word summary for photosynthesis Plants gain mineral nutrients and water from the soil via their roots Plants gain mineral nutrients and water from the soil via their roots The interdependence of organisms in an ecosystem, including food webs The interdependence of organisms in an ecosystem, including food webs
5 the importance of insects The interdependence of organisms in an ecosystem, including insect-pollinated crops The importance of plant reproduction through insect pollination in human food security Looking at other examples of interdependence How organisms affect, and are affected by, their environment, including the accumulation of toxic materials interactions in the environment How organisms affect, and are affected by, their environment, including the accumulation of toxic materials Learning about ecological balance How organisms affect, and are affected by, their environment, including the accumulation of toxic materials the effects of toxins in the environment How organisms affect, and are affected by, their environment, including the accumulation of toxic materials how organisms coexist How organisms affect, and are affected by, their environment, including the accumulation of toxic materials Topic Name Chemistry Using particles to explain matter Content The properties of different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure Revision Tally (How many times have you completed a revision activity connected to this?) Other Comments
6 solids Brownian motion liquids and gases Changing state evaporation thermal expansion Making sense of models Explaining density of solids and liquids Explaining the density of gases Explaining concentration and pressure diffusion The properties of different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure Brownian motion in gases The properties of different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure Changes of state in terms of the particle model Changes of state in terms of the particle model Energy changes on changes of state (qualitative) Changes with temperature in motion and spacing of particles A simple Dalton atomic model The differences in arrangements, in motion and in closeness of particles explaining changes of state, shape and density, the anomaly of ice water transition Similarities and differences, including density differences, between solids, liquids and gases The differences in arrangements, in motion and in closeness of particles explaining changes of state, shape and density, the anomaly of ice water transition Similarities and differences, including density differences, between solids, liquids and gases The properties of different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure Diffusion in liquids and gases driven by differences in concentration Diffusion in terms of the particle model
7 Conserving mass Deciding between physical and chemical changes Explaining the properties of mixtures Using particle models acids alkalis Using indicators Using universal indicator neutralisation Explaining neutralisation Conservation of mass Changes of state Conservation of material and mass, and reversibility, in melting, freezing, evaporation, sublimation, condensation, dissolving Mixtures, including dissolving The difference between chemical and physical changes Mixtures, including dissolving The properties of different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure The differences in arrangements, in motion and in closeness of particles explaining changes of state, shape and density, the anomaly of ice water transition Defining acids and alkalis Defining acids and alkalis The ph scale for measuring acidity/alkalinity; and indicators The ph scale for measuring acidity/alkalinity; and indicators Defining acids and alkalis in terms of neutralisation reactions The ph scale for measuring acidity/alkalinity; and indicators Defining acids and alkalis in terms of neutralisation reactions Chemical reactions as the rearrangement of atoms Representing chemical reactions using formulas and using equations
8 salts the reactions of acids with metals the reactions of acids with carbonates the effectiveness of antacids the importance of acids and alkalis combustion combustion and the use of fuels the effects of burning Reactions of acids with alkalis to produce a salt plus water Chemical reactions as the rearrangement of atoms Representing chemical reactions using formulas and using equations Reactions of acids with alkalis to produce a salt plus water Reactions of acids with metals to produce a salt plus hydrogen Chemical reactions as the rearrangement of atoms Representing chemical reactions using formulas and using equations Reactions of acids with alkalis to produce a salt plus water Defining acids and alkalis in terms of neutralisation reactions Reactions of acids with alkalis to produce a salt plus water Combustion Fuels and energy resources Combustion Fuels and energy resources Combustion Chemical reactions as the rearrangement of atoms Representing chemical reactions using formulas and using equations The production of carbon dioxide by human activity
9 acid rain Topic Name Physics magnets Combustion The composition of the atmosphere Content Non-contact forces: forces between magnets Magnetic poles, attraction and repulsion Revision Tally (How many times have you completed a revision activity connected to this?) Other Comments magnetic fields Magnetic poles, attraction and repulsion Magnetic fields by plotting with compass, representation by field lines Earth s magnetism static charge Non-contact forces: forces due to static electricity Separation of positive or negative charges when objects are rubbed together: transfer of electrons, forces between charged objects Explaining static charge Non-contact forces: forces due to static electricity Separation of positive or negative charges when objects are rubbed together: transfer of electrons, forces between charged objects electric fields Non-contact forces: forces due to static electricity Separation of positive or negative charges when objects are rubbed together: transfer of electrons, forces between charged objects The idea of electric field, forces acting across the space between objects not in contact Applying what we know about electrostatics Non-contact forces: forces due to static electricity Separation of positive or negative charges when objects are rubbed together: transfer of electrons,
10 gravity on Earth Applying our understanding of gravity to space travel pressure on a solid surface Calculating pressure pressure in a liquid Explaining floating and sinking gas pressure Working with pressure Looking at the history of magnets forces between charged objects The idea of electric field, forces acting across the space between objects not in contact Non-contact forces: gravity forces acting at a distance on Earth and in space Non-contact forces: gravity forces acting at a distance on Earth and in space Pressure measured by ratio of force over area acting normal to any surface Pressure measured by ratio of force over area acting normal to any surface Pressure in liquids, increasing with depth; upthrust effects, floating and sinking Pressure in liquids, increasing with depth; upthrust effects, floating and sinking Atmospheric pressure; decreases with increase of height as weight of air above decreases with height Atmospheric pressure; decreases with increase of height as weight of air above decreases with height Earth s magnetism, compass and navigation
11 magnetic materials Testing the strength of magnets Describing the Earth s magnetic field electromagnetism Using electromagnets D.C. motors batteries Describing electric circuits energy in circuits Explaining resistance Magnetic poles, attraction and repulsion Magnetic poles, attraction and repulsion Earth s magnetism, compass and navigation The magnetic effect of a current, electromagnets Electromagnets Other processes that involve energy transfer: completing an electrical circuit The magnetic effect of a current, D.C. motors (principles only) Other processes that involve energy transfer: completing an electrical circuit Other processes that involve energy transfer: completing an electrical circuit Electric current, measured in amperes, in circuits Other processes that involve energy transfer: completing an electrical circuit Electric current, measured in amperes, in circuits Potential difference, measured in volts, battery and bulb ratings Potential difference, measured in volts, battery and bulb ratings Resistance, measured in ohms, as the ratio of potential difference (p.d.) to current
12 factors affecting resistance Explaining circuits using models Describing series and parallel circuits Comparing series and parallel circuits Applying circuits Resistance, measured in ohms, as the ratio of potential difference (p.d.) to current Differences in resistance between conducting and insulating components (quantitative) Potential difference, measured in volts, battery and bulb ratings Resistance, measured in ohms, as the ratio of potential difference (p.d.) to current Series and parallel circuits, currents add where branches meet and current as flow of charge Electric current, measured in amperes, in circuits Series and parallel circuits, currents add where branches meet and current as flow of charge Potential difference, measured in volts, battery and bulb ratings Series and parallel circuits, currents add where branches meet and current as flow of charge
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Keywords
 Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Science Scheme of Work
 Cherry Tree Hill Primary School Science Scheme of Work Essential characteristics: High-quality science education provides the foundations for understanding the world through the specific disciplines of
Cherry Tree Hill Primary School Science Scheme of Work Essential characteristics: High-quality science education provides the foundations for understanding the world through the specific disciplines of
Year 7. Knowledge/Content Understanding Skills
 Age Related Expectations in KS3 Science 2017-2018 These are the age related expectations for KS3 science for year 7 and 8; they are based on the KS3 core science curriculum. This knowledge, understanding
Age Related Expectations in KS3 Science 2017-2018 These are the age related expectations for KS3 science for year 7 and 8; they are based on the KS3 core science curriculum. This knowledge, understanding
Year 8 Tracking Document. Year 8 Science National Curriculum. Health and Lifestyle
 Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Science. Programme of study for Key Stage 3
 Science Programme of study for Key Stage 3 February 2013 Contents Purpose of study 3 Aims 3 Attainment targets 3 Working scientifically 4 Subject content 6 Biology 6 Structure and function of living organisms
Science Programme of study for Key Stage 3 February 2013 Contents Purpose of study 3 Aims 3 Attainment targets 3 Working scientifically 4 Subject content 6 Biology 6 Structure and function of living organisms
Science curriculum overview Yr7 (Draft arrangement as the school may need flexibility as the need arises)
 Science curriculum overview Yr7 (Draft arrangement as the school may need flexibility as the need arises) Term Topic and key questions Assessment structure Autumn 1 CHEMISTRY Test 1: The particle 1.The
Science curriculum overview Yr7 (Draft arrangement as the school may need flexibility as the need arises) Term Topic and key questions Assessment structure Autumn 1 CHEMISTRY Test 1: The particle 1.The
Programme of study references
 This -Year Scheme of Work offers a suggested topic order for KS using AQA KS Science Student s and, assuming that one teacher teaching all three sciences rotates through the sciences to give variety. Other
This -Year Scheme of Work offers a suggested topic order for KS using AQA KS Science Student s and, assuming that one teacher teaching all three sciences rotates through the sciences to give variety. Other
KS3 Science Levelness Posters
 KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
YEAR 7. St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map New AQA Course Started November 2016
 YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
Programme of study references
 Five- Scheme of Work leading to AQA GCSE Biology, Chemistry and Physics (Two- KS and Three- KS4) This - Scheme of Work offers a suggested topic order for KS using AQA KS Student Books and, assuming that
Five- Scheme of Work leading to AQA GCSE Biology, Chemistry and Physics (Two- KS and Three- KS4) This - Scheme of Work offers a suggested topic order for KS using AQA KS Student Books and, assuming that
Year 8 Key Performance Indicators Science (Biology)
 Year 8 Key Performance Indicators Science (Biology) S8.1 B1: To understand key concepts in Biology. I can compare the rate of digestion of different enzymes by linking to their surroundings. S8.2 B3: To
Year 8 Key Performance Indicators Science (Biology) S8.1 B1: To understand key concepts in Biology. I can compare the rate of digestion of different enzymes by linking to their surroundings. S8.2 B3: To
National Curriculum Programme of Study for Science
 National Curriculum Programme of Study for Science Extracted from Science programmes of study: key stage 3 National Curriculum in England, September 2013. Amended to include reference numbers in place
National Curriculum Programme of Study for Science Extracted from Science programmes of study: key stage 3 National Curriculum in England, September 2013. Amended to include reference numbers in place
Links to national curricula
 Links to national curricula Progress Test in Science (PTS) has been designed to sample the main science knowledge and skills set out in the national curricula for England, Wales, Scotland and Northern
Links to national curricula Progress Test in Science (PTS) has been designed to sample the main science knowledge and skills set out in the national curricula for England, Wales, Scotland and Northern
Lesson Developing Secure Extending
 Cells B1 1.1 Observing cells B1 1.2 Plant and animal cells B1 1.3 Specialised cells B1 1.4 Movement of substances B1 1.5 Unicellular organisms I can state what a cell is. I can describe how to use a microscope
Cells B1 1.1 Observing cells B1 1.2 Plant and animal cells B1 1.3 Specialised cells B1 1.4 Movement of substances B1 1.5 Unicellular organisms I can state what a cell is. I can describe how to use a microscope
GCSE Science: Progression in key ideas
 The Collins GCSE Science (9-1) Five Year Scheme of Work: Identifies ten key scientific concepts Outlines the development of students understanding in these concepts over the five years from age 11 to 16
The Collins GCSE Science (9-1) Five Year Scheme of Work: Identifies ten key scientific concepts Outlines the development of students understanding in these concepts over the five years from age 11 to 16
KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST. YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas.
 KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas. Topic Name BIOLOGY Historical ideas about living things Content Cells as the
KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas. Topic Name BIOLOGY Historical ideas about living things Content Cells as the
Subject Link to prior learning: Term Duration (approx.) Module
 . Cells and organisation Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe, interpret and record cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall, cell
. Cells and organisation Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe, interpret and record cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall, cell
- know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues can be massed together to form organs
 Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Year 7 Science - Learning Aims
 Year 7 Science - Learning Aims Learning Aim 1 - Beginning 2 - Working towards 3 - Secure 4 - Mastered 1 2 7.1.1 Scientific enquiry Observe, interpret and record cell structures using a light microscope
Year 7 Science - Learning Aims Learning Aim 1 - Beginning 2 - Working towards 3 - Secure 4 - Mastered 1 2 7.1.1 Scientific enquiry Observe, interpret and record cell structures using a light microscope
UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection
 UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection Know what inheritance means Know what characteristics are Know that sexual reproduction needs two parents Know that animals and plants can be bred for their characteristics
UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection Know what inheritance means Know what characteristics are Know that sexual reproduction needs two parents Know that animals and plants can be bred for their characteristics
The Science Department Academic Year Year 7 Science Curriculum Overview
 The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 7 Science Curriculum Overview Subject: Science Term 1 Year Level: 7 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 7 Science Curriculum Overview Subject: Science Term 1 Year Level: 7 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
Primary Curriculum 2014
 Primary Curriculum 201 Suggested Key Objectives for Science at Key Stages 2 Year 3 Science Key Objectives 1 Setting up simple practical enquiries, comparative and fair tests 2 Gathering, recording, classifying
Primary Curriculum 201 Suggested Key Objectives for Science at Key Stages 2 Year 3 Science Key Objectives 1 Setting up simple practical enquiries, comparative and fair tests 2 Gathering, recording, classifying
Year 7 Science Booklet Name:
 Year 7 Science Booklet Name: Acids and Alkalis Use a dictionary or internet to look up the key words and write a definition. Acid Alkali Litmus Fizz Neutral Reactant Product Irritant Harmful indicator
Year 7 Science Booklet Name: Acids and Alkalis Use a dictionary or internet to look up the key words and write a definition. Acid Alkali Litmus Fizz Neutral Reactant Product Irritant Harmful indicator
Interactive Science Integrated, Grade
 A Correlation of Interactive Science Integrated, 2017 To the 2018 Mississippi College-and-Career Readiness Standards for Science GRADE SEVEN GRADE SEVEN: Life Science 7.3 Ecology and Interdependence Conceptual
A Correlation of Interactive Science Integrated, 2017 To the 2018 Mississippi College-and-Career Readiness Standards for Science GRADE SEVEN GRADE SEVEN: Life Science 7.3 Ecology and Interdependence Conceptual
K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities
 K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities The physical science strand encourages the basic observations of what our physical reality is made of and how it interacts matter, energy, forces, atoms and
K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities The physical science strand encourages the basic observations of what our physical reality is made of and how it interacts matter, energy, forces, atoms and
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants Animals, including humans Rocks Light Forces and magnets
 Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants
Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants
Key Skills (to be covered during the year) (from CQ Milestones)
 Science Whole School Unit Overview and Key Skills Checklist Essential Learning Objectives (Chris Quigley): Year 3 National Curriculum Unit To work scientifically Ask relevant questions. Key Skills (to
Science Whole School Unit Overview and Key Skills Checklist Essential Learning Objectives (Chris Quigley): Year 3 National Curriculum Unit To work scientifically Ask relevant questions. Key Skills (to
Science subject progression and skills
 Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Skills and Knowledge Progression. Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6
 Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST GRADE 5 SCIENCE (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 10/02)
 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 0/02) Physical Sciences 8 30 Physical Sciences Grade 5. Elements and their combinations account for all the varied types of
CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 0/02) Physical Sciences 8 30 Physical Sciences Grade 5. Elements and their combinations account for all the varied types of
In the event of snow:
 BIOLOGY Units Learning Objectives: Pupils should be taught (underlined = level 2 only) YEAR 7 Cells and Cell Functions 1a-e Nutrition and movement 2a-e Reproduction 2f-h Breathing and Respiration 2i-l
BIOLOGY Units Learning Objectives: Pupils should be taught (underlined = level 2 only) YEAR 7 Cells and Cell Functions 1a-e Nutrition and movement 2a-e Reproduction 2f-h Breathing and Respiration 2i-l
Primary Curriculum 2014
 Primary Curriculum 2014 Suggested Key Objectives for Science at Key Stages 1 and 2 www.primarycurriculum.me.uk , 2014 Year 1 Science Key Objectives 1 Asking simple questions and recognising that they can
Primary Curriculum 2014 Suggested Key Objectives for Science at Key Stages 1 and 2 www.primarycurriculum.me.uk , 2014 Year 1 Science Key Objectives 1 Asking simple questions and recognising that they can
CHAPTER 5 WARM UPS. Mrs. Hilliard
 CHAPTER 5 WARM UPS Mrs. Hilliard CHAPTER 5 VOCABULARY 1. Photosynthesis 2. Cellular respiration 3. Producer 4. Consumer 5. Decomposer 6. Food chain 7. Food web 8. Trophic level 9. Carbon cycle 10. Nitrogen-fixing
CHAPTER 5 WARM UPS Mrs. Hilliard CHAPTER 5 VOCABULARY 1. Photosynthesis 2. Cellular respiration 3. Producer 4. Consumer 5. Decomposer 6. Food chain 7. Food web 8. Trophic level 9. Carbon cycle 10. Nitrogen-fixing
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
Midterm Study Guide Major Concepts
 Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Untitled Document Eco Photo Cell resp Use the information below to answer the following question(s).
 Untitled Document Eco Photo Cell resp 25 1. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). The drawing below shows a field habitat. 3. An increase in which atmospheric gas would most likely
Untitled Document Eco Photo Cell resp 25 1. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). The drawing below shows a field habitat. 3. An increase in which atmospheric gas would most likely
Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview
 Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview Forces and Magnets Light Rocks * compare how things move on different surfaces * notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act
Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview Forces and Magnets Light Rocks * compare how things move on different surfaces * notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act
Science. synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis Using physics to make things work 3 Magnetic fields to keep things moving Energy calculations 4 Energy
 Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Year 7 Science - Learning Aims
 Year 7 Science - Learning Aims Learning Aim 1 - Beginning 2 - Working towards 3 - Secure 4 - Mastered 1 Living Organisms. List the seven life processes. Define sensitivity, excretion, respiration and nutrition.
Year 7 Science - Learning Aims Learning Aim 1 - Beginning 2 - Working towards 3 - Secure 4 - Mastered 1 Living Organisms. List the seven life processes. Define sensitivity, excretion, respiration and nutrition.
Stewards Pooi Kei College Integrated Science Secondary One Teaching Schedule in Textbook Chapter 1 Introducing Science Book 1A, 1B
 Stewards Pooi Kei College Integrated Science Secondary One Teaching Schedule 2014-15 Chapter 1 Introducing Science Book 1A, 1B 1 1.1 Science and Us Book 1A Unit 1 (3/9-12/9) Know the scope of science 1.1
Stewards Pooi Kei College Integrated Science Secondary One Teaching Schedule 2014-15 Chapter 1 Introducing Science Book 1A, 1B 1 1.1 Science and Us Book 1A Unit 1 (3/9-12/9) Know the scope of science 1.1
Science 9-1 Grades Guidance
 U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
8 th Grade Integrated Science Curriculum
 Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the curriculum, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. 8.1 Scientific Thinking and Practice 1. Use scientific methods to develop
Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the curriculum, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. 8.1 Scientific Thinking and Practice 1. Use scientific methods to develop
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2. Science. Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC
 Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6. Herts for Learning Ltd.
 HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
Curriculum Mapping Subject: Science Year Group Autumn Term 1a Autumn Term 1b Spring Term 2a Spring Term 2b Summer Term 3a Summer Term 3b
 Curriculum Mapping Subject: Science Year Group Autumn Term 1a Autumn Term 1b Spring Term 2a Spring Term 2b Summer Term 3a Summer Term 3b Year 11 Topic(s) Forces and Energy Atomic Structure Electromagnetism
Curriculum Mapping Subject: Science Year Group Autumn Term 1a Autumn Term 1b Spring Term 2a Spring Term 2b Summer Term 3a Summer Term 3b Year 11 Topic(s) Forces and Energy Atomic Structure Electromagnetism
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST
 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage
 National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage Aims: The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils: FCCE Primary School - National Curriculum 2014 develop scientific knowledge and conceptual
National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage Aims: The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils: FCCE Primary School - National Curriculum 2014 develop scientific knowledge and conceptual
Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1. Two Year rolling programme KS1
 Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1 Two Year rolling programme KS1 Pupils should be taught to; Ø develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology,
Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1 Two Year rolling programme KS1 Pupils should be taught to; Ø develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology,
1 Name. ECOSYSTEMS: THE ROLE OF ABIOTIC FACTORS from the series Biology: The Science of Life Pre-Test
 1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each of the following either true or false: 1. In ecosystems, non-living (abiotic) factors usually have insignificant effects on living things. True False 2. Carbon dioxide
1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each of the following either true or false: 1. In ecosystems, non-living (abiotic) factors usually have insignificant effects on living things. True False 2. Carbon dioxide
Key Stage 3 Science Revision Guide
 Key Stage 3 Science Revision Guide Use this guide to check that you cover all the topics you have studied at key stage 3. You can use your classwork books, revision guides and the internet to help you
Key Stage 3 Science Revision Guide Use this guide to check that you cover all the topics you have studied at key stage 3. You can use your classwork books, revision guides and the internet to help you
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration. mages/life/chap1_2/ph otosyn.swf://
 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration http://mrescience.com/i mages/life/chap1_2/ph otosyn.swf:// Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. Plants use light to make their own food. Where does
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration http://mrescience.com/i mages/life/chap1_2/ph otosyn.swf:// Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. Plants use light to make their own food. Where does
2 sentences. Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct
 2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
JULY GRADE 8 (SCIENCE) OBJECTIVE LEARNER PROFILE ATL INTERDISCIPLINARY TOPIC- PHOTOSYNTHESIS AOI- Environments. Thinker( D ) Risk Taker (D)
 JULY GRADE 8 (SCIENCE) OBJECTIVE LEARNER PROFILE ATL INTERDISCIPLINARY TOPIC- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Thinker( D ) Risk Taker (D) Chemistry Significant Concepts- Water and plant life. Factors needed for the process
JULY GRADE 8 (SCIENCE) OBJECTIVE LEARNER PROFILE ATL INTERDISCIPLINARY TOPIC- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Thinker( D ) Risk Taker (D) Chemistry Significant Concepts- Water and plant life. Factors needed for the process
Comparison of new and current primary science curriculum
 Comparison of new and current primary science curriculum Summary of changes A focus on identifying and naming plants and animals at KS1 and KS2 Sound, Light and Forces have been removed from KS1 and moved
Comparison of new and current primary science curriculum Summary of changes A focus on identifying and naming plants and animals at KS1 and KS2 Sound, Light and Forces have been removed from KS1 and moved
UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms.
 UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. 1 Law
UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. 1 Law
SCIENCE HIGHER LEVEL
 J.37 PRE-JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2014 SCIENCE HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name, school s name and teacher s name in the boxes provided on this page. 2. Answer all questions.
J.37 PRE-JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2014 SCIENCE HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name, school s name and teacher s name in the boxes provided on this page. 2. Answer all questions.
LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES. Science. Di Barton. SUB Q6ttlngen B1842 LONGMAN
 LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES Science Di Barton SUB Q6ttlngen 206 451 652 97B1842 LONGMAN CONTENTS Editors' Preface vii Acknowledgements vii Information about this book viii 1 Revision, examinations and coursework
LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES Science Di Barton SUB Q6ttlngen 206 451 652 97B1842 LONGMAN CONTENTS Editors' Preface vii Acknowledgements vii Information about this book viii 1 Revision, examinations and coursework
NUTRIENT CYCLES. Water Carbon Nitrogen
 NUTRIENT CYCLES Water Carbon Nitrogen NUTRIENT CYCLES Energy transfer through an ecosystem is ONE WAY Most energy is lost as heat Nutrients such as nitrogen, water and carbon are able to cycle through
NUTRIENT CYCLES Water Carbon Nitrogen NUTRIENT CYCLES Energy transfer through an ecosystem is ONE WAY Most energy is lost as heat Nutrients such as nitrogen, water and carbon are able to cycle through
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP. KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy.
 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. Molecules in food store chemical
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. Molecules in food store chemical
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Test
 Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Test 1. When bonds are made energy is, when bonds are broken energy is. A. stored / released C. released / stored B. used / not used D. created / destroyed 2. Aerobic
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Test 1. When bonds are made energy is, when bonds are broken energy is. A. stored / released C. released / stored B. used / not used D. created / destroyed 2. Aerobic
Chapter19-Magnetism and Electricity
 Chapter19-Magnetism and Electricity Magnetism: attraction of a magnet for another object. Magnetic poles: north & south ends of a magnet, they exert the strongest forces Like poles repel each other, unlike
Chapter19-Magnetism and Electricity Magnetism: attraction of a magnet for another object. Magnetic poles: north & south ends of a magnet, they exert the strongest forces Like poles repel each other, unlike
2.2 CELL METABOLISM. Photosynthesis is the way green plants use light to make their own food
 2.2.4 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the way green plants use light to make their own food Role of photosynthesis Makes food for plants Makes food for animals as they eat plants Makes oxygen for plants
2.2.4 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the way green plants use light to make their own food Role of photosynthesis Makes food for plants Makes food for animals as they eat plants Makes oxygen for plants
Living Things. Lower KS2 Learning Objective. Ideas for practice. knowledge
 Lower KS2 Learning Objective Living Things Plants: 1. Identify and describe the functions of different parts of plants: roots, stem, leaves and flowers 2. Identify the requirements of plants for life and
Lower KS2 Learning Objective Living Things Plants: 1. Identify and describe the functions of different parts of plants: roots, stem, leaves and flowers 2. Identify the requirements of plants for life and
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cells and Energy
 Cells and Energy Answer Key SECTION 1. CHEMICAL ENERGY AND ATP 1. molecule; food molecules 2. high-energy; lower-energy 3. phosphate group 4. a; d; b; c 5. b; e 6. c; d 7. a; f 8. chemical energy; light
Cells and Energy Answer Key SECTION 1. CHEMICAL ENERGY AND ATP 1. molecule; food molecules 2. high-energy; lower-energy 3. phosphate group 4. a; d; b; c 5. b; e 6. c; d 7. a; f 8. chemical energy; light
Year 7 Science Bohunt Standards Autumn Term
 Year 7 Science Bohunt Standards Autumn Term Grade Particle theory and matter Motion, forces and space Suggest methods to separate a complex mixture or Calculate moments on both sides of a pivot.. 8 compound
Year 7 Science Bohunt Standards Autumn Term Grade Particle theory and matter Motion, forces and space Suggest methods to separate a complex mixture or Calculate moments on both sides of a pivot.. 8 compound
National Curriculum 2014: Progression in Science
 Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Science Curriculum Map Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2
 The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
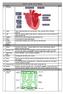 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
The properties of water in all phases are determined by its structure.
 Section 5 Water Water is a familiar substance in all three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas. On Earth, water is by far the most abundant liquid. Oceans, rivers, and lakes cover about 75% of Earth
Section 5 Water Water is a familiar substance in all three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas. On Earth, water is by far the most abundant liquid. Oceans, rivers, and lakes cover about 75% of Earth
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
Alcester Academy Curriculum Planning: Key Stage 3
 Department: Science Year Group: 7 Term Topic/ subject Assessment Objectives Knowledge Skills Include detail of any differentiation Literacy, numeracy and SMSC opportunities Final assessment task and title
Department: Science Year Group: 7 Term Topic/ subject Assessment Objectives Knowledge Skills Include detail of any differentiation Literacy, numeracy and SMSC opportunities Final assessment task and title
Year 1 Science overview
 Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Fairlawn Primary School Science Curriculum
 Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc humans
 Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Carbon Cycling Internal
 Carbon Cycling Internal The 4 subcycles Atmosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth has a radius of some 6400 km. Ninety-nine percent of the earth's atmosphere is contained within a layer approximately
Carbon Cycling Internal The 4 subcycles Atmosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth has a radius of some 6400 km. Ninety-nine percent of the earth's atmosphere is contained within a layer approximately
Science Curriculum Map: KS1 & KS
 Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Primary Science Curriculum Pupil Assessment Record
 Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes. For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Molecular Modeling of Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name: Date: Hour: Molecular Modeling of Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Introduction Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants capture energy from sunlight and use it to make food molecules
Name: Date: Hour: Molecular Modeling of Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Introduction Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants capture energy from sunlight and use it to make food molecules
IN THE PAST WEEKS WE SPOKE ABOUT THE 4 ORGANIC MOLECULES THAT ARE INSIDE THE CELL, SUCH AS PROTEINS, CARBOHYDRATES, LIPIDS AND NUCLEIC ACIDS
 IN THE PAST WEEKS WE SPOKE ABOUT THE 4 ORGANIC MOLECULES THAT ARE INSIDE THE CELL, SUCH AS PROTEINS, CARBOHYDRATES, LIPIDS AND NUCLEIC ACIDS CARBOHYDRATES ARE THE IMMEDIATE SOURCE OF ENERGY FOR THE CELL
IN THE PAST WEEKS WE SPOKE ABOUT THE 4 ORGANIC MOLECULES THAT ARE INSIDE THE CELL, SUCH AS PROTEINS, CARBOHYDRATES, LIPIDS AND NUCLEIC ACIDS CARBOHYDRATES ARE THE IMMEDIATE SOURCE OF ENERGY FOR THE CELL
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document. September 2014
 Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
DAY 1 Leaf Structure
 DAY 1 Leaf Structure Design a Leaf!! What would be the best structure for a leaf to carry out its major function PHOTOSYNTHESIS!!!??? Place the following in order from the top of the leaf to the bottom.
DAY 1 Leaf Structure Design a Leaf!! What would be the best structure for a leaf to carry out its major function PHOTOSYNTHESIS!!!??? Place the following in order from the top of the leaf to the bottom.
The Green Machine curriculum addresses the following California Science Content Standards: KINDERGARTEN
 The Green Machine curriculum addresses the following California Science Content Standards: KINDERGARTEN PHYSICAL SCIENCES 1. Properties of materials can be observed, measured and predicted. a. Objects
The Green Machine curriculum addresses the following California Science Content Standards: KINDERGARTEN PHYSICAL SCIENCES 1. Properties of materials can be observed, measured and predicted. a. Objects
New Mexico Public Education Department. Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course (EoC) Exam
 New Mexico Public Education Department PRELIMINARY Assessment Blueprint Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course (EoC) Exam Version 001 Purpose Statement Science: Grade 8 EoC The Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course Exam
New Mexico Public Education Department PRELIMINARY Assessment Blueprint Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course (EoC) Exam Version 001 Purpose Statement Science: Grade 8 EoC The Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course Exam
Energy and Matter. Principles of Biology. Organisms interact with their environment, exchanging energy and matter. Topics Covered in this Module
 Principles of Biology contents 2 Energy and Matter Organisms interact with their environment, exchanging energy and matter. The Sun. Most ecosystems receive their energy from the Sun's radiation. NASA/European
Principles of Biology contents 2 Energy and Matter Organisms interact with their environment, exchanging energy and matter. The Sun. Most ecosystems receive their energy from the Sun's radiation. NASA/European
TAKE A LOOK 3. Complete Carbon dioxide in the air is used for. The Cycles of Matter continued
 CHAPTER 2 1 The Cycles of Matter SECTION Cycles in Nature BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Why does matter need to be recycled? How are water,
CHAPTER 2 1 The Cycles of Matter SECTION Cycles in Nature BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Why does matter need to be recycled? How are water,
Semester 1: Unit 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Semester 1: Unit 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Obtaining and Using Energy What do you know? What is energy? What do you need energy for? How does your body use/store energy? Energy is the ability to do
Semester 1: Unit 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Obtaining and Using Energy What do you know? What is energy? What do you need energy for? How does your body use/store energy? Energy is the ability to do
KS3 Science - Assessment Overview
 KS3 Science - Assessment Overview Students work through the units as indicated below. At the end of each unit the students sit a test which assesses their knowledge and application of the unit content
KS3 Science - Assessment Overview Students work through the units as indicated below. At the end of each unit the students sit a test which assesses their knowledge and application of the unit content
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
Pre-AP Biology Energy Unit Study Guide Part I
 Pre-AP Biology Energy Unit Study Guide Part I The Law of conservation of matter/mass : matter can not be created or destroyed However, matter may be rearranged in space In chemical reactions, the mass
Pre-AP Biology Energy Unit Study Guide Part I The Law of conservation of matter/mass : matter can not be created or destroyed However, matter may be rearranged in space In chemical reactions, the mass
Parkstone Primary School Science Long Term Plan Updated January 2017
 Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
DOSTHILL PRIMARY SCHOOL I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science
 I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
S Illustrate and explain how carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are cycled through an ecosystem.
 Biogeochemical Cycles S2-1-01 Illustrate and explain how carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are cycled through an ecosystem. Biogeochemical Cycles Let s take a closer look at the interactions between LIVING
Biogeochemical Cycles S2-1-01 Illustrate and explain how carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are cycled through an ecosystem. Biogeochemical Cycles Let s take a closer look at the interactions between LIVING
McKinley Presidential Library & Museum Planetarium Show Ohio Science Standards Fifth Grade
 Fifth Grade-Interconnections Within Systems: Cycles on, such as those occurring in ecosystems, in the solar system, and in the movement of light and sound result in describable patterns. Speed is a measurement
Fifth Grade-Interconnections Within Systems: Cycles on, such as those occurring in ecosystems, in the solar system, and in the movement of light and sound result in describable patterns. Speed is a measurement
Key Stage 3 Science Revision Guide
 Key Stage 3 Science Revision Guide Use this guide to check that you cover all the topics you have studied at key stage 3. You can use your classwork books, revision guides and the internet to help you
Key Stage 3 Science Revision Guide Use this guide to check that you cover all the topics you have studied at key stage 3. You can use your classwork books, revision guides and the internet to help you
Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets
 Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets 1 Complete the sentences using the words in the box. Plants can make their own using light from the. They also need carbon gas and. 2 Label the parts of the diagram to
Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets 1 Complete the sentences using the words in the box. Plants can make their own using light from the. They also need carbon gas and. 2 Label the parts of the diagram to
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
