PLANT KINGDOM
|
|
|
- Beatrice Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PLANT KINGDOM 1. All organisms belonging to the following kingdoms have cell wall I. Monera II. Protista III. Fungi IV. Plantae a) All except II and III *b) All except I and II c) All except I and III d) All except I, II, III 2. Organisms with cellulosic cell walls are seen in the Kingdom a) Monera b) Fungi *c) Protista d) None 3. Match the following A) Unicellular alga I) Kelp *a) II IV V I B) Coenobial alga II) Chlamydomonas b) III IV V I C) Filamentous alga III) Albugo c) II V IV III Alga with massive D) body IV) Volvox d) IV II III V V) Ulothrix 4. [A]: All algae of kingdom plantae are multicellular [R]: Volvox has massive body * 5. Spermatophytes in the plant kingdom are a) Algae b) Bryophytes c) Pteridophytes *d) Gymnosperms 6. Choose the correct statement. *a) All Lichens have an organism belonging to kingdom Fungi b) All Lichens have one of the organisms belonging to Monera c) All Lichens have one of the organisms belonging to Plantae d) All Lichens have one of the organisms belonging to Protista 7. Match the following Some species of A) Flagellated isogametes I) Chalmydomonas a) V IV II I B) Non-flagellated Most of the species II) isogametes of Chlamydomonas *b) II III IV I Female gamete is always C) III) Spirogyra non-flagellated c) II III V IV D) Flagellated anisogametes IV) Volvox d) II III IV V V) Chlorella
2 8. [A]: Life cycle in algae is usually haplontic. [R]: All stages in the life cycle of algae are haploid * 9. Chemically the pyrenoids are made of a) Lipids b) Nucleotides *c) Amino acids d) Fatty acids 10. Cell wall of Chlorophyceae has a) Cellulose and Lignin b) Algin, Cellulose c) Pectin, Algin *d) Cellusose, Pectin 11. Match the following A) Algin I) Chara a) III IV V I B) Carrageen II) Laminaria *b) III IV V II C) Agar-Agar III) Brown algae c) II IV V III D) Iodine IV) Red algae d) III V II IV V) Gelidium 12. [A]: Sexual reproduction in Fucus is described as Oogamous [R]: It has motle, very large female gamete * 13. Choose the wrong statement a) Chlorophycean algae have pyrenoids b) The reserve food material in Chara is starch c) Chlorella is used as food by spece travellers *d) Zoospore formation is uncommon in Chlorophyceae 14. Volvox is a/an a) Colonial brown alga b) Multicellular fungus *c) Coenobial green alga d) Unicellular alga 15. Match the following A) All algae of Plantae have I) Carrageen *a) III IV II I All algae of chlorophyceae B) have II) Algin b) II IV I III C) Kelp III) Chlorophyll a c) III V I II D) Hydrocolloid IV) Chlorophyll b d) II V III IV V) Chlorophyll c 16. Zoospores of Phaeophyceae are a) Isokontic b) spherical c) ellipsoidal *d) Heterokontic
3 17. This is filamentous brown alga *a) Ectocarpus b) Laminaria c) Fucus d) Sargassum 18. Match the following A) Cell wall lacks pectin I) Eubacterium *a) II III IV I Cell wall with B) polysulphate esters II) Laminaria b) II V IV III C) Cell wall with Chitin III) Polysiphonia c) III IV V II D) Cell wall with Mureins IV) Neurospora d) II III IV V V) Mycoplasma 19. [A]: Ectocarpus reproduces asexually by zoospores [R]: It produces asexual spores with anterior flagella * 20. Red coloration to red algae is due to a) α-carotene b) β-carotene c) Anthaxanthin *d) Phycoerythrin 21. The pear shaped structures of Phaeophyceae are a) Chloroplast, Gametes b) Zoospores, Chloroplast *c) Gametes, Zoospores d) Oogonium, Spermatangium 22. Match the following A) Photosynthetic organ I) Zoospore of brown alga *a) IV III II I B) Resembles amylopectin II) Sex organ b) IV V II I C) Carpogonium III) Floridean starch c) V III II I D) Unequal flagella IV) Frond d) IV III I II V) Laminarin 23. [A]: Red algae can grow in deep waters of the sea. [R]: They have Phycoerythrin * 24. Choose the odd alga a) Polysiphonia *b) Dictyota c) Porphyra d) Gelidium 25. Mannitol is the reserve food of *a) Ectocarpus b) Volvox c) Gelidium d) Gracilaria
4 26. Match the following A) Colonial form I) Ulothrix a) IV II I III B) Oogamy II) Polysiphonia b) V IV III II C) Green alga III) Fucus c) V III I II D) Brown alga IV) Noctiluca *d) V II I III V) Volvox 27. [A]: Chlamydomonas is a green alga [R]: It is eukaryotic; single celled and has two flagella at the anterior * 28. The common cell wall material among algae is a) Pectin b) Carrageen c) Algin *d) Cellulose 29. The life cycle of algae is usually a) Diplo-haplontic b) Diplontic *c) Haplontic d) Haplo-diplontic 30. [A]: Laminaria is a phaeophyceae member. [R]: It has Chlorophyll a and c. * 31. The following plants play a role in plant succession on bare rock/soil. a) Lichens b) Mosses c) Ferns *d) a and b 32. The prevalent tissue among the Bryophytes is a) Sclerenchyma *b) Parenchyma c) Collenchyma d) Complex tissue 33. Match the following A) Archegonium I) Male sex organ *a) II IV V I B) Cauloid II) Female sex organ b) III IV V II C) Bud III) Root like structure c) IV V III II D) Antheridium IV) Stem like structure d) II V IV III V) Gemma 34. [A]: Bryophytes are called as Amphibians of Plant Kingdom [R]: Most of the bryophytes grow on moist soil and need water for fertilization. * 35. Sex organs of Bryophytes are I. Jacketed II. Multicellular III. Stalked a) I and II b) II and III c) I and III *d) I, II, III
5 36. Life cycle of Bryophyte is a) Diplo-haplontic b) Haplo-biontic *c) Haplo-diplontic d) Diplo-biontic 37. Match the following A) Biflagellated structure I) Capsule *a) IV V II I B) Flask shaped structure II) Elaters b) V IV I III Help in spore C) dispersal III) Antheridium c) III V I II D) Forms spores IV) Antherozoids d) IV V III I V) Archegonium 38. [A]: Sporophyte of Bryophyte is homosporous [R]: Spores in Bryophytes are formed as a result of mitotic division. * 39. Sexual reproduction in Bryophytes is a) Isogamous b) Anisogamous c) Non-zoidogamous oogamy *d) Zooidogamousoogamy 40. Sporophyte of Bryophytes is a) Independent b) Always photosynthetic c) Always non-photosynthetic *d) Parasitic on gametophyte 41. Match the following A) Soil conditioner I) Funaria a) IV III I II B) Elaters II) Anthoceros *b) III IV II I C) Pseudo elaters III) Sphagnum c) V IV I II D) Peristomial teeth IV) Marchantia d) III V II I V) Porphyra 42. [A]: Anthoceros is called as Hornwort. [R]: It has indefinitely growing elongated horn-like sporophyte. * 43. Gametophyte has leaf like structures in I. Hepaticopsida II. Anthocerotopsida III. Bryopsida IV. Rhodophyceae a) I, II b) I, II, III *c) I, III d) I, II, III, IV 44. Antheridia and Archegonia are formed on different thalli in *a) Marchantia b) Riccia c) Sphagnum d)funaria
6 45. Match the following A) Intercalary meristem I) Sphagnum *a) III IV I II B) Gemma cups II) Polytrichum b) III IV I V C) Paraphyses III) Anthoceros c) II IV I V D) Haircap moss IV) Marchantia d) III V II IV V) Funaria 46. Pteridophytes are a) First land plants b) First archegoniates c) First embryophytes *d) First tracheophytes 47. Pteridiphyta has a) Mosses b) Liverworts *c) Club mosses d) Hornworts 48. Match the following A) Siphonostele I) Scattered vascular bundles a) V IV III I B) Protostele II) Overlapping leaf gaps *b) V IV III II C) Solenostele III) Scattered leaf gaps c) IV V I II Xylem surrounded by D) Dictiyostele IV) phloem d) V III II I Medullated stele with xylem V) surrounded by Phloem. 49. [A]: Leaves of Selaginella are microphyllous [R]: Leaf gaps are absent in all heterosporous species * 50. Choose the correct statement a) Heterospory is more common in Pteridophytes *b) Homospory is more common in Pteridophytes c) Pteridophytes show only heterospory d) Primitive pteridophytes do not show heterospory at all. 51. This is Sphenopsid a) Salvinia b) Marselia c) Selaginella *d) Equisetum 52. Match the following A) Indusium I) Leaves of ferns a) IV II III I Membranous covering of B) Ramenta II) sorus *b) II IV III I C) Strobilus Aggregation of sporophylls III) on common axis c) IV III II V D) Fronds IV) Brown hair on petiole d) II V I III V) gametophyte
7 53. [A]: Adiantum has multiciliated male gametes [R]: It is a fern * 54. Choose the odd plant a) Pteris b) Adiantum c) Dryopteris *d) Lycopodium 55. Psilotum is a a) Bryophyte b) Alga *c) Pteridophyte d) Gymnosperm 56. Match the following Sori on abaxial surface of A) leaf I) Lycopodium a) V IV I II B) False indusium II) Selaginella *b) V IV II I C) Heterospory III) Polytrichum c) IV V III I D) Homospory IV) Pteris d) V III I II V) Dryopteris 57. [A]: Pteridophytes are limited to narrow geographical area. [R]: They are terrestrial plants which always require water for fertilization. * 58. Prothallus is a) Juvenile gametophyte of Bryophytes b) Thallus of Algae *c) Gametophyte of Pteridophytes d) Young sporophyte of Pteridophytes 59. Photosynthetic independent gametophytes and sporophytes are seen in a) Bryophytes b) Thallophyta c) Spermatophyta *d)pteridophyta 60. Match the following Pinnate compound A) leaves I) Equisetum a) V IV II III B) Primitive pteridophyte II) Adiantum b) IV V I II C) Fern III) Ginkgo c) V I II IV D) Horse tail IV) Psilotum *d) V IV II I V) Dryopteris 61. [A]: The larger leaves of ferns are called as Fronds. [R]: Fronds of ferns are not involved in reproduction *
8 62. Sex organs of Pteridophytes are a) Unicellular, jacketed, sessile b) Multicellular, stalked, Jacketed *c) Multicellular, Jacketed, Sessile 63. The first step to seed habit is *a) Heterospory d) Unicellular, Jacketed, Sessile b) Fertilisation in the female gametophyte c) Retention of female gametophyte in the sporophyte d) Development of embryo in the female gametophyte. 64. Match the following Open dichotomous A) venation I) Pteris a) V II III I B) Cones II) Selaginella b) IV III II I C) Heterospory III) Equisetum c) V IV I III Reflexed leaf margin of D) sporophyll IV) Psilotum *d) V III II I V) Dryopteris 65. [A]: Fertilisation in Pteridophytes is by zooidogamousoogamy [R]: In all Pteridophytes, the female gamete is larger, non-flagellate and stationary but the male gamete is multiflagellate. * 66. Gymnosperms are *a) Archegoniate spermatophytes b) Archegoniate non-spermatophytes c) Non-archegoniate spermatophytes d) Spermatophytes with aflagellate male gametes 67. Strobili are seen in a) All archegoniates b) All spermatophytes *c) Tracheatearechegoniates d) All embryophytes' 68. Match the following A) Living fossil I) Sequoia *a) III IV II I B) Needle like leaves II) Cycas b) IV V I II C) Pinnate compound leaves III) Ginkgo biloba c) V IV II I D) Tallest Gymnosperm IV) Pinus d) III IV II V V) Gnetum
9 69. [A]: Stems of Gymnosperms show Eustele [R]: Vascular bundles are regularly arranged in the stele of archegoniate spermatophytes. * 70. Mycorrhizal roots are seen in a) Cedrus b) Cycas *c) Pinus d)gnetum 71. Pinus is *a) Monoecious b) Dioecious c) Polygamous d)trioecious 72. [A]:Cycas shows fern characters. [R]: Male gametophyte of Cycas is independent * 73. Circinate vernation of leaves is shown by *a) Cycas b) Pinus c) Cedrus d) Ginkgo 74. Gymnosperm with unbranched stem is *a) Cycas b) Ginkgo c) Pinus d)gnetum 75. [A]: Cycas shows symbiosis [R]: Coralloid roots of Cycas have Cyanobacteria * 76. Gymnosperms do not show a) Syngamy b) Zooidogamy c) Siphonogamy *d) Triple fusion 77. The minimum number of female gametes seen in female gametophyte of Gymnosperms is *a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) [A]: Endosperm of Gymnosperms is haploid [R]: The multicellular structure developed from megaspore helps in nourishing the zygote to develop into embryo. * 79. Red wood tree is a) Pinus *b) Sequoia c) Cycas d)cedrus 80. Motile male gametes are seen in a) Pinus b) Ginkgo *c) Cycas d)gnetum
10 81. [A]: Seeds of Pinus are naked [R]: Seed coat is absent in Gymnosperm seeds * 82. Cones of Gymnosperms are equivalent to *a) Flowers b) Androecium c) Gynoecium d)perianth 83. Branched stem is seen in I. Cycas II. Pinus III. Cedrus a) I, II,III *b) II, III c) I, II d) I, III 84. [A]: Pinus shows less transpiration in high wind velosity [R]: Leaves of Pinus are reduced to needle like structures. * 85. [A]: Pollination is Gymnosperms is direct. [R]: Ovules of gymnosperms are not enclosed * 86. Perianth is present in I. Angiosperms II.Gymnosperms III.Pteridophytes IV. Dicots a) I, II b) II, III c) III, IV *d) I, IV 87. Embryosac is a) Diploid b) Triploid *c) Haploid d) Tetraploid 88. Match the following A) Companion cells I) Microsporophyll *a) III V IV II B) Embryosac II) Megasporophyll b) III V IV I C) Triple fusion III) Phloem c) IV III V II D) Carpel IV) Endosperm d) III IV V I V) Female gametophyte 89. [A]: Endosperm is present in angiosperms [R]: Angiosperms show double fertilization * 90. Pollination is Angiosperms is a) Anemophilous b) Hydrophilous c) Zoophilous *d) All
11 91. Female sex organ of angiosperms is a) Cone *b) Carpel c) Microsporophyll d) Embryosac 92. Match the following with respect to angiosperms A) 3 celled structure I) Central cell a) II I V IV B) Binucleate structure II) Synergids b) III II IV V Smallest cells of C) embryosac III) Egg apparatus *c) III I V IV D) Gamete of embryosac IV) Egg cell d) III I IV II V) Antipodals 93. [A]: Pollination in Angiosperms is indirect. [R]: Pollen grains are deposited on the stigma in plants with true flowers * 94. The smallest angiosperm is *a) Wolfia b) Lemna c) Cuscuta d) Arceuthobium 95. The tallest angiosperm is *a) Eucalyptus b) Sequoia c) Pseudoptsuga d) Casuarina 96. Match the following A) Diplontic life cycle I) Polysiphonia *a) IV V II I B) Haplontic life cycle II) Marchantia b) V IV I II Haplodiplontic life C) cycle III) Pteris c) IV III II I D) Diplobiontic life cycle IV) Fucus d) IV V II III V) Spirogyra 97. [A]: Life cycle in Laminaria is Haplodiplontic [R]: Laminaria has multicellular dominant gametophyte and unicellular sporophytic stages in its life cycle. * 98. Life cycle of Ectocarpus resembles the life cycle of a) Pteridophytes b) Volvox *c) Bryophytes d)polysiphonia 99. Life cycle in Tracheophytes is a) Haplodiplontic *b) diplohaplontic c) Diplobiontic d)haplobiontic
12 100. [A]: In Angiosperms the male gametes are discharged into the female gametophyte. [R]: Pollen tube penetrates the synergid of embryosac. * 101. Angiosperms do not have a) Archegonia b) motile male gametes c) Motile female gamete d) All 102. Endosperm of Angiosperms belongs to a) gametophytic generation b) sporophytic generation *c) neither gametophytic nor sporophytic generation d) usuallysporophytic generation and sometimes gametophytic generation 103. [A]: Ovules of angiosperms are enclosed [R]: Ovules of angiosperms have covering layers called integuments * 104. The total number of haploid nuclei involved in double fertilization is a) Two b) Three c) Four *d) Five 105. The cells of embryo sac that perish after fertilization are a) Synergids b) Antipodals c) Central cell *d) a and b
Downloaded from
 3. Plant Kingdom POINTS TO REMEMBER : CLASSIFICATION : Artificial System of Classification : Used superficial morphological characters. Based on a few characteristics like habit, colors, number and shape
3. Plant Kingdom POINTS TO REMEMBER : CLASSIFICATION : Artificial System of Classification : Used superficial morphological characters. Based on a few characteristics like habit, colors, number and shape
CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM. K C Meena PGT Biology KVS
 CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Classification System Artificial classification oldest classification and it is based on few vegetative and sexual characters. Natural classification
CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Classification System Artificial classification oldest classification and it is based on few vegetative and sexual characters. Natural classification
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM Eukaryotic, multicellular, chlorophyll containing and having cell wall, are grouped the kingdom Plantae, popularly known as plant kingdom.
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM Eukaryotic, multicellular, chlorophyll containing and having cell wall, are grouped the kingdom Plantae, popularly known as plant kingdom.
Points to Remember. Based on cytological informations. Gives importance to chromosome number, structure and behaviour.
 Points to Remember Classification : Arti cial System of Classi cation By Carolus Linnaeus, based on androecium structure and vegetative characters. Natural System of Classi cation Based on natural af nities
Points to Remember Classification : Arti cial System of Classi cation By Carolus Linnaeus, based on androecium structure and vegetative characters. Natural System of Classi cation Based on natural af nities
Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology
 Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
 Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions
Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions
TEST on PLANT TAXONOMY for NEET 2017
 TEST on PLANT TAXONOMY for NEET 2017 1. Which one of the following shows isogamy with non-flagellated gametes? a) Sargassum b) Ectocarpus c) Ulothrix d) Spirogyra 2. Which of the following is responsible
TEST on PLANT TAXONOMY for NEET 2017 1. Which one of the following shows isogamy with non-flagellated gametes? a) Sargassum b) Ectocarpus c) Ulothrix d) Spirogyra 2. Which of the following is responsible
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) HABITAT:
 ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
Plant Evolution & Diversity
 Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Quick 50 In Plant Kingdom
 Quick 50 In Plant Kingdom 1. Identify the plants shown in figure and select the incorrect statement. (a) Plant A is Chara, which is fixed to the substratum by means of highly branched multicellular rhizoids.
Quick 50 In Plant Kingdom 1. Identify the plants shown in figure and select the incorrect statement. (a) Plant A is Chara, which is fixed to the substratum by means of highly branched multicellular rhizoids.
Downloaded from
 A.I.P.M.T. Foundation - XI Biology MCQs Time: 30 min MCQ#8 Full Marks: 40 Choose the most appropriate answer. 1. They are non-vascular plants: 1. Hosrsetails 2. Conifers 3. Club mosses 4. Liverworts 2.
A.I.P.M.T. Foundation - XI Biology MCQs Time: 30 min MCQ#8 Full Marks: 40 Choose the most appropriate answer. 1. They are non-vascular plants: 1. Hosrsetails 2. Conifers 3. Club mosses 4. Liverworts 2.
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land
 Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land
 Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
AP Biology. Evolution of Land Plants. Kingdom: Plants. Plant Diversity. Animal vs. Plant life cycle. Bryophytes: mosses & liverworts
 Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation:
 Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation: Homosporous ( one type of spore. a single type of spore produces a single type of gametophyte which produces both male and female
Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation: Homosporous ( one type of spore. a single type of spore produces a single type of gametophyte which produces both male and female
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I How Plants Colonized Land 1. Evolutionary History of Plants 2. General Features of Plants 3. Survey of the Plant Kingdom A. Nonvascular Plants B. Seedless Vascular Plants
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I How Plants Colonized Land 1. Evolutionary History of Plants 2. General Features of Plants 3. Survey of the Plant Kingdom A. Nonvascular Plants B. Seedless Vascular Plants
Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams. They are the earliest know vascular plants which originated in the Silurian period of
 Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams. They are the earliest know vascular plants which originated in the Silurian period of Palaeozoic era. They are the successful colonizers on land habit.
Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams. They are the earliest know vascular plants which originated in the Silurian period of Palaeozoic era. They are the successful colonizers on land habit.
Unit 2B- The Plants. Plants can be classified according to the presence or absence of vascular tissue.
 Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT
 Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014
 BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at how plants are classified Define Alternation of generations Summarise the main characteristics of four groupings of
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at how plants are classified Define Alternation of generations Summarise the main characteristics of four groupings of
Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure
 Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure Plant evolution Plant Evolution Chlorophytes Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophytes are a green
Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure Plant evolution Plant Evolution Chlorophytes Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophytes are a green
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
STUDY QUESTIONS TEST 2 ANTHOCEROPHYTA, TRACHEOPHYTES AND PLANT STRUCTURE
 STUDY QUESTIONS TEST 2 ANTHOCEROPHYTA, TRACHEOPHYTES AND PLANT STRUCTURE 1. Name the Bryophyte phylum that is most closely related to vascular plants? 2. How do Anthocerophyta differ from other Bryophytes?
STUDY QUESTIONS TEST 2 ANTHOCEROPHYTA, TRACHEOPHYTES AND PLANT STRUCTURE 1. Name the Bryophyte phylum that is most closely related to vascular plants? 2. How do Anthocerophyta differ from other Bryophytes?
Kingdom Plantae. A Brief Survey of Plants
 Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Bryophyte Gametophytes. Bryophyte Gametophytes. A spore germinates into a gametophyte. composed of a protonema and gamete producing gametophore
 A spore germinates into a composed of a protonema and gamete producing gametophore Rhizoids Anchor s to substrate Lack of vascular :ssues Bryophyte Gametophytes Restricts the height of s Mature s produce
A spore germinates into a composed of a protonema and gamete producing gametophore Rhizoids Anchor s to substrate Lack of vascular :ssues Bryophyte Gametophytes Restricts the height of s Mature s produce
-plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem. -spores with tough walls. -life history of alternation of generations
 Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses
 The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses Mosses Phylum Bryophyta - ~12,000 species Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta - ~8,500 species Hornworts - Phylum Anthocerophyta
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses Mosses Phylum Bryophyta - ~12,000 species Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta - ~8,500 species Hornworts - Phylum Anthocerophyta
Plants I. Introduction
 Plants I Objectives: 1. List the characteristics of plants that link them to their ancestral green algae. 2. Describe the problems faced by plants that moved onto the land. 3. Describe the adaptations
Plants I Objectives: 1. List the characteristics of plants that link them to their ancestral green algae. 2. Describe the problems faced by plants that moved onto the land. 3. Describe the adaptations
Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages ) Generation Description Haploid or Diploid? Gamete-producing plant Spore-producing plant
 Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555) What Is a Plant? (page 551) 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about plants. a. Plants are multicellular prokaryotes. b. Plants
Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555) What Is a Plant? (page 551) 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about plants. a. Plants are multicellular prokaryotes. b. Plants
BRYOPHYTA, PTERIDOPHYTA
 Botany Rexine Charts CYTOLOGY (ELB.106.125).01 Cell Membrane showing structure & functions.02 Cell Wall, showing structure & functions.03 Endoplasmic Reticulum showing structure & functions.04 Mitochondrion
Botany Rexine Charts CYTOLOGY (ELB.106.125).01 Cell Membrane showing structure & functions.02 Cell Wall, showing structure & functions.03 Endoplasmic Reticulum showing structure & functions.04 Mitochondrion
Plant Structure Size General Observations
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Structure Size General Observations Diversity Within the Plant Kingdom Pine Trees What is a plant? Multicellular Eukaryotes Perform Photosynthesis (base of all terrestrial food chains)
Kingdom Plantae Plant Structure Size General Observations Diversity Within the Plant Kingdom Pine Trees What is a plant? Multicellular Eukaryotes Perform Photosynthesis (base of all terrestrial food chains)
askiitians Q2. When and where does reduction division take place in the life cycle of a liverwort, a moss, a fern, a gymnosperm and an angiosperm?
 Class: XI Subject: Biology Topic: Plant kingdom No. of Questions: 25 Q1. What is the basis of classification of algae? Earlier, the algae were classified on the basis of single visible character, viz.,
Class: XI Subject: Biology Topic: Plant kingdom No. of Questions: 25 Q1. What is the basis of classification of algae? Earlier, the algae were classified on the basis of single visible character, viz.,
Reproductive Morphology
 Week 3; Wednesday Announcements: 1 st lab quiz TODAY Reproductive Morphology Reproductive morphology - any portion of a plant that is involved with or a direct product of sexual reproduction Example: cones,
Week 3; Wednesday Announcements: 1 st lab quiz TODAY Reproductive Morphology Reproductive morphology - any portion of a plant that is involved with or a direct product of sexual reproduction Example: cones,
Biology Lab: The Diversity of the Plant Kingdom
 Biology Lab: The Diversity of the Plant Kingdom Name Date Introduction: Simply put, life on Earth relies on the plants for survival. By carrying out photosynthesis, plants provide enough food for themselves
Biology Lab: The Diversity of the Plant Kingdom Name Date Introduction: Simply put, life on Earth relies on the plants for survival. By carrying out photosynthesis, plants provide enough food for themselves
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response
 Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Types of Plants. Unit 6 Review 5/2/2011. Plants. A. pine B. moss C. corn plant D. bean plant E. liverwort
 Unit 6 Review Plants Initial questions are worth 1 point each. Each question will be followed by an explanation All questions will be asked a second time at the very end, each of those questions will be
Unit 6 Review Plants Initial questions are worth 1 point each. Each question will be followed by an explanation All questions will be asked a second time at the very end, each of those questions will be
Major groups of algae
 Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Major lineages and life cycles of land plants. Green plants: viridiplantae
 Liverworts Mosses Hornworts Lycophytes Major lineages and life cycles of land plants Green plants: viridiplantae Green plants Embryophytes (land plants) Bryophytes Tracheophytes (vascular plants) Seed
Liverworts Mosses Hornworts Lycophytes Major lineages and life cycles of land plants Green plants: viridiplantae Green plants Embryophytes (land plants) Bryophytes Tracheophytes (vascular plants) Seed
Plant Kingdom. C l a s s i f i c a t i o n Artificially grouped into Nonvascular or Vascular Plants
 Plant Kingdom C h a r a c t e r i s t i c s Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Multicellular Sexually reproducing Life History involves an alternation of a haploid phase (Gametophyte) with a diploid phase (Sporophyte)
Plant Kingdom C h a r a c t e r i s t i c s Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Multicellular Sexually reproducing Life History involves an alternation of a haploid phase (Gametophyte) with a diploid phase (Sporophyte)
MODEL ANSWER SEMESTER - V
 Q1. Multiple choice/one sentence/fill in the blanks i. a) Gelidium ii. a) Blue green algae iii. c) Glycogen iv. d) Cell wall is chitinous and chlorophyll is absent v. d) all of these vi. b) perithecium
Q1. Multiple choice/one sentence/fill in the blanks i. a) Gelidium ii. a) Blue green algae iii. c) Glycogen iv. d) Cell wall is chitinous and chlorophyll is absent v. d) all of these vi. b) perithecium
Introduction to the Plant Kingdom - 1
 Introduction to the Plant Kingdom - 1 The Plant Kingdom comprises a large and varied group of organisms that have the following characteristics in common. All plants are: Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Multicellular
Introduction to the Plant Kingdom - 1 The Plant Kingdom comprises a large and varied group of organisms that have the following characteristics in common. All plants are: Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Multicellular
Comparing Plants & Animals
 Section 6.1 Comparing Plants & Animals p. 164-168 Major Similarities: They are both multi-cellular, eukaryotes. Their sizes both range from microscopic to very large. Major Differences: How they obtain
Section 6.1 Comparing Plants & Animals p. 164-168 Major Similarities: They are both multi-cellular, eukaryotes. Their sizes both range from microscopic to very large. Major Differences: How they obtain
Introduction to Bryophyta
 Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
The overall category of plants are 1) eukaryotic 2) multicellular 3)organisms capable of photosynthesis 4)built with cellulose 5) and have
 Chapter 23 The overall category of plants are 1) eukaryotic 2) multicellular 3)organisms capable of photosynthesis 4)built with cellulose 5) and have alternation of generations. Plants most likely first
Chapter 23 The overall category of plants are 1) eukaryotic 2) multicellular 3)organisms capable of photosynthesis 4)built with cellulose 5) and have alternation of generations. Plants most likely first
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Phylum Bryophyta : (Page 169)
 Kingdom Plantae : Plants... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic organisms - rigid cell walls built of cellulose - life cycles show alternation of generations...two distinct phases called
Kingdom Plantae : Plants... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic organisms - rigid cell walls built of cellulose - life cycles show alternation of generations...two distinct phases called
Test Lesson 18 Plants - Answer Key Page 1
 Test Lesson 18 Plants - Answer Key Page 1 1. Algae are. A. protists B. early plants C. multicellular eukaryotes D. forms of euglenia 2. Algae reproduce by what two methods? A. conjugation and meiosis B.
Test Lesson 18 Plants - Answer Key Page 1 1. Algae are. A. protists B. early plants C. multicellular eukaryotes D. forms of euglenia 2. Algae reproduce by what two methods? A. conjugation and meiosis B.
Test Lesson 18 Plants Page 1
 Test Lesson 18 Plants Page 1 1. Algae are. A. protists B. early plants C. multicellular eukaryotes D. forms of euglenia 2. Algae reproduce by what two methods? A. conjugation and meiosis B. binary fission
Test Lesson 18 Plants Page 1 1. Algae are. A. protists B. early plants C. multicellular eukaryotes D. forms of euglenia 2. Algae reproduce by what two methods? A. conjugation and meiosis B. binary fission
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review! Chapter 31!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Classification of Plants
 Classification of Plants Plants Aquatic Plants Ex. green algae Similarities between green algae and land plants: A) have chlorophylls a and b B) cellulose cell walls C) store food energy in the form of
Classification of Plants Plants Aquatic Plants Ex. green algae Similarities between green algae and land plants: A) have chlorophylls a and b B) cellulose cell walls C) store food energy in the form of
Plants. and their classi.ication
 + Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
+ Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae
 Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae I. General Characteristics II. Reproduction and Life History Patterns III. Photosynthetic Pigments IV. Chloroplast types V. Major Polysaccharide Reserves
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae I. General Characteristics II. Reproduction and Life History Patterns III. Photosynthetic Pigments IV. Chloroplast types V. Major Polysaccharide Reserves
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide Onto Land
 Slide 1 18.1 Onto Land 18.1.1 Describe the evolutionary relationship between green algae and land plants. 18.1.2 List the five significant events in the evolution of land plants. 18.1.3 Describe the alternation
Slide 1 18.1 Onto Land 18.1.1 Describe the evolutionary relationship between green algae and land plants. 18.1.2 List the five significant events in the evolution of land plants. 18.1.3 Describe the alternation
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND. Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution
 CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
Unit 7: Plant Evolution, Structure and Function
 Time: 7 Days (some time spent working over breaks on this topic) and then an exam 16% of the AP Exam is on this material. Topics Covered: Reproduction, growth, and development Structural, physiological,
Time: 7 Days (some time spent working over breaks on this topic) and then an exam 16% of the AP Exam is on this material. Topics Covered: Reproduction, growth, and development Structural, physiological,
Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Some History: In the life cycle of the kelp Laminaria. One way to separate algae from protozoa is that. Rocks of Cambrian Age (ca.
 One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
Topic 22. Introduction to Vascular Plants: The Lycophytes
 Topic 22. Introduction to Vascular Plants: The Lycophytes Introduction to Vascular Plants Other than liverworts, hornworts, and mosses, all plants have vascular tissues. As discussed earlier, the mosses
Topic 22. Introduction to Vascular Plants: The Lycophytes Introduction to Vascular Plants Other than liverworts, hornworts, and mosses, all plants have vascular tissues. As discussed earlier, the mosses
Plants Notes. Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light
 Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter in class follow along lecture notes
 Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Plant Evolution and Diversity. B. Importance of plants. C. Where do plants fit, evolutionarily? What are the defining traits of plants?
 Plant Evolution and Diversity Reading: Chap. 30 I. What is a plant? A. Basic structure and function B. Why are plants important? C. What are plants, evolutionarily? D. Problems of living on land II. Overview
Plant Evolution and Diversity Reading: Chap. 30 I. What is a plant? A. Basic structure and function B. Why are plants important? C. What are plants, evolutionarily? D. Problems of living on land II. Overview
Mock Exam I (BY 124) 8. Sori can be found on which of the following? A. Pterophytes B. Mosses C. Liverworts D. Hornworts E.
 1. When you see a green leafy moss, you are looking at the. A. Structure where meiosis occurs B. Sporophyte generation C. Gametophyte generation D. Spore-producing structure 2. Which of the following traits
1. When you see a green leafy moss, you are looking at the. A. Structure where meiosis occurs B. Sporophyte generation C. Gametophyte generation D. Spore-producing structure 2. Which of the following traits
LAB 13 The Plant Kingdom
 LAB 13 The Plant Kingdom Overview The importance of plants for life on earth cannot be overstated. Plants along with photosynthetic microbes produce all of the oxygen gas (O 2 ) in our atmosphere. Essentially
LAB 13 The Plant Kingdom Overview The importance of plants for life on earth cannot be overstated. Plants along with photosynthetic microbes produce all of the oxygen gas (O 2 ) in our atmosphere. Essentially
The Classification of Plants, II.
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 6, Issue 1 (November, 1905) 1905-11 The Classification of Plants, II.
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 6, Issue 1 (November, 1905) 1905-11 The Classification of Plants, II.
Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls
 1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
Announcements. Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology. Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers
 Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
NUCLEUS ALBUMINOUS CELL SIEVE CELL SIEVE AREA SMALL PORES SIEVE CELL PHLOEM L.S. SUGAR
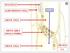 NUCLEUS? ALBUMINOUS CELL SUGAR SIEVE CELL SIEVE AREA SMALL PORES SIEVE CELL PHLOEM L.S. NUCLEUS S ALBUMINOUS CELL SUGAR SIEVE? CELL SIEVE PLATE LARGE PORES SIEVE? CELL PHLOEM L.S. NUCLEUS? ALBUMINOUS CELL
NUCLEUS? ALBUMINOUS CELL SUGAR SIEVE CELL SIEVE AREA SMALL PORES SIEVE CELL PHLOEM L.S. NUCLEUS S ALBUMINOUS CELL SUGAR SIEVE? CELL SIEVE PLATE LARGE PORES SIEVE? CELL PHLOEM L.S. NUCLEUS? ALBUMINOUS CELL
BIOLOGY. Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular Plants CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 29 Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Greening of Earth
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 29 Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Greening of Earth
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
 SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
BIO10 Plant Lecture Notes ch. 17. Plant Kingdom
 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Nonvascular Plants. Believed to have evolved from green-algae. Major adaptations in going from water to land. Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids
 Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
 Name Class EXAM Date Unit 11 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants Multicellular- made of cells Eukaryotes- have & membrane bound organelles Cell - made of Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
Name Class EXAM Date Unit 11 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants Multicellular- made of cells Eukaryotes- have & membrane bound organelles Cell - made of Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
Chapters 29 & 30: Plant Diversity
 Chapters 29 & 30: Plant Diversity AP Biology 2013 1 Chara species, a pond organism 5 mm Colonization of the Land Coleochaete orbicularis, a disk-shaped charophyte that also lives in ponds (LM) Since colonizing
Chapters 29 & 30: Plant Diversity AP Biology 2013 1 Chara species, a pond organism 5 mm Colonization of the Land Coleochaete orbicularis, a disk-shaped charophyte that also lives in ponds (LM) Since colonizing
22 3 Seedless Vascular Plants Slide 1 of 33
 22 3 Seedless Vascular Plants 1 of 33 Evolution of Vascular Tissue Plants have vascular tissue, which is specialized to conduct water and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem carries water from the roots
22 3 Seedless Vascular Plants 1 of 33 Evolution of Vascular Tissue Plants have vascular tissue, which is specialized to conduct water and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem carries water from the roots
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants
 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Kingdom Plantae. Plants or metaphytes are, autotrophic multicellular eukaryotes, with tissues.
 Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
1/15/2014. Monocots, Dicots, Gymnosperms & Ferns. Classification of Plants. Classification of Plants
 Monocots, Dicots, Gymnosperms & Ferns Plant Classification & Basic Plant Groups for the Landscape Classification of Plants Taxonomic classification starts with the least specific it s a plant And ends
Monocots, Dicots, Gymnosperms & Ferns Plant Classification & Basic Plant Groups for the Landscape Classification of Plants Taxonomic classification starts with the least specific it s a plant And ends
Biol 203 Botany Sample Exam. Name:
 Biol 203 Botany Sample Exam Name: Section I. Multiple choice. Check any and all correct items; this means: there may be no correct response for you to check, or there might be more than one correct item
Biol 203 Botany Sample Exam Name: Section I. Multiple choice. Check any and all correct items; this means: there may be no correct response for you to check, or there might be more than one correct item
All about plants: Overview of Plants
 All about plants: Overview of Plants Plants (also called autotrophs or producers) trap energy from the sun by photosynthesis & store it in organic compounds; contain chlorophyll inside of chloroplasts;
All about plants: Overview of Plants Plants (also called autotrophs or producers) trap energy from the sun by photosynthesis & store it in organic compounds; contain chlorophyll inside of chloroplasts;
Name: Date: Period: Forms a spore producing structure called an ascus Morals Truffles Yeast
 Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom
 Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom IMPORTANT POINTS Five kingdom classification system was given by Whittaker on the basis of following four criteria : (i) Cell structure (ii) Body Structure
Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom IMPORTANT POINTS Five kingdom classification system was given by Whittaker on the basis of following four criteria : (i) Cell structure (ii) Body Structure
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes-
 -Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants
Plants and Fungi. Bryophytes Bryophytes, most commonly mosses Sprawl as low mats over acres of land
 Plants and Fungi Terrestrial Adaptations of Plants Structural Adaptations A plant is a multicellular eukaryote and a photoautotroph, making organic molecules by photosynthesis In terrestrial habitats,
Plants and Fungi Terrestrial Adaptations of Plants Structural Adaptations A plant is a multicellular eukaryote and a photoautotroph, making organic molecules by photosynthesis In terrestrial habitats,
Bryophytes Pteridophytes Progymnosperms Gymnosperms Angiosperms. Vascularity
 Biology 3B Laboratory Vascular Seed Plants Gymnosperm & Angiosperm Objectives To understand the general systematic relationships of gymnosperms and angiosperms To describe the general features of gymnosperms
Biology 3B Laboratory Vascular Seed Plants Gymnosperm & Angiosperm Objectives To understand the general systematic relationships of gymnosperms and angiosperms To describe the general features of gymnosperms
Plants Have Changed the World
 Chapter 19 Plants Man: G. R. "Dick" Roberts/Natural Sciences Image Library Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill
Chapter 19 Plants Man: G. R. "Dick" Roberts/Natural Sciences Image Library Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill
Seed Plants. Gymnosperms & Angiosperms
 Seed Plants Gymnosperms & Angiosperms 1 Quick Defs Vascular = xylem and phloem Xylem = Brings water/nutrients from roots to the plant. Phloem = Brings sugars down from the leaves 2 Evolution Of Land Plants
Seed Plants Gymnosperms & Angiosperms 1 Quick Defs Vascular = xylem and phloem Xylem = Brings water/nutrients from roots to the plant. Phloem = Brings sugars down from the leaves 2 Evolution Of Land Plants
Chapter 15. Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets. (Opening image copyright Jonathan Lingel, Used under license from Shutterstock.com.
 Chapter 15 Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets (Opening image copyright Jonathan Lingel, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 15.1: Introduction to the Plant Kingdom Lesson
Chapter 15 Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets (Opening image copyright Jonathan Lingel, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 15.1: Introduction to the Plant Kingdom Lesson
Prokaryotes Divide Asexually! Cell Cycles & Life Cycles. Heyer 1. Cell Cycles, Sex, & Ploidy! Cells divide to reproduce! Growth & Development
 Cell Cycles, Sex, & Ploidy! 1. DNA is the molecule of inheritance. 2. A chromosome is one long dsdna. In eukaryotes, the dsdna molecule is wrapped with histones & other proteins to form chromatin. 3. A
Cell Cycles, Sex, & Ploidy! 1. DNA is the molecule of inheritance. 2. A chromosome is one long dsdna. In eukaryotes, the dsdna molecule is wrapped with histones & other proteins to form chromatin. 3. A
Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
PLANTS AND FUNGI. Lecture Outline
 PLANTS AND FUNGI Lecture Outline I. Pioneers In a New World A. Millions of years ago the only photosynthesizers were cells living in the seas. B. The invasion of land began with the cyanobacteria, followed
PLANTS AND FUNGI Lecture Outline I. Pioneers In a New World A. Millions of years ago the only photosynthesizers were cells living in the seas. B. The invasion of land began with the cyanobacteria, followed
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003
 [LH4] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003 Date: Friday 15 January 2016 Time: 10.00 am
[LH4] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003 Date: Friday 15 January 2016 Time: 10.00 am
Chapter 30. Plant Diversity II The Seed Plants
 Chapter 30 Plant Diversity II The Seed Plants The rise of the seed plants Recall that our discussions on terrestrial plants up until this point have focused on a transition from the aquatic green algae
Chapter 30 Plant Diversity II The Seed Plants The rise of the seed plants Recall that our discussions on terrestrial plants up until this point have focused on a transition from the aquatic green algae
