Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology
|
|
|
- Phebe Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 1 Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
2 Overview: Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, a beach mouse s light, dappled fur acts as camouflage, allowing the mouse to blend into its surroundings Inland mice of the same species are darker in color, matching their surroundings Evolution is the process of change that has transformed life on Earth
3 Figure 1.1
4 Figure 1.2
5 Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions such as How does a single cell develop into an organism? How does the human mind work? How do different forms of life in a forest interact?
6 Concept 1.1: The study of life reveals common themes To organize and make sense of all the information encountered in biology, focus on a few big ideas These unifying themes help to organize biological information: Organization Information Energy and Matter Interactions Evolution
7 Theme: New Properties Emerge at Successive Levels of Biological Organization Life can be studied at different levels, from molecules to the entire living planet The study of life can be divided into different levels of biological organization In reductionism, complex systems are reduced to simpler components to make them more manageable to study
8 Figure The Biosphere 7 Tissues 2 Ecosystems 6 Organs 3 Communities 4 Populations 5 Organisms 10 Molecules 8 Cells 9 Organelles
9 Figure The Biosphere
10 Figure Ecosystems
11 Figure Communities
12 Figure Populations
13 Figure Organisms
14 Figure Organs
15 Figure Tissues 50 m
16 Figure Cell 10 m 8 Cells
17 Figure Organelles Chloroplast 1 m
18 Figure Atoms Chlorophyll molecule 10 Molecules
19 Emergent Properties Emergent properties result from the arrangement and interaction of parts within a system Emergent properties characterize nonbiological entities as well For example, a functioning bicycle emerges only when all of the necessary parts connect in the correct way
20 Biologists today complement reductionism with systems biology, the exploration of a biological system by analyzing the interactions among its parts The systems approach poses questions such as How do networks of genes in our cells function to generate our 24-hour cycle of wakefulness and sleep? How does increasing CO 2 alter the biosphere?
21 Structure and Function At each level of the biological hierarchy we find a correlation between structure and function Analyzing a biological structure can give clues about what it does and how it works
22 The Cell: An Organism s Basic Unit of Structure and Function The cell is the smallest unit of life that can perform all the required activities All cells share certain characteristics, such as being enclosed by a membrane The two main forms of cells are prokaryotic and eukaryotic
23 A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-enclosed organelles, including a DNA-containing nucleus Some organelles, such as the chloroplast, are limited only to certain cell types, that is, those that carry out photosynthesis Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles and are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells
24 Figure 1.4 Eukaryotic cell Membrane Cytoplasm Prokaryotic cell DNA (no nucleus) Membrane Membraneenclosed organelles 1 m Nucleus (membraneenclosed) DNA (throughout nucleus)
25 Figure Eukaryotic cell Membrane Cytoplasm Membraneenclosed organelles 1 m Nucleus (membraneenclosed) DNA (throughout nucleus)
26 Figure Prokaryotic cell DNA (no nucleus) Membrane 1 m
27 Theme: Life s Processes Involve the Expression and Transmission of Genetic Information Chromosomes contain most of a cell s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
28 Figure m
29 Figure m
30 Figure m
31 DNA, the Genetic Material A DNA molecule holds hundreds or thousands of genes, each a stretch of DNA along the chromosome Genes are the units of inheritance that transmit information from parents to offspring As cells grow and divide, the genetic information encoded by DNA directs their development
32 Figure 1.6 Nuclei containing DNA Sperm cell Egg cell Fertilized egg with DNA from both parents Embryo s cells with copies of inherited DNA Offspring with traits inherited from both parents
33 Figure 1.6-1
34 A DNA molecule is made of two long chains (strands) arranged in a double helix Each link of a chain is one of four kinds of chemical building blocks called nucleotides, abbreviated A, T, C, and G
35 Figure 1.7 Cell Nucleus DNA Nucleotide A C T A T A C C G T A G T A (a) DNA double helix (b) Single strand of DNA
36 DNA provides blueprints for making proteins, the major players in building and maintaining a cell Genes control protein production indirectly, using RNA as an intermediary Gene expression is the process of converting information from gene to cellular product
37 Figure 1.8 (b) A lens cell uses information in DNA to make crystallin proteins. Crystallin gene (a) Lens cells are tightly packed with transparent proteins called crystallin. Lens cell DNA TRANSCRIPTION A C C A A A C C G A G T T G G T T T G G C T C A mrna U G G U U U G G C U C A TRANSLATION Chain of amino acids PROTEIN FOLDING Protein Crystallin protein
38 Figure (a) Lens cells are tightly packed with transparent proteins called crystallin. Lens cell
39 Figure 1.8-1a
40 Figure 1.8-1b Lens cell
41 Figure (b) A lens cell uses information in DNA to make crystallin proteins. Crystallin gene A C C A A A C C G A G T DNA T G G T T T G G C T C A TRANSCRIPTION mrna U G G U U U G G C U C A
42 Figure (b) A lens cell uses information in DNA to make crystallin proteins. mrna U G G U U U G G C U C A TRANSLATION Chain of amino acids PROTEIN FOLDING Protein Crystallin protein
43 Genomics: Large-Scale Analysis of DNA Sequences An organism s genome is its entire set of genetic instructions Genomics is the study of sets of genes within and between species Proteomics refers to the study of sets of proteins and their properties The entire set of proteins expressed by a cell or group of cells is called a proteome
44 High-throughput technology refers to tools that can analyze biological samples very rapidly Bioinformatics is the use of computational tools to store, organize, and analyze the huge volume of data Interdisciplinary research teams aim to learn how activities of all proteins and noncoding RNAs are coordinated in cells and whole organisms
45 Theme: Life Requires the Transfer and Transformation of Energy and Matter Input of energy, mainly from the sun, and transformation of energy from one form to another make life possible Plants and other photosynthetic organisms convert the energy of sunlight into the chemical energy of sugars This chemical energy of these producers is then passed to consumers that feed on the producers
46 Energy flows through an ecosystem, generally entering as light and exiting as heat Chemical elements are recycled within an ecosystem
47 Figure 1.9 ENERGY FLOW L Chemicals pass to organisms that eat the plants. Light energy comes from the sun. Plants take up chemicals from the soil and air. Plants convert sunlight to chemical energy. Organisms use chemical energy to do work. Heat is lost from the ecosystem. Decomposers return chemicals to the soil. Chemicals
48 Theme: Organisms Interact with Other Organisms and the Physical Environment Every organism interacts with other organisms and with physical factors in its environment Both organisms and their environments are affected by the interactions between them For example, a plant takes up water and minerals from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air; the tree releases oxygen to the air, and roots help form soil
49 Interactions between organisms include those that benefit both organisms and those in which both organisms are harmed Interactions affect individual organisms and the way that populations evolve over time
50 Figure 1.10
51 Scientists calculate that the CO 2 that human activities have added to the atmosphere has increased the average temperature of the planet by 1 C since 1900 Climate change is a directional change in global climate that lasts three decades or more Climate change has already affected organisms and their habitats all over the planet
52 Figure 1.11
53 Evolution, the Core Theme of Biology Evolution makes sense of everything we know about living organisms Evolution explains patterns of unity and diversity in living organisms Similar traits among organisms are explained by descent from common ancestors Differences among organisms are explained by the accumulation of heritable changes
54 Concept 1.2: The Core Theme: Evolution accounts for the unity and diversity of life The remarkably diverse forms of life on this planet arose by evolutionary processes
55 Classifying the Diversity of Life Humans group diverse items according to their similarities and relationships to each other Careful analysis of form and function has been used to classify life-forms New methods of assessing species relationships, especially comparisons of DNA sequences, have led to a reevaluation of larger groupings
56 Biologists currently divide the kingdoms of life into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya Domains Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes
57 Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotic organisms Domain Eukarya includes three multicellular kingdoms: Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia Plants produce their own food by photosynthesis Fungi absorb nutrients Animals ingest their food
58 Figure m 2 m (a) Domain Bacteria (b) Domain Archaea (c) Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia 100 m Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Fungi Protists
59 Figure m (a) Domain Bacteria
60 Figure m (b) Domain Archaea
61 Figure (c) Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia 100 m Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Fungi Protists
62 Figure a (c) Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae
63 Figure b (c) Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi
64 Figure c (c) Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia
65 Figure d (c) Domain Eukarya Protists 100 m
66 Unity in the Diversity of Life A striking unity underlies the diversity of life For example, DNA is the universal genetic language common to all organisms Similarities between organisms are evident at all levels of the biological hierarchy Fossils and other evidence document the evolution of life on Earth over billions of years
67 Figure 1.13
68 Charles Darwin and the Theory of Natural Selection Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859 Darwin made two main points Species showed evidence of descent with modification from common ancestors Natural selection is the mechanism behind descent with modification Darwin s theory captured the duality of unity and diversity
69 Figure 1.14
70 Figure
71 Figure
72 Figure 1.15 American flamingo European robin Gentoo penguin
73 Figure American flamingo
74 Figure European robin
75 Figure Gentoo penguin
76 Darwin observed that Individuals in a population vary in their traits, many of which are heritable More offspring are produced than survive, and competition is inevitable Species generally suit their environment
77 Darwin inferred that Individuals that are best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce Over time, more individuals in a population will have the advantageous traits
78 In other words, the environment selects for the propagation of beneficial traits Darwin called this process natural selection
79 Figure 1.16-s1 Population with varied inherited traits
80 Figure 1.16-s2 Population with varied inherited traits Elimination of individuals with certain traits
81 Figure 1.16-s3 Population with varied inherited traits Elimination of individuals with certain traits Reproduction of survivors
82 Figure 1.16-s4 Population with varied inherited traits Elimination of individuals with certain traits Reproduction of survivors Increased frequency of traits that enhance survival
83 Video: Albatross Courtship
84 Video: Soaring Hawk
85 Video: Boobies Courtship
86 Video: Galápagos Islands
87 Video: Marine Iguana
88 Video: Sea Lion
89 Video: Tortoise
90 The Tree of Life The forelimb of a human, foreleg of a horse, flipper of a whale, and wing of a bat all share a common skeletal architecture The shared anatomy of mammalian limbs reflects inheritance of a limb structure from a common ancestor The diversity of mammalian limbs results from modification by natural selection over millions of years
91 Darwin proposed that natural selection could cause an ancestral species to give rise to two or more descendent species For example, the finch species of the Galápagos Islands are descended from a common ancestor Evolutionary relationships are often illustrated with treelike diagrams that show ancestors and their descendants
92 Figure 1.17 ANCESTRAL FINCH Green warbler finch Certhidea olivacea (insect-eater) Vegetarian finch Platyspiza crassirostris (fruit-eater) Woodpecker finch Camarhynchus pallidus (insect-eater) Small tree finch Camarhynchus parvulus (insect-eater) Common cactus finch Geospiza scandens (cactus-eater) Large ground finch Geospiza magnirostris (seed-eater)
93 Concept 1.3: In studying nature, scientists form and test hypotheses The word science is derived from a Latin verb meaning to know Inquiry is the search for information and explanation The scientific process includes making observations, forming logical hypotheses, and testing them
94 Exploration and Discovery Biology begins with careful observations Biologists describe natural structures and processes By reading about and understanding past studies, scientists can build on the foundations of existing knowledge
95 Gathering and Analyzing Data Recorded observations are called data Data fall into two categories Qualitative data, or descriptions rather than measurements For example, Jane Goodall s observations of chimpanzee behavior Quantitative data, or recorded measurements, which are sometimes organized into tables and graphs
96 Figure 1.18
97 Figure
98 Figure
99 Inductive reasoning draws conclusions through the logical process of induction Through induction, generalizations are drawn from a large number of observations For example, all organisms are made of cells was based on two centuries of microscopic observations
100 Forming and Testing Hypotheses In science, a hypothesis is a rational accounting for a set of observations, guided by inductive reasoning It is an explanation on trial A scientific hypothesis leads to predictions that can be tested with additional observations or an experiment An experiment is a scientific test, often carried out under controlled conditions
101 The initial observations may lead to multiple hypotheses to be tested For example Observation: Your desk lamp doesn t work Question: Why doesn t your lamp work? Hypothesis 1: The bulb is burnt out Hypothesis 2: The lamp is broken Both these hypotheses are testable
102 Deductive Reasoning Deductive reasoning extrapolates from general premises to specific predictions The hypothesis is then tested experimentally
103 A hypothesis can never be conclusively proven to be true because we can never test all the alternatives Hypotheses gain credibility by surviving multiple attempts at falsification, while alternative hypotheses are eliminated by testing
104 Questions That Can and Cannot Be Addressed by Science A hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable For example, hypotheses involving supernatural explanations cannot be tested Such explanations are outside the bounds of science
105 The Flexibility of the Scientific Process Very few scientific studies adhere rigidly to the sequence of steps typically used to describe the scientific method
106 Figure 1.19 EXPLORATION AND DISCOVERY SOCIETAL BENEFITS AND OUTCOMES FORMING AND TESTING HYPOTHESES COMMUNITY ANALYSIS AND FEEDBACK
107 Figure T Testing Ideas Forming hypotheses Predicting results Doing experiments and/or making observations Gathering data Analyzing results Interpreting Results Data may Support a hypothesis Contradict a hypothesis Inspire a revised or new hypothesis
108 Figure Observing nature Asking questions Reading the scientific literature
109 Figure Developing technology Informing policy Solving problems Building knowledge
110 Figure Feedback and peer review Replication of findings Publication Consensus building
111 Figure
112 Figure
113 Figure
114 Figure
115 A Case Study in Scientific Inquiry: Investigating Coat Coloration in Mouse Populations Color patterns in animals vary widely in nature, even among members of the same species Two mouse populations that reside in different habitats have different coat colors What accounts for the match between the coat colors of the mice and the color of the sand or soil in their habitats?
116 Figure 1.20 Beach population Florida Inland population GULF OF MEXICO Beach population Inland population
117 Figure
118 Figure
119 Figure
120 Figure
121 The natural predators of the mice are all visual hunters Francis Bertody Sumner hypothesized that the color patterns in the mice had evolved as adaptations that camouflage the mice to protect them from predation Recently Hopi Hoekstra and a group of her students tested the predictions of this hypothesis
122 Prediction: Mice with coloration that does not match the habitat should suffer heavier predation than the native, well-matched mice The group built many models of mice that resembled either beach or inland mice and placed equal numbers of models randomly in both habitats The results showed that the camouflaged models suffered much lower rates of predation than the mismatched ones
123 Figure 1.21 Percentage of attacked models Results 100 Beach habitat Inland habitat 50 0 Light models Dark models Light models Dark models Camouflaged (control) Non-camouflaged (experimental) Non-camouflaged (experimental) Camouflaged (control)
124 Figure Camouflaged (control)
125 Figure Non-camouflaged (experimental)
126 Figure Non-camouflaged (experimental)
127 Figure Camouflaged (control)
128 Experimental Variables and Controls A controlled experiment compares an experimental group (the non-camouflaged mice) with a control group (the camouflaged mice) The factor that is manipulated and the effect of the factor on the system are both experimental variables The factor manipulated by the researchers color is called the independent variable The effect of the manipulated factor amount of predation is called the dependent variable
129 Researchers usually control unwanted variables not by eliminating them, but by canceling them out using control groups
130 Theories in Science In the context of science, a theory is Broader in scope than a hypothesis General enough to lead to new testable hypotheses Supported by a large body of evidence in comparison to a hypothesis
131 Science as a Social Process Anyone who becomes a scientist benefits from the rich storehouse of discoveries by others who have come before Most scientists work in teams Scientists working in the same research field often check one another s claims by attempting to confirm observations or repeat experiments
132 The relationship between science and society is clearer when technology is considered The goal of technology is to apply scientific knowledge for some specific purpose Science and technology are interdependent
133 Figure 1.UN01
134 Figure 1.UN02-1 Number of mice caught Number of mice caught Light coat Dark coat Light coat Dark coat Full moon No moon Full moon No moon A: Light-colored soil B: Dark-colored soil Data from D. W. Kaufman, Adaptive coloration in Peromyscus polionotus: Experimental selection by owls, Journal of Mammalogy 55: (1974).
135 Figure 1.UN02-2
136 Figure 1.UN03 ENERGY FLOW
137 Figure 1.UN03-1
138 Figure 1.UN03-2
139 Figure 1.UN03-3 ENERGY FLOW
140 Figure 1.UN03-4
141 Figure 1.UN03-5
142 Figure 1.UN04
AP Biology: Chapter 1: Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology
 AP Biology: Chapter 1: Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Overview: Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, a beach
AP Biology: Chapter 1: Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Overview: Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, a beach
1 Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 1 Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview:
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 1 Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview:
Theme: New Properties Emerge at Successive Levels of Biological Organization. Concept 1.1: Studying the diverse forms of life reveals common themes
 Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions How does a single cell develop into an organism? How does the human mind work? How do different forms of life in a forest interact? Chapter
Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions How does a single cell develop into an organism? How does the human mind work? How do different forms of life in a forest interact? Chapter
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
1/17/2017. General Biology I SPRING 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# What is wrong with this picture? is the flu virus a living organism?
 General Biology I SPRING 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18581 What is wrong with this picture? is the flu virus a living organism? 1 Figure 1.1 How is the dandelion adapted to its environment? the seeds
General Biology I SPRING 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18581 What is wrong with this picture? is the flu virus a living organism? 1 Figure 1.1 How is the dandelion adapted to its environment? the seeds
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Welcome to BIOSC 041, Evolution & Animal Biology Prof. Taylor
 Welcome to BIOSC 041, Evolution & Animal Biology Prof. Taylor Today s lecture: Intro/syllabus Chapter 1 Tonight s lab: Graphing & data analysis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman
Welcome to BIOSC 041, Evolution & Animal Biology Prof. Taylor Today s lecture: Intro/syllabus Chapter 1 Tonight s lab: Graphing & data analysis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by
BIOLOGY. Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Inquiring
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Inquiring
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1. Biology: Exploring Life. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Richard
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Richard
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1 Overview: Inquiring About Life Evolution Biology Concept 1.1: The themes of this book make connections across different areas of biology
 Overview: Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, the ghost plant is adapted to conserving water; this helps it to survive in the crevices
Overview: Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, the ghost plant is adapted to conserving water; this helps it to survive in the crevices
1. Unifying Themes in Biology
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life 1. Unifying Themes in Biology 2. Evolution and the Diversity of Life 3. The Process of Scientific Inquiry 1. Unifying Themes in Biology Chapter Reading
CHAPTER 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life 1. Unifying Themes in Biology 2. Evolution and the Diversity of Life 3. The Process of Scientific Inquiry 1. Unifying Themes in Biology Chapter Reading
Chapter 1. Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry. Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Objectives (Chapter 1; 1 st set of objectives): Students will differentiate
Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Objectives (Chapter 1; 1 st set of objectives): Students will differentiate
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction Snowy owls exhibit
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction Snowy owls exhibit
Chapter 1 Themes of Biology
 Chapter 1 Themes of Biology Overview: Inquiring About the World of Life Evolution is the process of change that has transformed life on Earth Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions
Chapter 1 Themes of Biology Overview: Inquiring About the World of Life Evolution is the process of change that has transformed life on Earth Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
Introduction: AP Biology
 Chapter 1 Introduction: AP Biology Major Themes of AP Biology Biology consists of more than memorizing factual details Unifying constructs in AP Biology: Science as a Process Evolution Energy Transfer
Chapter 1 Introduction: AP Biology Major Themes of AP Biology Biology consists of more than memorizing factual details Unifying constructs in AP Biology: Science as a Process Evolution Energy Transfer
Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
 Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result
Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result
Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
 Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result
Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Inquiring About Life An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Objectives: You will Identify
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Objectives: You will Identify
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
BSC 1010C Biology I. Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1
 BSC 1010C Biology I Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 Objectives Distinguish among the three domains of life. Distinguish between the Levels of Biological Organization. Note the differences in the
BSC 1010C Biology I Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 Objectives Distinguish among the three domains of life. Distinguish between the Levels of Biological Organization. Note the differences in the
Chapter 1. Introduction to Biology. The cell is the basic unit of life 1665-Robert Hooke- 1 st discovered cells in cork. The Seven Properties of Life
 The Science of Life Student Learning Goals - Biology Science and Life SC.912.N.1.1 Goal: Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, & earth/space
The Science of Life Student Learning Goals - Biology Science and Life SC.912.N.1.1 Goal: Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, & earth/space
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 1. Introduction: Biology Today. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey
BIOLOGY. The Path to Success. Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry. Outline. Course Overview. Exams.
 1 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Dr Burns NVC Outline Introduction Class organization, exams, grading
1 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Dr Burns NVC Outline Introduction Class organization, exams, grading
Chp 1 Biology: Exploring Life 1.10 Biology, Technology, & Society are Connected
 Chp 1 Biology: Exploring Life 1.10 Biology, Technology, & Society are Connected What current Biology-related news topics have you read/heard about? 1 1.1 All Life Forms Share Common Properties What common
Chp 1 Biology: Exploring Life 1.10 Biology, Technology, & Society are Connected What current Biology-related news topics have you read/heard about? 1 1.1 All Life Forms Share Common Properties What common
Mother of pearl (Ghost plant) Chapter 1. The Process of Science and Themes in Study of Life
 Mother of pearl (Ghost plant) Chapter 1 The Process of Science and Themes in Study of Life Evolution An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, the ghost plant
Mother of pearl (Ghost plant) Chapter 1 The Process of Science and Themes in Study of Life Evolution An organism s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution For example, the ghost plant
Life at Its Many Levels
 Slide 1 THE SCOPE OF BIOLOGY Biology is the scientific study of life Slide 2 Life at Its Many Levels Biologists explore life at levels ranging from the biosphere to the molecules that make up cells Slide
Slide 1 THE SCOPE OF BIOLOGY Biology is the scientific study of life Slide 2 Life at Its Many Levels Biologists explore life at levels ranging from the biosphere to the molecules that make up cells Slide
Chapter 1. Introduction: Biology Today. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
the Foundations of Biology
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Key Concepts 1.1 The study of life reveals common themes 1.2 The Core Theme: Evolution accounts for the unity and diversity of life 1.3
CHAPTER 1 Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Key Concepts 1.1 The study of life reveals common themes 1.2 The Core Theme: Evolution accounts for the unity and diversity of life 1.3
Welcome to AP BIOLOGY!!!! NOTES: Chapter 1 Exploring Life
 Welcome to AP BIOLOGY!!!! NOTES: Chapter 1 Exploring Life The phenomenon we call life defies a simple, onesentence definition Exploring LIFE: We recognize life by what living things DO Some Properties
Welcome to AP BIOLOGY!!!! NOTES: Chapter 1 Exploring Life The phenomenon we call life defies a simple, onesentence definition Exploring LIFE: We recognize life by what living things DO Some Properties
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1)
 EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
A.P. Biology Lecture Notes Unit 1A - Themes of Life
 A.P. Biology Lecture Notes Unit 1A - Themes of Life I. Why study biology? A. Life is attractive, diverse, and interesting. B. The study of biology is enormous in scope C. Organisms span size scales from
A.P. Biology Lecture Notes Unit 1A - Themes of Life I. Why study biology? A. Life is attractive, diverse, and interesting. B. The study of biology is enormous in scope C. Organisms span size scales from
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
Introduction to the Study of Life
 1 Introduction to the Study of Life Bio 103 Lecture GMU Dr. Largen 2 Outline Biology is the science of life The process of science Evolution, unity and diversity Core principles of biology 3 The Science
1 Introduction to the Study of Life Bio 103 Lecture GMU Dr. Largen 2 Outline Biology is the science of life The process of science Evolution, unity and diversity Core principles of biology 3 The Science
Campbell Essential Biology, 5e (Simon/Yeh) Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Essential Biology, 5e (Simon/Yeh) Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today Multiple-Choice Questions 1) In what way(s) is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture? A) by helping
Campbell Essential Biology, 5e (Simon/Yeh) Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today Multiple-Choice Questions 1) In what way(s) is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture? A) by helping
Test Bank for Biology 7th edition by Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Test Bank for Biology 7th edition by Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-biology-7th-edition-bycampbell-and-reece/ Chapter 1: Exploring
Test Bank for Biology 7th edition by Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-biology-7th-edition-bycampbell-and-reece/ Chapter 1: Exploring
and just what is science? how about this biology stuff?
 Welcome to Life on Earth! Rob Lewis 512.775.6940 rlewis3@austincc.edu 1 The Science of Biology Themes and just what is science? how about this biology stuff? 2 1 The Process Of Science No absolute truths
Welcome to Life on Earth! Rob Lewis 512.775.6940 rlewis3@austincc.edu 1 The Science of Biology Themes and just what is science? how about this biology stuff? 2 1 The Process Of Science No absolute truths
Chapter 1. Introduction: Biology Today. THE SCOPE OF LIFE The Properties of Life. Properties of Life: Biology is the scientific study of life.
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today 1 PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today 1 PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Lecture Outline. Defining life by properties of being alive (7)
 Lecture Outline Defining life by properties of being alive (7) Order of structural hierarchy levels of the living world Ascending/up & descending/down emergent properties Unifying themes Form and function
Lecture Outline Defining life by properties of being alive (7) Order of structural hierarchy levels of the living world Ascending/up & descending/down emergent properties Unifying themes Form and function
Chapter 1: Biology Today
 General Biology Chapter 1: Biology Today Introduction Dr. Jeffrey P. Thompson Text: Essential Biology Biology Is All Around US! What is Biology? The study of life bio- meaning life; -ology meaning study
General Biology Chapter 1: Biology Today Introduction Dr. Jeffrey P. Thompson Text: Essential Biology Biology Is All Around US! What is Biology? The study of life bio- meaning life; -ology meaning study
Chapter 1. Invitation to Biology
 Chapter 1 Invitation to Biology Biology Is the scientific study of life Is a quest, an ongoing inquiry about the nature of life Life s levels of organization Atom - Fundamental unit of all substances Molecule
Chapter 1 Invitation to Biology Biology Is the scientific study of life Is a quest, an ongoing inquiry about the nature of life Life s levels of organization Atom - Fundamental unit of all substances Molecule
1. The basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms is the A) aggregate. B) organelle. C) organism. D) membrane. E) cell.
 Name: Date: Test File Questions 1. The basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms is the A) aggregate. B) organelle. C) organism. D) membrane. E) cell. 2. A cell A) can be composed
Name: Date: Test File Questions 1. The basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms is the A) aggregate. B) organelle. C) organism. D) membrane. E) cell. 2. A cell A) can be composed
Campbell Essential Biology, 4/e (Simon/Reece/Dickey)
 Campbell Essential Biology, 4/e (Simon/Reece/Dickey) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Using the branching tree of life for
Campbell Essential Biology, 4/e (Simon/Reece/Dickey) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Using the branching tree of life for
Chapter 1 Scientific Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Scientific Study of Life Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. 2012 No reproduction Pearson or Education, distribution without Inc. the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Chapter 1 Scientific Study of Life Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. 2012 No reproduction Pearson or Education, distribution without Inc. the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
98 Washington State K-12 Science Learning Standards Version 1.2
 EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
Chapter 1. How Do Biologists Study Life?
 Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life The introduction to the study of biology in Chapter 1 highlights seven book -wide themes, with special emphasis on the core theme of evolution. How scientists
Chapter 1 Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life The introduction to the study of biology in Chapter 1 highlights seven book -wide themes, with special emphasis on the core theme of evolution. How scientists
Theme: New Properties Emerge at Successive Levels of Biological Organization
 Theme: New Properties Emerge at Successive Levels of Biological Organization Organization The study of life on Earth extends from the microscopic scale of the molecules and cells that make up organisms
Theme: New Properties Emerge at Successive Levels of Biological Organization Organization The study of life on Earth extends from the microscopic scale of the molecules and cells that make up organisms
Case study: spider mimicry
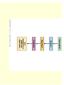 Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped on fly) Case study: spider mimicry Control group (untreated flies) Experimental group (wing markings masked) Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped
Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped on fly) Case study: spider mimicry Control group (untreated flies) Experimental group (wing markings masked) Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped
We are living in a golden age of biology. Scientists are studying a myriad of questions that are relevant to our lives.
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 1. Introduction: Biology Today. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Fundamentals of Biology Valencia College BSC1010C
 1 Fundamentals of Biology Valencia College BSC1010C 1 Studying Life Chapter objectives: What Is Biology? Is All Life on Earth Related? How Do Biologists Investigate Life? How Does Biology Influence Public
1 Fundamentals of Biology Valencia College BSC1010C 1 Studying Life Chapter objectives: What Is Biology? Is All Life on Earth Related? How Do Biologists Investigate Life? How Does Biology Influence Public
Organizing Diversity Taxonomy is the discipline of biology that identifies, names, and classifies organisms according to certain rules.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Outline 1.1 Introduction to AP Biology 1.2 Big Idea 1: Evolution 1.3 Big Idea 2: Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 1.4 Big Idea 3: Information Storage, Transmission, and Response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Outline 1.1 Introduction to AP Biology 1.2 Big Idea 1: Evolution 1.3 Big Idea 2: Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 1.4 Big Idea 3: Information Storage, Transmission, and Response
Pick up a composition notebook Choose a seat Cut out the calendar and contents pages
 1. 2. 3. Pick up a composition notebook Choose a seat Cut out the calendar and contents pages p o t p a l a t Ge the om. o m r o fr age r o t s Login to a laptop Review the syllabus Join Remind NOW!!!
1. 2. 3. Pick up a composition notebook Choose a seat Cut out the calendar and contents pages p o t p a l a t Ge the om. o m r o fr age r o t s Login to a laptop Review the syllabus Join Remind NOW!!!
Chapter 1. Introduction: Biology Today. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Third Edition
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Third Edition
Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero 1. Go to: http://campbellbiology.com/
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero 1. Go to: http://campbellbiology.com/
Chapter 1 Exploring Life Lecture Outline
 Overview: Biology s Most Exciting Era Chapter 1 Exploring Life Lecture Outline Biology is the scientific study of life. You are starting your study of biology during its most exciting era. The largest
Overview: Biology s Most Exciting Era Chapter 1 Exploring Life Lecture Outline Biology is the scientific study of life. You are starting your study of biology during its most exciting era. The largest
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In what way(s) is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture? A) by
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In what way(s) is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture? A) by
Introduction: Biology Today
 Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today 1 THE SCOPE OF LIFE The Properties of Life Biology is the scientific study of life. What is life? The study of biology encompasses a wide scale of size and a huge
Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today 1 THE SCOPE OF LIFE The Properties of Life Biology is the scientific study of life. What is life? The study of biology encompasses a wide scale of size and a huge
Grade 7 Science Learning Standards
 Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Chapter 1 Exploring Life. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 1 Exploring Life Lecture Outline Overview: Biology s Most Exciting Era Biology is the scientific study of life. You are starting your study of biology during its most exciting era. The largest
Chapter 1 Exploring Life Lecture Outline Overview: Biology s Most Exciting Era Biology is the scientific study of life. You are starting your study of biology during its most exciting era. The largest
Link full download:download here Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of biology, and Scientific Inquiry
 Link full download:download here Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of biology, and Scientific Inquiry 1) Cells are. A) only found in pairs, because single cells cannot exist
Link full download:download here Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of biology, and Scientific Inquiry 1) Cells are. A) only found in pairs, because single cells cannot exist
THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY SECTION 1-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank.
 SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
An Introduction to the Science of Botany. Chapter 1
 An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
6 th Grade Life Science Strand 3: Characteristics and Interactions of Living Organisms
 Middle School Life Science Standards There are 15 standards that encompass the proposed middle school life science standards. The new standards are listed 4 times to match the four times life science is
Middle School Life Science Standards There are 15 standards that encompass the proposed middle school life science standards. The new standards are listed 4 times to match the four times life science is
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life An Introduction to the Science of Life: Chapter Learning Outcomes 1.1) Describe the properties of life common to all living things. (Module
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life An Introduction to the Science of Life: Chapter Learning Outcomes 1.1) Describe the properties of life common to all living things. (Module
Chapter 1: Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
 Name Period Begin your study of biology this year by reading Chapter 1. It will serve as a reminder about biological concepts that you may have learned in an earlier course and give you an overview of
Name Period Begin your study of biology this year by reading Chapter 1. It will serve as a reminder about biological concepts that you may have learned in an earlier course and give you an overview of
2/16/2018. Chapter 1. Essential Biology with Physiology. The Process of Science (2 of 2) Introduction: Biology Today. The Scientific Study of Life
 Essential Biology with Physiology Fifth Edition Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today The Process of Science (2 of 2) This basic human drive to understand our natural world is manifest in two main scientific
Essential Biology with Physiology Fifth Edition Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today The Process of Science (2 of 2) This basic human drive to understand our natural world is manifest in two main scientific
Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Life on Earth
 Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Life on Earth Characteristics of Living Things What are the characteristics of living things? Living things: ORGANISMS 1. Living Things are Organized subatomic particles
Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Life on Earth Characteristics of Living Things What are the characteristics of living things? Living things: ORGANISMS 1. Living Things are Organized subatomic particles
CH 16: Evolution of Population
 CH 16: Evolution of Population 16.1 Genes and Variation A. Introduction 1. Darwin s theory of evolution by natural selection explained how 2. What Darwin did not know was how were passed down through each
CH 16: Evolution of Population 16.1 Genes and Variation A. Introduction 1. Darwin s theory of evolution by natural selection explained how 2. What Darwin did not know was how were passed down through each
Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry 1 Figure 1.1 What can this beach mouse (Peromyscus polionotus) teach us about biology? Key Concepts Inquiring About Life 1.1 The study of life reveals
Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry 1 Figure 1.1 What can this beach mouse (Peromyscus polionotus) teach us about biology? Key Concepts Inquiring About Life 1.1 The study of life reveals
Study of Life. Intro to AP Biology
 Study of Life Intro to 2007-2008 Big Ideas Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks
Study of Life Intro to 2007-2008 Big Ideas Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks
Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Key Concepts 1.1 The study of life reveals common themes 1.2 The Core Theme: Evolution accounts for the unity and diversity of life 1.3 In studying
1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Key Concepts 1.1 The study of life reveals common themes 1.2 The Core Theme: Evolution accounts for the unity and diversity of life 1.3 In studying
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
Why Biology?? General (Comparative) Biology. Diversity is a hallmark of life Biologists explore life across its great diversity of species
 General (Comparative) Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 Thursday: 13:30pm 15:00pm; Ro-# H77-201 " Friday: 13:30pm - 15:00pm; Ro-# H77-201" Why Biology?? Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese
General (Comparative) Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 Thursday: 13:30pm 15:00pm; Ro-# H77-201 " Friday: 13:30pm - 15:00pm; Ro-# H77-201" Why Biology?? Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese
Unit # - Title Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry
 Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry What is Biology? What is Science? What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? How do the rules
Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry What is Biology? What is Science? What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? How do the rules
Performance Indicators: Students who demonstrate this understanding can:
 OVERVIEW The academic standards and performance indicators establish the practices and core content for all Biology courses in South Carolina high schools. The core ideas within the standards are not meant
OVERVIEW The academic standards and performance indicators establish the practices and core content for all Biology courses in South Carolina high schools. The core ideas within the standards are not meant
Define: Alleles. Define: Chromosome. In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways.
 Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Campbell Biology, 11e (Urry) Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
 Campbell Biology, 11e (Urry) Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Cells are. A) only found in pairs, because single cells cannot exist independently
Campbell Biology, 11e (Urry) Chapter 1 Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Cells are. A) only found in pairs, because single cells cannot exist independently
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY Telephone Number: (845) ext Fax Number: (845)
 Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Introduction to Biology
 Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology
 1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Kentucky Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program
 Kentucky Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WILD PACK: FASTEST CUTTERS Program description: Using inquiry skills, students will observe the leaf cutter ant colony in the Zoo s Insect World to
Kentucky Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WILD PACK: FASTEST CUTTERS Program description: Using inquiry skills, students will observe the leaf cutter ant colony in the Zoo s Insect World to
Biology 10 th Grade. Textbook: Biology, Miller and Levine, Pearson (2010) Prerequisite: None
 Biology 10 th Grade SCI 401, 402 Biology 1 credit 5 days a week; 2 semesters Taught in English Biology - The Study of Life! This is a required course for all 10 th grade students in both the Mexican and/or
Biology 10 th Grade SCI 401, 402 Biology 1 credit 5 days a week; 2 semesters Taught in English Biology - The Study of Life! This is a required course for all 10 th grade students in both the Mexican and/or
4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]
![4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1] 4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]](/thumbs/84/91138454.jpg) Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Unit 2: ECE/AP Biology Cell Biology 12 class meetings. Essential Questions. Enduring Understanding with Unit Goals
 Essential Questions How does cellular structure impact the function of life? How does energy flow freely through biological systems? Why is cellular reproduction essential to life? Enduring Understanding
Essential Questions How does cellular structure impact the function of life? How does energy flow freely through biological systems? Why is cellular reproduction essential to life? Enduring Understanding
Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution.
 The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
Use evidence of characteristics of life to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Oklahoma Academic Standards for Biology I
 A Correlation of Miller & Levine Biology To the Oklahoma Academic Standards A Correlation of, BIOLOGY I HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1 Students who demonstrate for
A Correlation of Miller & Levine Biology To the Oklahoma Academic Standards A Correlation of, BIOLOGY I HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1 Students who demonstrate for
AP Curriculum Framework with Learning Objectives
 Big Ideas Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. AP Curriculum Framework with Learning Objectives Understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over
Big Ideas Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. AP Curriculum Framework with Learning Objectives Understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over
Companion to Cells, Heredity & Classification Student Resources
 Companion to Cells, Heredity & Classification Student Resources The 21st Century Center for Research and Development in Cognition and Science Instruction The CaSEbook Companion: Student Resource Book
Companion to Cells, Heredity & Classification Student Resources The 21st Century Center for Research and Development in Cognition and Science Instruction The CaSEbook Companion: Student Resource Book
Evolution. Taxonomy. Domains. Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Evolution Taxonomy Domains Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Evolution unifying theme in biology Explains Both similarities and differences among living things How groups of organisms are related How organisms
Evolution Taxonomy Domains Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Evolution unifying theme in biology Explains Both similarities and differences among living things How groups of organisms are related How organisms
