Biology 122L Invertebrate zoology lab Molluscan diversity lab guide Author: Allison J. Gong foot radula shell visceral mass mantle cavity
|
|
|
- Julia Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
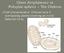
1 Page 1 of 1 Biology 122L Invertebrate zoology lab Molluscan diversity lab guide Author: Allison J. Gong Figure source: Brusca and Brusca, Invertebrates, 2nd edition. Sinauer Associates, Inc. The Mollusca comprise a huge taxon, second only to the Arthropoda in terms of number of extant species. They are successful in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial habitats. There are probably close to 100,000 species of living molluscs, including such diverse forms as snails, clams, slugs, and squids. There are also some 35,000 fossil species. You have already dissected two common local marine molluscs a snail (Chlorostoma funebralis) and a bivalve (Mytilus californianus) and should be familiar with their internal and external anatomy. This understanding will help you make sense of the diversity of body forms you will observe in representatives of other molluscan taxa. With any luck I will have specimens from four of the seven extant molluscan classes for you: Polyplacophora, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda, and Gastropoda. In strictly pedagogical terms, we can use a non-existent creature called a Hypothetical Ancestral Mollusc (HAM) as a starting point on which natural selection has acted to produce the variety of molluscan body plans that we see today. This HAM was a benthic animal adapted for life on hard surfaces, crawling around on its muscular ventral foot and using its radula to scrape algal and detrital films. It was poorly cephalized with an anterior head and had a single, cap-shaped shell that could be clamped down to protect the visceral mass and other soft body parts. The mantle cavity enclosed several pairs of bipectinate ctenidia, or gills. See pages in your textbook (Ruppert et al, 2004) for a diagram and description of the HAM. As you make your observations, keep in mind these characteristics of the HAM. In general, these are the features that biologists use to group all molluscs into a single phylum, although you will find them modified in different ways among the animals that you observe today. How are these modifications (adaptations, right?) reflected in the current taxonomy of the group? Don't forget that the reduction of a given feature can be just as adaptive as its elaboration. In living specimens, the most easily observed of these features are the shell, foot, and (in some cases) the mantle. Other structures, such as the ctenidium and radula, are difficult to observe without dissection, and you will probably not be able to see them in the live animals available to you in this lab. However, this should not keep you from speculating about the nature of these structures. What can you infer from the fact that you CAN'T see them from the outside? Does this say anything about their function? Or about their "importance" to the animal?
2 Page 2 of 2 General molluscan features The diagram below demonstrates how some of the major features of the Phylum Mollusca have been modified in the most frequently encountered classes. Which of these adaptations can you detect in the animals you observe? Annotation for this lab (and all diversity labs) should include comparisons of, for example, shell morphology in bivalves vs. prosobranchs vs. pulmonates vs. cephalopods.
3 Page 3 of 3 Observations of the shell The ancestral molluscan shell was a simple cap- or dome-shaped structure that the animal could pull over its body. Modern limpets exemplify this type of shell. The shell is secreted by glands in the dorsal mantle and is attached to the body by a few or several retractor muscles remember the columellar muscle in Chlorostoma? Some molluscs (e.g., snails) can move their shells relative to the position of the body, while others cannot. Some can be entirely enclosed within the shell(s). Others have internal shells, or remnants thereof. Many molluscs have elaborated on this simple shell design, and some have lost it altogether. You will see examples of both extremes. In each case, consider what the shell morphology tells you of the animal's habitat and lifestyle. What are the shell's functions? Are these functions the same in all molluscs? Notice that a chiton's shell consists of eight calcareous plates. How does this design enable the animal to clamp tightly to its substrate? A snail's shell is coiled in what way(s) is this feature adaptive? Nudibranchs and some cephalopods have lost the shell entirely. How do these animals manage without a shell? Do you think they are at a disadvantage compared to their shelled relatives?
4 Page 4 of 4
5 Page 5 of 5 Radula The radula is one of the features unique to molluscs. In ancestral molluscs such as prosobranch gastropods it is used for scraping, and in cephalopods it functions as a conveyor belt to propel food into the mouth. Bivalves have lost the radula entirely. The radula sits atop a cartilaginous structure called the odontophore, and various muscles serve to move it in and out of the buccal cavity. Radular teeth are replaced continually, as they erode while the animal feeds. Radular scraping on a surface covered with algal film often produces a characteristic zig-zag pattern. You can see these patterns on rocks in the intertidal. In addition to scraping algal growth, grazing by the molluscan radula also removes newly settled larvae. Some intertidal animals (e.g., Lottia gigantea) maintain territories of cleared space in this fashion. A large female Lottia actively "farms" her territory, allowing algal scum to grow on one part of her territory while she grazes elsewhere.
6 Page 6 of 6
7 Class Polyplacophora Page 7 of 7
8 Class Gastropoda Page 8 of 8
9 Class Bivalvia Page 9 of 9
10 Anatomy of Loligo opalescens (Class Cephalopoda) Page 10 of 10
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Soft bodied Triploblastic Mouth and Anus True Coelum Bilaterally symmetrical Moist environments
 PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Soft bodied Triploblastic Mouth and Anus True Coelum Bilaterally symmetrical Moist environments http://infusion.allconet.org/webquest/phylummollusca.ht ml Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Soft bodied Triploblastic Mouth and Anus True Coelum Bilaterally symmetrical Moist environments http://infusion.allconet.org/webquest/phylummollusca.ht ml Mollusca Phylum Mollusca includes
Game Ranging / Field Guiding Course. Phylum Mollusca. To gain an understanding of the morphology and biology of common molluscs.
 1 Module # 2 Component # 6 Phylum Mollusca Objectives: To gain an understanding of the morphology and biology of common molluscs. Expected Outcomes: To develop a good understanding of the internal and
1 Module # 2 Component # 6 Phylum Mollusca Objectives: To gain an understanding of the morphology and biology of common molluscs. Expected Outcomes: To develop a good understanding of the internal and
Mollusca: General Characteristics
 Mollusca: General Characteristics Molluscan Taxonomic Classes Polyplacophora Cephalopoda Bivalvia 7,650 sp Other 5 Classes ~1100 Gastropoda Scaphopoda Gastropoda 40,000 sp and Aplacophora Monoplacophora
Mollusca: General Characteristics Molluscan Taxonomic Classes Polyplacophora Cephalopoda Bivalvia 7,650 sp Other 5 Classes ~1100 Gastropoda Scaphopoda Gastropoda 40,000 sp and Aplacophora Monoplacophora
The Mollusks. Phylum Mollusca
 The Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Mollusks- Latin molluscus = soft Coelomates Exhibit cephalization Many mollusks have larval stage- trochophore Hatch from egg case Easily dispersed by ocean currents and tides
The Mollusks Phylum Mollusca Mollusks- Latin molluscus = soft Coelomates Exhibit cephalization Many mollusks have larval stage- trochophore Hatch from egg case Easily dispersed by ocean currents and tides
Zoology Mollusks Block 1 Nabinger
 Mollusks Block 1 Nabinger Purpose This lesson is intended to introduce the phylum Mollusca and to go over its general physical characteristics. It will also be used to setup a comparison between the major
Mollusks Block 1 Nabinger Purpose This lesson is intended to introduce the phylum Mollusca and to go over its general physical characteristics. It will also be used to setup a comparison between the major
2. There are roughly this many described species in the phylum Mollusca. A) 1,000 B) 10,000 C) 100,000 D) 1 million E) 10 million
 Chapter 11 1. Molluscs are A) deuterostomes. B) ecdysozoaons. C) lophotrochozoans. D) chordates. E) hemichordates. 2. There are roughly this many described species in the phylum Mollusca. A) 1,000 B) 10,000
Chapter 11 1. Molluscs are A) deuterostomes. B) ecdysozoaons. C) lophotrochozoans. D) chordates. E) hemichordates. 2. There are roughly this many described species in the phylum Mollusca. A) 1,000 B) 10,000
1 1:29 PM 2 1:29 PM. Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida
 Phylum Mollusca 1 Extant Animalia ~1,300,000 species Parazoa (1.2%) Radiata (0.9%) Protostomia (3.9%) Platyzoa (2.2%) Platyhelminthes (1.9%) Others (0.3%) Lophotrochozoa (9.8%) Mollusca (8.5%) Annelida
Phylum Mollusca 1 Extant Animalia ~1,300,000 species Parazoa (1.2%) Radiata (0.9%) Protostomia (3.9%) Platyzoa (2.2%) Platyhelminthes (1.9%) Others (0.3%) Lophotrochozoa (9.8%) Mollusca (8.5%) Annelida
Sponges. What is the sponge s habitat. What level of organization do sponges have? Type of symmetry?
 Sponges What is the sponge s habitat Marine (few freshwater species) What level of organization do sponges have? Cell level Type of symmetry? None Type of digestive system (none, complete or incomplete)?
Sponges What is the sponge s habitat Marine (few freshwater species) What level of organization do sponges have? Cell level Type of symmetry? None Type of digestive system (none, complete or incomplete)?
Animal Phyla: A Summary. Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. Faculty, College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University
 Animal Phyla: A Summary Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. Faculty, College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University Phylum Platyhelminthes The phylum consists of four classes Turbellaria
Animal Phyla: A Summary Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. Faculty, College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University Phylum Platyhelminthes The phylum consists of four classes Turbellaria
Marine Invertebrates in the Paleozoic Seas
 Marine Invertebrates in the Paleozoic Seas The fossils of shell-bearing invertebrates that inhabited shallow seas are common in Paleozoic rocks. Archaeocyathids, sponges, corals, bryozoans, trilobites,
Marine Invertebrates in the Paleozoic Seas The fossils of shell-bearing invertebrates that inhabited shallow seas are common in Paleozoic rocks. Archaeocyathids, sponges, corals, bryozoans, trilobites,
Molluscs: Gastropod High School Student Edition
 SNIPS AND SNAILS AND GASTROPOD TAILS Molluscs are a clan of closely related animals that includes snails and slugs, clams and oysters, and even squid and octopi. The name comes from the Latin mollus, meaning
SNIPS AND SNAILS AND GASTROPOD TAILS Molluscs are a clan of closely related animals that includes snails and slugs, clams and oysters, and even squid and octopi. The name comes from the Latin mollus, meaning
c. Can you locate the planaria eyespots? What do the eyespots sense?
 Invertebrate Lab II Learning Objectives State the phyla of the organisms discussed in the lab activities Use the characteristics of symmetry, coelom, embryo tissue layers, and patterns of development to
Invertebrate Lab II Learning Objectives State the phyla of the organisms discussed in the lab activities Use the characteristics of symmetry, coelom, embryo tissue layers, and patterns of development to
Carolina Biological Supply Company. SQUID INK-QUIRY: Inquiry-Based Invertebrate Anatomy Through Squid Dissection
 Carolina Biological Supply Company SQUID INK-QUIRY: Inquiry-Based Invertebrate Anatomy Through Squid Dissection Objectives Learn ways to incorporate inquiry methods in dissection laboratories Motivate,
Carolina Biological Supply Company SQUID INK-QUIRY: Inquiry-Based Invertebrate Anatomy Through Squid Dissection Objectives Learn ways to incorporate inquiry methods in dissection laboratories Motivate,
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY
 INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
LOPHOTROCHOZOA. Find the whole mount slide of Bugula or Pectinatella. Add the zoids to the drawing below. Find and add the lophophores.
 LOPHOTROCHOZOA 1.a. Examine specimens of preserved and fossil ectoprocts. How do they resemble colonial hydroids? This kind of similarity between organisms in different clades is called what? 1.b. Find
LOPHOTROCHOZOA 1.a. Examine specimens of preserved and fossil ectoprocts. How do they resemble colonial hydroids? This kind of similarity between organisms in different clades is called what? 1.b. Find
Radiolaria and the Rock Record
 1 Radiolaria and the Rock Record Radiolarians are important constituents of chert at certain times in geologic history. Their tests accumulate on the seafloor today to form radiolarian ooze, particularly
1 Radiolaria and the Rock Record Radiolarians are important constituents of chert at certain times in geologic history. Their tests accumulate on the seafloor today to form radiolarian ooze, particularly
UNIT 8A MARINE SCIENCE: Lower Invertebrates
 UNIT 8A MARINE SCIENCE: Lower Invertebrates Essential Questions: What are the characteristics of the simple body structured organisms? Unit Objectives/I Can Statements: General Invertebrates 1. List taxa
UNIT 8A MARINE SCIENCE: Lower Invertebrates Essential Questions: What are the characteristics of the simple body structured organisms? Unit Objectives/I Can Statements: General Invertebrates 1. List taxa
MOLLUSCAN AQUACULTURE - INTRODUCTION
 1 MOLLUSCAN AQUACULTURE - INTRODUCTION Mollusks have been cultured since the time of the Romans, who in particular, considered oysters a delicacy. The latest aquaculture production figures from FAO (see
1 MOLLUSCAN AQUACULTURE - INTRODUCTION Mollusks have been cultured since the time of the Romans, who in particular, considered oysters a delicacy. The latest aquaculture production figures from FAO (see
Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, and Lophotrochozoa
 1 Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, and Lophotrochozoa Objectives: Be able to distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. Be able to identify which of the phyla
1 Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, and Lophotrochozoa Objectives: Be able to distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. Be able to identify which of the phyla
TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 7: MOLLUSCA
 TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 7: MOLLUSCA Husni Mubarok, S.Pd., M.Si. Tadris Biologi IAIN Jember Some lophotrochozoans develop a structure called a lophophore, a crown of ciliated tentacles that functions
TAKSONOMI HEWAN CHAPTER 7: MOLLUSCA Husni Mubarok, S.Pd., M.Si. Tadris Biologi IAIN Jember Some lophotrochozoans develop a structure called a lophophore, a crown of ciliated tentacles that functions
Natural Sciences 360 Legacy of Life Lecture 07 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida ANIMALIA. (More Similar to Fungi than Plants)
 Natural Sciences 360 Legacy of Life Lecture 07 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida ANIMALIA (More Similar to Fungi than Plants) ANIMAL SIMILARITIES PLANTS FUNGI Cell Walls - Immobile - Often need - substrate - Heterotrophs
Natural Sciences 360 Legacy of Life Lecture 07 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida ANIMALIA (More Similar to Fungi than Plants) ANIMAL SIMILARITIES PLANTS FUNGI Cell Walls - Immobile - Often need - substrate - Heterotrophs
Worms and Mollusks (pp )
 Worms and Mollusks (pp. 424 432) This section tells about the characteristics of the three main groups of worms and the main characteristics of mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, take notes
Worms and Mollusks (pp. 424 432) This section tells about the characteristics of the three main groups of worms and the main characteristics of mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, take notes
Invertebrate Survey Lab
 Answer these questions before lab. 1. What kingdom do all animals fall into? a. Protist b. Animalia c. Eukarya 2. How many phyla of invertebrates are in appendix E on pages 1074-1076? a. 9 b. 7 c. 8 3.
Answer these questions before lab. 1. What kingdom do all animals fall into? a. Protist b. Animalia c. Eukarya 2. How many phyla of invertebrates are in appendix E on pages 1074-1076? a. 9 b. 7 c. 8 3.
Figure 1. Cladogram of the Major Animal Phyla based upon SSU-rRNA
 Biology 4B Laboratory Invertebrates II: Mollusca, Annelida and Nematoda Objectives To understand the basic differences among the invertebrate animal phyla To investigate and learn the obvious external
Biology 4B Laboratory Invertebrates II: Mollusca, Annelida and Nematoda Objectives To understand the basic differences among the invertebrate animal phyla To investigate and learn the obvious external
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA. Introduction. Polyplacophora
 Introduction Polyplacophora PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Because the Mollusca are designated as a phylum we know that all the organisms in the taxon must share a common body plan that they have inherited from the ancestral
Introduction Polyplacophora PHYLUM MOLLUSCA Because the Mollusca are designated as a phylum we know that all the organisms in the taxon must share a common body plan that they have inherited from the ancestral
Invertebrate Diversity
 CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups
 Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups The objective of this lab is to classify all of the fossils from your site to phylum (or to plant group)
Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups The objective of this lab is to classify all of the fossils from your site to phylum (or to plant group)
EJC Honours Day 2013
 EJC Honours Day 2013 A soft-bodied animal, typically with a hard shell of one or more pieces. It is an invertebrate meaning it doesn t have a backbone and is of the phylum (group) Mollusca. The word mollusk
EJC Honours Day 2013 A soft-bodied animal, typically with a hard shell of one or more pieces. It is an invertebrate meaning it doesn t have a backbone and is of the phylum (group) Mollusca. The word mollusk
GY 112L: Earth History Lab
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 9: Paleozoic Part 3 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 3 (Week 9 exercises) 1) Brachiopods 2) Molluscs 3) Alabama
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 9: Paleozoic Part 3 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 3 (Week 9 exercises) 1) Brachiopods 2) Molluscs 3) Alabama
Gen Bio III Lab 7 Animal Diversity Part II
 Gen Bio III Lab 7 Animal Diversity Part II Introduction Last lab you were introduced to animals and provided with some ways to think about them (body plan, phylogenies and trait mapping, adaptations for
Gen Bio III Lab 7 Animal Diversity Part II Introduction Last lab you were introduced to animals and provided with some ways to think about them (body plan, phylogenies and trait mapping, adaptations for
Mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills. b. invertebrate c. segmented body d. unsegmented body
 Name Date Class Mollusks This section descnbes the features of mollusks aud identifies three mapr groups of mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills As vou read, compare and contrast the three groups of mollusks
Name Date Class Mollusks This section descnbes the features of mollusks aud identifies three mapr groups of mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills As vou read, compare and contrast the three groups of mollusks
Today: Animal Body Plans. Animal Body Plans: The Gut. The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Animal Body Plans: Symmetry
 Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
2. Examine the external anatomy of the squid and identify the following structures: tentacles, arms, fins, siphon, mantle, eyes and collar.
 Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Systematic summary for the phylum Mollusca :
 Lecture 2 PHYLUM MOLLUSCA The molluscs rival the arthropods in their diversity of body forms and sizes, as well as their ecological success. The phylum also provides some of the most familiar animals,
Lecture 2 PHYLUM MOLLUSCA The molluscs rival the arthropods in their diversity of body forms and sizes, as well as their ecological success. The phylum also provides some of the most familiar animals,
Recent Aedvances in Cephalopod Systematics
 Recent Aedvances in Cephalopod Systematics Kotaro TSUCHIYA Lab. Invertebrate Zoology What the Cephalopoda Paleozoic Mesozoic Neozoic Million yr Squid Cuttlefish Vampire squid Octopus Bobtil squid Molluscan
Recent Aedvances in Cephalopod Systematics Kotaro TSUCHIYA Lab. Invertebrate Zoology What the Cephalopoda Paleozoic Mesozoic Neozoic Million yr Squid Cuttlefish Vampire squid Octopus Bobtil squid Molluscan
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny
 Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
By Sudha Vashisht P.G.G.C.G. -11 CHD
 By Sudha Vashisht P.G.G.C.G. -11 CHD Pila is the common Apple snail which is found in ponds ditches, rivers and in watery fileds. The soft body is covered by a coiled shell. The first chamber of the shell
By Sudha Vashisht P.G.G.C.G. -11 CHD Pila is the common Apple snail which is found in ponds ditches, rivers and in watery fileds. The soft body is covered by a coiled shell. The first chamber of the shell
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Moving Forward Quizlet Each section we cover, 1 group will go to our class on Quizlet and create 20 flash cards on the topic (/5mks) If I warn you about talking while I m talking,
Introduction to Animals Moving Forward Quizlet Each section we cover, 1 group will go to our class on Quizlet and create 20 flash cards on the topic (/5mks) If I warn you about talking while I m talking,
Chapter 33: Invertebrates
 Name Period Chapters 31, 32, and 33 should be considered as a single unit, and you should try to put all of them together in a single conceptual framework. Due to the scope of our course, you are likely
Name Period Chapters 31, 32, and 33 should be considered as a single unit, and you should try to put all of them together in a single conceptual framework. Due to the scope of our course, you are likely
Squid Instructor s Guide Instructor Guide - Middle and High School
 LESSON: Life in the Fast Lane From Hunted to Hunter Overview: Lab dissection of a squid, a member of Class Cephalopoda (along with the octopus and nautilus). Supported by several Shape of Life segments,
LESSON: Life in the Fast Lane From Hunted to Hunter Overview: Lab dissection of a squid, a member of Class Cephalopoda (along with the octopus and nautilus). Supported by several Shape of Life segments,
Biology 11. The Kingdom Animalia
 Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Who s On First? A Relative Dating Activity
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: Who s On First? A Relative Dating Activity Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very old, approximately four and one-half billion years old. Scientific measurements such
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: Who s On First? A Relative Dating Activity Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very old, approximately four and one-half billion years old. Scientific measurements such
A Brief History of Slime: 550 Million Years of Mollusks. David C. Campbell Gardner-Webb University
 A Brief History of Slime: 550 Million Years of Mollusks David C. Campbell Gardner-Webb University pleuronaia@gmail.com What is a mollusk? Snails, slugs, clams, octopi, squid, etc. Common characteristics
A Brief History of Slime: 550 Million Years of Mollusks David C. Campbell Gardner-Webb University pleuronaia@gmail.com What is a mollusk? Snails, slugs, clams, octopi, squid, etc. Common characteristics
Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 1- Fall 2015
 Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 1- Fall 2015 Name Read through the exam before you begin. This exam consists of four (4) Parts. You must provide answers for each Part. However, you are required to answer
Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 1- Fall 2015 Name Read through the exam before you begin. This exam consists of four (4) Parts. You must provide answers for each Part. However, you are required to answer
An Introduction to the Invertebrates
 An Introduction to the Invertebrates Janet Moore New Hall, Cambridge niustrations by Raith Overhill Second Edition. :::.. CAMBRIDGE :: UNIVERSITY PRESS ~nts ao Paulo, Delhi rcss, New York._ MOO 586 List
An Introduction to the Invertebrates Janet Moore New Hall, Cambridge niustrations by Raith Overhill Second Edition. :::.. CAMBRIDGE :: UNIVERSITY PRESS ~nts ao Paulo, Delhi rcss, New York._ MOO 586 List
Types of intertidal communities
 Between the tides Marine ecosystems 1 Intertidal Delimited by the highest high tide and the lowest low tides marks The best studied and best-understood by humans Relatively easy to sample compared to other
Between the tides Marine ecosystems 1 Intertidal Delimited by the highest high tide and the lowest low tides marks The best studied and best-understood by humans Relatively easy to sample compared to other
The practice of naming and classifying organisms is called taxonomy.
 Chapter 18 Key Idea: Biologists use taxonomic systems to organize their knowledge of organisms. These systems attempt to provide consistent ways to name and categorize organisms. The practice of naming
Chapter 18 Key Idea: Biologists use taxonomic systems to organize their knowledge of organisms. These systems attempt to provide consistent ways to name and categorize organisms. The practice of naming
Characteristics of Echinoderms
 Characteristics of Echinoderms Adult echinoderms have a body plan with five parts organized symmetrically around a center Does not have an anterior nor posterior end or a brain Most echinoderms are two
Characteristics of Echinoderms Adult echinoderms have a body plan with five parts organized symmetrically around a center Does not have an anterior nor posterior end or a brain Most echinoderms are two
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 18: The Evolution of Invertebrate Diversity Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Animal evolution and diversity Answer the following questions as you read modules 18.1 18.4: 1. The eating
Name Period Chapter 18: The Evolution of Invertebrate Diversity Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Animal evolution and diversity Answer the following questions as you read modules 18.1 18.4: 1. The eating
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
Evolution and Biodiversity Laboratory Identifying Microorganisms in Aquatic Samples
 Evolution and Biodiversity Laboratory Identifying Microorganisms in Aquatic Samples Being able to identify organisms is important if you wish to discover what is already known about their natural history,
Evolution and Biodiversity Laboratory Identifying Microorganisms in Aquatic Samples Being able to identify organisms is important if you wish to discover what is already known about their natural history,
Lesson Plan Taxonomy and Classiicaion
 Lesson Plan Taxonomy and Classiicaion Summary This lesson will introduce students to the classiicaion of living things, how animals are grouped and why all living things have a scieniic name. Content Area
Lesson Plan Taxonomy and Classiicaion Summary This lesson will introduce students to the classiicaion of living things, how animals are grouped and why all living things have a scieniic name. Content Area
Ecology: The science concerned with the relationships among living things and their environment.
 ECOSYSTEM VOCABULARY IN PACKET Ecology: The science concerned with the relationships among living things and their environment. Ecosystem: A community that includes all the living and nonliving things
ECOSYSTEM VOCABULARY IN PACKET Ecology: The science concerned with the relationships among living things and their environment. Ecosystem: A community that includes all the living and nonliving things
Kingdom Animalia. Special Features: Advanced nervous systems means cephalization (faces), brains, and efficient mobility (walk/run/swim/grab)
 Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Cell Number: Multicellular with extensive specialization Cell Type: Eukaryotic Animal Cells (no cell wall) Food: Heterotrophic Carnivore (meat), Herbivore (plants), Omnivore
Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Cell Number: Multicellular with extensive specialization Cell Type: Eukaryotic Animal Cells (no cell wall) Food: Heterotrophic Carnivore (meat), Herbivore (plants), Omnivore
Arms Calyx Stem Scale
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #11, Winter 2014 Lab day: Tu W Th Mesozoic & Cenozoic invertebrates life forms, and hominids This week s laboratory will complete the study of the major invertebrate fossil
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #11, Winter 2014 Lab day: Tu W Th Mesozoic & Cenozoic invertebrates life forms, and hominids This week s laboratory will complete the study of the major invertebrate fossil
GY 112 Lecture Notes Significance of Fossils: Paleoenvironmental Interpretations
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Significance of Fossils: Paleoenvironmental Interpretations Lecture Goals: A) The oceans today B) Estimating water depths C) Adaptations to
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Significance of Fossils: Paleoenvironmental Interpretations Lecture Goals: A) The oceans today B) Estimating water depths C) Adaptations to
Introduction. 1 Background Information...2 Adaptation Scavenger Hunt...3 Science Standards.. 4
 Please arrive 30 minutes before your program. Teachers and chaperones must be present during the staff-facilitated 45-minute program. Introduction. 1 Background Information.....2 Adaptation Scavenger Hunt......3
Please arrive 30 minutes before your program. Teachers and chaperones must be present during the staff-facilitated 45-minute program. Introduction. 1 Background Information.....2 Adaptation Scavenger Hunt......3
2/17/2017. Lecture 10: Chapter 31 Protostome Diversity
 1 Lecture 10: Chapter 31 Protostome Diversity 2 3 Protostomes: one of two monophyletic groups of bilaterally symmetrical, coelomate animals The other group is the Deuterostomes Differ in pattern of early
1 Lecture 10: Chapter 31 Protostome Diversity 2 3 Protostomes: one of two monophyletic groups of bilaterally symmetrical, coelomate animals The other group is the Deuterostomes Differ in pattern of early
Taxonomy: Classification of slugs and snails
 Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-4 Taxonomy: Classification of slugs and snails Standards addressed: Next Generation
Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-4 Taxonomy: Classification of slugs and snails Standards addressed: Next Generation
Who s on First?
 Who s on First? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fosrec/barbar.html Focus on Inquiry The students will focus on inquiry by identifying patterns in fossils and explaining their understanding of how rock layers
Who s on First? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fosrec/barbar.html Focus on Inquiry The students will focus on inquiry by identifying patterns in fossils and explaining their understanding of how rock layers
Introduction: Natural Bridges Setting and Tidepool Habitats
 Introduction: Natural Bridges Setting and Tidepool Habitats 1. Physical setting microcosm of coast- zone influenced by 1) river, 2) waves/tides, 3) wind (NW) Rock Types (wave cut bench) Santa Cruz Mudstone
Introduction: Natural Bridges Setting and Tidepool Habitats 1. Physical setting microcosm of coast- zone influenced by 1) river, 2) waves/tides, 3) wind (NW) Rock Types (wave cut bench) Santa Cruz Mudstone
WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY
 WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY MARSHA BARBER and DIANA SCHEIDLE BARTOS INTRODUCTION PALEONTOLOGY, AND in particular the study of dinosaurs, is an exciting topic to people of all ages. Although
WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY MARSHA BARBER and DIANA SCHEIDLE BARTOS INTRODUCTION PALEONTOLOGY, AND in particular the study of dinosaurs, is an exciting topic to people of all ages. Although
Taxonomy Lab: An exercise in taxonomy, evolution, and classification, Interdisciplinary... Introduction. Background. The Role of Taxonomy
 Page 1 of 5 Introduction We use this lab in Patterns and Processes, Evolution of Past & Present Ecosystems, and Tropical Marine Ecology. This exercise illustrates the creativity involved in taxonomy and
Page 1 of 5 Introduction We use this lab in Patterns and Processes, Evolution of Past & Present Ecosystems, and Tropical Marine Ecology. This exercise illustrates the creativity involved in taxonomy and
Name Fossils lab Mr. Kaiser
 Name Fossils lab Mr. Kaiser Purpose Fossils give us a window as to what life was like when it first appeared some billions of years ago. Some fossil remains can give us insight into how prehistoric plants
Name Fossils lab Mr. Kaiser Purpose Fossils give us a window as to what life was like when it first appeared some billions of years ago. Some fossil remains can give us insight into how prehistoric plants
Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch Animals Invertebrates
 Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch 10-11 Animals Invertebrates Write the correct word in the blanks to show directions on an animal body: ** Word Bank (Posterior, Ventral, Dorsal, Anterior) top surface front
Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch 10-11 Animals Invertebrates Write the correct word in the blanks to show directions on an animal body: ** Word Bank (Posterior, Ventral, Dorsal, Anterior) top surface front
Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time. Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic
 Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time Soft bodied fauna Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic Modern fauna Cambrian fauna Paleozoic
Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time Soft bodied fauna Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic Modern fauna Cambrian fauna Paleozoic
Porifera Sponges Features:
 Porifera Sponges The Phylum Porifera consists only of sponges, which is unique since these animals are entirely aquatic; with 98% found only in marine environments and a small percentage found in freshwater
Porifera Sponges The Phylum Porifera consists only of sponges, which is unique since these animals are entirely aquatic; with 98% found only in marine environments and a small percentage found in freshwater
Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet Chapter 33 Introduction to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia: 1. Approximately how many different animal species are alive on Earth currently. How many those species have
Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet Chapter 33 Introduction to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia: 1. Approximately how many different animal species are alive on Earth currently. How many those species have
Animal Diversity. Name Date Period
 Name Date Period Laboratory Objectives: After completing this lab topic, you should be able to: 1. Compare the anatomy of the representative animals, describing similarities and differences in organs and
Name Date Period Laboratory Objectives: After completing this lab topic, you should be able to: 1. Compare the anatomy of the representative animals, describing similarities and differences in organs and
Classification. Grouping & Identifying Living Things
 Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Classifying Living Things We put livings things into three Domains Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Which are divided into 6 Kingdoms Plant Animal Fungi Protist
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Classifying Living Things We put livings things into three Domains Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Which are divided into 6 Kingdoms Plant Animal Fungi Protist
Classification. The three-domains. The six-kingdom system. The traditional five-kingdom system. Bacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Classification The three-domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya The six-kingdom system Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia The traditional five-kingdom system Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
Classification The three-domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya The six-kingdom system Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia The traditional five-kingdom system Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
Eukaryote Phylogeny. Glycogen. Kingdom Animalia. Amoebozoa Animalia. Plantae. Chromalveolata Rhizaria. Fungi. Excavata
 Eukaryote Phylogeny most protozoans, brown algae, & water molds Excavata Chromalveolata Rhizaria Plantae Amoebozoa Animalia Fungi cpsts. w/ 2 memb. chitin, hyphae glycogen eukaryotic cells (nucleus, etc.)
Eukaryote Phylogeny most protozoans, brown algae, & water molds Excavata Chromalveolata Rhizaria Plantae Amoebozoa Animalia Fungi cpsts. w/ 2 memb. chitin, hyphae glycogen eukaryotic cells (nucleus, etc.)
GY 112L Lab Assignment 5 Modes of Fossil Preservation
 Name: Grade /100 (+5 bonus) Percent: GY 112L Lab Assignment 5 Modes of Fossil Preservation Note: In this lab we will begin to look at fossilized animals, plants, and their traces. You will soon become
Name: Grade /100 (+5 bonus) Percent: GY 112L Lab Assignment 5 Modes of Fossil Preservation Note: In this lab we will begin to look at fossilized animals, plants, and their traces. You will soon become
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia body symmetry embryonic germ layers ontogenetic origins I. What is an Animal? II. Germ Layers
 Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia by Dana Krempels Perhaps even more than the other Eukarya, Animalia is characterized by a distinct progression of complexity in form and function as one moves from the
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia by Dana Krempels Perhaps even more than the other Eukarya, Animalia is characterized by a distinct progression of complexity in form and function as one moves from the
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Marine symbiosis. Evolution by association. Types of symbiosis. Some examples of symbiosis that we may not normally think about
 Marine symbiosis Type of symbiotic associations Mutualism - partners mutually benefit (+ +). Commensalism - one partner derives some benefit while the other is unaffected (+ 0). Parasitism - one partner
Marine symbiosis Type of symbiotic associations Mutualism - partners mutually benefit (+ +). Commensalism - one partner derives some benefit while the other is unaffected (+ 0). Parasitism - one partner
Volunteer-based Stream. Macroinvertebrates. Paul Steen Watershed Ecologist Huron River Watershed Council
 Volunteer-based Stream Monitoring- Aquatic Macroinvertebrates Paul Steen Watershed Ecologist Huron River Watershed Council Aquatic Insects are Diverse and Interesting! 3 Reasons to love aquatic bugs 1.
Volunteer-based Stream Monitoring- Aquatic Macroinvertebrates Paul Steen Watershed Ecologist Huron River Watershed Council Aquatic Insects are Diverse and Interesting! 3 Reasons to love aquatic bugs 1.
Antarctic Undersea Foodweb
 Details Completion Time: 2-3 hours Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Antarctic Undersea Foodweb Overview Using photos from a variety of websites, including the PolarTREC and SCINI websites, students
Details Completion Time: 2-3 hours Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Antarctic Undersea Foodweb Overview Using photos from a variety of websites, including the PolarTREC and SCINI websites, students
Form and function of radular teeth of herbivorous molluscs: Focus on the future
 AMERICAN MALACOLOGICAL BULLETIN 18 1/2 2003 Form and function of radular teeth of herbivorous molluscs: Focus on the future Dianna K. Padilla Department of Ecology and Evolution, Stony Brook University,
AMERICAN MALACOLOGICAL BULLETIN 18 1/2 2003 Form and function of radular teeth of herbivorous molluscs: Focus on the future Dianna K. Padilla Department of Ecology and Evolution, Stony Brook University,
THE INTERTIDAL ZONE AND BENTHIC ORGANISMS
 THE INTERTIDAL ZONE AND BENTHIC ORGANISMS EPSS 15 Lab #8 OUTLINE I. Intertidal zonation Tides Biotic zonation Physical conditions & biotic interactions II. Intertidal organisms & adaptations Snails Mussels
THE INTERTIDAL ZONE AND BENTHIC ORGANISMS EPSS 15 Lab #8 OUTLINE I. Intertidal zonation Tides Biotic zonation Physical conditions & biotic interactions II. Intertidal organisms & adaptations Snails Mussels
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification
 Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Chapter 6. Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal?
 Chapter 6 Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient life which have been preserved by natural causes in the Earth's crust. Fossils include both the remains
Chapter 6 Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient life which have been preserved by natural causes in the Earth's crust. Fossils include both the remains
Survival of the Sweetest
 Biology Survival of the Sweetest A Tasty Tale of Natural Selection and Community Dynamics MATERIALS AND RESOURCES EACH GROUP teacher-provided materials 2 dice TEACHER bags, brown paper, small 3 bags Skittles,
Biology Survival of the Sweetest A Tasty Tale of Natural Selection and Community Dynamics MATERIALS AND RESOURCES EACH GROUP teacher-provided materials 2 dice TEACHER bags, brown paper, small 3 bags Skittles,
Animals are in Domain Eukarya
 The Diversity of Animals 1: invertebrates Chapter 23 Animals are in Domain Eukarya Immediate ancestors are a type of Protista Key features Multicellular Kingdom Animalia Heterotrophic: gain energy by consuming
The Diversity of Animals 1: invertebrates Chapter 23 Animals are in Domain Eukarya Immediate ancestors are a type of Protista Key features Multicellular Kingdom Animalia Heterotrophic: gain energy by consuming
Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 3- Fall Part I. Answer nine (9) of the following twelve (12) questions: (18 points; 2 points each)
 1 Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 3- Fall 2015 You have one hour to complete this portion of the exam. After one hour your paper will be collected and you will be given the second, comprehensive essay
1 Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 3- Fall 2015 You have one hour to complete this portion of the exam. After one hour your paper will be collected and you will be given the second, comprehensive essay
CHITON (SYPHAROCHITON) PELLISERPENTIS AT MUDS'I'ONE BAY, KAIKOURA, NEW ZEALAND PETER L. HORN
 MAURI ORA, 1984, 11: 57-61 tleachl
MAURI ORA, 1984, 11: 57-61 tleachl
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
"PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200B Spring 2011
 "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200B Spring 2011 Evolution and development ("evo-devo") The last frontier in our understanding of biological forms is an understanding
"PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200B Spring 2011 Evolution and development ("evo-devo") The last frontier in our understanding of biological forms is an understanding
Class Amphineura or Polyplacophora The Chitons. Chief characteristics: Chitons have 8 overlapping plates covering an ovoid, flattened body.
 Class Amphineura or Polyplacophora The Chitons Chief characteristics: Chitons have 8 overlapping plates covering an ovoid, flattened body. Class Amphineura or Polyplacophora The Chitons Name: Polyplacophora
Class Amphineura or Polyplacophora The Chitons Chief characteristics: Chitons have 8 overlapping plates covering an ovoid, flattened body. Class Amphineura or Polyplacophora The Chitons Name: Polyplacophora
BIOS1101 Lab Notes. Contents ANIMALS. Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates. Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates
 Contents ANIMALS Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates Lab 3: Animal Structure 1 Gross morphology Lab 4: Animal Structure 2 Histology Lab 5: The Nervous System & Sensory
Contents ANIMALS Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates Lab 3: Animal Structure 1 Gross morphology Lab 4: Animal Structure 2 Histology Lab 5: The Nervous System & Sensory
In the space below, draw and label all the possible horizontal and vertical regions of a typical lake (4)
 Bio 20c Spring 2016 Final Exam Name/SID Refer to the graphic below and in the appropriate labeled space to the right, fill in the name of the major terrestrial biome that is characterized by the temperature
Bio 20c Spring 2016 Final Exam Name/SID Refer to the graphic below and in the appropriate labeled space to the right, fill in the name of the major terrestrial biome that is characterized by the temperature
INVERTEBRATES. The Earth and Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1
 INVERTEBRATES Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1 How many animals can you see? ant rose coral snake anemone fish grass bee Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 2 Invertebrates There are animals without
INVERTEBRATES Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1 How many animals can you see? ant rose coral snake anemone fish grass bee Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 2 Invertebrates There are animals without
The Blue Mussel: A Not-So-Typical Mollusc Lab Activity: Dissection of a Bivalve Middle School Version
 Overview: Through a sequence of engaging laboratory investigations coupled to vivid segments from the acclaimed Shape of Life video series, students explore the fascinating structural and behavioral adaptations
Overview: Through a sequence of engaging laboratory investigations coupled to vivid segments from the acclaimed Shape of Life video series, students explore the fascinating structural and behavioral adaptations
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS
 KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
STATION 4. STATION refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version. Can you name this fossil? Class
 STATION 1 Can you name this fossil? Phylum Class STATION 2 --- refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version Identify the Phylum of each specimen Genus When did he live? Cambrian,
STATION 1 Can you name this fossil? Phylum Class STATION 2 --- refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version Identify the Phylum of each specimen Genus When did he live? Cambrian,
Zoological Systematics & Taxonomy
 Name: PRE-LAB This lab is designed to introduce you to the basics of animal classification (systematics) and taxonomy of animals. This is a field that is constantly changing with the discovery of new animals,
Name: PRE-LAB This lab is designed to introduce you to the basics of animal classification (systematics) and taxonomy of animals. This is a field that is constantly changing with the discovery of new animals,
The Shell Detective VORTEX
 The Shell Detective Objectives. Compare and contrast non-native rapa whelk ( venosa) shells with native channelled ( canaliculatus) and knobbed ( carica) whelk shells.. Identify diagnostic characters of
The Shell Detective Objectives. Compare and contrast non-native rapa whelk ( venosa) shells with native channelled ( canaliculatus) and knobbed ( carica) whelk shells.. Identify diagnostic characters of
Skeletal grains. Pores. Matrix <20 m) Cement. Non-skeletal grains. 1 cm
 Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix
Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix
Name: Date: ID: 3. What are some limitations to scientific models? - Most models include simplifications, approximations, and/or lack details
 Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
What defines the zygote, the blastula, and the gastrula? Draw pictures.
 What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
