Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae
|
|
|
- Georgiana Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary Information Supplementary Text S1 Description of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila (Nu.cle.i.cul'trix. L. n. nucleus, a nut, and in biology a nucleus; L. fem. n. cultrix, inhabitant; a.mo.e.bi'phi.la. N.L. n. amoeba; N.L. fem. adj. phila, friend, loving; N.L. fem. adj. amoebiphila, amoeba-loving). Bacteria infecting and replicating in the nucleus of Hartmannella and Acanthamoeba species; the organism was originally discovered in a Hartmannella sp. isolate obtained from a denitrifying bioreactor; it has not been cultured in host-free media. The bacteria appear as coccoid rods of 0.5 to 1 µm in length and 0.3 to 0.4 µm in diameter and show a Gram-negative type cell wall. The organism is a member of the Alphaproteobacteria; its classification is based on 16S rrna and 23S rrna gene sequences (Genbank acc. numbers KF697195, KF697196) and fluorescence in situ hybridization with the 16S rrna-targeted oligonucleotide probe CBR125 (5 -TTCACTCTCAAGTCGCCC-3 ).
2 Figure S1. Phylogenetic relationship of Hartmannella sp. FS5. The tree is based on a 18S rrna alignment (Schmitz-Esser, 2008); the isolate Hartmannella sp. FS5 and selected relatives in Genbank/EMBL/DDBJ were added, and the tree was calculated with FastTree2 (Price et al., 2010). Hartmannella sp. FS5 is highlighted in grey. Accession numbers are provided in Table S1. 2
3 Figure S2. Identification and intranuclear location of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila in the original amoeba isolate Hartmannella sp. FS5. Hartmannella sp. cells infected by Nucleicultrix were stained by DAPI (blue) and FISH using the general bacterial probe mix EUB338 I-III (labeled in red resulting in a pink color due to the overlay with the blue DAPI signal) and the eukaryotic probe EUK516 (shown in grey). Arrows indicate amoeba trophozoites with bacteria in the nuclear compartment. Bar, 5 µm. 3
4 Figure S3. 16S rrna-based maximum likelihood tree showing the relationship of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila with other Alphaproteobacteria. Nucleicultrix and its closest relatives are highlighted in grey. Maximum likelihood bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities are indicated at the nodes. 4
5 Figure S4. 23S rrna-based maximum likelihood tree showing the relationship of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila with other Alphaproteobacteria. Nucleicultrix and its closest relatives are highlighted in grey. Maximum likelihood bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities are indicated at the nodes. 5
6 Figure S5. Maximum likelihood tree showing the relationship of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila with other Alphaproteobacteria based on concatenated 16S and 23S rrna. Nucleicultrix and its closest relatives are highlighted in grey. Maximum likelihood bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities are indicated at the nodes. 6
7 Figure S6. Escape of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila from phagolysosomes. A. castellanii cells were incubated with LysoTracker-Yellow HCK-123 (Lifetechnologies; 2 µm) in 1xPAS for 1 hour and infected with Nucleicultrix as described. The cell suspension was then transferred to a chambered cover glass system (NalgeNunc Int.), and DAPI (0.2 µg/ml) was added. The infection process was monitored over a period of 6 hours with a confocal microscope (Leica SP8). The images shown here display the same amoeba trophozoites approximately 2 h post infection. (a) Nucleicultrix (blue, arrowhead) was initially located in phagolysosomes (shown in green). (b) The bacteria remained intact and 5 minutes later escaped into the cytoplasm. 7
8 Figure S7. Infection cycle of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila in Acanthamoeba castellanii. The infection process was monitored over a course of 120 hours and visualized by FISH using the Nucleicultrix-specific probe CBR125 (shown in orange) and probe EUK516 targeting the amoeba host (shown in grey). Single bacteria colonize the nucleus within 6 hours p.i., the nucleoplasm is completely filled with bacteria after hours, which is accompanied by significantly enlarged nuclei. Host cell lysis occurs from 72 hours p.i. on. Bar, 10 µm. 8
9 Figure S8. The presence of E. coli increases infection rate of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila in Hartmannella sp. FS5. The percentage of infected amoebae 48 hours p.i. is shown in the absence or presence of E. coli (at two different cell numbers given in colony forming units, CFU). Error bars indicate standard deviation based on three replicate infection experiments. 9
10 Figure S9. Influence of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila on Hartmannella sp. growth at different temperatures amoebae from either infected or uninfected cultures were seeded in 12-well plates, containing 1 ml PAS supplemented with E. coli tolc- and ampicillin (200 ng/ml). Cultures were incubated at three distinct temperatures (14 C, 24 C, and 37 C), and cells were detached and counted every 24 hours. As soon as stationary growth phase was reached, amoebae were harvested and fixed with 4% PFA. The percentage of infected amoebae was determined using FISH combined with DAPI staining. (a) Number of amoeba trophozoites with or without symbionts during incubation at 14 C, 24 C, and 37 C, respectively. (b) Percentage of infected amoebae at the beginning and end of the experiment. Error bars indicate standard deviation based on at least three replicate experiments. Differences in amoeba cell numbers between infected and uninfected cultures were not significant at all incubation temperatures (p>0.05; two-way ANOVA). 10
11 Figure S10. Environmental sequences similar to the 16S rrna of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila. The number of amplicon sequences (> 200 nt) found in SRA and VAMPs using different similarity thresholds are shown and classified based on their environmental origin. Additional details are provided in Table S2. 11
12 Table S1. Genbank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers of 16S, 18S and 23S rrna sequences used for phylogenetic analysis. Provided as Excel file. Table S2. List of samples in SRA and VAMPS that include sequences similar to the 16S rrna gene of Candidatus Nucleicultrix amoebiphila. Provided as Excel file. References Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. (2010). FastTree 2--approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One 5: e9490. Schmitz-Esser S, Toenshoff E, Haider S, Heinz E, Hoenninger VM, Wagner M, Horn M. (2008). Diversity of bacterial endosymbionts of environmental Acanthamoeba isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Fig. 1. Infection of three C. elegans strains used for spatially restricted enzymatic tagging. Animals infected with N.
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Infection of three C. elegans strains used for spatially restricted enzymatic tagging. Animals infected with N. parisii stained with a FISH probe (red) specific for Nematocida rrna.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Infection of three C. elegans strains used for spatially restricted enzymatic tagging. Animals infected with N. parisii stained with a FISH probe (red) specific for Nematocida rrna.
concentration ( mol l -1 )
 concentration ( mol l -1 ) 8 10 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 methane sulfide ammonium oxygen sulfate (/10) b depth (m) 12 14 Supplementary Figure 1. Water column parameters from August 2011. Chemical
concentration ( mol l -1 ) 8 10 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 methane sulfide ammonium oxygen sulfate (/10) b depth (m) 12 14 Supplementary Figure 1. Water column parameters from August 2011. Chemical
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 2: Inside Cells
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions
 Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for
 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Complex Function by Design Using Spatially Pre-Structured Synthetic Microbial Communities: Degradation of Pentachlorophenol in the Presence of Hg(II) Supporting
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Complex Function by Design Using Spatially Pre-Structured Synthetic Microbial Communities: Degradation of Pentachlorophenol in the Presence of Hg(II) Supporting
Morphological and behavioral characterization of Corallomyxa tenera.
 Lorenzo Lagostina Microbial Diversity 2015 Morphological and behavioral characterization of Corallomyxa tenera. Corallomyxa tenera is a poorly known reticulose amoeba belonging to a clade that comprises
Lorenzo Lagostina Microbial Diversity 2015 Morphological and behavioral characterization of Corallomyxa tenera. Corallomyxa tenera is a poorly known reticulose amoeba belonging to a clade that comprises
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S3 (box) Methods Methods Genome weighting The currently available collection of archaeal and bacterial genomes has a highly biased distribution of isolates across taxa. For example,
Supplementary information S3 (box) Methods Methods Genome weighting The currently available collection of archaeal and bacterial genomes has a highly biased distribution of isolates across taxa. For example,
This supplementary information includes the data and corresponding citations
 S1 (table) This supplementary information includes the data and corresponding citations presented in Box 1 Figure for the proportion of inactive cells in different systems. Active cells were assessed using
S1 (table) This supplementary information includes the data and corresponding citations presented in Box 1 Figure for the proportion of inactive cells in different systems. Active cells were assessed using
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/eaao4709/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Pushing the limits of photoreception in twilight conditions: The rod-like cone retina of the deep-sea pearlsides Fanny
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/eaao4709/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Pushing the limits of photoreception in twilight conditions: The rod-like cone retina of the deep-sea pearlsides Fanny
ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION
 ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION Eric Pomper Microbiology 9 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Grade 9 Introduction Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) were grown together
ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION Eric Pomper Microbiology 9 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Grade 9 Introduction Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) were grown together
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
Fig. 16. Majority rule consensus tree depicting phylogenetic relationships inferred among 74 species of heterokont algae. Note that A.
 Plate 1 Figs. 1-8. Light microscopic images of Anthophysa vegetans colonies and individual motile cells. Figs 1-5. Stalked (arrow; Figs 1,2) or unstalked (Figs 3-5) colonies consisting of ca. 10-20 spherical
Plate 1 Figs. 1-8. Light microscopic images of Anthophysa vegetans colonies and individual motile cells. Figs 1-5. Stalked (arrow; Figs 1,2) or unstalked (Figs 3-5) colonies consisting of ca. 10-20 spherical
Bacillus anthracis. Last Lecture: 1. Introduction 2. History 3. Koch s Postulates. 1. Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote 2. Classifying prokaryotes
 Last Lecture: Bacillus anthracis 1. Introduction 2. History 3. Koch s Postulates Today s Lecture: 1. Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote 2. Classifying prokaryotes 3. Phylogenetics I. Basic Cell structure: (Fig.
Last Lecture: Bacillus anthracis 1. Introduction 2. History 3. Koch s Postulates Today s Lecture: 1. Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote 2. Classifying prokaryotes 3. Phylogenetics I. Basic Cell structure: (Fig.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Techneau, 30. September Validation of the FISH-based detection and quantification of E.coli and coliform bacteria in water samples
 Techneau, 30. September 2009 Validation of the FISH-based detection and quantification of E.coli and coliform bacteria in water samples Techneau, 30. September 2009 Validation of the FISH-based detection
Techneau, 30. September 2009 Validation of the FISH-based detection and quantification of E.coli and coliform bacteria in water samples Techneau, 30. September 2009 Validation of the FISH-based detection
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Microbial Taxonomy. Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Ch 10. Classification of Microorganisms
 Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Modeling of magnetic field In this study, the magnetic field was generated with N52 grade nickel-plated neodymium block magnets (K&J Magnetics). The residual flux density of the magnets
Supplementary Methods Modeling of magnetic field In this study, the magnetic field was generated with N52 grade nickel-plated neodymium block magnets (K&J Magnetics). The residual flux density of the magnets
NucView TM 488 Caspase-3 Assay Kit for Live Cells
 NucView TM 488 Caspase-3 Assay Kit for Live Cells Catalog Number: 30029 (100-500 assays) Contact Information Address: Biotium, Inc. 3423 Investment Blvd. Suite 8 Hayward, CA 94545 USA Telephone: (510)
NucView TM 488 Caspase-3 Assay Kit for Live Cells Catalog Number: 30029 (100-500 assays) Contact Information Address: Biotium, Inc. 3423 Investment Blvd. Suite 8 Hayward, CA 94545 USA Telephone: (510)
Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy. Slowly evolving molecules (e.g., rrna) used for large-scale structure; "fast- clock" molecules for fine-structure.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr
 Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Supplemental Information. Inferring Cell-State Transition. Dynamics from Lineage Trees. and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements
 Cell Systems, Volume 3 Supplemental Information Inferring Cell-State Transition Dynamics from Lineage Trees and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements Sahand Hormoz, Zakary S. Singer, James M. Linton, Yaron
Cell Systems, Volume 3 Supplemental Information Inferring Cell-State Transition Dynamics from Lineage Trees and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements Sahand Hormoz, Zakary S. Singer, James M. Linton, Yaron
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan
 no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD
 MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD Precaution processes are extremely important when working with cultures in the lab for the safety of the microbiologist from getting diseases from bacteria
MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD Precaution processes are extremely important when working with cultures in the lab for the safety of the microbiologist from getting diseases from bacteria
Introduction. Key Concepts I: Mitosis. AP Biology Laboratory 3 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Virtual Student Guide http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/index.html AP Biology Laboratory 3 Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction For organisms to grow and reproduce, cells must divide. Mitosis
Virtual Student Guide http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/index.html AP Biology Laboratory 3 Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction For organisms to grow and reproduce, cells must divide. Mitosis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
What Is a Cell? What Defines a Cell? Figure 1: Transport proteins in the cell membrane
 What Is a Cell? Trees in a forest, fish in a river, horseflies on a farm, lemurs in the jungle, reeds in a pond, worms in the soil all these plants and animals are made of the building blocks we call cells.
What Is a Cell? Trees in a forest, fish in a river, horseflies on a farm, lemurs in the jungle, reeds in a pond, worms in the soil all these plants and animals are made of the building blocks we call cells.
Day 2 - Viewing a prepared slide of mixed bacteria on high power.
 Purpose Bacteria Lab To compare the quantity and the different types of bacteria from four different locations within the school. To identify 3 different bacterial colonies on a prepared slide. Materials
Purpose Bacteria Lab To compare the quantity and the different types of bacteria from four different locations within the school. To identify 3 different bacterial colonies on a prepared slide. Materials
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date:
 Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
The Prokaryotes & Viruses
 The Prokaryotes & Viruses Lab Exercise Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2 Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae 2 Activity.3 Viruses 3 Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria
The Prokaryotes & Viruses Lab Exercise Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2 Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae 2 Activity.3 Viruses 3 Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria
Virtual Beach Building a GBM Model
 Virtual Beach 3.0.6 Building a GBM Model Building, Evaluating and Validating Anytime Nowcast Models In this module you will learn how to: A. Build and evaluate an anytime GBM model B. Optimize a GBM model
Virtual Beach 3.0.6 Building a GBM Model Building, Evaluating and Validating Anytime Nowcast Models In this module you will learn how to: A. Build and evaluate an anytime GBM model B. Optimize a GBM model
Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011). 10.1105/tpc.110.080788 Supplemental Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of MYC2-related proteins from Arabidopsis and other plants. Phenogram representation
Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011). 10.1105/tpc.110.080788 Supplemental Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of MYC2-related proteins from Arabidopsis and other plants. Phenogram representation
Supplementary Information for. Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria
 Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
End of Course Biology Reporting Category 1 Cell Structure and Function
 End of Course Biology Reporting Category 1 Cell Structure and Function 1. An iodine solution is placed on the cut side of a potato. Within seconds, a blue-black color appears. What is most likely occurring?
End of Course Biology Reporting Category 1 Cell Structure and Function 1. An iodine solution is placed on the cut side of a potato. Within seconds, a blue-black color appears. What is most likely occurring?
Elements of Bioinformatics 14F01 TP5 -Phylogenetic analysis
 Elements of Bioinformatics 14F01 TP5 -Phylogenetic analysis 10 December 2012 - Corrections - Exercise 1 Non-vertebrate chordates generally possess 2 homologs, vertebrates 3 or more gene copies; a Drosophila
Elements of Bioinformatics 14F01 TP5 -Phylogenetic analysis 10 December 2012 - Corrections - Exercise 1 Non-vertebrate chordates generally possess 2 homologs, vertebrates 3 or more gene copies; a Drosophila
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Nexcelom ViaStain Live Caspase 3/7 Detection for 2D/3D Culture
 Nexcelom ViaStain Live Caspase 3/7 Detection for 2D/3D Culture Product Numbers: CSK-V0002-1, CSK-V0003-1 This product is for RESEARCH USE ONLY and is not approved for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Table
Nexcelom ViaStain Live Caspase 3/7 Detection for 2D/3D Culture Product Numbers: CSK-V0002-1, CSK-V0003-1 This product is for RESEARCH USE ONLY and is not approved for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Table
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Bacterial Gram Staining
 PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed with the invention
The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed with the invention
Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Name :
 Midterm Exam #1 MB 451 : Microbial Diversity Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Signed : Date : Name : 1. What are the three primary evolutionary branches of
Midterm Exam #1 MB 451 : Microbial Diversity Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Signed : Date : Name : 1. What are the three primary evolutionary branches of
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes
 Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 CELL THEORY & FUNCTION DISCOVERY OF THE CELL Can t see cells, so who knew they existed? Discovered after the microscope was invented. Mid 1600s when scientists began using microscopes Robert Hooke
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION DISCOVERY OF THE CELL Can t see cells, so who knew they existed? Discovered after the microscope was invented. Mid 1600s when scientists began using microscopes Robert Hooke
Cells. Structural and functional units of living organisms
 Cells Structural and functional units of living organisms Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells Proks Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells
Cells Structural and functional units of living organisms Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells Proks Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE 5/14/18
 THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
3.1: Place of collection of entomopathogenic nematode isolates : Measurement of 12 bacterial isolates 45
 List of Tables 3.1: Place of collection of entomopathogenic nematode isolates... 39 3.2: Measurement of 12 bacterial isolates 45 3.3: Colony morphology of bacteria on nutrient agar 46 3.4: Colony morphology
List of Tables 3.1: Place of collection of entomopathogenic nematode isolates... 39 3.2: Measurement of 12 bacterial isolates 45 3.3: Colony morphology of bacteria on nutrient agar 46 3.4: Colony morphology
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) Co-housed CD300f WT. CD300f KO. Colon length (cm) Day 9. Microscopic inflammation score
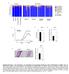 y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Smith et al. American Journal of Botany 98(3): Data Supplement S2 page 1
 Smith et al. American Journal of Botany 98(3):404-414. 2011. Data Supplement S1 page 1 Smith, Stephen A., Jeremy M. Beaulieu, Alexandros Stamatakis, and Michael J. Donoghue. 2011. Understanding angiosperm
Smith et al. American Journal of Botany 98(3):404-414. 2011. Data Supplement S1 page 1 Smith, Stephen A., Jeremy M. Beaulieu, Alexandros Stamatakis, and Michael J. Donoghue. 2011. Understanding angiosperm
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Past climate change on Sky Islands drives novelty in a core developmental gene network and its phenotype
 Supplementary tables and figures Past climate change on Sky Islands drives novelty in a core developmental gene network and its phenotype Marie-Julie Favé 1, Robert A. Johnson 2, Stefan Cover 3 Stephan
Supplementary tables and figures Past climate change on Sky Islands drives novelty in a core developmental gene network and its phenotype Marie-Julie Favé 1, Robert A. Johnson 2, Stefan Cover 3 Stephan
Required Materials: immersion oil microscopes Kim-wipes prepared microscope slides
 Microbiology CA/IA Lab Microscopic Examination of Microbes September 10 Objectives: 1. learn how to use a microscope to examine microbes 2. learn to recognize the characteristics of different microbes
Microbiology CA/IA Lab Microscopic Examination of Microbes September 10 Objectives: 1. learn how to use a microscope to examine microbes 2. learn to recognize the characteristics of different microbes
Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 A prokaryotic cell Basic unit of living organisms is the cell; the smallest unit capable of life. Features found in all cells: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Genetic Material Cytoplasm ATP Energy External Stimuli
A prokaryotic cell Basic unit of living organisms is the cell; the smallest unit capable of life. Features found in all cells: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Genetic Material Cytoplasm ATP Energy External Stimuli
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Microscope Lab Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
 Name: Date: Period: Microscope Lab Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and distinguish each type under the microscope. 2. Compare animal
Name: Date: Period: Microscope Lab Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and distinguish each type under the microscope. 2. Compare animal
CELL LAB OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION: CELL UNIT. After completing this lab you should be able to:
 AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
ydci GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC
 Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Water sampling for Oomycetes
 Water sampling for Oomycetes Oomycetes are fungus-like organisms found in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments. Some, such as Phytophthora, Pythium, and Saprolegnia, are parasites of plants
Water sampling for Oomycetes Oomycetes are fungus-like organisms found in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments. Some, such as Phytophthora, Pythium, and Saprolegnia, are parasites of plants
Microscopy, Staining, and Classification
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 4. Discuss how microscopy has revealed the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 4. Discuss how microscopy has revealed the structure
The Evolution of DNA Uptake Sequences in Neisseria Genus from Chromobacteriumviolaceum. Cory Garnett. Introduction
 The Evolution of DNA Uptake Sequences in Neisseria Genus from Chromobacteriumviolaceum. Cory Garnett Introduction In bacteria, transformation is conducted by the uptake of DNA followed by homologous recombination.
The Evolution of DNA Uptake Sequences in Neisseria Genus from Chromobacteriumviolaceum. Cory Garnett Introduction In bacteria, transformation is conducted by the uptake of DNA followed by homologous recombination.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Icm/Dot secretion system region I in 41 Legionella species.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Icm/Dot secretion system region I in 41 Legionella species. Homologs of the effector-coding gene lega15 (orange) were found within Icm/Dot region I in 13 Legionella species. In four
Supplementary Figure 1 Icm/Dot secretion system region I in 41 Legionella species. Homologs of the effector-coding gene lega15 (orange) were found within Icm/Dot region I in 13 Legionella species. In four
Initiation of DNA Replication Lecture 3! Linda Bloom! Office: ARB R3-165! phone: !
 Initiation of DNA Replication Lecture 3! Linda Bloom! Office: ARB R3-165! email: lbloom@ufl.edu! phone: 392-8708! 1! Lecture 3 Outline! Students will learn! Basic techniques for visualizing replicating
Initiation of DNA Replication Lecture 3! Linda Bloom! Office: ARB R3-165! email: lbloom@ufl.edu! phone: 392-8708! 1! Lecture 3 Outline! Students will learn! Basic techniques for visualizing replicating
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses. Name Class Date
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic pipeline for single-cell genome assembly, cleaning and annotation. a. The assembly process was optimized to account for multiple cells putatively
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic pipeline for single-cell genome assembly, cleaning and annotation. a. The assembly process was optimized to account for multiple cells putatively
Part 2. The Basics of Biology:
 Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
Computational Biology, Part 24 Clustering and Unmixing of Subcellular Patterns
 Computational Biology, Part 24 Clustering and Unmixing of Subcellular Patterns Robert F. Murphy Copyright 1996, 1999, 2000-2009. All rights reserved. Unsupervised Learning to Identify High-Resolution Protein
Computational Biology, Part 24 Clustering and Unmixing of Subcellular Patterns Robert F. Murphy Copyright 1996, 1999, 2000-2009. All rights reserved. Unsupervised Learning to Identify High-Resolution Protein
A. Incorrect! In the binomial naming convention the Kingdom is not part of the name.
 Microbiology Problem Drill 08: Classification of Microorganisms No. 1 of 10 1. In the binomial system of naming which term is always written in lowercase? (A) Kingdom (B) Domain (C) Genus (D) Specific
Microbiology Problem Drill 08: Classification of Microorganisms No. 1 of 10 1. In the binomial system of naming which term is always written in lowercase? (A) Kingdom (B) Domain (C) Genus (D) Specific
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Sediment Microbiology. Guangyi Wang POST 103B
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Sediment Microbiology Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu Three Domains of Life 1) Unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed based on small-subunit rrna genes; 2) Members
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Sediment Microbiology Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu Three Domains of Life 1) Unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed based on small-subunit rrna genes; 2) Members
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
Biology 2180 Laboratory # 5 Name Plant Cell Fractionation
 Biology 2180 Laboratory # 5 Name Plant Cell Fractionation In this lab, you will work with plant tissue to learn about cell fractionation. Cell Fractionation is the process that isolates different components
Biology 2180 Laboratory # 5 Name Plant Cell Fractionation In this lab, you will work with plant tissue to learn about cell fractionation. Cell Fractionation is the process that isolates different components
Purpose (1 point) Investigate differences to cell size and shape across various kingdoms
 Living Cells Lab 61 points total As will be seen through this lab, there is no such thing as a typical cell. Though both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are often shown as general cells (p. 206), rarely
Living Cells Lab 61 points total As will be seen through this lab, there is no such thing as a typical cell. Though both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are often shown as general cells (p. 206), rarely
Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes
 Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes Lawrence D. Goodridge Department of Animal Sciences Colorado State University Lawrence.Goodridge@colostate.edu
Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes Lawrence D. Goodridge Department of Animal Sciences Colorado State University Lawrence.Goodridge@colostate.edu
Taxonomy. Content. How to determine & classify a species. Phylogeny and evolution
 Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Reconstruction of the Nuclear Sites of Salmonella typhimurium from Electron Micrographs of Serial Sections
 327 BIRCH-ANDERSEN, A. (1955). J. gen. Microbial. 13, 327429 Reconstruction of the Nuclear Sites of Salmonella typhimurium from Electron Micrographs of Serial Sections BY A. BIRCH-ANDERSEN Statens Seruminstitut,
327 BIRCH-ANDERSEN, A. (1955). J. gen. Microbial. 13, 327429 Reconstruction of the Nuclear Sites of Salmonella typhimurium from Electron Micrographs of Serial Sections BY A. BIRCH-ANDERSEN Statens Seruminstitut,
KnowIT Questions AQA GCSE Cell Biology
 A. Cell structure part 1 Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and animal and plant cells 1. Where is the genetic material in a prokaryotic cell? 2. Where is the genetic material in a eukaryotic cell? 3. Complete the
A. Cell structure part 1 Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and animal and plant cells 1. Where is the genetic material in a prokaryotic cell? 2. Where is the genetic material in a eukaryotic cell? 3. Complete the
DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE - FALL 2014 LAB PROCEDURES AND MICROBIOLOGY AH 174 E- MAIL:
 DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE - FALL 2014 LAB PROCEDURES AND MICROBIOLOGY AH 174 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Chris Mizzi Kristy Mergeart, RAHT PHONE: 780-835-6617 780-835-6779 OFFICE: AS 133
DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE - FALL 2014 LAB PROCEDURES AND MICROBIOLOGY AH 174 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Chris Mizzi Kristy Mergeart, RAHT PHONE: 780-835-6617 780-835-6779 OFFICE: AS 133
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
ACT Science Quick Guide
 ACT Science Quick Guide Use this packet as a quick reference for the most important ACT Science tips and strategies. Key Strategy #1: Use your first 20 seconds on each passage to do a few key things: 1.
ACT Science Quick Guide Use this packet as a quick reference for the most important ACT Science tips and strategies. Key Strategy #1: Use your first 20 seconds on each passage to do a few key things: 1.
PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
Table of Contents. Experiment: Apoptosis Assay using Caspase 3/7 with Hoechst... 2
 Table of Contents Experiment: Apoptosis Assay using Caspase 3/7 with Hoechst... 2 Celigo Setup... 2 Assay Protocol and Plate Setup... 2 Results... 3 Drug-treated MDA-MB-231 and Jurkat cells showed an increase
Table of Contents Experiment: Apoptosis Assay using Caspase 3/7 with Hoechst... 2 Celigo Setup... 2 Assay Protocol and Plate Setup... 2 Results... 3 Drug-treated MDA-MB-231 and Jurkat cells showed an increase
BMC Evolutionary Biology 2013, 13:6
 BMC Evolutionary Biology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Correction: Male-killing
BMC Evolutionary Biology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Correction: Male-killing
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sana et al. 10.1073/pnas.1608858113 Fig. S1. Representation of the SPI-6 type VI secretion system. (A) Representation of the SPI-6 genetic locus starting at STM0266 and ending at
Supporting Information Sana et al. 10.1073/pnas.1608858113 Fig. S1. Representation of the SPI-6 type VI secretion system. (A) Representation of the SPI-6 genetic locus starting at STM0266 and ending at
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Agronomy 485/585 Test #1 October 2, 2014
 Agronomy 485/585 Test #1 October 2, 2014 Name Part I. Circle the one best answer (2 points each). 1. The most important microbial group in promoting soil structure likely is the. a) actinomycetes b) algae
Agronomy 485/585 Test #1 October 2, 2014 Name Part I. Circle the one best answer (2 points each). 1. The most important microbial group in promoting soil structure likely is the. a) actinomycetes b) algae
SPECIES OF ARCHAEA ARE MORE CLOSELY RELATED TO EUKARYOTES THAN ARE SPECIES OF PROKARYOTES.
 THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
Figure A1. Phylogenetic trees based on concatenated sequences of eight MLST loci. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on concatenated sequences
 A. B. Figure A1. Phylogenetic trees based on concatenated sequences of eight MLST loci. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on concatenated sequences of eight housekeeping loci for 12 unique STs
A. B. Figure A1. Phylogenetic trees based on concatenated sequences of eight MLST loci. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on concatenated sequences of eight housekeeping loci for 12 unique STs
