Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes
|
|
|
- Wilfred Carpenter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23 June, 2014
2
3 Microb Ecol DOI /s MINIREVIEWS Comparison of 61 Sequenced Escherichia coli Genomes Oksana Lukjancenko & Trudy M. Wassenaar & David W. Ussery Note: Include title slide with names of the group, title of the project 23 June,
4 Abstract Escherichia coli is an important component of the biosphere and is an ideal model for studies of processes involved in bacterial genome evolution. Sixty-one publically available E. coli and Shigella spp. sequenced genomes are compared, using basic methods to produce phylogenetic and proteomics trees, and to identify the pan- and core genomes of this set of sequenced strains. A hierarchical clustering of variable genes allowed clear separation of the strains into clusters, including known pathotypes; clinically relevant serotypes can also be resolved in this way. In contrast, when in silico MLST was performed, many of the various strains appear jumbled and less well resolved. The predicted pan-genome comprises 15,741 gene families, and only 993 (6%) of the families are represented in every genome, comprising the core genome. The variable or accessory genes thus make up more than 90% of the pan-genome and about 80% of a typical genome; some of these variable genes tend to be co-localized on genomic islands. The diversity within the species E. coli, andthe overlap in gene content between this and related species, suggests a continuum rather than sharp species borders in this group of Enterobacteriaceae. 23 June,
5 O. Lukjancenko et al. Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree based on extracted 16S rrna sequences. a Comparison of 20 different Enterobacteriaceae, based on extracted 16S rrna sequences from the GenBank sequence files. E. coli and Shigella are shown in green. b Tree of 61 sequenced E. coli (black) andrelatedspecies (colored), based on the alignment of the 16S rrna gene sequence. Apart from Shigella spp., the genes from E. albertii and E. fergusonii are also included (arrows). The 16S rrna gene of S. enterica Typhimurium LT2 was used as the root. Bootstrap values, indicated in red, show that most nodes are predicted with uncertainty; nevertheless, the genera Escherichia spp. and Shigella spp. are not separated in this tree, and the three Escherichia species are also mixed a Enterobacteriaceae genera 16S rrna tree Wigglesworthia glossinidia endosymbiont of Glossina brevipalpis Yersinia pestis Angola Proteus mirabilis HI4320 Xenorhabdus bovienii SS-2004 Photorhabdus asymbiotica ATCC Edwardsiella ictaluri Dickeya dadantii Ech586 Serratia proteamaculans 568 Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI The Big Picture 16S rrna tree Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 Eneterobacter species Erwinia amylovora ATCC Citrobacter sakazakii ATCC BAA Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2 954 Citrobacter koseri ATCC BAA Shigella boydii CDC Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 Q: How does E. coli relate? Sodalis glossinidius 'morsitans' Candidatus Hamiltonella defensa 5AT (Acyrthosiphon pisum) Buchnera aphidicola str 5A (Acyrthosiphon pisum) 23 June,
6 2. Delve into details - first results.. b Question: Why is there poor resolution between E. coli genomes? 343 E. coli S. dysenteriae Sd197 E. coli CFT073 E. coli E22 E. coli O103:H2 str E. coli B str. REL606 E. coli BL21 (DE3) E. coli BL21 (DE3) S. sonnei Ss046 E. coli E. coli E E. coli 536 S. flexneri 5 str S. flexneri 2a str. 2457T S. boydii Sb S. flexneri 2a str. 301 S. boydii CDC E. coli O26:H11 str E. coli B7A 790 E. albertii TW E. coli BL21 (DE3) E. coli APEC O E. fergusonii ATCC35469 E. coli UTI89 E. coli SE15 E. coli O127:H6 str. E2348/69 S. dysenteriae E. coli S E. coli ED1a E. coli Oslo O103 E. coli F11 E. coli IAI E. coli HS E. coli K12 str. ATCC E. coli O111:H- str E. coli E24377A 404 E. coli K12 str. BW2952 E. coli E. coli IAI1 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4042 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4045 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4076 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4113 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4115 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4196 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4401 E. coli O157:H7 str. Sakai E. coli O157:H7 str. TW14588 E. coli SMS-3-5 E. coli SE11 E. coli UMN E. coli K12 str. DH1 16S rrna tree S. enterica Typhimurium str. LT2 E. coli O157:H7 str. EDL933 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4501 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4486 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4206 E. coli O157:H7 str. LANL ECF 225 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC508 E. coli O157:H7 str. LANL ECA E. coli K12 str. W E. coli K12 str. MG1655 E. coli K12 str. DH10B June,
7 pan-genome family tree Relati ve manhattan distance E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4196 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4113 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC508 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4501 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4076 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4115 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4042 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4486 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC869 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4206 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4401 E. coli O157:H7 str. EDL933 E. coli O157:H7 str. Sakai E. coli O157:H7 str. TW14588 E. coli O157:H7 str. LANL ECF E. coli O157:H7 str. LANL ECA E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4045 E. coli K12 str. W3110 E. coli K12 str. MG1655 E. coli K12 str. DH1 E. coli K12 str. BW2952 E. coli K12 DH10B E. coli K12ATCC8739 E. coli B str. REL606 E. coli BL21 (DE3Korea) E. coli BL21 (DE3 AU) E. coli BL21 (DE3 DOE) E. coli HS E. coli SE11 E. coli IAI1 E. coli E. coli E24377A E. coli O26:H11 str E. coli O103:H2 str E. coli O111:H str E. coli O103 Oslo E. coli SMS 3 5 E. coli UMN026 E. coli E. coli IAI39 E. coli UTI89 E. coli S88 E. coli CFT073 E. coli SE15 E. coli 536 E. coli O127:H6 str. E2348/69 E. coli ED1a E. coli F11 E. coli APECO1 E. coli E E. coli E22 E. coli B7A E. coli S. boydii CDC S. boydii Sb227 S. sonnei Ss046 S. flexneri 2a str. 2457T S. flexneri 2a str. 301 S. flexneri 5 str Salmonella enterica Typhimurium str. LT2 E. fergusonii ATCC E. albertii TW07627 S. dysenteriae 1012 S. dysenteriae Sd Figure 3 Pan-genome clustering of E. coli (black) and related species (colored), based on the alignment of their variable gene content. The genomes now cluster according to species and a relatedness between E. coli K12 derivatives (green block) and group B isolates (orange block) is visible Question: Does the grouping of the E. coli genomes make sense? 23 June,
8 pan- / core-genome plot O. Lukjancenko et al. Number of gene families Core genome Pan genome New gene families : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC508 4 : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. EDL : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. TW : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. Sakai 15 : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 EC : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. LANL ECF 17 : Escherichia coli 0157:H7 str. LANL ECA 18 : Escherichia coli K12 str. DH10B 19 : Escherichia coli K12 str. MG : Escherichia coli K12 str. W : Escherichia coli K12 str. DH1 22 : Escherichia coli BW : Escherichia coli ATCC : Escherichia coli B REL : Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3 Korea) 26 : Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3 AU) 27 : Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3 DOE) 28 : Escherichia coli HS 29 : Escherichia coli SE11 30 : Escherichia coli IAI1 31 : Escherichia coli : Escherichia coli E24377A 33 : Escherichia coli O26:H11 str : Escherichia coli 0127:H6 str. E2348/69 35 : Escherichia coli O103:H2 str : Escherichia coli O111:H- str : Escherichia coli 0103 Oslo 38 : Escherichia coli SMS : Escherichia coli UMN : Escherichia coli : Escherichia coli IAI39 42 : Escherichia coli UTI89 43 : Escherichia coli S88 44 : Escherichia coli CFT : Escherichia coli SE15 46 : Escherichia coli : Escherichia coli ED1a 48 : Escherichia coli F11 49 : Escherichia coli APECO1 50 : Escherichia coli E : Escherichia coli E22 52 : Escherichia coli B7A 53 : Escherichia coli : Shigella flexneri 2a 2457T 55 : Shigella flexneri 2a : Shigella flexneri : Shigella boydii CDC : Shigella boydii Sb : Shigella sonnei Ss : Escherichia fergusonii ATCC : Escherichia albertii TW : Salmonella enterica Typhimurium LT2 63 : Shigella dysenteriae Sd : Shigella dysenteriae 1012 Figure 4 Pan- and core genome plot of the analyzed genomes. The blue pan-genome curve connects the cumulative number of gene families present in the analyzed genomes. The red core genome curve connects the conserved number of gene families. The gray bars show the numbers of novel gene families identified in each genome Question: What happened when E. coli genome #18 was added? 23 June,
9 MLST tree Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree of concatenated MLST gene alleles (adk, fumc, icd, gyrb, mdh, pura, reca), extracted from the genome sequences. Color use is the same as in Fig. 1 E. coli O157:H7 str. LANL ECA E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4113 E. coli O157:H7 str. TW14588 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4196 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC869 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4486 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC508 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4042 E. coli O157:H7 str. LANL ECF E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4501 E. coli O157:H7 str. EDL933 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4045 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4076 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4115 E. coli O157:H7 str. Sakai E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4206 E. coli O157:H7 str. EC4401 Shigella flexneri 2a str. 301 Shigella flexneri 5 str Shigella flexneri 2a str. 2457T Shigella dysenteriae Sd197 E. coli E24377A Shigella boydii Sb227 Shigella boydii CDC Shigella sonnei Ss E. coli E E. coli O26:H11 str E. coli O111:H- str E. coli SE11 E. coli B7A E. coli O103:H2 str E. coli E22 E. coli Oslo O103 E. coli E. coli IAI1 E. coli E. coli HS E. coli K12 str. ATCC 8739 E. coli UMN026 E. coli SMS-3-5 E. coli IAI39 E. coli SE15 E. coli O127:H6 str. E2348/69 E. coli ED1a E. coli CFT073 E. coli APEC O1 E. coli UTI89 E. coli S88 E. coli F11 E. coli 536 Shigella dysenteriae 1012 E. coli BW2952 E. coli K12 str. W E. coli K12 str. DH10B E. coli K12 str. DH1 830 E. coli K12 str. MG1655 E. coli E. coli B str. REL606 E. coli BL21(DE3) E. coli BL21(DE3) E. coli BL21(DE3) O. Lukjancenko et al. E. albertii TW07627 E. fergusonii ATCC354 Question: Why is there poor resolution between the O157 E. coli genomes? June,
10 Comparison of 61 Sequenced Escherichia coli Genomes BLAST atlas Figure 5 BLAST atlas. In the middle, a genome atlas of E. coli O157:H7 strain EC4115 is shown, around which BLAST lanes are shown. Every lane corresponds to a genome, with the following colors (going outwards): green E. coli O157: H7 (15 lanes); light blue E. coli LANL strains (two lanes); dark blue Shigella spp. (eight lanes); red E. coli K12 and derivatives (six lanes); orange E. coli strain Bphylogroup(fourlanes); followed by all other E. coli genomes in different colors. The outermost three lanes represent E. fergusonii, E. albertii, ands. enterica Typhimurium LT2. Lack of color indicates that the genes at that position in strain EC4115 were not found in the genome of that lane. The position of replication origin and terminus is indicated Origin 4M 4.5M 3.5M 5M 3M 0M 2.5M 0.5M Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EC4115 2M 1M 1.5M Terminus Question: What is the cluster of highly conserved E. coli genes unique to O157? 23 June,
11
Design of an Enterobacteriaceae Pan-genome Microarray Chip
 Design of an Enterobacteriaceae Pan-genome Microarray Chip Oksana Lukjancenko and David W. Ussery DTU CBS 2010 2 Background Pan-genome complete collection of variuos genes located within populations at
Design of an Enterobacteriaceae Pan-genome Microarray Chip Oksana Lukjancenko and David W. Ussery DTU CBS 2010 2 Background Pan-genome complete collection of variuos genes located within populations at
Saturday (18 Aug 2007)
 E rrl Center for Biological Sequence analysis Comparative icrobial Genomics group BLAST atlases O r i g i 0 rrlc 4 0.5 rrla 3.5 4,641,433 bp rrld rrlb 1.5 3 2 2.5 Te r mi Dave Ussery nu 4th annual workshop
E rrl Center for Biological Sequence analysis Comparative icrobial Genomics group BLAST atlases O r i g i 0 rrlc 4 0.5 rrla 3.5 4,641,433 bp rrld rrlb 1.5 3 2 2.5 Te r mi Dave Ussery nu 4th annual workshop
Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated
 Figure S1 Figure S2 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated genomes. To generate these plots all strains within a species were
Figure S1 Figure S2 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated genomes. To generate these plots all strains within a species were
Comparison of 61 Sequenced Escherichia coli Genomes
 Microb Ecol DOI 10.1007/s00248-010-9717-3 MINIREVIEWS Comparison of 61 Sequenced Escherichia coli Genomes Oksana Lukjancenko & Trudy M. Wassenaar & David W. Ussery Received: 24 February 2010 / Accepted:
Microb Ecol DOI 10.1007/s00248-010-9717-3 MINIREVIEWS Comparison of 61 Sequenced Escherichia coli Genomes Oksana Lukjancenko & Trudy M. Wassenaar & David W. Ussery Received: 24 February 2010 / Accepted:
Pan- and core- Genomics
 Pan- and core- Genomics Dave Ussery Workshop on Comparative Genomics King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi Bangkok, Thailand First Talk for Wednesday 22 June, 2011 Center for Biological Sequence
Pan- and core- Genomics Dave Ussery Workshop on Comparative Genomics King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi Bangkok, Thailand First Talk for Wednesday 22 June, 2011 Center for Biological Sequence
Opening the pan-genomics box for E. coli
 Opening the pan-genomics box for E. coli Comparison of 20 sequenced genomes Dave Ussery Workshop on Comparative Microbial Genomics Oslo, Norway 19 October, 2006 Dave Ussery Genomics of pathogenic : European
Opening the pan-genomics box for E. coli Comparison of 20 sequenced genomes Dave Ussery Workshop on Comparative Microbial Genomics Oslo, Norway 19 October, 2006 Dave Ussery Genomics of pathogenic : European
genomes The minimal set of conserved proteins across a thousand bacterial Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology
 The minimal set of conserved proteins across a thousand bacterial genomes Dave Ussery Comparative Bacterial Genomics Workshop Centers for Disease Control Atlanta, Georgia, USA Thursday, 3 August, 212 Center
The minimal set of conserved proteins across a thousand bacterial genomes Dave Ussery Comparative Bacterial Genomics Workshop Centers for Disease Control Atlanta, Georgia, USA Thursday, 3 August, 212 Center
Supplemental. Location Year Source. 1412G Dalidag, Georgia 1979 Flea
 Supplemental Table S1: pestis strains (n=59) a Strain designation / bei # Location Year Source -- 1391G 1392G 1393G Ninotsminda, 1979 Common vole 1412G Dalidag, 1979 Flea 1413G 1670G 1851G 1852G 1853G
Supplemental Table S1: pestis strains (n=59) a Strain designation / bei # Location Year Source -- 1391G 1392G 1393G Ninotsminda, 1979 Common vole 1412G Dalidag, 1979 Flea 1413G 1670G 1851G 1852G 1853G
Indicator Organisms SCI5508
 Indicator Organisms SCI5508 Indicator Organisms REFLECTS microbiological quality organisms and/or their metabolic products whose presence in given foods at certain levels may be used to assess existing
Indicator Organisms SCI5508 Indicator Organisms REFLECTS microbiological quality organisms and/or their metabolic products whose presence in given foods at certain levels may be used to assess existing
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss
 Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
7 Multiple Genome Alignment
 94 Bioinformatics I, WS /3, D. Huson, December 3, 0 7 Multiple Genome Alignment Assume we have a set of genomes G,..., G t that we want to align with each other. If they are short and very closely related,
94 Bioinformatics I, WS /3, D. Huson, December 3, 0 7 Multiple Genome Alignment Assume we have a set of genomes G,..., G t that we want to align with each other. If they are short and very closely related,
Figure A1. Phylogenetic trees based on concatenated sequences of eight MLST loci. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on concatenated sequences
 A. B. Figure A1. Phylogenetic trees based on concatenated sequences of eight MLST loci. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on concatenated sequences of eight housekeeping loci for 12 unique STs
A. B. Figure A1. Phylogenetic trees based on concatenated sequences of eight MLST loci. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on concatenated sequences of eight housekeeping loci for 12 unique STs
Genetic Characterization of Atypical Citrobacter freundii
 Genetic Characterization of Atypical Citrobacter freundii Gabriela Delgado 1, Valeria Souza 2, Rosario Morales 1, René Cerritos 3, Andrea González-González 2, José Luis Méndez 1, Virginia Vázquez 4{, Alejandro
Genetic Characterization of Atypical Citrobacter freundii Gabriela Delgado 1, Valeria Souza 2, Rosario Morales 1, René Cerritos 3, Andrea González-González 2, José Luis Méndez 1, Virginia Vázquez 4{, Alejandro
Microbial Bioinformatics
 1 Microbial Bioinformatics Introduction These exercises are for you to learn how to use bioinformatics tools to explore bacterial genomes, and complements the Microbiology of Safe Food 2 nd Edition (Wiley-
1 Microbial Bioinformatics Introduction These exercises are for you to learn how to use bioinformatics tools to explore bacterial genomes, and complements the Microbiology of Safe Food 2 nd Edition (Wiley-
Evolutionary Relationships of Three New Species of Enterobacteriaceae Living as Symbionts of Aphids and Other Insects
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2005, p. 3302 3310 Vol. 71, No. 6 0099-2240/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aem.71.6.3302 3310.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2005, p. 3302 3310 Vol. 71, No. 6 0099-2240/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aem.71.6.3302 3310.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Understanding microbes through the lens of comparative genomics... a biased perspective. Aaron Darling A/Prof. ithree institute UTS
 Understanding microbes through the lens of comparative genomics... a biased perspective Aaron Darling A/Prof. ithree institute UTS Molecular Evolution of Bacteria Bacteria reproduce clonally A brief history
Understanding microbes through the lens of comparative genomics... a biased perspective Aaron Darling A/Prof. ithree institute UTS Molecular Evolution of Bacteria Bacteria reproduce clonally A brief history
Bacterial phylogenetic tree construction based on genomic translation stop signals
 Xu et al. Microbial Informatics and Experimentation 2012, 2:6 RESEARCH Open Access Bacterial phylogenetic tree construction based on genomic translation stop signals Lijing Xu 1, Jimmy Kuo 2, Jong-Kang
Xu et al. Microbial Informatics and Experimentation 2012, 2:6 RESEARCH Open Access Bacterial phylogenetic tree construction based on genomic translation stop signals Lijing Xu 1, Jimmy Kuo 2, Jong-Kang
Whole Genome based Phylogeny
 Whole Genome based Phylogeny Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student DTU Bioinformatics Short about me Johanne Ahrenfeldt johah@dtu.dk PhD student at DTU Bioinformatics Whole Genome based Phylogeny Graduate Engineer
Whole Genome based Phylogeny Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student DTU Bioinformatics Short about me Johanne Ahrenfeldt johah@dtu.dk PhD student at DTU Bioinformatics Whole Genome based Phylogeny Graduate Engineer
Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas
 December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
Development of Compact Dry SL for Salmonella detection
 Development of Compact Dry SL for Salmonella detection S.Mizuochi 1),H.Teramura 1),S.Nirazuka 1),H.Kodaka 1),K.Inoue ) K.Tamura 3) 1)Research Dept., Nissui Pharmaceutical, ) Saitama Pref. Ranzango Hp.,
Development of Compact Dry SL for Salmonella detection S.Mizuochi 1),H.Teramura 1),S.Nirazuka 1),H.Kodaka 1),K.Inoue ) K.Tamura 3) 1)Research Dept., Nissui Pharmaceutical, ) Saitama Pref. Ranzango Hp.,
Evolution of bacteria to populate a new environment necessarily. Structure and Function of the D-Galactose Network in Enterobacteria
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure and Function of the D-Galactose Network in Enterobacteria Zsolt Csiszovszki, a Sandeep Krishna, b László Orosz, c Sankar Adhya, a and Szabolcs Semsey c,d Laboratory of Molecular
RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure and Function of the D-Galactose Network in Enterobacteria Zsolt Csiszovszki, a Sandeep Krishna, b László Orosz, c Sankar Adhya, a and Szabolcs Semsey c,d Laboratory of Molecular
UNCORRECTED PROOF. AUTHOR'S PROOF Microb Ecol DOI /s
 Microb Ecol DOI 10.1007/s00248-011-9880-1 1 3 MINIREVIEWS 2 4 The Salmonella enterica Pan-genome 5 Annika Jacobsen & Rene S. Hendriksen & 6 Frank M. Aaresturp & David W. Ussery & Carsten Friis Q2 Q3 7
Microb Ecol DOI 10.1007/s00248-011-9880-1 1 3 MINIREVIEWS 2 4 The Salmonella enterica Pan-genome 5 Annika Jacobsen & Rene S. Hendriksen & 6 Frank M. Aaresturp & David W. Ussery & Carsten Friis Q2 Q3 7
ydci GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC
 Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Interpreting the Molecular Tree of Life: What Happened in Early Evolution? Norm Pace MCD Biology University of Colorado-Boulder
 Interpreting the Molecular Tree of Life: What Happened in Early Evolution? Norm Pace MCD Biology University of Colorado-Boulder nrpace@colorado.edu Outline What is the Tree of Life? -- Historical Conceptually
Interpreting the Molecular Tree of Life: What Happened in Early Evolution? Norm Pace MCD Biology University of Colorado-Boulder nrpace@colorado.edu Outline What is the Tree of Life? -- Historical Conceptually
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA. Phylogenetic Classification
 Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA Ya Zhang and Wen Tso Liu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Mark LeChevallier American Water Inc. Nov 2011 Phylogenetic Classification group organisms
Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA Ya Zhang and Wen Tso Liu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Mark LeChevallier American Water Inc. Nov 2011 Phylogenetic Classification group organisms
Chapter 19. Microbial Taxonomy
 Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
A Phylogenetic Gibbs Recursive Sampler for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites
 A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
Product Catalogue 2016 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome
 Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Phylogenetic Gibbs Recursive Sampler. Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites
 A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
Supplementary figures and tables MetaVelvet : An extension of Velvet assembler to de novo metagenome assembly from short sequence reads
 Supplementary figures and tables MetaVelvet : An extension of Velvet assembler to de novo metagenome assembly from short sequence reads Toshiaki Namiki 1,2, Tsuyoshi Hachiya 1, Hideaki Tanaka 1, and Yasubumi
Supplementary figures and tables MetaVelvet : An extension of Velvet assembler to de novo metagenome assembly from short sequence reads Toshiaki Namiki 1,2, Tsuyoshi Hachiya 1, Hideaki Tanaka 1, and Yasubumi
Product Catalogue 2015 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
SULFIDE-INDOLE-MOTILITY (SIM) TEST
 Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 5 Principle and Purpose SULFIDE-INDOLE-MOTILITY (SIM) TEST Using Sulfide-Indole-Motility (SIM) media, various Gram-negative enteric bacilli can be distinguished
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 5 Principle and Purpose SULFIDE-INDOLE-MOTILITY (SIM) TEST Using Sulfide-Indole-Motility (SIM) media, various Gram-negative enteric bacilli can be distinguished
SSI ENTERIC PRODUCT INFORMATION. Detects all Enterobacteria. Direct identification. Rapid diagnosis. Cost saving
 SSI ENTERIC M E D I U M Detects all Enterobacteria Direct identification Rapid diagnosis Cost saving SSI Diagnostica 2 Herredsvejen 3400 Hillerød Denmark PRODUCT INFORMATION Tel: +45 4829 9100 Fax: +45
SSI ENTERIC M E D I U M Detects all Enterobacteria Direct identification Rapid diagnosis Cost saving SSI Diagnostica 2 Herredsvejen 3400 Hillerød Denmark PRODUCT INFORMATION Tel: +45 4829 9100 Fax: +45
Evaluation of the Modified Micro-ID System for Identification
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1979, p. 454-458 0095-1 137/79/10-0454/05$02.00/0 Vol. 10, No. 4 Evaluation of the Modified Micro-ID System for Identification of Enterobacteriaceae WILLIAM J. BUESCHING,'
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1979, p. 454-458 0095-1 137/79/10-0454/05$02.00/0 Vol. 10, No. 4 Evaluation of the Modified Micro-ID System for Identification of Enterobacteriaceae WILLIAM J. BUESCHING,'
Classification of Enterobacteria Based on Overall
 JOURNAL OF BAcTERIOLOGY, Nov., 1966 Copyright 1966 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 92, No. 5 Printed In U.S.A. Classification of Enterobacteria Based on Overall Similarity1 R. E. KRIEG AND W. R.
JOURNAL OF BAcTERIOLOGY, Nov., 1966 Copyright 1966 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 92, No. 5 Printed In U.S.A. Classification of Enterobacteria Based on Overall Similarity1 R. E. KRIEG AND W. R.
Essentiality in B. subtilis
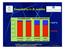 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Caroline M. O Hara* Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia 30333
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2006, p. 928 933 Vol. 44, No. 3 0095-1137/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.44.3.928 933.2006 Evaluation of the Phoenix 100 ID/AST System and NID Panel for Identification
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2006, p. 928 933 Vol. 44, No. 3 0095-1137/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.44.3.928 933.2006 Evaluation of the Phoenix 100 ID/AST System and NID Panel for Identification
Genes order and phylogenetic reconstruction: application to γ-proteobacteria
 Genes order and phylogenetic reconstruction: application to γ-proteobacteria Guillaume Blin 1, Cedric Chauve 2 and Guillaume Fertin 1 1 LINA FRE CNRS 2729, Université de Nantes 2 rue de la Houssinière,
Genes order and phylogenetic reconstruction: application to γ-proteobacteria Guillaume Blin 1, Cedric Chauve 2 and Guillaume Fertin 1 1 LINA FRE CNRS 2729, Université de Nantes 2 rue de la Houssinière,
Title: Gut microbiota predict pulmonary infiltrates after allogeneic hematopoietic cell
 Online Data Supplement Title: Gut microbiota predict pulmonary infiltrates after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation Author list: Bianca Harris,Sejal M. Morjaria, Eric R. Littmann, Alexander
Online Data Supplement Title: Gut microbiota predict pulmonary infiltrates after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation Author list: Bianca Harris,Sejal M. Morjaria, Eric R. Littmann, Alexander
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2015), 65, Pathology, 500 Chipeta Way, Salt Lake City, UT, USA
 International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2015), 65, 1400 1405 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.000091 Phenotypic characterization of Sodalis praecaptivus sp. nov., a close non-insect-associated
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2015), 65, 1400 1405 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.000091 Phenotypic characterization of Sodalis praecaptivus sp. nov., a close non-insect-associated
Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae
 Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary
Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary
The Evolution of Infectious Disease
 The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
Polynucleotide Sequence Divergence Among
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Mar. 1972, p. 953-965 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 109, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Polynucleotide Sequence Divergence Among Strains of Escherichia coli and
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Mar. 1972, p. 953-965 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 109, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Polynucleotide Sequence Divergence Among Strains of Escherichia coli and
of the Family Enterobacteriaceae
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMATIC BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 1995, p. 5261 00207713/ 95/$04.00 0 Copyright 0 1995, International Union of Microbiological Societies Vol. 45, No. 2 Heterogeneous Patterns of Acid
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMATIC BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 1995, p. 5261 00207713/ 95/$04.00 0 Copyright 0 1995, International Union of Microbiological Societies Vol. 45, No. 2 Heterogeneous Patterns of Acid
ID Membranes for Microbial Rapid Identification
 ID Membranes for Microbial Rapid Identification Chromogenic Reaction by Specific Substrates on Membranes Classical plates are still used today as first steps in modern microbiology. Smart, inexpensive
ID Membranes for Microbial Rapid Identification Chromogenic Reaction by Specific Substrates on Membranes Classical plates are still used today as first steps in modern microbiology. Smart, inexpensive
Phylogeny of the Enterobacteriaceae based on genes encoding elongation factor Tu and F-ATPase b-subunit
 International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2005), 55, 2013 2025 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.63539-0 Phylogeny of the Enterobacteriaceae based on genes encoding elongation factor Tu and F-ATPase
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2005), 55, 2013 2025 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.63539-0 Phylogeny of the Enterobacteriaceae based on genes encoding elongation factor Tu and F-ATPase
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research SJIF Impact Factor 8.074
 SJIF Impact Factor 8.074 Volume 7, Issue 5, 966-973. Research Article ISSN 2277 7105 MOLECULAR DETECTION OF ENTEROTOXIGENIC ISOLATES OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM, SHIGELLA FLEXNERI AND STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
SJIF Impact Factor 8.074 Volume 7, Issue 5, 966-973. Research Article ISSN 2277 7105 MOLECULAR DETECTION OF ENTEROTOXIGENIC ISOLATES OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM, SHIGELLA FLEXNERI AND STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
10ml. Set (4 poly and 17 monovalent, 2ml each)
 120314TR Bordetella pertussis Antigen 10ml Contents 1 Bordetella pertussis Antigen 1 Clostridium perfringens Type A 2 Escherichia coli 5 Legionella pneumophila 5 Listeria monocytogenes 6 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
120314TR Bordetella pertussis Antigen 10ml Contents 1 Bordetella pertussis Antigen 1 Clostridium perfringens Type A 2 Escherichia coli 5 Legionella pneumophila 5 Listeria monocytogenes 6 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Chronology and pattern of integration of tandem genomic islands associated with the tmrna gene in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica
 Article Bioinformatics December 2011 Vol.56 No.35: 3836 3844 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4749-8 Chronology and pattern of integration of tandem genomic islands associated with the tmrna gene in Escherichia
Article Bioinformatics December 2011 Vol.56 No.35: 3836 3844 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4749-8 Chronology and pattern of integration of tandem genomic islands associated with the tmrna gene in Escherichia
Numerical Diagnostic Key for the Identification of Enterobacteriaceae
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1972, p. 108-112 Copyright 0 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 23, No. 1 Printed in U.SA. Numerical Diagnostic Key for the Identification of Enterobacteriaceae HERMAN
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1972, p. 108-112 Copyright 0 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 23, No. 1 Printed in U.SA. Numerical Diagnostic Key for the Identification of Enterobacteriaceae HERMAN
Outline. I. Methods. II. Preliminary Results. A. Phylogeny Methods B. Whole Genome Methods C. Horizontal Gene Transfer
 Comparative Genomics Preliminary Results April 4, 2016 Juan Castro, Aroon Chande, Cheng Chen, Evan Clayton, Hector Espitia, Alli Gombolay, Walker Gussler, Ken Lee, Tyrone Lee, Hari Prasanna, Carlos Ruiz,
Comparative Genomics Preliminary Results April 4, 2016 Juan Castro, Aroon Chande, Cheng Chen, Evan Clayton, Hector Espitia, Alli Gombolay, Walker Gussler, Ken Lee, Tyrone Lee, Hari Prasanna, Carlos Ruiz,
Pan-genome analysis provides much higher strain typing resolution than multi-locus sequence typing
 Microbiology (2010), 156, 1060 1068 DOI 10.1099/mic.0.035188-0 Pan-genome analysis provides much higher strain typing resolution than multi-locus sequence typing Barry G. Hall, 1,2 Garth D. Ehrlich 2,3
Microbiology (2010), 156, 1060 1068 DOI 10.1099/mic.0.035188-0 Pan-genome analysis provides much higher strain typing resolution than multi-locus sequence typing Barry G. Hall, 1,2 Garth D. Ehrlich 2,3
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
A phylogenomic analysis of Escherichia coli / Shigella group: implications of genomic features associated with pathogenicity and ecological adaptation
 Zhang and Lin BMC Evolutionary Biology 2012, 12:174 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A phylogenomic analysis of Escherichia coli / Shigella group: implications of genomic features associated with pathogenicity
Zhang and Lin BMC Evolutionary Biology 2012, 12:174 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A phylogenomic analysis of Escherichia coli / Shigella group: implications of genomic features associated with pathogenicity
Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity
 19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
Most common dose (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1. Maximum dose schedule (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1
 Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
An Inclusivity and Exclusivity Evaluation of the Invisible Sentinel Veriflow Salmonella Species Method for the Detection of Salmonella species
 An Inclusivity and Exclusivity Evaluation of the Invisible Sentinel Veriflow Salmonella Species for the Detection of Salmonella species AOAC PTM Evaluation September 20, 2013 Erin S. Crowley, Patrick M.
An Inclusivity and Exclusivity Evaluation of the Invisible Sentinel Veriflow Salmonella Species for the Detection of Salmonella species AOAC PTM Evaluation September 20, 2013 Erin S. Crowley, Patrick M.
Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy. Slowly evolving molecules (e.g., rrna) used for large-scale structure; "fast- clock" molecules for fine-structure.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures
 Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Gram negative bacilli
 Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material S1. Alignment of promoter sequences Figure S1 shows the alignment of the promoter regions of the E. coli wild isolates sequenced. Figure S1. Promoter alignment of the sequenced strains.
Supplemental Material S1. Alignment of promoter sequences Figure S1 shows the alignment of the promoter regions of the E. coli wild isolates sequenced. Figure S1. Promoter alignment of the sequenced strains.
Multicenter Evaluation of the MicroScan Rapid Gram-Negative Identification Type 3 Panel
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1997, p. 2531 2536 Vol. 35, No. 10 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Multicenter Evaluation of the MicroScan Rapid Gram-Negative
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1997, p. 2531 2536 Vol. 35, No. 10 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Multicenter Evaluation of the MicroScan Rapid Gram-Negative
Topology. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 Topology 1 Introduction 2 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 G+C content 7 Codon usage 27 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr The big picture Eukaryota Bacteria Many linear chromosomes
Topology 1 Introduction 2 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 G+C content 7 Codon usage 27 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr The big picture Eukaryota Bacteria Many linear chromosomes
Database and Comparative Identification of Prophages
 Database and Comparative Identification of Prophages K.V. Srividhya 1, Geeta V Rao 1, Raghavenderan L 1, Preeti Mehta 1, Jaime Prilusky 2, Sankarnarayanan Manicka 1, Joel L. Sussman 3, and S Krishnaswamy
Database and Comparative Identification of Prophages K.V. Srividhya 1, Geeta V Rao 1, Raghavenderan L 1, Preeti Mehta 1, Jaime Prilusky 2, Sankarnarayanan Manicka 1, Joel L. Sussman 3, and S Krishnaswamy
ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Microbiol Immunol 2016; 60: 303 311 doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Phylogenetics of family Enterobacteriaceae and proposal to reclassify Escherichia hermannii and Salmonella subterranea
Microbiol Immunol 2016; 60: 303 311 doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Phylogenetics of family Enterobacteriaceae and proposal to reclassify Escherichia hermannii and Salmonella subterranea
Bacterial pan-genomics
 Bacterial pan-genomics Dave Ussery 4 th annual workshop on Comparative Microbial Genomics and Taxonomy Petropolois, Brazil Lecture #3 Wednesday, 5 August, 2009 What we DO know What we DON'T know Outline
Bacterial pan-genomics Dave Ussery 4 th annual workshop on Comparative Microbial Genomics and Taxonomy Petropolois, Brazil Lecture #3 Wednesday, 5 August, 2009 What we DO know What we DON'T know Outline
Clinical Laboratory Evaluation of the AutoMicrobic System
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, OCt. 1981, p. 370-375 0095-1 137/81/100370-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 4 Clinical Laboratory Evaluation of the AutoMicrobic System Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Card JAMES
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, OCt. 1981, p. 370-375 0095-1 137/81/100370-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 4 Clinical Laboratory Evaluation of the AutoMicrobic System Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Card JAMES
High Throughput Scientific Computing in Vaccine Research: Challenges and Opportunities
 High Throughput Scientific Computing in Vaccine Research: Challenges and Opportunities Riccardo Beltrami Head, Data Science Unit Novartis Vaccines Univ. di Siena, Dec. 10 th 2014 Rev. 1.2.3 PDC# SIE-14-0923
High Throughput Scientific Computing in Vaccine Research: Challenges and Opportunities Riccardo Beltrami Head, Data Science Unit Novartis Vaccines Univ. di Siena, Dec. 10 th 2014 Rev. 1.2.3 PDC# SIE-14-0923
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Comparative Genome Analysis of Three Pathogenic Strains of E. coli, Salmonella and Shigella
 Comparative Genome Analysis of Three Pathogenic Strains of E. coli, Salmonella and Shigella Chandra Shivani* 1, Kumari Abha 1, Grover Alka 1 and Nehra Sampat 2 1 Amity University Uttar Pradesh, Noida 2
Comparative Genome Analysis of Three Pathogenic Strains of E. coli, Salmonella and Shigella Chandra Shivani* 1, Kumari Abha 1, Grover Alka 1 and Nehra Sampat 2 1 Amity University Uttar Pradesh, Noida 2
The dnd operon for DNA phosphorothioation modification system in Escherichia coli is located in diverse genomic islands
 Ho et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:199 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1421-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The dnd operon for DNA phosphorothioation modification system in Escherichia coli is located in diverse genomic
Ho et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:199 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1421-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The dnd operon for DNA phosphorothioation modification system in Escherichia coli is located in diverse genomic
Enterobacterial Fimbriae
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Mar. 1987, P. 934-938 0021-9193/87/030934-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 169, No. 3 Enterobacterial Fimbriae STEVEN CLEGG* AND GERALD F. GERLACH
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Mar. 1987, P. 934-938 0021-9193/87/030934-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 169, No. 3 Enterobacterial Fimbriae STEVEN CLEGG* AND GERALD F. GERLACH
BD BBL CHROMagar Salmonella* / XLD Agar (Biplate)
 PA-257372.02 Page 1 of 7 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257372.02 Rev.: Mar 2013 BD BBL CHROMagar Salmonella* / XLD Agar (Biplate) * U.S. Patent # 5,098,832, 5,194,374 INTENDED USE BBL
PA-257372.02 Page 1 of 7 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257372.02 Rev.: Mar 2013 BD BBL CHROMagar Salmonella* / XLD Agar (Biplate) * U.S. Patent # 5,098,832, 5,194,374 INTENDED USE BBL
Repeated Sequences SOPHIE BACHELLIER, ERIC GILSON, MAURICE HOFNUNG, AND CHARLES W. HILL
 Repeated Sequences SOPHIE BACHELLIER, ERIC GILSON, MAURICE HOFNUNG, AND CHARLES W. HILL 112 INTRODUCTION Sequence repetition in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium (official designation, Salmonella
Repeated Sequences SOPHIE BACHELLIER, ERIC GILSON, MAURICE HOFNUNG, AND CHARLES W. HILL 112 INTRODUCTION Sequence repetition in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium (official designation, Salmonella
Nonhomogeneous Model of Sequence Evolution Indicates Independent Origins of Primary Endosymbionts Within the Enterobacteriales (c-proteobacteria)
 Nonhomogeneous Model of Sequence Evolution Indicates Independent Origins of Primary Endosymbionts Within the Enterobacteriales (c-proteobacteria) Joshua T. Herbeck, 1 Patrick H. Degnan, and Jennifer J.
Nonhomogeneous Model of Sequence Evolution Indicates Independent Origins of Primary Endosymbionts Within the Enterobacteriales (c-proteobacteria) Joshua T. Herbeck, 1 Patrick H. Degnan, and Jennifer J.
Salmonella enteritidis Identification and Isolation
 Department of Microbiology, Qom Branch, Islamic Azad University. Qom, Iran Start Here Advisor Dr.Mohsen Zargar Consulting Advisor Dr.Taghi Salehi Zahraei Presented by Zeinab Yazdanpanah 1 Outcome Enterobacteriaceae
Department of Microbiology, Qom Branch, Islamic Azad University. Qom, Iran Start Here Advisor Dr.Mohsen Zargar Consulting Advisor Dr.Taghi Salehi Zahraei Presented by Zeinab Yazdanpanah 1 Outcome Enterobacteriaceae
ijo1366 Escherichia coli Model
 -1- ijo1366 Escherichia coli Model -2- ijo1366 E.coli Model Learning Objectives Each student should be able to: Describe the major differences between the iaf1260 and ijo1366 E.coli models. Describe the
-1- ijo1366 Escherichia coli Model -2- ijo1366 E.coli Model Learning Objectives Each student should be able to: Describe the major differences between the iaf1260 and ijo1366 E.coli models. Describe the
Taxonomic Study of Campylobacter Species using hsp60 Protein
 Taxonomic Study of Campylobacter Species using hsp60 Protein Mohammed Z. Saeed Al-khayyat Department of Biology College of Education University of Mosul Mosul City, Iraq E-mail: mzalkhayat@yahoo.com Received:
Taxonomic Study of Campylobacter Species using hsp60 Protein Mohammed Z. Saeed Al-khayyat Department of Biology College of Education University of Mosul Mosul City, Iraq E-mail: mzalkhayat@yahoo.com Received:
Erosion of Interaction Networks in Reduced and Degraded Genomes
 JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL ZOOLOGY (MOL DEV EVOL) 308B (2007) Erosion of Interaction Networks in Reduced and Degraded Genomes HOWARD OCHMAN 1, RENYI LIU 1, AND EDUARDO P.C. ROCHA 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL ZOOLOGY (MOL DEV EVOL) 308B (2007) Erosion of Interaction Networks in Reduced and Degraded Genomes HOWARD OCHMAN 1, RENYI LIU 1, AND EDUARDO P.C. ROCHA 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
μ gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli gyra E. coli parc gyra parc gyra Escherichia coli E. coli E.
 gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
Microbial Taxonomy. Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy. C. Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy 1. Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eucaryote, is in a mess we are stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy 1. Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eucaryote, is in a mess we are stuck with it for traditional
Stability. Received for publication 1 August to be fl-lactamase-producing strains.
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1978, p. 584-588 0066-4804/78/0013-0584$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Cefaclor: In Vitro Spectrum
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1978, p. 584-588 0066-4804/78/0013-0584$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Cefaclor: In Vitro Spectrum
AOAC SMPR Standard Method Performance Requirements for Detection of Salmonella species in Romaine Lettuce and Baby Spinach
 AOAC SMPR 2014.017 Standard Method Performance Requirements for Detection of Salmonella species in Romaine Lettuce and Baby Spinach Intended Use: Routine Surveillance and Monitoring by a Trained Technician
AOAC SMPR 2014.017 Standard Method Performance Requirements for Detection of Salmonella species in Romaine Lettuce and Baby Spinach Intended Use: Routine Surveillance and Monitoring by a Trained Technician
PATHfinder. User Manual. PATHfinder Salmonella spp. Assay. Real-Time PCR kit for Salmonella spp. detection. Cat. # PMB01A/PMB01A-50
 PATHfinder PATHfinder Salmonella spp. Assay Real-Time PCR kit for Salmonella spp. detection Cat. # PMB01A/PMB01A-50 User Manual Via San Geminiano, 4 41030 San Prospero (MO)- Italy : +39 059 8637161 : +39
PATHfinder PATHfinder Salmonella spp. Assay Real-Time PCR kit for Salmonella spp. detection Cat. # PMB01A/PMB01A-50 User Manual Via San Geminiano, 4 41030 San Prospero (MO)- Italy : +39 059 8637161 : +39
Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy. The ultimate goal in taxonomy. Pragmatic towards diagnostics
 Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy - MLSA - Dirk Gevers Different needs for taxonomy Describe bio-diversity Understand evolution of life Epidemiology Diagnostics Biosafety...
Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy - MLSA - Dirk Gevers Different needs for taxonomy Describe bio-diversity Understand evolution of life Epidemiology Diagnostics Biosafety...
Identification and Characterization of Cronobacter spp. Iron Acquisition Systems
 AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 15 June 2012 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.01457-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Identification
AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 15 June 2012 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.01457-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Identification
Insilico Analysis of Novel Relb, Rele and Mazf Toxin-Antitoxin Homolog s from the Genome of Xenorhabdus Nematophila
 American Journal of Bioinformatics Research 2012, 2(3): 21-32 DOI: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120203.02 Insilico Analysis of Novel Relb, Rele and Mazf Toxin-Antitoxin Homolog s from the Genome of Xenorhabdus
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research 2012, 2(3): 21-32 DOI: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120203.02 Insilico Analysis of Novel Relb, Rele and Mazf Toxin-Antitoxin Homolog s from the Genome of Xenorhabdus
BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER
 BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Vol. 25 no. 24 2009, pages 3221 3227 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp590 Genome analysis Efficient estimation of pairwise distances between genomes Mirjana Domazet-Lošo 1,2
BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Vol. 25 no. 24 2009, pages 3221 3227 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp590 Genome analysis Efficient estimation of pairwise distances between genomes Mirjana Domazet-Lošo 1,2
EZ-COMP EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Product Details
 EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Identification of Enterobacteriaceae by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry using the VITEK MS system
 DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1912-y ARTICLE Identification of Enterobacteriaceae by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry using the VITEK MS system S. S. Richter & L. Sercia
DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1912-y ARTICLE Identification of Enterobacteriaceae by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry using the VITEK MS system S. S. Richter & L. Sercia
Alternative tools for phylogeny. Identification of unique core sequences
 Alternative tools for phylogeny Identification of unique core sequences Workshop on Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis, 19-21 Mar. 2018 Learning objective: After this lecture you should be able to account
Alternative tools for phylogeny Identification of unique core sequences Workshop on Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis, 19-21 Mar. 2018 Learning objective: After this lecture you should be able to account
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) as a tool for monitoring purposes. Henrik Hasman DTU - Food
 Whole genome sequencing (WGS) as a tool for monitoring purposes Henrik Hasman DTU - Food The Challenge Is to: Continue to increase the power of surveillance and diagnostic using molecular tools Develop
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) as a tool for monitoring purposes Henrik Hasman DTU - Food The Challenge Is to: Continue to increase the power of surveillance and diagnostic using molecular tools Develop
