Understanding microbes through the lens of comparative genomics... a biased perspective. Aaron Darling A/Prof. ithree institute UTS
|
|
|
- Asher Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Understanding microbes through the lens of comparative genomics... a biased perspective Aaron Darling A/Prof. ithree institute UTS
2 Molecular Evolution of Bacteria Bacteria reproduce clonally
3 A brief history of recombination Joshua Lederberg Discovered conjugative gene transfer in bacteria Won Nobel Prize in 1958 Early work on phage transduction at UW Madison
4 Genomics revolutionizes our understanding of bacterial evolution Perna et al 2001 Nature, Welch et al 2002 PNAS Three genomes, same species, nearly identical 16S rrna, only 40% genes in common What is a bacterial species??
5 Need to compare genomes automatically! How?? Positional homology: Mauve, M-GCAT, MUMmer, Mugsy, TBA, others Glocal: Enredo/PECAN, Cactus, SuperMap/Multi-LAGAN, euleralign, Repeatoire Darling et al 2004, 2006, 2010
6 Sequence alignment Most sequence alignment utilizes dynamic programming Key assumption: each site evolves independently of neighbors (I.i.d.) Substitution matrix: A C G T A C G T Gap open: -2 Gap extend: -2
7 Scaling up to genomes: anchored alignment Calculate only parts of the DP matrix that are very likely to be part of the optimal path Each diagonal band is a high-scoring local alignment of the sequences. The highest scoring chain of local alignments become anchors Multiple alignment: some algorithms anchor in N dimensions, others progressively build from 2...N dimensions
8 The architecture of Mauve C++ command-line aligner Java GUI 69k lines of C++ code. Organized into two development libraries plus refactored Clustal-W and MUSCLE into libraries. Uses: Boost, Subversion, Doxygen, valgrind Cross-platform autotools and Viz Studio builds snapshot server runs VMs with 4 OSes to complete nightly builds Automated accuracy testing using cluster computing (SGE + perl + R) Java GUI is 31k lines of code 5 developers, 25 years effort under basic COCOMO model
9 US$ per million nucleotides Mauve 1.0 could align genomes in but soon there were too many!! Introduction of 454 technology Illumina/Solexa/SOLiD
10 With many genomes, subsets become critical Mauve 1.0 only aligned core genome Many almost core regions conserved in some, but not all genomes
11 A. D'hont et al 2012 Nature
12 Main innovations in progressivemauve Tolerate mismatches in initial alignment anchors Sum of pairs breakpoint score: z Score ( z )= Q( z i + k, z j +k ) k =1 Score(z) is the sum of substitution scores for all sites in genome i and j that are aligned in block z Penalize blocks containing repeats (not shown) Define a genome-pair-specific breakpoint penalty βij Add & remove blocks to OPTIMIZE: β Z + Score ( z ) z Z Apply a HMM to determine gain/loss regions Darling et al 2010 PLoS ONE
13 Darling et al 2010, PLoS ONE Alignment accuracy based on simulation studies Blue asterisk indicates rates predicted among Enterobacteriacae 50 large gene gain/loss events means total flux of 2Mbp in the 1Mbp genomes 10k small events means total flux of 3.56Mbp in the 1Mbp genomes Darling et al 2010 PLoS ONE
14 The Alignathon: more alignment accuracy metrics Data simulated to mimic four primate genomes Some variation in precision & recall among methods For some applications, precision more important than recall & vice versa Earl et al 2014, Genome Research
15 Alignments are hard to get right... A: gap wander B, C: gap attraction D: gap annihilation Source: Lunter et al 2008 Genome Research Prakash and Tompa, 2007 Genome Biology: We identify 9.7% (21 Mbp) of the human chromosome 1 alignment as suspiciously aligned. in the UCSC genome browser
16 Great so do we learn any new biology? Some case studies: Genome rearrangement in Yersinia Gene gain and loss in E. coli and Shigella Homologous recombination in E. coli
17 Genome alignment of nine Yersinia Darling et al 2008 PLoS Genetics
18 A phylogeny of the Yersinia What inversions happened on this branch? Use Bayesian MCMC to sample all possible inversion histories according to their probability
19 Maximum a posteriori estimate of Y. pestis Antiqua inversion history Darling et al 2008 PLoS Genetics
20 Maximum a posteriori estimate of Y. pestis Antiqua inversion history Darling et al 2008 PLoS Genetics
21 Rearrangement hotspots in Yersinia Few rearrangements surrounding dif site Could disorient FtsK binding sites (KOPS) Darling et al 2008 PLoS Genetics
22 Great so do we learn any new biology? Some case studies: Genome rearrangement in Yersinia Gene gain and loss in E. coli and Shigella Homologous recombination in E. coli
23 Inferring rate changes in gain&loss Phylogenetic tree from ClonalFrame on core genome Bayesian mapping of gains, losses onto tree Compound Poisson process BLUE: rate of gene loss RED: rate of gene gain Didelot, Darling, Falush. Genome Research 2009
24 Great so do we learn any new biology? Some case studies: Genome rearrangement in Yersinia Gene gain and loss in E. coli and Shigella Homologous recombination in E. coli
25 Bayesian inference of homologous recombination Given a genome alignment, infer: - species phylogeny The weak ARG model: Species tree in black Recombination in red - local phylogenies - boundaries of recombination events Approach: - Bayesian phylogenetic model - Recombination are edges connecting points on species tree - Each recombination affects a local region of the genome - Inference via MCMC sampler ClonalOrigin Didelot et al 2010 Genetics, Didelot et al 2012 BMC Genomics
26 Inferring recombination in E. coli Mauve Genome Alignment of 27 finished E. coli genomes alignment blocks Million alignment columns in core genome only - Interrupted by gene content differences, rearrangements *** * * * * + * * + + * * * *+ * + + and * are in our study * * * * + + Darling, Mau, Perna 2010
27 Global spatial pattern of recombination O antigen proteins Membrane-localizing proteins Mystery hotspot Mucho differential gene content Integron?? Ribosomal protein cluster E. coli K12 red bar terminus, black bar origin Y-axis = Average number of recombination events per site Didelot, Meric, Falush, Darling BMC Genomics
28 Asymmetric gene flow across clonal lineages E. coli ATCC8739 E. coli HS E. coli BL21/DE3 E. coli B REL606 E. coli BW2952 E. coli K-12 DH10B E. coli K-12 MG1655 E. coli K-12 W3110 E. coli IAI1 E. coli SE11 E. coli E. coli O103:H2 E. coli E24377A E. coli O111:HE. coli O26:H11 E. coli O157:H7 EC4115 E. coli O157:H7 TW14359 E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 E. coli O157:H7 Sakai E. coli O55:H7 E. coli APEC O1 E. coli UTI89 E. coli S88 E. coli CFT073 E. coli ED1A E. coli 536 E. coli E2348/69 Heat colors give Observed/Expected recombination events Blue=fewer than expected, Red=more Didelot, Meric, Falush, Darling BMC Genomics
29 Functional enrichment of recombination Global over- and under-representation in the class of highly recombinogenic genes: Obs Exp Chi2 Function Under Protein related information transfer Over Metabolism of other compounds Under Energy production/transport Under Function Unknown Over Accessory Factors Involved in Transport Over Building block biosynthesis Over DNA related information transfer Categories with Chi2 values < 4 not shown Darling, unpublished
30 Thanks to Daniel Falush Xavier Didelot Daniel Lawson Max Plank Institut Imperial College Nicole T. Perna Bob Mau Univ. of Bristol Mark Ragan Univ. of Wisconsin Univ. of Wisconsin Univ. of Queensland Erick Matsen FHCRC Todd Treangen BNBI, Johns Hopkins Jonathan Eisen UC Davis, JGI Guillaume Jospin Jenna Lang Dongying Wu Students and other staff involved in this work: - Anna Rissman, Andrew Tritt, Paul Infield-Harm, Andres Esteban-Marcos,Tiffanie Nelson Eric Lowe, John Zhang, David Larsen, A/Prof Marc Facciotti, A/Prof Rachel Whitaker Open source software: - Mauve - ClonalOrigin - GenoPlast Funding: NSF, NIH, NLM, Mars Inc., US Dept. of Homeland Security, Gordon & Betty Moore Foundation
17 Non-collinear alignment Motivation A B C A B C A B C A B C D A C. This exposition is based on:
 17 Non-collinear alignment This exposition is based on: 1. Darling, A.E., Mau, B., Perna, N.T. (2010) progressivemauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One 5(6):e11147.
17 Non-collinear alignment This exposition is based on: 1. Darling, A.E., Mau, B., Perna, N.T. (2010) progressivemauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One 5(6):e11147.
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes
 Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
7 Multiple Genome Alignment
 94 Bioinformatics I, WS /3, D. Huson, December 3, 0 7 Multiple Genome Alignment Assume we have a set of genomes G,..., G t that we want to align with each other. If they are short and very closely related,
94 Bioinformatics I, WS /3, D. Huson, December 3, 0 7 Multiple Genome Alignment Assume we have a set of genomes G,..., G t that we want to align with each other. If they are short and very closely related,
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Genome Comparison. Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics & Computing, IUB
 I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, 2015 Genome Comparison Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Whole genome comparison/alignment Build better phylogenies Identify polymorphism
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, 2015 Genome Comparison Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Whole genome comparison/alignment Build better phylogenies Identify polymorphism
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.gn] 30 Oct 2009
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.gn] 30 Oct 2009 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.gn] 30 Oct 2009](/thumbs/84/90800978.jpg) arxiv:0910.5780v1 [q-bio.gn] 30 Oct 2009 Progressive Mauve: Multiple alignment of genomes with gene flux and rearrangement Aaron E. Darling 1,2,3 Bob Mau 4 Nicole T. Perna 5 Running title: Multiple genome
arxiv:0910.5780v1 [q-bio.gn] 30 Oct 2009 Progressive Mauve: Multiple alignment of genomes with gene flux and rearrangement Aaron E. Darling 1,2,3 Bob Mau 4 Nicole T. Perna 5 Running title: Multiple genome
BMI/CS 776 Lecture #20 Alignment of whole genomes. Colin Dewey (with slides adapted from those by Mark Craven)
 BMI/CS 776 Lecture #20 Alignment of whole genomes Colin Dewey (with slides adapted from those by Mark Craven) 2007.03.29 1 Multiple whole genome alignment Input set of whole genome sequences genomes diverged
BMI/CS 776 Lecture #20 Alignment of whole genomes Colin Dewey (with slides adapted from those by Mark Craven) 2007.03.29 1 Multiple whole genome alignment Input set of whole genome sequences genomes diverged
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Genome Comparison. Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics & Computing, IUB
 I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, 2011 Genome Comparison Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Whole genome comparison/alignment Build better phylogenies Identify polymorphism
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, 2011 Genome Comparison Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Whole genome comparison/alignment Build better phylogenies Identify polymorphism
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss
 Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
Genômica comparativa. João Carlos Setubal IQ-USP outubro /5/2012 J. C. Setubal
 Genômica comparativa João Carlos Setubal IQ-USP outubro 2012 11/5/2012 J. C. Setubal 1 Comparative genomics There are currently (out/2012) 2,230 completed sequenced microbial genomes publicly available
Genômica comparativa João Carlos Setubal IQ-USP outubro 2012 11/5/2012 J. C. Setubal 1 Comparative genomics There are currently (out/2012) 2,230 completed sequenced microbial genomes publicly available
Quantifying sequence similarity
 Quantifying sequence similarity Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 16 th 2016 After this lecture, you can define homology, similarity, and identity
Quantifying sequence similarity Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 16 th 2016 After this lecture, you can define homology, similarity, and identity
Phylogenetics without multiple sequence alignment
 Phylogenetics without multiple sequence alignment Mark Ragan Institute for Molecular Bioscience and School of Information Technology & Electrical Engineering The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Phylogenetics without multiple sequence alignment Mark Ragan Institute for Molecular Bioscience and School of Information Technology & Electrical Engineering The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
a-dB. Code assigned:
 This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
Whole Genome Alignment. Adam Phillippy University of Maryland, Fall 2012
 Whole Genome Alignment Adam Phillippy University of Maryland, Fall 2012 Motivation cancergenome.nih.gov Breast cancer karyotypes www.path.cam.ac.uk Goal of whole-genome alignment } For two genomes, A and
Whole Genome Alignment Adam Phillippy University of Maryland, Fall 2012 Motivation cancergenome.nih.gov Breast cancer karyotypes www.path.cam.ac.uk Goal of whole-genome alignment } For two genomes, A and
Course: Visual Analytics of largescale biological data. Kay Nieselt Center for Bioinformatics Tübingen University of Tübingen
 Course: Visual Analytics of largescale biological data Kay Nieselt Center for Bioinformatics Tübingen University of Tübingen THE SUPERGENOME AND GENOMERING Overview A revolution in genomics Flood of genomes:
Course: Visual Analytics of largescale biological data Kay Nieselt Center for Bioinformatics Tübingen University of Tübingen THE SUPERGENOME AND GENOMERING Overview A revolution in genomics Flood of genomes:
Essentiality in B. subtilis
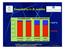 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
THEORY. Based on sequence Length According to the length of sequence being compared it is of following two types
 Exp 11- THEORY Sequence Alignment is a process of aligning two sequences to achieve maximum levels of identity between them. This help to derive functional, structural and evolutionary relationships between
Exp 11- THEORY Sequence Alignment is a process of aligning two sequences to achieve maximum levels of identity between them. This help to derive functional, structural and evolutionary relationships between
Introduction to Evolutionary Concepts
 Introduction to Evolutionary Concepts and VMD/MultiSeq - Part I Zaida (Zan) Luthey-Schulten Dept. Chemistry, Beckman Institute, Biophysics, Institute of Genomics Biology, & Physics NIH Workshop 2009 VMD/MultiSeq
Introduction to Evolutionary Concepts and VMD/MultiSeq - Part I Zaida (Zan) Luthey-Schulten Dept. Chemistry, Beckman Institute, Biophysics, Institute of Genomics Biology, & Physics NIH Workshop 2009 VMD/MultiSeq
Hidden Markov models in population genetics and evolutionary biology
 Hidden Markov models in population genetics and evolutionary biology Gerton Lunter Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Oxford, UK April 29, 2013 Topics for today Markov chains Hidden Markov models
Hidden Markov models in population genetics and evolutionary biology Gerton Lunter Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Oxford, UK April 29, 2013 Topics for today Markov chains Hidden Markov models
The problem Lineage model Examples. The lineage model
 The lineage model A Bayesian approach to inferring community structure and evolutionary history from whole-genome metagenomic data Jack O Brien Bowdoin College with Daniel Falush and Xavier Didelot Cambridge,
The lineage model A Bayesian approach to inferring community structure and evolutionary history from whole-genome metagenomic data Jack O Brien Bowdoin College with Daniel Falush and Xavier Didelot Cambridge,
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Phylogenies Show Evolutionary Relationships
 Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
InDel 3-5. InDel 8-9. InDel 3-5. InDel 8-9. InDel InDel 8-9
 Lecture 5 Alignment I. Introduction. For sequence data, the process of generating an alignment establishes positional homologies; that is, alignment provides the identification of homologous phylogenetic
Lecture 5 Alignment I. Introduction. For sequence data, the process of generating an alignment establishes positional homologies; that is, alignment provides the identification of homologous phylogenetic
a-dB. Code assigned:
 This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
Comparison of Cost Functions in Sequence Alignment. Ryan Healey
 Comparison of Cost Functions in Sequence Alignment Ryan Healey Use of Cost Functions Used to score and align sequences Mathematically model how sequences mutate and evolve. Evolution and mutation can be
Comparison of Cost Functions in Sequence Alignment Ryan Healey Use of Cost Functions Used to score and align sequences Mathematically model how sequences mutate and evolve. Evolution and mutation can be
Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated
 Figure S1 Figure S2 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated genomes. To generate these plots all strains within a species were
Figure S1 Figure S2 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated genomes. To generate these plots all strains within a species were
Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013
 AP Biology Name Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013 1. The following table shows the percentage similarity in sequences of nucleotides from a homologous gene derived from five different species
AP Biology Name Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013 1. The following table shows the percentage similarity in sequences of nucleotides from a homologous gene derived from five different species
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Microbiome: 16S rrna Sequencing 3/30/2018
 Microbiome: 16S rrna Sequencing 3/30/2018 Skills from Previous Lectures Central Dogma of Biology Lecture 3: Genetics and Genomics Lecture 4: Microarrays Lecture 12: ChIP-Seq Phylogenetics Lecture 13: Phylogenetics
Microbiome: 16S rrna Sequencing 3/30/2018 Skills from Previous Lectures Central Dogma of Biology Lecture 3: Genetics and Genomics Lecture 4: Microarrays Lecture 12: ChIP-Seq Phylogenetics Lecture 13: Phylogenetics
Handling Rearrangements in DNA Sequence Alignment
 Handling Rearrangements in DNA Sequence Alignment Maneesh Bhand 12/5/10 1 Introduction Sequence alignment is one of the core problems of bioinformatics, with a broad range of applications such as genome
Handling Rearrangements in DNA Sequence Alignment Maneesh Bhand 12/5/10 1 Introduction Sequence alignment is one of the core problems of bioinformatics, with a broad range of applications such as genome
a-fB. Code assigned:
 This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
AP Bio Module 16: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
Sequence Alignment Techniques and Their Uses
 Sequence Alignment Techniques and Their Uses Sarah Fiorentino Since rapid sequencing technology and whole genomes sequencing, the amount of sequence information has grown exponentially. With all of this
Sequence Alignment Techniques and Their Uses Sarah Fiorentino Since rapid sequencing technology and whole genomes sequencing, the amount of sequence information has grown exponentially. With all of this
Taming the Beast Workshop
 Workshop and Chi Zhang June 28, 2016 1 / 19 Species tree Species tree the phylogeny representing the relationships among a group of species Figure adapted from [Rogers and Gibbs, 2014] Gene tree the phylogeny
Workshop and Chi Zhang June 28, 2016 1 / 19 Species tree Species tree the phylogeny representing the relationships among a group of species Figure adapted from [Rogers and Gibbs, 2014] Gene tree the phylogeny
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity
 Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Microbes and you ON THE LATEST HUMAN MICROBIOME DISCOVERIES, COMPUTATIONAL QUESTIONS AND SOME SOLUTIONS. Elizabeth Tseng
 Microbes and you ON THE LATEST HUMAN MICROBIOME DISCOVERIES, COMPUTATIONAL QUESTIONS AND SOME SOLUTIONS Elizabeth Tseng Dept. of CSE, University of Washington Johanna Lampe Lab, Fred Hutchinson Cancer
Microbes and you ON THE LATEST HUMAN MICROBIOME DISCOVERIES, COMPUTATIONAL QUESTIONS AND SOME SOLUTIONS Elizabeth Tseng Dept. of CSE, University of Washington Johanna Lampe Lab, Fred Hutchinson Cancer
Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression)
 Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... More accurately... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression) "A comparison of the structures
Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... More accurately... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression) "A comparison of the structures
Graph Alignment and Biological Networks
 Graph Alignment and Biological Networks Johannes Berg http://www.uni-koeln.de/ berg Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Cologne Germany p.1/12 Networks in molecular biology New large-scale
Graph Alignment and Biological Networks Johannes Berg http://www.uni-koeln.de/ berg Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Cologne Germany p.1/12 Networks in molecular biology New large-scale
MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas
 December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016)
 CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions CISC636, F16, Lec22, Liao 1 Background Proteins do not function as isolated entities. Protein-Protein
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions CISC636, F16, Lec22, Liao 1 Background Proteins do not function as isolated entities. Protein-Protein
"Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Theodosius Dobzhansky
 MOLECULAR PHYLOGENY "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Theodosius Dobzhansky EVOLUTION - theory that groups of organisms change over time so that descendeants differ structurally
MOLECULAR PHYLOGENY "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Theodosius Dobzhansky EVOLUTION - theory that groups of organisms change over time so that descendeants differ structurally
08/21/2017 BLAST. Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega
 BLAST Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega What does basic BLAST do (e.g. what is input sequence and how does BLAST look for matches?) Susan Parrish McDaniel College Multiple Sequence Alignments
BLAST Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega What does basic BLAST do (e.g. what is input sequence and how does BLAST look for matches?) Susan Parrish McDaniel College Multiple Sequence Alignments
Phylogenetics: Building Phylogenetic Trees
 1 Phylogenetics: Building Phylogenetic Trees COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University 2 Four Questions Need to be Answered What data should we use? Which method should we use? Which evolutionary model should
1 Phylogenetics: Building Phylogenetic Trees COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University 2 Four Questions Need to be Answered What data should we use? Which method should we use? Which evolutionary model should
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection. Horizontal Gene Transfer. General Principles 10/2/17.
 Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection What about organisms that do not have sexual reproduction? Horizontal Gene Transfer Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin In prokaryotes:
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection What about organisms that do not have sexual reproduction? Horizontal Gene Transfer Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin In prokaryotes:
Copyright Warning & Restrictions
 Copyright Warning & Restrictions The copyright law of the United States (Title 17, United States Code) governs the making of photocopies or other reproductions of copyrighted material. Under certain conditions
Copyright Warning & Restrictions The copyright law of the United States (Title 17, United States Code) governs the making of photocopies or other reproductions of copyrighted material. Under certain conditions
Phylogenetics: Building Phylogenetic Trees. COMP Fall 2010 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Phylogenetics: Building Phylogenetic Trees COMP 571 - Fall 2010 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Four Questions Need to be Answered What data should we use? Which method should we use? Which evolutionary
Phylogenetics: Building Phylogenetic Trees COMP 571 - Fall 2010 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Four Questions Need to be Answered What data should we use? Which method should we use? Which evolutionary
6.047 / Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.047 / 6.878 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.047 / 6.878 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Inferring phylogeny. Constructing phylogenetic trees. Tõnu Margus. Bioinformatics MTAT
 Inferring phylogeny Constructing phylogenetic trees Tõnu Margus Contents What is phylogeny? How/why it is possible to infer it? Representing evolutionary relationships on trees What type questions questions
Inferring phylogeny Constructing phylogenetic trees Tõnu Margus Contents What is phylogeny? How/why it is possible to infer it? Representing evolutionary relationships on trees What type questions questions
Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy. The ultimate goal in taxonomy. Pragmatic towards diagnostics
 Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy - MLSA - Dirk Gevers Different needs for taxonomy Describe bio-diversity Understand evolution of life Epidemiology Diagnostics Biosafety...
Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy - MLSA - Dirk Gevers Different needs for taxonomy Describe bio-diversity Understand evolution of life Epidemiology Diagnostics Biosafety...
Taxonomy. Content. How to determine & classify a species. Phylogeny and evolution
 Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Bioinformatics. Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics
 Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Microbial Taxonomy. Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
General context Anchor-based method Evaluation Discussion. CoCoGen meeting. Accuracy of the anchor-based strategy for genome alignment.
 CoCoGen meeting Accuracy of the anchor-based strategy for genome alignment Raluca Uricaru LIRMM, CNRS Université de Montpellier 2 3 octobre 2008 1 / 31 Summary 1 General context 2 Global alignment : anchor-based
CoCoGen meeting Accuracy of the anchor-based strategy for genome alignment Raluca Uricaru LIRMM, CNRS Université de Montpellier 2 3 octobre 2008 1 / 31 Summary 1 General context 2 Global alignment : anchor-based
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Bio 119 Bacterial Genomics 6/26/10
 BACTERIAL GENOMICS Reading in BOM-12: Sec. 11.1 Genetic Map of the E. coli Chromosome p. 279 Sec. 13.2 Prokaryotic Genomes: Sizes and ORF Contents p. 344 Sec. 13.3 Prokaryotic Genomes: Bioinformatic Analysis
BACTERIAL GENOMICS Reading in BOM-12: Sec. 11.1 Genetic Map of the E. coli Chromosome p. 279 Sec. 13.2 Prokaryotic Genomes: Sizes and ORF Contents p. 344 Sec. 13.3 Prokaryotic Genomes: Bioinformatic Analysis
Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions
 Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions Tomi Peltola T-61.6070 Special course in bioinformatics I 3.4.2008 Outline Biological background Protein-protein interactions Computational
Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions Tomi Peltola T-61.6070 Special course in bioinformatics I 3.4.2008 Outline Biological background Protein-protein interactions Computational
Bayesian Models for Phylogenetic Trees
 Bayesian Models for Phylogenetic Trees Clarence Leung* 1 1 McGill Centre for Bioinformatics, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada ABSTRACT Introduction: Inferring genetic ancestry of different species
Bayesian Models for Phylogenetic Trees Clarence Leung* 1 1 McGill Centre for Bioinformatics, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada ABSTRACT Introduction: Inferring genetic ancestry of different species
Multiple Alignment of Genomic Sequences
 Ross Metzger June 4, 2004 Biochemistry 218 Multiple Alignment of Genomic Sequences Genomic sequence is currently available from ENTREZ for more than 40 eukaryotic and 157 prokaryotic organisms. As part
Ross Metzger June 4, 2004 Biochemistry 218 Multiple Alignment of Genomic Sequences Genomic sequence is currently available from ENTREZ for more than 40 eukaryotic and 157 prokaryotic organisms. As part
Tools and Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Tools and Algorithms in Bioinformatics GCBA815, Fall 2015 Week-4 BLAST Algorithm Continued Multiple Sequence Alignment Babu Guda, Ph.D. Department of Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy Bioinformatics and
Tools and Algorithms in Bioinformatics GCBA815, Fall 2015 Week-4 BLAST Algorithm Continued Multiple Sequence Alignment Babu Guda, Ph.D. Department of Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy Bioinformatics and
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences
 Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri 2008 Free for Academic
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri 2008 Free for Academic
Introduction to the SNP/ND concept - Phylogeny on WGS data
 Introduction to the SNP/ND concept - Phylogeny on WGS data Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student Overview What is Phylogeny and what can it be used for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) methods CSI Phylogeny
Introduction to the SNP/ND concept - Phylogeny on WGS data Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student Overview What is Phylogeny and what can it be used for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) methods CSI Phylogeny
Whole Genome Alignments and Synteny Maps
 Whole Genome Alignments and Synteny Maps IINTRODUCTION It was not until closely related organism genomes have been sequenced that people start to think about aligning genomes and chromosomes instead of
Whole Genome Alignments and Synteny Maps IINTRODUCTION It was not until closely related organism genomes have been sequenced that people start to think about aligning genomes and chromosomes instead of
METHODS FOR DETERMINING PHYLOGENY. In Chapter 11, we discovered that classifying organisms into groups was, and still is, a difficult task.
 Chapter 12 (Strikberger) Molecular Phylogenies and Evolution METHODS FOR DETERMINING PHYLOGENY In Chapter 11, we discovered that classifying organisms into groups was, and still is, a difficult task. Modern
Chapter 12 (Strikberger) Molecular Phylogenies and Evolution METHODS FOR DETERMINING PHYLOGENY In Chapter 11, we discovered that classifying organisms into groups was, and still is, a difficult task. Modern
EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCES
 EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCES FROM STRINGS TO TREES Luca Bortolussi 1 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste luca@dmi.units.it Trieste, 14 th November 2007 OUTLINE 1 STRINGS:
EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCES FROM STRINGS TO TREES Luca Bortolussi 1 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste luca@dmi.units.it Trieste, 14 th November 2007 OUTLINE 1 STRINGS:
Concepts and Methods in Molecular Divergence Time Estimation
 Concepts and Methods in Molecular Divergence Time Estimation 26 November 2012 Prashant P. Sharma American Museum of Natural History Overview 1. Why do we date trees? 2. The molecular clock 3. Local clocks
Concepts and Methods in Molecular Divergence Time Estimation 26 November 2012 Prashant P. Sharma American Museum of Natural History Overview 1. Why do we date trees? 2. The molecular clock 3. Local clocks
Lecture 7 Sequence analysis. Hidden Markov Models
 Lecture 7 Sequence analysis. Hidden Markov Models Nicolas Lartillot may 2012 Nicolas Lartillot (Universite de Montréal) BIN6009 may 2012 1 / 60 1 Motivation 2 Examples of Hidden Markov models 3 Hidden
Lecture 7 Sequence analysis. Hidden Markov Models Nicolas Lartillot may 2012 Nicolas Lartillot (Universite de Montréal) BIN6009 may 2012 1 / 60 1 Motivation 2 Examples of Hidden Markov models 3 Hidden
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #5 -- Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #5 -- Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
Processes of Evolution
 15 Processes of Evolution Forces of Evolution Concept 15.4 Selection Can Be Stabilizing, Directional, or Disruptive Natural selection can act on quantitative traits in three ways: Stabilizing selection
15 Processes of Evolution Forces of Evolution Concept 15.4 Selection Can Be Stabilizing, Directional, or Disruptive Natural selection can act on quantitative traits in three ways: Stabilizing selection
Microbes usually have few distinguishing properties that relate them, so a hierarchical taxonomy mainly has not been possible.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy. Slowly evolving molecules (e.g., rrna) used for large-scale structure; "fast- clock" molecules for fine-structure.
 Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification through identification and nomenclature of microbes, both "prokaryote" and eukaryote, has been in a mess we were stuck with it for traditional
Hidden Markov Models and some applications
 Oleg Makhnin New Mexico Tech Dept. of Mathematics November 11, 2011 HMM description Application to genetic analysis Applications to weather and climate modeling Discussion HMM description Application to
Oleg Makhnin New Mexico Tech Dept. of Mathematics November 11, 2011 HMM description Application to genetic analysis Applications to weather and climate modeling Discussion HMM description Application to
Sifting through genomes with iterative-sequence clustering produces a large, phylogenetically diverse protein-family resource
 Sharpton et al. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13:264 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sifting through genomes with iterative-sequence clustering produces a large, phylogenetically diverse protein-family resource
Sharpton et al. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13:264 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sifting through genomes with iterative-sequence clustering produces a large, phylogenetically diverse protein-family resource
Bioinformatics tools for phylogeny and visualization. Yanbin Yin
 Bioinformatics tools for phylogeny and visualization Yanbin Yin 1 Homework assignment 5 1. Take the MAFFT alignment http://cys.bios.niu.edu/yyin/teach/pbb/purdue.cellwall.list.lignin.f a.aln as input and
Bioinformatics tools for phylogeny and visualization Yanbin Yin 1 Homework assignment 5 1. Take the MAFFT alignment http://cys.bios.niu.edu/yyin/teach/pbb/purdue.cellwall.list.lignin.f a.aln as input and
Algorithms in Bioinformatics FOUR Pairwise Sequence Alignment. Pairwise Sequence Alignment. Convention: DNA Sequences 5. Sequence Alignment
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics FOUR Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Pairwise Sequence Alignment Homology Similarity Global string alignment Local string alignment Dot
Algorithms in Bioinformatics FOUR Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Pairwise Sequence Alignment Homology Similarity Global string alignment Local string alignment Dot
Outline. I. Methods. II. Preliminary Results. A. Phylogeny Methods B. Whole Genome Methods C. Horizontal Gene Transfer
 Comparative Genomics Preliminary Results April 4, 2016 Juan Castro, Aroon Chande, Cheng Chen, Evan Clayton, Hector Espitia, Alli Gombolay, Walker Gussler, Ken Lee, Tyrone Lee, Hari Prasanna, Carlos Ruiz,
Comparative Genomics Preliminary Results April 4, 2016 Juan Castro, Aroon Chande, Cheng Chen, Evan Clayton, Hector Espitia, Alli Gombolay, Walker Gussler, Ken Lee, Tyrone Lee, Hari Prasanna, Carlos Ruiz,
Phylogenomics, Multiple Sequence Alignment, and Metagenomics. Tandy Warnow University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Phylogenomics, Multiple Sequence Alignment, and Metagenomics Tandy Warnow University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Phylogeny (evolutionary tree) Orangutan Gorilla Chimpanzee Human From the Tree of the
Phylogenomics, Multiple Sequence Alignment, and Metagenomics Tandy Warnow University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Phylogeny (evolutionary tree) Orangutan Gorilla Chimpanzee Human From the Tree of the
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
Effects of Gap Open and Gap Extension Penalties
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 200-10-01 Effects of Gap Open and Gap Extension Penalties Hyrum Carroll hyrumcarroll@gmail.com Mark J. Clement clement@cs.byu.edu See
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 200-10-01 Effects of Gap Open and Gap Extension Penalties Hyrum Carroll hyrumcarroll@gmail.com Mark J. Clement clement@cs.byu.edu See
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec1 Building a Multiple Sequence Alignment Learning Outcomes 1- Understanding Why multiple
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec1 Building a Multiple Sequence Alignment Learning Outcomes 1- Understanding Why multiple
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Molecular phylogeny - Using molecular sequences to infer evolutionary relationships. Tore Samuelsson Feb 2016
 Molecular phylogeny - Using molecular sequences to infer evolutionary relationships Tore Samuelsson Feb 2016 Molecular phylogeny is being used in the identification and characterization of new pathogens,
Molecular phylogeny - Using molecular sequences to infer evolutionary relationships Tore Samuelsson Feb 2016 Molecular phylogeny is being used in the identification and characterization of new pathogens,
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 05: Index-based alignment algorithms Slides adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University of Central Florida) Real applications of alignment Database search
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 05: Index-based alignment algorithms Slides adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University of Central Florida) Real applications of alignment Database search
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea
 Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic pipeline for single-cell genome assembly, cleaning and annotation. a. The assembly process was optimized to account for multiple cells putatively
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic pipeline for single-cell genome assembly, cleaning and annotation. a. The assembly process was optimized to account for multiple cells putatively
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Unsupervised Learning in Spectral Genome Analysis
 Unsupervised Learning in Spectral Genome Analysis Lutz Hamel 1, Neha Nahar 1, Maria S. Poptsova 2, Olga Zhaxybayeva 3, J. Peter Gogarten 2 1 Department of Computer Sciences and Statistics, University of
Unsupervised Learning in Spectral Genome Analysis Lutz Hamel 1, Neha Nahar 1, Maria S. Poptsova 2, Olga Zhaxybayeva 3, J. Peter Gogarten 2 1 Department of Computer Sciences and Statistics, University of
Motivating the need for optimal sequence alignments...
 1 Motivating the need for optimal sequence alignments... 2 3 Note that this actually combines two objectives of optimal sequence alignments: (i) use the score of the alignment o infer homology; (ii) use
1 Motivating the need for optimal sequence alignments... 2 3 Note that this actually combines two objectives of optimal sequence alignments: (i) use the score of the alignment o infer homology; (ii) use
Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity
 19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
An Automated Phylogenetic Tree-Based Small Subunit rrna Taxonomy and Alignment Pipeline (STAP)
 An Automated Phylogenetic Tree-Based Small Subunit rrna Taxonomy and Alignment Pipeline (STAP) Dongying Wu 1 *, Amber Hartman 1,6, Naomi Ward 4,5, Jonathan A. Eisen 1,2,3 1 UC Davis Genome Center, University
An Automated Phylogenetic Tree-Based Small Subunit rrna Taxonomy and Alignment Pipeline (STAP) Dongying Wu 1 *, Amber Hartman 1,6, Naomi Ward 4,5, Jonathan A. Eisen 1,2,3 1 UC Davis Genome Center, University
Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab
 Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Phylogenies Scores for Exhaustive Maximum Likelihood and Parsimony Scores Searches
 Int. J. Bioinformatics Research and Applications, Vol. x, No. x, xxxx Phylogenies Scores for Exhaustive Maximum Likelihood and s Searches Hyrum D. Carroll, Perry G. Ridge, Mark J. Clement, Quinn O. Snell
Int. J. Bioinformatics Research and Applications, Vol. x, No. x, xxxx Phylogenies Scores for Exhaustive Maximum Likelihood and s Searches Hyrum D. Carroll, Perry G. Ridge, Mark J. Clement, Quinn O. Snell
Genomic Comparison of Bacterial Species Based on Metabolic Characteristics
 Genomic Comparison of Bacterial Species Based on Metabolic Characteristics Gaurav Jain 1, Haozhu Wang 1, Li Liao 1*, E. Fidelma Boyd 2* 1 Department of Computer and Information Sciences University of Delaware
Genomic Comparison of Bacterial Species Based on Metabolic Characteristics Gaurav Jain 1, Haozhu Wang 1, Li Liao 1*, E. Fidelma Boyd 2* 1 Department of Computer and Information Sciences University of Delaware
Supplemental Materials
 JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY & BIOLOGY EDUCATION, May 2013, p. 107-109 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.496 Supplemental Materials for Engaging Students in a Bioinformatics Activity to Introduce Gene
JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY & BIOLOGY EDUCATION, May 2013, p. 107-109 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.496 Supplemental Materials for Engaging Students in a Bioinformatics Activity to Introduce Gene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Microbial Diversity. Yuzhen Ye I609 Bioinformatics Seminar I (Spring 2010) School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University
 Microbial Diversity Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) I609 Bioinformatics Seminar I (Spring 2010) School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University Contents Microbial diversity Morphological, structural,
Microbial Diversity Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) I609 Bioinformatics Seminar I (Spring 2010) School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University Contents Microbial diversity Morphological, structural,
Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 A prokaryotic cell Basic unit of living organisms is the cell; the smallest unit capable of life. Features found in all cells: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Genetic Material Cytoplasm ATP Energy External Stimuli
A prokaryotic cell Basic unit of living organisms is the cell; the smallest unit capable of life. Features found in all cells: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Genetic Material Cytoplasm ATP Energy External Stimuli
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
 Basic Local Alignment Search Tool Alignments used to uncover homologies between sequences combined with phylogenetic studies o can determine orthologous and paralogous relationships Local Alignment uses
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool Alignments used to uncover homologies between sequences combined with phylogenetic studies o can determine orthologous and paralogous relationships Local Alignment uses
Biological Networks: Comparison, Conservation, and Evolution via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor
 Biological Networks:,, and via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor Presented by: Noga Grebla Content of the presentation Presenting the goals of the research Reviewing basic terms
Biological Networks:,, and via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor Presented by: Noga Grebla Content of the presentation Presenting the goals of the research Reviewing basic terms
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Ap Biology Chapter 17 Packet Answers
 AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 PACKET ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for ap biology chapter 17 packet answers Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time ap biology chapter 17 packet answers PDF is available
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 17 PACKET ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for ap biology chapter 17 packet answers Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time ap biology chapter 17 packet answers PDF is available
