Oceanography Lecture 8
|
|
|
- Berniece Burns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Monday is an awful way to spend 1/7 of your week A A clear conscience is usually a sign of a bad memory I I used to have an open mind, but my brains kept falling out Oceanography Lecture 8 The surface of the Ocean: 2) Tides Tides: a. Equilibrium tidal theory b. Dynamical tidal theory The Surface of the Ocean: 2) Tides a. Equilibrium tidal theory Earth covered with a uniform and ideal layer of water (geoid( geoid) simplification of the relationships between the Oceans and the tide- rising bodies, the Moon and the Sun. The Earth-Moon System The system orbits the Sun around a common center of mass: the barycenter ( within the Earth s s mantle,! radius from center) a. Equilibrium tidal theory The rotation of the Earth-Moon System creates a motion that is equal at all points within and upon the Earth. Each point will also have the same angular velocity and hence a similar centrifugal force (CF)!
2 a. Equilibrium tidal theory The total centrifugal force within the Earth-Moon system exactly balances the forces of gravitational attraction between the two bodies so that the system as a whole is in equilibrium We should neither lose the Moon nor collide with it! Therefore F g = GMm D 2 = CF Where: G: Universal gravity cst M: Mass of the Earth m: Mass of the Moon D: Distance between M-E Let s s work it out! Tidal Producing Force (TPF) The tidal producing force at A is equal to the TPF at B but of opposite sign! TPF x = GMm (D ± r) " GMm 2 D 2 Which is approximately equal to TPF A = GMm2r D 3 = TPF B How does it compare to the Earth s s gravitational force? TPF F g = GMm2r D 3 gm = Gm2r gd 3 =10 7 The Tidal Force is 10 million times smaller than Earth s s gravitational pull! There is, therefore, no possible vertical movement of water! Tidal Producing Force (TPF) Gravitational attraction and centrifugal force produce two tidal bulges of water of approximately the same size, positioned on opposite sides of the Earth. Tidal Producing Force (TPF) The effects of tides are due to horizontal components (tractive( forces) of the tidal producing force: It is the tractive forces that cause the water to move, because this horizontal component is unopposed by any other lateral force. Formation of the tidal bulge Production of unequal tides!
3 Tidal Producing Force (TPF) What about the Sun? Mass TPF # (Distance) 3 Sun " 27.10! M = 3 ( Sun " 390! D) = = 0.46 Thus the sun has 46% the tide-generating force of the Moon! ) Tidal Day While the Earth rotates upon its axis, the Moon is moving in the same direction along its orbit about the Earth. After 24 hours, the Earth point that began directly under the Moon is no longer under the Moon! The Earth must turn an additional 50 minutes to bring the starting point back in line with the Moon. Therefore, a tidal day is not 24 hours but 24hrs and 50 min! (Tides arrive at locations an hour later each day) Spring Tides and Neap Tides The Moon orbits the Earth (29" days) and the Earth-Moon system orbits the Sun (365 days). 2) Spring Tides and Neap Tides.. The Moon orbits the Earth (29" days) and the Earth- Moon system orbits the Sun (365 days).
4 The Moon s s and Earth s s elliptical orbits (REM: TPF! 1/D 3 )! Perigee vs. Apogee (13% difference) (27.5 days)! Perihelion vs. aphelion (4% difference) (" a year) 3) Additional Tidal variations! The Moon s s declination Maximum tides!!moon at Perigee!Sun at Perihelion!Sun and Moon at zero declination!full (or new) Moon This condition occurs only every 1600 yrs! Next time is in 3300! b. Dynamical tide theory A more accurate depiction of tides is possible if we assume that the Oceans are dynamic (active) rather than static (still): Dynamical model of tides 1) Water is assumed to respond actively to the tide-generating force. No longer have stationary tidal bulge of water that stay aligned with the Moon as the Earth rotates. 2) Consider the effects due to the presence of continents and shapes of basins (horizontal and vertical) In the Dynamic model, the Ocean basins drag the tidal bulges with them each day as they rotate with the Earth. b. Dynamical tide theory The propagation of the tidal wave is deflected due to the Coriolis Force (North to the right; South to the left): rotary wave. 1) The rotary wave creates high tides (the crest) and low tides (the trough) each day. 2) The water surface moves up and down about a node in the center of the basin! (the antinodes, where amplitude is greatest, are located furthest away from the node). The amphidromic system: a) Cotidal lines: : connect points at which any given tide level is simultaneous, b) Corange lines: : connect points on the water surface that have equal tidal range.
5 Global Amphidromic System Lines are cotidal lines that converge on nodes (amphidromic( points) Cotidal lines are not evenly spaced:! Tides are shallow-water waves (C = (gh)( )!! Ocean basins have uneven shapes and depths wave refraction!! Combined effect of all these factors produces considerable regional variation in type and range of tides. Tides in coastal basins Tides in coastal basins will differ from large amphidromic systems! Broad and symmetrical basin (i.e. Gulf of St. Lawrence)! Narrow elongated basin (i.e. Bay of Fundy) Standing waves (Resonance) Standing waves do not move horizontally but remain stationary (Guitar string). The water oscillates back and forth about a fixed point: Node. The properties of a standing wave depend on the geometry of the basin. The larger the container, the longer its characteristic standing wave will take to oscillate. In an open basin (seiche), Comparison of Actual and Forecasted Water Levels for Galveston (Spring 97)
6 Galveston Pleasure Pier during the spring of 1999 (Cox, Tissot, Michaud) Neural Network Forecasting of Water Levels Water Level History Wind Stress History Wind Stress Forecast Barometric Pressure History Input Layer " (a 1,i x i ) b 1 " (a 2,i x i ) b 2 Hidden Layer ƒ (X 1 +b 1 ) ƒ (X 2 +b 2 ) " (a 3,i x i ) b 3 Output Layer ƒ (X 3 +b 3 ) H (t+i) Water Level Forecast Philippe Tissot ! Measures water levels (black),! Tidal chart forecasts (blue),! 24 hour neural network forecasts (red) The neural network model was trained for a period of 90 days during the spring of 1997 and is applied here to a frontal passage during the spring of The accuracy of the 24 hour neural network forecast shows the ability to predict the timing and the intensity of frontal passages.
Chapter 10 Tides. Introductory Oceanography 10 th Edition
 Chapter 10 Tides Introductory Oceanography 10 th Edition Most ocean waves are wind-generated The medium itself (solid, liquid, gas) does NOT actually travel in the direction of energy Figure 8-2 What causes
Chapter 10 Tides Introductory Oceanography 10 th Edition Most ocean waves are wind-generated The medium itself (solid, liquid, gas) does NOT actually travel in the direction of energy Figure 8-2 What causes
Chapter 10: Tides. Tides: 1. Understanding the Earth-Moon system
 Chapter 10: Tides Remember that tides are waves that are caused by the gravitational attraction of moon and sun. Tidal waves are the longest of all waves, L can be up to half the Earth s circumference.
Chapter 10: Tides Remember that tides are waves that are caused by the gravitational attraction of moon and sun. Tidal waves are the longest of all waves, L can be up to half the Earth s circumference.
Tides The Largest Waves in the Ocean
 Tides Tides The Largest Waves in the Ocean Understanding Tides Understanding Tides You will study several topics: Why Earth has tides Why tides vary daily Why tides vary monthly Tide Generation Tide Generation
Tides Tides The Largest Waves in the Ocean Understanding Tides Understanding Tides You will study several topics: Why Earth has tides Why tides vary daily Why tides vary monthly Tide Generation Tide Generation
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1. Demonstrate understanding of the effects of astronomical cycles on planet Earth.
 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 90954 Demonstrate understanding of the effects of astronomical cycles on planet
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 90954 Demonstrate understanding of the effects of astronomical cycles on planet
The Giant Tides of Fundy What are tides?
 The Giant Tides of Fundy What are tides? The tide is the natural change in elevation of water over time and can easily be observed along any ocean coastline. Some areas of the world have one high tide
The Giant Tides of Fundy What are tides? The tide is the natural change in elevation of water over time and can easily be observed along any ocean coastline. Some areas of the world have one high tide
Tides ( gravity waves ): this is what we see. (bay of Fundy, CAN)
 Tides ( gravity waves ): this is what we see (bay of Fundy, CAN) Which of the following are correct? A. Coastlines experience two high tides each day. B. Tides are 12 hours apart. C. High tide occurs simultaneously
Tides ( gravity waves ): this is what we see (bay of Fundy, CAN) Which of the following are correct? A. Coastlines experience two high tides each day. B. Tides are 12 hours apart. C. High tide occurs simultaneously
Tides: this is what we see
 Last time Wind generated waves and Tsunami These are wind and earthquake generated waves Today: Tides These are Gravity waves How are they generated What are their intersting complexities? Low tide (decrease
Last time Wind generated waves and Tsunami These are wind and earthquake generated waves Today: Tides These are Gravity waves How are they generated What are their intersting complexities? Low tide (decrease
Tides Supplement. Brian Arbic
 Tides Supplement Brian Arbic OVERVIEW QUESTIONS What causes the tides? How is a lunar day different from a solar day? Which body creates a larger tidal influence on Earth: the Moon or the Sun? How do the
Tides Supplement Brian Arbic OVERVIEW QUESTIONS What causes the tides? How is a lunar day different from a solar day? Which body creates a larger tidal influence on Earth: the Moon or the Sun? How do the
The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity
 The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity Pulls all points on Earth toward Moon s center of mass. near side of Earth is attracted more than far side because force of gravity decreases with increasing distance.
The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity Pulls all points on Earth toward Moon s center of mass. near side of Earth is attracted more than far side because force of gravity decreases with increasing distance.
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Chapter 2 Case Studies and Study Guide: Energy Sources of Earth Processes and Disasters
 Chapter 2 Case Studies and Study Guide: Energy Sources of Earth Processes and Disasters Key Concepts The four principal types of energy relevant to natural disasters are kinetic, potential, rotational
Chapter 2 Case Studies and Study Guide: Energy Sources of Earth Processes and Disasters Key Concepts The four principal types of energy relevant to natural disasters are kinetic, potential, rotational
Which of the following are correct?
 The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity Pulls all points on earth toward Moon s center of mass. near side of Earth is attracted more than far side because force of gravity decreases with increasing distance.
The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity Pulls all points on earth toward Moon s center of mass. near side of Earth is attracted more than far side because force of gravity decreases with increasing distance.
Where do objects get their energy?
 Where do objects get their energy? Energy makes matter move. Energy is always 'conserved' Conservation of Energy Energy can neither be created nor destroyed The total energy content of the universe was
Where do objects get their energy? Energy makes matter move. Energy is always 'conserved' Conservation of Energy Energy can neither be created nor destroyed The total energy content of the universe was
Overview: In this activity, students will learn how the moon affects ocean tides and also will create and interpret graphs of regional tide data.
 Tides & Lunar Cycles Overview: In this activity, students will learn how the moon affects ocean tides and also will create and interpret graphs of regional tide data. Episode Connection: Tides At the conclusion
Tides & Lunar Cycles Overview: In this activity, students will learn how the moon affects ocean tides and also will create and interpret graphs of regional tide data. Episode Connection: Tides At the conclusion
Tides. Gm 1 m2. F gravity=
 1 Tides Newton's gravitational force law says that the force of gravitation attraction depends strongly on the separation between two objects. The same applies to different portions of an extended object
1 Tides Newton's gravitational force law says that the force of gravitation attraction depends strongly on the separation between two objects. The same applies to different portions of an extended object
Tides. Tides are the slow, periodic vertical rise and fall of the ocean surface.
 PART 2 Tides Tides are the slow, periodic vertical rise and fall of the ocean surface. Tide is a giant wave caused by gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun on the rotating Earth. The gravitational pull
PART 2 Tides Tides are the slow, periodic vertical rise and fall of the ocean surface. Tide is a giant wave caused by gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun on the rotating Earth. The gravitational pull
TIDES. Sea Gmllt Oregon ORESU-G-0O-O01 'I--.
 UNLPLK) IANLPIN(j TIDES 'I--. Sea Gmllt Oregon ORESU-G-0O-O01 2000 by Oregon State University Oregon Sea Grant Oregon State University 402 Kerr Admin. Bldg. Corvallis, OR 97331-2134 (541)737-2716 seagrant.orst.edu
UNLPLK) IANLPIN(j TIDES 'I--. Sea Gmllt Oregon ORESU-G-0O-O01 2000 by Oregon State University Oregon Sea Grant Oregon State University 402 Kerr Admin. Bldg. Corvallis, OR 97331-2134 (541)737-2716 seagrant.orst.edu
CHAPTER 5 WATER LEVELS AND FLOW
 253 CHAPTER 5 WATER LEVELS AND FLOW 1. INTRODUCTION The purpose of this chapter is to provide the hydrographer and technical reader the fundamental information required to understand and apply water levels,
253 CHAPTER 5 WATER LEVELS AND FLOW 1. INTRODUCTION The purpose of this chapter is to provide the hydrographer and technical reader the fundamental information required to understand and apply water levels,
TIDES. A tide just after the first or third quarters of the moon There is the least difference between high and low water Spring Tides
 TIDES Earth and Moon Interaction The Earth is pulled to the Sun by gravity. The moon is pulled to the Earth by gravity. The moon s gravity effects the Earth s tides. Neap Tides A tide just after the first
TIDES Earth and Moon Interaction The Earth is pulled to the Sun by gravity. The moon is pulled to the Earth by gravity. The moon s gravity effects the Earth s tides. Neap Tides A tide just after the first
Figure 1 Different gravity force of the moon on different places on earth
 TIDES How the Sun and Moon cause tides. Spring tides, neap tides, and the three patterns of tides on earth caused by the rotation of Earth and local topographical features: Diurnal, Semi-Diurnal and Mixed
TIDES How the Sun and Moon cause tides. Spring tides, neap tides, and the three patterns of tides on earth caused by the rotation of Earth and local topographical features: Diurnal, Semi-Diurnal and Mixed
MS 20 Tides Exercise
 MS 20 Tides Exercise Name Time class meets Introduction Tides are the cyclical rise and fall of sea level caused by the gravitational attraction of the moon and, to a lesser extent, by the sun. Gravitational
MS 20 Tides Exercise Name Time class meets Introduction Tides are the cyclical rise and fall of sea level caused by the gravitational attraction of the moon and, to a lesser extent, by the sun. Gravitational
4 Tides. What causes tides? How do tides vary?
 CHAPTER 14 4 Tides SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes tides? How do tides vary? National Science
CHAPTER 14 4 Tides SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes tides? How do tides vary? National Science
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface.
 1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna Laurea Magistrale in Fisica del Sistema Terra Corso: Oceanografia Costiera
 Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna Laurea Magistrale in Fisica del Sistema Terra Corso: Oceanografia Costiera Marco.Zavatarelli@unibo.it Tides (Part 1) Main references Open University: Waves tides
Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna Laurea Magistrale in Fisica del Sistema Terra Corso: Oceanografia Costiera Marco.Zavatarelli@unibo.it Tides (Part 1) Main references Open University: Waves tides
Create a bulleted list of everything you know about the moon!
 The Moon Create a bulleted list of everything you know about the moon! If given the opportunity, would you want to go to the moon? A. YES! That would be really cool. B. NO! Why would anyone want to go
The Moon Create a bulleted list of everything you know about the moon! If given the opportunity, would you want to go to the moon? A. YES! That would be really cool. B. NO! Why would anyone want to go
Moon Occurrences. Eclipses. Tides
 Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
TIDAL POWER!
 Tide Notes terms: spring tide, neap tide, flood tide,ebb tide, slack tide, mean low water, mean high water, sea level, diurnal tides, semidiurnal tides http://www.iit.edu/~johnsonp/smart00/lesson4.htm#highest
Tide Notes terms: spring tide, neap tide, flood tide,ebb tide, slack tide, mean low water, mean high water, sea level, diurnal tides, semidiurnal tides http://www.iit.edu/~johnsonp/smart00/lesson4.htm#highest
Lecture: October 1, 2010
 Lecture: October 1, 2010 How long would it take to walk to Alpha Centauri? Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Wednesday October 6 Phases of Matter the phases solid liquid gas plasma depend on
Lecture: October 1, 2010 How long would it take to walk to Alpha Centauri? Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Wednesday October 6 Phases of Matter the phases solid liquid gas plasma depend on
A) M D) The Moon s distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
7 th Grade Science. Name: Date: Friday, November 4, Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon. Homeroom: Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review Name: Date: Friday, November 4, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT demonstrate
7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review Name: Date: Friday, November 4, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT demonstrate
Moon Occurrences. Eclipses. Tides
 Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Oceanography Quiz 2. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Oceanography Quiz 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The highest and lowest tides are known as the spring tides. When do these occur? a.
Oceanography Quiz 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The highest and lowest tides are known as the spring tides. When do these occur? a.
Chapter 6. The Tidal Force
 Chapter 6. The Tidal Force The so-called tidal force is not a separate force from gravity it is simply the differential gravitational force. That is, if two parts of an object have different distances
Chapter 6. The Tidal Force The so-called tidal force is not a separate force from gravity it is simply the differential gravitational force. That is, if two parts of an object have different distances
UNDERSTANDING TIDES. Steacy Dopp Hicks Physical Oceanographer. Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services Michael Szabados, Director
 UNDERSTANDING TIDES UNDERSTANDING TIDES by Steacy Dopp Hicks Physical Oceanographer Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services Michael Szabados, Director December 2006 U.S. DEPARTMENT
UNDERSTANDING TIDES UNDERSTANDING TIDES by Steacy Dopp Hicks Physical Oceanographer Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services Michael Szabados, Director December 2006 U.S. DEPARTMENT
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to. SWBAT explain how the gravity of the moon causes tides in Earth s oceans.
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 9_ Tides 1 Name: Date: Thursday, October 27, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT explain how the
7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 9_ Tides 1 Name: Date: Thursday, October 27, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT explain how the
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system.
 1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
Dynamics of the Earth
 Time Dynamics of the Earth Historically, a day is a time interval between successive upper transits of a given celestial reference point. upper transit the passage of a body across the celestial meridian
Time Dynamics of the Earth Historically, a day is a time interval between successive upper transits of a given celestial reference point. upper transit the passage of a body across the celestial meridian
Ocean and Coastal Processes. Ocean Basins. Chapter 20. Ocean Basins and Plates. Ocean Terms. Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast.
 Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
The SMILE Program August Teachers Workshop, 2004 Tracking Tides Tracking the Tides
 Tracking the Tides Tides are the periodic rise and fall of the ocean waters. They are caused by the gravitational pulls of the moon and (to a lesser extent) sun, as well as the rotation of the Earth. The
Tracking the Tides Tides are the periodic rise and fall of the ocean waters. They are caused by the gravitational pulls of the moon and (to a lesser extent) sun, as well as the rotation of the Earth. The
4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy
 4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy Our goals for learning: Why do objects move at constant velocity if no force acts on them? What keeps a planet rotating and orbiting the Sun? Where do objects get their
4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy Our goals for learning: Why do objects move at constant velocity if no force acts on them? What keeps a planet rotating and orbiting the Sun? Where do objects get their
Oscillations. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Position, Velocity, Acceleration SHM Forces SHM Energy Period of oscillation Damping and Resonance
 Oscillations Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Position, Velocity, Acceleration SHM Forces SHM Energy Period of oscillation Damping and Resonance 1 Revision problem Please try problem #31 on page 480 A pendulum
Oscillations Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Position, Velocity, Acceleration SHM Forces SHM Energy Period of oscillation Damping and Resonance 1 Revision problem Please try problem #31 on page 480 A pendulum
1. Determine the length of time between the two high tides shown for May 13.
 Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
CHAPTER 9 TIDES AND TIDAL CURRENTS
 CHAPTER 9 TIDES AND TIDAL CURRENTS ORIGINS OF TIDES 900. Introduction Tides are the periodic motion of the waters of the sea due to changes in the attractive forces of the moon and sun upon the rotating
CHAPTER 9 TIDES AND TIDAL CURRENTS ORIGINS OF TIDES 900. Introduction Tides are the periodic motion of the waters of the sea due to changes in the attractive forces of the moon and sun upon the rotating
Tides Unit II: The Bulge Theory of the Tides (3.5 pts)
 T. James Noyes, ECC Tides Unit II: The Bulge Theory of the Tides (Topic 7A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Tides Unit II: The Bulge Theory of the Tides (3.5 pts) The Bulge Theory of the Tides is the Simplest,
T. James Noyes, ECC Tides Unit II: The Bulge Theory of the Tides (Topic 7A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Tides Unit II: The Bulge Theory of the Tides (3.5 pts) The Bulge Theory of the Tides is the Simplest,
A = 6561 times greater. B. 81 times greater. C. equally strong. D. 1/81 as great. E. (1/81) 2 = 1/6561 as great Pearson Education, Inc.
 Q13.1 The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on the Moon, the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on the Earth is A. 81 2
Q13.1 The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on the Moon, the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on the Earth is A. 81 2
Guided Notes Astronomy. Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses
 Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
TIDES. n What are tides? The periodic rise and fall of the sea level under the gravitational pull of the moon. n Tides are one of the most
 Tides TIDES What are tides? The periodic rise and fall of the sea level under the gravitational pull of the moon Tides are one of the most reliable phenomena in the world. As the sun rises in the east
Tides TIDES What are tides? The periodic rise and fall of the sea level under the gravitational pull of the moon Tides are one of the most reliable phenomena in the world. As the sun rises in the east
3. Equilibrium tidal theory
 3. Equilibrium tidal theory 3.1 Definition and development of equilibrium tidal theory The equilibrium tidal theory is based on the assumption that pressure and gravitation forces are always in full balance.
3. Equilibrium tidal theory 3.1 Definition and development of equilibrium tidal theory The equilibrium tidal theory is based on the assumption that pressure and gravitation forces are always in full balance.
Earth-Moon System Fun with Gravity Sarazin. Sizes of Earth and Moon
 Earth-Moon System Fun with Gravity Sarazin Sizes of Earth and Moon Earth-Moon System Fun with Gravity Sarazin Sizes of Earth and Moon Precession: Gravity not parallel to rotation axis rotation axis gravity
Earth-Moon System Fun with Gravity Sarazin Sizes of Earth and Moon Earth-Moon System Fun with Gravity Sarazin Sizes of Earth and Moon Precession: Gravity not parallel to rotation axis rotation axis gravity
CHAPTER 35 TIDES AND TIDAL CURRENTS
 CHAPTER 35 TIDES AND TIDAL CURRENTS ORIGINS OF TIDES 3500. Introduction Tides are the periodic motion of the waters of the sea due to changes in the attractive forces of the Moon and Sun upon the rotating
CHAPTER 35 TIDES AND TIDAL CURRENTS ORIGINS OF TIDES 3500. Introduction Tides are the periodic motion of the waters of the sea due to changes in the attractive forces of the Moon and Sun upon the rotating
Lecture 19: The Moon & Mercury. The Moon & Mercury. The Moon & Mercury
 Lecture 19: The Moon & Mercury The Moon & Mercury The Moon and Mercury are similar in some ways They both have: Heavily cratered Dark colored surfaces No atmosphere No water They also have some interesting
Lecture 19: The Moon & Mercury The Moon & Mercury The Moon and Mercury are similar in some ways They both have: Heavily cratered Dark colored surfaces No atmosphere No water They also have some interesting
PSI AP Physics C Universal Gravity Multiple Choice Questions
 PSI AP Physics C Universal Gravity Multiple Choice Questions 1. Who determined the value of the gravitational constant (G)? (A) Newton (B) Galileo (C) Einstein (D) Schrödinger (E) Cavendish 2. Who came
PSI AP Physics C Universal Gravity Multiple Choice Questions 1. Who determined the value of the gravitational constant (G)? (A) Newton (B) Galileo (C) Einstein (D) Schrödinger (E) Cavendish 2. Who came
Understanding Oceans, Gulfs & Tides
 SCS-2005-13 Water and Me Series Understanding s, Gulfs & Tides Monty C. Dozier Assistant Professor and Extension Water Resources Specialist The dictionary defines the ocean as the whole body of saltwater
SCS-2005-13 Water and Me Series Understanding s, Gulfs & Tides Monty C. Dozier Assistant Professor and Extension Water Resources Specialist The dictionary defines the ocean as the whole body of saltwater
Chapter 13, Vibrations and Waves. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only m. What is the spring constant of the spring?
 CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
1. Determine the length of time between the two high tides shown for May 13.
 Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up. Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Stars, Galaxies & Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & Universe Lecture #3. Reading Quiz questions. Phases of the Moon & Eclipses
 Stars, Galaxies & Universe Announcements - Science library (120 Iowa Ave (across from Joe s Place) has copies of the textbook on reserve -Labs start this week print out lab document before class (see link
Stars, Galaxies & Universe Announcements - Science library (120 Iowa Ave (across from Joe s Place) has copies of the textbook on reserve -Labs start this week print out lab document before class (see link
Lesson 9. Luis Anchordoqui. Physics 168. Tuesday, October 24, 17
 Lesson 9 Physics 168 1 Static Equilibrium 2 Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it but that is not moving is said to be in equilibrium 3 Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) First
Lesson 9 Physics 168 1 Static Equilibrium 2 Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it but that is not moving is said to be in equilibrium 3 Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) First
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA G.F. ABELA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 UNIVERSITY OF MALTA G.F. ABELA JUNIOR COLLEGE FIRST YEAR END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATION SUBJECT: PHYSICS DATE: JUNE 2010 LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE TIME: 09.00h to 12.00h Show ALL working Write units where appropriate
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA G.F. ABELA JUNIOR COLLEGE FIRST YEAR END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATION SUBJECT: PHYSICS DATE: JUNE 2010 LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE TIME: 09.00h to 12.00h Show ALL working Write units where appropriate
The Night Sky 1st Grade PSI Science Classwork. Draw and write about what you think the night sky looks like. 1st Grade PSI The Moon
 The Night Sky Classwork Draw and write about what you think the night sky looks like. The Moon Classwork For #1-5, fill in the blank with the correct word. Word Bank Natural near craters hot astronaut
The Night Sky Classwork Draw and write about what you think the night sky looks like. The Moon Classwork For #1-5, fill in the blank with the correct word. Word Bank Natural near craters hot astronaut
Sample Final Exam SPH4U0
 Sample Final Exam SPH4U0 Part A: Multiple Choice (30 pts.) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which variable is most closely related to inertia?
Sample Final Exam SPH4U0 Part A: Multiple Choice (30 pts.) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which variable is most closely related to inertia?
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Sun Earth Moon Mars Mass kg kg kg kg Radius m m m 3.
 Sun Earth Moon Mars Mass 1.99 10 30 kg 5.97 10 24 kg 7.35 10 22 kg 6.42 10 23 kg Radius 6.96 10 8 m 6.38 10 6 m 1.74 10 6 m 3.40 10 6 m Orbital Radius - 1.50 10 11 m 3.84 10 8 m 2.28 10 11 m Orbital Period
Sun Earth Moon Mars Mass 1.99 10 30 kg 5.97 10 24 kg 7.35 10 22 kg 6.42 10 23 kg Radius 6.96 10 8 m 6.38 10 6 m 1.74 10 6 m 3.40 10 6 m Orbital Radius - 1.50 10 11 m 3.84 10 8 m 2.28 10 11 m Orbital Period
Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics
 Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics The position of the Earth Ptolemy (90 168 AD) Made tables that allowed a user to locate the position of a planet at any past, present, or future date. In order to maintain circular
Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics The position of the Earth Ptolemy (90 168 AD) Made tables that allowed a user to locate the position of a planet at any past, present, or future date. In order to maintain circular
AS300-U1C2L2 - The Moon: Earth's Fellow Traveler Page 1
 AS300-U1C2L2 - The Moon: Earth's Fellow Traveler Page 1 Name: Flight Date: 1 What was Aristarchus s map of the Earth, Sun, and Moon missing? A Scale B Relative size of the Earth, Moon and Sun C A geocentric
AS300-U1C2L2 - The Moon: Earth's Fellow Traveler Page 1 Name: Flight Date: 1 What was Aristarchus s map of the Earth, Sun, and Moon missing? A Scale B Relative size of the Earth, Moon and Sun C A geocentric
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity. Chapter 4 Lecture
 Chapter 4 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding
Chapter 4 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding
Page Tides ANIMATION. Tidal forces
 Page 194 7.5 Tides ANIMATION Tidal forces Anyone who has spent even a few hours by the sea knows that the ocean's level rises and falls during the day. A blanket set on the sand 10 feet from the water's
Page 194 7.5 Tides ANIMATION Tidal forces Anyone who has spent even a few hours by the sea knows that the ocean's level rises and falls during the day. A blanket set on the sand 10 feet from the water's
Gravitation. Luis Anchordoqui
 Gravitation Kepler's law and Newton's Synthesis The nighttime sky with its myriad stars and shinning planets has always fascinated people on Earth. Towards the end of the XVI century the astronomer Tycho
Gravitation Kepler's law and Newton's Synthesis The nighttime sky with its myriad stars and shinning planets has always fascinated people on Earth. Towards the end of the XVI century the astronomer Tycho
Astronomy Regents Review
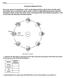 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space. Earth s Rotation
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
What if we didn t have The Moon?
 The Moon Minds-on Inquiry Moon Stats What if we had no Moon? Orbit of the Moon Rotation of the Moon The Dark Side of the Moon The Phases of the Moon The Tides The Moon Illusion What if we didn t have The
The Moon Minds-on Inquiry Moon Stats What if we had no Moon? Orbit of the Moon Rotation of the Moon The Dark Side of the Moon The Phases of the Moon The Tides The Moon Illusion What if we didn t have The
Explained by Dr CJC Rees (York)
 HOW THE TIDES WORK Explained by Dr CJC Rees (York) TIDES AND WATER MARKS TIDES and the - SYSTEM The earth-moon system rotates in space about its common centre of mass, there being a stabilising balance
HOW THE TIDES WORK Explained by Dr CJC Rees (York) TIDES AND WATER MARKS TIDES and the - SYSTEM The earth-moon system rotates in space about its common centre of mass, there being a stabilising balance
4.1 Describing Motion. How do we describe motion? Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation
 Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
In this chapter, you will consider the force of gravity:
 Gravity Chapter 5 Guidepost In this chapter, you will consider the force of gravity: What were Galileo s insights about motion and gravity? What were Newton s insights about motion and gravity? How does
Gravity Chapter 5 Guidepost In this chapter, you will consider the force of gravity: What were Galileo s insights about motion and gravity? What were Newton s insights about motion and gravity? How does
SUPERMOONS AND OTHER SUN-MOON CONCEPTS March 18, By Michael Erlewine
 SUPERMOONS AND OTHER SUN-MOON CONCEPTS March 18, 2011 By Michael Erlewine (Michael@Erlewine.net) Tidal Force There is some talk right now about the so-called Supermoon (a term coined by astrologer Richard
SUPERMOONS AND OTHER SUN-MOON CONCEPTS March 18, 2011 By Michael Erlewine (Michael@Erlewine.net) Tidal Force There is some talk right now about the so-called Supermoon (a term coined by astrologer Richard
Chapter 4: Energy, Motion, Gravity. Enter Isaac Newton, who pretty much gave birth to classical physics
 Chapter 4: Energy, Motion, Gravity Enter Isaac Newton, who pretty much gave birth to classical physics Know all of Kepler s Laws well Chapter 4 Key Points Acceleration proportional to force, inverse to
Chapter 4: Energy, Motion, Gravity Enter Isaac Newton, who pretty much gave birth to classical physics Know all of Kepler s Laws well Chapter 4 Key Points Acceleration proportional to force, inverse to
Equation of orbital velocity: v 2 =GM(2/r 1/a) where: G is the gravitational constant (G=6.67x10 11 N/m 3 kg), M is the mass of the sun (or central
 Everything in Orbit Orbital Velocity Orbital velocity is the speed at which a planetary body moves in its orbit around another body. If orbits were circular, this velocity would be constant. However, from
Everything in Orbit Orbital Velocity Orbital velocity is the speed at which a planetary body moves in its orbit around another body. If orbits were circular, this velocity would be constant. However, from
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
Complete the body of your
 Complete the body of your notes All blanks filled in All vocabulary words highlighted All pictures drawn with at least 3 labels each. Revise in pen. Review your notes and write the questions. Write the
Complete the body of your notes All blanks filled in All vocabulary words highlighted All pictures drawn with at least 3 labels each. Revise in pen. Review your notes and write the questions. Write the
Course evaluations. Go to the Physics and Astronomy Department website. Click on Online Course Evaluation link
 Course evaluations. Go to the Physics and Astronomy Department website. www.pa.uky.edu Click on Online Course Evaluation link Link is open now. Do it soon. The nearest stars to the Sun. Barnard s Star
Course evaluations. Go to the Physics and Astronomy Department website. www.pa.uky.edu Click on Online Course Evaluation link Link is open now. Do it soon. The nearest stars to the Sun. Barnard s Star
a. 0.1 AU b. 10 AU c light years d light years
 1 AST104 Sp2006: EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the bubble form. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1.
1 AST104 Sp2006: EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the bubble form. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1.
Chapter 13. Gravitation
 Chapter 13 Gravitation e = c/a A note about eccentricity For a circle c = 0 à e = 0 a Orbit Examples Mercury has the highest eccentricity of any planet (a) e Mercury = 0.21 Halley s comet has an orbit
Chapter 13 Gravitation e = c/a A note about eccentricity For a circle c = 0 à e = 0 a Orbit Examples Mercury has the highest eccentricity of any planet (a) e Mercury = 0.21 Halley s comet has an orbit
Some Questions We ll Address Today
 Some Questions We ll Address Today What makes a rocket go? How can a rocket work in outer space? How do things get into orbit? What s s special about geo-synchronous orbit? How does the force of gravity
Some Questions We ll Address Today What makes a rocket go? How can a rocket work in outer space? How do things get into orbit? What s s special about geo-synchronous orbit? How does the force of gravity
2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Daily Life Some of the topics we will explore: How do we describe motion? (Speed,
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Daily Life Some of the topics we will explore: How do we describe motion? (Speed,
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 117.3 MIDTERM TEST February 12, 2015 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 117.3 MIDTERM TEST February 12, 2015 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
A dynamical picture of the oceanic tides
 A dynamical picture of the oceanic tides Eugene I. Butikov a) Department of Physics, St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg 198904, Russia Received 5 November 2001; accepted 11 June 2002 A detailed
A dynamical picture of the oceanic tides Eugene I. Butikov a) Department of Physics, St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg 198904, Russia Received 5 November 2001; accepted 11 June 2002 A detailed
SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY ROTATION AND REVOLUTION This paper consists of 5 printed pages.
 SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY ROTATION AND REVOLUTION 2017-2018 This paper consists of 5 printed pages. 1. Name the motions of the earth. A. They are Rotation and Revolution. 2. What is Rotation? A. Rotation is
SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY ROTATION AND REVOLUTION 2017-2018 This paper consists of 5 printed pages. 1. Name the motions of the earth. A. They are Rotation and Revolution. 2. What is Rotation? A. Rotation is
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions
 because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
Ocean Tides. Lexile 960L
 6E3 tmosphere, Water ycle, Waves, and urrents Ocean Tides Lexile 960L 1 The gritty sand oozes between your toes as you stroll along the beach. The gentle lapping of the waves lulls you into a peaceful
6E3 tmosphere, Water ycle, Waves, and urrents Ocean Tides Lexile 960L 1 The gritty sand oozes between your toes as you stroll along the beach. The gentle lapping of the waves lulls you into a peaceful
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology
 AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E S 8-9 Part B, Lectures 8-9 23 March, 2017 C O N T E N T S In this lecture, we will look at factors that cause an orbit to change over time orbital
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E S 8-9 Part B, Lectures 8-9 23 March, 2017 C O N T E N T S In this lecture, we will look at factors that cause an orbit to change over time orbital
Lecture 2. Lecture 1. Forces on a rotating planet. We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their:
 Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lunar Motion. V. Lunar Motion. A. The Lunar Calendar. B. Motion of Moon. C. Eclipses. A. The Lunar Calendar. 1) Phases of the Moon. 2) The Lunar Month
 Lunar Motion Dr. Bill Pezzaglia V. Lunar Motion A. The Lunar Calendar B. Motion of Moon 2 Updated 2012Oct03 C. Eclipses A. The Lunar Calendar 3 1. Phases of Moon 4 1) Phases of the Moon 2) The Lunar Month
Lunar Motion Dr. Bill Pezzaglia V. Lunar Motion A. The Lunar Calendar B. Motion of Moon 2 Updated 2012Oct03 C. Eclipses A. The Lunar Calendar 3 1. Phases of Moon 4 1) Phases of the Moon 2) The Lunar Month
Chapter 9 Lecture. Pearson Physics. Gravity and Circular Motion. Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Lecture Pearson Physics Gravity and Circular Motion Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Newton's Law of Universal Gravity Applications of Gravity Circular Motion Planetary Motion and
Chapter 9 Lecture Pearson Physics Gravity and Circular Motion Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Newton's Law of Universal Gravity Applications of Gravity Circular Motion Planetary Motion and
Time, Seasons, and Tides
 Time, Seasons, and Tides Celestial Sphere Imagine the sky as a great, hollow, sphere surrounding the Earth. The stars are attached to this sphere--- some bigger and brighter than others--- which rotates
Time, Seasons, and Tides Celestial Sphere Imagine the sky as a great, hollow, sphere surrounding the Earth. The stars are attached to this sphere--- some bigger and brighter than others--- which rotates
