1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface.
|
|
|
- Malcolm Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the Hudson River at Newburgh, New York. According to the diagram, where will high ocean tides and low ocean tides most likely be located? A) High tides at A and B; low tides at C and D B) high tides at B and D; low tides at A and C C) high tides at A and C; low tides at B and D D) high tides at C and D; low tides at A and B According to the graph, the time difference between high tide and the next low tide is approximately A) 2 hours B) 3 hours C) 6 hours D) 12 hours
2 3. The graph below shows ocean tide height in feet (ft) over a 44-hour period for a coastal location in the northeastern United States. The dots represent either high or low tides. If the pattern shown continued, the next low tide occurred on Day 3 at approximately A) 12 midnight B) 1:30 a.m. C) 1:00 p.m. D) 6:00 p.m. 4. The graph below shows ocean water levels for a shoreline location on Long Island, New York. The graph also indicated the dates and times of high and low tides. Based on the data, the next high tide occurred at approximately A) 4 p.m. on July 13 B) 10 p.m. on July 13 C) 4 p.m. on July 14 D) 10 p.m. on July 14
3 5. The diagram below represents eight positions of the Moon in its orbit. Why are high tides on Earth greatest when the Moon is in position A and in position E? A) The Moon is closer to the Sun. B) The Moon is closer to Earth. C) The Moon, the Sun, and Earth are aligned. D) The Moon is in the same phase at both locations.
4 Base your answers to questions 6 and 7 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents the Moon at different positions, labeled A, B, C, and D, in its orbit around Earth. 6. During which Moon phase could an observer on Earth see a lunar eclipse occur? A) B) C) D) 7. At which two Moon positions would an observer on Earth most likely experience the highest high tides and the lowest low tides? A) A and B B) B and C C) C and A D) D and B 8. The table below shows the times of ocean high tides and low tides on a certain date at a New York State location. At approximately what time on the following day did the next high tide occur at this location? A) 4:40 a.m. B) 5:40 a.m. C) 4:40 p.m. D) 5:40 p.m.
5 Base your answers to questions 9 through 11 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents eight numbered positions of the Moon in its orbit around Earth. 9. A solar eclipse might be observed from Earth when the Moon is at which position? A) 1 B) 5 C) 3 D) Which two motions cause the Moon to show a complete cycle of phases each month when viewed from New York State? A) the Moon's rotation and Earth's rotation B) the Moon's revolution and Earth's rotation C) the Moon's rotation and the Sun's rotation D) the Moon's revolution and the Sun's rotation 11. Which phase of the Moon will be observed in New York State when the Moon is at position 8? A) B) C) D)
6 Base your answers to questions 12 through 14 on the graph below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows the tidal range (the difference between the highest tide and the lowest tide) recorded in Minas Basin, Nova Scotia, during November The phase of the Moon on selected days is shown above the graph. The dates that the Moon was farthest from Earth (apogee) and closest to Earth (perigee) are indicated under the graph. 12. The next first-quarter Moon after November 17 occurred closest to A) December 9 B) December 14 C) December 17 D) December The highest high tides and the lowest low tides occurred when the Moon was near A) apogee and a new-moon phase B) apogee and a full-moon phase C) perigee and a new-moon phase D) perigee and a full-moon phase 14. The tidal range on November 8 was approximately A) 11 m B) 2 m C) 13 m D) 15 m
7 Base your answers to questions 15 through 17 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents the Moon in eight positions, A through H, in its orbit around Earth. 15. Which Moon phase is observed in New York State when the Moon is located at position F? A) B) C) D) 16. How many days are required for the Moon to complete a cycle of phases from the new Moon position represented in the diagram to the new Moon the following month? A) 2.2 d B) 27.3 d C) 29.5 d D) d 17. When a solar eclipse is viewed from Earth, the Moon must be located at orbital position A) A B) E C) C D) G
8 18. A graph of tidal sea-level changes at a coastal city is shown below. The number of hours from one high tide to the next high tide is approximately A) 4 h B) 8 h C) 12 h D) 24 h 19. Ocean tides observed at coastal locations each day are primarily caused by A) Earth's revolution around the Sun B) the changing phases of the Moon C) the gravitational attraction between the Moon and Earth D) seasonal changes in the compass location of sunrise
9 20. The photographs below show the same coastal location at two different times during the same day. Which statement best explains the cause for the higher water level at 6:52 p.m.? A) The Moon rotates on its axis at the same rate that it revolves around Earth. B) The Moon exerts a gravitational pull on a rotating Earth. C) Earth's rotation causes a deflection of surface ocean currents. D) Earth's tilted axis causes different amounts of insolation throughout the day.
10 21. The diagram below shows the Moon at one position in its orbit around Earth. Letter Xindicates the location of an observer in New York State. Which phase of the Moon will the observer see when the Moon is at the position shown in its orbit? A) B) C) D)
11 22. The diagram below represents a total solar eclipse as seen from Earth. Which diagram correctly represents the relative positions of the Sun (S), Earth (E), and the Moon (M) in space during a total solar eclipse? [The diagrams are not drawn to scale.] A) B) C) D)
12 23. The diagram below shows the relative positions of Earth and Mars in their orbits on a particular date during the winter of Which diagram correctly shows the locations of Earth and Mars on the same date during the winter of 2008? A) B) C) D) 24. A high tide occurred at 6:00 a.m. at a beach on Long Island. The next high tide at this same beach would occur at approximately A) 12:15 p.m. on the same day B) 6:30 p.m. on the same day C) 12:45 p.m. on the following day D) 7:00 a.m. on the following day
13 Base your answers to questions 25 through 27 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 25. Which statement best explains why the same side of the Moon is viewed from Earth as the Moon goes through its phases? A) The Moon does not rotate as it revolves around Earth. B) The Moon's period of rotation equals Earth's period of rotation. C) The Moon's period of rotation equals Earth's period of revolution around the Sun. D) The Moon's period of rotation equals the Moon's period of revolution around Earth. 26. During which Moon phase might a solar eclipse be viewed on Earth? A) new Moon B) first quarter C) full Moon D) last quarter 27. Approximately how many days occur between the Moon's first-quarter phase and the Moon's last-quarter phase? A) 7 d B) 15 d C) 29.5 d D) d
14 Base your answers to questions 28 through 31 on the calendar below, which shows the month of July of a recent year. The dates of major Moon phases, as seen in New York State, are shown. The diagram below represents the phase of the Moon observed from New York State one night during the month of July. 28. Why does the Moon's gravity have a greater effect on Earth's ocean tides than the Sun's gravity? A) The Sun is composed mostly of gases. B) The Sun's gravity influences more planets. C) The Moon has a greater mass. D) The Moon is much closer to Earth. 29. Eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon's A) rate of rotation is 15 each hour B) orbit is inclined to Earth's orbit C) period of revolution is 27.3 days D) period of rotation and period of revolution are the same 30. On which date will the next first-quarter Moon phase occur? A) August 6 B) August 10 C) August 16 D) August On which date was this phase of the Moon visible from New York State? A) July 4 B) July 11 C) July 19 D) July 26
15 32. The diagram below shows the position of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth during a solar eclipse. The full shadow (umbra) and partial shadow (penumbra) of the Moon and Earth are shown. Which diagram best represents the appearance of the Sun and the Moon to an observer located within the umbra of the Moon's shadow on Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
16 33. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole. The date of one of the four positions has been labeled. Which photograph shows the appearance of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State on May 17, 2000? A) B) C) D) 34. Which phase of the Moon would be observed on Earth when the Moon is at location A? A) B) C) D)
17 35. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows Earth and the Moon in relation to the Sun. Positions A, B, C, and D show the Moon at specific locations in its orbit. Point X is a location on Earth's surface. A solar eclipse might occur when the Moon is at location A) A B) B C) C D) D
18 36. Which diagram best represents the size of the Moon, compared to Earth, when drawn to scale? A) B) C) D) 37. How many days are required for the Moon to go from one full-moon phase to the next full-moon phase when viewed from Earth? A) 24 B) 27.3 C) 29.5 D) 365
19 38. The photographs below show the surface of the Moon as seen from Earth over an 80-minute period during a single night. Which motion is responsible for this changing appearance of the Moon? A) The Moon moves into the shadow of Earth. B) The Moon moves into the shadow of the Sun. C) The Sun moves into the shadow of Earth. D) The Sun moves into the shadow of the Moon. 39. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in its orbit. Which Moon phase would be seen by an observer in New York State when the Moon is at position 2? A) B) C) D)
20 40. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows two days of tidal data from a coastal location in the northeastern United States. The change in the tides as shown on the graph is primarily the result of A) Earth's rotation and the Moon's revolution B) Earth's rotation and revolution C) the Moon's rotation and Earth's revolution D) the Moon's rotation and revolution
21 Base your answers to questions 41 through 43 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M1, M2, M3, and M4 indicate positions of the Moon in its on Letter A indicates a location on Earth's surface. 41. An observer at location A noticed that the apparent size of the Moon varied slightly from month to month when the Moon was at position M4 in its orbit. Which statement best explains this variation in the apparent size of the Moon? A) The Moon expands in summer and contracts in winter. B) The Moon shows complete cycles of phases throughout the year. C) The Moon's period of rotation is equal to its period of revolution. D) The Moon's distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner. 42. At which Moon position could a solar eclipse be seen from Earth? A) M1 B) M2 C) M3 D) M4 43. An observer at location A on Earth views the Moon when it is at position M3. Which phase of the Moon will the observer see? A) B) C) D)
22 44. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) 45. Diagram 1 shows the Moon in its orbit at four positions labeled A, B, C, and D. Diagram 2 shows a phase of the Moon as viewed from New York State. At which labeled Moon position would the phase of the Moon shown in diagram 2 be observed from New York State? A) A B) B C) C D) D
23 46. The diagram below represents the Sun's rays striking Earth and the Moon. Numbers 1 through 4 represent positions of the Moon in its orbit around Earth. The highest tides on Earth occur when the Moon is in positions A) 1 and 3 B) 2 and 4 C) 3 and 2 D) 4 and Which sequence of Moon phases could be observed from Earth during a 2-week period? A) B) C) D)
24 Base your answers to questions 48 and 49 on the diagram below, which shows the Moon, Earth, and the Sun's rays as viewed from space. Letter A indicates a certain position of the Moon in its orbit. 48. Which diagram represents the phase of the Moon, as seen by an observer on Earth, when the Moon is located at position A in its orbit? A) B) C) D) 49. Which diagram correctly shows the direction of Earth's rotation and revolution? A) B) C) D)
25 50. The diagrams below represent Earth's ocean tides at four different positions of the Moon. Which diagram shows the Moon position that will produce the highest high tides and the lowest iow tides? (The diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) 51. The same side of the Moon always faces Earth because the A) Moon's period of rotation is longer than its period of revolution around Earth B) Moon's period of rotation is shorter than its period of revolution around Earth C) Moon rotates once as it completes one revolution around Earth D) Moon does not rotate as it completes one revolution around Earth B) C) D)
26 Base your answers to questions 52 and 53 on the diagram below, which has lettered arrows showing the motions of Earth and the Moon. 52. Which lettered arrow represents the motion that causes the Moon to show phases when view from Earth A) A B) B C) C D) D 53. Which two motions are completed in about the same amount of time? A) A and B B) B and C C) C and D D) A and D
27 54. The diagram below shows Earth's orbit around the Sun and different positions of the Moon as it travels around Earth. Letters A through D represent four different positions of the Moon. 56. Which object is closest to Earth? A) the Sun B) Venus C) the Moon D) Mars An eclipse of the Moon is most likely to occur when the Moon is at position A) A B) B C) C D) D 55. The diagram below shows the Moon orbiting Earth, as viewed from space above Earth's North Pole. The Moon is shown at eight positions in its orbit. Spring ocean tides occur when the difference in height between high tide and low tide is greatest. At which two positions of the Moon will spring tides occur on Earth? A) 1 and 5 B) 2 and 6 C) 3 and 7 D) 4 and 8
28 Base your answers to questions 57 through 59 on the world map below, which shows regions of Earth where a solar eclipse was visible on May 20, Location A, B, C, and D are on Earth's surface. 57. Which diagram best represents the positions of Earth (E), the Sun, and the Moon that created the solar eclipse? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) 58. Which statement best describes the visibility of this eclipse from locations in New York State? A) A total eclipse was visible all day. B) A total eclipse was visible only from noon until sunset. C) A partial eclipse was visible only from noon until sunset. D) Neither a partial nor a total eclipse was visible. 59. At which location could an observer have viewed this total solar eclipse if the skies were clear? A) A B) B C) C D) D
29 60. The diagram below represents the Moon in its orbit, as viewed from above Earth's North Pole. Position 1 represents a specific location of the Moon in its orbit. 61. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth. Which phase of the Moon will be seen from Earth when the Moon is at position 1? A) B) C) D) An observer on Earth could see a solar eclipse when the Moon is at position A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) One complete cycle of the phases of the Moon takes approximately one A) day B) week C) month D) year 63. The time required for the Moon to show a complete cycle of phases when viewed from Earth is approximately A) 1 day B) 1 week C) 1 month D) 1 year
30 Base your answers to questions 64 and 65 on the graph below. The graph shows the recorded change in water level (ocean tides) at a coastal city in the northeastern United States during 1 day. 64. According to the pattern shown on the graph, the next high tide will occur on the following day at approximately A) 12:30 a.m. B) 2:00 a.m. C) 3:15 a.m. D) 4:00 a.m. 65. Which inference about tides is best made from this graph? A) The hourly rate of tidal change is always the same. B) The rate of tidal change is greatest at high tide. C) The tidal change is a random event. D) The tidal change is cyclic.
31 66. What is represented by the diagram below? A) changing phases of the Sun B) changing phases of the Moon C) stages in an eclipse of the Sun D) stages in an eclipse of the Moon 67. The diagram below shows the positions of the Moon and the Sun at sunset during an evening in New York State. Points A, B, C, and D represent positions along the western horizon. At sunset on the following evening, the Moon will be located at position A) A B) B C) C D) D
32 68. The diagram below shows the relative positions of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth when an eclipse was observed from Earth. Positions A and B are locations on Earth's surface. Which statement correctly describes the type of eclipse that was occurring and the position on Earth where this eclipse was observed? A) A lunar eclipse was observed from position A. B) A lunar eclipse was observed from position B. C) A solar eclipse was observed from position A. D) A solar eclipse was observed from position B. 69. Which diagram sequence correctly shows the order of Moon phases, as viewed from Earth, for a period of 1 month? [Note that some phases have been omitted.] A) B) C) D) 70. A cycle of Moon phases can be seen from Earth because the A) Moon s distance from Earth changes at a predictable rate B) Moon s axis is tilted C) Moon spins on its axis D) Moon revolves around Earth
33 71. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole. Beginning with the Moon at position X (the new-moon phase), which sequence of Moon phases would be seen by an observer on Earth during 1 month? A) B) C) D)
34 Base your answers to questions 72 through 75 on the graph below, which shows the maximum altitude of the Moon, measured by an observer located at a latitude of 43 N during June in a particular year. The names and appearance of the four major Moon phases are shown at the top of the graph, directly above the date on which the phase occurred. 72. Which terms describe both the changes in the maximum altitude of the Moon and the changes in the Moon s phases over a period of several years? A) cyclic and predictable B) cyclic and unpredictable C) noncyclic and predictable D) noncyclic and unpredictable 73. Which city is closest in latitude to the location where these observations were made? A) Binghamton B) New York City C) Albany D) Syracuse 74. Which diagram best represents the Moon s phase observed on June 11? A) B) C) D) 75. What was the maximum altitude of the Moon on June 22? A) 40 B) 43 C) 46 D) 50
35 76. The diagram below shows the Moon orbiting Earth as viewed from space above the North Pole. The Moon is shown at eight different positions in its orbit. 78. The diagram below shows the Moon in different positions as it revolves around Earth, as observed from above the North Pole (NP). At which two positions of the Moon is an eclipse of the Sun or Moon possible? A) 1 and 5 B) 2 and 6 C) 3 and 7 D) 4 and The passage of the Moon into Earth's shadow causes a A) lunar eclipse B) solar eclipse C) new Moon D) full Moon Which image correctly represents the Moon at position 8, as observed from Earth? A) B) C) D)
36 79. Base your answer to the following question on the map below. Letters A through F are locations on Earth s surface. An observer at location C sees a full Moon at its highest point in the sky. When the observation is being made at location C, at which other location would it be impossible for a second observer also to see the full Moon? A) A B) B C) F D) D
37 Base your answers to questions 80 through 83 on the diagram below, which represents the Moon orbiting Earth as viewed from space above the North Pole. The Moon is shown at eight different positions in its orbit. 80. When the Moon is in position 2, which phase would be visible to an observer in Maine? A) B) C) D) 81. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from Earth? A) rotation of Earth B) rotation of the Sun C) revolution of Earth D) revolution of the Moon 82. As the Moon changes location from position 2 to position 6, the visible portion of the Moon as observed from Earth A) decreases, only B) increases, only C) decreases, then increases D) increases, then decreases 83. The approximate time required for the Moon to move from position 3 to position 7 is A) 1 hour B) 2 weeks C) 3 months D) 4 days 84. If the distance between the Moon and Earth were double its present distance, the Moon s cycle of phases would occur A) in reverse order and more slowly B) in reverse order and more quickly C) in the same order but more slowly D) in the same order but more quickly
38 85. The diagram below shows Earth, the Moon, and the Sun's rays as viewed from space. For observers on Earth, which phase of the Moon is represented by the diagram? A) B) C) D) 86. The diagram below shows a model of the Moon's orbit around Earth. Letters A, B, C, and D represent four positions in the Moon's orbit. What is the approximate length of time the Moon takes to travel from position A to position C? A) 1 day B) 15 days C) 30 days D) 365 days
39 Base your answers to questions 87 through 90 on the chart below, which shows phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer on Earth during What is the approximate diameter of the Moon? A) km B) km C) km D) km 88. Why does the Moon show these phases when viewed by an observer on Earth? A) The Moon rotates on its axis. B) Earth s orbit is nearly circular. C) The Sun lights only half of Earth. D) The Moon revolves around Earth. 89. The Moon goes through a complete cycle of phases approximately every A) 14 days B) 23 days C) 29 days D) 365 days 90. During 1996, the maximum intensity of moon-light was received on Earth twice in the month of A) February B) June C) October D) December
40 Base your answers to questions 91 through 94 on the diagram below, which represents a model of the Earth-Moon system as viewed from above the North Pole. The numbers 1 through 8 represent positions of the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The parts of the diagram lettered A through D show how the Moon's phases appear to an observer in New Jersey. 91. Which Moon phase appears highest in the sky at midnight to an observer on Earth? A) full moon B) new moon C) first quarter D) last quarter 92. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from Earth? A) rotation of Earth B) revolution of Earth C) rotation of the Moon D) revolution of the Moon 93. As the Moon's phase changes from first quarter to last quarter, the visible portion of the Moon as observed from Earth will A) decrease, only B) increase, only C) decrease, then increase D) increase, then decrease 94. The time required for the Moon to complete one cycle of phases is about one A) day B) week C) month D) year
41 95. Which statement best explains why different phases of the Moon can be observed from the Earth? A) The size of the Earth's shadow falling on the Moon changes. B) The Moon moves into different parts of the Earth's shadow. C) Differing amounts of the Moon's sunlit surface are seen because the Moon revolves around the Sun. D) Differing amounts of the Moon's sunlit surface are seen because the Moon revolves around the Earth. 96. The new-moon phase occurs when the Moon is positioned between the Earth and the Sun. However, these positions do not always cause an eclipse (blocking) of the Sun because the A) Moon's orbit is tilted relative to the Earth's orbit B) new-moon phase is visible only at night C) night side of the Moon faces toward the Earth D) apparent diameter of the Moon is greatest during the new-moon phase 97. The diagram below shows the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun for a 1-month period. 98. Which motion causes the apparent rising and setting of the Moon each day, as seen from a location in Kansas? A) the Earth revolving around the Sun B) the Moon revolving around the Earth C) the Earth rotating on its axis D) the Moon rotating on its axis 99. The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at different times in August. Which phase could have been observed on August 17? A) B) C) D) Which diagram best represents the appearance of the Moon at position P when viewed from the Earth? A) B) C) D)
42 Base your answers to questions 100 through 103 on the diagram below which represents nine positions of the Earth in orbit around the Sun during one complete orbit of the Moon around the Earth The diagram below represents eight positions of the Moon as it revolves around the Earth The Earth rotates on its axis, causing the Moon to appear to rise each day. Moonrise occurs about 52 minutes later each day because as the Earth completes one rotation, the Moon also A) completes one rotation on its axis B) wobbles on its axis C) is inclined 23 D) revolves part way around the Earth 101. During the time that the Earth travels from position 1 to position 9, an observer on the Earth will see the lighted portion of the Moon A) decrease, only B) increase, only C) decrease, then increase D) increase, then decrease 102. At which position might the Moon block part of the Sun, making a solar eclipse visible from Earth? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) Which phase of the Moon will be seen from the Earth at position 5? A) B) When viewed from the Earth, which phase of the Moon will be seen when the Moon is at point E? A) first quarter B) full moon C) new moon D) last quarter C) D)
43 Base your answers to questions 105 through 108 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents the Moon at four positions, labeled A, B, C, and D, in its orbit around Earth. The position of the full-moon phase is labeled Solar and lunar eclipses rarely happen during a cycle of phases because the A) Moon's orbit is circular and Earth's orbit is elliptical B) Moon's orbit is elliptical and Earth's orbit is elliptical C) plane of the Moon's orbit is different from the plane of Earth's orbit D) plane of the Moon's orbit is the same as the plane of Earth's orbit 106. The same side of the Moon always faces Earth because the Moon's period of revolution A) is longer than the Moon's period of rotation B) equals the Moon's period of rotation C) is longer than Earth's period of rotation D) equals Earth's period of rotation 107. Which phase of the Moon could be observed from New York State when the Moon is at position C? A) B) C) D) 108. Approximately how many days (d) does it take for the Moon to move from the phase shown at position A to the full-moon phase? A) 7.4 d B) 14.7 d C) 27.3 d D) 29.5 d
44 Earth Science Name Class Date
A) M D) The Moon s distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Mid Term Prep-Moon Review 2
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 1. Which statement best explains why
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which shows positions of the Moon in its orbit and phases of the Moon as viewed from New York State. 1. Which statement best explains why
Mid Term Prep-The Moon
 1. A high tide occurred at 6:00 a.m. at a beach on Long Island. The next high tide at this same beach would occur at approximately A) 12:15 p.m. on the same day B) 6:30 p.m. on the same day C) 12:45 p.m.
1. A high tide occurred at 6:00 a.m. at a beach on Long Island. The next high tide at this same beach would occur at approximately A) 12:15 p.m. on the same day B) 6:30 p.m. on the same day C) 12:45 p.m.
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Which phase of the Moon will be seen from the Earth at position 5? A) B) C) D)
 Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
Name Date 1. Which motion causes the Moon to show phases when viewed from the Earth? A) the rotation of the Moon on its axis B) the revolution of the Moon around the Earth C) the rotation of the Sun on
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
C) D) 2. The model below shows the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer in New York State on the first day of one of the four seasons.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
2. The diagram below represents the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer at 65 N on March 21.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions
 because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
A. the spinning of Earth on its axis B. the path of the Sun around Earth
 stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
Which table correctly shows the dates on which the apparent paths of the Sun were observed? A) B) C) D)
 1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
Midterm Review #2-2018
 1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date
 Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. Determine the length of time between the two high tides shown for May 13.
 Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
D. most intense and of longest duration C. D.
 Astronomy Take Home Test Answer on a separate sheet of paper In complete sentences justify your answer Name: 1. The Moon s cycle of phases can be observed from Earth because the Moon 4. The accompanying
Astronomy Take Home Test Answer on a separate sheet of paper In complete sentences justify your answer Name: 1. The Moon s cycle of phases can be observed from Earth because the Moon 4. The accompanying
Astronomy Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Guided Notes Astronomy. Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses
 Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up. Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
PHASES, ECLIPSES, AND TIDES
 PHASES, ECLIPSES, AND TIDES MOTIONS OF THE MOON The changing relative positions of the moon, Earth, and sun cause the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. The moon rotates once on its axis in the same
PHASES, ECLIPSES, AND TIDES MOTIONS OF THE MOON The changing relative positions of the moon, Earth, and sun cause the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. The moon rotates once on its axis in the same
Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice
 A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
1. Determine the length of time between the two high tides shown for May 13.
 Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagrams and tables below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Each diagram represents the Moon's orbital position and each table lists
2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which has lettered arrows showing the motions of Earth and the Moon.
 Practice Moon Test 1. Base your answer to the following question on the information and the cross section below. The cross section represents a possible model of the Moon's interior. Seismographs left
Practice Moon Test 1. Base your answer to the following question on the information and the cross section below. The cross section represents a possible model of the Moon's interior. Seismographs left
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system.
 1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at different times in August.
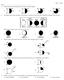 Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 Name The Sun-Earth-Moon System Section 28.3 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Date Main Idea Details Read the title of Section 3. List three things that might be discussed in this section. 1. 2. 3. Review Vocabulary
Name The Sun-Earth-Moon System Section 28.3 The Sun-Earth-Moon System Date Main Idea Details Read the title of Section 3. List three things that might be discussed in this section. 1. 2. 3. Review Vocabulary
Full Moon. Phases of the Moon
 Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 3 TUTORIAL QUIZ
 TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 3 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. When Neap tides are occurring, a. a person experiences the lowest tides close to sunset and sunrise. b. the Sun and the Moon are separated by
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 3 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. When Neap tides are occurring, a. a person experiences the lowest tides close to sunset and sunrise. b. the Sun and the Moon are separated by
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space. Earth s Rotation
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
Astronomy Regents Review
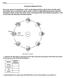 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide
 Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When are tides highest? a. during the moon s first quarter phase
Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When are tides highest? a. during the moon s first quarter phase
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System
 CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
Define umbra and penumbra. Then label the umbra and the penumbra on the diagram below. Umbra: Penumbra: Light source
 Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.9, SC.8.N.1.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will learn from the lesson. Discuss
Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.9, SC.8.N.1.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will learn from the lesson. Discuss
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
STANDARD. S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position.
 STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Earth Science Seasons Test Name Per Date
 Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent
Name Per Date Page 1 1. The diagram below represents four positions of the Earth as it revolves around the Sun. 5. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows the apparent
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
a. 0.1 AU b. 10 AU c light years d light years
 1 AST104 Sp2006: EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the bubble form. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1.
1 AST104 Sp2006: EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the bubble form. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1.
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide. Assessment Date : Term Rotation Revolution
 Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy
 Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Intro to Astronomy. Looking at Our Space Neighborhood
 Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy, Universe
 Dr. V s Study Guide : Astronomy Unit 1) Place the following in order of increasing size: The Galaxy, the Solar System, a Star, the Universe,a Moon and a Planet. Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy,
Dr. V s Study Guide : Astronomy Unit 1) Place the following in order of increasing size: The Galaxy, the Solar System, a Star, the Universe,a Moon and a Planet. Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy,
The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space.
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: 3653-1 - Page 1 The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: 3653-1 - Page 1 The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements
 ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM
 Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System. Chapter 22.3: Earth s Moon
 Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Chapter 22.3: Earth s Moon Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Motions of the Earth The two main motions of the Earth are rotation and revolution Rotation
Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Chapter 22.3: Earth s Moon Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Motions of the Earth The two main motions of the Earth are rotation and revolution Rotation
Name: Exam 1, 9/30/05
 Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
A User s Guide to the Sky
 A User s Guide to the Sky Constellations Betelgeuse Rigel Stars are named by a Greek letter ( ) according to their relative brightness within a given constellation plus the possessive form of the name
A User s Guide to the Sky Constellations Betelgeuse Rigel Stars are named by a Greek letter ( ) according to their relative brightness within a given constellation plus the possessive form of the name
Syosset High School Midterm Review
 Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
The Earth & its good friend, the Moon. SNC1D7 - Space
 The Earth & its good friend, the Moon SNC1D7 - Space Key Questions! What causes... day and night? the seasons? the tides? What are eclipses? Let s eat some space oreos! How do we know the Earth is round?
The Earth & its good friend, the Moon SNC1D7 - Space Key Questions! What causes... day and night? the seasons? the tides? What are eclipses? Let s eat some space oreos! How do we know the Earth is round?
Earth in Space. The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 in Space The --Moon System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if
in Space The --Moon System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if
EARTHS SHAPE AND POLARIS PRACTICE 2017
 1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
7.4 Universal Gravitation
 Circular Motion Velocity is a vector quantity, which means that it involves both speed (magnitude) and direction. Therefore an object traveling at a constant speed can still accelerate if the direction
Circular Motion Velocity is a vector quantity, which means that it involves both speed (magnitude) and direction. Therefore an object traveling at a constant speed can still accelerate if the direction
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science. Solar System Review
 Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
SC.8.E.5.9. Summer and Winter Gizmo
 8 th Grade Science Quarter 1 Recovery Packet SC.8.E.5.9 DAYS/YEARS/SEASONS Go to www.explorelearning.com and search for the Summer and Winter Gizmo. Answer the following questions: Gizmo Warm-up Summer
8 th Grade Science Quarter 1 Recovery Packet SC.8.E.5.9 DAYS/YEARS/SEASONS Go to www.explorelearning.com and search for the Summer and Winter Gizmo. Answer the following questions: Gizmo Warm-up Summer
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
4 Explain why a Blue Moon never occurs during the month of February.
 1 A list of three observed relationships is shown below. Erosional rate = depositional rate insolation = amount of terrestrial radiation Rate of condensation = rate of evaporation In which situation would
1 A list of three observed relationships is shown below. Erosional rate = depositional rate insolation = amount of terrestrial radiation Rate of condensation = rate of evaporation In which situation would
Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky
 Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky Motions of the Planets Mercury Venus Earth All planets in almost circular (elliptical) orbits around the sun, in approx. the same plane, the ecliptic plane. The Moon is orbiting
Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky Motions of the Planets Mercury Venus Earth All planets in almost circular (elliptical) orbits around the sun, in approx. the same plane, the ecliptic plane. The Moon is orbiting
SPI Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe.
 SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
2. Identify the nuclear process that occurs when lighter elements in a star combine to form heavier elements, producing the star's radiant energy.
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the flowchart below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The flowchart represents possible pathways in the evolution of stars. 1. Circle the relative surface
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the flowchart below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The flowchart represents possible pathways in the evolution of stars. 1. Circle the relative surface
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation
 Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
What is in outer space?
 What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
March 21. Observer located at 42 N. Horizon
 March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
Lunar Motion. V. Lunar Motion. A. The Lunar Calendar. B. Motion of Moon. C. Eclipses. A. The Lunar Calendar. 1) Phases of the Moon. 2) The Lunar Month
 Lunar Motion Dr. Bill Pezzaglia V. Lunar Motion A. The Lunar Calendar B. Motion of Moon 2 Updated 2014Jan17 C. Eclipses A. The Lunar Calendar 3 1. Phases of Moon 4 1) Phases of the Moon 2) The Lunar Month
Lunar Motion Dr. Bill Pezzaglia V. Lunar Motion A. The Lunar Calendar B. Motion of Moon 2 Updated 2014Jan17 C. Eclipses A. The Lunar Calendar 3 1. Phases of Moon 4 1) Phases of the Moon 2) The Lunar Month
Moon Occurrences. Eclipses. Tides
 Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Moon Occurrences Eclipses Tides Notes page: What is an eclipse? An eclipse is an event during which one object casts a shadow onto another. Two types of Eclipses Two types of Eclipses: Lunar Eclipse Solar
Earth is rotating on its own axis
 Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Chapter 10 Tides. Introductory Oceanography 10 th Edition
 Chapter 10 Tides Introductory Oceanography 10 th Edition Most ocean waves are wind-generated The medium itself (solid, liquid, gas) does NOT actually travel in the direction of energy Figure 8-2 What causes
Chapter 10 Tides Introductory Oceanography 10 th Edition Most ocean waves are wind-generated The medium itself (solid, liquid, gas) does NOT actually travel in the direction of energy Figure 8-2 What causes
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
 MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
2. The distance between the Sun and the next closest star, Proxima Centuari, is MOST accurately measured in
 Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Passwords. ScienceVocabulary
 Passwords ScienceVocabulary F To the Student Mitosis. Apogee. Ion. Sometimes it seems that scientists speak a language all their own. Passwords: Science Vocabulary will help you learn the words you need
Passwords ScienceVocabulary F To the Student Mitosis. Apogee. Ion. Sometimes it seems that scientists speak a language all their own. Passwords: Science Vocabulary will help you learn the words you need
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017
 Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester Review: Unit 1 and Unit 2
 IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet!
IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet!
Astronomy 101 Lab: Lunar Phases and Eclipses
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Lunar Phases and Eclipses Pre-Lab Assignment: In this week's lab, you will be using a lamp, a globe, and a ball to simulate the Sun, Earth, and the Moon. You will be able to see
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Lunar Phases and Eclipses Pre-Lab Assignment: In this week's lab, you will be using a lamp, a globe, and a ball to simulate the Sun, Earth, and the Moon. You will be able to see
Answer Questions 1 4
 Name Date Period Introduction: Even though the moon does not appear to turn on its own axis from the Earth s point of view, it is indeed rotating as it revolves around the Earth. In the following activity,
Name Date Period Introduction: Even though the moon does not appear to turn on its own axis from the Earth s point of view, it is indeed rotating as it revolves around the Earth. In the following activity,
7 th Grade Science. Name: Date: Friday, November 4, Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon. Homeroom: Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review Name: Date: Friday, November 4, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT demonstrate
7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review Name: Date: Friday, November 4, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT demonstrate
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER)
 L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
