TOPIC 6: ALDOL REACTIONS AND THE SYNTHESIS AND. COMPOUNDS (Chapters 17 and 19)
|
|
|
- Logan Marsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 L TPI 6: ALDL EATINS AND TE SYNTESIS AND EATINS F β-diabnyl MPUNDS (hapters 17 and 19) BJETIVES 1. Provide a rationale for the acidity of α-hydrogens 2. Illustrate the behavior of enols and enolates as nucleophiles in reactions with a variety of electrophiles 3. Develop stategies for the formation of complex molecules form simple starting ti materials by making carbon-carbon b bonds 4. Describe the reactions of ester enolates (nucleophiles) with esters (electrophiles) to give β-keto esters via laisen and crossed laisen condensatiions. 5. Describe the synthesis of ketones using the above products. 6. Describe the reactions of other active methyene compounds and the synthesis of acid derivatives. 7. Describe the preparation and alkylation of enamines. 8. Use this knowledge to predict the products of reactions of this type and to be able to synthesize compounds using these procedures. EM2312: Spring 2009
2 EVIEW F TE ELETPILIITY F ABNYLS Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition-elimination pathways Nucleophile: -Nu N 2 -Nu. Nu 3 P- 2 Nu Acid Derivatives undergo substitution via additionelimination pathways l () 2 ' L Nu Nu N' 2 Nu ' PEVIEW F ENLATE EMISTY ydrogens α- to a carbonyl are acidic NaEt LDA NaEt Enolates are nucleophilic EM2312: Spring 2009
3 Enolates react with. Alkyl halides Br Aldehydes and ketones Esters TE AIDITY F TE α-ydgens F ABNYL MPUNDS: ENLATE ANINS S:17.1 Prob: Protons α- to arbonyl Groups are More Acidic Than ther Protons on arbon pkp pk a a Note: Protons attached to the carbonyl carbon of aldehydes are not particularly acidic, the conjugate base is not resonance stabilized. EM2312: Spring 2009
4 KET AND ENL TAUTMES S17.2 Base atalyzed Tautomerization B B- Keto and enol forms are in equilibrium apidly interconverting are called tautomers Acid atalyzed Tautomerization A e.g., 3 + A A The keto form is usually more stable K eq EM2312: Spring 2009
5 Equilibrium onstants for Tautomerization K = 3 x 10-7 K = 6 x 10-9 K = 1 x 10-2 K = 4 K > a b D D b a EM2312: Spring 2009
6 EATINS VIA ENLS AND ENLATE ANINS Preview: Both Enols and enolates are nucleophilic S:17.3 Prob:17.37,39 E E E compare to: 2 2 Diethylpropion is a stimulant, is marketed as Tenuate for appetite suppression. Propose a synthesis of diethylpropion from benzene and any other starting materials. N? EM2312: Spring 2009
7 α-alogenation of Aldehydes and Ketones Under Acidic conditions Enolizable protons are subject to substitution with bromine upon treatment with Br 2. Br 2, + Br 3 2 Mechanistic ationale: The nucleophilic enol undergoes reaction with bromine 3 + Br Br 2 Under basic conditions: All of the enolizable protons are substituted with bromine and the resulting trihalomethyl group itself is cleaved. Br 2, - Br 3 3 Mechanistic ationale: 1. The nucleophilic enolate undergoes reaction with bromine Br Br 2 2 All enolizable s substituted with Br EM2312: Spring 2009
8 Br 3 l 2 l 3 -chloroform Br 2 Br 3 - bromoform I 2 I 3 - iodoform pale yellow solid good test for presence of a methyl ketone hemical Tests for Functional Groups Methyl ketones give positive iodoform test I 2, Na in Et, 2 EM2312: Spring 2009
9 α-alo arboxylic Acids ell-volhard-zelinski reaction 1. P, Br eactions of α-halo acids Br 1. Na Br N 3 Br KN acemization of Aldehydes and Ketones Experimental bservation: ompounds with a stereogenic center bearing a hydrogen atom adjacent to a carbonyl group undergo rapid racemization in mildly acidic or basic conditions. Me or Me EM2312: Spring 2009
10 Mechanistic ationale: Me Ibuprofen 3 Ibuprofen marketed as racemate nly the S isomer is active Body converts to S by inversion of stereogenic center adjacent to carbonyl /D Exchange eactions Experimental bservation: Treatment of ketones with NaD/D 2 results in replacement of α-hydrogen atoms with deuerium. NaD via D 2 NaD D 2 D D via D D D EM2312: Spring 2009
11 NaD D 2 D D D D via allylic anion NaD D 2 -D exchange EM2312: Spring 2009
12 ? Problems 17.37,39? L TE ALDL EATIN: ADDITIN F ENLATES T ALDEYDES & KETNES SYNTESIS F 3-YDXY ABNYL MPUNDS AND α,β-unsatuated ABNYL MPUNDS S:17.4,5 Prob:17.31, 33,35 The Aldol l eaction: The eaction of an Aldehyde d with an Aldehyde Enolate 3 Na, 2 5 o EM2312: Spring 2009
13 Aldol ondensation eating causes dehydration to form α,β-unsaturated aldehyde Mechanism: 3 Na, 2 Δ 3 e.g. Na, 2 Δ ecognizing Products and Starting Materials of Aldol eactions Aldol condensations give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds EM2312: Spring 2009
14 EM2312: Spring 2009 rossed-aldol (or Mixed Aldol ) eactions Problem: Propose starting materials to prepare 2-methyl-2-pentenal by an aldol reaction Mixed aldols between two aldehydes with enolizable protons can give four different products Na, 2 Δ
15 rossed aldol condensations are only useful when one of the components is non-enolizable and a good electrophile (e.g., an aldehyde) e.g., Na, 2 Δ Examples of Aldol eactions with Ketones Na, 2 Δ 3 3 Na, 2 Δ 3 3 emember: Avoid proposing crossed-aldol reactions if both components are enolizable EM2312: Spring 2009
16 Problem [Solomons 17.31b] - ow would you achieve the following transformation?? Aldol eactions are also atalyzed by Acid. Problem: Write the mechanistic steps of the following reaction (show curved arrows and intermediates) 3 + Δ protonation elimination protonation acid catalyzed dehydration (rg-i) 2 3 deprotonation nucleophilic addition = deprotonation 3 EM2312: Spring 2009
17 and eversible The aldol reaction is reversible. The reverse reaction proceeds through exactly the same intermediates as the forward reaction. Problem: Write the mechanistic steps of the following reaction (show curved arrows and intermediates). deprotonation Δ addition deprotonation 2 3 protonation = protonation elimination Problem: Pulegone, which has a pleasant peppermintcamphor smell, is isolated from the oil of pennyroyal (pennyroyal tea is commonly used as an herbal remedy; pulegone is extremely toxic). Treatment of pulegone with steam yields 3-methylcyclohexanone. Propose a pathway for this reaction. What is the byproduct of this reaction. EM2312: Spring 2009
18 yclizations via Aldol ondensations S:17.6 Na, 2 Δ not + Na, 2 Δ 3 major product S: EM2312: Spring 2009
19 Problem [Solomons 17.33] Identify the structures of compounds A-.? 1. NaN 2 2. acetone 3. N 4 l, 2 g 2+, Na A ( 5 8 ) B ( ) ( )? Problems 17.31,33,35? EM2312: Spring 2009
20 L ALKYLATIN F ALDEYDES AND KETNES S Prob Problem: With or Et, enolates are generated in equilibrium. They are not isolated, but react in situ with a second molecule of carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) in an aldol reaction. K eq =10-4 Na Na pk a = 20 pk a = 16 NaEt Br Solutions: 1. Use a much stronger base lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) 1. LDA 2. Br 2. onvert ketone to enamine, alkylate and hydrolyze N N 1. Br amine enamine EM2312: Spring 2009
21 Lithium Enolates Use of a stronger base (e.g., lithium diisopropylamide, LDA) allows for S:17.7 Prob:17.34 generation of the lithium enolate, and then, in a separate step, the addition of an electrophile. N Li K =10 18 eq Li N pk a = 20 pk a = 38 Lithium Enolates in Alkylation eactions 1. LDA in TF, -78 o 2. -Br (1 o ) 3. 3 The Effect of Temperature on the Alkylation of Lithium Enolates: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Products The regiochemistry of lithiation is controlled by temperature Major Product via: o 1. LDA -78 o 2. Br 1. LDA room temp 2. Br kinetic product thermodynamic product EM2312: Spring 2009
22 Lithium Enolates in Directed rossed-aldol eactions 1. LDA in TF, -78 o 2. not: 3. 3 Synthesis of Enamines ecall that aldehydes and ketones react with primary amines to form imines. Analogous reactions with secondary amines form enamines. 1 amines N 3 N N imine 2 amines 3 N 3 N 3 + N enamine 3 EM2312: Spring 2009
23 Examples of Enamines eacting as Nucleophiles N 1. 3 l l N( 3 ) N 1. N α,β-unsatuated ABNYL MPUNDS Synthesis of α,β-unsaturated arbonyl ompounds S17.8,9 Prob:17.32 Aldol reactions (see above) α-selenation 1. LDA in TF, -78 o 2. Sel EM2312: Spring 2009
24 Selective eduction of α,β-unsaturated arbonyl ompounds 3 2 (high pressure) Ni 2 (2-3 atm) Pd LiAl 4 Electron Distribution in α,β-unsaturated Ketones In the absence of the electron-withdrawing =, akenes are weakly nucleophilic. EM2312: Spring 2009
25 Nucleophilic Additions to α,β-unsaturated Ketones 1,2-addition Nu conjuga jugate addition Nucleophile (Nu ) MgBr Li N N 2 2 uli enolate anions Use of Nucleophilicity of Enolates and Electrophilicity of Enones in the Design of Syntheses. Br M EM2312: Spring 2009
26 L β-diabnyl MPUNDS: INTDUTIN S.19.1 β α ' ' ' β dicarbonyl b l β keto ester β diketone β diester + B + B pk a ~10 Question: Why is the β-dicarbonyl system more acidic than an alcohol (pk a ~18)? Answer: The anion is stabilized by resonance onsequently, there is a lot of enol in equilibrium EM2312: Spring 2009
27 SYNTESIS F 1,3-DIABNYL MPUNDS: TE LAISEN NDENSATIN S:19.2 Prob:19.25,41 verall eaction: The eaction of Ester Enolates with Esters 2 1. NaEt Et Et Et + Et Et Et 2 Et 1. NaEt Et Mechanism First step formation of enolate Et Et Question: ow much enolate forms? What are the pk a values? EM2312: Spring 2009
28 Second step - attack of enolate (nucleophile) on the carbonyl carbon (electrophile) of another molecule of ester Et Et Question: Is this reaction favorable? Third step - deprotonation of β-dicarbonyl compound (product) to form enolate Et Et Question: Is this reaction favorable? What are the pk a values? EM2312: Spring 2009
29 Fourth step - protonation of enolate to form the β-dicarbonyl product by addition of acid Et Question: It this reaction favorable? What are the pk a values? free energy Gibbs 2 2 Et Na Deprotonation K<1 (ester is weaker acid than ethanol) Et 2 Et Na Nucleophilic addition K<1 (= -) Et Et Na Elimination Deprotonation K>1 (1,3-dicarbonyl is stronger acid than ethanol) Na 2 Et Et Et 2 Et Na Et Et Et 2 Et EM2312: Spring 2009
30 So, why does the reaction fail when the ester has two substituents on the α carbon? 1. NaEt 2 Et Et No eaction Et Et Et Et Et Et yclizations via laisen ondensation Et Et 1. NaEt Et Et not Et Et Et Et Et Et + Et Et EM2312: Spring 2009
31 rossed laisen and other ondensations emember the rule for crossed aldol condensation reactions (i.e., one component cannot form an enolate) Et + 3 Et 1. NaEt Et Et 1. NaEt Et Et + Et ethyl oxalate 1. NaEt Et Problem ow would you achieve the following transformations? Et Et? Et Et EM2312: Spring 2009
32 ? Problems 19.25,41? L TE AETAETI ESTE SYNTESIS: SYNTESIS F METYL KETNES S:19.3 Prob: verall reaction Et 1. NaEt, Et 2. -X 3. 2 Et 1. Na heat = 3, 1 eminder: Simple esters cannot be alkylated in this fashion Et 1. NaEt, Et 2. -X 3. 2 Et EM2312: Spring 2009
33 Pathway Deprotonation: Enolate formation Et NaEt Et + Et Alkylation X Et Saponification Et 1. Na S:18.10 Decarboxylation of β-keto arboxylic Acids heat to EM2312: Spring 2009
34 Examples 1. NaEt, 3 I 2. NaEt, 3 2 Br Et Na , heat 1. NaEt Br 2 2 Et Et Na , heat Synthetic Design EM2312: Spring 2009
35 TE MALNI ESTE SYNTESIS: SYNTESIS F SUBSTITUTED AETI AIDS verall reaction Et 1. NaEt, Et 2. -X Et 3. 2 = 3, 1 (2 ) Et Et 1. Na heat S:19.4 Prob: EM2312: Spring 2009
36 Mechanism Deprotonation: Enolate formation Et Et NaEt Et Et + Et Alkylation X Et Et Et Et Ester hydrolysis (see 18.7B) and decarboxylation (see 18.10) Et Et Examples 1. NaEt, 3 I Et Et 2. 2, Na , heat 1. NaEt Br 2 Et Et 2. 2, Na , heat 1. 2NaEt Br( 2 ) 3 Br Et Et 2. 2, Na , heat EM2312: Spring 2009
37 PS What is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? Et 1. NaEt, Et 2. 2 Br 1. Na, heat 1. LiAl Et Synthetic Design Using Malonate Ester Synthesis EM2312: Spring 2009
38 Problem [Solomons 19.26e,27] - ow would you achieve the following transformations? Et? Et Et EM2312: Spring 2009
39 ? Problems 19.36? S:19.12 Prob: Et Et + 2 N 2 N NaEt -2Et N N barbituric acid (pk a ~4) Et Et 2 N + 2 N NaEt -2Et N N ow would you synthesize this malonic ester? (see prob ) phenobarbital - a highly addictive sleep inducer and tranquilizer EM2312: Spring 2009
40 TE - BND FMING EATINS Michael addition onjugate addition of a stabilized enolate to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound Et Et EtNa obinson annulation Michael addition and subsequent aldol cyclization Na, 2 Michael Aldol EM2312: Spring 2009
41 The Knoevenagel ondensation Aldol condensation of a stabilized enolate 1. base - 2 S:19.8 Prob: e.g., Na L TE MPUNDS WIT AIDI YDGEN ATMS N ABN Esters, nitriles and nitroalkanes can also be deprotonated with a strong base (LDA) S: N 2 N 3 N 2 N.and the conjugate bases react as nucleophiles with alkyl halides (alkylation via S N 2), carbonyls (addition, or addition-elimination, e.g., aldol reaction), and esters (addition-elimination, e.g., laisen condensation). EM2312: Spring 2009
42 ompounds with two electron withdrawing groups attached to the same carbon are deprotonated with weaker bases (NaEt, Na). N N N Et N N cyanoacetaldehyde cyanoacetone ethyl cyanoacetate malonitrile N phenylacetone benzylcyanide Direct Alkylation of Esters, Nitriles, Nitroalkanes S:19.6 Et 1. LDA 2. 2 Br N 1. NaEt 2. 3 Br N 2 1. LDA Br EM2312: Spring 2009
43 Methadone, a synthetic opioid, is used to treat addiction to heroin. Methadone occupies the opioid receptor in the brain hereby blocking the binding of other drugs from attaching to the receptor. Br Br 2 N N All 3 bromination via enol Friedel-rafts alkylation N S N Na l N N l N N 1. EtMgBr 2. l(aq) N L TPI 5 EVIEW Enolate Anions Protons α- to carbonyl groups are more acidic than other protons on carbon; enotates are nucleophilic pk a 19.2 enolate (50) E Enols are nucleophilic E enol EM2312: Spring 2009
44 The aldol reaction: The reaction of an aldehyde with an aldehyde enolate 3 Na, 2 5 o heat - 2 Na, 2 Δ 3 3 Na, 2 Δ rossed aldol condensations are only useful when one of the components is non-enolizable and a good electrophile (e.g., an aldehyde). e.g., Na, 2 Δ Na, 2 Δ 3 3 EM2312: Spring 2009
45 Lithium enolates are useful in directed crossed-aldol reactions and in alkylation reactions 1. LDA in TF, -78 o LDA in TF, -78 o 2. -Br (1 o ) Additions to α,β-unsaturated ketones MgBr Li N N 2 2 uli enolate anions Michael addition and subsequent aldol cyclization (obinson annulation) Na, 2 EM2312: Spring 2009
46 The ß-dicarbonyl system more acidic than an alcohol (pk a ~18). The anion is stabilized by resonance The laisen condensation: the synthesis of ß-keto esters 2 Et 1. NaEt Et + Et 1. NaEt 2 Et N rossed laisen and other ondensations emember the rule for crossed aldol condensation reactions (i.e., one component cannot form an enolate) Et + 3 Et 1. NaEt Et Et 1. NaEt Et Et + Et 1. NaEt Et EM2312: Spring 2009
47 The Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis: Synthesis of Methyl Ketones 1. NaEt, Et 1. Na 2. -X Et Et 2 = 3, heat The Malonic Ester Synthesis: Synthesis of Substituted Acetic Acids 1. NaEt, Et 1. Na Et Et 2 Et Et = 3, X heat Synthesis f Enamines Stork Enamine eactions eaction of ketones and aldehydes with secondary amines form enamines + N N nitrogen nucleophilic carbon nucleophilic N N 2 amine enamine N 3 I EM2312: Spring 2009
48 PBLEM SLVING AND SYNTETI STATEGIES Problem - Propose a synthetic pathway to achieve the following transformation.? Problem [Solomons 19.39] - ow could you prepare Darvon, a powerful analgesic, from ethyl phenyl ketone? N February 20, 2009 FDA Panel ecommends Davron Be emoved From Market An FDA panel, citing safety risks, voted Jan. 30 to remove a pair of painkillers from pharmacy shelves. The panel of outside experts voted to end sales of Davron because of concerns that their safety risks outweigh their benefits. Davron (propoxyphene) is a opioid painkiller used for mild to moderate pain. Like all opioids, it carries a high potential for addiction and abuse and are not safe when combined with alcohol. EM2312: Spring 2009
49 ? Problem [Solomons 19.38] - Fenchone is a terpenoid isolated from fennel oil. Provide the structure of intermediates and reagents (a)-(n) in the following scheme (cont. next slide). Fenchone + (a) Δ 2 3 (b) (c) (d) mixture of (e) and (f) 1. (g) (h) (i) (j) (l) (k) (m) (n) EM2312: Spring 2009
50 Problem [Solomons 17.32] Describe the key mechanistic steps in the following reaction (i.e., write a mechanism). + Na?? Problems 19.30,31,50? EM2312: Spring 2009
51 TPI 6 (APTE 17,19) N EXAM 5 Types of Questions - Predict the products obtained from given starting materials - ationalize the outcome of a reaction (i.e., propose a mechanism, draw key intermediates) - Develop multistep synthetic strategies. Do the problems in the book; they are great examples of the types of problems on the exam! Preparing for Exam 5 - Get up-to-date NW! - Work as many problems as possible. Do the problems first, then consult the solutions manual. - Work in groups, discuss chemistry, teach and test each other. - Do the Learning Group Problem at the end of the chapter. EM2312: Spring 2009
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
Michael and Aldol CH391 December 4, 2002
 Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III: REACTIONS AT THE ALPHA-CARBON
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Summary of π Bond Chemistry
 Chapter 10 Summary of π Bond Chemistry to π C=C 13.01 Chapter 11 at π C=C to π C=C Chapter 1 LG at π C=C Chapter 13 at α position C= activates position ow does C= activation α position? Via or. E base
Chapter 10 Summary of π Bond Chemistry to π C=C 13.01 Chapter 11 at π C=C to π C=C Chapter 1 LG at π C=C Chapter 13 at α position C= activates position ow does C= activation α position? Via or. E base
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha ( ) Substitution
 Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
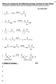 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 24 arbonyl ondensation eactions 24.1 The aldol reaction 24.2 rossed aldol reactions 24.3 Directed aldol reactions 24.4 Intramolecular aldol reactions 24.5 The laisen reaction 24.6 The crossed laisen and
24 arbonyl ondensation eactions 24.1 The aldol reaction 24.2 rossed aldol reactions 24.3 Directed aldol reactions 24.4 Intramolecular aldol reactions 24.5 The laisen reaction 24.6 The crossed laisen and
CHEM 234: Organic Chemistry II Reaction Sheets
 EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
TOPIC 4. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON (Chapter 18)
 L TPI 4. ABXYLI AIDS AND THEI DEIVATES: NULEPHILI ADDITIN-ELIMINATIN AT THE AYL ABN (hapter 18) BJETIVES 1. Name carboxylic acids and acid derivatives: acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides and nitriles
L TPI 4. ABXYLI AIDS AND THEI DEIVATES: NULEPHILI ADDITIN-ELIMINATIN AT THE AYL ABN (hapter 18) BJETIVES 1. Name carboxylic acids and acid derivatives: acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides and nitriles
CHAPTER 24 HW: CARBONYL CONDENSATIONS
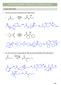 CAPTER 24 W: CARBNYL CNDENSATINS ALDL REACTIN 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism for each aldol reaction. Na 2 product Na Et prod. 2. Give the curved arrow mechanism for this aldol reaction (and dehydration
CAPTER 24 W: CARBNYL CNDENSATINS ALDL REACTIN 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism for each aldol reaction. Na 2 product Na Et prod. 2. Give the curved arrow mechanism for this aldol reaction (and dehydration
Chem 263 Nov 19, Cl 2
 Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
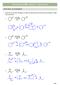 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
Aldehydes and Ketones
 9 Aldehydes and Ketones hapter Summary The carbonyl group, =, is present in both aldehydes (=) and ketones ( 2 =). The IUPA ending for naming aldehydes is -al, and numbering begins with the carbonyl carbon.
9 Aldehydes and Ketones hapter Summary The carbonyl group, =, is present in both aldehydes (=) and ketones ( 2 =). The IUPA ending for naming aldehydes is -al, and numbering begins with the carbonyl carbon.
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH CONDENSATION CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates
Chem 263 Nov 14, e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents)
 hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
20.3 Alkylation of Enolate Anions
 864 APTER 20 ELATE AD TER ARB ULEPILES which precipitates as a yellow solid, provides a positive test for the presence of a methyl ketone The reaction can also be used in synthesis to convert a methyl
864 APTER 20 ELATE AD TER ARB ULEPILES which precipitates as a yellow solid, provides a positive test for the presence of a methyl ketone The reaction can also be used in synthesis to convert a methyl
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
C h a p t e r T w e n t y - o n e : Enols, Enolates, and Aldol-like Condensations
 h a p t e r T w e n t y o n e : Enols, Enolates, and Aldollike ondensations Li LDA 1. R TF R 2. 3 R A directed aldol reaction, used in the synthesis of periplanone B, a cockroach attractant M 323: Summary
h a p t e r T w e n t y o n e : Enols, Enolates, and Aldollike ondensations Li LDA 1. R TF R 2. 3 R A directed aldol reaction, used in the synthesis of periplanone B, a cockroach attractant M 323: Summary
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Important Concepts. Problems. Chapter Problems. Cuprate additions followed by enolate alkylations. 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11)
 Problems hapter 18 861 uprate additions followed by enolate alkylations P 1. R 2uLi, TF 2. RX A A R R N 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11) D P D R P R A RR 16. Robinson Annulation (Section 18-11) Important
Problems hapter 18 861 uprate additions followed by enolate alkylations P 1. R 2uLi, TF 2. RX A A R R N 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11) D P D R P R A RR 16. Robinson Annulation (Section 18-11) Important
Carbonyl Chemistry IV + C O C. Lecture 10. Chemistry /30/02
 arbonyl hemistry IV Ō - + Lecture 10 Addition of Nitrogen Nucleophiles Primary Amines RN 2 Imines Secondary Amines R 2 N Enamines ydrazine derivatives RNN 2 ydrazones ydroxyl Amine N 2 ximes Imine Formation
arbonyl hemistry IV Ō - + Lecture 10 Addition of Nitrogen Nucleophiles Primary Amines RN 2 Imines Secondary Amines R 2 N Enamines ydrazine derivatives RNN 2 ydrazones ydroxyl Amine N 2 ximes Imine Formation
Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds.
 1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Organic Chemistry, Third Edition. Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations
 rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
CH 3 CHCH 3 CH 3 CHCH 3 Isopropyl cation. Oxomium ion intermediate. intermediate (an electrophile)
 Understanding (as opposed to memorizing) mechanisms is critical to mastering organic chemistry. Although the mechanisms you encounter throughout the course may seem entirely different, they are actually
Understanding (as opposed to memorizing) mechanisms is critical to mastering organic chemistry. Although the mechanisms you encounter throughout the course may seem entirely different, they are actually
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Chapter 21 Ester Enolates
 hapter 21 Ester Enolates Introduction R R' H H The preparation and reactions of β-dicarbonyl compounds, especially β-keto esters, is the main focus of this chapter. A proton on the carbon flanked by the
hapter 21 Ester Enolates Introduction R R' H H The preparation and reactions of β-dicarbonyl compounds, especially β-keto esters, is the main focus of this chapter. A proton on the carbon flanked by the
Score: Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320N Due Monday, April 17. NAME (Print): Chemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 9th Homework April 10, 2017
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
Module No and Title. PAPER No: 5 ; TITLE : Organic Chemistry-II MODULE No: 25 ; TITLE: S E 1 reactions
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 25; S E 1 reactions CHE_P5_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. S E 1 reactions 3.1
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 25; S E 1 reactions CHE_P5_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. S E 1 reactions 3.1
How to make pyridines: the Hantzsch pyridine synthesis
 ow to make pyridines: the antzsch pyridine synthesis 1191 Zinc in acetic acid (Chapter 24) reduces the oxime to the amine and we can start the synthesis by doing the conjugate addition and then reducing
ow to make pyridines: the antzsch pyridine synthesis 1191 Zinc in acetic acid (Chapter 24) reduces the oxime to the amine and we can start the synthesis by doing the conjugate addition and then reducing
You must have your answers written in PERMANENT ink if you want a regrade!!!! This means no test written in pencil or ERASABLE INK will be regraded.
 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 3rd Midterm April 20, 2017 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 3rd Midterm April 20, 2017 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
20.10 Conjugate Additions
 894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
 11 R R R ALDEYDES AND KETNES APTER SUMMARY 111 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones both have a carbonyl group (carbonoxygen double bond); aldehydes have at least one carbon bonded
11 R R R ALDEYDES AND KETNES APTER SUMMARY 111 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones both have a carbonyl group (carbonoxygen double bond); aldehydes have at least one carbon bonded
Note: You must have your answers written in pen if you want a regrade!!!!
 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 310N Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 29, 2007 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 310N Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 29, 2007 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
Chem 263 Nov 24, Properties of Carboxylic Acids
 Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3. Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic
 hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
235 Organic II. Final Exam Review REACTIONS OF CONJUGATED DIENES 1,2 VS 1,4 ADDITION REACTIONS OF CONJUGATED DIENES
 b. the ompound 7 i 1 Spectral Data: singlet, 196.5 ppm singlet, 14.1 ppm singlet, 14.4 ppm doublet, 19.1 ppm doublet, 18.5 ppm 1 MR Mass Spectrum Absorbance Intensity Infrared Spectrum 65 91 9. Structure:
b. the ompound 7 i 1 Spectral Data: singlet, 196.5 ppm singlet, 14.1 ppm singlet, 14.4 ppm doublet, 19.1 ppm doublet, 18.5 ppm 1 MR Mass Spectrum Absorbance Intensity Infrared Spectrum 65 91 9. Structure:
2 - ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND DERIVATIVES
 2 - ALDEYDES, KETNES AND DEIVATIVES Carbonyl chemistry is one of the most important areas of organic chemistry. You have been introduced to the chemistry of carboxylic acids in CEM*2700, and in this course
2 - ALDEYDES, KETNES AND DEIVATIVES Carbonyl chemistry is one of the most important areas of organic chemistry. You have been introduced to the chemistry of carboxylic acids in CEM*2700, and in this course
Chem 263 March 28, 2006
 Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
Lecture 19. Carboxylic Acids O C OH O R C O - + H + O - Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 19 arboxylic Acids R R - + + R - March 29, 2018 Review: Selectivity in Reduction LiAl 4 reduces any and all carbonyl compounds to the corresponding alcohols NaB 4 only reduces aldehydes and ketone
Lecture 19 arboxylic Acids R R - + + R - March 29, 2018 Review: Selectivity in Reduction LiAl 4 reduces any and all carbonyl compounds to the corresponding alcohols NaB 4 only reduces aldehydes and ketone
Appendix A. Common Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols. Abbreviations
 smi97462_apps.qxd 12/6/04 1:09 PM Page A-1 Appendix A ommon Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols Abbreviations Ac acetyl, 3 BBN 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane BINAP 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
smi97462_apps.qxd 12/6/04 1:09 PM Page A-1 Appendix A ommon Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols Abbreviations Ac acetyl, 3 BBN 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane BINAP 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
O O O CH 2 O 7. 2 = C=O hydration H B. 6 = reverse aldol H O. 9b = acetal formation add alcohol (step 2)
 1 equences For Practice 1. 1 2 3 7 2 6 5 4 8 9 Possible Key 3 = AD + oxidation 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 AD + 7 1 = AD + oxidation 7 = aldol AD 2 = = hydration 2 6 6 = aldol AD + AD 5 5 = β-keto decarboxylation
1 equences For Practice 1. 1 2 3 7 2 6 5 4 8 9 Possible Key 3 = AD + oxidation 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 AD + 7 1 = AD + oxidation 7 = aldol AD 2 = = hydration 2 6 6 = aldol AD + AD 5 5 = β-keto decarboxylation
Note: You must have your answers written in pen if you want a regrade!!!!
 AME (Print): SIGATURE: hemistry 310 Dr. ent Iverson 3rd Midterm April 26, 2007 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please ote: This test may be a bit long, but there
AME (Print): SIGATURE: hemistry 310 Dr. ent Iverson 3rd Midterm April 26, 2007 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please ote: This test may be a bit long, but there
The Organic Acids. Carboxylic Acids * *
 arboxylic Acids The rganic Acids Some Notation: Acids and their conjugate bases pka ~ 15 - weak acid arboxylic Acid pka ~ 4 moderate acid - arboxylate Anion pka ~ -7 very strong acid l - l arboxylic acids
arboxylic Acids The rganic Acids Some Notation: Acids and their conjugate bases pka ~ 15 - weak acid arboxylic Acid pka ~ 4 moderate acid - arboxylate Anion pka ~ -7 very strong acid l - l arboxylic acids
18: Reactions of Enolate Ions and Enols
 18: Reactions of Enolate Ions and Enols 18.1 Enolate Ions and Enols 18-3 Halogenation, Alkylation, and Condensation Reactions (18.1A) 18-3 Acidity of α-c-h's (18.1B) 18-4 Resonance Stabilization Enol Form
18: Reactions of Enolate Ions and Enols 18.1 Enolate Ions and Enols 18-3 Halogenation, Alkylation, and Condensation Reactions (18.1A) 18-3 Acidity of α-c-h's (18.1B) 18-4 Resonance Stabilization Enol Form
Name. Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003
 INSTRUTINS Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003 This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice format and the answers should
INSTRUTINS Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003 This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice format and the answers should
CHEM Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
You must have your answers written in PERMANENT ink if you want a regrade!!!! This means no test written in pencil or ERASABLE INK will be regraded.
 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 310N Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 25, 2010 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 310N Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 25, 2010 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
Carbonyl Chemistry. aldehydes ketones. carboxylic acid and derivatives. Wednesday, April 29, 2009
 Carbonyl Chemistry X aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid and derivatives Electrophiles (eg. + ) Nucleophiles (eg. C 3 MgBr) an enolate Base β β β α α α 1 2 3 4 Nuc- 1 2 Nuc 3 4 1,2-addition 1 2 3 4 Nuc-
Carbonyl Chemistry X aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid and derivatives Electrophiles (eg. + ) Nucleophiles (eg. C 3 MgBr) an enolate Base β β β α α α 1 2 3 4 Nuc- 1 2 Nuc 3 4 1,2-addition 1 2 3 4 Nuc-
Lecture 23. The Aldol Condensation. an Aldol! April 12, 2018 O H O H - Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 23 The Aldol Condensation - b a an Aldol! April 12, 2018 Exam III - Wed April 18 WEL 2.122 7-9 PM Covers thru today omework ydrolysis Reactions Synthesis Get an A!!! Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA)
Lecture 23 The Aldol Condensation - b a an Aldol! April 12, 2018 Exam III - Wed April 18 WEL 2.122 7-9 PM Covers thru today omework ydrolysis Reactions Synthesis Get an A!!! Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA)
Carbonyl Chemistry IV: Enolate Alkylations and Aldols. Aldol Madness O O O N M + substrate. aldehyde. (Z)-enolate H
 Carbonyl Chemistry IV: nolate Alkylations and Aldols Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 9 Section Agenda 1) o office hours Thursday 2) The Great Joe Young is covering section next onday 3) andout: Carbonyl Chemistry
Carbonyl Chemistry IV: nolate Alkylations and Aldols Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 9 Section Agenda 1) o office hours Thursday 2) The Great Joe Young is covering section next onday 3) andout: Carbonyl Chemistry
Answers to HT2, Chemistry A
 Answers to T2, hemistry 302-302A - 2004 1. There are many ways to do these problems - here is just one. For all three parts we can use diphenyl ketone (benzophenone) so let s make that first: 1. 2 Eq.
Answers to T2, hemistry 302-302A - 2004 1. There are many ways to do these problems - here is just one. For all three parts we can use diphenyl ketone (benzophenone) so let s make that first: 1. 2 Eq.
Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position
 Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position D 3 + D 3 C CD 3 2 C 2 the keto form the enol form chanism: + C 2 C 2 C 2 D D 2 D 2 repeat 5 times D 3 C CD 3 alogenation At The α-position Br 2, 2 C 2 Br
Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position D 3 + D 3 C CD 3 2 C 2 the keto form the enol form chanism: + C 2 C 2 C 2 D D 2 D 2 repeat 5 times D 3 C CD 3 alogenation At The α-position Br 2, 2 C 2 Br
Practice Synthetic Problems: CHEM 235 Page 2
 Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases
 hapter 3 Acids and Bases Basic Definitions Associated with Acids and Bases Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases Molecular Models of Selected Acids Brønsted-Lowry Theory 1. In a Brønsted-Lowry reaction,
hapter 3 Acids and Bases Basic Definitions Associated with Acids and Bases Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases Molecular Models of Selected Acids Brønsted-Lowry Theory 1. In a Brønsted-Lowry reaction,
Note: You must have your answers written in pen if you want a regrade!!!!
 AME (Print): SIGATURE: hemistry 310 Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 29, 2007 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please ote: This test may be a bit long, but there
AME (Print): SIGATURE: hemistry 310 Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 29, 2007 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please ote: This test may be a bit long, but there
Carboxylic Acids O R C + H + O - Chemistry 618B
 arboxylic Acids R H R + H + - R - Nomenclature - IUPA IUPA names: drop the -e from the parent alkane and add the suffix -oic acid If the compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond, change the infix
arboxylic Acids R H R + H + - R - Nomenclature - IUPA IUPA names: drop the -e from the parent alkane and add the suffix -oic acid If the compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond, change the infix
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
Aldehydes and Ketones
 Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
CHAPTER 16 CONJUGATE ADDITION
 HAPTER 16 NJUGATE ADDITIN onjugated Pi Bonds onjugated double bonds are separated by only one single bond. Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds. arbonyl ompounds with onjugated
HAPTER 16 NJUGATE ADDITIN onjugated Pi Bonds onjugated double bonds are separated by only one single bond. Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds. arbonyl ompounds with onjugated
When H and OH add to the alkyne, an enol is formed, which rearranges to form a carbonyl (C=O) group:
 Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
18.10 Conjugate Additions O O. O X BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CCH 3 ± ± BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3. TsOH 1 O C O O W 3 CH 3 CCH 3 CH 3 CCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3
 80 NJUGATE ADDITINS 779 An attempt to form a Grignard reagent from 5-bromo- 2-pentanone is doomed to failure because the Grignard will react with the carbonyl group Therefore, the carbonyl group is first
80 NJUGATE ADDITINS 779 An attempt to form a Grignard reagent from 5-bromo- 2-pentanone is doomed to failure because the Grignard will react with the carbonyl group Therefore, the carbonyl group is first
CH318N Spring 2012 Final Exam. Chemistry 318N. Spring 2012 Dr. Willson. Final Exam
 318N Spring 2012 Final Exam 3 hemistry 318N Spring 2012 Dr. Willson Final Exam This afternoon you will take two tests, one in chemistry and one in integrity. I want you to get A s on both of these tests
318N Spring 2012 Final Exam 3 hemistry 318N Spring 2012 Dr. Willson Final Exam This afternoon you will take two tests, one in chemistry and one in integrity. I want you to get A s on both of these tests
(1) Recall the different types of intermolecular interactions. (2) Look at the structure and determine the correct answer.
 MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 11: Carboxylic Acids Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. What kinds of interactions are holding together the carboxylic acid dimer shown? Question #01 3 C C 3 (A) Van
MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 11: Carboxylic Acids Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. What kinds of interactions are holding together the carboxylic acid dimer shown? Question #01 3 C C 3 (A) Van
Carbonyl Chemistry V + C O C. Chemistry /30/02
 arbonyl hemistry V Ō - + Keto-enol enol Tautomerism H 3 H 3 Ketone H H R 2 H R' H H 3 H 2 H Enol H Acid atalyzed α Halogenation R 2 R' + X 2 H + R 2 R' + HX H X X 2 can be l 2, Br 2, or I 2. Substitution
arbonyl hemistry V Ō - + Keto-enol enol Tautomerism H 3 H 3 Ketone H H R 2 H R' H H 3 H 2 H Enol H Acid atalyzed α Halogenation R 2 R' + X 2 H + R 2 R' + HX H X X 2 can be l 2, Br 2, or I 2. Substitution
ENOLATES IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Loudon Chapter 20 & 21 Review: Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 20 & 21 eview: Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 These two chapters cover compounds which are all at the three bonds to more electronegative
Loudon Chapter 20 & 21 eview: Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 These two chapters cover compounds which are all at the three bonds to more electronegative
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Sul Ross State University Syllabus for Organic Chemistry II: CHEM 3408 (Spring 2017)
 Sul Ross State University Syllabus for Organic Chemistry II: CHEM 3408 (Spring 2017) Class: Organic Chemistry II Instructor: Dr. David J. Leaver Room: WSB 307 Office: WSB 318 Time: MWF 9:00-9:50am Office
Sul Ross State University Syllabus for Organic Chemistry II: CHEM 3408 (Spring 2017) Class: Organic Chemistry II Instructor: Dr. David J. Leaver Room: WSB 307 Office: WSB 318 Time: MWF 9:00-9:50am Office
Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes. Carbonyl Compounds. Chapter 18: Aldehydes and Ketones Slide 18-2
 hapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes arbonyl ompounds hapter 18: Aldehydes and Ketones Slide 18-2 1 arbonyl Structure arbon is sp 2 hybridized. = bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than = bond in alkenes.
hapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes arbonyl ompounds hapter 18: Aldehydes and Ketones Slide 18-2 1 arbonyl Structure arbon is sp 2 hybridized. = bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than = bond in alkenes.
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Final Exam Version 1. Chemistry 140C. Fall Good Luck! Dec 5, :30 am 2:30 pm This exam accounts for 50% of the final grade.
 Chemistry 140C Final Exam Version 1 Fall 2006 Dec 5, 2006 11:30 am 2:30 pm This exam accounts for 50% of the final grade. Mark your final answer clearly. Completely erase irrelevant information! Exams
Chemistry 140C Final Exam Version 1 Fall 2006 Dec 5, 2006 11:30 am 2:30 pm This exam accounts for 50% of the final grade. Mark your final answer clearly. Completely erase irrelevant information! Exams
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones
 Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Suggested solutions for Chapter 41
 s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
Basic Organic Chemistry
 Basic rganic hemistry ourse code: EM 12162 (Pre-requisites : EM 11122) hapter 06 hemistry of Aldehydes & Ketones Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana ffice: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720 (Mobile) Email: dinesh@kln.ac.lk
Basic rganic hemistry ourse code: EM 12162 (Pre-requisites : EM 11122) hapter 06 hemistry of Aldehydes & Ketones Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana ffice: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720 (Mobile) Email: dinesh@kln.ac.lk
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
Conjugate Addition Reactions 2:02 PM
 1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
