|
|
|
- Poppy Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power measurements, when the power factor is 0.5 a) the readings of the two wattmeters are equal and positive b) the readings of the two wattmeters are equal and positive c) the total power is measured by only one wattmeter d) the readings of the two wattmeters are not equal and positive. 2. The reading of the wattmeter connected to measure the reactive power in a 3-phase circuit is given by zero when the line voltage is 400 volts and the line current is 15 amps. Then the power factor of the circuit is a) zero b) 0.6 c) 0.8 d) unity 3. The resistance which should be connected between terminals P and Q for maximum transfer of power from source to the combined load is source a) zero Ω b) 2 Ω c) 4 Ω d) infinity ohms 4. In the given circuit below, the current is i(t) = 4 sin (500 t) amps. The applied i(t) voltage v(t) in volts is a) 40 sin (500 t) b) sin (500 t 45 0 ) c) 40 cos (500 t) - 10V d) cos (500 t 45 0 ) 2 Ω 4 Ω v(t) P Q Combined Load 10 Ω 20 mh
2 5. In a two port network, open circuit impedance parameters express a) V 1, V 2 in terms of I 1, I 2 b) I 1, I 2 in terms of V 1, V 2 c) V 1, I 1 in terms of V 2, I 2 d) V 1, I 2 in terms of V 2, I 1 6. When two 2-port networks are connected in parallel, it is convenient to use a) open circuit impedance parameters b) short circuit admittance parameters c) transmission parameters d) inverse hybrid parameters 7. On increasing the Q-factor of a coil a) its power factor increases b) its power factor decreases c) its power factor remains unaltered d) its power may increase or decrease 8. The value of current at resonance in a series RLC circuit is affected by the value of a) R b) L c) C d) R, L and C 9. The equivalent inductance of the below given circuit at the terminals P- Q is P Q 4H a) 4H b) 2H c) 6H d) 8H 10. A capacitor C at time t = 0, with initial charge Q 0 acts as a) short circuit b) open circuit c) current source d) voltage source 11. An electrical network with 8 independent nodes will have a) 4 nodal equations b) 8 nodal equations c) 7 nodal equations d) 9 nodal equations Z Impedance Z 1 = Ω and Z 2 = Ω Then is Z 2 a) Ω b) Ω c) Ω d) Ω 13. Transformers used in conjunction with measuring instruments for measurement of high voltage and high currents are called a) transformer meters b) power transformers c) pulse transformers d) instrument transformers 2H 2H
3 14. Swamping resistance is used in moving coil instruments to reduce error due to a) thermal emf b) temperature c) power taken by instrument d) galvanometer sensitivity 15. It is required to measure pf of an electrical load. No power factor meter is available. The following combination is used to determine pf a) a Wattmeter b) a voltmeter and ammeter c) a voltmeter, ammeter and wattmeter d) a kwh meter 16. The dielectric loss of a capacitor can be measured by a) Wein bridge b) Owen bridge c) Schering bridge d) Maxwell bridge 17. One of the following is an active transducer a) Strain gauge b) Selsyn c) Photo voltaic cell d) Photo emissive cell 18. The breakaway point of the root from the real axis for a closed loop system with loop gain K(s 10) G(s) H(s) = lies (s 2((s 5) a) between - 10 and - b) at - c) between - 2 and origin d) between -2 and A system has 12 poles and 2 zeros. Its high frequency asymptote in its magnitude plot will have a slope of a) -60db/dec b) -120 db/dec c) -200 db/dec d) -240 db/dec 20. jω The Nyquist plot of a transfer function is shown in the figure. The gain margin is σ \ a) 5 b) 8-3 c) 10 d) If the gain of the open loop system doubled, the gain margin a) gets one forth b) gets halved c) gets doubled d) is not affected 22. The maximum phase shift that can be obtained by using a lead compensator with transfer function 4(1 0.15s) G(s) = is equal to (1 0.05s) a) 15 0 b) 30 0 c) 45 0 d) 60 0
4 23. In a monostable multivibrator using 555 timer, the time delay is 100 m sec. timing resistor is 100 kw, the value of timing capacitor is a) 9 mf b) 0.9 µf c) 9 F d) 1.8 µf 24. The ideal operational amplifier has a) R i =, R 0 = b) R i = 0, R 0 = c) R i =, R 0 = 0 d) R i = 0, R 0 = In the LM 741, LM stands for a) Motoral b) RCA c) Texas instruments d) National semiconductor 26. ADC preferred for digital panel meters and multimeters a) Flash ADC b) Servo ADC c) Successive approximation ADC d) Dual slope ADC 27. The output of an op-amp voltage follower is a triangular wave as shown in the figure for a square wave input of frequency 2 MHz and 8 V peak to peak amplitude. The slew rate of the op amp is 3V -3V 0.5µs a) 6 µs b) 8 V/µs c) 14 V/µs d) 14 µs 28. Match the following with parts in List - I with machines in List - II List - I List - II p. damper bars 1. dc machine q. rotor bars 2. syschronous machine r. commutator 3. induction machine a) p-1 q-2 r-3 b) p-3 q-1 r-2 c) p-2 q-3 r-1 d) p-3 q-2 r The following is the apparent disadvantage of auto transformer as compared to two winding transformer a) power rating is greater b) efficiency is low c) conductive isolation is not present d) voltage regulation is low 30. A 230/2300 V, Y/D 3-phase transformer is rated at 230 KVA. Its rated secondary current/phase is a) 33.33A b) A c) 66.66A d) 30.33A 31. A 3 phase induction motor is run in counter clockwise direction as motor with reverse phase sequence of supply. The range of slip variation for this mode is a) 0 < s < 1 b) 2 < s < 1 c) 0 < s < -1 d) 3 < s < 2 t
5 32. The following is phasor diagram or rotor variables of 3 phase induction motor with Ej as injected emf. This provides a) sub synchronous speed without pf E j improvement b) super synchronous speed without pf β improvement Flux c) sub synchronous speed with pf I improvement 2 Z 2s d) super synchronous speed with pf se 2 improvement 33. The variation of synchronising power for variation of power angle for a salient pole machine will be P sy P sy a) b) 0 90 c) d) α 34. If the supply frequency and voltage applied to a synchronous motor are both reduced to fractions Kf, KV the maximum power of the motor becomes a) K times of P max at 'f' 1 b) times of P max at f K c) K 2 times of P max at f 1 d) times of P max at f K For a salient pole syschronous machine, when the speed becomes super syschronous, during hunting, the damper bars develop a) syschronous motor torque b) dc motor torque c) induction motor torque d) induction generator torque 36. The output waveform given below can be obtained from α P sy π a α wt P sy a) controlled rectifier b) AC chopper c) DC chopper d) DIAC TRIAC phase control circuit α α
6 37. The candle power of a lamp placed normal to a working plane is 30 C.P. Find the distance if the illumination is 15 lux a) 2m b) 0.5m c) m 1 d) m The luminous intensity of a lamp is 750 C.P. Then the flux given out is a) lumen b) 750 π lumen c) lumen π 2π d) 1500 π lumen 39. Furnaces used for electric crematorium are of type a) Resistance heating b) Induction heating c) Dielectric heating d) Arc heating 40. For the same rating the amount of radiant heat produced is least in a) fluorescent lamp b) filament lamp c) sodium vapour lamp d) mercury vapour lamp 41. In electric traction, the friction at the track is proportional to 1 1 a) b) speed (speed) 2 c) speed d) (speed) Polar form of (1 - a 2 a) is a) b) 2-60 c) d) The number of strands on a 3 layer cable is a) 24 b) 7 c) 37 d) Given maximum power transmitted through a line Pmax, then with 60% of series capacitor compensation the maximum power transfer becomes P max P max a) b) 0.4 P max c) d) 0.6P max Z L 45. In A, B, C, D parameters, in the T-equivalent shown can be represented as 2 Z L /2 Z L /2 Y L a) (A-1)C b) (A-1)B c) (A-1)/C d) B/(A-1) 46. An industrial consumer has a load of 1500 kw at 0.8 pf lag for 12 hrs and 1000 kw at Upf for 12 hours during a day. the Daily load factor of the consumer is a) b) c) 0.8 d) In a power system with negligible resistance, the fault current at a point is 8.0 pu. The series reactance to be connected at the fault point to reduce the short circuit current to 5.0 pu is a) 3.0 pu b) 0.25 pu c) pu d) pu
7 48. Merz price protection is more suitable for a) transformers b) generators c) transmission lines d) loads 49. The load torque vs speed characteristic of an industrial load is given below The motor suitable for the above load is a) dc shunt motor b) 3 phase induction motor c) dc series motor d) capacitor motor 50. Between 2 supports, due to sag, the conductor takes the shape of a) parabola b) hyperbola c) catenary d) semicircle 51. In suspension type insulator, the potential drop is maximum across a) top disc N b) centre disc c) lowest disc d) depends on number of discs of the string 52. The chances of occurrence of corona is maximum during a) dry weather b) humid weather c) winter d) hot summer 53. Equal area criterion can be applied to a) Multi machine systems b) to any system with any number of loads and generators c) single machine connected to infinite bus system d) system with induction machines 54. An ideal current source has zero T L a) internal conductance b) internal resistance c) voltage on no load d) ripple
8 55. Three resistances of 1 ohm, 2 ohms and 3 ohms are connected in delta. These resistance are to be replace by star connection as shown in the figure below, maintaining the same terminal conditions. 1Ω 3Ω The value of highest resistance in star will be a) ohm b) ohm c) ohm d) 1 ohm 56. Superposition theorem required as many circuits to be solved as there are a) sources b) nodes c) sources nodes d) sources nodes meshes Ω P 2Ω A The circuit shown above can be easily solved by a) Series parallel network b) Star mesh theorem c) Thevenin's theorem d) Reciprocity theorem 6Ω 18Ω B R Y B C E D R 2 12Ω 4Ω 6 Ω 72Ω 9Ω R 1 R 3 F G H R Y B
9 58. At Half power frequencies, the current in the RLC series circuit is 1 1 a) current at resonance b) Current at resonance c) current at resonance d) current at resonance In RLC circuits, the current at resonance is a) maximum in parallel resonance and minimum in series resonance b) maximum in series resonance and minimum in parallel resonance c) maximum in both series and parallel resonance d) maximum in both series and parallel resonance 60. The equivalent inductance of the circuit between terminals P and Q is equal to (L 1 L 2 2M) a) (L 1 L 2-2M) b) (L 1 L 2 - M 2 ) (L 1 L 2 - M 2 ) (L 1 L 2 - M 2 ) c) (L 1 L 2 - M 2 ) d) (L 1 L 2 2M) (L 1 L 2-2M) 61. In the given circuit below, the voltage across the inductor is V S P Q 220 volts 100 Hz 2π L 1 100Ω 220 a) volts b) volts 2 V R M L 2 VL 1 Henry c) 220 volts d) 110 volts
10 62. In the given R-C circuit, the current reaches its maximum value - 10 volts a) After 50µ sec. of turning on the switch S b) after 100 µ sec. of turning on the switch S c) after 1000 µ sec. of turning on the switch S d) immediately after turning on the switch S 63. The time constant of a series R-L circuit is given by L a) L 2 R b) LR 2 c) LR' d) R 64. For the circuit given below, the current through 1 ohm resistor will be 1 Ω S 100Ω 10 volts, 50 Hz a) 2 amps b) 4 amps c) 6 amps d) 8 amps 65. Admittance is the reciprocal of a) impedance b) inductance c) susceptance d) reactance 66. The power expression in 3-phase circuit in terms of line voltage V L, line current I L and power factor of the load is 3 V L I L cos φ where φ is the angle between a) line voltage and line current b) line voltage and phase current c) phase voltage and line current d) phase voltage and phase current 67. K The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is given by G(s) = s(s 1) L 8 volts 5 µf If the gain K is increased to infinity then the damping ratio will tend to become 1 a) b) 1 c) 0 d) 2
11 68. The overall gain for the block diagram shown below is given by in a) G 1 G 2 G 3 G 4 b) G 1 G 2 G 3 G 4 c) G 1 G 2 G 3 G 4 d) (G 1 G 2 ) (G 3 G 4 ) 69. Which of the following systems does have the tendency to oscillate? a) closed loop system b) open loop system c) either (A) or (B) d) both (A) and (B) 70. The feedback system with characteristics equation s 4 2Ks 3 s 2 5s 5 = 0 is a) unstable for all values of K b) stable for all values of K c) stable for positive values of K d) stable for zero value of K 71. For making an unstable system as stable system a) gain of the system should be decreases b) gain of the system should be increases c) the number of zeros of the loop transfer function should be decreased d) the number of poles of the loop transfer function should be increased 72. For the BJT shown in figure, V BE = 0.7V β = 100, find I B V 1 G 1 G K G 3 G 4 V CC = 20 V 1K 2K out V 2 a) µa b) 19.3 ma c) 38.6 ma d) 57 µa
12 73. The value of transconductance at a bias voltage of 0V for the JFET which is having I DSS = 9 ma and V P = -3V is a) 6 mv b) 6mS c) 27 S d) 3 ms 74. The efficiency of a class B amplifier for a supply voltage VCC = 24 V with peak to peak output of 6V is a) 4% b) 48% c) 19.6% d) 39.2% 75. The ripple voltage of a FWR with a 100 µf filter capacitor connected to a load of 50 ma is a) 2.4 V b) 1.2 V c) 4.4 V d) 6.6 V 76. The timing resistor is 10 kω and timing capacitor is 200 PF for a 565 PLL. The free running frequency is a) 500 KHz b) 350 KHz c) 250 KHz d) 150 KHz 77. A dc motor is driving a load that requires constant output power. The pu value of torque with its field current reduced to half would be (consider rated quantities as 1.0 pu) a) 0.5 pu b) 1.0 pu c) 2.0 pu d) 1.5 pu 78. A 2-pole wave wound dc generator has 120 conductors in each parallel path of its armature. If it is driven at 1200 rpm and excited to have 0.02 wb/pole, the induced emf would be a) 48 V b) 96 V c) 24 V d) 124 V 79. The variation of open circuit emf of a separate excited generator when I f = constant and variable speed would be Emf 4 3 a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) A 220V/ V transformer has an emf/turn of 1V. The number of turns on secondary would be a) 12 with centre tap b) 220 with centre tap c) 24 with no centre tap d) 24 with centre tap 81. An ideal transformer has N 1 = 100 turns N 2 = 200 turns with a mutual flux of φ m (t) = (t 2-2t). The induced emf of secondary in volts is a) -5 (t - 1) b) -10 (t - 1) c) -5 (t 2-1) d) -20 (t - 1) speed 2 1
13 82. Four conductors in a stationary armature (alternator) are shown as 1, 1', 2, 2'. For the given direction of rotation of rotor the direction of induced emf (at the instant shown) in the conductors respectively 2 ' Conductor 1 1 ' 2 2 ' 1 1 ' N S a) B) c) d) 83. A synchronous machine has X s = 1pu and operates at V = 1 pu. When its emf is 1.5 pu with load angle 0 e, current as (0 j0.5), the mode of operation is a) generator with lagging pf b) generator with leading pf c) motor with lagging pf d) motor with leading pf 84. A 3-phase, 16 pole, 108-slot alternator will have the following phase grouping in each phase with 60 phase spread a) 2, 2, 2, 2 coil in basic unit of 4 poles b) 3, 2, 2, 2 coil in basic unit of 4 poles c) 3, 2, 2, 2 coils in basic unit of 16 poles d) 2, 2, 2, 2 coils in basic unit of 8 poles 85. For the power circuit given below. SCR is operated at 1 khz with T ON of 0.5 m sec. 200 V 2 V - Motor ratings: 200 V dc, 1000 rpm, 10A Neglecting armature resistance the speed of motor at given duty circle (TN - constant) a) 1000 rpm b) 500 rpm c) 1500 rpm d) 750 rpm
14 86. A converter is feeding a dc machine as shown below: A mode of operation of machine is a) Motoring b) Regenerating c) Plugging d) Rheostatic braking 87. The output of a single phase inverted bridge is as given below: V o V -V 120 In the above output voltage a) 5 th and 7 th harmonics will be absent b) 3 rd, 5 th, 7 th harmonics will be absent c) 3 rd, 9th, 15th harmonics will be absent d) 3 rd and 7 th harmonics will be absent 88. A 4 pole turbo generator rated 500 MVA, 22KV has its angular acceleration ele. degrees/sec 2. It is equivalent to a) 1500 rpm/sec. b) rpm/sec. c) rpm/sec d) rpm/sec 89. A 50 HZ generator having H = 6 MJ/MVA is connected to syschronous motor having H = 4 MJ/MVA through a network of reactances. The generator is delivering power of 1.0 pu to the motor which reduces to 0.6 pu when fault occurs. The angular acceleration in ele. degrees /sec 2 is a) 360 b) 180 c) 1500 d) Syschronizing power coefficient can be written as a) P a.cos δ 0 b) P max.cos δ 0 c) P e.cos δ 0 d) P max.sin δ The relay that most likely to operate during power swings is a) Reactance relay b) Impedance relay c) Mho relay d) Bucholtz's relay V s ωt
15 92. An OCB is rated 1500 A, 2000 MVA 33kV. It making current is ka is a) b) 35 c) d) The rating of lightning arrestor used for 220 kv, 3 phase system is a) 220 kv, 10 ka b) 220 kv, 5 ka c) 198 kv, ka d) 198 kv, 2 ka 94. A generating station has maximum demand of 30 MW, a load factor of 0.6 and plant capacity factor The reserve capacity of the plant is a) 37.5 MW b) 7.5 MW c) 19.5 MW d) 12 MW 95. A transformer of 10 MVA, 33 kv has reactance 0.1 pu. On 20 MVA, 11 kv the new pu value is a) 0.45 b) 1.8 c) 1.2 d) In which type of fault, zero sequence currents are absent a) L-L b) L-G c) L-L-G d) L-L-L-G 97. In a single machine connected to infinite bus bar system, alternator voltage is 1.5 pu and its reactance is 1.0 pu are connected through a line reactance of 0.3 pu. The maximum steady state power transfer is a) pu b) 5.0 pu c) 1.5 pu d) 0.76 pu 98. Value of acceleration factor used in Gauss Seidal method in load flow studies is a) 1.59 b) 1.66 c) 1.0 d) The Z-bus of the following system of impedances j.08 j.2 j.2 [ j 0.08 j 0.5 ] [ j 0.08 j 0.08 ] [ j j 0.5 ] [ j j 0.08 a) b) c) d) j 0.5 j 0.58 j 0.8 j j 0.5 j j 0.08 j 0.58 ] 100. An over current relay having a current setting of 125% is connected to a supply circuit through a current transformer of ratio 400/5. The pick up value will be a) 6.25 A b) 500 A c) 100 A d) 80A ANSWERS 1-c; 2-d; 3-c; 4-b; 5-a; 6-b; 7-b; 8-a; 9-b; 10-d; 11-c; 12-d; 13-d; 14-b; 15-c; 16-c; 17-b; 18-d; 19-c; 20-a; 21-b; 22-b; 23-b; 24-c; 25-d; 26-d; 27-a; 28-c; 29-c; 30-a; 31-a; 32-c; 33-a; 34-a; 35-d; 36-d; 37-c; 38-d; 39-d; 40-a; 41-a; 42-d; 43-c; 44-c; 45-c; 46-b; 47-c; 48-b; 49-c; 50-c; 51-c; 52-b; 53-c; 54-a; 55-d; 56-d; 57-b; 58-b; 59-b; 60-c; 61-a; 62-a; 63-d; 64-c; 65-a; 66-a; 67-c; 68-b; 69-a; 70-c; 71-d; 72-a; 73-d; 74-c; 75-b; 76-?; 77-a; 78-a; 79-a; 80-c; 81-d; 82-a; 83-d; 84-b; 85-b; 86-b; 87-c; 88-b; 89-c; 90-b; 91-c; 92-d; 93-c; 94-?; 95-b; 96-a; 97-b; 98-d; 99-b; 100-a. j j.08
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
SECTION - A. A current impulse, 5δ(t), is forced through a capacitor C. The voltage, Vc(t), across the capacitor is given by. 5 t C.
 SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL
 Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
POWER SEMICONDUCTOR BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES
 POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
coil of the circuit. [8+8]
![coil of the circuit. [8+8] coil of the circuit. [8+8]](/thumbs/80/81218867.jpg) Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
+ ( )= with initial condition
 Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A- Two marks questions
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
QUESTION BANK ENGINEERS ACADEMY. Power Systems Power System Stability 1
 ower ystems ower ystem tability QUETION BANK. A cylindrical rotor generator delivers 0.5 pu power in the steady-state to an infinite bus through a transmission line of reactance 0.5 pu. The generator no-load
ower ystems ower ystem tability QUETION BANK. A cylindrical rotor generator delivers 0.5 pu power in the steady-state to an infinite bus through a transmission line of reactance 0.5 pu. The generator no-load
a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system.
 1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous)
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
18 - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTS ( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page 1
 ( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page ) The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 0 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of 8 µ F (
( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page ) The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 0 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of 8 µ F (
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL
 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL Prepared by B.SAIDAMMA R13 Regulation Any 10 of the following experiments are to be conducted 1. Calibration and Testing of single phase energy Meter 2. Calibration of
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL Prepared by B.SAIDAMMA R13 Regulation Any 10 of the following experiments are to be conducted 1. Calibration and Testing of single phase energy Meter 2. Calibration of
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State. Y. Baghzouz
 EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A 1. What are the advantages of an inter connected system? The advantages of an inter-connected system are
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A 1. What are the advantages of an inter connected system? The advantages of an inter-connected system are
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 26 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Recently increase in energy demand and limited energy sources in the world caused the researchers
26 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Recently increase in energy demand and limited energy sources in the world caused the researchers
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
POWER SYSTEM STABILITY
 LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
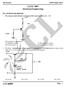 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Introduction to Synchronous. Machines. Kevin Gaughan
 Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
GATEFORUM- India s No.1 institute for GATE training 1
 EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
GATE-2015 ELECTRICAL ENGG 7th February 2015 Forenoon Session
 Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-I - TRANSFORMER 1. What is a transformer? 2. Briefly explain the principle of operation of transformers. 3. What are the parts of a transformer? 4. What are the types
EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-I - TRANSFORMER 1. What is a transformer? 2. Briefly explain the principle of operation of transformers. 3. What are the parts of a transformer? 4. What are the types
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines
 Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
GATE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol 1 of 4
 GATE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol 1 of 4 Second Edition GATE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol 1 of 4 RK Kanodia Ashish Murolia NODIA & COMPANY GATE Electrical Engineering Vol 1, 2e RK Kanodia & Ashish Murolia
GATE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol 1 of 4 Second Edition GATE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol 1 of 4 RK Kanodia Ashish Murolia NODIA & COMPANY GATE Electrical Engineering Vol 1, 2e RK Kanodia & Ashish Murolia
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015
 ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
LESSON 20 ALTERNATOR OPERATION OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems LESSON 20 ALTERNATOR OPERATION OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After this presentation you will be able to: Interpret alternator phasor diagrams
ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems LESSON 20 ALTERNATOR OPERATION OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After this presentation you will be able to: Interpret alternator phasor diagrams
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2013 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2013 Caribbean Examinations Council
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2013 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2013 Caribbean Examinations Council
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Chapter 31 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively
 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively In the LC circuit the charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally (with period T and angular
Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively In the LC circuit the charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally (with period T and angular
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES. School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION. Session
 Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
The simplest type of alternating current is one which varies with time simple harmonically. It is represented by
 ALTERNATING CURRENTS. Alternating Current and Alternating EMF An alternating current is one whose magnitude changes continuously with time between zero and a maximum value and whose direction reverses
ALTERNATING CURRENTS. Alternating Current and Alternating EMF An alternating current is one whose magnitude changes continuously with time between zero and a maximum value and whose direction reverses
PHYSICS : CLASS XII ALL SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT TEST ASAT
 PHYSICS 202 203: CLASS XII ALL SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT TEST ASAT MM MARKS: 70] [TIME: 3 HOUR General Instructions: All the questions are compulsory Question no. to 8 consist of one marks questions, which
PHYSICS 202 203: CLASS XII ALL SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT TEST ASAT MM MARKS: 70] [TIME: 3 HOUR General Instructions: All the questions are compulsory Question no. to 8 consist of one marks questions, which
VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON:
 VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON: 10EE35 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION BY DR. M.S. RAVIPRAKASHA PROFESSOR & HEAD DEPT. OF E&E ENGG. MALNAD COLLEGE OF ENGG. HASSAN 573 201. SUBJECT CODE
VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON: 10EE35 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION BY DR. M.S. RAVIPRAKASHA PROFESSOR & HEAD DEPT. OF E&E ENGG. MALNAD COLLEGE OF ENGG. HASSAN 573 201. SUBJECT CODE
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]
![Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark] Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]](/thumbs/88/115570773.jpg) Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Electric Machines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
ANDERSON S BRIDGE & SCHERING S BRIDGE
 ANDERSON S BRIDGE & SCHERING S BRIDGE ANDERSON S BRIDGE AIM: A)To measure inductance of a given coil by Anderson s bridge. B) To determine the value of a given capacitor and to obtain for its dissipation
ANDERSON S BRIDGE & SCHERING S BRIDGE ANDERSON S BRIDGE AIM: A)To measure inductance of a given coil by Anderson s bridge. B) To determine the value of a given capacitor and to obtain for its dissipation
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies
 Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Code No: RR Set No. 1
 Code No: RR410209 Set No. 1 1. What are the gases mainly used in insulating medium at high pressures? Which is more suitable? Why? What about its dielectric strength? Explain. [16] 2. (a) Define time lags
Code No: RR410209 Set No. 1 1. What are the gases mainly used in insulating medium at high pressures? Which is more suitable? Why? What about its dielectric strength? Explain. [16] 2. (a) Define time lags
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults
 Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
Module 3 Electrical Fundamentals
 3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
Alternating Current Circuits
 Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B
 GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. 1. For the circuit shown in the figure, the voltage and current expressions are v(t) = and. The average power measured by the Wattmeter
GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. 1. For the circuit shown in the figure, the voltage and current expressions are v(t) = and. The average power measured by the Wattmeter
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION
 EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
fusion production of elements in stars, 345
 I N D E X AC circuits capacitive reactance, 278 circuit frequency, 267 from wall socket, 269 fundamentals of, 267 impedance in general, 283 peak to peak voltage, 268 phase shift in RC circuit, 280-281
I N D E X AC circuits capacitive reactance, 278 circuit frequency, 267 from wall socket, 269 fundamentals of, 267 impedance in general, 283 peak to peak voltage, 268 phase shift in RC circuit, 280-281
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA
 EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
mywbut.com Lesson 16 Solution of Current in AC Parallel and Seriesparallel
 esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
Fault Analysis Power System Representation
 .1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
.1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
SSC-JE EE POWER SYSTEMS: GENERATION, TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University College of Engineering. Electrical Engineering Department EE 3360 Electrical Machines (II)
 Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS
 EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS Condensed Text Prepared by: Rajesh Karki, Ph.D., P.Eng. Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan About the EE 212 Condensed Text The major topics in the course
EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS Condensed Text Prepared by: Rajesh Karki, Ph.D., P.Eng. Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan About the EE 212 Condensed Text The major topics in the course
OR Explain thermal breakdown in solid dielectrics. How this mechanism is
 Subject : High Voltage Engineering (2090) ITM Universe, Vadodara Electrical Engineering Department Class : Electrical Sem : th Long Questions Sr. No Question Unit No : 0 Explain Charge Simulation method
Subject : High Voltage Engineering (2090) ITM Universe, Vadodara Electrical Engineering Department Class : Electrical Sem : th Long Questions Sr. No Question Unit No : 0 Explain Charge Simulation method
Page 2 GATE EE
 Page GATE EE 009 www.gatehelp.com SOL. Overall gain of the system is written as G = GG G 3 We know that for a quantity that is product of two or more quantities total percentage error is some of the percentage
Page GATE EE 009 www.gatehelp.com SOL. Overall gain of the system is written as G = GG G 3 We know that for a quantity that is product of two or more quantities total percentage error is some of the percentage
7. Transient stability
 1 7. Transient stability In AC power system, each generator is to keep phase relationship according to the relevant power flow, i.e. for a certain reactance X, the both terminal voltages V1and V2, and
1 7. Transient stability In AC power system, each generator is to keep phase relationship according to the relevant power flow, i.e. for a certain reactance X, the both terminal voltages V1and V2, and
PHYS 241 EXAM #2 November 9, 2006
 1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
Generators. What its all about
 Generators What its all about How do we make a generator? Synchronous Operation Rotor Magnetic Field Stator Magnetic Field Forces and Magnetic Fields Force Between Fields Motoring Generators & motors are
Generators What its all about How do we make a generator? Synchronous Operation Rotor Magnetic Field Stator Magnetic Field Forces and Magnetic Fields Force Between Fields Motoring Generators & motors are
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018
 ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018 Name: KEY UIN: Section: Score: Part 1 / 40 Part 2 / 0 Part / 0 Total / 100 This exam is 75 minutes, closed-book, closed-notes. A standard calculator and one 8.5 x11 note sheet
ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018 Name: KEY UIN: Section: Score: Part 1 / 40 Part 2 / 0 Part / 0 Total / 100 This exam is 75 minutes, closed-book, closed-notes. A standard calculator and one 8.5 x11 note sheet
PARALLEL A.C. CIRCUITS
 C H A P T E R 4 earning Objectives Solving Parallel Circuits Vector or Phasor Method Admittance Method Application of Admittance Method Complex or Phasor Algebra Series-Parallel Circuits Series Equivalent
C H A P T E R 4 earning Objectives Solving Parallel Circuits Vector or Phasor Method Admittance Method Application of Admittance Method Complex or Phasor Algebra Series-Parallel Circuits Series Equivalent
