Organic LEDs part 8. Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films. Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., Nature 420, 800 (2002).
|
|
|
- Dora Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Organic LEDs part 8 Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films Quantum Dot LEDs Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., ature 420, 800 MIT April 29, 2003 Organic Optoelectronics - Lecture 20b 1
2 Exciton Dynamics in Time Dependant PL 2 time 25 nm 2 ns time wavelength wavelength
3 Intensity [ arb. units ] Dynamic Spectral Shifts of DCM2 in Alq 3 Measurement performed on doped DCM2:Alq 3 films Excitation at λ=490 nm (only DCM2 absorbs) Wavelength [ nm ] Alq 3 DCM2 ormalized Intensity % DCM2:Alq 3 time 0 ns 0.1 ns 0.3 ns 0.6 ns 1.0 ns 1.6 ns 2.2 ns 3.4 ns 6.2 ns Energy [ ev ] Energy [ ev ] ~ DCM2 PL red shifts > 20 nm over 6 ns ~ 3
4 Time Evolution of 4% DCM2 in Alq 3 PL Spectrum Wavelength [nm] ormalized Intensity Spectrum at 4 ns Integrated Spectrum (0-10 ns) Spectrum at 1 ns Energy [ev] 4
5 Electronic Processes in Molecules 10 ps Energy density of available S1 or T1 states FÖRSTER, DEXTER or RADIATIVE EERGY TRASFER S 1 ABSORPTIO ITERAL COVERSIO FLUORESCECE 1-10 ns PHOSPHORESCECE T 1 >100 ns S 0 5
6 Time Evolution of DCM2 Solution PL Spectra Benzene 580 Energy [ev] CHCl 3 CHCl 2 Acetone Wavelength [nm] CH 3 C DMSO Time [ns]
7 Spectral Shift due to ~ Exciton Diffusion ~ ~ Intermolecular Solid State Interactions ~ 5 4 wavelength shift 35 nm 10% DCM2 in Alq 3 Time [ns] Wavelength [nm] 7
8 Excitonic Energy Variations Each dye molecule experiences a different local medium variations in excitonic energies on-zero width to excitonic density of states Intensity Molecular PL Spectra Frequency Excitonic Density of States Energy Energy 8
9 Exciton Distribution in the Excited State (S 1 or T 1 ) ~ Time Evolved Exciton Thermalization ~ S 1 or T 1 Energy fwhm hν log(time) EXCITO DIFFUSIO LEADS TO REDUCTIO I FWHM 9
10 2.10 Low E midpoint 4% DCM2 in Alq 3 FWHM High E midpoint 2.05 High E midpoint T = 15~125 K 600 Energy Energy [ev] Low E midpoint Wavelength [nm] Time [ns] 10
11 x% DCM in Alq Energy [ev] Alq3 0.2 % 0.4 % 0.6 % Wavelength [nm] % 2 % Time [ns] 11
12 X% DCM in Alq Initial Peak PL 570 Energy [ev] Final Peak PL Wavelength [nm] % of DCM in Alq 3 12
13 Time Evolution of Peak PL in eat Thin Films 2.45 Energy [ev] Alq Ir(ppy) Time [ns] 13
14 Parameters for Simulating Exciton Diffusion ormalized Integrated Spectral Intensity observed radiative lifetime (τ) Förster radius (R F ) τ = 3.3 ns decreasing doping (5% down to 0.5%) Time [ ns ] Assign value for allowed transfers: Γ F 6 1 RF τ R 0 E excitonic density of states (g ex (E)) Assume Gaussian shape of width, w DOS Center at peak of initial bulk PL spectrum Molecular PL spectrum implied ormalized Intensity [ arb. units ] Wavelength [ nm ] FWHMs S init (E) : 0.27 ev S mol (E) : 0.22 ev g ex (E) : 0.15 ev Energy [ ev ] 14
15 Fitting Simulation to Experiment Doped Films Energy [ ev ] % DCM2:Alq 3 R F =0.88 w DOS =0.185 ev R F =0.98 w DOS =0.161 ev R F =1.08 w DOS =0.146 ev R F =1.18 w DOS =0.136 ev R F =1.28 w DOS =0.130 ev Time [ ns ] Wavelength [ nm ] Energy [ ev ] Peak PL of x% DCM2:Alq % 640 1% 650 2% 660 5% Time [ ns ] Wavelength [ nm ] Good fits possible for all data sets R F decreases with increasing doping, falling from 52 Å to 22 Å w DOS also decreases with increasing doping, ranging from ev to ev 15
16 2.40 Fitting Simulation eat Films Energy [ ev ] Ir(ppy) 3 w DOS ~0.21 ev Time [ ns ] Spectral shift observed in each material system Molecular dipole and w DOS are correllated: lower dipoles correspond to less dispersion Even with no dipole, some dispersion exists Experimental technique general, and yields first measurements of excitonic energy dispersion in amorphous organic solids Energy [ ev ] Alq 3 w DOS ~0.15 ev Energy [ ev ] PD w DOS ~0.10 ev Time [ ns ] Time [ ns ] 16
17 Temporal Solid State Solvation upon excitation both magnitude and direction of lumophore dipole moment can change FOR EXAMPLE for DCM: µ 1 µ 0 > 20 Debye! ~ from 5.6 D to 26.3 D ~ µ 0 µ 1 µ 1 t < 0 E loc t = 0 E loc E loc t ~ 1 ns following the excitation the environment surrounding the excited molecule will reorganize to minimize the overall energy of the system (maximize µ E loc ) 17
18 Exciton Distribution in the Excited State (S 1 or T 1 ) ~ Time Evolved Molecular Reconfiguration ~ Energy E DIPOLE-DIPOLE ITERACTIO LEADS TO EERGY SHIFT I DESITY OF EXCITED STATES log(time) 18
19 Efficient Fusion of Two Material Sets Organic Semiconductors Flexible Absorption [a.u.] Emissive Tunable Colloidal QDs Photo by F. Frankel anoscale Wavelength [nm] Hybrid devices could enable LEDs, Solar Cells, Photodetectors, Modulators, and Lasers which utilize the best properties of each individual material. Fabrication of rational structures has been the main obstacle to date. 19
20 Inorganic anocrystals Quantum Dots E CdSe ZnS D Quantum Dot SIZE Lowest allowed energy level Absorption [a.u.] D= 120Å 80Å 72Å 55Å 45Å 33Å 29Å 20Å 17Å Wavelength [nm] Photo by F. Frankel Synthetic route of Murray et al, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 8706 (1993). 20
21 Fusion of Two Material Sets Quantum Dots Organic Molecules Absorption Spectra EMISSIVE AOSCALE TUABLE Alq 3 O Al O TAZ O CH 3 TPD H 3 C PD CdSe(ZnS) PbSe Wavelength [nm] Wavelength [µm] 21
22 ZnS overcoating shell (0 to 5 monolayers) Synthetic routes of Murray et al, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 8706 (1993) and Chen, et al, MRS Symp. Proc. 691,G10.2. Alq 3 O Al O Tris(8-hydroxyquinoline) Aluminum (III) O Integration of anoscale Materials Quantum Dots and Organic Semiconductors PbSe or CdSe Core D = Å (~50Å pictured) Oleic Acid or TOPO caps Trioctylphosphine oxide HO O Oleic Acid CH 3 10Å TPD H 3 C TAZ,'-Bis(3-methylphenyl)-,'-bis-(phenyl)-benzidine 3-(4-Biphenylyl)-4-phenyl-5- tert-butylphenyl-1,2,4-triazole PD,'-Bis(naphthalen-1-yl)-,'-bis(phenyl)benzidine poly-tpd Differences in: Molecular Organics Quantum Dots Chemistry Aromatic Aliphatic Caps Phase Segregation Size Small Big 22
23 Phase Segregation and Self-Assembly QD Solution TPD Solution 1 2 QDs 3 TPD/solvent Substrate 4 close packed QDs TPD Substrate 1. A solution of an organic material, QDs, and solvent 2. is spin-coated onto a clean substrate. 3. During the solvent drying time, the QDs rise to the surface 4. and self-assemble into grains of hexagonally close packed spheres. ~8nm PbSe QDs Organic hosts that deposit as flat films allow for imaging via AFM, despite the AFM tip being as large as the QDs. Phase segregation is driven by a combination of size and chemistry. Flat TPD background 50nm 23
24 Monolayer Coverage QD concentration QD coverage = 20% 50% 80% 250nm 500nm 500nm 500nm 90% 100% 100nm As the concentration of QDs in the spin-casting solution is increased, the coverage of QDs on the monolayer is also increased. 24
25 QD-LED Performance 50nm Ag 50nm Mg:Ag 30nm Alq 3 10nm TAZ Current Density [A cm -2 ] Control QD-LED 40nm TPD ITO Glass CdSe(ZnS)/TOPO 1 Voltage [V] 10 PbSe/oleic acid Vacuum Level = 0 ev Electron Energy [ev] EA=2.1 TPD E F =4.7 ITO IE=5.4 QD EA=4.6 CdSe IE=6.8 EA=3.0 TAZ IE=6.5 EA=3.1 Alq 3 E F =3.7 Mg IE=5.8 ormalized counts ZnS TOPO Wavelength [nm] 25
26 Structure of a Single anocrystal Full Size Series of PbSe anocrystals from 3 nm to 10 nm in Diameter 9 peak absorption 4 nm HRTEM Jonny Steckel and Seth Coe Absorbance (arbitrary units) nm 2036 nm 1812 nm 1708 nm 1600 nm 1504 nm 1404 nm nm 8 nm AFM Ordered Monolayer of PbSe anocrystals Wavelength (nm) 1136 nm 26
27 QDs are poor charge transport materials... QD CdSe ZnS TOPO caps e - QD intersite spacing Isolate layer functions of maximize device performance. 1. Generate excitons on organic sites. 2. Transfer excitons to QDs via Förster or Dexter energy transfer. 3. QD electroluminescence. eed a new fabrication method in order to be able to make such double heterostructures: Phase Segregation. Design of Device Structures ZnS QD monolayer shell 50nm Ag 50nm Mg:Ag But efficient emitters 30nm Alq 3 Electron Energy [ev] E F =4.7 ITO Vacuum Level = 0 ev EA=2.1 TPD IE=5.4 10nm TAZ 40nm TPD ITO Glass Use organics for charge transport. QD EA=4.6 CdSe IE=6.8 ZnS TOPO EA=3.0 EA=3.1 TAZ Alq 3 E F =3.7 IE=6.5 CdSe core IE=5.8 QD Mg TOPO caps 27
28 A general method? Phase segregation occurs for different 1) organic hosts: TPD, PD, and poly-tpd. 2) solvents: chloroform, chlorobenzene, and mixtures with toluene. 3) QD core materials: PbSe, CdSe, and CdSe(ZnS). 4) QD capping molecules: oleic acid and TOPO. 5) QD core size: 4-8nm. 6) substrates: Silicon, Glass, ITO. 7) Spin parameters: speed, acceleration and time. This process is robust, but further exploration is needed to broadly generalize these findings. For the explored materials, consistent description is possible. We have shown that the process is not dependent on any one material component. Phase segregation QD-LED structures 2) Solvent 7) Spin Parameters QD monolayer shell Cathode ETL 1) Organic Host 6) Substrate/Anode 5) QD size QD 4) caps 3) core 28
29 EL Recombination Region Dependence on Current increasing current depth Cathode Alq 3 (35 nm) exciton density R F 2% DCM2 in Alq3 (5nm) ormalized Intensity J [ma/cm 2 ] Alq 3 DCM2 EL Fraction [%] DCM EL Alq 3 EL log(j[ma/cm 2 ]) TPD (40 nm) Anode Glass Wavelength [nm] Coe et al., Org. Elect. (2003) 29
30 Spectral Dependence on Current Density J [ma/cm 2 ] 380 Alq 3 TOP DOW VIEW of the QD MOOLAYER Device Area Grain Boundary QD R F Wavelength [nm] Interstitial Space Monolayer Void Exciton recombination width far exceeds the QD monolayer thickness at high current density. To achieve true monochrome emission, new exciton confinement techniques are needed. ETL electron HTL hole Cathode Anode Glass Alq 3 EL QD EL depth increasing current exciton density R F CROSS-SECTIOAL VIEW of QD-LED 30
31 Benefits of Quantum Dots in Organic LEDs Demonstrated: Spectrally Tunable single material set can access most of visible range. Saturated Color linewidths of < 35nm Full Width at Half of Maximum. Can easily tailor external chemistry without affecting emitting core. Can generate large area infrared sources. Potential: High luminous efficiency LEDs possible even in red and blue. Inorganic potentially more stable, longer lifetimes. The ideal dye molecule! QD FWHM 32nm CIE Diagram Potential QD-LED colors standard CRT color triangle x Coe et al, ature 420, 800 (2002) y
Organic LEDs part 7. Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films. Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., Nature 420, 800 (2002).
 Organic LEDs part 7 Solvation Effect - Review Solid State Solvation Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films Quantum Dot LEDs Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., ature 420, 800 (2002). @ MIT April
Organic LEDs part 7 Solvation Effect - Review Solid State Solvation Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films Quantum Dot LEDs Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., ature 420, 800 (2002). @ MIT April
E L E C T R O P H O S P H O R E S C E N C E
 Organic LEDs part 4 E L E C T R O P H O S P H O R E S C E C E. OLED efficiency 2. Spin 3. Energy transfer 4. Organic phosphors 5. Singlet/triplet ratios 6. Phosphor sensitized fluorescence 7. Endothermic
Organic LEDs part 4 E L E C T R O P H O S P H O R E S C E C E. OLED efficiency 2. Spin 3. Energy transfer 4. Organic phosphors 5. Singlet/triplet ratios 6. Phosphor sensitized fluorescence 7. Endothermic
Organic LEDs part 6. Exciton Recombination Region in Organic LEDs. Handout: Bulovic, et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 287, 455 (1998); 308, 317 (1999).
 Organic LEDs part 6 Exciton Recombination Region in Organic LEDs White OLED Flexible OLEDs Solvation Effect Solid State Solvation Handout: Bulovic, et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 287, 455 (1998); 308, 317 (1999).
Organic LEDs part 6 Exciton Recombination Region in Organic LEDs White OLED Flexible OLEDs Solvation Effect Solid State Solvation Handout: Bulovic, et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 287, 455 (1998); 308, 317 (1999).
Tuning the performance of hybrid organic/inorganic quantum dot light-emitting devices
 Organic Electronics 4 (2003) 123 130 www.elsevier.com/locate/orgel Tuning the performance of hybrid organic/inorganic quantum dot light-emitting devices Seth Coe-Sullivan a,1, Wing-Keung Woo b,1, Jonathan
Organic Electronics 4 (2003) 123 130 www.elsevier.com/locate/orgel Tuning the performance of hybrid organic/inorganic quantum dot light-emitting devices Seth Coe-Sullivan a,1, Wing-Keung Woo b,1, Jonathan
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices
 Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Morphology of CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs coated on textured surface with SiN X film of a
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary/supporting information Morphology of CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs coated on textured
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary/supporting information Morphology of CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs coated on textured
Supporting Information: Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stamp Coated with a. Low-Surface-Energy, Diffusion-Blocking,
 Supporting Information: Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stamp Coated with a Low-Surface-Energy, Diffusion-Blocking, Covalently Bonded Perfluoropolyether Layer and Its Application to the Fabrication of Organic Electronic
Supporting Information: Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stamp Coated with a Low-Surface-Energy, Diffusion-Blocking, Covalently Bonded Perfluoropolyether Layer and Its Application to the Fabrication of Organic Electronic
Spiro-Configured Bifluorenes: Highly Efficient Emitter for UV Organic Light-Emitting Device and Host Material for Red Electrophosphorescence
 Spiro-Configured Bifluorenes: Highly Efficient Emitter for UV Organic Light-Emitting Device and Host Material for Red Electrophosphorescence Ken-Tsung Wong,* a Yuan-Li Liao, a Yu-Ting Lin, b Hai-Ching
Spiro-Configured Bifluorenes: Highly Efficient Emitter for UV Organic Light-Emitting Device and Host Material for Red Electrophosphorescence Ken-Tsung Wong,* a Yuan-Li Liao, a Yu-Ting Lin, b Hai-Ching
Tianle Guo, 1 Siddharth Sampat, 1 Kehao Zhang, 2 Joshua A. Robinson, 2 Sara M. Rupich, 3 Yves J. Chabal, 3 Yuri N. Gartstein, 1 and Anton V.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Order of magnitude enhancement of monolayer MoS photoluminescence due to near-field energy influx from nanocrystal films Tianle Guo, Siddharth Sampat, Kehao Zhang, Joshua
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Order of magnitude enhancement of monolayer MoS photoluminescence due to near-field energy influx from nanocrystal films Tianle Guo, Siddharth Sampat, Kehao Zhang, Joshua
TECHNICAL INFORMATION. Quantum Dot
 Quantum Dot Quantum Dot is the nano meter sized semiconductor crystal with specific optical properties originates from the phenomenon which can be explained by the quantum chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Quantum Dot Quantum Dot is the nano meter sized semiconductor crystal with specific optical properties originates from the phenomenon which can be explained by the quantum chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Devices with Electroluminescence Tunable over the Entire Visible Spectrum
 Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Devices with Electroluminescence Tunable over the Entire Visible Spectrum NANO LETTERS 2009 Vol. 9, No. 7 2532-2536 Polina O. Anikeeva,, Jonathan E. Halpert,, Moungi G. Bawendi,
Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Devices with Electroluminescence Tunable over the Entire Visible Spectrum NANO LETTERS 2009 Vol. 9, No. 7 2532-2536 Polina O. Anikeeva,, Jonathan E. Halpert,, Moungi G. Bawendi,
Introduction. Fang-Chung Chen Department of Photonics and Display Institute National Chiao Tung University. Organic light-emitting diodes
 rganic light-emitting diodes Introduction Fang-Chung Chen Department of Photonics and Display Institute National Chiao Tung University rganic light-emitting diodes --The emerging technology LED Displays
rganic light-emitting diodes Introduction Fang-Chung Chen Department of Photonics and Display Institute National Chiao Tung University rganic light-emitting diodes --The emerging technology LED Displays
Inverted Quantum-dot Light-Emitting Diode with Solution-Processed Aluminum-Zinc- Oxide as Cathode Buffer
 Normalized Absorbance (a.u.) Normalized PL Intensity (a.u.) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 22 SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Normalized Absorbance (a.u.) Normalized PL Intensity (a.u.) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 22 SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Abstract. Introduction
 Organic Materials in Optoelectronic Applications: Physical Processes and Active Devices Jonnalagadda Padmarani Department of Physics (Opto Electronics), Osmania University, TS, India Abstract The present
Organic Materials in Optoelectronic Applications: Physical Processes and Active Devices Jonnalagadda Padmarani Department of Physics (Opto Electronics), Osmania University, TS, India Abstract The present
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 High-Efficiency Light-Emitting Devices based on Quantum Dots with Tailored Nanostructures Yixing Yang 1, Ying Zheng 1, Weiran Cao 2, Alexandre Titov 1, Jake Hyvonen 1, Jiangeng Xue 2*, Paul H. Holloway
High-Efficiency Light-Emitting Devices based on Quantum Dots with Tailored Nanostructures Yixing Yang 1, Ying Zheng 1, Weiran Cao 2, Alexandre Titov 1, Jake Hyvonen 1, Jiangeng Xue 2*, Paul H. Holloway
Structure Property Relationships of. Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Michael Kochanek May 19, 2006 MS&E 542 Flexible Electronics
 Structure Property Relationships of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Michael Kochanek May 19, 2006 MS&E 542 Flexible Electronics Introduction Many of today s solid-state inorganic microelectronic devices
Structure Property Relationships of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Michael Kochanek May 19, 2006 MS&E 542 Flexible Electronics Introduction Many of today s solid-state inorganic microelectronic devices
not to be confused with using the materials to template nanostructures
 Zeolites as Templates: continued Synthesis: Most zeolite syntheses are performed by using template-synthesis not to be confused with using the materials to template nanostructures templates are often surfactants
Zeolites as Templates: continued Synthesis: Most zeolite syntheses are performed by using template-synthesis not to be confused with using the materials to template nanostructures templates are often surfactants
Semiconductor quantum dots
 Semiconductor quantum dots Quantum dots are spherical nanocrystals of semiconducting materials constituted from a few hundreds to a few thousands atoms, characterized by the quantum confinement of the
Semiconductor quantum dots Quantum dots are spherical nanocrystals of semiconducting materials constituted from a few hundreds to a few thousands atoms, characterized by the quantum confinement of the
1. Transition dipole moment
 1. Transition dipole moment You have measured absorption spectra of aqueous (n=1.33) solutions of two different chromophores (A and B). The concentrations of the solutions were the same. The absorption
1. Transition dipole moment You have measured absorption spectra of aqueous (n=1.33) solutions of two different chromophores (A and B). The concentrations of the solutions were the same. The absorption
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications Crystal Structure and Chemistry Synthesis of Tetrahexahedral Platinum Nanocrystals with High-Index Facets and High Electro-Oxidation Activity Na Tian
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications Crystal Structure and Chemistry Synthesis of Tetrahexahedral Platinum Nanocrystals with High-Index Facets and High Electro-Oxidation Activity Na Tian
Making OLEDs efficient
 Making OLEDs efficient cathode anode light-emitting layer η = γ EL r ηpl k st External Efficiency Outcoupling Internal efficiency of LEDs η = γ EL r ηpl k st γ = excitons formed per charge flowing in the
Making OLEDs efficient cathode anode light-emitting layer η = γ EL r ηpl k st External Efficiency Outcoupling Internal efficiency of LEDs η = γ EL r ηpl k st γ = excitons formed per charge flowing in the
High-Performance Photocoupler Based on Perovskite Light Emitting Diode and Photodetector
 Supporting information for High-Performance Photocoupler Based on Perovskite Light Emitting Diode and Photodetector Zhi-Xiang Zhang, Ji-Song Yao, Lin Liang, Xiao-Wei Tong, Yi Lin, Feng-Xia Liang, *, Hong-Bin
Supporting information for High-Performance Photocoupler Based on Perovskite Light Emitting Diode and Photodetector Zhi-Xiang Zhang, Ji-Song Yao, Lin Liang, Xiao-Wei Tong, Yi Lin, Feng-Xia Liang, *, Hong-Bin
Solar Cell Materials and Device Characterization
 Solar Cell Materials and Device Characterization April 3, 2012 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy (PHYS 4400) and Fundamentals
Solar Cell Materials and Device Characterization April 3, 2012 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy (PHYS 4400) and Fundamentals
Semiconductor Nanocrystals from Nonthermal Plasmas. Rebecca J. Anthony University of Minnesota
 Semiconductor Nanocrystals from Nonthermal Plasmas Rebecca J. Anthony University of Minnesota 1 Nanocrystals in devices efficient light emitters and absorbers versatile deposition schemes possibility for
Semiconductor Nanocrystals from Nonthermal Plasmas Rebecca J. Anthony University of Minnesota 1 Nanocrystals in devices efficient light emitters and absorbers versatile deposition schemes possibility for
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Sample characterization The presence of Si-QDs is established by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), by which the average QD diameter of d QD 2.2 ± 0.5 nm has been determined
Supplementary Materials Sample characterization The presence of Si-QDs is established by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), by which the average QD diameter of d QD 2.2 ± 0.5 nm has been determined
Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering with enhanced mass transport
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information InP@ZnSeS, Core@Composition Gradient Shell Quantum Dots with Enhanced Stability Jaehoon Lim, Wan Ki Bae, Donggu Lee #, Min Ki Nam, Joohyun Jung, Changhee Lee #, Kookheon Char *,,
Supporting Information InP@ZnSeS, Core@Composition Gradient Shell Quantum Dots with Enhanced Stability Jaehoon Lim, Wan Ki Bae, Donggu Lee #, Min Ki Nam, Joohyun Jung, Changhee Lee #, Kookheon Char *,,
Spectroscopic Study of FTO/CdSe (MPA)/ZnO Artificial Atoms Emitting White Color
 Spectroscopic Study of FTO/CdSe (MPA)/ZnO Artificial Atoms Emitting White Color Batal MA *, and Alyamani K Department of Physics, College of Science, Aleppo, Syria * Corresponding author: Batal MA, Department
Spectroscopic Study of FTO/CdSe (MPA)/ZnO Artificial Atoms Emitting White Color Batal MA *, and Alyamani K Department of Physics, College of Science, Aleppo, Syria * Corresponding author: Batal MA, Department
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Study of Diffusion Assisted Bimolecular Electron Transfer Reactions: CdSe/ZnS Core Shell Quantum Dot acts as an Efficient Electron Donor as well as Acceptor. Somnath Koley, Manas
Supporting Information Study of Diffusion Assisted Bimolecular Electron Transfer Reactions: CdSe/ZnS Core Shell Quantum Dot acts as an Efficient Electron Donor as well as Acceptor. Somnath Koley, Manas
Self-Assembled InAs Quantum Dots
 Self-Assembled InAs Quantum Dots Steve Lyon Department of Electrical Engineering What are semiconductors What are semiconductor quantum dots How do we make (grow) InAs dots What are some of the properties
Self-Assembled InAs Quantum Dots Steve Lyon Department of Electrical Engineering What are semiconductors What are semiconductor quantum dots How do we make (grow) InAs dots What are some of the properties
Device performance and carrier dynamics in blue mixing host organic light-emitting devices
 evice performance and carrier dynamics in blue mixing host organic light-emitting devices Jiun-Haw Lee *a, S. W Liu b, hih-hung Teng a, Jian-Hong Lin a, Tian-hiun Lin a and.. Yang a a Graduate Institute
evice performance and carrier dynamics in blue mixing host organic light-emitting devices Jiun-Haw Lee *a, S. W Liu b, hih-hung Teng a, Jian-Hong Lin a, Tian-hiun Lin a and.. Yang a a Graduate Institute
Supplementary Figure 1. Potential energy, volume, and molecular distribution of the
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplementary Figure 1. Potential energy, volume, and molecular distribution of the organic substrates prepared by MD simulation. (a) Change of the density and total potential energy of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplementary Figure 1. Potential energy, volume, and molecular distribution of the organic substrates prepared by MD simulation. (a) Change of the density and total potential energy of
Surface Plasmon Enhanced Light Emitting Devices
 Surface Plasmon Enhanced Light Emitting Devices Alexander Mikhailovsky, Jacek Ostrowski, Hadjar Benmansour, and Guillermo Bazan + Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California Santa
Surface Plasmon Enhanced Light Emitting Devices Alexander Mikhailovsky, Jacek Ostrowski, Hadjar Benmansour, and Guillermo Bazan + Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California Santa
Luminescence basics. Slide # 1
 Luminescence basics Types of luminescence Cathodoluminescence: Luminescence due to recombination of EHPs created by energetic electrons. Example: CL mapping system Photoluminescence: Luminescence due to
Luminescence basics Types of luminescence Cathodoluminescence: Luminescence due to recombination of EHPs created by energetic electrons. Example: CL mapping system Photoluminescence: Luminescence due to
Role of Surface Chemistry on Charge Carrier Transport in Quantum Dot Solids
 Role of Surface Chemistry on Charge Carrier Transport in Quantum Dot Solids Cherie R. Kagan, University of Pennsylvania in collaboration with the Murray group Density of Electronic States in Quantum Dot
Role of Surface Chemistry on Charge Carrier Transport in Quantum Dot Solids Cherie R. Kagan, University of Pennsylvania in collaboration with the Murray group Density of Electronic States in Quantum Dot
The CdS and CdMnS nanocrystals have been characterized using UV-visible spectroscopy, TEM, FTIR, Particle Size Measurement and Photoluminiscence.
 Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
quantum dots, metallic nanoparticles, and lanthanide ions doped upconversion
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Background Nanostructured materials have significantly different characteristics from their bulk counterparts. 1 Inorganic nanoparticles such as semiconductor quantum dots, metallic
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Background Nanostructured materials have significantly different characteristics from their bulk counterparts. 1 Inorganic nanoparticles such as semiconductor quantum dots, metallic
CHAPTER 3. FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES. 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES
 CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
Quantum Dots The Pennsylvania State University Quantum Dots 1
 Quantum Dots www.nano4me.org 2018 The Pennsylvania State University Quantum Dots 1 Outline Introduction Quantum Confinement QD Synthesis Colloidal Methods Epitaxial Growth Applications Biological Light
Quantum Dots www.nano4me.org 2018 The Pennsylvania State University Quantum Dots 1 Outline Introduction Quantum Confinement QD Synthesis Colloidal Methods Epitaxial Growth Applications Biological Light
Luminescence. Photoluminescence (PL) is luminescence that results from optically exciting a sample.
 Luminescence Topics Radiative transitions between electronic states Absorption and Light emission (spontaneous, stimulated) Excitons (singlets and triplets) Franck-Condon shift(stokes shift) and vibrational
Luminescence Topics Radiative transitions between electronic states Absorption and Light emission (spontaneous, stimulated) Excitons (singlets and triplets) Franck-Condon shift(stokes shift) and vibrational
Physical Properties and Design of Light-Emitting Devices Based on Organic Materials and Nanoparticles. Polina Olegovna Anikeeva
 Physical Properties and Design of Light-Emitting Devices Based on Organic Materials and Nanoparticles by Polina Olegovna Anikeeva Submitted to the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in partial
Physical Properties and Design of Light-Emitting Devices Based on Organic Materials and Nanoparticles by Polina Olegovna Anikeeva Submitted to the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in partial
Development of active inks for organic photovoltaics: state-of-the-art and perspectives
 Development of active inks for organic photovoltaics: state-of-the-art and perspectives Jörg Ackermann Centre Interdisciplinaire de Nanoscience de Marseille (CINAM) CNRS - UPR 3118, MARSEILLE - France
Development of active inks for organic photovoltaics: state-of-the-art and perspectives Jörg Ackermann Centre Interdisciplinaire de Nanoscience de Marseille (CINAM) CNRS - UPR 3118, MARSEILLE - France
Electroluminescence from Silicon and Germanium Nanostructures
 Electroluminescence from silicon Silicon Getnet M. and Ghoshal S.K 35 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electroluminescence from Silicon and Germanium Nanostructures Getnet Melese* and Ghoshal S. K.** Abstract Silicon
Electroluminescence from silicon Silicon Getnet M. and Ghoshal S.K 35 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electroluminescence from Silicon and Germanium Nanostructures Getnet Melese* and Ghoshal S. K.** Abstract Silicon
Q. Shen 1,2) and T. Toyoda 1,2)
 Photosensitization of nanostructured TiO 2 electrodes with CdSe quntum dots: effects of microstructure in substrates Q. Shen 1,2) and T. Toyoda 1,2) Department of Applied Physics and Chemistry 1), and
Photosensitization of nanostructured TiO 2 electrodes with CdSe quntum dots: effects of microstructure in substrates Q. Shen 1,2) and T. Toyoda 1,2) Department of Applied Physics and Chemistry 1), and
maximal photofluorescence decay time of 6 hours (purchased from Shenzhen HuiDuoSheng
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental section Preparation of m-tio 2 /LPP photoanodes. TiO 2 colloid was synthesized according
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental section Preparation of m-tio 2 /LPP photoanodes. TiO 2 colloid was synthesized according
in Organic Host Matrices Seth Alexander Coe Brown University
 Efficient Light Emitting Devices Utilizing CdSe(ZnS) Quantum Dots in Organic Host Matrices by Seth Alexander Coe Sc.B., Electrical Engineering (1999) Brown University Submitted to the Department of Electrical
Efficient Light Emitting Devices Utilizing CdSe(ZnS) Quantum Dots in Organic Host Matrices by Seth Alexander Coe Sc.B., Electrical Engineering (1999) Brown University Submitted to the Department of Electrical
Fabrication / Synthesis Techniques
 Quantum Dots Physical properties Fabrication / Synthesis Techniques Applications Handbook of Nanoscience, Engineering, and Technology Ch.13.3 L. Kouwenhoven and C. Marcus, Physics World, June 1998, p.35
Quantum Dots Physical properties Fabrication / Synthesis Techniques Applications Handbook of Nanoscience, Engineering, and Technology Ch.13.3 L. Kouwenhoven and C. Marcus, Physics World, June 1998, p.35
interband transitions in semiconductors M. Fox, Optical Properties of Solids, Oxford Master Series in Condensed Matter Physics
 interband transitions in semiconductors M. Fox, Optical Properties of Solids, Oxford Master Series in Condensed Matter Physics interband transitions in quantum wells Atomic wavefunction of carriers in
interband transitions in semiconductors M. Fox, Optical Properties of Solids, Oxford Master Series in Condensed Matter Physics interband transitions in quantum wells Atomic wavefunction of carriers in
Efficient and High-Color-Purity Light-Emitting Diodes Based on In-Situ Grown Films of CsPbX 3 (X = Br, I) Nanoplates with Controlled Thicknesses
 Supporting Information Efficient and High-Color-Purity Light-Emitting Diodes Based on In-Situ Grown Films of CsPbX 3 (X = Br, I) Nanoplates with Controlled Thicknesses Junjie Si, Yang Liu, Zhuofei He,
Supporting Information Efficient and High-Color-Purity Light-Emitting Diodes Based on In-Situ Grown Films of CsPbX 3 (X = Br, I) Nanoplates with Controlled Thicknesses Junjie Si, Yang Liu, Zhuofei He,
In a metal, how does the probability distribution of an electron look like at absolute zero?
 1 Lecture 6 Laser 2 In a metal, how does the probability distribution of an electron look like at absolute zero? 3 (Atom) Energy Levels For atoms, I draw a lower horizontal to indicate its lowest energy
1 Lecture 6 Laser 2 In a metal, how does the probability distribution of an electron look like at absolute zero? 3 (Atom) Energy Levels For atoms, I draw a lower horizontal to indicate its lowest energy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.63 Bright infrared quantum-dot light-emitting diodes through inter-dot spacing control Liangfeng Sun, Joshua J. Choi, David Stachnik, Adam C. Bartnik,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.63 Bright infrared quantum-dot light-emitting diodes through inter-dot spacing control Liangfeng Sun, Joshua J. Choi, David Stachnik, Adam C. Bartnik,
Langmuir-Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers. Supporting Information
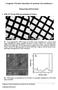 Langmuir-Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers Supporting Information I. AFM, UV-VIS and TEM characterization of LS layers S1 Low-magnification TEM images of Q-CdSe layers, deposited on a carbon-coated
Langmuir-Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers Supporting Information I. AFM, UV-VIS and TEM characterization of LS layers S1 Low-magnification TEM images of Q-CdSe layers, deposited on a carbon-coated
Organic Solar Cells. All Organic solar cell. Dye-sensitized solar cell. Dye. τ inj. τ c. τ r surface states D*/D + V o I 3 D/D.
 The 4th U.S.-Korea NanoForum April 26-27, 2007, Honolulu, USA Improvement of Device Efficiency in Conjugated Polymer/Fullerene NanoComposite Solar Cells School of Semiconductor & Chemical Engineering *
The 4th U.S.-Korea NanoForum April 26-27, 2007, Honolulu, USA Improvement of Device Efficiency in Conjugated Polymer/Fullerene NanoComposite Solar Cells School of Semiconductor & Chemical Engineering *
Physics of Organic Semiconductor Devices: Materials, Fundamentals, Technologies and Applications
 Physics of Organic Semiconductor Devices: Materials, Fundamentals, Technologies and Applications Dr. Alex Zakhidov Assistant Professor, Physics Department Core faculty at Materials Science, Engineering
Physics of Organic Semiconductor Devices: Materials, Fundamentals, Technologies and Applications Dr. Alex Zakhidov Assistant Professor, Physics Department Core faculty at Materials Science, Engineering
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTIG IFORMATIO [1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-based Host Materials for Green Phosphorescent and Delayed-Fluorescence OLEDs with Low Efficiency Roll-off Wenxuan Song, a Yi Chen, a Qihao Xu, a Haichuan
SUPPORTIG IFORMATIO [1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-based Host Materials for Green Phosphorescent and Delayed-Fluorescence OLEDs with Low Efficiency Roll-off Wenxuan Song, a Yi Chen, a Qihao Xu, a Haichuan
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Bicolour electroluminescence of 2 (carbazol 9 yl)anthraquinone
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Bicolour electroluminescence of 2 (carbazol 9 yl)anthraquinone
Materials as particle in a box models: Synthesis & optical study of CdSe quantum dots
 Lab Week 3 Module α 2 Materials as particle in a box models: Synthesis & optical study of CdSe quantum dots Instructor: Francesco Stellacci OBJECTIVES Introduce the particle-wave duality principle Introduce
Lab Week 3 Module α 2 Materials as particle in a box models: Synthesis & optical study of CdSe quantum dots Instructor: Francesco Stellacci OBJECTIVES Introduce the particle-wave duality principle Introduce
Plastic Electronics. Joaquim Puigdollers.
 Plastic Electronics Joaquim Puigdollers Joaquim.puigdollers@upc.edu Nobel Prize Chemistry 2000 Origins Technological Interest First products.. MONOCROMATIC PHILIPS Today Future Technological interest Low
Plastic Electronics Joaquim Puigdollers Joaquim.puigdollers@upc.edu Nobel Prize Chemistry 2000 Origins Technological Interest First products.. MONOCROMATIC PHILIPS Today Future Technological interest Low
CHARGE TRANSPORT IN QUANTUM DOT LIGHT EMITTING DEVICES
 CHARGE TRANSPORT IN QUANTUM DOT LIGHT EMITTING DEVICES A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY BRIJESH KUMAR IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
CHARGE TRANSPORT IN QUANTUM DOT LIGHT EMITTING DEVICES A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY BRIJESH KUMAR IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Solution-Processed CuInS 2 -Based White QD-LEDs with Mixed Active Layer Architecture Svenja Wepfer 1,2, Julia Frohleiks 1,2, A-Ra Hong 3, Ho Seong Jang 3, Gerd Bacher, 2, Ekaterina
Supporting Information Solution-Processed CuInS 2 -Based White QD-LEDs with Mixed Active Layer Architecture Svenja Wepfer 1,2, Julia Frohleiks 1,2, A-Ra Hong 3, Ho Seong Jang 3, Gerd Bacher, 2, Ekaterina
Multiple Exciton Generation in Quantum Dots. James Rogers Materials 265 Professor Ram Seshadri
 Multiple Exciton Generation in Quantum Dots James Rogers Materials 265 Professor Ram Seshadri Exciton Generation Single Exciton Generation in Bulk Semiconductors Multiple Exciton Generation in Bulk Semiconductors
Multiple Exciton Generation in Quantum Dots James Rogers Materials 265 Professor Ram Seshadri Exciton Generation Single Exciton Generation in Bulk Semiconductors Multiple Exciton Generation in Bulk Semiconductors
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mulifunctional Dendritic Emitter: Aggregation-Induced Emission Enhanced, Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Material for Solution- Processed Multilayered Organic Light-Emitting
Supporting Information Mulifunctional Dendritic Emitter: Aggregation-Induced Emission Enhanced, Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Material for Solution- Processed Multilayered Organic Light-Emitting
OLEDs and PLEDs Nele Schumacher Incoherent Lightsources - Prof. Thomas Jüstel
 OLEDs and PLEDs 28.5.2014 Nele Schumacher Incoherent Lightsources - Prof. Thomas Jüstel Contents 1. History 2. Working principle 4. Preparation of multilayer devices 5. Advantages and disadvantages 6.
OLEDs and PLEDs 28.5.2014 Nele Schumacher Incoherent Lightsources - Prof. Thomas Jüstel Contents 1. History 2. Working principle 4. Preparation of multilayer devices 5. Advantages and disadvantages 6.
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
 Fluorescence Spectroscopy Frequency and time dependent emission Emission and Excitation fluorescence spectra Stokes Shift: influence of molecular vibrations and solvent Time resolved fluorescence measurements
Fluorescence Spectroscopy Frequency and time dependent emission Emission and Excitation fluorescence spectra Stokes Shift: influence of molecular vibrations and solvent Time resolved fluorescence measurements
Supplementary documents
 Supplementary documents Low Threshold Amplified Spontaneous mission from Tin Oxide Quantum Dots: A Instantiation of Dipole Transition Silence Semiconductors Shu Sheng Pan,, Siu Fung Yu, Wen Fei Zhang,
Supplementary documents Low Threshold Amplified Spontaneous mission from Tin Oxide Quantum Dots: A Instantiation of Dipole Transition Silence Semiconductors Shu Sheng Pan,, Siu Fung Yu, Wen Fei Zhang,
熊本大学学術リポジトリ. Kumamoto University Repositor
 熊本大学学術リポジトリ Kumamoto University Repositor Title Characteristics of organic light-em consisting of dye-doped spin crosso fil Author(s) Matsuda, Masaki; Kiyoshima, Kinoshita, Nobuaki; Tajima, Keita; Hiroyuk
熊本大学学術リポジトリ Kumamoto University Repositor Title Characteristics of organic light-em consisting of dye-doped spin crosso fil Author(s) Matsuda, Masaki; Kiyoshima, Kinoshita, Nobuaki; Tajima, Keita; Hiroyuk
Theoretical Study on Graphene Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cell
 Copyright 2015 American Scientific Publishers All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America Journal of Nanoelectronics and Optoelectronics Vol. 10, 1 5, 2015 Theoretical Study on Graphene
Copyright 2015 American Scientific Publishers All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America Journal of Nanoelectronics and Optoelectronics Vol. 10, 1 5, 2015 Theoretical Study on Graphene
Nanoscience galore: hybrid and nanoscale photonics
 Nanoscience galore: hybrid and nanoscale photonics Pavlos Lagoudakis SOLAB, 11 June 2013 Hybrid nanophotonics Nanostructures: light harvesting and light emitting devices 2 Hybrid nanophotonics Nanostructures:
Nanoscience galore: hybrid and nanoscale photonics Pavlos Lagoudakis SOLAB, 11 June 2013 Hybrid nanophotonics Nanostructures: light harvesting and light emitting devices 2 Hybrid nanophotonics Nanostructures:
Photocatalysis: semiconductor physics
 Photocatalysis: semiconductor physics Carlos J. Tavares Center of Physics, University of Minho, Portugal ctavares@fisica.uminho.pt www.fisica.uminho.pt 1 Guimarães Where do I come from? 3 Guimarães 4 Introduction>>
Photocatalysis: semiconductor physics Carlos J. Tavares Center of Physics, University of Minho, Portugal ctavares@fisica.uminho.pt www.fisica.uminho.pt 1 Guimarães Where do I come from? 3 Guimarães 4 Introduction>>
Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Ceramici. Modulo 2: Materiali Nanostrutturati
 Università degli Studi di Trieste Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura A.A. 2016-2017 Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Ceramici Modulo 2: Materiali Nanostrutturati - Lezione 5 - Vanni Lughi vlughi@units.it
Università degli Studi di Trieste Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura A.A. 2016-2017 Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Ceramici Modulo 2: Materiali Nanostrutturati - Lezione 5 - Vanni Lughi vlughi@units.it
Facile and purification-free synthesis of nitrogenated amphiphilic graphitic carbon dots
 Supporting Information Facile and purification-free synthesis of nitrogenated amphiphilic graphitic carbon dots Byung Joon Moon, 1 Yelin Oh, 1 Dong Heon Shin, 1 Sang Jin Kim, 1 Sanghyun Lee, 1,2 Tae-Wook
Supporting Information Facile and purification-free synthesis of nitrogenated amphiphilic graphitic carbon dots Byung Joon Moon, 1 Yelin Oh, 1 Dong Heon Shin, 1 Sang Jin Kim, 1 Sanghyun Lee, 1,2 Tae-Wook
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Band Gap Tuning of CH 3 NH 3 Pb(Br 1-x Cl x ) 3 Hybrid Perovskite for Blue Electroluminescence Naresh K. Kumawat 1, Amrita Dey 1, Aravindh Kumar 2, Sreelekha P. Gopinathan 3, K.
Supporting Information Band Gap Tuning of CH 3 NH 3 Pb(Br 1-x Cl x ) 3 Hybrid Perovskite for Blue Electroluminescence Naresh K. Kumawat 1, Amrita Dey 1, Aravindh Kumar 2, Sreelekha P. Gopinathan 3, K.
Colloidal Single-Layer Quantum Dots with Lateral Confinement Effects on 2D Exciton
 Supporting Information Colloidal Single-Layer Quantum Dots with Lateral Confinement Effects on 2D Exciton Ho Jin,, Minji Ahn,,,, Sohee Jeong,,, Jae Hyo Han,,, Dongwon Yoo,, Dong Hee Son, *, and Jinwoo
Supporting Information Colloidal Single-Layer Quantum Dots with Lateral Confinement Effects on 2D Exciton Ho Jin,, Minji Ahn,,,, Sohee Jeong,,, Jae Hyo Han,,, Dongwon Yoo,, Dong Hee Son, *, and Jinwoo
University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida
 University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida PI: Dr. Sarath Witanachchi Students: Marak Merlak, Ph.D Description: This proposal is aimed at developing a smart
University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida PI: Dr. Sarath Witanachchi Students: Marak Merlak, Ph.D Description: This proposal is aimed at developing a smart
Supporting Information. A Facile Methodology for Engineering the Morphology of CsPbX 3 Perovskite Nanocrystals under Ambient Condition
 Supporting Information A Facile Methodology for Engineering the Morphology of CsPbX 3 Perovskite Nanocrystals under Ambient Condition Sudipta Seth and Anunay Samanta School of Chemistry, University of
Supporting Information A Facile Methodology for Engineering the Morphology of CsPbX 3 Perovskite Nanocrystals under Ambient Condition Sudipta Seth and Anunay Samanta School of Chemistry, University of
Engineering Challenges in Quantum Dot Displays
 Engineering Challenges in Quantum Dot Displays Any great technology that pushes the boundaries of performance also has a set of challenges to overcome. Quantum dot displays are not an exception. Whether
Engineering Challenges in Quantum Dot Displays Any great technology that pushes the boundaries of performance also has a set of challenges to overcome. Quantum dot displays are not an exception. Whether
Single Photon detectors
 Single Photon detectors Outline Motivation for single photon detection Semiconductor; general knowledge and important background Photon detectors: internal and external photoeffect Properties of semiconductor
Single Photon detectors Outline Motivation for single photon detection Semiconductor; general knowledge and important background Photon detectors: internal and external photoeffect Properties of semiconductor
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1176706/dc1 Supporting nline Material for High-Detectivity Polymer Photodetectors with Spectral Response from 300 nm to 1450 nm Xiong Gong,* Minghong Tong, Yangjun Xia,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1176706/dc1 Supporting nline Material for High-Detectivity Polymer Photodetectors with Spectral Response from 300 nm to 1450 nm Xiong Gong,* Minghong Tong, Yangjun Xia,
III-V nanostructured materials synthesized by MBE droplet epitaxy
 III-V nanostructured materials synthesized by MBE droplet epitaxy E.A. Anyebe 1, C. C. Yu 1, Q. Zhuang 1,*, B. Robinson 1, O Kolosov 1, V. Fal ko 1, R. Young 1, M Hayne 1, A. Sanchez 2, D. Hynes 2, and
III-V nanostructured materials synthesized by MBE droplet epitaxy E.A. Anyebe 1, C. C. Yu 1, Q. Zhuang 1,*, B. Robinson 1, O Kolosov 1, V. Fal ko 1, R. Young 1, M Hayne 1, A. Sanchez 2, D. Hynes 2, and
Chapter 6 Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
 Chapter 6 Photoluminescence Spectroscopy Course Code: SSCP 4473 Course Name: Spectroscopy & Materials Analysis Sib Krishna Ghoshal (PhD) Advanced Optical Materials Research Group Physics Department, Faculty
Chapter 6 Photoluminescence Spectroscopy Course Code: SSCP 4473 Course Name: Spectroscopy & Materials Analysis Sib Krishna Ghoshal (PhD) Advanced Optical Materials Research Group Physics Department, Faculty
Introduction to semiconductor nanostructures. Peter Kratzer Modern Concepts in Theoretical Physics: Part II Lecture Notes
 Introduction to semiconductor nanostructures Peter Kratzer Modern Concepts in Theoretical Physics: Part II Lecture Notes What is a semiconductor? The Fermi level (chemical potential of the electrons) falls
Introduction to semiconductor nanostructures Peter Kratzer Modern Concepts in Theoretical Physics: Part II Lecture Notes What is a semiconductor? The Fermi level (chemical potential of the electrons) falls
Laser Crystallization of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid
 Supporting information Laser Crystallization of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells Taewoo Jeon, Hyeong Min Jin, Seung Hyun Lee, Ju Min Lee, Hyung Il Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Keon Jae Lee, Byungha
Supporting information Laser Crystallization of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells Taewoo Jeon, Hyeong Min Jin, Seung Hyun Lee, Ju Min Lee, Hyung Il Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Keon Jae Lee, Byungha
Dielectric constant measurement of P3HT, polystyrene, and polyethylene
 Dielectric constant measurement of P3HT, polystyrene, and polyethylene Supervisor: prof. dr. J.C. Hummelen Daily supervisor: Jenny Douvogianni Name: Si Chen (s2660482) 1. Introduction Dielectric constant
Dielectric constant measurement of P3HT, polystyrene, and polyethylene Supervisor: prof. dr. J.C. Hummelen Daily supervisor: Jenny Douvogianni Name: Si Chen (s2660482) 1. Introduction Dielectric constant
Size-Dependent Biexciton Quantum Yields and Carrier Dynamics of Quasi-
 Supporting Information Size-Dependent Biexciton Quantum Yields and Carrier Dynamics of Quasi- Two-Dimensional Core/Shell Nanoplatelets Xuedan Ma, Benjamin T. Diroll, Wooje Cho, Igor Fedin, Richard D. Schaller,
Supporting Information Size-Dependent Biexciton Quantum Yields and Carrier Dynamics of Quasi- Two-Dimensional Core/Shell Nanoplatelets Xuedan Ma, Benjamin T. Diroll, Wooje Cho, Igor Fedin, Richard D. Schaller,
Organo-metal halide perovskite-based solar cells with CuSCN as inorganic hole selective contact
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Organo-metal halide perovskite-based solar cells with CuSCN as inorganic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Organo-metal halide perovskite-based solar cells with CuSCN as inorganic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cyclodextrin Supramolecular Complex as Water Soluble Ratiometric Sensor for ferric Ion Sensing Meiyun Xu, Shuizhu Wu,* Fang Zeng, Changmin Yu College of Materials Science & Engineering,
Supporting Information Cyclodextrin Supramolecular Complex as Water Soluble Ratiometric Sensor for ferric Ion Sensing Meiyun Xu, Shuizhu Wu,* Fang Zeng, Changmin Yu College of Materials Science & Engineering,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Challenges in to-electric Energy Conversion: an Introduction
 Challenges in Solar-to to-electric Energy Conversion: an Introduction Eray S. Aydil Chemical Engineering and Materials Science Department Acknowledgements: National Science Foundation Minnesota Initiative
Challenges in Solar-to to-electric Energy Conversion: an Introduction Eray S. Aydil Chemical Engineering and Materials Science Department Acknowledgements: National Science Foundation Minnesota Initiative
QUANTUM DOTS, ADVANTAGES AND DRAWBACKS FOR LIGHTING APPLICATIONS. David Schmidmayr, Johann Zehetner
 Abstract QUANTUM DOTS, ADVANTAGES AND DRAWBACKS FOR LIGHTING APPLICATIONS David Schmidmayr, Johann Zehetner Research Centre for Microtechnology, Vorarlberg University of Applied Sciences, Hochschulstrasse
Abstract QUANTUM DOTS, ADVANTAGES AND DRAWBACKS FOR LIGHTING APPLICATIONS David Schmidmayr, Johann Zehetner Research Centre for Microtechnology, Vorarlberg University of Applied Sciences, Hochschulstrasse
The Current Status of Perovskite Solar Cell Research at UCLA
 The Current Status of Perovskite Solar Cell Research at UCLA Lijian Zuo, Sanghoon Bae, Lei Meng, Yaowen Li, and Yang Yang* Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of California, Los
The Current Status of Perovskite Solar Cell Research at UCLA Lijian Zuo, Sanghoon Bae, Lei Meng, Yaowen Li, and Yang Yang* Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of California, Los
Inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes using transparent conductive NiO electrode
 Applied Surface Science 244 (2005) 439 443 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes using transparent conductive NiO electrode Se-W. Park a, Jeong-M. Choi a, Eugene
Applied Surface Science 244 (2005) 439 443 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes using transparent conductive NiO electrode Se-W. Park a, Jeong-M. Choi a, Eugene
Semiconductor Quantum Dots
 Semiconductor Quantum Dots M. Hallermann Semiconductor Physics and Nanoscience St. Petersburg JASS 2005 Outline Introduction Fabrication Experiments Applications Porous Silicon II-VI Quantum Dots III-V
Semiconductor Quantum Dots M. Hallermann Semiconductor Physics and Nanoscience St. Petersburg JASS 2005 Outline Introduction Fabrication Experiments Applications Porous Silicon II-VI Quantum Dots III-V
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Highly luminescent water-dispersible NIR-emitting wurtzite CuInS 2 /ZnS core/shell colloidal quantum dots Chenghui Xia, a,b Johannes D. Meeldijk, c Hans C. Gerritsen, b and Celso
Supporting Information Highly luminescent water-dispersible NIR-emitting wurtzite CuInS 2 /ZnS core/shell colloidal quantum dots Chenghui Xia, a,b Johannes D. Meeldijk, c Hans C. Gerritsen, b and Celso
Lecture 6: Individual nanoparticles, nanocrystals and quantum dots
 Lecture 6: Individual nanoparticles, nanocrystals and quantum dots Definition of nanoparticle: Size definition arbitrary More interesting: definition based on change in physical properties. Size smaller
Lecture 6: Individual nanoparticles, nanocrystals and quantum dots Definition of nanoparticle: Size definition arbitrary More interesting: definition based on change in physical properties. Size smaller
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013123 TITLE: The Effect of Deuterium on the Optical Properties of Free Standing Porous Silicon Layers DISTRIBUTION: Approved
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013123 TITLE: The Effect of Deuterium on the Optical Properties of Free Standing Porous Silicon Layers DISTRIBUTION: Approved
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures. based on a nano-obelisk
 Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
Supporting information. and/or J -aggregation. Sergey V. Dayneko, Abby-Jo Payne and Gregory C. Welch*
 Supporting information Inverted P3HT:PC61BM organic solar cells incorporating a -extended squaraine dye with H- and/or J -aggregation. Sergey V. Dayneko, Abby-Jo Payne and Gregory C. Welch* Department
Supporting information Inverted P3HT:PC61BM organic solar cells incorporating a -extended squaraine dye with H- and/or J -aggregation. Sergey V. Dayneko, Abby-Jo Payne and Gregory C. Welch* Department
PRESENTED BY: PROF. S. Y. MENSAH F.A.A.S; F.G.A.A.S UNIVERSITY OF CAPE COAST, GHANA.
 SOLAR CELL AND ITS APPLICATION PRESENTED BY: PROF. S. Y. MENSAH F.A.A.S; F.G.A.A.S UNIVERSITY OF CAPE COAST, GHANA. OUTLINE OF THE PRESENTATION Objective of the work. A brief introduction to Solar Cell
SOLAR CELL AND ITS APPLICATION PRESENTED BY: PROF. S. Y. MENSAH F.A.A.S; F.G.A.A.S UNIVERSITY OF CAPE COAST, GHANA. OUTLINE OF THE PRESENTATION Objective of the work. A brief introduction to Solar Cell
Crosslight Software Overview, New Features & Updates. Dr. Peter Mensz
 1 Crosslight Software Overview, New Features & Updates Dr. Peter Mensz 2 Device Simulators Lastip/Pics3d Laser diode FEM models in 2D/3D Apsys 2D and 3D Any other compound semiconductors device FEM models,
1 Crosslight Software Overview, New Features & Updates Dr. Peter Mensz 2 Device Simulators Lastip/Pics3d Laser diode FEM models in 2D/3D Apsys 2D and 3D Any other compound semiconductors device FEM models,
Photoconductive Atomic Force Microscopy for Understanding Nanostructures and Device Physics of Organic Solar Cells
 Photoconductive AFM of Organic Solar Cells APP NOTE 15 Photoconductive Atomic Force Microscopy for Understanding Nanostructures and Device Physics of Organic Solar Cells Xuan-Dung Dang and Thuc-Quyen Nguyen
Photoconductive AFM of Organic Solar Cells APP NOTE 15 Photoconductive Atomic Force Microscopy for Understanding Nanostructures and Device Physics of Organic Solar Cells Xuan-Dung Dang and Thuc-Quyen Nguyen
