In this chapter, we will examine
|
|
|
- Oscar Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 In this chapter, we will examine Surface and upper level pressure charts The forces that influence the winds The equations that govern atmospheric motion Simple balanced flows Geostrophic wind (quantitative) Gradient wind (qualitative) Boundary layer wind Read Stull pp ,
2 A model of the atmosphere where air density remains constant with height. The air pressure at the surface is related to the number of molecules above. When air of the same temperature is stuffed into the column, the surface air pressure rises. When air is removed from the column, the surface pressure falls. Figure 8-1 p200
3 It takes a shorter column of cold air to exert the same pressure as a taller column of warm air. Because of this fact, aloft, cold air is associated with low pressure aloft and warm air with high pressure aloft. The pressure differences aloft create a force that causes the air to move from a region of higher pressure toward a region of lower pressure. The removal of air from column 2 causes its surface pressure to drop, whereas the addition of air into column 1 causes its surface pressure to rise. (The difference in height between the two columns is greatly exaggerated.) Figure 8-2 p201
4 The statement on Ahrens (10 th Edition) p.200, RHS column, last 3 lines, should read as follows: Warm air aloft is normally associated with high atmospheric pressure aloft, and cold air aloft is associated with low atmospheric pressure aloft. Fig. 8.3 suggests the following: Warm air aloft is normally associated with low atmospheric pressure at the surface, and cold air aloft is associated with high atmospheric pressure at the surface.
5 The top diagram (a) shows four cities (A, B, C, and D) at varying elevations above sea level, all with different station pressures. The middle diagram (b) represents sea-level pressures of the four cities plotted on a sealevel pressure chart. The bottom diagram (c) shows isobars drawn on the chart (dark lines) at intervals of 4 millibars. Figure 8-9 p205
6 Station Pressure: Actual pressure measured at weather stations Because pressure changes rapidly with altitude, plots of station pressure are mainly dominated by the effects of elevation (Fig. 8.9a) Sea Level Pressure: To show distribution of pressure on a horizontal surface, all pressure observations are normally adjusted to a level of mean sea level (Fig. 8.9bc) This adjusted sea level pressure is what is usually plotted on surface weather charts (Fig. 8.10)
7 Each map shows isobars on a constant height chart. The isobars represent variations in horizontal pressure at that altitude. An average isobar at sea level would be about 1000 mb; at 3000 m, about 700 mb; and at 5600 m, about 500 mb. Figure 8-11 p207
8 When there are no horizontal variations in pressure, constant pressure surfaces are parallel to constant height surfaces. In the diagram, a measured pressure of 500 mb is 5600 m above sea level everywhere. Figure 8-12 p207
9 The two horizontal lines represent levels having same pressure. When an air column is cooled, the whole air column shrinks, and the height of the pressure level lowers. On the other hand, when an air column is warmed, the whole air column expands, and the height of the pressure level rises. Note that high pressure aloft corresponds with high height of the pressure surface, while low pressure aloft corresponds with low height of the pressure surface. Fig. 8-2, p. 193
10 The area shaded gray in the above diagram represents a surface of constant pressure, or isobaric surface. Because of the changes in air density, the isobaric surface rises in warm, less-dense air and lowers in cold, more-dense air. Where the horizontal temperature changes most quickly, the isobaric surface changes elevation most rapidly. Figure 8-13 p207
11 Upper-level charts: Usually, instead of plotting pressure at a constant altitude, height of a constant pressure surface is plotted instead A rule-of-thump for interpreting constant pressure charts: High height on a constant pressure chart is equivalent to high pressure on a constant height chart (and vice-versa)
Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Frode Stordal, University of Oslo
 Chapter 4 Lecture Understanding Weather and Climate Seventh Edition Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Frode Stordal, University of Oslo Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University The Concept of Pressure
Chapter 4 Lecture Understanding Weather and Climate Seventh Edition Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Frode Stordal, University of Oslo Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University The Concept of Pressure
The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind. AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9
 The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9 Recall that Pressure is force per unit area Air pressure is determined by the weight of air above A change in pressure over some distance
The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9 Recall that Pressure is force per unit area Air pressure is determined by the weight of air above A change in pressure over some distance
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars
 Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Quick Review: Pressure
 Quick Review: Pressure The pressure force is the force exerted by an air mass on its surroundings (and vice-versa) In the atmosphere, the surroundings are usually other air masses three air masses, each
Quick Review: Pressure The pressure force is the force exerted by an air mass on its surroundings (and vice-versa) In the atmosphere, the surroundings are usually other air masses three air masses, each
PLOTTING WEATHER DATA to perform a SURFACE ANALYSIS
 PLOTTING WEATHER DATA to perform a SURFACE ANALYSIS The surface analysis permits one to identify and locate the large scale features of the sea level pressure field and the surface fronts. Isobars with
PLOTTING WEATHER DATA to perform a SURFACE ANALYSIS The surface analysis permits one to identify and locate the large scale features of the sea level pressure field and the surface fronts. Isobars with
Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday. Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1
 Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure Atmospheric Pressure & Its Measurement Ideal Gas Law (Equation of State) Pressure Gradient
Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure Atmospheric Pressure & Its Measurement Ideal Gas Law (Equation of State) Pressure Gradient
2. Usually, the air pressure inside a building is the air pressure outside the building. a. greater than b. about the same as c.
 CHAPTER 5 AIR PRESSURE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The magnitude of pressure exerted by the gas molecules composing air depends on a. the mass of the air molecules. b. the pull of gravity. c. the kinetic
CHAPTER 5 AIR PRESSURE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The magnitude of pressure exerted by the gas molecules composing air depends on a. the mass of the air molecules. b. the pull of gravity. c. the kinetic
NATS 101. Lecture 15 Surface and Upper-Air Maps
 NATS 101 Lecture 15 Surface and Upper-Air Maps Due Today Turn in 4 by 6 card, include Comments on Lecture PIN (Optional) Signature (Mandatory and Legible) Supplemental References for Today s s Lecture
NATS 101 Lecture 15 Surface and Upper-Air Maps Due Today Turn in 4 by 6 card, include Comments on Lecture PIN (Optional) Signature (Mandatory and Legible) Supplemental References for Today s s Lecture
The Behaviour of the Atmosphere
 3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A.
 Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
2 Atmospheric Pressure
 2 Atmospheric Pressure METEOROLOGY 2.1 Definition and Pressure Measurement 2.1.1 Definition Pressure acts in all directions, up and sideways as well as down, but it is convenient in meteorology to regard
2 Atmospheric Pressure METEOROLOGY 2.1 Definition and Pressure Measurement 2.1.1 Definition Pressure acts in all directions, up and sideways as well as down, but it is convenient in meteorology to regard
Page 1. Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period.
 Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Please write neatly when completing this assignment if we can t read your answer you will not get credit for it.
 ATOC 1050-001 Homework #2 - Due Thursday March 10, 2011 Instructions: Make sure that you answer all of the questions and complete all of the tables for maximum credit. Use appropriate units on all numerical
ATOC 1050-001 Homework #2 - Due Thursday March 10, 2011 Instructions: Make sure that you answer all of the questions and complete all of the tables for maximum credit. Use appropriate units on all numerical
Pressure Conversion in Millibars
 Name Date The Weather Map Biggie Lab: Make it Colorful and Purty! Now that you have learned about all of the different variables that contribute to daily changes in weather, it is now time to bring it
Name Date The Weather Map Biggie Lab: Make it Colorful and Purty! Now that you have learned about all of the different variables that contribute to daily changes in weather, it is now time to bring it
3. As warm, moist air moves into a region, barometric pressure readings in the region will generally 1. decrease 2. increase 3.
 Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Chapter 10 Atmospheric Forces & Winds
 Chapter 10 Atospheric Forces & Winds Chapter overview: Atospheric Pressure o Horizontal pressure variations o Station vs sea level pressure Winds and weather aps Newton s 2 nd Law Horizontal Forces o Pressure
Chapter 10 Atospheric Forces & Winds Chapter overview: Atospheric Pressure o Horizontal pressure variations o Station vs sea level pressure Winds and weather aps Newton s 2 nd Law Horizontal Forces o Pressure
WEATHER PATTERNS NAME DATE. VOCABULARY: Synoptic weather map- Isotherm- Barometric Pressure- Isobar- Convergence- Divergence- Cyclone- Anticyclone-
 NAME DATE VOCABULARY: Synoptic weather map- WEATHER PATTERNS Isotherm- Barometric Pressure- Isobar- Convergence- Divergence- Cyclone- Anticyclone- Air mass- Source region- Front- OBJECTIVE: Construct a
NAME DATE VOCABULARY: Synoptic weather map- WEATHER PATTERNS Isotherm- Barometric Pressure- Isobar- Convergence- Divergence- Cyclone- Anticyclone- Air mass- Source region- Front- OBJECTIVE: Construct a
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Common Elements: Nitrogen, 78%
 Chapter 23 Notes Name: Period: 23.1 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is a layer of that surrounds the earth and influences all living things. Meteorology is the study of the. WHAT S IN
Chapter 23 Notes Name: Period: 23.1 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is a layer of that surrounds the earth and influences all living things. Meteorology is the study of the. WHAT S IN
Name Period Date L.O: students will be able to describe air temperature and air pressure
 Name Period Date L.O: students will be able to describe air temperature and air pressure 1. As the altitude increases within Earth s stratosphere, air temperature generally A) decreases, only B) increases,
Name Period Date L.O: students will be able to describe air temperature and air pressure 1. As the altitude increases within Earth s stratosphere, air temperature generally A) decreases, only B) increases,
Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation. 1. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic. 2. The atmosphere is approximately geostrophic.
 Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation For large-scale flow in the atmosphere, we have learned about two very important characteristics:. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic.. The atmosphere is approximately
Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation For large-scale flow in the atmosphere, we have learned about two very important characteristics:. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic.. The atmosphere is approximately
Quick Review: Pressure
 Quick Review: Pressure The pressure force is the force exerted by an air mass on its surroundings (and vice-versa) In the atmosphere, the surroundings are usually other air masses three air masses, each
Quick Review: Pressure The pressure force is the force exerted by an air mass on its surroundings (and vice-versa) In the atmosphere, the surroundings are usually other air masses three air masses, each
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Earth Science. Lab 21: Weather Patterns
 Name: Lab 21: Weather Patterns Earth Science Date: Introduction: A basic principle in Earth Science is that energy is constantly bringing about changes. In order to understand the changing Earth, we must
Name: Lab 21: Weather Patterns Earth Science Date: Introduction: A basic principle in Earth Science is that energy is constantly bringing about changes. In order to understand the changing Earth, we must
UNIT 13: WEATHER AND CLIMATE
 UNIT 13: WEATHER AND CLIMATE After Unit 13 you should be able to: o Be able to use Selected Properties of Earth s Atmosphere, Planetary Wind and Moisture Belts in the Troposphere, Temperature, Pressure,
UNIT 13: WEATHER AND CLIMATE After Unit 13 you should be able to: o Be able to use Selected Properties of Earth s Atmosphere, Planetary Wind and Moisture Belts in the Troposphere, Temperature, Pressure,
ERTH 465 Fall Lab 3. Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness. (300 points)
 Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 3 Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness (300 points) 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show
Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 3 Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness (300 points) 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show
SPI Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI Recognize the connection between the
 SPI 0607.8.1 - Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI 0607.8.2 - Recognize the connection between the sun s energy and the wind. o Energy from the Sun creates
SPI 0607.8.1 - Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI 0607.8.2 - Recognize the connection between the sun s energy and the wind. o Energy from the Sun creates
Weather Station Model
 Fun with Weather Maps! (no, really stop laughing) AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Station Model Temperature Maps Pressure Maps Fronts Lecture
Fun with Weather Maps! (no, really stop laughing) AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Station Model Temperature Maps Pressure Maps Fronts Lecture
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone
 Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
San Francisco State University Department of Earth & Climate Sciences. Homework 7 Key: Pressure Tendency Equation
 San Francisco State University Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Name Homework 7 Key: Pressure Tendency Equation 1. On November 11, 2012 at 12 UTC, the 300 mb divergence over extreme southcentral
San Francisco State University Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Name Homework 7 Key: Pressure Tendency Equation 1. On November 11, 2012 at 12 UTC, the 300 mb divergence over extreme southcentral
Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations. Earth-Sun Distance. Eccentricity 2/2/2010. ATS351 Lecture 3
 Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations ATS351 Lecture 3 Earth-Sun Distance Change in distance has only a minimal effect on seasonal temperature. Note that during the N. hemisphere winter, we are CLOSER to
Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations ATS351 Lecture 3 Earth-Sun Distance Change in distance has only a minimal effect on seasonal temperature. Note that during the N. hemisphere winter, we are CLOSER to
The Atmosphere. 1 Global Environments: 2 Global Environments:
 1 Global Environments: 2 Global Environments: Composition Vertical structure Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Global Environments: The earth s atmosphere
1 Global Environments: 2 Global Environments: Composition Vertical structure Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Global Environments: The earth s atmosphere
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART TWO SC 208 DECEMBER 2, 2014 JOHN BUSH
 INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART TWO SC 208 DECEMBER 2, 2014 JOHN BUSH Meteorology ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES Short term weather systems in time spans of hours, days, weeks or months Emphasis is on forecasting
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART TWO SC 208 DECEMBER 2, 2014 JOHN BUSH Meteorology ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES Short term weather systems in time spans of hours, days, weeks or months Emphasis is on forecasting
The Atmosphere in the Vertical ACTIVITY. Introduction. Materials. Investigations
 ACTIVITY Activity The Atmosphere in the Vertical After completing this activity, you should be able to: Describe the vertical structure of the atmosphere in the troposphere (the "weather" layer) and in
ACTIVITY Activity The Atmosphere in the Vertical After completing this activity, you should be able to: Describe the vertical structure of the atmosphere in the troposphere (the "weather" layer) and in
Metr 201 Quiz #2 100 pts. A. Short Answer and Definitions. (4 points each for a total of 28 points in this section).
 Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Name San Francisco State University February 23, 2015 Metr 201 Quiz #2 100 pts. A. Short Answer and Definitions. (4 points each for a total of 28 points in this section).
Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Name San Francisco State University February 23, 2015 Metr 201 Quiz #2 100 pts. A. Short Answer and Definitions. (4 points each for a total of 28 points in this section).
LAB G - ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE LAB I TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE PRESSURE PORTION
 LAB G - ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE LAB I TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE PRESSURE PORTION Introduction This lab will provide the student with the opportunity to become familiar with the concepts introduced in Chapter
LAB G - ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE LAB I TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE PRESSURE PORTION Introduction This lab will provide the student with the opportunity to become familiar with the concepts introduced in Chapter
Changes in Density Within An Air are Density Velocity Column Fixed due and/or With Respect to to Advection Divergence the Earth
 The Continuity Equation: Dines Compensation and the Pressure Tendency Equation 1. General The Continuity Equation is a restatement of the principle of Conservation of Mass applied to the atmosphere. The
The Continuity Equation: Dines Compensation and the Pressure Tendency Equation 1. General The Continuity Equation is a restatement of the principle of Conservation of Mass applied to the atmosphere. The
5. Which type of front is represented by letter X?
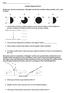 Name Weather Regents Review ased your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the four weather station models,,,, and D, below. D 82 012 56 999 78 978 32 002 62 75 24 1. List the letters of the four station
Name Weather Regents Review ased your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the four weather station models,,,, and D, below. D 82 012 56 999 78 978 32 002 62 75 24 1. List the letters of the four station
Department of Geosciences San Francisco State University Spring Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points)
 Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
ERTH 465 Fall Lab 5. Absolute Geostrophic Vorticity. 200 points.
 Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 5 Absolute Geostrophic Vorticity 200 points. 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show all work in mathematical
Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 5 Absolute Geostrophic Vorticity 200 points. 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show all work in mathematical
Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C
 1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
Cyclones and Anticyclones, Ridges and Troughs
 Cyclones and Anticyclones, Ridges and Troughs Isobars on surface maps often have a closed appearance (as illustrated) Areas of low pressure are called cyclones, while areas with high pressure are called
Cyclones and Anticyclones, Ridges and Troughs Isobars on surface maps often have a closed appearance (as illustrated) Areas of low pressure are called cyclones, while areas with high pressure are called
The Atmosphere EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen
 1 Physical Environment: EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Physical Environment: Atmosphere Composition Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Physical Environment:
1 Physical Environment: EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Physical Environment: Atmosphere Composition Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Physical Environment:
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Forecasts include: Temperature. Barometric (air) Pressure. Wind direction/speed Humidity
 Meteorology I Intro. to Weather 1. What is Weather? A) Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given time and place. B) Weather changes on a regular basis. C) Meteorologists forecast weather conditions
Meteorology I Intro. to Weather 1. What is Weather? A) Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given time and place. B) Weather changes on a regular basis. C) Meteorologists forecast weather conditions
ERTH 465 Fall Lab 3. Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness
 Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 3 Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show all work
Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 3 Vertical Consistency and Analysis of Thickness 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show all work
Chapter 12 Fronts & Air Masses
 Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Final Examination. Part A Answer ONLY TWELVE QUESTIONS in Part A. (Each question is 3 points)
 ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
Winds and Currents in the Oceans
 Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture
 Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Dynamic Meteorology 1
 Dynamic Meteorology 1 Lecture 14 Sahraei Department of Physics, Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei Buys-Ballot rule (Northern Hemisphere) If the wind blows into your back, the Low will be to
Dynamic Meteorology 1 Lecture 14 Sahraei Department of Physics, Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei Buys-Ballot rule (Northern Hemisphere) If the wind blows into your back, the Low will be to
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns. Meteorology
 Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Wednesday February 1 st, Daily Science: How are the upper and the lower part of the stratosphere different?
 Wednesday February 1 st, 2017 Daily Science: How are the upper and the lower part of the stratosphere different? Properties of Air Because air has mass, it also has other properties, including density
Wednesday February 1 st, 2017 Daily Science: How are the upper and the lower part of the stratosphere different? Properties of Air Because air has mass, it also has other properties, including density
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Activity: The Atmosphere in the Vertical
 Activity: The Atmosphere in the Vertical Educational Outcomes: The atmosphere has thickness as well as horizontal extent. For a more complete understanding of weather, knowledge of atmospheric conditions
Activity: The Atmosphere in the Vertical Educational Outcomes: The atmosphere has thickness as well as horizontal extent. For a more complete understanding of weather, knowledge of atmospheric conditions
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate CHAPTER 1 LECTURE 1. Question: Introduction to the Atmosphere
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
PRACTICAL ACTIVITY: DRAWING ISOLINES OR CONTOURS
 COME RAIN OR SHINE PRACTICAL ACTIVITY: DRAWING ISOLINES OR CONTOURS Ideally you would need a pencil for this activity (rather than a pen) and coloured pencils are useful too. These activities maybe a little
COME RAIN OR SHINE PRACTICAL ACTIVITY: DRAWING ISOLINES OR CONTOURS Ideally you would need a pencil for this activity (rather than a pen) and coloured pencils are useful too. These activities maybe a little
u g z = g T y (1) f T Margules Equation for Frontal Slope
 Margules Equation for Frontal Slope u g z = g f T T y (1) Equation (1) is the thermal wind relation for the west wind geostrophic component of the flow. For the purposes of this derivation, we assume that
Margules Equation for Frontal Slope u g z = g f T T y (1) Equation (1) is the thermal wind relation for the west wind geostrophic component of the flow. For the purposes of this derivation, we assume that
Name: Regents Earth Science. Weather and Climate - Review Questions
 Name: Regents Earth Science Weather and Climate - Review Questions Date: Thayer - 279 1. People sometimes release substances into the atmosphere to increase the probability of rain by A) raising the air
Name: Regents Earth Science Weather and Climate - Review Questions Date: Thayer - 279 1. People sometimes release substances into the atmosphere to increase the probability of rain by A) raising the air
PREDICTING THE WEATHER
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) PREDICTING THE WEATHER How well does your local weatherman do in predicting the weather? Is he or she more accurate for the next day or for a week in the future? Why do you think that
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) PREDICTING THE WEATHER How well does your local weatherman do in predicting the weather? Is he or she more accurate for the next day or for a week in the future? Why do you think that
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
RR#4 - Multiple Choice
 1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
Unit 5. Seasons and Atmosphere
 Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 12 Vorticity
 ESCI 34 tmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vorticity Reference: n Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), Holton n Informal Introduction to Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Lighthill Reading: Martin,
ESCI 34 tmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vorticity Reference: n Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), Holton n Informal Introduction to Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Lighthill Reading: Martin,
Pressure System Circulation
 NAME 1. Base your answer to the following question on the surface weather map shown below. The map shows weather systems over the United States and weather station data for cities A, B, C, and D. Note
NAME 1. Base your answer to the following question on the surface weather map shown below. The map shows weather systems over the United States and weather station data for cities A, B, C, and D. Note
Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere
 14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
Atmospheric Fronts. The material in this section is based largely on. Lectures on Dynamical Meteorology by Roger Smith.
 Atmospheric Fronts The material in this section is based largely on Lectures on Dynamical Meteorology by Roger Smith. Atmospheric Fronts 2 Atmospheric Fronts A front is the sloping interfacial region of
Atmospheric Fronts The material in this section is based largely on Lectures on Dynamical Meteorology by Roger Smith. Atmospheric Fronts 2 Atmospheric Fronts A front is the sloping interfacial region of
Fun with Weather Maps! (no, really stop laughing) AOSC 200 Tim Canty
 Fun with Weather Maps! (no, really stop laughing) AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Observations Station Model Temperature Maps Pressure Maps
Fun with Weather Maps! (no, really stop laughing) AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Observations Station Model Temperature Maps Pressure Maps
10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp of BC Science 10)
 10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 424-435 of BC Science 10) kinetic molecular theory: explains that matter is made up of tiny that are constantly. These atoms
10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 424-435 of BC Science 10) kinetic molecular theory: explains that matter is made up of tiny that are constantly. These atoms
Class Notes: Weather
 Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/7/2019
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414)
 NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
DOWNLOAD PDF READING CLIMATE MAPS
 Chapter 1 : Template:Climate chart/how to read a climate chart - Wikipedia Maps don't just tell you which way to go they can tell you practically everything about an area of land, even the weather. Learn
Chapter 1 : Template:Climate chart/how to read a climate chart - Wikipedia Maps don't just tell you which way to go they can tell you practically everything about an area of land, even the weather. Learn
The Water Cycle. Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site:
 Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
Ocean Currents and Climate
 Ocean Currents and Climate Ocean water contains streamlike movements of water called ocean currents. Currents are influenced by a number of factors, including weather, the Earth's rotation, and the position
Ocean Currents and Climate Ocean water contains streamlike movements of water called ocean currents. Currents are influenced by a number of factors, including weather, the Earth's rotation, and the position
Weather. Describing Weather
 Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
WEATHER MAPS NAME. Temperature: Dew Point: Wind Direction: Wind Velocity: % of Sky Covered: Current Pressure:
 NAME WEATHER MAPS For decades hundreds of weather stations throughout the United States have been making standard observations of temperature, moisture, air pressure and winds. The data are collected centrally
NAME WEATHER MAPS For decades hundreds of weather stations throughout the United States have been making standard observations of temperature, moisture, air pressure and winds. The data are collected centrally
Weather Practice. 4. As wind velocity decreases, the distance between isobars on a weather map will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
 1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
STATION If relative humidity is 60% and saturation vapor pressure is 35 mb, what is the actual vapor pressure?
 STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere
 ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems
 The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/2/2015
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
4. Which map best represents the type of fronts and direction of movement of these fronts in relation to the low-pressure center?
 1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
Anticipation Guide #2
 Weather Systems Anticipation Guide #2 Density differences in the atmosphere are responsible for redistributing earth s heat When air is heated it rises, cools and expands releasing energy mt air masses
Weather Systems Anticipation Guide #2 Density differences in the atmosphere are responsible for redistributing earth s heat When air is heated it rises, cools and expands releasing energy mt air masses
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
