Heat Burst Detection by a Temporally Fine-Scale Mesonet
|
|
|
- Joel Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heat Burst Detection by a Temporally Fine-Scale Mesonet JAY TROBEC KELO-TV, Sioux Falls, SD (Submitted 19 December 2007; In final form 3 March 2008) ABSTRACT A heat burst which occurred at Sioux Falls, South Dakota, early in the morning of 11 August 2007, took place in close proximity to both the KFSD WSR-88D and to privately owned mesonet sensors which record data in 1-min increments. The event began with the decay of a thunderstorm, when precipitation a few hundred meters AGL descended to the ground and was immediately followed by the heat burst. Two mesonet sensors 2-km apart reported a marked temperature increase rate, averaging 0.23 C min -1. The barometric pressure fell at an average rate of 0.13 hpa min -1 during the combined precipitation heat burst period. The rise and fall of temperatures corresponding with the heat burst concluded within 45 min. 1. Introduction A heat burst is defined as a localized, sudden increase in surface temperature associated with a thunderstorm, shower, or mesoscale convective system (Johnson 1983; Glickman 2000). Such an event occurred at Sioux Falls, South Dakota, between UTC ( CDT) on 11 August With decaying thunderstorms over and south of the city, the National Weather Service (NWS) Automated Surface Observing System (ASOS) sensor located at the airport in northern Sioux Falls (KFSD) reported a marked rise and subsequent fall in the hourly temperature report, accompanied by a temporary shift in wind direction and an increase in wind speed, with gusts to 30 knots (Table 1). The event was also documented by privately owned Texas Weather Instruments sensors located at the Washington Pavilion of Arts and Sciences in central Sioux Falls (5 km south of the airport), and at Patrick Henry Middle School (7 km south of the airport). Observations from both sensors were transmitted over the Internet to the Iowa Environmental Mesonet (IEM), where they were recorded in 1-min increments. Archived and real-time IEM data are freely available online ( Corresponding author address: Dr. Jay Trobec, Chief Meteorologist, KELO-TV, 501 South Phillips Avenue, Sioux Falls, SD jtrobec@keloland.com; jay@trobec.net
2 Heat bursts arguably are not rare in South Dakota. A short-lived, minor heat burst occurred at the Sioux Falls airport during the afternoon before the case detailed in this paper (P. Schumacher, 2007, personal communication). Previous significant heat bursts that occurred in the state have been documented by Heitkamp and Holmes (1998), Harding (2000), and Johnson (2003), among others. Another heat burst was observed in Pierre on 20 June 1989, when the temperature rose from 30 to 40 C (86 to 104 F) in two hours (NCDC 1989). However, observations of these events involved data that were recorded in time increments of 5- to 60- min a coarser temporal scale. 2. Pre-existing conditions Numerous severe thunderstorms affected the Upper Midwest on the evening and night of 10 August The heat burst discussed herein was preceded by a cluster of thunderstorms that moved from west to east through central and extreme southern South Dakota. Those storms evolved into a line of severe storms that produced hail and high winds from UTC along the eastern portion of the South Dakota Nebraska border (Fig. 1). No severe weather was experienced in Sioux Falls, itself, but the heat burst closely followed a brief period of light rainfall as these storms decayed. Because it occurred in close proximity to the KFSD radar, the precipitation was scanned at levels very near the surface. The composite reflectivity from the KFSD Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) radar at 0709 UTC (Fig. 2a) shows a moderate convective shower over southwestern Sioux Falls, moving toward the northeast due to the prevailing southwesterly flow aloft. At that time, the highest reflectivity values ( 30 dbz) were found at the 1.3 deg elevation and above, at a height >200 m AGL; weaker echoes were located below. In the following volume scan (Fig. 2b) the precipitation moved toward the center of Sioux Falls, passing over the mesonet sites. Light rain (<0.254 mm or < 0.01 in.) was recorded in the tipping bucket gage at Washington Pavilion (which records precipitation in 0.01-inch increments) between 0700 UTC and 0709 UTC. KFSD WSR-88D Level 2 data can be used to provide a three-dimensional view of the precipitation core for the same time periods (Fig. 3). At 0708 UTC there was a precipitation core suspended from 0.2 to 3.2 km AGL. The actual echo top was probably higher, but data at greater heights were lost due to the lack of sampling directly above the radar (i.e., the cone of silence ). During the 0713 UTC volume scan, some of the aforementioned 30 dbz core had descended 2
3 and was detectable in the lowest elevation scan (0.05 km AGL), so precipitation may have been reaching the surface. By 0717 UTC, the precipitation core had noticeably diminished, and dissipated over Sioux Falls by 0721 UTC. The composite reflectivity (Fig. 4) indicated echoes 35 dbz were no longer present at 0726 UTC over the mesonet stations in central Sioux Falls. 3. Satellite imagery Coincident with the dissipation of the precipitation core, satellite imagery shows that the cloud tops were warming directly over Sioux Falls. GOES-12 was in a rapid scanning mode during the event (although not all images are shown here for the sake of brevity), and the µm channel (i.e., the infrared channel) measured a cloud top brightness temperature of -55 C over Sioux Falls at 0645 UTC (Fig. 5a). By 0702 the cloud top had warmed to -50 C over the city (Fig. 5b), and at 0715 UTC the cloud top over Sioux Falls had reached -45 C (Fig. 5c) just as the heat burst event was being detected at the surface (discussed in the next section below). The localized region of cloud top warming was similar in appearance to the signature created by downbursts on satellite imagery noted in Conway et al. (1997). The low-level echo dissipation combined with desiccation of the surface air is further indication of descent (Johnson 1983). Desiccation was quantified, along with the temperature rise, by mesonet sensors at the surface. 4. One-minute sensor data The mesonet station at Washington Pavilion was the first to detect abrupt changes in surface parameters, coinciding with the thunderstorm and its collapse. As the radar-indicated precipitation core descended to the surface, the barometer showed a strong pressure fall (Fig. 6a). At 0702 UTC the Pavilion barometer reading was hpa. However, during the weak thunderstorm the pressure fell 4.74 hpa in 18 min, reaching a local minimum of hpa at 0720 UTC. As the weak thunderstorm ended, the pressure fell another 1.36 hpa as the heat burst became more pronounced at this site. The temperature at 0720 UTC was 25 C (77 F). It then rose sharply, reaching 31 C (88 F) at 0748 UTC, and 32 C (90 F) at 0808 UTC (Fig. 6b). The dew point also dropped sharply during the corresponding time periods, from 23 C (74 F) at the start of the heat burst to a 3
4 minimum of 11 C (52 F) during the peak of the heat burst. The station s anemometer recorded a maximum wind gust of 21 m s -1 (41 knots) at 0720 UTC. Minor tree damage was reported. Similar abrupt, fine-scale changes were detected in the 1-min data from the Patrick Henry sensors 2 km to the south-southeast. A sharp drop in pressure, 5.76 hpa, occurred between 0700 and 0747 UTC (Fig. 7a), and a wind gust of 16 m s -1 (31 knots) was recorded. Unlike at Washington Pavilion, light rain was not recorded by the sensor s rain gage. The temperature at Patrick Henry (Fig. 7b) rose 6 C (11 F) in 17 min, before returning to a pre-event reading by 0900 UTC. It appears there is a dry bias in the humidity sensor at Patrick Henry (approximately 5.6 C or 10 F), but the trace pattern itself follows the same trend as was observed at the Pavilion: a rapid decrease in dew point corresponding to the temperature rise during the heat burst itself. When precipitation ended (0720 UTC), the rate of temperature change at Washington Pavilion was C min -1 (+0.34 F min -1 ) and at Patrick Henry was C min -1 (+0.49 F min -1 ). The rate of pressure fall was 0.14 hpa min -1 at Washington Pavilion and 0.12 hpa min -1 at Patrick Henry. While the pressure trends were relatively consistent between the mesonet stations, instrument calibration was suspect because initial barometric pressure readings at 0700 UTC were significantly different from the hourly reading at Sioux Falls airport (KFSD), and were not adjusted to mean sea level pressure. Otherwise, the temperature component of the heat burst event lasted approximately 45 min, but dew point values took longer to recover. Rapid temperatures rises were also recorded on Davis Instruments sensors at schools in nearby communities between UTC (Fig. 8). The temperature rises were sharp in Colton (A), Baltic (B), Garretson (C), and Brandon (D), which were also under the area of rapid cloud top warming observed by satellite in Fig. 5. The rate of warming was not as pronounced farther southeast in Hills, MN (E). None of the surrounding communities had heat bursts of the same 5.6 C (10 F) magnitude as those observed in Sioux Falls. 5. Vertical profile Sioux Falls is located more than 230 kilometers from the nearest radiosonde lauch site, midway between Aberdeen (KABR) to the north and Omaha Valley (KOAX) to the south. The heat burst also occurred between balloon launches temporally, so observed sounding data for the event were not representative of the lower troposphere over Sioux Falls. Moreover, 4
5 Tropospheric Airborne Meteorological Data Reporting (TAMDAR) aircraft data were not available over KFSD until 1300 UTC. A sounding profile derived from the Rapid Update Cycle (RUC) 1-h forecast valid for Sioux Falls at 0700 UTC 11 August 2007 (Fig. 9) is somewhat onion-shaped, with a shallow surface inversion and very dry air above 930 hpa. Shallow stable layers are conducive to penetration by thunderstorm downdrafts (Johnson et al. 1989; Horgan et al. 2007). Downdraft CAPE (DCAPE; Emanuel 1994) was 1433 J kg -1, indicating the potential for strong rain-cooled downdraft flow. The mid-level lapse rate (between hpa) was 8.9 C km -1 ; between hpa it was 9.8 C km -1 (dry-adiabatic). Heat bursts are usually associated with nearly dry-adiabatic lapse rates in mid-levels (Heinselman et al. 1998). Based upon the RUC sounding and parcel theory, in order for the surface temperature to reach 32 C (90 F) at Washington Pavilion, an air parcel (mesoscale downdraft) from a minimum height of 907 hpa (0.912 km AGL) had to descend through its equilibrium point to the surface and warm at the dry-adiabatic rate to achieve the surface temperatures observed. Subject to the limitations of parcel theory, such a parcel descent would have to have sufficient momentum to overcome the positive buoyancy attained by descent through the stable layer (Bernstein and Johnson 1994). 6. Conclusion Mesonet data at 1-min resolution are valuable for detecting heat burst activity, through the ability to observe temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure trends on a temporally fine-scale. In this case, the data showed that the onset of a steep pressure fall preceded the heat bust, commencing as a precipitation core aloft began its descent, and continuing through the resulting temperature increase. It should be noted that data quality can be an issue with privately owned mesonet data, due to uncertainty about calibration and accuracy of measuring equipment. Despite this limitation, the widespread nature of this event and the consistent trends from station to station provide great confidence in its occurrence and impact. 5
6 Acknowledgements. I would like to thank Daryl Herzmann for archiving data at the IEM, Scott Bachmeier of CIMSS for providing satellite imagery, and Ben Bernstein and Jon Zeitler for providing beneficial reviews. REFERENCES Bernstein, B. C., and R. H. Johnson, 1994: A dual-doppler radar study of an OK PRE-STORM heat burst event, Mon. Wea. Rev., 122, Conway, E. D., and the Maryland Space Grant Consortium, 1997: An Introduction to Satellite Image Interpretation, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 242 pp. Emanuel, K. A., 1994: Atmospheric Convection, Oxford University Press, New York, 883 pp. Heitkamp, T., and R. Holmes, 1998: Tri-state area experiences heat burst overnight. Public information statement, NWS Sioux Falls, NOAA weather wire, 26 March Glickman, T., ed., 2000: Glossary of Meteorology, 2nd edition. Amer. Meteor. Soc., Boston. Harding, K., 2000: A review of a possible heat burst affecting Pierre, South Dakota. NWSO ABR website [ accessed 2007]. Horgan, K. L., D. M. Schultz, J. E. Hales Jr., S. F. Corfidi, and R. H. Johns, 2007: A five-year climatology of elevated severe convective storms in the United States east of the Rocky Mountains. Wea. Forecasting, 22, Johnson, B. C., 1983: The heat burst of 29 May Mon. Wea. Rev., 111, Johnson, R. H., S. Chen, and J. J. Toth, 1989: Circulations associated with a mature-to-decaying midlatitude mesoscale convective system. Part I: Surface features Heat bursts and mesolow development. Mon. Wea. Rev., 117, Johnson, J. S., 2003: Examination of a long-lived heat burst event in the northern plains. Nat. Wea. Digest, National Weather Association, December 2003, 27, Heinselman, P. L., D. Andra, and D. Morris, 1998: The May 1996 heatburst: A severe wind event. Preprints, 19th Conf. on Severe Local Storms, Minneapolis, MN, Amer. Meteor. Soc., NCDC, 1989: Climate-radar data inventories, KPIR, available online at 6
7 TABLES AND FIGURES Table 1. Hourly station observations at the Sioux Falls ASOS (KFSD) for 0700 to 0900 UTC 11 August UTC Temp Dew Pt Wind Pressure C ( F) C ( F) (knots) (hpa) Sky (77) 19 (67) S 9G Thunderstorm with light rain (87) 12 (53) W 13G Clear below 12 kft (79) 14 (58) S Clear below 12 kft Figure 1. Storm reports from the NOAA Storm Prediction Center (SPC), 10 August
8 Figure 2. KFSD WSR-88D composite reflectivity data for (a) 0708 UTC 11 August 2007 in the top panel and (b) 0713 UTC 11 August 2007 in the bottom panel. The data are from the KFSD Level 3 archive. The white box in the upper-middle portion of the images represents the location of the KFSD WSR-88D. 8
9 Figure 3. Base reflectivity three-dimensional representation using KFSD WSR-88D Level 2 data valid UTC 11 August Reflectivity values 35 dbz are depicted in green. Cube dimensions are 12 km on each side. 9
10 Figure 4. As in Fig. 2, except for 0726 UTC 11 August The white areas in the northwestern portion of this image indicate reflectivity <5 dbz. 10
11 Figure 5. GOES-12 satellite 10.7-µm channel (infrared) images on 11 August 2007 for (a) 0645 UTC in the top panel, (b) 0702 UTC in the middle panel, and (c) 0715 UTC in the bottom panel. 11
12 Figure 6. (a) In the top panel, 1-min barometric pressure trace at Washington Pavilion in Sioux Falls, SD, on 11 August (b) In the bottom panel, temperature (red line) and dew point (blue line) in F during the same time period (images in C were not available). Time stamps are in UTC along the abscissa. 12
13 Figure 7. Same as Fig. 6 except for Patrick Henry School in Sioux Falls, SD. 13
14 Figure 8. Map of mesonet stations near Sioux Falls, SD (KFSD, small red diamond), showing temperature increases over short time periods occurring between UTC 11 August
15 Figure 9. Skew-T log-p sounding diagram below 400 hpa from the 0600 UTC 11 August 2007 Rapid Update Cycle (RUC) 1-hr forecast, valid 0700 UTC. CAPE is shaded red, and CIN is shaded blue. 15
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL. Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS
 P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
Thunderstorm Downburst Prediction: An Integrated Remote Sensing Approach. Ken Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS)
 Thunderstorm Downburst Prediction: An Integrated Remote Sensing Approach Ken Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Topics of Discussion Thunderstorm Life Cycle Thunderstorm
Thunderstorm Downburst Prediction: An Integrated Remote Sensing Approach Ken Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Topics of Discussion Thunderstorm Life Cycle Thunderstorm
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801
 Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES 3. RESULTS
 16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA
 2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On
2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS ON SEVERE CONVECTIVE WEATHER COMBINING SATELLITE, CONVENTIONAL OBSERVATION AND NCEP DATA
 12.12 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS ON SEVERE CONVECTIVE WEATHER COMBINING SATELLITE, CONVENTIONAL OBSERVATION AND NCEP DATA Zhu Yaping, Cheng Zhoujie, Liu Jianwen, Li Yaodong Institute of Aviation Meteorology
12.12 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS ON SEVERE CONVECTIVE WEATHER COMBINING SATELLITE, CONVENTIONAL OBSERVATION AND NCEP DATA Zhu Yaping, Cheng Zhoujie, Liu Jianwen, Li Yaodong Institute of Aviation Meteorology
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
Multi-day severe event of May 2013
 Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD
 P1.57 GOES WMSI PROGRESS AND DEVELOPMENTS Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. INTRODUCTION A multi-parameter index has
P1.57 GOES WMSI PROGRESS AND DEVELOPMENTS Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. INTRODUCTION A multi-parameter index has
Tropical Cyclone Forecasting Applications of the GOES WMSI
 1. Introduction Tropical Cyclone Forecasting Applications of the GOES WMSI Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD The Geostationary Operational Environmental
1. Introduction Tropical Cyclone Forecasting Applications of the GOES WMSI Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD The Geostationary Operational Environmental
1. INTRODUCTION * Figure 1. National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center (SPC) storm reports for December 1, 2006.
 P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England
 P 1.5 22nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service,
P 1.5 22nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service,
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002
 P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA. Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV
 P5.17 SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 9 AUGUST 2000 APPALACHIAN-CROSSING DERECHOS Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV 1. INTRODUCTION
P5.17 SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 9 AUGUST 2000 APPALACHIAN-CROSSING DERECHOS Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV 1. INTRODUCTION
Figure 1: Tephigram for radiosonde launched from Bath at 1100 UTC on 15 June 2005 (IOP 1). The CAPE and CIN are shaded dark and light gray,
 Figure 1: Tephigram for radiosonde launched from Bath at 1100 UTC on 1 June 200 (IOP 1). The CAPE and CIN are shaded dark and light gray, respectively; the thin solid line partially bounding these areas
Figure 1: Tephigram for radiosonde launched from Bath at 1100 UTC on 1 June 200 (IOP 1). The CAPE and CIN are shaded dark and light gray, respectively; the thin solid line partially bounding these areas
4/18/2010. National Weather Service. Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study
 National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains
 Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS), Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA Abstract A favorable
Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS), Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA Abstract A favorable
Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A rapidly deepening surface cyclone raced
Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A rapidly deepening surface cyclone raced
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Orographically enhanced heavy rainfall of 23 May 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Orographically enhanced heavy rainfall of 23 May 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION During the overnight hours and into the early morning of
Orographically enhanced heavy rainfall of 23 May 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION During the overnight hours and into the early morning of
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017
 Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014
 Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes Photographs Todd Lindley Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system 1 Bright
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes Photographs Todd Lindley Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system 1 Bright
Convective downbursts are known to produce potentially hazardous weather
 Investigation of Convective Downburst Hazards to Marine Transportation Mason, Derek Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Alexandria, VA Abstract Convective downbursts are known to produce
Investigation of Convective Downburst Hazards to Marine Transportation Mason, Derek Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Alexandria, VA Abstract Convective downbursts are known to produce
Boundary Layer Turbulence Index: Progress and Recent Developments
 Boundary Layer Turbulence Index: Progress and Recent Developments Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. Introduction Turbulence is a frequently
Boundary Layer Turbulence Index: Progress and Recent Developments Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. Introduction Turbulence is a frequently
Mid Atlantic Heavy rainfall event 1. Overview 2. Methods and Data 3. Pattern
 1. Overview Mid Atlantic Heavy rainfall event With an inertial gravity wave? By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 Contributions from the Albany MAP An unseasonably strong
1. Overview Mid Atlantic Heavy rainfall event With an inertial gravity wave? By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 Contributions from the Albany MAP An unseasonably strong
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin
 April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
P0.98 Composite Analysis of Heavy-Rain-Producing Elevated Thunderstorms in the MO-KS-OK region of the United States
 P0.98 Composite Analysis of Heavy-Rain-Producing Elevated Thunderstorms in the MO-KS-OK region of the United States Laurel P. McCoy and Patrick S. Market Department of Soil, Environmental, and Atmospheric
P0.98 Composite Analysis of Heavy-Rain-Producing Elevated Thunderstorms in the MO-KS-OK region of the United States Laurel P. McCoy and Patrick S. Market Department of Soil, Environmental, and Atmospheric
P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL
 P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL John T. DiStefano* National Weather Service Office, Wilmington, Ohio 1. INTRODUCTION During the early
P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL John T. DiStefano* National Weather Service Office, Wilmington, Ohio 1. INTRODUCTION During the early
THE MAP ROOM. BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall
 THE MAP ROOM BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall BY CHARLES E. GRAVES, JAMES T. MOORE, MARC J. SINGER, AND SAM NG AFFILIATIONS: GRAVES, MOORE, AND NG Department
THE MAP ROOM BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall BY CHARLES E. GRAVES, JAMES T. MOORE, MARC J. SINGER, AND SAM NG AFFILIATIONS: GRAVES, MOORE, AND NG Department
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries
 11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
Fundamentals of Radar Display. Atmospheric Instrumentation
 Fundamentals of Radar Display Outline Fundamentals of Radar Display Scanning Strategies Basic Geometric Varieties WSR-88D Volume Coverage Patterns Classic Radar Displays and Signatures Precipitation Non-weather
Fundamentals of Radar Display Outline Fundamentals of Radar Display Scanning Strategies Basic Geometric Varieties WSR-88D Volume Coverage Patterns Classic Radar Displays and Signatures Precipitation Non-weather
Tool for Storm Analysis Using Multiple Data Sets
 Tool for Storm Analysis Using Multiple Data Sets Robert M. Rabin 1,2 and Tom Whittaker 2 1 NOAA/National Severe Storms Laboratory, Norman OK 73069, USA 2 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite
Tool for Storm Analysis Using Multiple Data Sets Robert M. Rabin 1,2 and Tom Whittaker 2 1 NOAA/National Severe Storms Laboratory, Norman OK 73069, USA 2 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite
A Case Study on Diurnal Boundary Layer Evolution
 UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA A Case Study on Diurnal Boundary Layer Evolution Meteorological Measurement Systems Fall 2010 Jason Godwin 12/9/2010 Lab partners: Sam Irons, Charles Kuster, Nathan New, and Stefan
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA A Case Study on Diurnal Boundary Layer Evolution Meteorological Measurement Systems Fall 2010 Jason Godwin 12/9/2010 Lab partners: Sam Irons, Charles Kuster, Nathan New, and Stefan
Heavy Rainfall Event of June 2013
 Heavy Rainfall Event of 10-11 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A 500 hpa short-wave moved over the eastern United States (Fig. 1) brought a surge of
Heavy Rainfall Event of 10-11 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A 500 hpa short-wave moved over the eastern United States (Fig. 1) brought a surge of
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP
 Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
8.2 EVALUATING THE BENEFITS OF TAMDAR DATA IN CONVECTIVE FORECASTING. Cyrena-Marie Druse 1 AirDat LLC. Evergreen, CO
 8.2 EVALUATING THE BENEFITS OF TAMDAR DATA IN CONVECTIVE FORECASTING Cyrena-Marie Druse 1 AirDat LLC. Evergreen, CO 1. INTRODUCTION 1 The TAMDAR (Tropospheric Airborne Meteorological Data Reporting) Sensor
8.2 EVALUATING THE BENEFITS OF TAMDAR DATA IN CONVECTIVE FORECASTING Cyrena-Marie Druse 1 AirDat LLC. Evergreen, CO 1. INTRODUCTION 1 The TAMDAR (Tropospheric Airborne Meteorological Data Reporting) Sensor
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Evolution and Maintenance of the June 2003 Nocturnal Convection
 Evolution and Maintenance of the 22-23 June 2003 Nocturnal Convection Jerilyn Billings NOAA/NWS Wichita, KS August 6 th, 2011 Work Completed at North Carolina State University for MS Thesis During the
Evolution and Maintenance of the 22-23 June 2003 Nocturnal Convection Jerilyn Billings NOAA/NWS Wichita, KS August 6 th, 2011 Work Completed at North Carolina State University for MS Thesis During the
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY. Metr Fall 2014 Test #1 September 30, 2014
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 302.02 Fall 2014 Test #1 September 30, 2014 200 pts (4 pts each answer) Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Questions 1
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 302.02 Fall 2014 Test #1 September 30, 2014 200 pts (4 pts each answer) Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Questions 1
P1.22 A FIVE-YEAR CLIMATOLOGY OF ELEVATED SEVERE CONVECTIVE STORMS IN THE UNITED STATES EAST OF THE ROCKY MOUNTAINS
 P1.22 A FIVE-YEAR CLIMATOLOGY OF ELEVATED SEVERE CONVECTIVE STORMS IN THE UNITED STATES EAST OF THE ROCKY MOUNTAINS Katherine L. Horgan National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates,
P1.22 A FIVE-YEAR CLIMATOLOGY OF ELEVATED SEVERE CONVECTIVE STORMS IN THE UNITED STATES EAST OF THE ROCKY MOUNTAINS Katherine L. Horgan National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates,
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017
 Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A cluster of thunderstorms developed in eastern Ohio around 1800 UTC on 19
Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A cluster of thunderstorms developed in eastern Ohio around 1800 UTC on 19
The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England
 P 12.9 23rd Conference on Severe Local Storms Saint Louis, MO, 6-10 November 2006 The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England *Thomas A. Wasula and Kenneth D. LaPenta
P 12.9 23rd Conference on Severe Local Storms Saint Louis, MO, 6-10 November 2006 The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England *Thomas A. Wasula and Kenneth D. LaPenta
AMDAR Forecast Applications. Richard Mamrosh NWS Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA
 AMDAR Forecast Applications Richard Mamrosh NWS Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA AMDAR has many applications Aviation Low level wind shear Ceilings and visibilities Icing and turbulence Winter Storms Precipitation
AMDAR Forecast Applications Richard Mamrosh NWS Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA AMDAR has many applications Aviation Low level wind shear Ceilings and visibilities Icing and turbulence Winter Storms Precipitation
OPTIMIZATION OF WIND POWER PRODUCTION FORECAST PERFORMANCE DURING CRITICAL PERIODS FOR GRID MANAGEMENT
 OPTIMIZATION OF WIND POWER PRODUCTION FORECAST PERFORMANCE DURING CRITICAL PERIODS FOR GRID MANAGEMENT WINDPOWER 2007 Los Angeles, CA June 3-6, 2007 POSTER PRESENTATION John W. Zack AWS Truewind, LLC 185
OPTIMIZATION OF WIND POWER PRODUCTION FORECAST PERFORMANCE DURING CRITICAL PERIODS FOR GRID MANAGEMENT WINDPOWER 2007 Los Angeles, CA June 3-6, 2007 POSTER PRESENTATION John W. Zack AWS Truewind, LLC 185
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation 1.
 Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation Kevin Gray and Jeffrey Frame Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois
Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation Kevin Gray and Jeffrey Frame Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois
A Numerical Model-derived Boundary Layer Turbulence Product
 A Numerical Model-derived Boundary Layer Turbulence Product Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD Abstract A suite of numerical model-derived turbulence
A Numerical Model-derived Boundary Layer Turbulence Product Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD Abstract A suite of numerical model-derived turbulence
P4.6 OBSERVATIONS FROM THE 13 APRIL 2004 WAKE LOW DAMAGING WIND EVENT IN SOUTH FLORIDA. Robert R. Handel and Pablo Santos NOAA/NWS, Miami, Florida
 P4.6 OBSERVATIONS FROM THE 13 APRIL 2004 WAKE LOW DAMAGING WIND EVENT IN SOUTH FLORIDA Robert R. Handel and Pablo Santos NOAA/NWS, Miami, Florida 1. INTRODUCTION Damaging winds affected portions of South
P4.6 OBSERVATIONS FROM THE 13 APRIL 2004 WAKE LOW DAMAGING WIND EVENT IN SOUTH FLORIDA Robert R. Handel and Pablo Santos NOAA/NWS, Miami, Florida 1. INTRODUCTION Damaging winds affected portions of South
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 5 Content: Weather Maps Notes
 Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
THE MESOSCALE CONVECTIVE SYSTEM FROM
 RISCURI I CATASTROFE, NR.X, VOL.9, NR. 1/2011 THE MESOSCALE CONVECTIVE SYSTEM FROM 24.07.2010 ELZA HAUER, 1 C. NICHITA 1 ABSTRACT. The Mesoscale Convective System from 24.07.2010. A severe weather event
RISCURI I CATASTROFE, NR.X, VOL.9, NR. 1/2011 THE MESOSCALE CONVECTIVE SYSTEM FROM 24.07.2010 ELZA HAUER, 1 C. NICHITA 1 ABSTRACT. The Mesoscale Convective System from 24.07.2010. A severe weather event
MSG FOR NOWCASTING - EXPERIENCES OVER SOUTHERN AFRICA
 MSG FOR NOWCASTING - EXPERIENCES OVER SOUTHERN AFRICA Estelle de Coning and Marianne König South African Weather Service, Private Bag X097, Pretoria 0001, South Africa EUMETSAT, Am Kavalleriesand 31, D-64295
MSG FOR NOWCASTING - EXPERIENCES OVER SOUTHERN AFRICA Estelle de Coning and Marianne König South African Weather Service, Private Bag X097, Pretoria 0001, South Africa EUMETSAT, Am Kavalleriesand 31, D-64295
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
2 July 2013 Flash Flood Event
 2 July 2013 Flash Flood Event By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A retrograding 500 hpa cyclone and anticyclone (Fig. 1) set up deep southerly flow
2 July 2013 Flash Flood Event By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A retrograding 500 hpa cyclone and anticyclone (Fig. 1) set up deep southerly flow
Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event of 23 June 2015
 Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event of 23 June 2015 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event occurred in the eastern United States on 23
Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event of 23 June 2015 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event occurred in the eastern United States on 23
CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A thunderstorm is considered to be a weather system. a. synoptic-scale b. micro-scale c. meso-scale 2. By convention, the mature stage
CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A thunderstorm is considered to be a weather system. a. synoptic-scale b. micro-scale c. meso-scale 2. By convention, the mature stage
Final Report. We will discuss the project accomplishments in two sub sections, reflecting the two major efforts given in Section 1.
 Final Report to Cooperative Program for Operational Meteorology, Education and Training (COMET) University: University of Illinois in Urbana Champaign Name of University Researcher Preparing Report: David
Final Report to Cooperative Program for Operational Meteorology, Education and Training (COMET) University: University of Illinois in Urbana Champaign Name of University Researcher Preparing Report: David
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox
 Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
2.2 APPLICATIONS OF AIRCRAFT SOUNDING DATA IN SHORT-TERM CONVECTIVE FORECASTING
 2.2 APPLICATIONS OF AIRCRAFT SOUNDING DATA IN SHORT-TERM CONVECTIVE FORECASTING Phillip G. Kurimski* and Eugene S. Brusky Jr. NOAA/National Weather Service, Green Bay, WI 1. INTRODUCTION Automated real-time
2.2 APPLICATIONS OF AIRCRAFT SOUNDING DATA IN SHORT-TERM CONVECTIVE FORECASTING Phillip G. Kurimski* and Eugene S. Brusky Jr. NOAA/National Weather Service, Green Bay, WI 1. INTRODUCTION Automated real-time
Sunday, 13 June 1999
 Sunday, 13 June 1999 Julian Day 164 Meteorological Summary A cold front moved in over night, cooling the air at low levels. Warming aloft occurred and stabilized the air in mid-levels, suppressing convective
Sunday, 13 June 1999 Julian Day 164 Meteorological Summary A cold front moved in over night, cooling the air at low levels. Warming aloft occurred and stabilized the air in mid-levels, suppressing convective
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona
 P12.1 SUPERCE EVOUTION IN ENVIRONMENTS WITH UNUSUA HODOGRAPHS David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION The events that transpired across northern
P12.1 SUPERCE EVOUTION IN ENVIRONMENTS WITH UNUSUA HODOGRAPHS David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION The events that transpired across northern
Southern Plains Heavy rain and Flooding
 Abstract: Southern Plains Heavy rain and Flooding By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A severe weather event affected the southern Plains on 31 May 2013. The severe weather event
Abstract: Southern Plains Heavy rain and Flooding By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A severe weather event affected the southern Plains on 31 May 2013. The severe weather event
Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes
 Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front moved across central Pennsylvania and the Mid-Atlantic
Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front moved across central Pennsylvania and the Mid-Atlantic
P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY
 P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY 2009 Stephen S. Parker* National Weather Service, Boise, ID 1. INTRODUCTION During the early afternoon hours of 3 May
P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY 2009 Stephen S. Parker* National Weather Service, Boise, ID 1. INTRODUCTION During the early afternoon hours of 3 May
MESOSCALE WINDS IN VICINITY OF CONVECTION AND WINTER STORMS. Robert M. Rabin
 MESOSCALE WINDS IN VICINITY OF CONVECTION AND WINTER STORMS Robert M. Rabin NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab (NSSL), Norman, OK Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS), Madison,
MESOSCALE WINDS IN VICINITY OF CONVECTION AND WINTER STORMS Robert M. Rabin NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab (NSSL), Norman, OK Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS), Madison,
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part V ñ Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and MCCs. Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part V ñ Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and MCCs Photographs Todd Lindley (This part contains materials taken from UCAR MCS training module) Bright band associated with stratiform
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part V ñ Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and MCCs Photographs Todd Lindley (This part contains materials taken from UCAR MCS training module) Bright band associated with stratiform
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters
 Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Using Cell-Based VIL Density to Identify Severe-Hail Thunderstorms in the Central Appalachians and Middle Ohio Valley
 EASTERN REGION TECHNICAL ATTACHMENT NO. 98-9 OCTOBER, 1998 Using Cell-Based VIL Density to Identify Severe-Hail Thunderstorms in the Central Appalachians and Middle Ohio Valley Nicole M. Belk and Lyle
EASTERN REGION TECHNICAL ATTACHMENT NO. 98-9 OCTOBER, 1998 Using Cell-Based VIL Density to Identify Severe-Hail Thunderstorms in the Central Appalachians and Middle Ohio Valley Nicole M. Belk and Lyle
MET Lecture 34 Downbursts
 MET 4300 Lecture 34 Downbursts Downbursts A strong downdraft that originates within the lower part of a cumulus cloud or thunderstorms and spreads out at the surface Downbursts do not require strong thunderstorms
MET 4300 Lecture 34 Downbursts Downbursts A strong downdraft that originates within the lower part of a cumulus cloud or thunderstorms and spreads out at the surface Downbursts do not require strong thunderstorms
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview
 The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
24: Monthly Report September Seeding Operations & Atmospheric Research (SOAR) Snapshot of Seeding Operations
 0.3.05 Monthly Report September 05 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker Snapshot of Seeding Operations Date Flight Time (hours) Number of Flares (total) September 0:04
0.3.05 Monthly Report September 05 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker Snapshot of Seeding Operations Date Flight Time (hours) Number of Flares (total) September 0:04
1. INTRODUCTION GSP Dr, Greer, SC tropical cyclones. 1 This study did not include tornadoes associated with
 4.5 OBSERVATIONS OF A NON-SUPERCELL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM FROM A TERMINAL DOPPLER WEATHER RADAR Justin D. Lane * and Patrick D. Moore NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, SC 1. INTRODUCTION Despite numerous
4.5 OBSERVATIONS OF A NON-SUPERCELL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM FROM A TERMINAL DOPPLER WEATHER RADAR Justin D. Lane * and Patrick D. Moore NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, SC 1. INTRODUCTION Despite numerous
Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Production in Strongly Forced, Low- Instability Convective Lines
 Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Production in Strongly Forced, Low- Instability Convective Lines Matthew S. Van Den Broeke National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates, and Valparaiso University
Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Production in Strongly Forced, Low- Instability Convective Lines Matthew S. Van Den Broeke National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates, and Valparaiso University
Meteorology 311. RADAR Fall 2016
 Meteorology 311 RADAR Fall 2016 What is it? RADAR RAdio Detection And Ranging Transmits electromagnetic pulses toward target. Tranmission rate is around 100 s pulses per second (318-1304 Hz). Short silent
Meteorology 311 RADAR Fall 2016 What is it? RADAR RAdio Detection And Ranging Transmits electromagnetic pulses toward target. Tranmission rate is around 100 s pulses per second (318-1304 Hz). Short silent
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
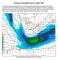 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
P5.11 TACKLING THE CHALLENGE OF NOWCASTING ELEVATED CONVECTION
 P5.11 TACKLING THE CHALLENGE OF NOWCASTING ELEVATED CONVECTION Huaqing Cai*, Rita Roberts, Dan Megenhardt, Eric Nelson and Matthias Steiner National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, 80307,
P5.11 TACKLING THE CHALLENGE OF NOWCASTING ELEVATED CONVECTION Huaqing Cai*, Rita Roberts, Dan Megenhardt, Eric Nelson and Matthias Steiner National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, 80307,
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Jon M. Schrage 1 and A.H. Fink 2 3. CASES
 .3 CASE STUDIES OF MESOSCALE CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS IN SUB-SAHELIAN WEST AFRICA Jon M. Schrage and A.H. Fink 2 Creighton University Omaha, Nebraska 2 University of Cologne Cologne, Germany. INTRODUCTION Tropical
.3 CASE STUDIES OF MESOSCALE CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS IN SUB-SAHELIAN WEST AFRICA Jon M. Schrage and A.H. Fink 2 Creighton University Omaha, Nebraska 2 University of Cologne Cologne, Germany. INTRODUCTION Tropical
A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE NOCTURNAL QLCS TORNADOES THAT MOVED THROUGH OMAHA, NEBRASKA, ON 8 JUNE 2008
 JP1.10 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE NOCTURNAL QLCS TORNADOES THAT MOVED THROUGH OMAHA, NEBRASKA, ON 8 JUNE 2008 Barbara E. Mayes *1, Jason T. Martinelli #, and Daniel Nietfeld * * National Weather Service
JP1.10 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE NOCTURNAL QLCS TORNADOES THAT MOVED THROUGH OMAHA, NEBRASKA, ON 8 JUNE 2008 Barbara E. Mayes *1, Jason T. Martinelli #, and Daniel Nietfeld * * National Weather Service
Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE. Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS WFO Sioux Falls, SD
 11B.2 Influence of Diabatic Potential Vorticity Anomalies upon Warm Conveyor Belt Flow. Part II: 3-5 January 2005 Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS WFO Sioux
11B.2 Influence of Diabatic Potential Vorticity Anomalies upon Warm Conveyor Belt Flow. Part II: 3-5 January 2005 Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS WFO Sioux
THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON
 THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON Matthew R. Kramar, Andrew B. Woodcock, Jared R. Klein and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Baltimore/Washington
THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON Matthew R. Kramar, Andrew B. Woodcock, Jared R. Klein and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Baltimore/Washington
Flooding and Severe weather of 27 June 2013
 Flooding and Severe weather of 27 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Flooding and severe weather affected Pennsylvania on 27 June 2013 (Fig 1). The severe
Flooding and Severe weather of 27 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Flooding and severe weather affected Pennsylvania on 27 June 2013 (Fig 1). The severe
Mesoscale Convective Systems. The COMET Program March 2002
 Mesoscale Convective Systems The COMET Program March 2002 Overview! Introduction to MCSs! Squall Lines! Bow Echoes! Mesoscale Convective Complexes Introduction Definition! Mesoscale convective systems
Mesoscale Convective Systems The COMET Program March 2002 Overview! Introduction to MCSs! Squall Lines! Bow Echoes! Mesoscale Convective Complexes Introduction Definition! Mesoscale convective systems
Correction for Dry Bias in Vaisala Radiosonde RH Data
 Correction for Dry Bias in Vaisala Radiosonde RH Data E. R. Miller, J. Wang, and H. L. Cole National Center for Atmospheric Research Atmospheric Technology Division Boulder, Colorado Abstract Extensive
Correction for Dry Bias in Vaisala Radiosonde RH Data E. R. Miller, J. Wang, and H. L. Cole National Center for Atmospheric Research Atmospheric Technology Division Boulder, Colorado Abstract Extensive
P4.6 DOCUMENTATION OF THE OVERLAND REINTENSIFICATION OF TROPICAL STORM ERIN OVER OKLAHOMA, AUGUST 18, 2007
 P4.6 DOCUMENTATION OF THE OVERLAND REINTENSIFICATION OF TROPICAL STORM ERIN OVER OKLAHOMA, AUGUST 18, 2007 John P. Monteverdi* San Francisco State University, San Francisco, CA Roger Edwards Storm Prediction
P4.6 DOCUMENTATION OF THE OVERLAND REINTENSIFICATION OF TROPICAL STORM ERIN OVER OKLAHOMA, AUGUST 18, 2007 John P. Monteverdi* San Francisco State University, San Francisco, CA Roger Edwards Storm Prediction
Mesoscale Convective System and heat episode July 2005 by Richard H. Grumm and Mathew Steinbugl
 Mesoscale Convective System and heat episode 25-27 July 2005 by Richard H. Grumm and Mathew Steinbugl 1. INTRODUCTION A strong upper-level ridge brought unseasonably high temperatures to the Midwest and
Mesoscale Convective System and heat episode 25-27 July 2005 by Richard H. Grumm and Mathew Steinbugl 1. INTRODUCTION A strong upper-level ridge brought unseasonably high temperatures to the Midwest and
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Frontal Analysis in the Light of Abrupt Temperature Changes in a Shallow Valley
 1125 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Frontal Analysis in the Light of Abrupt Temperature Changes in a Shallow Valley FREDERICK SANDERS Marblehead, Massachusetts EDWIN KESSLER Purcell, Oklahoma 2 February 1998
1125 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Frontal Analysis in the Light of Abrupt Temperature Changes in a Shallow Valley FREDERICK SANDERS Marblehead, Massachusetts EDWIN KESSLER Purcell, Oklahoma 2 February 1998
Tornadoes. tornado: a violently rotating column of air
 Tornadoes tornado: a violently rotating column of air Tornadoes What is the typical size of a tornado? What are typical wind speeds for a tornado? Five-stage life cycle of a tornado Dust Swirl Stage Tornado
Tornadoes tornado: a violently rotating column of air Tornadoes What is the typical size of a tornado? What are typical wind speeds for a tornado? Five-stage life cycle of a tornado Dust Swirl Stage Tornado
DOPPLER RADAR AND STORM ENVIRONMENT OBSERVATIONS OF A MARITIME TORNADIC SUPERCELL IN SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA
 155 DOPPLER RADAR AND STORM ENVIRONMENT OBSERVATIONS OF A MARITIME TORNADIC SUPERCELL IN SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA Harald Richter *, Alain Protat Research and Development Branch, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne,
155 DOPPLER RADAR AND STORM ENVIRONMENT OBSERVATIONS OF A MARITIME TORNADIC SUPERCELL IN SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA Harald Richter *, Alain Protat Research and Development Branch, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne,
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers
 Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Large hail in Estonia on 12th August 2015
 Large hail in Estonia on 12th August 2015 Taimi Paljak, Velle Toll, Tanel Voormansik, Estonian Weather Service Introduction Hail is not as common in Northern Europe as in the rest of Europe due to the
Large hail in Estonia on 12th August 2015 Taimi Paljak, Velle Toll, Tanel Voormansik, Estonian Weather Service Introduction Hail is not as common in Northern Europe as in the rest of Europe due to the
A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA
 J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
Eastern United States Wild Weather April 2014-Draft
 1. Overview Eastern United States Wild Weather 27-30 April 2014-Draft Significant quantitative precipitation bust By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA and Joel Maruschak Over
1. Overview Eastern United States Wild Weather 27-30 April 2014-Draft Significant quantitative precipitation bust By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA and Joel Maruschak Over
